Glancing Angle Deposition in Gas Sensing: Bridging Morphological Innovations and Sensor Performances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Glancing Angle Deposition Technique
2.1. GLAD Configuration and Principles
2.2. Tailoring the Morphology of Nanostructures via GLAD
- Vertically aligned NRs (Figure 3A): Achieved by fast, continuous rotation at a fixed , producing symmetric structures with uniform exposure.
- Tilted NRs (Figure 3B): Formed by fixing without azimuthal rotation, leading to slanted rods due to preferential growth on the flux-facing side, commonly referred to as oblique angle deposition (OAD).
- Zig-zag NRs (Figure 3C): Generated by alternating in discrete steps during deposition, creating kinked structures that increase surface complexity.
- Helical NRs (Figure 3D): Produced via slow, continuous azimuthal rotation, wrapping the material into a spiral trajectory. The pitch is controlled by rotation speed relative to the deposition rate.
- Beaded NRs (Figure 3E): Formed by modulating or dynamically during growth, resulting in periodic constrictions that enhance surface area.
- Helical-zigzag NRs (Figure 3F): Constructed by combining rotation profiles mid-growth, producing multilayered architectures suitable for multifunctional applications.
- Multilayered NRs (Figure 3G): Constructed by alternating material sources during growth, forming vertical heterojunctions along the rod axis. The number of layers and the thickness of each segment can be precisely controlled by tailoring functional properties. For example, WO3/TiO2 layers can enhance photocatalytic activity [45].
- Side-coated NRs (Figure 3H): Achieved by depositing a secondary material at a distinct angle ( or ), coating one side of the rods. The extent of side coverage can be tuned by adjusting the deposition angle of the second source. This asymmetry supports directional sensing or catalytic activity.
- Sandwiched NRs (Figure 3I): Fabricated through a two-step side coating by rotating the substrate 180° azimuthally after the first side-coating, leading to symmetric dual-side heterostructures.
- Double helices or “candy cane” twisted NRs (Figure 3M): Created by co-deposition during helical rotation, producing twisted, asymmetric rods for chiral or plasmonic applications.
- Nanoparticle (NP)-decorated NRs (Figure 3N): Fabricated via co-deposition or post-deposition sputtering, enhancing catalytic activity and surface reactivity [52,53] (See Section 3.1.4).
2.3. The Advantages of GLAD Structures for Gas Sensors
2.3.1. Surface Area and Porosity
2.3.2. Connectivity or Percolation
2.3.3. Material Selection
| Material | Ref. | Material | Ref. | Material | Ref. | Material | Ref. | Material | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | |||||||||
| [32] | [32] | [32] | [32] | [32] | |||||
| [32] | [32] | [32] | [119] | [32] | |||||
| [32] | [32] | [32] | [32] | [32] | |||||
| [124] | [32] | [32] | [32] | [32] | |||||
| [32] | [32] | [32] | [32] | [125] | |||||
| Two Element—Oxide | |||||||||
| [32] | [32] | [32] | [126] | [32] | |||||
| [32] | [127] | [128] | [32] | [32] | |||||
| [129] | [32] | [32] | [32] | [32] | |||||
| [130] | [73] | [32] | [131] | ||||||
| [132] | [32] | [32] | [133] | ||||||
| Two Element—non-Oxide | |||||||||
| [32] | CrN | [32] | InN | [32] | Ta3N5 | [32] | ZnS | [32] | |
| [134] | [32] | [32] | [32] | ||||||
| [135] | [32] | [108] | [136] | ||||||
| Three Element—Oxide | Three Element—non-Oxide | ||||||||
| ATO | [32] | CrN1−xOx | [137] | WxSiyOx | [32] | GeSbSn | [32] | TiAlN | [32] |
| [32] | [32] | [32] | [138] | [32] | |||||
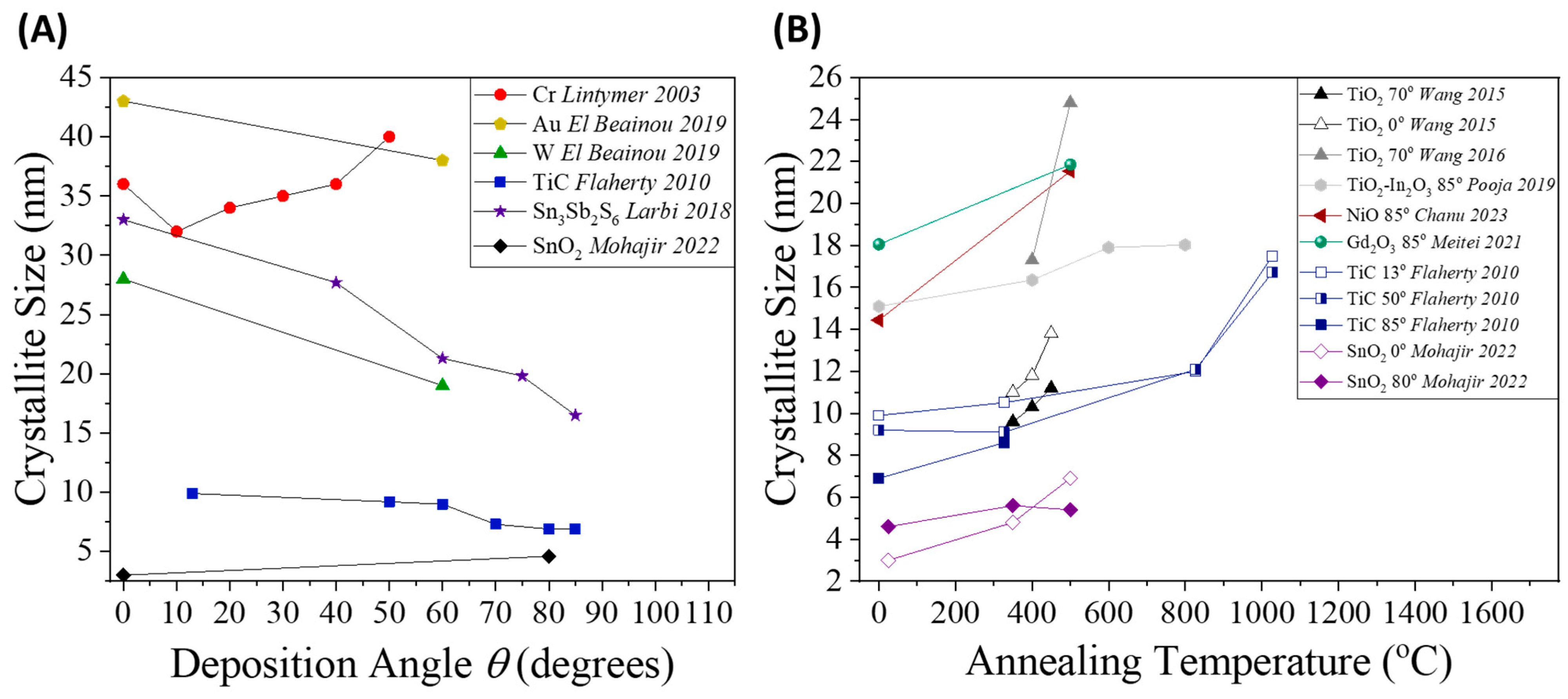
2.3.4. Crystal Quality
2.3.5. Surface Reactivity Engineering
3. GLAD-Enabled Gas Sensing Mechanisms and Device Integration
3.1. Resistive Gas Sensors
3.1.1. Pure MOS-Based Gas Sensors
3.1.2. Mixed Oxide and Multilayer MOS NR Array
3.1.3. Metal Doped or Decorated MOS for Gas Sensing
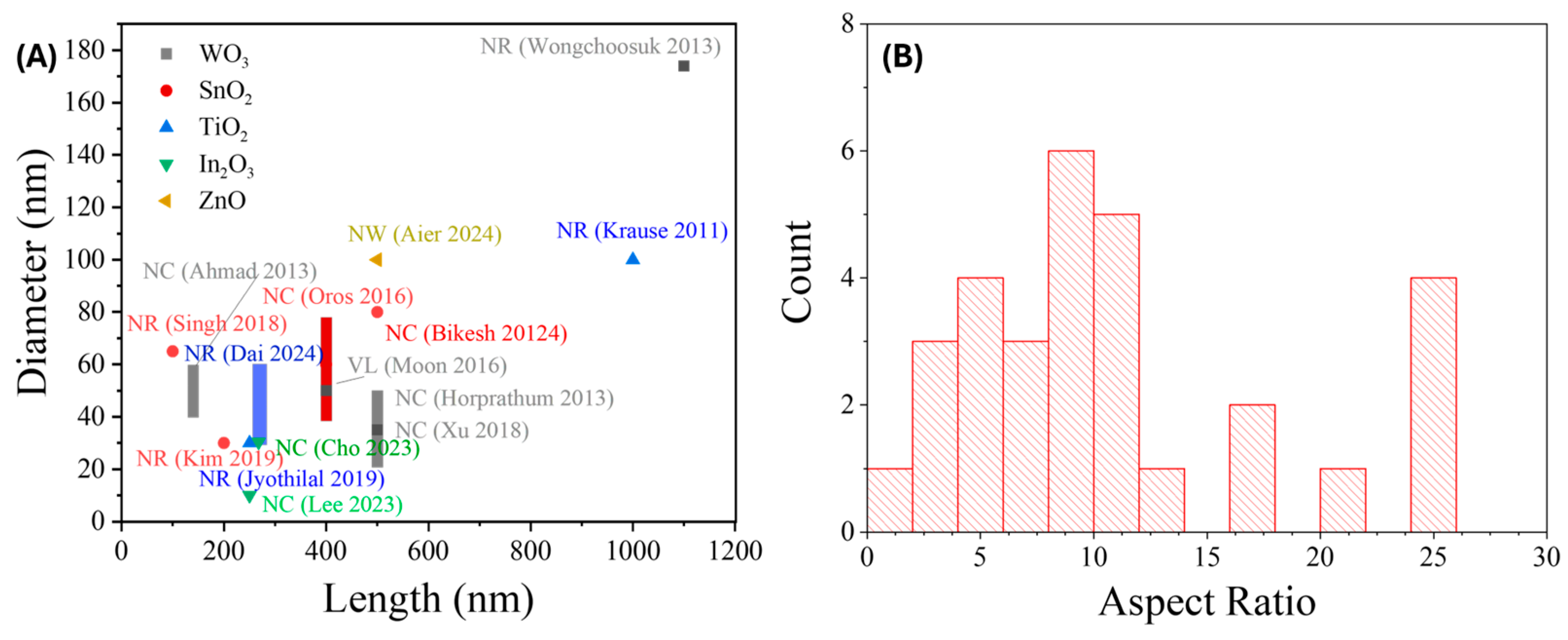
3.1.4. Summary of GLAD-Based Resistive Gas Sensors
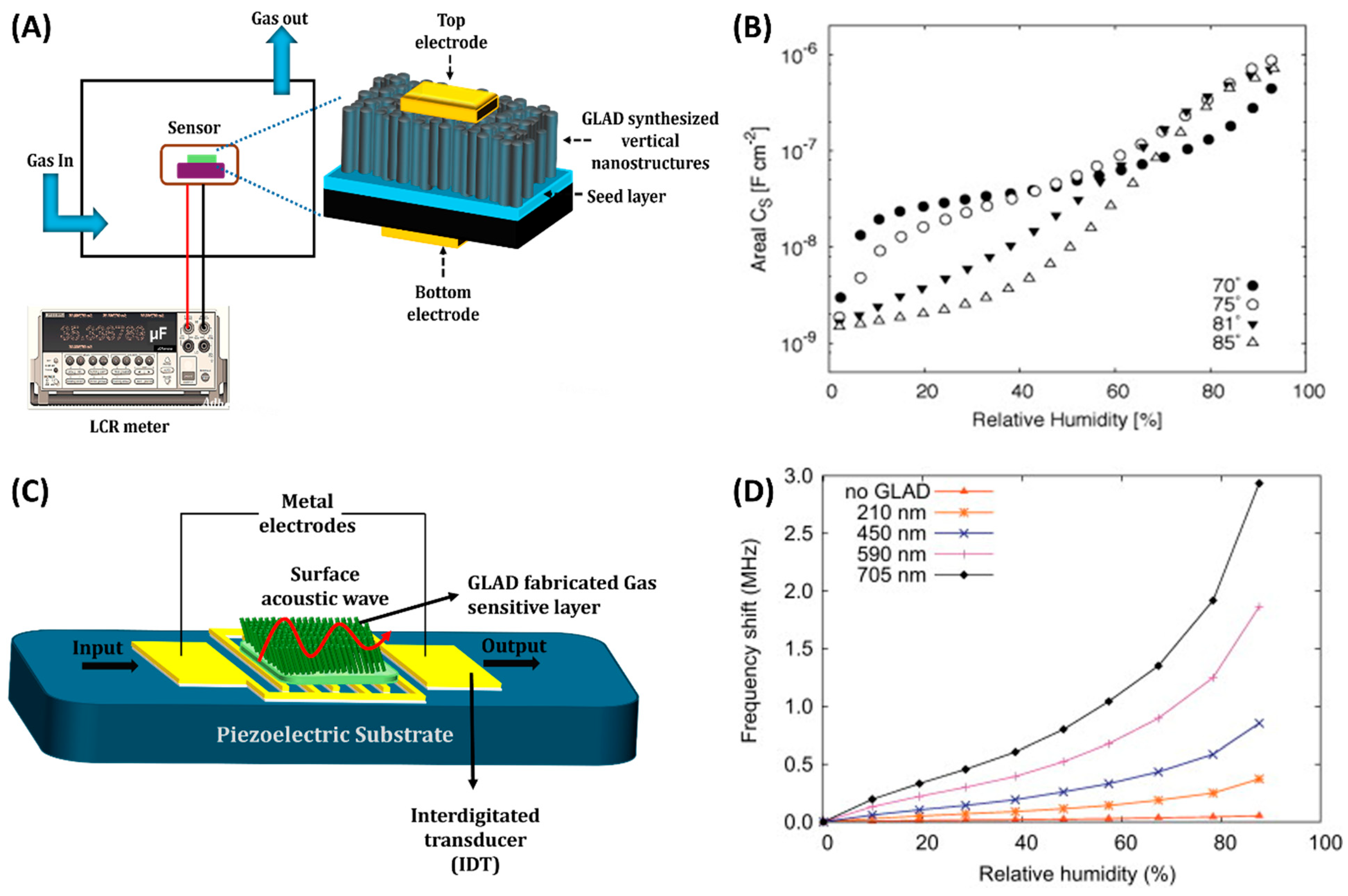
3.2. Capacitive Gas Sensors
| Mat | Structure | Deposition Condition | Target Gas | Response and Sensitivity | Operation Frequency | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacitive | |||||||
| Vertical columns | E-beam: | Humidity | S (nF/RH%): 34.4 @ 78% RH | 1 kHz@1 | [144] | ||
| Vertical columns | E-beam evaporation, θ = 60–80°; | Humidity | Ti electrodes: C 233–1050 pF at 11–93% RH TiN electrodes: C 375 pF at 11–52% RH & abrupt >52% | N/A | 20 Hz to 2 MHz, V = −3 V to 3 V | [260] | |
| Vertical columns | E-beam evaporation, = 81 | Humidity | C 2–1000 @ 0–92%RH | (78% RH) | 25 Hz, 1 , @ 20 °C to 22 °C | [261] | |
| Vertical columns | PVD: = 81° | Humidity | C 1–1000 @ 0–92%RH | 1 kHz, 1 | [262] | ||
| Vertical columns | E-beam evaporation = 80° | Humidity | C 2–2200 nF @ 2–92%RH | N/A | 20 Hz to 1 MHz, 1 | [263] | |
| Vertical columns | E-beam evaporation θ = 70–85° | Humidity | C 1–800 @ 2–95%RH | 1 kHz, 1 | [258] | ||
| Vertical columns | E-beam: = 81° | Humidity | C 1–1600 nF @ 6–92%RH | N/A | 1 kHz, 1 | [264] | |
| Vertical columns | E-beam evaporation, = 81° | Humidity | C 2–1600 @ 2–92%RH (untreated) C 2–14,000 @ 2–92%RH (treated) | NA | 1 kHz, 1 | [242] | |
| Vertical columns | E-beam: | Humidity | S(nF/RH%): MAX @ 55% RH | 1 kHz at 1 | [144] | ||
| Vertical columns | E-beam evaporation | Alcohols | C 1–2000 nF (0–6.5% Ethanol), C 3–7000 nF (0–14.1% Methanol), C 0.7–300 nF (0–2.8% 1-PrOH), C 2–300 nF (0–3.4% 2-PrOH), C 0.7–15 nF (0–6.8% 1-BuOH), LoD (Ethanol) | , | 20 Hz to 1 kHz, 22 °C | [265] | |
| SiO | Helical columns | Thermal evaporation | Humidity | C = 0.063–425 nF@1.1–97% RH | 120 Hz at 23 °C | [257] | |
| Helical columns templates | PVD = 85 | Humidity | C 0.120 nF@15–65% RH C 0.120–1.240 nF @ 65–90% RH | NA | [266] | ||
| Si | Vertical columns | E-beam: = 81° | Humidity | C 2–6400 @ 2–90%RH | NA | 1 kHz, 1 | [242] |
| Vertical columns | E-beam evaporation: | Humidity | S(nF/RH%): MAX @ 80% RH | 1 kHz@1 | [144] | ||
| Vertical columns | E-beam evaporation: θ = 60–85° | Humidity | C 0.060 @ 10–50%RH C 0.060–0.950 @ 50–85%RH | (θ = 85°) (θ = 75°) | 1 kHz | [267] | |
| Piezoelectric | |||||||
| 2 | Vertical columns | E-beam: θ = 70° | Humidity | S = 15.50–65.4 kHz/%RH @ 25–75% RH | N/A | ~123.3 MHz | [259] |
3.3. Piezoelectric-Based Gas Sensors
3.4. Optical Gas Sensors
3.4.1. Optical Absorption Spectroscopy
3.4.2. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
3.5. GLAD-Based Electronic Nose Systems for Multi-Gas Sensing
4. Emerging Strategies for Enhancing GLAD-Based Gas Sensors
4.1. Hybrid Nanostructures and Composite Architectures
4.2. Functional Coatings and Selectivity Enhancement
- Atomic layer deposition. ALD provides conformal, sub-nanometer-thick coatings that are ideal for modifying high-aspect-ratio GLAD nanorods (e.g., Figure 3N). When deposited onto GLAD scaffolds, ALD layers can form core–shell structures that introduce catalytic activity (e.g., Pt or Pd), passivate surface defects, or tune band alignment. For example, ALD-coated ITO GLAD NRs with a Pt shell exhibit improved electrochemical sensor performance [290]. The uniformity of ALD is particularly beneficial for densely packed NR arrays where precise surface modification is required throughout the full depth of the structure.
- Chemical vapor deposition (CVD). CVD enables the growth of high-quality crystalline films, including 2D materials like graphene or MoS2. When applied to GLAD nanostructures, CVD-derived coatings can significantly improve charge transport and gas adsorption through synergistic interfacial interactions. For instance, GLAD NRs coated with graphene layers can support hybrid electrical–chemical sensing and multifunctional detection schemes involving both electronic and optical readouts. These hybrid architectures combine the vertical access channels provided by GLAD with the conductivity and surface chemistry of 2D materials.
- Plasma etching. Plasma processing serves as a versatile post-GLAD modification tool to tailor surface roughness, porosity, and chemistry. Oxygen plasma, for example, can introduce hydrophilic functional groups that improve polar gas adsorption. Selective etching of NR sidewalls or tips can reveal buried catalytic zones or create hierarchical porosity, which enhances gas diffusion and reduces response time. These effects are particularly useful for tuning sensing kinetics and surface specificity in dense GLAD arrays.
- Template-Assisted Fabrication. Combining GLAD with pre-patterned templates or nanosphere masks (e.g., nanosphere lithography (NSL)) enables precise spatial control over nanostructure geometry and placement [291]. This approach can produce nanohole arrays, nanocaps, or curved architectures with improved uniformity and spatial resolution. For example, recent studies have shown that combining GLAD and NSL significantly enhances hydrogen sensor performance [292,293]. Specifically, Pd80Co20 nanohole arrays demonstrated ultrafast response times (~1 s), part-per-billion detection limits, and excellent selectivity and stability, especially when coated with PMMA to exclude interfering gases and moisture [292]. Likewise, Pd67Co33 nanocap arrays demonstrated magneto-optical sensing with sub-second response times in high-humidity environments when paired with polymer barriers [293].
4.3. Integration with Low-Dimensional and Soft Materials
- 2D Materials. Layered materials such as graphene, MoS2, WS2, and MXenes can be integrated with GLAD NRs to enhance conductivity, introduce selective adsorption layers, or enable electron/hole transfer at the interface. For instance, MoS2-coated GLAD structures could show improved NO2 and NH3 sensing due to enhanced charge transport and selective adsorption. MXenes, with their metallic conductivity and surface terminations, can contribute hydrophilic or polar sensitivity while conformally covering complex GLAD morphologies without compromising porosity or anisotropy.
- Functional and Conducting Polymers. Polymers offer excellent chemical tunability and compatibility with GLAD substrates. Functional polymers, such as PMMA or polyacrylic acid, can serve as molecular sieves or humidity barriers, improving selectivity for target gases. Conducting polymers, including polyaniline (PANI), polypyrrole (PPy), and PEDOT:PSS, can introduce alternative transduction pathways, including conductivity changes due to doping or swelling, thereby enhancing signal diversity. These materials can be uniformly applied via spin-coating, spray deposition, or vapor processes and maintain performance under mechanical or thermal stress, making them well-suited for flexible or wearable sensing platforms.
- Metal–Organic Frameworks. MOFs, such as ZIF-8 and MIL-101, are crystalline, nanoporous materials that can offer precise molecular sieving and chemical specificity. When coated onto or infiltrated into GLAD structures, MOFs can create selective gas diffusion paths and enhance sensitivity by concentrating trace analytes like VOCs or ammonia. MOFs can also reduce humidity interference and support modular sensing through post-synthetic functionalization.
- Self-Assembled Monolayers. SAMs offer molecular-level control of surface chemistry, enabling the introduction of functional groups (–NH2, –COOH, –SH) for selective gas interaction or surface passivation. Applied to GLAD NRs, SAMs enhance stability, reduce fouling, and tailor wettability. Selective patterning of SAMs on sensor arrays also enables spatially distinct response profiles, supporting multi-analyte detection.
4.4. Device Engineering: Electrode Configuration and Signal Readout
4.4.1. Electrode Configuration and Conductance Anisotropy
4.4.2. Well-Separated NR Array Sensors
4.4.3. Porous Thin Film Sensors
4.5. Expanding the Modalities of GLAD-Fabricated Nanostructures for Optical Gas Sensing
4.5.1. LSPR: Unlocking Plasmonic Sensitivity Through Tailored Nanostructures
4.5.2. Fiber-Integrated GLAD Sensors: Toward Distributed, Multimodal Gas Detection
4.5.3. Fluorescence Amplification via GLAD: Enhancing Emission for Optical Readout
4.5.4. GLAD-Enabled Photoacoustics: Amplifying Acoustic Signals Through Optical Engineering
4.5.5. Structural Color Sensing: GLAD-Based Colorimetric Platforms for Visual Detection
4.5.6. Toward Rational Design: Bridging Nanostructure Morphology and Optical Function via Modeling and AI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, A.; Kumar, M.; Singh, R.K.; Bhattacharya, S. Gas Sensors: Manufacturing, Materials, and Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jaaniso, R.; Tan, O.K. Semiconductor Gas Sensors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fraden, J.; King, J. Handbook of Modern Sensors: Physics, Designs, and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Hu, S.; Zhang, D.; Ning, H. A survey on gas sensing technology. Sensors 2012, 12, 9635–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkinson, J.; Tatam, R.P. Optical gas sensing: A review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 24, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yue, G.; Chen, W.; Xing, Z.; Wang, J.; Wong, W.R.; Cheng, Z.; Set, S.Y.; Senthil Murugan, G.; Wang, X. On-chip optical gas sensors based on group-IV materials. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 2923–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba Hashwan, S.S.; Khir, M.H.M.; Nawi, I.M.; Ahmad, M.R.; Hanif, M.; Zahoor, F.; Al-Douri, Y.; Algamili, A.S.; Bature, U.I.; Alabsi, S.S. A review of piezoelectric MEMS sensors and actuators for gas detection application. Discov. Nano 2023, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Li, N. Micro-cantilever array and its application in gas sensor. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Nanjing, China, 21–24 April 2008; pp. 1547–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, H.P. Cantilever-Based Gas Sensing. In Solid State Gas Sensing; Comini, E., Faglia, G., Sberveglieri, G., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Khlebarov, Z.P.; Stoyanova, A.I.; Topalova, D.I. Surface acoustic wave gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1992, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.G.; Alder, J.F. Surface acoustic wave sensors for atmospheric gas monitoring. A review. Analyst 1989, 114, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G. Handbook of gas sensor materials. Conv. Approaches 2013, 1, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comini, E. Metal oxide nano-crystals for gas sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 568, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Luo, J.; Torun, H.; Hu, P.; Yang, C.; Grundmann, M.; Liu, X.; et al. Advances in designs and mechanisms of semiconducting metal oxide nanostructures for high-precision gas sensors operated at room temperature. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 470–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, P.T. Progress in the development of semiconducting metal oxide gas sensors: A review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.F.; Liu, S.B.; Meng, F.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Jin, Z.; Kong, L.T.; Liu, J.H. Metal oxide nanostructures and their gas sensing properties: A review. Sensors 2012, 12, 2610–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Lei, G.; Xu, H.; Lan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gu, H. Metal oxide based heterojunctions for gas sensors: A review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas sensors based on conducting polymers. Sensors 2007, 7, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, W.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, M.; Zhang, J. Conducting polymer-based nanostructures for gas sensors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 462, 214517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Yue, W.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhang, C.; Kan, H.; Niu, H.; Wang, W.; Guo, Y. Carbon-based nanomaterials for the detection of volatile organic compounds: A review. Carbon 2021, 180, 274–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raya, I.; Kzar, H.H.; Mahmoud, Z.H.; Al Ayub Ahmed, A.; Ibatova, A.Z.; Kianfar, E. A review of gas sensors based on carbon nanomaterial. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Li, N.; Fan, W.; Cai, H.; Zhao, D. Metal-organic framework based gas sensors. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.M.; Jo, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, H.W.; Hwang, I.S.; Yoo, D.J. MOF-based chemiresistive gas sensors: Toward new functionalities. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2206842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Jiang, C.; Wei, S.-h. Gas sensing in 2D materials. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2017, 4, 021304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, D.; Zeng, D. A review on two-dimensional materials for chemiresistive-and FET-type gas sensors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 15420–15439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Verma, G. Nanostructured Gas Sensors: Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Travlou, N.A.; Singh, K.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Bandosz, T.J. Cu–BTC MOF–graphene-based hybrid materials as low concentration ammonia sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 11417–11429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hou, Z.-L.; Zhang, B.-X.; Fang, H.-M.; Bi, S. High sensitivity self-recovery ethanol sensor based on polyporous graphene oxide/melamine composites. Carbon 2018, 137, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andringa, A.-M.; Spijkman, M.-J.; Smits, E.C.; Mathijssen, S.G.; van Hal, P.A.; Setayesh, S.; Willard, N.P.; Borshchev, O.V.; Ponomarenko, S.A.; Blom, P.W. Gas sensing with self-assembled monolayer field-effect transistors. Org. Electron. 2010, 11, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Chen, C.; Meng, L.; Lin, Y. Self-assembled monolayer of metal oxide nanosheet and structure and gas-sensing property relationship. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, M.; Sardar, S.; Jana, A. Nanofabrication techniques for semiconductor chemical sensors. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Sensing Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 119–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkeye, M.M.; Taschuk, M.T.; Brett, M.J. Glancing Angle Deposition of Thin Films Wiley Series in Materials for Electronic and Optoelectronic, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; p. 299. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, V.M.; Edgar, T.F. Control of lithography in semiconductor manufacturing. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2006, 26, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.P.; Ye, D.X.; Wang, G.C.; Lu, T.M. Designing nanostructures by glancing angle deposition. In Nanotubes and Nanowires; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bronicki, J.; Grochala, D.; Rydosz, A. Developing GLAD Parameters to Control the Deposition of Nanostructured Thin Film. Sensors 2022, 22, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barranco, A.; Borras, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Perspectives on oblique angle deposition of thin films: From fundamentals to devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 76, 59–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cao, W.; Larsen, G.K.; Toole, R.; Zhao, Y. Tilting angle of nanocolumnar films fabricated by oblique angle deposition. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2012, 30, 030606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, W.K.; Cabrera, N.; Frank, F.C.; Mott, N.F. The growth of crystals and the equilibrium structure of their surfaces. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1997, 243, 299–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapam, B.; Ngangbam, C.; Loitongbam, S.; Sougaijam, B. Recent Advancement of GLAD Technique for Growth of Nanostructures and its Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT), Hubli, India, 25–27 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhao, Y. Advanced multi-component nanostructures designed by dynamic shadowing growth. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2361–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.P. Dynamic shadowing growth and its energy applications. Front. Energy Res. 2014, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkeye, M.M.; Brett, M.J. Glancing angle deposition: Fabrication, properties, and applications of micro- and nanostructured thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2007, 25, 1317–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.X.; Zhao, Y.P.; Yang, G.R.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Wang, G.-C.; Lu, T.-M. Manipulating the column tilt angles of nanocolumnar films by glancing-angle deposition. Nanotechnology 2002, 13, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.P.; Ye, D.X.; Wang, P.-I.; Wang, G.C.; Lu, T.M. Fabrication of Si nanocolumns and Si square spirals on self-assembled monolayer colloid substrates. Int. J. Nanosci. 2002, 1, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Zhao, Y.P. Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity by Aligned WO3/TiO2 Two-Layer Nanorod Arrays. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 19635–19641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Wolcott, A.; Fitzmorris, R.C.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhao, Y. Quasi-core-shell TiO2/WO3 and WO3/TiO2 nanorod arrays fabricated by glancing angle deposition for solar water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 10792–10800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, O.; Zierold, R.; Patzig, C.; Bachmann, J.; Sturm, C.; Rheinländer, B.; Grundmann, M.; Görlitz, D.; Rauschenbach, B.; Nielsch, K. Tubular magnetic nanostructures based on glancing angle deposited templates and atomic layer deposition. Phys. Status Solidi B 2010, 247, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.P.; Fu, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.P.; Zhang, L.J.; Xia, A.L.; Cai, J.W. Multilayered Si/Ni nanosprings and their magnetic properties. Small 2007, 3, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.P.; Wu, J.S.; Zhao, Y.P. Designing catalytic nanomotors by dynamic shadowing growth. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, S.; Huang, W.J.; Zhao, Y.P. Combinatorial fabrication of composite nanorods using oblique angle co-deposition. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.M.; Li, H.F.; Gall, D. Multi-component nanostructure design by atomic shadowing. Thin Solid Films 2008, 517, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Hoffmann, C.; Zhao, Y.P. Embedding Ag nanoparticles into MgF2 nanorod Arrays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Z.; Basnet, P.; Murph, S.E.H.; Zhao, Y.P. Ag Nanoparticle Embedded TiO2 Composite Nanorod Arrays Fabricated by Oblique Angle Deposition: Toward Plasmonic Photocatalysis. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 11818–11827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Brown, C. Composition dependent nanocolumn tilting angle during the oblique angle co-deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 033106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, B.; Yang, K.; Brown, C.; Ramasamy, R.; Wang, H.; Lundgren, C.; Zhao, Y. Designing Si-based nanowall arrays by dynamic shadowing growth to tailor the performance of Li-ion battery anodes. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 8294–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N.; Shimanoe, K. Theory of power laws for semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 128, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Al-Dossary, O.; Kumar, G.; Umar, A. Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for NO2 Gas-Sensor Applications: A Review. Nanomicro Lett. 2015, 7, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poxson, D.J.; Mont, F.W.; Schubert, M.F.; Kim, J.K.; Schubert, E.F. Quantification of porosity and deposition rate of nanoporous films grown by oblique-angle deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 101914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Y. Spectroscopic ellipsometry investigations of porous SiO2 films prepared by glancing angle deposition. Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 1690–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, L.; Parra-Barranco, J.; Sanchez-Valencia, J.; Barranco, A.; Borras, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.C.; Hernandez, J.J.; Rueda, D.; Ezquerra, T. Correlation lengths, porosity and water adsorption in TiO2 thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 205701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydaghyan, G.; Buzea, C.; Cui, Y.; Elliott, C.; Robbie, K. Ex situ ellipsometric investigation of nanocolumns inclination angle of obliquely evaporated silicon thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 153103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.M.; Thommes, M.; Brett, M.J. Pore analysis of obliquely deposited nanostructures by krypton gas adsorption at 87 K. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 143, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gospodyn, J.; Sit, J.C. Characterization of dielectric columnar thin films by variable angle Mueller matrix and spectroscopic ellipsometry. Opt. Mater. 2006, 29, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.M.; Taschuk, M.T.; Harris, K.D.; Rider, D.A.; Wakefield, N.G.; Sit, J.C.; Buriak, J.M.; Thommes, M.; Brett, M.J. Surface Area Characterization of Obliquely Deposited Metal Oxide Nanostructured Thin Films. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4368–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-García, L.; González-Valls, I.; Lira-Cantu, M.; Barranco, A.; González-Elipe, A.R. Aligned TiO2 nanocolumnar layers prepared by PVD-GLAD for transparent dye sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3426–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Taga, Y. Numerical study of the effective surface area of obliquely deposited thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 5599–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharizadeh, S.; Sutton, M.; Robbie, K.; Brown, T. X-ray reflectometry characterization of porous silicon films prepared by a glancing-angle deposition method. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 125405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amassian, A.; Kaminska, K.; Suzuki, M.; Martinu, L.; Robbie, K. Onset of shadowing-dominated growth in glancing angle deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 173114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backholm, M.; Foss, M.; Nordlund, K. Roughness scaling in titanium thin films: A three-dimensional molecular dynamics study of rotational and static glancing angle deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 268, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liang, J.; Mo, Y.; Luo, D.; Jiang, S. Onset of shadowing-dominated growth of Ag films in glancing angle deposition: Kinetic Monte Carlo simulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 264, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potocnik, J.; Popovic, M. Optical properties of zigzag nickel nanostructures obtained at different deposition angles. Sci. Sinter. 2021, 53, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, C.; Martin, N.; Devel, M.; Ollitrault, J.; Billard, A. Correlation between structural and optical properties of WO3 thin films sputter deposited by glancing angle deposition. Thin Solid Films 2013, 534, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.D.; Noh, M.S.; Kim, S.; Shim, Y.S.; Song, Y.G.; Lee, K.; Lee, H.R.; Nahm, S.; Yoon, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Versatile approaches to tune a nanocolumnar structure for optimized electrical properties of In2O3 based gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2017, 248, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Dong, G.; Shao, J.; He, H.; Fan, Z. Optical and electrical properties of SnO2:Sb thin films deposited by oblique angle deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzea, C.; Kaminska, K.; Beydaghyan, G.; Brown, T.; Elliott, C.; Dean, C.; Robbie, K. Thickness and density evaluation for nanostructured thin films by glancing angle deposition. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2005, 23, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Karabacak, T.; Li, L.; Pelliccione, M.; Wang, G.C.; Lu, T.M. Power-law scaling during shadowing growth of nanocolumns by oblique angle deposition. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2007, 25, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbie, K.; Brett, M.J. Sculptured thin films and glancing angle deposition: Growth mechanics and applications. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 1997, 15, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.M.; Zhao, Y.P.; Drotar, J.T.; Karabacak, T.; Wang, G.C. Novel Mechanisms on the Growth Morphology of Films. MRS Proc. 2002, 749, W1.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lagally, M.G. Atomistic Processes in the Early Stages of Thin-Film Growth. Science 1997, 276, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagon, S.P.; Huang, H.; Kevin Baldwin, J.; Misra, A. Anomaly of film porosity dependence on deposition rate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 061601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, E.E.M.; Carrasco, I.S.S.; de Assis, T.A.; Reis, F. Statistics of adatom diffusion in a model of thin film growth. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 012805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Gall, D. Structure zone model for extreme shadowing conditions. Thin Solid Films 2013, 527, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, D.W.; Dohnálek, Z.; Dohnálková, A.; Arey, B.W.; McCready, D.E.; Ponnusamy, N.; Mullins, C.B.; Kay, B.D. Reactive ballistic deposition of porous TiO2 films: Growth and characterization. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 4765–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A. Growth Characteristics Of Glancing Angle Deposited (GLAD) Thin Films. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2014, 5, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaForge, J.M.; Taschuk, M.T.; Brett, M.J. Glancing angle deposition of crystalline zinc oxide nanorods. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, J.V.; Costantini, G.; Kern, K. Engineering atomic and molecular nanostructures at surfaces. Nature 2005, 437, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabacak, T.; Singh, J.P.; Zhao, Y.P.; Wang, G.-C.; Lu, T.-M. Scaling during shadowing growth of isolated nanocolumns. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 125408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzea, C.; Beydaghyan, G.; Elliott, C.; Robbie, K. Control of power law scaling in the growth of silicon nanocolumn pseudo-regular arrays deposited by glancing angle deposition. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 1986–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, R.; Regodon, G.; Acosta-Rivera, H.; Rico, V.; Alcala, G.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Structure and Void Connectivity in Nanocolumnar Thin Films Grown by Magnetron Sputtering at Oblique Angles. Coatings 2023, 13, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Shin, Y.C.; Kim, C.M.; Lee, B.G.; Kim, E.H.; Park, Y.J.; Sobahan, K.M.A.; Hwangbo, C.K.; Lee, Y.P.; Kim, T.G. Optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide thin films with tilted and spiral microstructures prepared by oblique angle deposition. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 2500–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhajhria, D.; Tiwari, P.; Chandra, R. Planar Microsupercapacitors Based on Oblique Angle Deposited Highly Porous TiN Thin Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 26162–26170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, P.; Lopes, C.; Martin, N.; Fonseca, C.; Vaz, F. Electrical characterization of Ag:TiN thin films produced by glancing angle deposition. Mater. Lett. 2014, 115, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, S.; Cote, J.-M.; Raschetti, M.; Roux, P.; Martin, N. Glancing angle deposition for tuning electronic transport properties of Si thin films. Phys. Lett. A 2023, 480, 128955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.W.; Poxson, D.J.; Mont, F.W.; Chhajed, S.; Cho, J.; Schubert, E.F.; Welser, R.E.; Dhar, N.K.; Sood, A.K. Experimental and theoretical study of the optical and electrical properties of nanostructured indium tin oxide fabricated by oblique-angle deposition. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 3950–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, H.; Cho, J. In-plane structural and electronic anisotropy of nanoporous Pt films formed by oblique angle deposition. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Beainou, R.; Chargui, A.; Pedrosa, P.; Mosset, A.; Euphrasie, S.; Vairac, P.; Martin, N. Electrical resistivity and elastic wave propagation anisotropy in glancing angle deposited tungsten and gold thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintymer, J.; Gavoille, J.; Martin, N.; Takadoum, J. Glancing angle deposition to modify microstructure and properties of sputter deposited chromium thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 174–175, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Larsen, G.K.; Zhao, Y. Anisotropic resistivity of tilted silver nanorod arrays: Experiments and modeling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 233101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vick, D.; Brett, M.J. Conduction anisotropy in porous thin films with chevron microstructures. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2006, 24, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Beainou, R.; Cote, J.M.; Tissot, V.; Potin, V.; Martin, N. Resistivity anisotropy of tilted columnar W and W–Cu thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 421, 127412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Barranco, J.; García-García, F.J.; Rico, V.; Borrás, A.; López-Santos, C.; Frutos, F.; Barranco, A.; González-Elipe, A.R. Anisotropic In-Plane Conductivity and Dichroic Gold Plasmon Resonance in Plasma-Assisted ITO Thin Films e-Beam-Evaporated at Oblique Angles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10993–11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, A.; Martin, N.; Carpentier, L.; Gallas, B. A theoretical model for the electrical properties of chromium thin films sputter deposited at oblique incidence. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 215301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G. Metal oxides for solid-state gas sensors: What determines our choice? Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2007, 139, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A. Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 229, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Shim, Y.S.; Song, Y.G.; Han, S.D.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, C.Y. Highly Sensitive Sensors Based on Metal-Oxide Nanocolumns for Fire Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savorianakis, G.; Rousseau, C.; Battie, Y.; En Naciri, A.; Maes, B.; Voué, M.; Konstantinidis, S. Optical anisotropy of nanostructured vanadium dioxide thermochromic thin films synthesized by reactive magnetron sputtering combined with glancing angle deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 502, 131938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.K.; Farghaly, A.A.; Silva, T.A.; Ye, D.; Collinson, M.M. Gold-Nanoparticle-Decorated Titanium Nitride Electrodes Prepared by Glancing-Angle Deposition for Sensing Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazideh, M.R.; Dizaji, H.R.; Ehsani, M.H.; Moghadam, R.Z. Modification of the morphology and optical properties of SnS films using glancing angle deposition technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 405, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossnagel, S.M. Thin film deposition with physical vapor deposition and related technologies. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2003, 21, S47–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M. (Ed.) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wongchoosuk, C.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Phokharatkul, D.; Horprathum, M.; Tuantranont, A.; Kerdcharoen, T. Carbon doped tungsten oxide nanorods NO2 sensor prepared by glancing angle RF sputtering. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2013, 181, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.M.; Shim, Y.S.; Han, S.D.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, C.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, M.; Jang, H.W. Vertically ordered SnO2 nanobamboos for substantially improved detection of volatile reducing gases. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17939–17945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.R.; Ming, A.J.; Wei, F. Enhanced NO2 sensing properties of Pt/WO3 films grown by glancing angle deposition. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 21388–21394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horprathum, M.; Srichaiyaperk, T.; Samransuksamer, B.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Eiamchai, P.; Limwichean, S.; Chananonnawathorn, C.; Aiempanakit, K.; Nuntawong, N.; Patthanasettakul, V.; et al. Ultrasensitive Hydrogen Sensor Based on Pt-Decorated WO3 Nanorods Prepared by Glancing-Angle dc Magnetron Sputtering. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22051–22060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Jang, B.; Kim, W.; Lee, W. Enhanced hydrogen sensing properties of Pd-coated SnO2 nanorod arrays in nitrogen and transformer oil. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2019, 283, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, M.S.; Jung, H.; Choe, Y.-S.; Kim, W.; Song, Y.G.; Kang, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, W. Selective C2H2 detection with high sensitivity using SnO2 nanorod based gas sensors integrated with a gas chromatography. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Tomar, M.; Gupta, V. Growth of highly porous ZnO nanostructures for carbon monoxide gas sensing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 343, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.R.; Ming, A.J.; Wei, F. NO2 gas sensing properties of Pd/WO3 films prepared by glancing angle deposition. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 5827–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.G.; Park, J.Y.; Suh, J.M.; Shim, Y.S.; Yi, S.Y.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, S.; Yuk, J.M.; Ju, B.K.; Kang, C.Y. Heterojunction Based on Rh-Decorated WO3 Nanorods for Morphological Change and Gas Sensor Application Using the Transition Effect. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Akbar, S.A.; Morris, P.A. Nanoscale metal oxide-based heterojunctions for gas sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-Y.; Ou, L.-X.; Mao, L.-W.; Wu, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.-P.; Lu, H.-L. Advances in noble metal-decorated metal oxide nanomaterials for chemiresistive gas sensors: Overview. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govardhan, K.; Grace, A.N. Metal/metal oxide doped semiconductor based metal oxide gas sensors—A review. Sens. Lett. 2016, 14, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, B.; Geng, X.; Debliquy, M. Hydrogen sensors based on noble metal doped metal-oxide semiconductor: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 20386–20397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K.; Kaur, J.; Arora, S.; Kumar, A.; Chawla, A.K.; Khanna, A. Effects of oblique angle deposition on structural, electrical and wettability properties of Bi thin films grown by thermal evaporation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforge, J.M. Fabrication of Highly Porous Zinc and Zinc Oxide Nanostructures. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2009, 1142, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chundak, M.; Khalakhan, I.; Kús, P.; Duchon, T.; Potin, V.; Cacucci, A.; Tsud, N.; Matolín, V.; Veltruska, K. Tailoring of highly porous SnO2 and SnO2-Pd thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 232, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitei, P.N.; Singh, N.K. Annealing effect on structural and optical properties of glad synthesized Gd2O3 nanorod. Discov. Mater. 2023, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanu, L.T.; Singh, N.K. Enhanced structural and photoluminescence properties on GLAD synthesized annealed vertically aligned NiO nanowires. J. Lumin. 2023, 257, 119704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydosz, A.; Dyndal, K.; Andrysiewicz, W.; Grochala, D.; Marszalek, K. GLAD Magnetron Sputtered Ultra-Thin Copper Oxide Films for Gas-Sensing Application. Coatings 2020, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Nacer, S.; Jlidi, D.; Labidi, A.; Akkari, F.C.; Touihri, S.; Maaref, M. Promising ethanol detection enhancement of Cu2O thin film deposited by GLAD technique. Measurement 2020, 151, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.B.; Krystianiak, A.; Dordor, E.; Heintz, O.; Geoffroy, N.; Martin, N. Nano-sculptured vanadium oxide thin films for benzene detection. Mater. Lett. 2024, 371, 136937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahy, S.; Dhar, J.C. Post Annealing Effects on Er2O3 Nanowire Arrays for Improved Photodetection. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2018, 17, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.D.; Moon, H.G.; Noh, M.S.; Pyeon, J.J.; Shim, Y.S.; Nahm, S.; Kim, J.S.; Yoo, K.S.; Kang, C.Y. Self-doped nanocolumnar vanadium oxides thin films for highly selective NO2 gas sensing at low temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokriyan, F.; Dizaji, H.R.; Ehsani, M.H.; Moghadam, R.Z. Tuning optical properties of CdS films using oblique angle deposition technique. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2021, 54, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.H.; Rezagholipour Dizaji, H.; Azizi, S.; Ghavami Mirmahalle, S.F.; Hosseini Siyanaki, F. Optical and structural properties of cadmium telluride films grown by glancing angle deposition. Phys. Scr. 2013, 88, 025602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Lee, S.H.; Su, T.Y.; Wu, S.C.; Chen, P.J.; Chueh, Y.L. Phase-modulated 3D-hierarchical 1T/2H WSe2 nanoscrews by a plasma-assisted selenization process as high performance NO gas sensors with a ppb-level detection limit. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 22314–22322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.; Correa, M.A.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Vaz, F. Flexible multifunctional hard coatings based on chromium oxynitride for pressure-sensing applications. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2022, 40, 063101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larbi, A.; Trabelsi, I.; Dahman, H.; Kanzari, M. Investigation on the AC and DC electrical conductivity of Sn3Sb2S6 thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 2907–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comini, E.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Stable and highly sensitive gas sensors based on semiconducting oxide nanobelts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 1869–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Conduction model of metal oxide gas sensors. J. Electroceramics 2001, 7, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricoli, A. Structural Stability and Performance of Noble Metal-Free SnO2-Based Gas Sensors. Biosensors 2012, 2, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, D.W.; May, R.A.; Berglund, S.P.; Stevenson, K.J.; Mullins, C.B. Low temperature synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline titanium carbide with tunable porous architectures. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajir, A.E.; Yazdi, M.A.P.; Krystianiak, A.; Heintz, O.; Martin, N.; Berger, F.; Sanchez, J.-B. Nanostructuring of SnO2 Thin Films by Associating Glancing Angle Deposition and Sputtering Pressure for Gas Sensing Applications. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.J.; Taschuk, M.T.; Brett, M.J. Nanostructured metal oxide thin films for humidity sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2008, 8, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, I.; Barna, P.B.; Hultman, L.; Greene, J.E. Microstructural evolution during film growth. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2003, 21, S117–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitei, P.N.; Alam, M.W.; Ngangbam, C.; Singh, N.K. Enhanced UV photodetection characteristics of annealed Gd2O3 nanorods. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, P.; Choudhuri, B.; Saranyan, V.; Chinnamuthu, P. Synthesis of coaxial TiO2/In2O3 nanowire assembly using glancing angle deposition for wettability application. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 9, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qi, H.; Chai, Y.; Li, M.; Guo, M.; Pan, M.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Shao, J. Alteration of titanium dioxide material properties by glancing angle deposition plus annealing treatment. Superlattices Microstruct. 2016, 90, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qi, H.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, J.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yi, K.; Shao, J. Morphology, structure and optical properties in TiO2 nanostructured films annealed at various temperatures. Opt. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, S.A.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Ali, I.M. Comparison of anatase and rutile TiO2 nanostructure for gas sensing application. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2020, 15, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Sui, N.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, T.; Tu, J.; Zhang, T. TiO2 nanostructures with different crystal phases for sensitive acetone gas sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasirian, S.; Milani Moghaddam, H. Effect of different titania phases on the hydrogen gas sensing features of polyaniline/TiO2 nanocomposite. Polymer 2014, 55, 1866–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrakatseli, V.E.; Kalarakis, A.N.; Kalampounias, A.G.; Amanatides, E.K.; Mataras, D.S. Glancing Angle Deposition Effect on Structure and Light-Induced Wettability of RF-Sputtered TiO2 Thin Films. Micromachines 2018, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, Y.; Kobayashi, S.-i.; Hoshi, Y. Photocatalytic properties of annealed TiO2 films with controlled structure fabricated using oxygen-ion-assisted reactive evaporation with glancing angle deposition technique. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ou, K.; Dai, J.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H. Effects of annealing conditions and multifold morphology on photocatalytic properties of TiO2 nanorods. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 129, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, R.K.; Nath, A.; Singh, L.R.; Sarkar, M.B. Effect of High–Temperature Annealing on Au Thin Film/TiO2 Nanowires for Enhanced Photodetection. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2023, 22, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Ou, K.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhu, H.; Liu, L.; Cai, F.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H. Effects of annealing conditions and nanostructures on photocatalytic and degradation properties of In2O3. Appl. Phys. A 2024, 130, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, S.; Sharma, S.; Tomar, M.; Chowdhuri, A. Effect of Annealing on Resistive Switching Properties of Glancing Angle Deposition-Assisted WO3 Thin Films. Phys. Status Solidi A 2023, 220, 2300358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanawikkam, C.; Bootchanont, A.; Porjai, P.; Jetjamnong, C.; Kowong, R.; Lertvanithphol, T.; Chananonnawathorn, C.; Chirawatkul, P.; Chanlek, N.; Nakajima, H.; et al. Phase evolution in annealed Ni-doped WO3 nanorod films prepared via a glancing angle deposition technique for enhanced photoelectrochemical performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 584, 152581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Tomar, M.; Gupta, V. Tunable nanostructured columnar growth of SnO2 for efficient detection of CO gas. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 065502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oros, C.; Horprathum, M.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Srichaiyaperk, T.; Samransuksamer, B.; Limwichean, S.; Eiamchai, P.; Phokharatkul, D.; Nuntawong, N.; Chananonnawathorn, C.; et al. Ultra-sensitive NO2 sensor based on vertically aligned SnO2 nanorods deposited by DC reactive magnetron sputtering with glancing angle deposition technique. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2016, 223, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Kwon, H.; Chhajed, S.; Byon, J.W.; Baik, J.M.; Im, J.; Oh, S.H.; Jang, H.W.; Yoon, S.J.; Kim, J.K. A near single crystalline TiO2 nanohelix array: Enhanced gas sensing performance and its application as a monolithically integrated electronic nose. Analyst 2013, 138, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, N.; Singh, M.; Comini, E. Materials engineering strategies to control metal oxides nanowires sensing properties. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Deng, Y.; Yang, H.; Liao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zou, Y.; Wu, L.; Deng, Y. Functionalization of mesoporous semiconductor metal oxides for gas sensing: Recent advances and emerging challenges. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Approaches for selectivity improvement of conductometric gas sensors: An overview. Sens. Diagn. 2024, 3, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.H.; Kaur, N.; Comini, E.; Pinna, N. Toward optimized radial modulation of the space-charge region in one-dimensional SnO2–NiO core–shell nanowires for hydrogen sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 4594–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuvaneshwari, S.; Gopalakrishnan, N. Effect of Fe doping on the NH3 sensing properties of CuO nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 6920–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.M.; Son, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Lim, M.H.; Han, J.K.; Jang, M.; Park, S.; Kang, S.; Yim, S.; Myung, S. Enhancing selectivity and sensitivity in gas sensors through noble metal-decorated ZnO and machine learning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 693, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hieu, N.; Thi Hong Van, P.; Le Nhan, T.; Van Duy, N.; Duc Hoa, N. Giant enhancement of H2S gas response by decorating n-type SnO2 nanowires with p-type NiO nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 253106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizhov, A.; Rumyantseva, M.; Vasiliev, R.; Filatova, D.; Drozdov, K.; Krylov, I.; Abakumov, A.; Gaskov, A. Visible light activated room temperature gas sensors based on nanocrystalline ZnO sensitized with CdSe quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 205, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kaur, N.; Drera, G.; Casotto, A.; Sangaletti, L.; Comini, E. SAM functionalized ZnO nanowires for selective acetone detection: Optimized surface specific interaction using APTMS and GLYMO monolayers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, H. Metal–organic framework coated devices for gas sensing. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 2471–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Zhao, Y. Nanocarpet effect induced superhydrophobicity. Langmuir 2010, 26, 8245–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Park, B.; Siragusa, G.; Jones, L.; Tripp, R.; Zhao, Y.; Cho, Y.-J. An Au/Si hetero-nanorod-based biosensor for Salmonella detection. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 155502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Cui, Z.; Chu, B.; Xie, N.; Wang, Z.; Bai, P.; Guo, X.; Lyu, J. Fabrication Methods of Continuous Pure Metal–Organic Framework Membranes and Films: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernikova, V.; Shekhah, O.; Eddaoudi, M. Advanced fabrication method for the preparation of MOF thin films: Liquid-phase epitaxy approach meets spin coating method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20459–20464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.P.; Liu, H.Y.; Bian, G.; Gao, X.; Zhao, S.; Kang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Bu, X.H. Metal-layer assisted growth of ultralong quasi-2D MOF nanoarrays on arbitrary substrates for accelerated oxygen evolution. Small 2019, 15, 1906086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balderas, J.; Navarro, D.; Vargas, V.; Tellez-Cruz, M.; Carmona, S.; Falcony, C. Ultrasonic spray deposition as a new route to luminescent MOF film synthesis. J. Lumin. 2019, 212, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Fu, Z.H.; Deng, W.H.; Wen, Y.; Wu, A.Q.; Ye, X.L.; Xu, G. The growth mechanism of a conductive MOF thin film in spray-based layer-by-layer liquid phase epitaxy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Ciufo, R.A.; Meyerson, M.L.; Keitz, B.K.; Mullins, C.B. Solvent-free vacuum growth of oriented HKUST-1 thin films. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 19396–19406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; McCarthy, T.J. Layer-by-layer deposition: A tool for polymer surface modification. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.P.; Lau, K.K.; Chan, K.; Mao, Y.; Gupta, M.; O’Shaughnessy, W.S.; Gleason, K.K. Initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) of polymeric nanocoatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 9400–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J. Mechanisms of plasma polymerization–reviewed from a chemical point of view. Plasma Process. Polym. 2011, 8, 783–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriven, L. Physics and applications of dip coating and spin coating. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 1988, 121, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, S.; Fok, E.; Sit, J.C.; Veinot, J.G.C. Surface Functionalization of Porous Nanostructured Metal Oxide Thin Films Fabricated by Glancing Angle Deposition. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5260–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.A.B.; Kumar, A.R. A review on resistive-based gas sensors for the detection of volatile organic compounds using metal-oxide nanostructures. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 133, 108893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horprathum, M.; Limwichean, K.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Eiamchai, P.; Aiempanakit, K.; Limnonthakul, P.; Nuntawong, N.; Pattantsetakul, V.; Tuantranont, A.; Chindaudom, P. NO2-sensing properties of WO3 nanorods prepared by glancing angle DC magnetron sputtering. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.H.; Yang, Y.W.; Ou, K.; Zhang, W.T.; Tang, Y.L.; Ni, Y.X.; Xia, Y.D.; Wang, H.Y. High-performance room temperature NH3 sensor based on zigzag morphology TiO2 nanorods. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 983, 173807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, K.; Abokifa, A.; An, S.; Lee, J.; Raman, B.; Biswas, P.; Fortner, J.D. Crumpled graphene oxide for enhanced room temperature gas sensing: Understanding the critical roles of surface morphology and functionalization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzoni, A. A Statistical Analysis of Response and Recovery Times: The Case of Ethanol Chemiresistors Based on Pure SnO2. Sensors 2022, 22, 6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Zoolfakar, A.S.; Ab Kadir, R.; Wlodarski, W. Investigation of RF sputtered tungsten trioxide nanorod thin film gas sensors prepared with a glancing angle deposition method toward reductive and oxidative analytes. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2013, 183, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Yazdi, M.A.P.; Sanchez, J.B.; Billard, A.; Berger, F.; Martin, N. Exploiting the dodecane and ozone sensing capabilities of nanostructured tungsten oxide films. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2018, 266, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Yazdi, M.A.P.; Sanchez, J.B.; Billard, A.; Berger, F.; Martin, N. Reactive co-sputtering of tungsten oxide thin films by glancing angle deposition for gas sensors. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Functionalized Surfaces and their Applications to Chemical and Bio-Sensors (SURFOCAP), Femto ST Inst, Besancon, France, 30–31 May 2017; pp. 314–318. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, H.G.; Choi, Y.R.; Shim, Y.S.; Choi, K.I.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, S.J.; Park, H.H.; Kang, C.Y.; Jang, H.W. Extremely sensitive and selective NO probe based on villi-like WO3 nanostructures for application to exhaled breath analyzers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10591–10596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarzycki, A.; Dyndal, K.; Sitarz, M.; Xu, J.; Gao, F.; Marszalek, K.; Rydosz, A. Influence of GLAD Sputtering Configuration on the Crystal Structure, Morphology, and Gas-Sensing Properties of the WO3 Films. Coatings 2020, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.G.; Shim, Y.S.; Kim, S.; Han, S.D.; Moon, H.G.; Noh, M.S.; Lee, K.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, J.S.; Ju, B.K.; et al. Downsizing gas sensors based on semiconducting metal oxide: Effects of electrodes on gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2017, 248, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aier, K.M.; Dhar, J.C. SO2 Gas Detection Using GLAD-Synthesized ZnO Nanowires. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2024, 8, 2000904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.X.; Xie, M.; Luo, J.T.; Kan, H.; Wei, Q.P. Nitric oxide sensors using nanospiral ZnO thin film deposited by GLAD for application to exhaled human breath. Rsc Adv. 2020, 10, 14877–14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikesh, S.; Singh, A.D.; Shougaijam, B. Development of Ethanol Sensor Based on Vertically Aligned SnO2/TiO2 Heterojunction Nanowire Using GLAD Technique. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2024, 71, 3867–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Lee, K.; Kang, M.; Kim, C.; Ha, J.H.; Han, H.; Yang, S.; Yang, D.; Seo, J.H.; Park, I. Room-temperature rapid oxygen monitoring system in high humidity hydrogen gas environment towards water electrolysis application. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2025, 422, 136693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y. Recent advances in SnO2 nanostructure based gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 364, 131876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurlo, A. Nanosensors: Towards morphological control of gas sensing activity. SnO2, In2O3, ZnO and WO3 case studies. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, H.; Li, Y.; Zeng, W. Substrate-free synthesis of WO3 nanorod arrays and their superb NH3-sensing performance. Mater. Lett. 2017, 209, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, C.S.; Hegde, M.; Rao, C.R. H2S sensors based on tungsten oxide nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 128, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, S.J.; Kandasamy, S.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Wlodarski, W. Hydrogen sensing characteristics of WO3 thin film conductometric sensors activated by Pt and Au catalysts. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Zavabeti, A.; Wang, Y.; Harrison, C.J.; Carey, B.J.; Mohiuddin, M.; Chrimes, A.F.; De Castro, I.A.; Zhang, B.Y.; Sabri, Y.M. Quasi physisorptive two dimensional tungsten oxide nanosheets with extraordinary sensitivity and selectivity to NO2. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 19162–19175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhao, Y.P. Structural and optical characterization of WO3 nanorods/films prepared by oblique angle deposition. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2007, 25, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, R.; Doi, I.; Cruz, T.G.; Lourenco, A. Deposition of WO3 Thin Films at Oblique Angle—Growth and Electrochemical Behavior. e-J. Surf. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 7, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hincheeranun, W.; Chananonnawathorn, C.; Horprathum, M.; Eiamchai, P.; Limwichean, S.; Pattantsetakul, V.; Aimpanakit, K. Omnidirectional antireflection and electrochromic properties of WO3 nanorods prepared by oblique angle deposition. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Sofia, Bulgaria, 26–30 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, D. Partially ionized beam growth of tungsten oxide nanowires by oblique angle deposition. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 2706–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, F.J.; Mosa, J.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Aparicio, M. Sodium ion storage performance of magnetron sputtered WO3 thin films. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 321, 134669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, R.; Cruz, T.G.; Gorenstein, A. WO3 pillar-type and helical-type thin film structures to be used in microbatteries. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydaghyan, G.; Renaud, J.-L.M.; Bader, G.; Ashrit, P. Enhanced electrochromic properties of heat treated nanostructured tungsten trioxide thin films. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, D.; Frankel, D.J.; Lad, R.J. Nanostructured tungsten and tungsten trioxide films prepared by glancing angle deposition. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 4095–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.G.; Jung, Y.; Han, S.D.; Shim, Y.S.; Shin, B.; Lee, T.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.; Jun, S.C.; Park, H.H.; et al. Chemiresistive Electronic Nose toward Detection of Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20969–20976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seekaew, Y.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Phokharatkul, D.; Wongchoosuk, C. Room temperature toluene gas sensor based on TiO2 nanoparticles decorated 3D graphene-carbon nanotube nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 279, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Z.; Song, Y.-Y. The Challenges and Opportunities for TiO2 Nanostructures in Gas Sensing. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyothilal, H.; Shukla, G.; Walia, S.; Kundu, S.; Angappane, S. Humidity sensing and breath analyzing applications of TiO2 slanted nanorod arrays. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 301, 111758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, S.; Brunet, E.; Maier, T.; Mutinati, G.C.; Köck, A.; Freudenberg, O.; Gspan, C.; Grogger, W.; Neuhold, A.; Resel, R. Gas sensing properties of novel CuO nanowire devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volanti, D.P.; Felix, A.A.; Orlandi, M.O.; Whitfield, G.; Yang, D.-J.; Longo, E.; Tuller, H.L.; Varela, J.A. The Role of Hierarchical Morphologies in the Superior Gas Sensing Performance of CuO-Based Chemiresistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Hwang, I.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, C.-Y.; Lee, J.-H. CuO nanowire gas sensors for air quality control in automotive cabin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 135, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Nearly Monodisperse Cu2O and CuO Nanospheres: Preparation and Applications for Sensitive Gas Sensors. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelcov, E.; Lilach, Y.; Kolmakov, A. Gas sensor based on metal− insulator transition in VO2 nanowire thermistor. Nano letters 2009, 9, 2322–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X. Glycothermal synthesis of VO2 (B) nanoparticles for gas sensing application. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Lou, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, K.; Xuan, C. NO2 gas sensing performance of a VO2 (B) ultrathin vertical nanosheet array: Experimental and DFT investigation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 31968–31977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrammouz, R.; Lazerges, M.; Pironon, J.; Taher, I.B.; Randi, A.; Halfaya, Y.; Gautier, S. V2O5 gas sensors: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 332, 113179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.; Lubecka, M.; Czapla, A. V2O5 thin films for gas sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.D.; Pazhanivel, T.; Kumar, P.S.; Mangalaraj, D.; Nataraj, D.; Ponpandian, N. Self assembled V2O5 nanorods for gas sensors. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado Ciprés, V. Nano-Structured Vanadium Oxide Thin Films for Gas Sensors; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, V.; Prathuru, A.; Fernandez, C.; Sujatha, D.; Panda, S.K.; Faisal, N.H. Indium tin oxide thin film preparation and property relationship for humidity sensing: A review. Eng. Rep. 2024, 6, e12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Patel, P.; Vaishnav, V. Indium tin oxide (ITO) thin film gas sensor for detection of methanol at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 96, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Toole, R.; Basnet, P.; Zhao, Y. Highly sensitive double-layered nanorod array gas sensors prepared by oblique angle deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 073110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.-J.; Xin, R.-F.; Li, S.-X. Metal oxide heterostructures for improving gas sensing properties: A review. Materials 2022, 16, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Cao, S.; Huang, Z.; Yang, D.; Zhang, G. Improving Gas-Sensing Performance Based on MOS Nanomaterials: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.S.; Na, C.W.; Lee, J.H. Design of Highly Selective Gas Sensors via Physicochemical Modification of Oxide Nanowires: Overview. Sensors 2016, 16, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, Z.; Zeng, D.; Xie, C. Metal-oxide-semiconductor based gas sensors: Screening, preparation, and integration. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 6313–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Cho, I.; Park, J.; Jeong, J.; Lee, K.; Lee, B.; Del Orbe Henriquez, D.; Yoon, K.; Park, I. High Accuracy Real-Time Multi-Gas Identification by a Batch-Uniform Gas Sensor Array and Deep Learning Algorithm. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.G.; Jung, Y.; Han, S.D.; Shim, Y.S.; Jung, W.S.; Lee, T.; Lee, S.; Park, J.H.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; et al. All villi-like metal oxide nanostructures-based chemiresistive electronic nose for an exhaled breath analyzer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kang, M.; Park, I. Development of Monolithic Micro-Led Gas Sensor Based E-Nose System for Real-Time, Selective Gas Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Munich, Germany, 15–19 January 2023; pp. 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.; Lee, K.; Sim, Y.C.; Jeong, J.S.; Cho, M.; Jung, H.; Kang, M.; Cho, Y.H.; Ha, S.C.; Yoon, K.J.; et al. Deep-learning-based gas identification by time-variant illumination of a single micro-LED-embedded gas sensor. Light Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayca, S.U.; Cansizoglu, M.F.; Biris, A.S.; Watanabe, F.; Karabacak, T. Enhanced oxidation resistance of magnesium nanorods grown by glancing angle deposition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 5998–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taschuk, M.T.; Harris, K.D.; Smetaniuk, D.P.; Brett, M.J. Decoupling sensor morphology and material: Atomic layer deposition onto nanocolumn scaffolds. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2012, 162, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Cho, I.; Kang, M.; Jeong, J.; Choi, M.; Woo, K.Y.; Yoon, K.J.; Cho, Y.H.; Park, I. Ultra-Low-Power E-Nose System Based on Multi-Micro-LED-Integrated, Nanostructured Gas Sensors and Deep Learning. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, G.; Kumar, C.; Angappane, S. Structural Properties and Wettability of TiO2 Nanorods. Phys. Status Solidi B 2019, 256, 1900032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.J.; Martin, N.; Jiménez, J.J.; García, R.; Morales, F.M. Enhancing luminous transmittance and hysteresis width of VO2-based thermochromic coatings by combining GLAD and RGPP approaches. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 419, 135472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiema, G.; Colgan, M.; Brett, M. Dye sensitized solar cells incorporating obliquely deposited titanium oxide layers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2005, 85, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, V.; Martin, N.; Pedrosa, P.; Rauch, J.-Y.; Horakova, M.; Yazdi, M.A.P.; Billard, A. Temperature dependence of electrical resistivity in oxidized vanadium films grown by the GLAD technique. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 304, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramola, R.C.; Negi, S.; Rawat, M.; Singh, R.C.; Singh, F. Annealing Effects on Gas Sensing Response of Ga-Doped ZnO Thin Films. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11660–11668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, A.; Sarkar, M.B. Surface-Plasmon-Induced Ag Nanoparticles Decorated In2O3 Nanowires for Low Noise Photodetectors. Plasmonics 2020, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmani, A.R.; Roe, E.F.; Stafford, C.M.; Richter, L.J. Role of the electronically-active amorphous state in low-temperature processed In2O3 thin-film transistors. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reghu, A.; LeGore, L.J.; Vetelino, J.F.; Lad, R.J.; Frederick, B.G. Distinguishing Bulk Conduction from Band Bending Transduction Mechanisms in Chemiresistive Metal Oxide Gas Sensors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 10607–10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhati, V.S.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Kumar, M. Enhanced sensing performance of ZnO nanostructures-based gas sensors: A review. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillero, P.; Roales, J.; Lopes-Costa, T.; Sánchez-Valencia, J.R.; Barranco, A.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Pedrosa, J.M. Optical Gas Sensing of Ammonia and Amines Based on Protonated Porphyrin/TiO2 Composite Thin Films. Sensors 2017, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, T.; Matsubara, S. Capacitive type gas sensors. J. Electroceramics 1998, 2, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Acharyya, D.; Dutta, K. Resistive and capacitive measurement of nano-structured gas sensors. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2019, 2, 25–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Chowdhury, N.; Roy, S.C.; Bhowmik, B. Review of thin film transistor gas sensors: Comparison with resistive and capacitive sensors. J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 1974–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.T.; Seto, M.; Brett, M.J. Capacitive SiO humidity sensors with novel microstructures. Sens. Mater. 1999, 11, 493–505. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, J.J.; Taschuk, M.T.; Brett, M.J. Response time of nanostructured relative humidity sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, J.K.; Sit, J.C. High sensitivity Love-wave humidity sensors using glancing angle deposited thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinmuang, P.; Ekpanyapong, M. The effect of metal electrodes and deposition angle on linearity of sculptured TiO2 humidity microsensors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupsta, M.R.; Taschuk, M.T.; Brett, M.J.; Sit, J.C. Reactive Ion Etching of Columnar Nanostructured TiO2 Thin Films for Modified Relative Humidity Sensor Response Time. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.J.; Fitzpatrick, G.A.; Brett, M.J. Capacitive humidity sensors with high sensitivity and subsecond response times. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 955–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetaniuk, D.P.; Taschuk, M.T.; Brett, M.J. Photocatalytic Titanium Dioxide Nanostructures for Self-Regenerating Relative Humidity Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taschuk, M.T.; Steele, J.J.; van Popta, A.C.; Brett, M.J. Photocatalytic regeneration of interdigitated capacitor relative humidity sensors fabricated by glancing angle deposition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 134, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, N.; Taschuk, M.; Brett, M. Selective room temperature nanostructured thin film alcohol sensor as a virtual sensor array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.D.; Huizinga, A.; Brett, M.J. High-speed porous thin film humidity sensors. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2002, 5, H27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.J.; Gospodyn, J.P.; Sit, J.C.; Brett, M.J. Impact of morphology on high-speed humidity sensor performance. IEEE Sens. J. 2006, 6, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kim, K.; Zhang, S.; Johnson, J.; Salazar, G. High-Temperature Piezoelectric Sensing. Sensors 2014, 14, 144–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, J.K. Engineered Nanostructured Thin Films for Enhanced Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, J.K.; Sit, J.C. Acoustic wave liquid sensors enhanced with glancing angle-deposited thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.-F.; Tao, R.; Luo, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, J.; McHale, G.; Reboud, J.; Torun, H.; Gibson, D.; Tao, K. Rayleigh and shear-horizontal surface acoustic waves simultaneously generated in inclined ZnO films for acoustofluidic lab-on-a-chip. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 442, 128336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, A.M.; Osipova, T.V. Latest Progress in Sensors for Pre-explosive Detection of Flammable Gases: A Review. Sens. Mater. 2022, 34, 3707–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Balendhran, S.; Sabri, Y.; Bhargava, S.K.; Crozier, K.B. Smart mid-infrared metasurface microspectrometer gas sensing system. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2024, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisitsoorat, A.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Yaacob, M.H.; Horpratum, M.; Phakaratkul, D.; Lomas, T.; Tuantranont, A.; Wlodarski, W. Optical H2 sensing properties of vertically aligned Pd/WO3 nanorods thin films deposited via glancing angle rf magnetron sputtering. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2013, 182, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Zou, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. High-performance real-time SERS detection with recyclable Ag nanorods@ HfO2 substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27162–27168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Ju, D.Q.; Niu, X.X.; Sarangan, A.M. Vapor Phase Sensing Using Metal Nanorod Thin Films Grown by Cryogenic Oblique Angle Deposition. J. Sens. 2013, 2013, 823041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlaut, S.K.; Devi, P.; Singh, J.P. Self-sustainable and recyclable Ag nanorods for developing Ag-Ag2S nano heterostructures using sewage gas: Applications in photocatalytic water purification, hydrogen evolution, SERS and antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 528, 147037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.K.; De, R.; Yim, S.Y. Highly sensitive VOC gas sensor employing deep cooling of SERS film. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Goel, P.; Singh, J.P. Flexible and robust SERS active substrates for conformal rapid detection of pesticide residues from fruits. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willets, K.A.; Van Duyne, R.P. Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Kumar, A.; Yang, Y. Unveiling practical considerations for reliable and standardized SERS measurements: Lessons from a comprehensive review of oblique angle deposition-fabricated silver nanorod array substrates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 1004–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Li, A.; Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, T. Detection of Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds Improved by Hollow Nanocages of Layered Double Hydroxide on Ag Nanowires. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16523–16527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rae, S.I.; Khan, I. Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) sensors for gas analysis. Analyst 2010, 135, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Cho, I.; Kang, M.; Yang, D.; Park, I. Thermally/mechanically robust anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) microheater platform for low power chemoresistive gas sensor. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2023, 33, 085011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, D.; Zhu, E.; Liu, K.; Wang, W.; Ling, Y.; Fu, W.; Zhang, Z. Dual-parameter gas sensing with functional graphene field-effect transistors. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2023, 4, 101564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Kang, M.; Lee, K.; Chae, Y.; Yoon, K.-J.; Lee, D.-S.; Park, I. Multigas Identification by Temperature-Modulated Operation of a Single Anodic Aluminum Oxide Gas Sensor Platform and Deep Learning Algorithm. ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.P.; Brown, C.; He, Y.Z.; Fan, J.G.; Lundgren, C.A.; Zhao, Y.P. Porous three-dimensional nanorod arrays through selective chemical etching of nanocomposites. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7741–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Li, X.; Ai, B.; Zhao, Y. Facile Fabrication of Composite Ag/Fe3O4 and Porous Fe3O4 Nanorods Based on Oblique Angle Codeposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 11750–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fan, J.G.; Zhao, Y.P. Engineering a Well-Aligned Composition-Graded CuSi Nanorod Array by an Oblique Angle Codeposition Technique. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 4954–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, E.K.; Aggarwal, D.; Bosnick, K.; Jemere, A.B.; Harris, K.D. Nanocolumnar platinum-coated ITO electrodes prepared by atomic layer deposition and glancing angle deposition for electrocatalytic hydrogen peroxide determination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 425, 136946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, B.; Zhao, Y.P. Glancing angle deposition meets colloidal lithography: A new evolution in the NNdesign of nanostructures. Nanophotonics 2019, 8, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, M.T.; Luong, H.M.; Pham, H.T.; Guin, T.; Zhao, Y.P.; Larsen, G.K.; Nguyen, T.D. Pd80Co20 Nanohole Arrays Coated with Poly(methyl methacrylate) for High-Speed Hydrogen Sensing with a Part-per-Billion Detection Limit. Acs Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 3664–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, H.M.; Ngo, T.A.; Pham, M.T.; Zhao, Y.P.; Larsen, G.K.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Nguyen, T.D. Ultra-fast and sensitive magneto-optical hydrogen sensors using a magnetic nano-cap array. Nano Energy 2023, 109, 108332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Taggart, D.K.; Penner, R.M. Fast, sensitive hydrogen gas detection using single palladium nanowires that resist fracture. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonezzer, M.; Hieu, N. Size-dependent response of single-nanowire gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 163, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipani, F.; Miller, D.; Ponce, M.A.; Aldao, C.M.; Akbar, S.; Morris, P.; Xu, J. Conduction mechanisms in SnO2 single-nanowire gas sensors: An impedance spectroscopy study. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.-Q.; Wang, X.; Lee, S.-T. Gas sensing properties of single crystalline porous silicon nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 243112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Toan, N.; Van Tong, P.; Van Duy, N.; Hoa, N.D.; Van Hieu, N. Synthesis of single-crystal SnO2 nanowires for NOx gas sensors application. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 6557–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Lee, J.-H.; Majhi, S.M.; Weber, M.; Bechelany, M.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Resistive gas sensors based on metal-oxide nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 241102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Suarez-Garcia, F.; Martinez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M. Influence of porous texture and surface chemistry on the CO2 adsorption capacity of porous carbons: Acidic and basic site interactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21237–21247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villiéras, F.; Cases, J.; François, M.; Michot, L.; Thomas, F. Texture and surface energetic heterogeneity of solids from modeling of low pressure gas adsorption isotherms. Langmuir 1992, 8, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Yan, C.; Lee, P.S. Room temperature CO gas sensing using Zn-doped In2O3 single nanowire field effect transistors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yeh, P.H.; Li, Z.; Wei, T.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Supersensitive, fast-response nanowire sensors by using Schottky contacts. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Li, Z. Schottky-contacted nanowire sensors. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tittl, A.; Giessen, H.; Liu, N. Plasmonic gas and chemical sensing. Nanophotonics 2014, 3, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, B.; Sun, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.P. Plasmonic Hydrogen Sensors. Small 2022, 18, 2107882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhao, Y. Oblique angle deposition and its applications in plasmonics. Front. Phys. 2014, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, G.; Fischer, P.; Jeong, H.H. Plasmonic nanostructure engineering with shadow growth. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2107917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gish, D.A.; Nsiah, F.; McDermott, M.T.; Brett, M.J. Localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor using silver nanostructures fabricated by glancing angle deposition. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4228–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.X.; Collins, A.; Zhao, Y.P. Optical Properties and Biosensor Application of Ultrathin Silver Films Prepared by Oblique Angle Deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 16784–16791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.X.; Zhao, Y.P. Au nanoparticle based localized surface plasmon resonance substrates fabricated by dynamic shadowing growth. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 175303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandieh, M.; Hosseini, S.N.; Vossoughi, M.; Khatami, M.; Abbasian, S.; Moshaii, A. Label-free and simple detection of endotoxins using a sensitive LSPR biosensor based on silver nanocolumns. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 548, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Su, X.; Free, P.; Zhou, X.; Neoh, K.G.; Teng, J.; Knoll, W. Plasmonic metal nanostructure array by glancing angle deposition for biosensing application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 183, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wood, A.; Pathak, A.; Mathai, J.; Bok, S.; Zheng, H.; Hamm, S.; Basuray, S.; Grant, S.; Gangopadhyay, K. Plasmonic gratings with nano-protrusions made by glancing angle deposition for single-molecule super-resolution imaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12189–12201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi, A.; Rahbarizadeh, F.; Abbasian, S.; Moshaii, A. Label-free LSPR prostate-specific antigen immune-sensor based on GLAD-fabricated silver nano-columns. Plasmonics 2020, 15, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Viphavakit, C. A review on all-optical fiber-based VOC sensors: Heading towards the development of promising technology. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 338, 113455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashry, I.; Mao, Y.; Wang, B.; Hveding, F.; Bukhamsin, A.Y.; Ng, T.K.; Ooi, B.S. A review of distributed fiber–optic sensing in the oil and gas industry. J. Light. Technol. 2022, 40, 1407–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.G.; Zhao, Y.P. Direct deposition of aligned nanorod array onto cylindrical objects. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2005, 23, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Dluhy, R.A.; Zhao, Y. Development of silver nanorod array based fiber optic probes for SERS detection. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2011, 157, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.X.; Park, B.; Zhao, Y.P. Nanorod-mediated surface plasmon resonance sensor based on effective medium theory. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 4637–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.X.; Park, B.; Zhao, Y.P. Limitation of a localized surface plasmon resonance sensor for Salmonella detection. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2009, 141, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Shen, Z.; Li, H.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y. Research Progress of fluorescent gas sensors based on MOFs. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 12692–12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y. Fluorescence based explosive detection: From mechanisms to sensory materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8019–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badshah, M.A.; Ju, J.; Lu, X.; Abbas, N.; Kim, S.-m. Enhancing the sensitivity of DNA microarrays by metal-enhanced fluorescence using vertical nanorod structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 274, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Abbas, N.; Badshah, M.A.; Kim, S.-m. Fabrication of Ag nanorods on micropost array for a metal-enhanced fluorescence substrate with a high signal-to-background ratio. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ganesh, N.; Mathias, P.C.; Cunningham, B.T. Enhanced fluorescence on a photonic crystal surface incorporating nanorod structures. Small 2008, 4, 2199–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Chen, W.; Wang, P. A review of all-optical photoacoustic spectroscopy as a gas sensing method. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2021, 56, 143–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A.; Sabry, Y.M.; Hunter, I.W.; Khalil, D.; Bourouina, T. Direct absorption and photoacoustic spectroscopy for gas sensing and analysis: A critical review. Laser Photonics Rev. 2022, 16, 2100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajireza, P.; Krause, K.; Brett, M.; Zemp, R. Glancing angle deposited nanostructured film Fabry-Perot etalons for optical detection of ultrasound. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 6391–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajireza, P.; Sorge, J.; Brett, M.; Zemp, R. In vivo optical resolution photoacoustic microscopy using glancing angle-deposited nanostructured Fabry–Perot etalons. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Hou, Y.; Yi, K.; Shao, J. Fabry-Perot Filter Constructed with Anisotropic Space Layer and Isotropic Mirrors. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2013, 17, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Suh, J.M.; Eom, T.H.; Kim, T.; Jang, H.W. Colorimetric sensors for toxic and hazardous gas detection: A review. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2021, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkeye, M.M.; Brett, M.J. Optimized colorimetric photonic-crystal humidity sensor fabricated using glancing angle deposition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3652–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A. Nanostructured NiO thin Films for Electrochemical and Colorimetric Biosensors. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Yoo, Y.J.; Ko, J.H.; Mahmud, A.A.; Song, Y.M. Trilayered gires–tournois resonator with ultrasensitive slow-light condition for colorimetric detection of bioparticles. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishan, U.; Ullah, W.; Muhammad, N.; Asad, M.; Afridi, S.; Khan, M.; Shah, M.; Khan, N.; Rahim, A. Development of a nonenzymatic colorimetric sensor for the detection of uric acid based on ionic liquid-mediated nickel nanostructures. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 26983–26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Huang, X.L.; Wang, C.; Xie, Z.; Al-Hartomy, O.; Al-Ghamdi, A. The rise of AI optoelectronic sensors: From nanomaterial synthesis, device design to practical application. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 27, 100812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
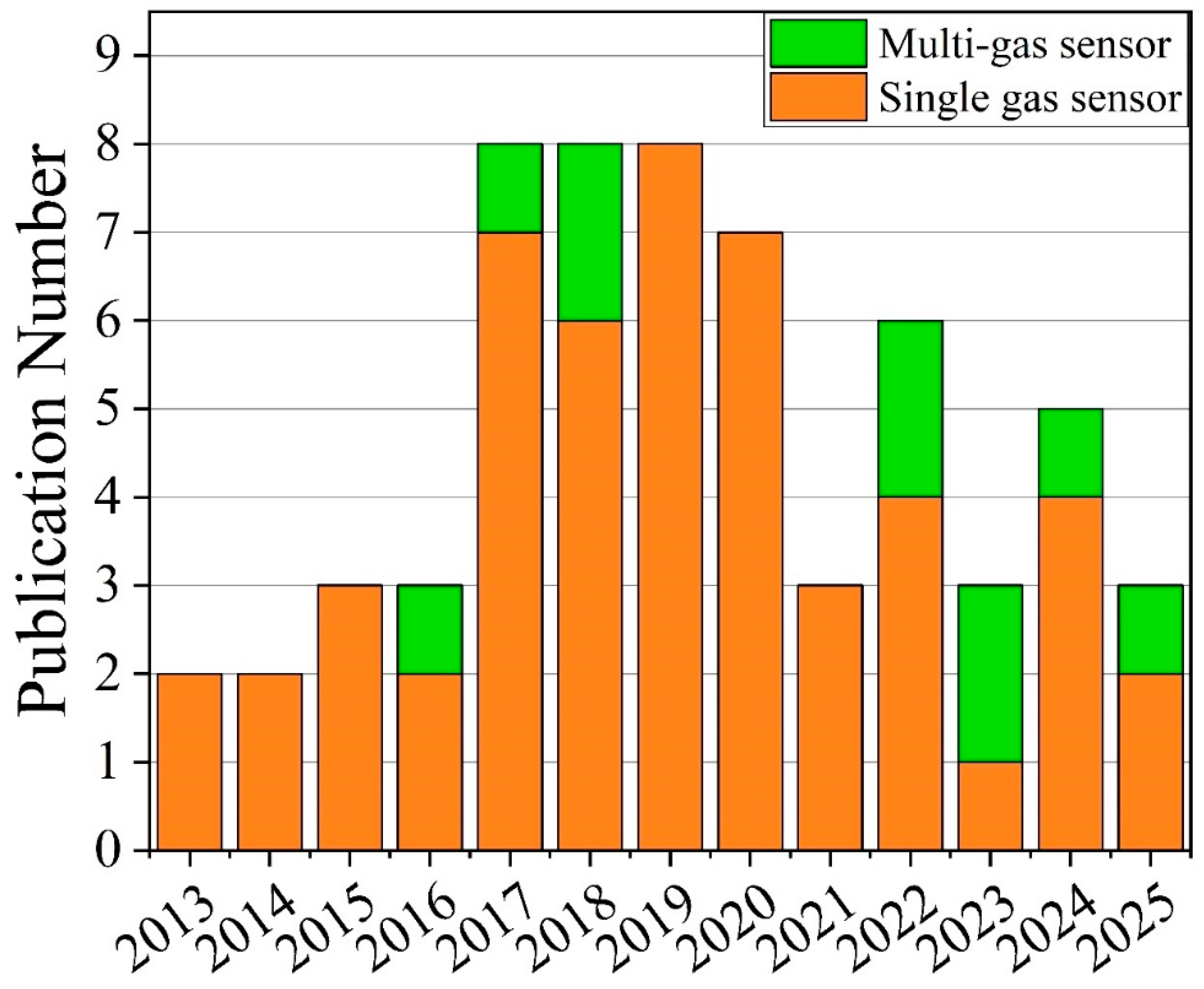

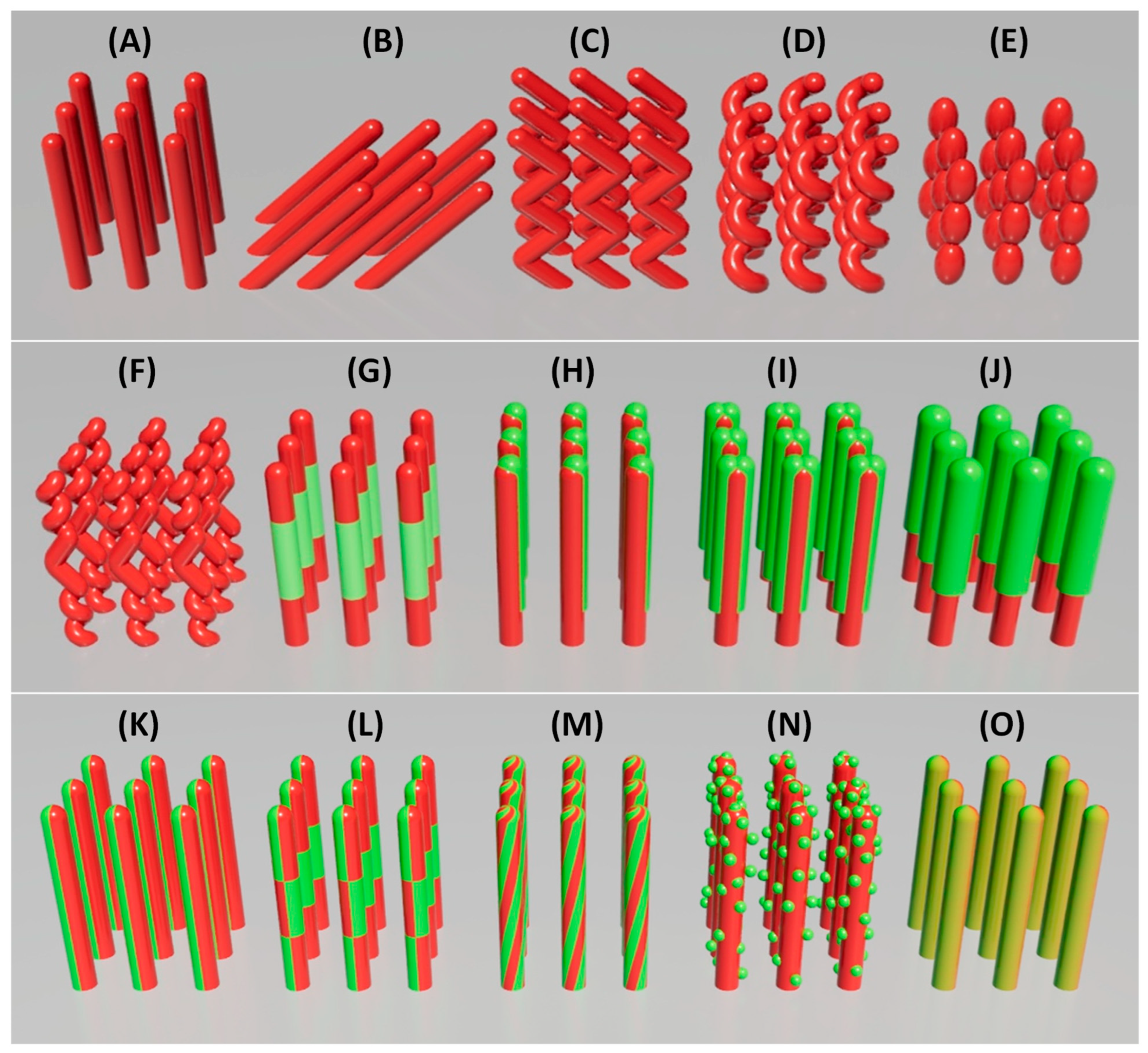
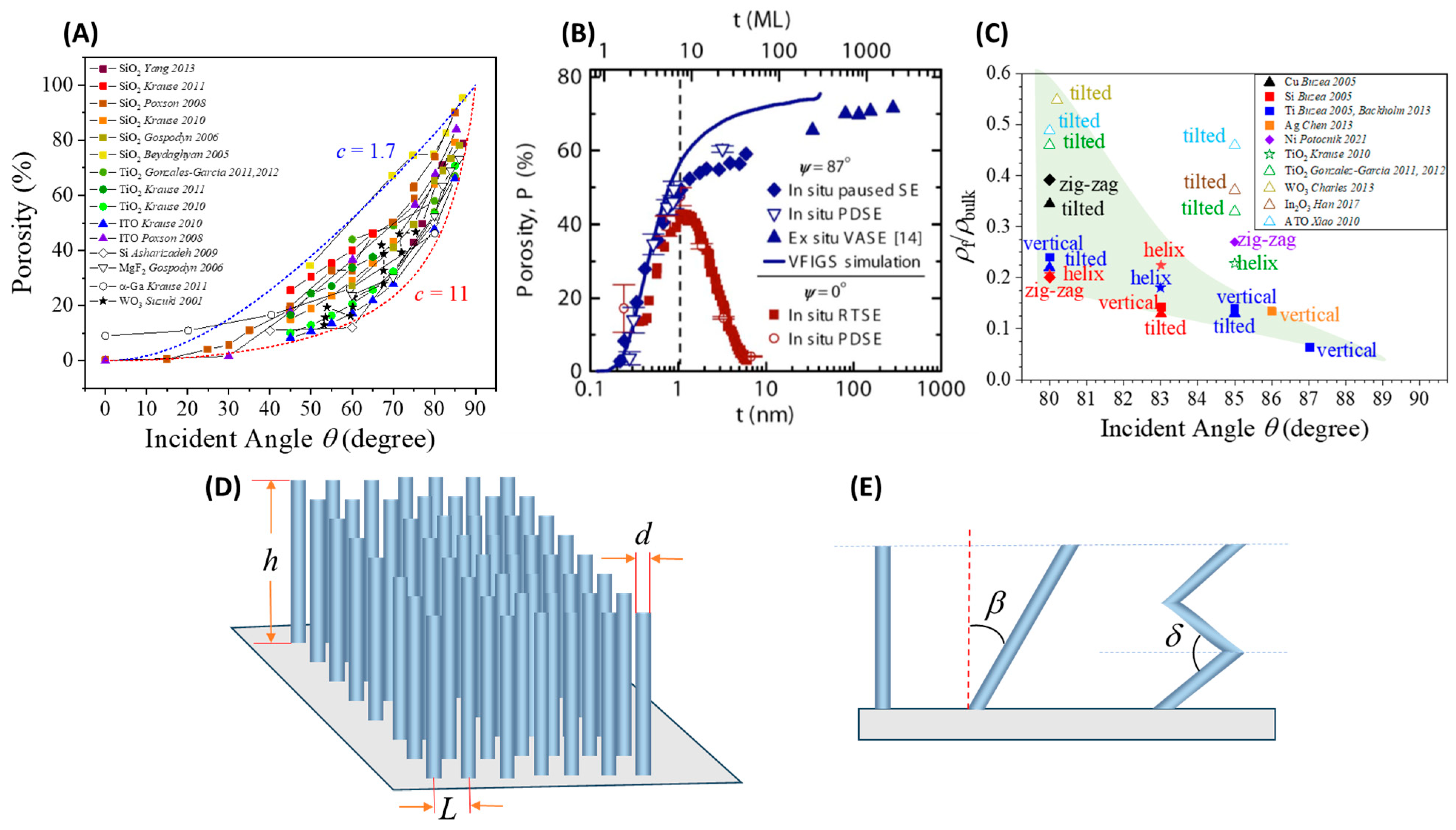
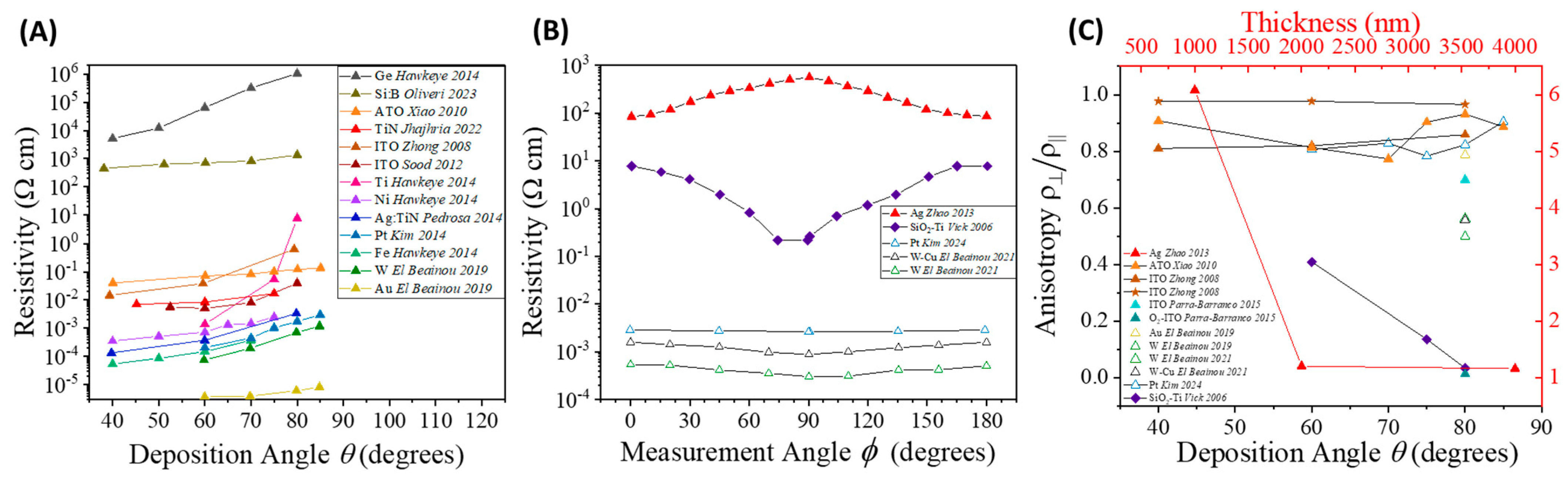
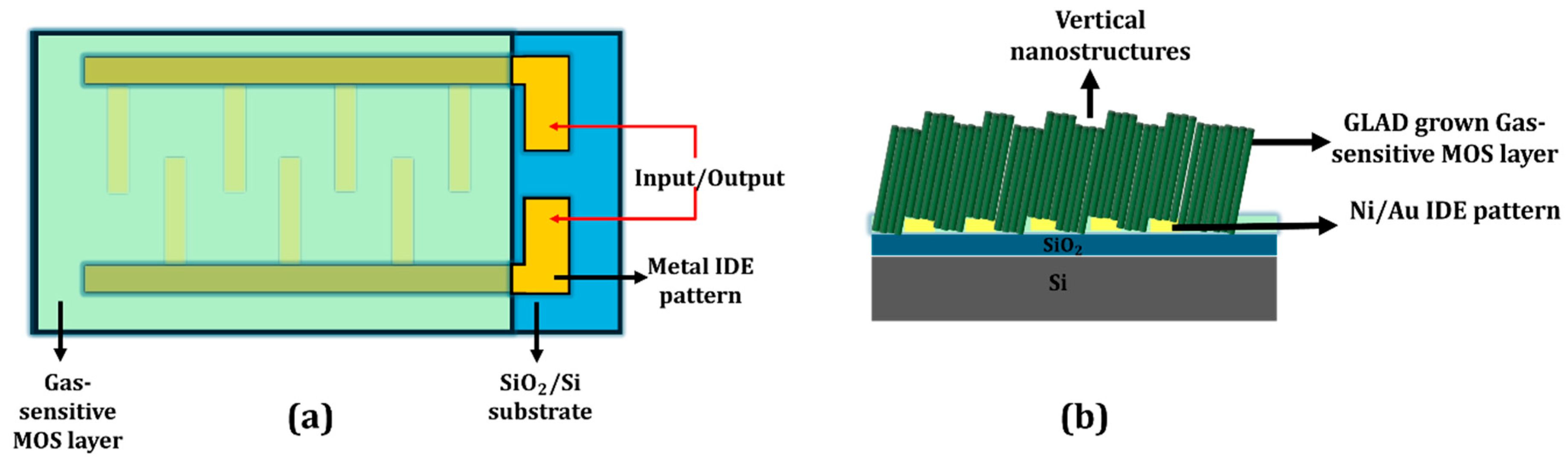

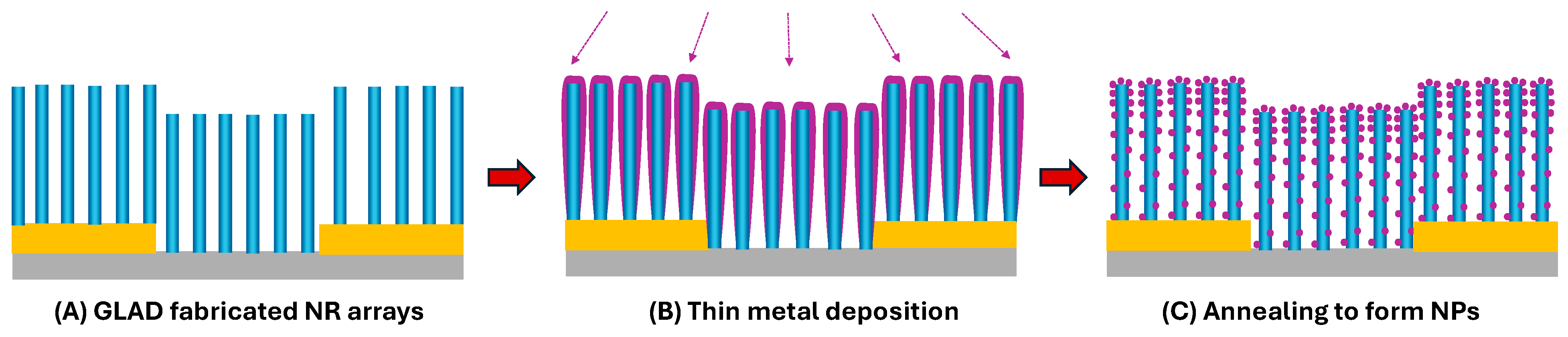

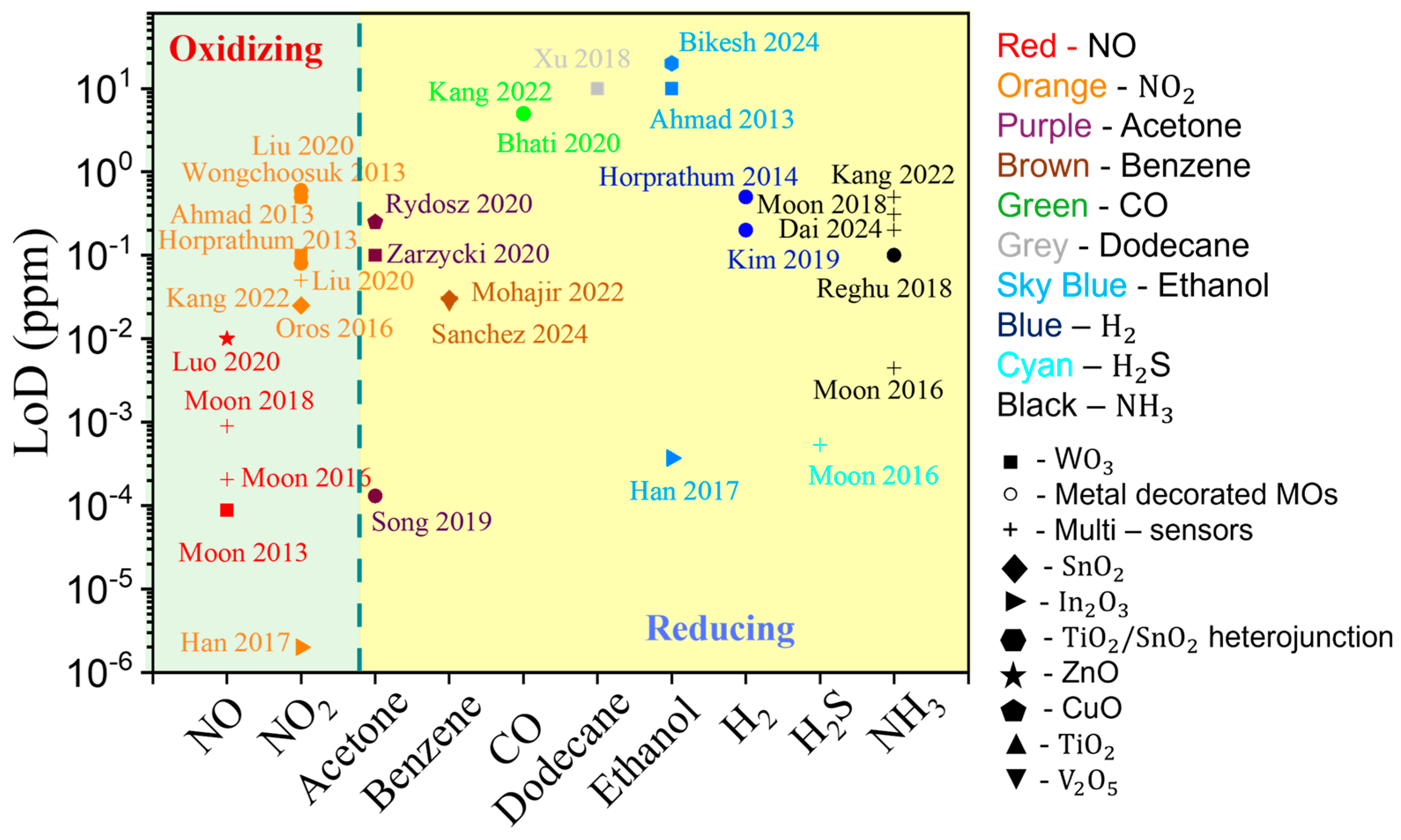
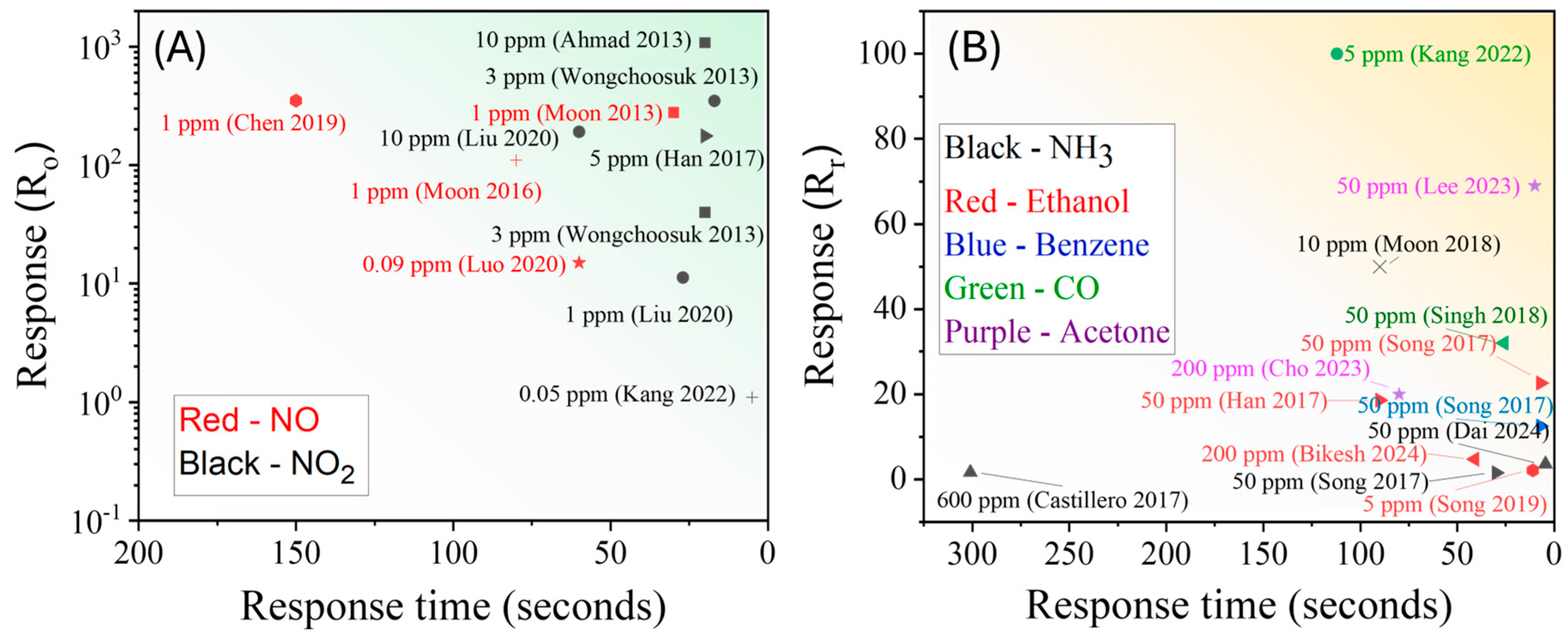

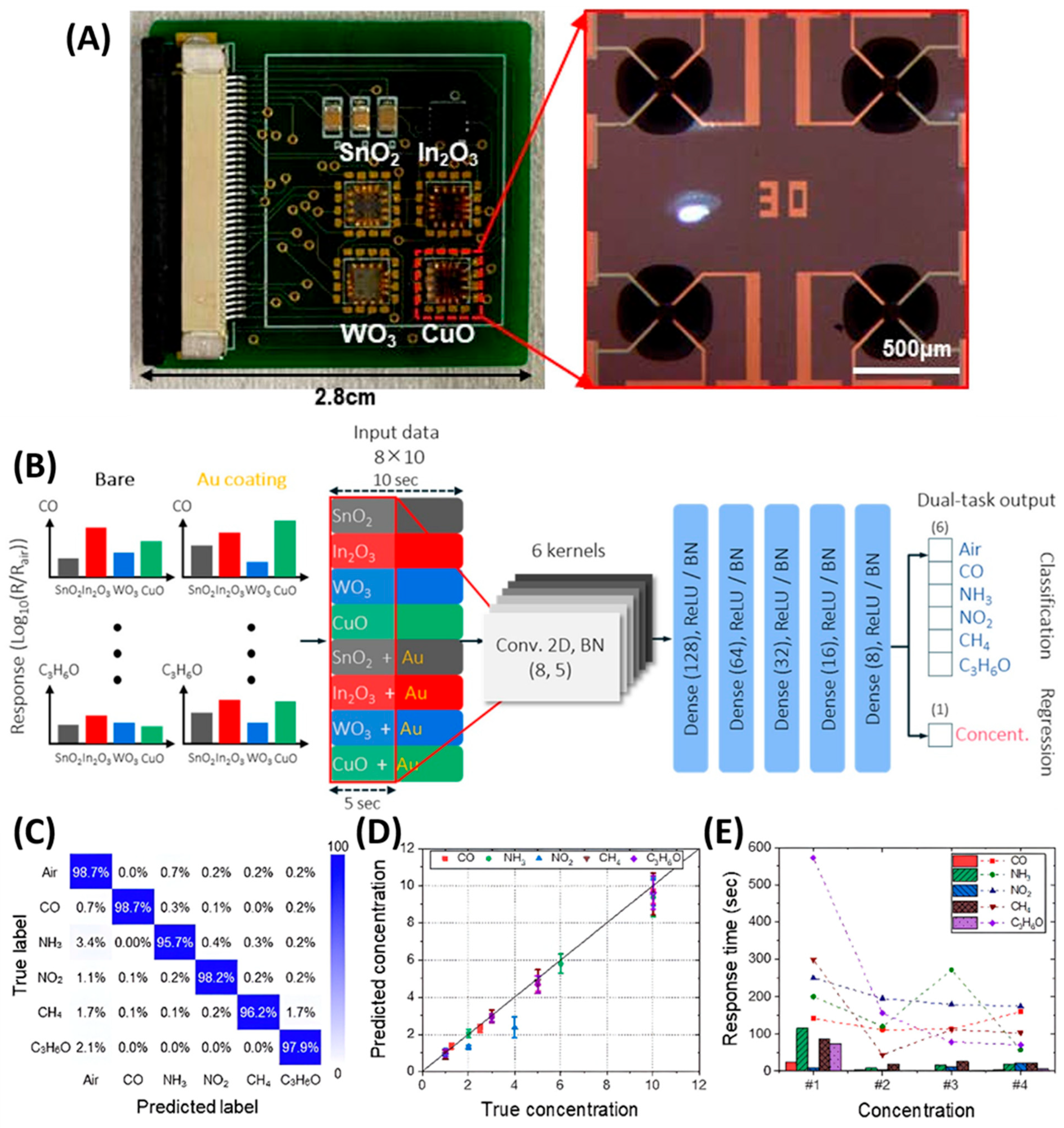

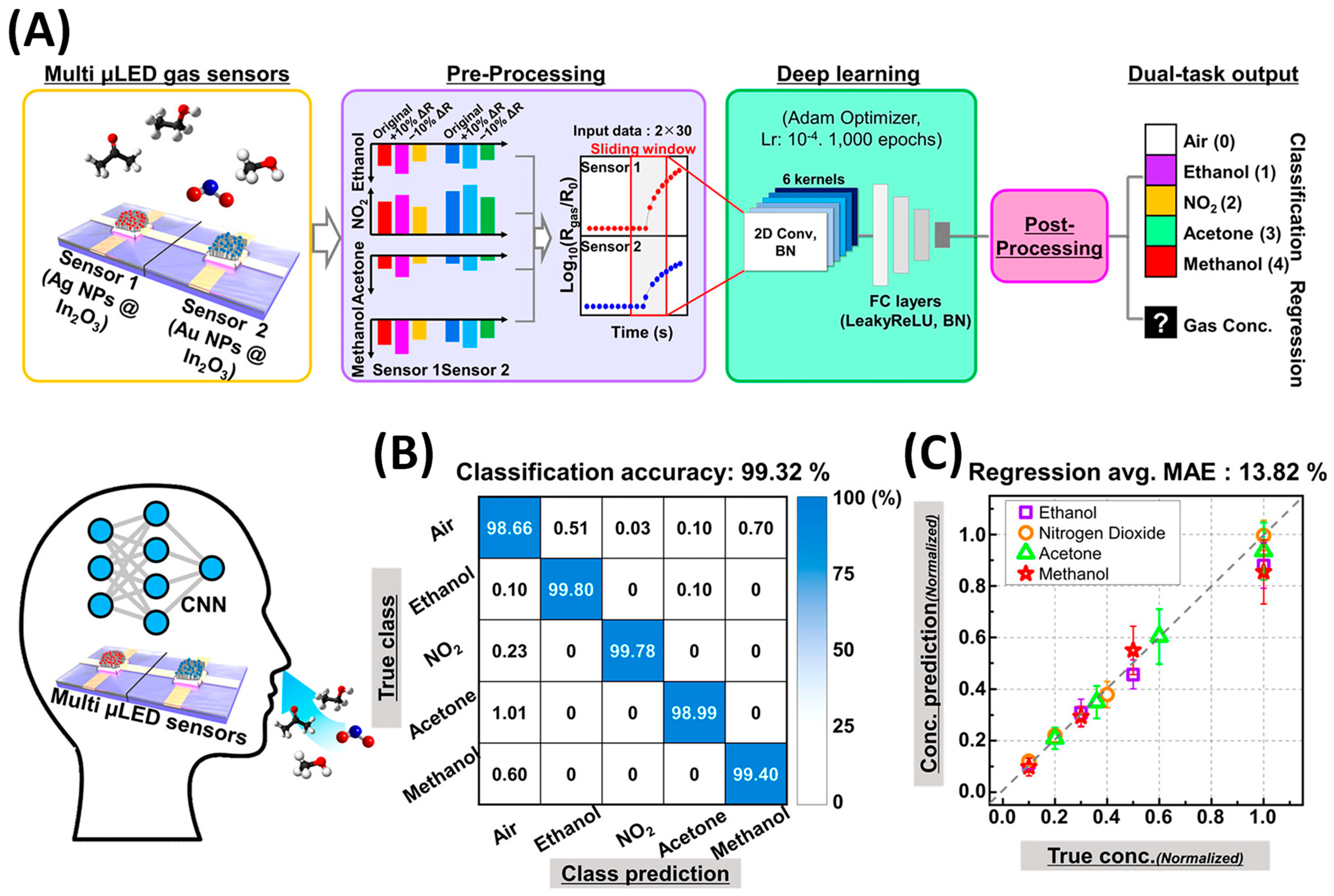
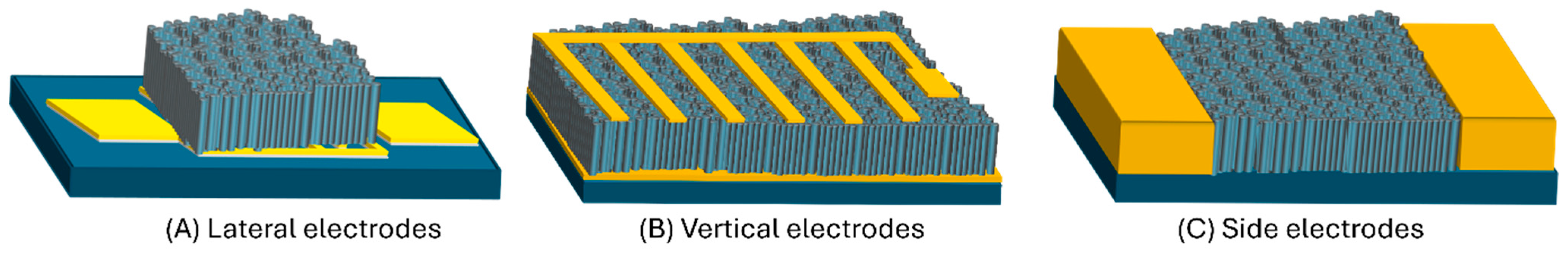
| PVD Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | Material Compatibility | Effect on GLAD Nanostructures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation [32] |
|
| Metals, organics, some oxides (via reactive evaporation) |
|
| E-beam Evaporation [32] |
|
| Refractory metals, oxides, semiconductors |
|
| IBAD [36] |
|
| Metals, oxides, nitrides |
|
| RF/DC Sputtering [36] |
|
| Metals, metal oxides, nitrides, alloys |
|
| Reactive Sputtering [106] |
|
| Oxides, nitrides, fluorides |
|
| PLD [36] |
|
| Complex oxides, multicomponent materials |
|
| Strategy | Mechanism | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heterostructures (p–n, n–n) | Band bending, charge depletion | ↑ Selectivity, ↑ Response |
| Core–Shell Structures | Shell controls gas access & charge modulation | ↑ Sensitivity, optimized depletion layer |
| Doping | Carrier modulation, oxygen vacancies | ↑ Active sites, ↓ Operating temp. |
| Noble Metal Decoration | Schottky barrier, spillover catalysis | ↑ Sensitivity, ↑ Stability |
| MOS NP Decoration | p–n junctions, charge modulation | ↑ Selectivity |
| Quantum Dot Functionalization | Light harvesting, surface sensitization | Room-temp sensing, ↑ Sensitivity |
| SAMs/Chemical Grafting | Functional group–gas interaction | Molecular specificity |
| MOF Coating | Molecular sieving, pre-concentration | ↑ Selectivity, ↓ Cross-interference |
| Coating Type | Method | Advantages | Potential Problems |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOF | In situ solvothermal/hydrothermal growth [175] | Strong adhesion; uniform crystal growth; conformal coating | Requires high temperature; may damage delicate nanostructures |
| Dip-coating/spin-coating [176] | Simple, low-cost; scalable | Non-uniform coverage; weak adhesion; film cracking after drying | |
| Interfacial layer-assisted growth [177] | Improved nucleation and adhesion via functional layer (e.g., APTES) | Additional processing step; limited MOF-substrate compatibility | |
| Spray coating/electro-spraying [178,179] | Good control over film thickness and coverage; scalable | May require multiple passes; lower crystallinity | |
| Solvent-free CVD-like growth [180] | Thin, conformal coatings without solvent exposure | Limited to volatile precursors; MOF diversity restricted | |
| Polymer | Layer-by-layer (LbL) deposition [181] | Nanometer-scale thickness control; high versatility for chemical tuning | Time-consuming; may require many layers for adequate functionality |
| Initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) [182] | Conformal coating; solvent-free; excellent for porous structures | Requires vacuum system; limited monomer choices | |
| Plasma polymerization [183] | Conformal and uniform coating; customizable surface chemistry | Surface damage possible; can alter GLAD morphology | |
| Dip-coating/spin-coating [184] | Simple and fast; compatible with many polymers | May bridge or clog porous structures; film uniformity may vary |
| Sensor Architecture | Method/Accuracy | Mat | Structure | Deposition Condition | Target Gases (LOD) | Response and Sensitivity | t90 & t10 (Seconds) | Selectivity | Operation Condition | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 × 4 array with micro-heater | Resistive based CNN 98.06% classification; 10.15% regression error | SnO2, In2O3, WO3, CuO, + Au decorated, 2x replicated (Total 16) | Vertical columns, Au decorated vertical columns | RF sputtering ; | Individual | / | CNN | No CNN | N/A | 250 °C; 11–15 mW | [237] |
| CO (5 ppm) | <5% variation | t90: 1 | t90: 112 | ||||||||
| NH3 (0.5 ppm) | t90: 8 | t90: 57 | |||||||||
| NO2 (0.05 ppm) | t90: 5 | t90: 174 | |||||||||
| CH4 (10 ppm) | t90: 19 | t90: 44 | |||||||||
| C3H6O (1 ppm) | t90: 2 | t90: 70 | |||||||||
| 3 × 3 array with micro-heater | Resistive based PCA-based gas separation | SnO2, WO3, In2O3, + Au decorated, + Bare (Total 9) | VLNs, Au-decorated thin films, thin films | E-beam | Individual | ΔV response | t90~Fast | High vs. Acetone, Ethanol, Benzene, CO | 168 °C; 800 mW heater | [215] | |
| H2S (0.534 ppb) | 50–100% | ||||||||||
| NH3 (4.45 ppb) | 50–100% | ||||||||||
| NO (0.206 ppb) | >110% | ||||||||||
| 2 × 2 array with micro-heater | Resistive based PCA-based gas separation PC1 + PC2 = 92.69 + 5.87 = 98.56% | SnO2, WO3, SnO2 @ Au, WO3 @ Au | VLNs, Au-decorated | E-beam | Individual | / | N/A | High vs. C2H5OH, CO, C7H8, C6H6, CH3COCH3 | 212 °C, 500 mW heater, 80% RH | [238] | |
| NO: (0.899 ppb) | (1 ppm) 9–133 | ||||||||||
| NH3: (312 ppb) | (10 ppm) 5–20 | ||||||||||
| 4-single sensors with micro-heater | Resistive based w/threshold decision, EWMA filtering | NiO, SnO2, WO3, In2O3 | Tilted Columns | E-beam | Simultaneously Fire gases from PVC (HCl, CO, VOCs) | (200 °C) NiO: 1.2 SnO2: 2.1 (350 °C); NiO: 577.1 SnO2: 294.9 | Time to reach detection: SnO2 1007 (200 °C); 948 (350 °C); | N/A | ~250 °C, | [105] | |
| 2 × 6 array using GFET | Resistive + capacitive based LDA; classification enhanced with dielectric channel | TiO2, SnO2 | Tilted Columns | E-beam TiO2, SnO2 | Individual SO2, CH2O, C7H8, C2H6O, NO2, NH3 (1 ppm) | Linear response; distinct Z’ and tan φ traces for each gas; | N/A | N/A | 175 °C, dry air, 10 mV at 8.223–13.158 kHz | [285] | |
| Single AAO microheater | Resistive + temp. modulation 1D-CNN (Gasses) 97.0% MAPE: 18.0% (Spices) 96.1% classification; MAPE: 7.7–26.1% | WO3 | Vertical Columns | RF sputtering | Individual NO2 (0.5 ppm) Acetone (1 ppm) NH3 (1 ppm) Ethanol (1 ppm) Simultaneous Coriander, cilantro, star anise, licorice | Distinct temp-modulated pulse patterns | Detection Time ≈ 30–90 | N/A | Up to 301.7 °C, 31.4 mW, 2.0–3.0 V staircase, 5.0 V at 10 Hz, dry air | [286] | |
| Single-μLED embedded sensor (photo-activated) | Resistive based D-CNN 96.99% classification MAPE: 31.99% | In2O3 | Vertical Columns | RF sputtering E-beam Au NPs | Individual | (ΔR/R0) | t90 = 80 t10 = 79 | N/A | RT, 395 nm pulse | [240] | |
| CH3OH (10 ppm) | (10 ppm) 0.56 | ||||||||||
| EtOH (10 ppm) | (10 ppm) 0.51 | ||||||||||
| Acetone (200 ppm) | (200 ppm) 0.17 | ||||||||||
| NO2 (0.5 ppm) | (10 ppm) 2.71 | ||||||||||
| Dual-μLED embedded sensor (photo-activated) | Resistive based CNN 99.32% classification MAPE: 13.82% | In2O3 | Vertical Columns + Au or Ag decorated | RF sputtering E-beam Au and Ag NPs | Individual | / | CNN detects in <30 | N/A | RT, 0.38 mW total power | [243] | |
| CH3OH (10 ppm) | (100 ppm) 0.50–0.69 | ||||||||||
| C2H5OH (10 ppm) | (100 ppm) 0.55–0.62 | ||||||||||
| CH3COCH3 (50 ppm) | (50 ppm) 0.89–0.92 | ||||||||||
| NO2 (0.5 ppm) | (5 ppm) 253–571 | ||||||||||
| Mat | Structure | Deposition Condition | Post-Treating | Target Gas | Response and Sensitivity | LOD | Selectivity | Operation Condition | Refs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Material | ||||||||||
| Tilted columns | DC reactive sputtering: | 350 & 500 °C/48 h in air | BTEX | 0.008–0.075 | 30 ppb (benzene) | (8% RH, 25 °C) | Enhanced BTEX selectivity | 300–500 °C tested, best ≥ 400 °C | [143] | |
| Vertical columns | DC Reactive sputtering: | 300 & 400 °C/3 h in air | 5310 5 ppm@150 °C | 6 ppb (400 °C) | (5 ppm, 150 °C) | High vs. , , CO, | 0.125–5 ppm@150 °C in air | [161] | ||
| Vertical columns | RF sputtering: | 300 °C/ 3 h in air | CO | 150 500 ppm@110 °C | 50 ppm (not calc.) | High vs. , , | 50–500 ppm@110 °C in dry air | [160] | ||
| Vertical columns | RF co-sputter: | 450 °C/ 2 h in air | 1075 10 ppm@150 °C | 0.5 ppm | Selects oxidizing or reducing gases by temperature | : 0.5–10 ppm 10–200 ppm @100–400 °C | [191] | |||
| 10 200 ppm@300 °C | 10 ppm | N/A | ||||||||
| Tilted/zigzag/spiral columns | DC sputtering (GLAD + RGGP): | 300 °C/ 12 h in air | 60% 300 ppm@250 °C | 10 ppm | N/A | 250 °C | [192] | |||
| 35,000% 1 ppm@250 °C | 0.2 ppm | |||||||||
| Tilted columns | DC and RF co-sputtering: | 300 °C/ 12 h in air | 63% 325 ppm@500 °C | N/A | N/A | 325 ppm@450–500 °C | [193] | |||
| Vertical columns | DC sputtering: | 400–500 °C/ 3 h in air | 27 2.0 ppm@250 °C | 0.1 ppm | N/A | 0.1–2 ppm @ 250 °C in air | [187] | |||
| Villa-like Nanostructures | RF sputtering: | 500 °C/1 h in air | NO | 278 @200 °C | 88 ppt | (1 ppm, 200 °C) | High vs. , , CO, | 500 sccm @200 °C | [194] | |
| Vertical columns | DC magnetron sputtering | 400 °C/4 h in air | 1.45 1.25 ppm@300 °C | 0.1 ppm | (θ = 75°, 1.25 ppm) | N/A | 300–400 °C | [195] | ||
| Tilted columns | E-beam evap.: | 550 °C/2 h in air | 1313 | 50 ppm (all gases) | High vs. VOCs at 300 °C; Low vs. oxidizing gases | 50 ppm@300 °C in dry air | [196] | |||
| 1130 | ||||||||||
| 623 | ||||||||||
| HCHO | 610 | |||||||||
| 320 | ||||||||||
| 166 | ||||||||||
| CO | 5.03 | |||||||||
| 0.28 | ||||||||||
| Vertical columns | E-beam evap.: | 500 °C/2 h in air | 176 5 ppm @ 200 °C | ~2 ppt | Tunable selectivity to redox gases | 1000 sccm@200–300 °C in air | [73] | |||
| 929 50 ppm@ 300 °C | ~370 ppt | |||||||||
| ZnO | Vertical columns | RF magnetron sputter: | N/A | 18.19% 3 ppm@300 °C | 3 ppm | (3 ppm) | High vs. (2.75%), CO (1.45%) | 300 °C in air | [197] | |
| Helical columns | RF sputtering: | 400 °C/2 h in air | NO | 15 90 ppb@150 °C | 10 ppb | 90 ppb | High vs. , , CO | 150–300 °C best@250 °C | [198] | |
| 1-,2-,4-fold zigzag columns | Thermal evap.: | N/A | 3.6@50 ppm 1.17@200 ppb | 0.2 ppm | (50 ppm) | High vs. , Low vs. , | 25 °C, 50–80%RH best@60% | [188] | ||
| CuO | Vertical columns | DC sputtering: | 400 °C/4 h in air | 2.1 2.5 ppm@350 °C | 0.25 ppm | N/A | N/A | 300–400 °C best@350 °C | [129] | |
| Nano-sculptured thin films | DC magnetron sputtering: | 500 °C/24 h | 0.9@100 ppb | ~28 ± 4 ppb | N/A | 450 °C, ≤60% RH | [131] | |||
| Hetero-Junction | ||||||||||
| Vertical hetero-junction columns | E-beam evap.: | N/A | ~14@200 ppm, 4.7@20 ppm | 20 ppm | N/A | 150 °C | [199] | |||
| ~3@200 ppm 1.2@20 ppm | ||||||||||
| Decorated and Doped | ||||||||||
| Vertical columns | DC sputtering: | 450 °C/4 h in air | 11.24@1 ppm | 80 ppb | (1 ppm) | High vs. , CO, , | 150 °C; 0.08–10 ppm , | [113] | ||
| Vertical columns | DC magnetron sputtering: | 400 °C/3 h in air | 3000 ppm@200 °C | 0.5 ppm | (0.3% ) | High vs. , , , CO | 200 °C in 2 L/min synth air | [114] | ||
| @ Pd | Vertical columns | E-beam evap. and DC sputtering: | 550 °C/2 h in air | 104@1% in 96@480 ppm in transformer oil | 0.2 ppm Oil: 0.3 ppm | : (1%); Oil: (480 ppm) | High vs. , CO, | RT in ; 80 °C in oil; 0.2 ppm–1% in | [115] | |
| Vertical columns | E-beam evap.: | 550 °C/2 h in air | 0.99 10 ppm@200 °C | 10 ppb | High vs. | 200 °C in dry air 0.01–50 ppm | [116] | |||
| ZnO @ Pd | Tilted columns | RF sputtering: | N/A | CO | 1020 500 ppm@150 °C | 10 ppm | High vs. , , , LPG, . | 150 °C, in dry air | [117] | |
| Vertical columns: | DC sputtering: | 450 °C/4 h in air | 2.72@1 ppm 191@10 ppm | 0.5 ppm | N/A | High vs. , CO, , | 150 °C, 0.5–10 ppm | [118] | ||
| @ Au | “Bamboo” vertical columns w/layered Au | E-beam evap.: | 550 °C/1 h in air | 338.8@50 ppm | 70 ppt | N/A | 350 °C in 1000 sccm dry air flow | [112] | ||
| 301.3@50 ppm | 78 ppt | |||||||||
| 153.8@50 ppm | 193 ppt | |||||||||
| Vertical columns | E-beam evap.: | 550 °C/2 h in air | 75@5 ppm | ~0.131 ppb | (5 ppm) | High vs. , , | 0.2–5 ppm @300 °C, 0–80% RH | [119] | ||
| @ Au, Ag, Pt, Cu | Vertical columns | RF sputtering: | 400 °C/1 h in air | 2.06@0.5% O2 3.34@2% O2 | 5000 ppm | (w/o CNN) (w/CNN); | High selectivity in humid | 22 °C, 30–90% RH, in | [200] | |
| Vertical columns | RF sputtering: | 400 °C/3 h in air | 320 3 ppm@250 °C | <0.5 ppm | High vs. , , CO, , | 150–250 °C best@250 °C 50 sccm in dry air | [111] | |||
| Mat | Structure | Deposition Condition | Target Gas | Response and Sensitivity | Operating Temperature (LoD) | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorption | |||||||
| Pd/ | NRs | RF sputtering: | , 0.1% | [274] | |||
| / protonated porphyrin | Tilted columns | E-beam evaporation | + Amines | 100 , 2.3% | [253] | ||
| SERS | |||||||
| Ag/Hf | NRs with Hf shell | E-beam evaporation | 2-NAT and 2MPy | 6000 for 600 ppb 2NAT vapor exposure | N/A | RT, 20 ppb 2-NAT | [275] |
| Ag | Tilted columns | E-beam evaporation | 4-ABT | Detection based on Raman peak intensity 4-ABT detected after 5 min exposure. Avg. signal from cryo-Ag (100 K) is 282% higher than RT | Detection ~5–60 min | RT, 5 min of 4-ABT exposure | [276] |
| Tilted columns | PVD | BPE and Rh6G showed strong peaks at 1200–1650 cm−1; dye degradation monitored by SERS showed signal drop over time | N/A | RT | [277] | ||
| Tilted columns | Thermal evaporation | Benzene (C6H6) | Benzene Raman peak (990 cm−1) used for detection; signal increased by 1000× when cooled to −80 °C | RT, 1 ppb benzene @ −80 °C | [278] | ||
| Configuration | Current Path | GLAD Structure Requirement | Gas Access | Fabrication Complexity | Sensor Performance Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical | Through film thickness (z-axis) | Vertically connected porous network | Moderate (blocked by top electrode) | Moderate to High | High if well integrated |
| Lateral | Along substrate surface (x-y plane) | Lateral connectivity (tilted rods or bridging) | High | Low | Moderate to High |
| Side (sandwiched) | Across film between side electrodes | Lateral conductivity and mechanical integrity | Very High | High | High, ideal for hybrid sensing |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, S.; Stiwinter, K.C.; Singh, J.P.; Zhao, Y. Glancing Angle Deposition in Gas Sensing: Bridging Morphological Innovations and Sensor Performances. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141136
Singh S, Stiwinter KC, Singh JP, Zhao Y. Glancing Angle Deposition in Gas Sensing: Bridging Morphological Innovations and Sensor Performances. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(14):1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141136
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Shivam, Kenneth Christopher Stiwinter, Jitendra Pratap Singh, and Yiping Zhao. 2025. "Glancing Angle Deposition in Gas Sensing: Bridging Morphological Innovations and Sensor Performances" Nanomaterials 15, no. 14: 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141136
APA StyleSingh, S., Stiwinter, K. C., Singh, J. P., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Glancing Angle Deposition in Gas Sensing: Bridging Morphological Innovations and Sensor Performances. Nanomaterials, 15(14), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141136








