pH-Responsive Nanophotosensitizer Boosting Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy by Hydroxyl Radical Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of Nanocomposites
2.3. Material Characterization
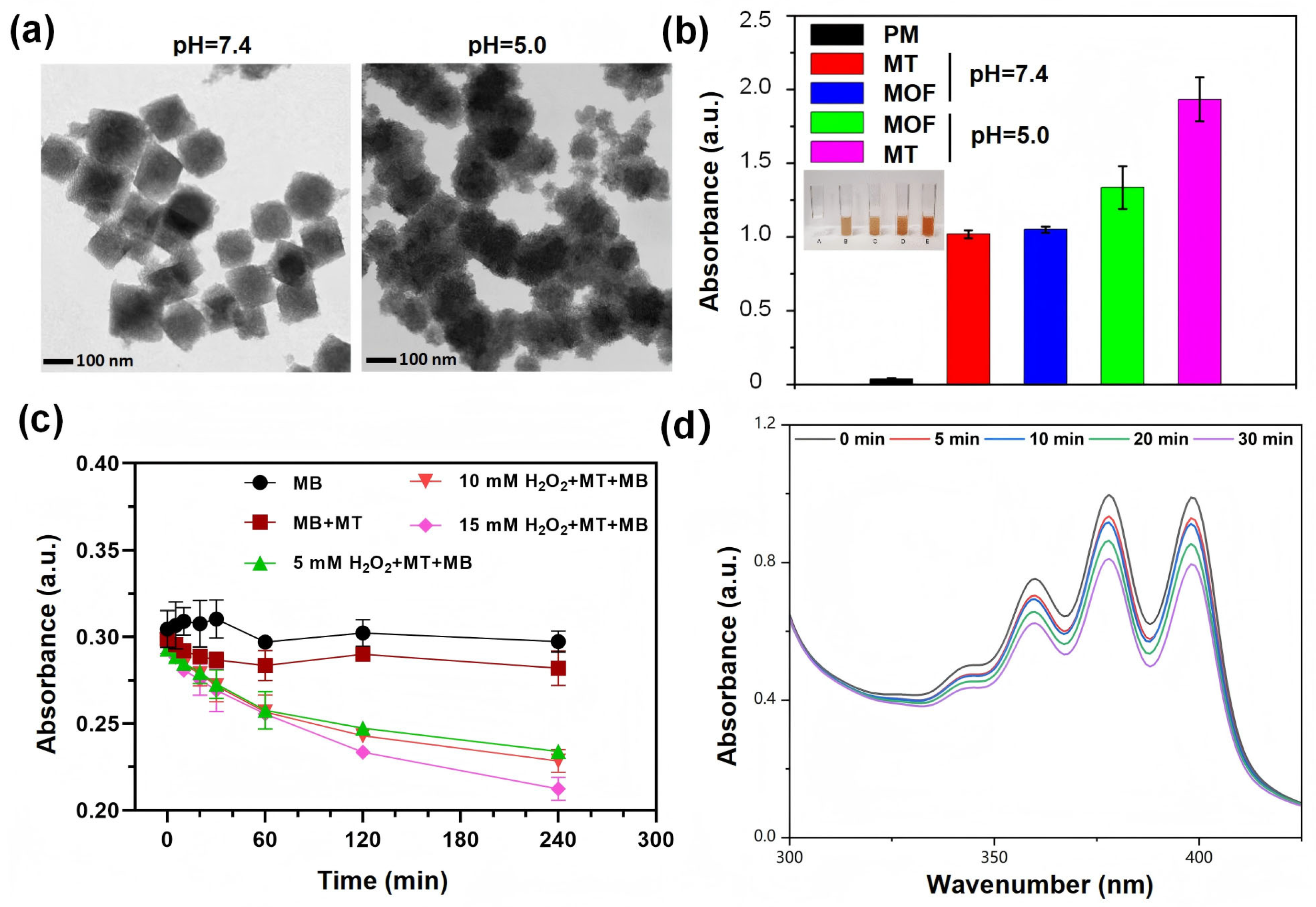
2.4. pH-Dependent Structural Evolution
2.5. Fe3+ Release Quantification
2.6. Hydroxyl Radical (•OH) Detection
2.7. 1O2 Generation
2.8. Intracellular ROS Detection
2.9. Membrane Damage Analysis
2.10. Antibacterial Efficacy
2.11. Animal Model and Wound Infection
2.12. Treatment Protocol and Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocomposites
3.2. pH-Responsive Degradation and Hydroxyl Radical Generation
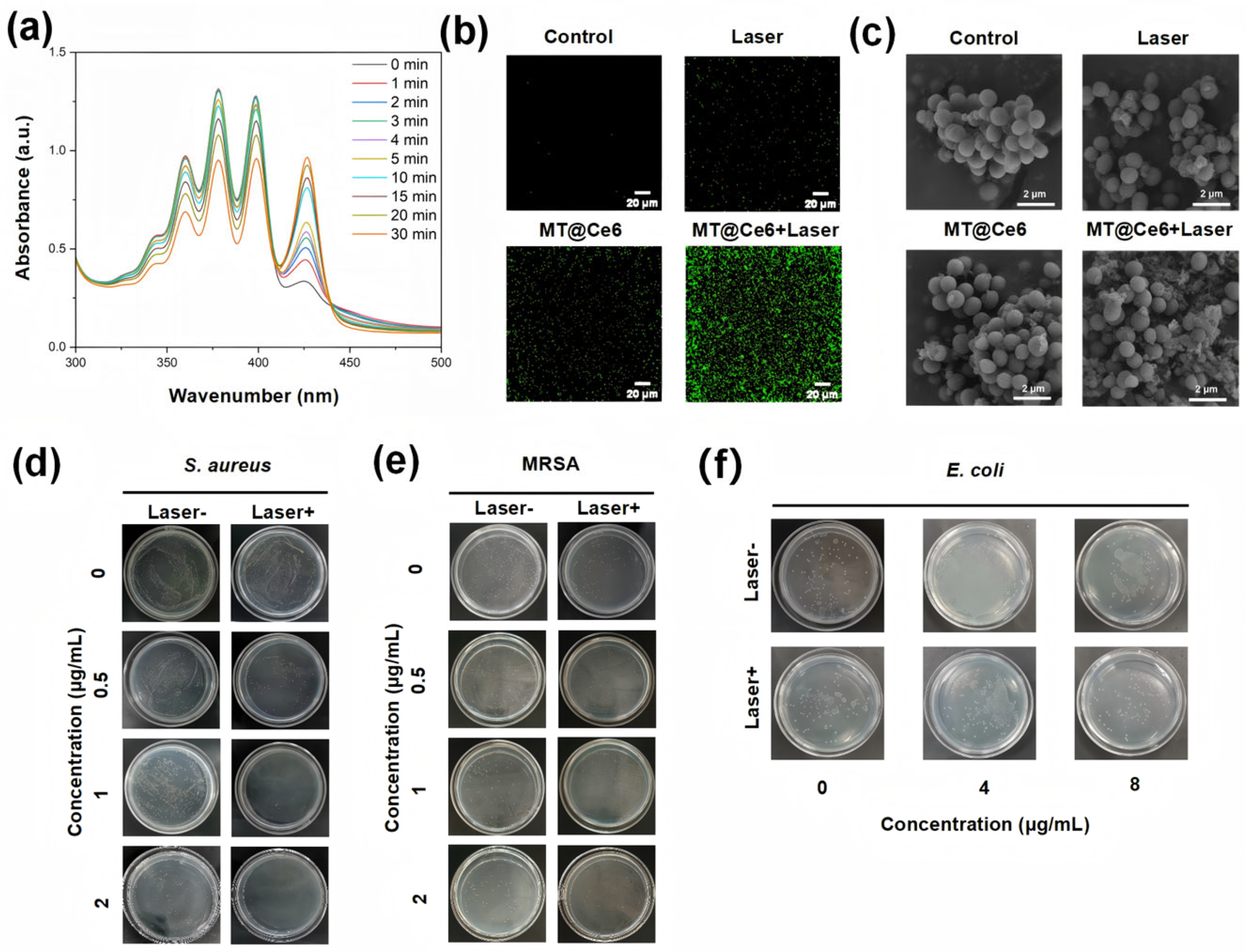
3.3. ROS Generation and Photodynamic Bactericidal Mechanism
3.4. In Vivo Antibacterial Efficacy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TA | tannic acid |
| PDT | photodynamic therapy |
| MOF | metal–organic frameworks |
| MRSA | methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
References
- Xu, X.; Lu, N.; Song, P.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X. Vancomycin, Daptomycin, Antistaphylococcal β-Lactam, and Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Monotherapy and Combination Therapy in the Management of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 805966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theuretzbacher, U.; Outterson, K.; Engel, A.; Karlén, A. The global preclinical antibacterial pipeline. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubrak, T.P.; Kołodziej, P.; Sawicki, J.; Mazur, A.; Koziorowska, K.; Aebisher, D. Some Natural Photosensitizers and Their Medicinal Properties for Use in Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebisher, D.; Czech, S.; Dynarowicz, K.; Misiołek, M.; Komosińska-Vassev, K.; Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Bartusik-Aebisher, D. Photodynamic Therapy: Past, Current, and Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieplik, F.; Deng, D.; Crielaard, W.; Buchalla, W.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Maisch, T. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy—What we know and what we don’t. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Chi, M.; Sun, X.; Xie, X.; Weir, M.D.; Oates, T.W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Xu, H.H. Novel nanomaterial-based antibacterial photodynamic therapies to combat oral bacterial biofilms and infectious diseases. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6937–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, K.; Nakamura, K.; Kanno, T.; Niwano, Y. Bactericidal Action of Photodynamic Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (PACT) with Photosensitizers Used as Plaque-Disclosing Agents against Experimental Biofilm. Biocontrol Sci. 2016, 21, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- de Melo, W.C.M.A.; Avci, P.; de Oliveira, M.N.; Gupta, A.; Vecchio, D.; Sadasivam, M.; Chandran, R.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yin, R.; Perussi, L.R.; et al. Photodynamic inactivation of biofilm: Taking a lightly colored approach to stubborn infection. Expert. Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 669–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation: A bright new technique to kill resistant microbes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 33, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, E.; Kang, K. Natural Photosensitizers in Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.-J.; Fang, Y.; Yao, M. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcanale, P.; Abbruzzetti, S.; Viappiani, C. Photodynamic treatment of pathogens. La Riv. Nuovo C. 2022, 45, 407–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, C.P.; Wainwright, M.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Sellera, F.P.; Dos Anjos, C.; Baptista, M.D.S.; Lincopan, N. Global priority multidrug-resistant pathogens do not resist photodynamic therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 208, 111893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Han, J.; Jin, F.; Du, Y. Recent Strategies to Address Hypoxic Tumor Environments in Photodynamic Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Huang, M.; Zeng, S.; Zheng, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, S. Innovative strategies for photodynamic therapy against hypoxic tumor. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 18, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kwon, N.; Guo, T.; Liu, Z.; Yoon, J. Innovative Strategies for Hypoxic-Tumor Photodynamic Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 11522–11531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-X.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.-F.; Xu, H.-Z.; Peng, X.-C.; Han, N.; Yu, T.-T.; Li, L.-G.; Li, Q.-R.; Chen, X.; et al. A nanoreactor boosts chemodynamic therapy and ferroptosis for synergistic cancer therapy using molecular amplifier dihydroartemisinin. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboorizadeh, B.; Zare-Dorabei, R.; Safavi, M.; Safarifard, V. Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) in Drug Delivery, Biosensing, and Therapy: A Comprehensive Review. Langmuir 2024, 40, 22477–22503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousian, B.; Khosravi, A.R.; Ghasemi, M.H.; Kadkhodaie, M. Biomimetic functionalized metal organic frameworks as multifunctional agents: Paving the way for cancer vaccine advances. Mater. Today Bio. 2024, 27, 101134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férey, G.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Dutour, J.; Surblé, S.; Margiolaki, I. A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. Science 2005, 309, 2040–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, D.; Lin, W. Metal-organic frameworks as a tunable platform for designing functional molecular materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13222–13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandash, F.; Leger, D.Y.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Sol, V.; Liagre, B. Porphyrin/chlorin derivatives as promising molecules for therapy of colorectal cancer. Molecules 2021, 26, 7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Xie, W.; Lu, J.; Guo, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, W.; Chi, Y.; Takuya, N.; Wu, H.; Zhao, L. Tannic acid-based metal phenolic networks for bio-applications: A review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 4098–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Ma, Q. Tannic acid: A crosslinker leading to versatile functional polymeric networks: A review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 7689–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yu, J.; Bu, C.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Ding, X.; Yuan, P. Antibiotic-Augmented Chemodynamic Therapy for Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in the Dynamic Stomach Environment. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 14983–14992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Song, J.; Wei, Z.; Yang, S.; Ma, Y.; Chen, W.R.; Lu, C.; Wen, L. Doxorubicin-Loaded Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles as Acid-Activatable Hydroxyl Radical Nanogenerators for Enhanced Chemo/Chemodynamic Synergistic Therapy. Materials 2022, 15, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swidan, M.M.; Wahba, N.S.; Sakr, T.M. An intelligent and self-assembled nanoscale metal organic framework (99mTC-DOX loaded Fe3O4@FeIII-tannic acid) for tumor targeted chemo/chemodynamic theranostics. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, L.; Lv, R.; Liu, M.; He, N.; Wang, Z. A metal-phenolic network-based multifunctional nanocomposite with pH-responsive ROS generation and drug release for synergistic chemodynamic/photothermal/chemo-therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wen, L.; Weng, Y.; Song, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhan, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Homologous-targeted and tumor microenvironment-activated hydroxyl radical nanogenerator for enhanced chemoimmunotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ren, X.; Guo, X.; Fu, C.; Wu, Q.; Tan, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhong, H.; et al. Multifunctional iron-based Metal-Organic framework as biodegradable nanozyme for microwave enhancing dynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2019, 214, 119223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setsukinai, K.; Urano, Y.; Kakinuma, K.; Majima, H.J.; Nagano, T. Development of Novel Fluorescence Probes That Can Reliably Detect Reactive Oxygen Species and Distinguish Specific Species. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3170–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, P.; Bai, X.; Feng, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, S.; Yu, X.; Fan, C.; Su, Q.; Song, J.; Lu, C. pH-Responsive Nanophotosensitizer Boosting Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy by Hydroxyl Radical Generation. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141075
Tian P, Bai X, Feng J, Xu L, Xu S, Yu X, Fan C, Su Q, Song J, Lu C. pH-Responsive Nanophotosensitizer Boosting Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy by Hydroxyl Radical Generation. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(14):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141075
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Peilin, Xianyue Bai, Jing Feng, Luyao Xu, Shihao Xu, Xiaoya Yu, Caiju Fan, Qian Su, Jiaxing Song, and Cuixia Lu. 2025. "pH-Responsive Nanophotosensitizer Boosting Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy by Hydroxyl Radical Generation" Nanomaterials 15, no. 14: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141075
APA StyleTian, P., Bai, X., Feng, J., Xu, L., Xu, S., Yu, X., Fan, C., Su, Q., Song, J., & Lu, C. (2025). pH-Responsive Nanophotosensitizer Boosting Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy by Hydroxyl Radical Generation. Nanomaterials, 15(14), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141075





