Nano-Enabled Insecticides for Efficient Pest Management: Definition, Classification, Synergistic Mechanism, and Safety Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definition and Connotation of Nano-Pesticides
- (i)
- Nano-emulsion, referring to oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions in which water-insoluble AIs are finely dispersed into nanoscale particles (1–100 nm) by surfactants and other functional agents, thereby forming kinetically stable nanoparticle-based emulsions. For example, Abd-Elnabi et al. [26] formulated nano-emulsions using essential oils from Portulaca oleracea and Rosmarinus officinalis, achieving mean particle sizes of 26.67 nm and 97.36 nm, respectively. These nanoscale emulsions exhibit substantially greater insecticidal activity against Aphis gossypii, Spodoptera littoralis, and Tetranychus urticae, with LC50 values significantly lower than those of their bulk oil counterparts. The enhanced efficacy is attributed to the smaller particle size, which can increase foliar coverage, improve wettability, and enhance cuticular penetration.
- (ii)
- Nano-suspension concentrate: A suspension formulation where the AI and solid excipients are present as nanosized particles (1–300 nm), stabilized in water via nano-techniques. For instance, Ding et al. [27] formulated a chlorantraniliprole nanosuspension with a mean particle size of 56 nm for controlling Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. Compared to a commercial suspension concentrate, the nano-suspension exhibits superior dispersibility, foliar wettability, and leaf retention, leading to improved bioavailability and efficacy. The formulation achieves equivalent control efficacy, even at a 40% reduced dose, and remains physically stable during storage at 25 °C.
- (iii)
- Nano-water dispersible granule (nano-WDG): A granule formulation has been prepared via nanotechnological processes that disintegrates in water to release nanoscale solid particles (1–300 nm). Li et al. [28] reported a solid nano-dispersion of emamectin benzoate with an average particle size of 17 nm and 50% loading content using PEG 4000 and surfactants through a melt-fusion method. This nano-WDG exhibits 1.8-fold higher insecticidal activity against Spodoptera exigua compared to commercial WDG, highlighting its improved dispersibility and bio-efficacy.
3. Classification and Preparation Method of Nano-Insecticides
3.1. Type I Nano-Insecticides
3.1.1. Metal-Based Nano-Insecticides
3.1.2. Non-Metallic Nano-Insecticides
3.2. Type II Nano-Insecticides
3.2.1. Nano-Insecticides Based on Inorganic Carriers
3.2.2. Nano-Insecticides Based on Organic Carriers
3.2.3. Nano-Insecticides Based on Inorganic–Organic Hybrid Carriers
3.2.4. Nano-Insecticides Based on Small Molecules
4. Advantages of Nano-Insecticides
4.1. Improved Adhesion and Deposition of Insecticides on Targets
4.2. Enhanced Absorption of Insecticides by Targets
4.3. Controlled and Sustained Release of Insecticides
4.4. Stronger Penetration and Damage of Nano-Insecticides on Biological Membrane
5. Insecticidal Performance of Nano-Insecticides
6. Environmental Safety of Nano-Insecticides
6.1. Impact on Beneficial Predators
6.2. Impact on Beneficial Microorganisms
6.3. Environmental Residues
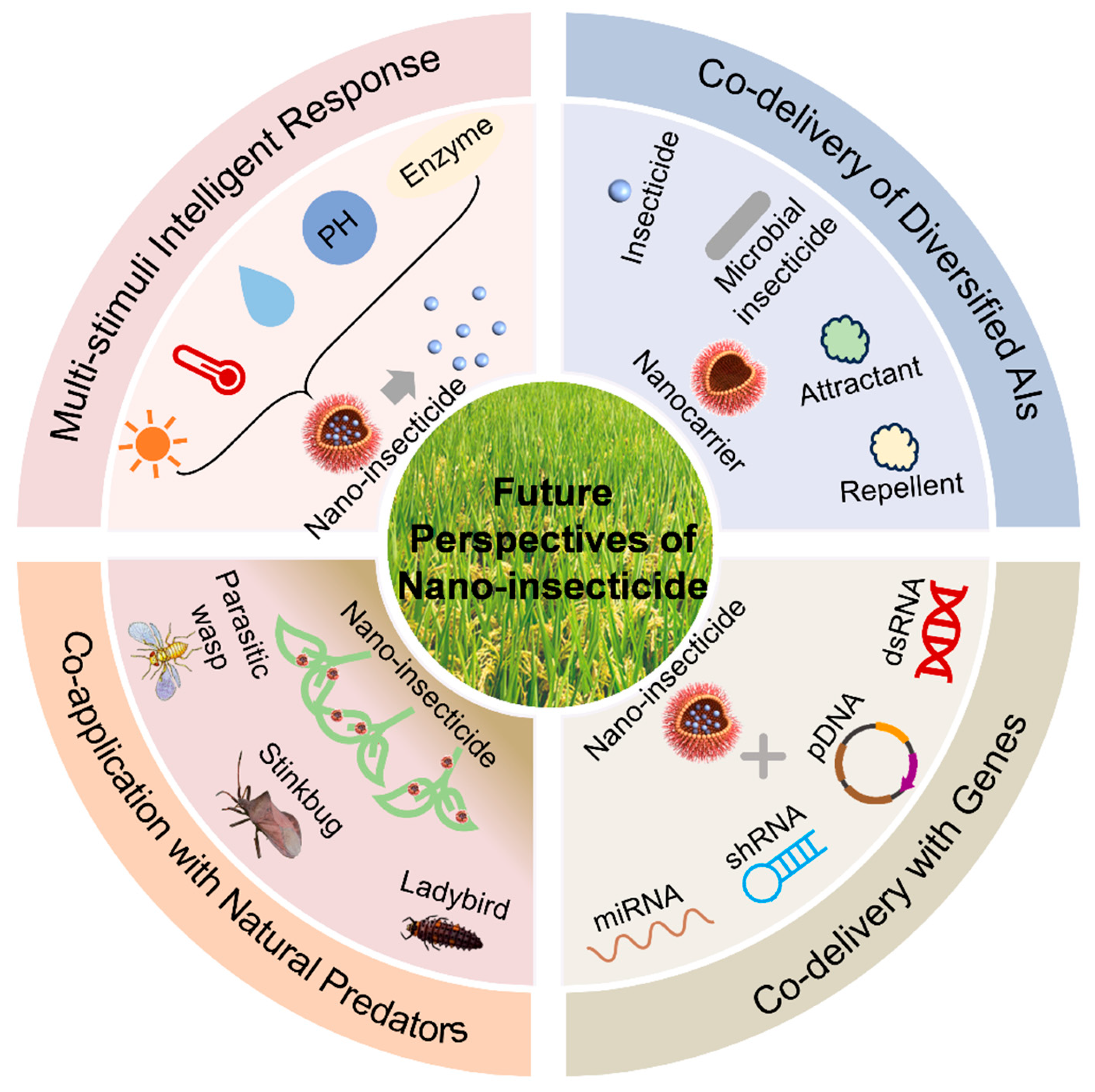
7. Future Perspectives
7.1. Multi-Stimuli Intelligent Response
7.2. Co-Delivery of Diversified AIs
7.3. Co-Delivery with Genes
7.4. Co-Application with Natural Predators
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Tian, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Xiao, Z. Perennial grain crops: A new option for the future food and ecoagricultural environment. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 361–363, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogoevski, Z.; Todorov, Z.; Gjosheva, M.; Efnusheva, D.; Cholakoska, A. A monitoring system design for smart agriculture. In Cybernetics Perspectives in Systems; Springer International Publishing: Chem, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 503, pp. 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- Tudi, M.; Ruan, H.D.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C.; Dung, T.P. Agriculture development, pesticide application and its impact on the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Saleh, N.B.; Byro, A.; Zepp, R.; Sahle-Demessie, E.; Luxton, T.P.; Ho, K.T.; Burgess, R.M.; Flury, M.; White, J.C.; et al. Nano-enabled pesticides for sustainable agriculture and global food security. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.; He, D.; Li, B.; Chen, X.; Luo, K.; Li, G. Environmentally friendly and effective alternative approaches to pest management: Recent advances and challenges. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivunen, M.; Duke, S.O.; Coats, J.C.; Beck, J.J. Pest Management with Natural Products; Springer: Chem, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 1141, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka, K.; Yadav, B.S.; Kote, A.; Yadav, R.; Shejwal, P. Comparative analysis of organic and chemical pesticides: Impacts on crop health and environmental sustainability. Uttar Pradesh J. Zool. 2024, 45, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P.; Maipas, S.; Kotampasi, C.; Stamatis, P.; Hens, L. Chemical pesticides and human health: The urgent need for a new concept in agriculture. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, N.E. An alternative to controversial pesticides still harms bumblebees. Nature 2018, 561, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shattuck, A.; Werner, M.; Mempel, F.; Dunivin, Z.; Galt, R. Global pesticide use and trade database (gloput): New estimates show pesticide use trends in low-income countries substantially underestimated. Glob. Environ. Change 2023, 81, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambec, S.; Desquilbet, M. Regulating to manage pesticide resistance development: The question of the sustainability of pest and disease sensitivity to pesticides and resistant varieties. INRA Sci. Soc. 2011, 2011, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, S.; Reade, J.P.H.; Burn, A.; Zappala, S. Pesticides. In Agricultural Chemicals and the Environment: Issues and Potential Solutions; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; Volume 43, pp. 45–93. [Google Scholar]
- Camara, M.C.; Campos, E.V.R.; Monteiro, R.A.; do Espirito Santo Pereira, A.; De Freitas Proença, P.L.; Fraceto, L.F. Development of stimuli-responsive nano-based pesticides: Emerging opportunities for agriculture. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.P.; Zhang, B.H.; Wang, J. Multiple roles of mesoporous silica in safe pesticide application by nanotechnology: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 6735–6754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Su, X.; Yan, S.; Shen, J. Multifunctional nanoparticles and nano-pesticides in agricultural application. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondéjar-López, M.; García-Simarro, M.P.; Navarro-Simarro, P.; Gómez-Gómez, L.; Ahrazem, O.; Niza, E. A review on the encapsulation of “eco-friendly” compounds in natural polymer-based nanoparticles as next generation nano-agrochemicals for sustainable agriculture and crop management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 136030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.H. Green pesticide practices and sustainability: Empirical insights into agricultural services in China. Int. J. Agric. Sust. 2024, 22, 2306713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, G.; Guo, Z.; Wang, M.; Qi, C.; Chen, G.; Huang, X.; Yan, S.; Xu, D. Stimuli-responsive pesticide carriers based on porous nanomaterials: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khot, L.R.; Sankaran, S.; Maja, J.M.; Ehsani, R.; Schuster, E.W. Applications of nanomaterials in agricultural production and crop protection: A review. Crop Prot. 2012, 35, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsalam, K.A. Special issue: Agricultural nanotechnology. Plants 2024, 13, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomollon-Bel, F.; Garcia Martinez, J.; Lawlor, H. Top ten emerging technologies in chemistry: A new initiative from iupac and chemistry international. In Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 257. [Google Scholar]
- Kah, M.; Hofmann, T. Nano-pesticide research: Current trends and future priorities. Environ. Int. 2014, 63, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Lin, H.; Ning, L.; Ma, N.; Wei, W.; Ji, X.; Wei, S.; Xu, P.; Zhang, D.; Wang, F. Advances in the design of functional cellulose based nano-pesticide delivery systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 11295–11307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shangguan, W.; Cheng, X.; Yu, M.; Cao, L. Preparation, development and future challenge of pesticide nanosuspension concentrate. Mod. Agrochem. 2025, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.D.; Zhao, P.Y.; Cao, C.; Li, F.M.; Huang, Q.L. Research progress and development prospect of nano-pesticide. Mod. Agrochem. 2023, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elnabi, A.D.; El-sawy, E.A.F.; Badawy, M.E.I. Plant oil nano-emulsions as a potential solution for pest control in sustainable agriculture. Neotrop. Entomol. 2025, 54, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Guo, L.; Du, Q.; Wang, T.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Gao, F.; Cui, B. Preparation and comprehensive evaluation of the efficacy and safety of chlorantraniliprole nanosuspension. Toxics 2024, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Cui, H. Fabrication and characterization of a novel solid nano-dispersion of emamectin benzoate with high dispersibility and wettability. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Wang, Y. Research advance on potentially involved insecticidal mechanisms and safety evaluation of nano-silver insecticide. Chin. J. Hyg. Insect Equip. 2019, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Han, Y.; Gao, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.X.; Wang, Y. Insecticidal activity of metallic nano-pesticides synthesized from natural resources: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 1141–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, M.; Bramuzzo, S.; Baratella, D.; Ugolotti, J.; Zoppellaro, G.; Chemello, G.; Olivotto, I.; Ballarin, C.; Radaelli, G.; Arcaro, B.; et al. Self-assembly of chlorin-e6 on γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: Application for larvicidal activity against. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 194, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- El-Abeid, S.E.; Ahmed, Y.; Daròs, J.A.; Mohamed, M.A. Reduced graphene oxide nanosheet-decorated copper oxide nanoparticles: A potent antifungal nanocomposite against Fusarium root rot and wilt diseases of tomato and pepper plants. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.L.M.; Barbosa, T.M.; Cabral, R.L.B.; Nascimento, J.H.O.; Gama, R.A. Effect of zinc oxide quantum dots (ZnO QD) on Aedes Aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2024, 44, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prospective biotechnological applications: An overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharani, R.S.A.; Namasivayam, S.K.R. Biogenic silver nanoparticles mediated stress on developmental period and gut physiology of major Lepidopteran pest Spodoptera litura (Fab.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)-an eco-friendly approach of insect pest control. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, A.N.; Balasubramanian, C. Myco-synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Beauveria bassiana against dengue vector, Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2869–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathipati, U.; Kanuparthi, P. Silver nanoparticles for insect control: Bioassays and mechanisms. In Silver Nanomaterials for Agri-Food Applications; Abd-Elsalam, K.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 471–494. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Cisterna, D.; Rubilar, O.; Tortella, G.; Chen, L.; Chacón-Fuentes, M.; Lizama, M.; Parra, P.; Bardehle, L. Silver nanoparticles as a potent nanopesticide: Toxic effects and action mechanisms on pest insects of agricultural importance—A review. Molecules 2024, 29, 5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, A.; Zaki, A.; Abdel-Rahim, E.; Khedr, M. Novel CuO nanoparticles for pest management and pesticides photodegradation. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2016, 10, 274–283. [Google Scholar]
- Murugesan, S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Perumal, E. Copper oxide nanoparticles induced reactive oxygen species generation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2025, 405, 111311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Thakur, S.; Kumari, P.; Shandilya, M.; Sharma, S.; Poczai, P.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Sayyed, R.Z. Nano-insecticide: Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of insecticidal activity of ZnO NPs against Spodoptera litura and Macrosiphum euphorbiae. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 3835–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, A.; Elabasy, A.; Waqas, M.; Lin, L.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Z. Entomotoxic effect of silicon dioxide nanoparticles on Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) under laboratory conditions. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2018, 100, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midhun Dominic, C.D.; Neenu, K.V.; Begum, P.M.S.; Joseph, R.; Rosa, D.D.S.; Duan, Y.; Balan, A.; Ajithkumar, T.G.; Soumya, M.; Shelke, A.; et al. Nanosilica from Averrhoa bilimbi juice pre-treated rice husk: Preparation and characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 413, 137476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahi, D.; Bisht, K.; Gautam, S.; Salvi, P.; Lohani, P. Green synthesized nano silica: Foliar and soil application provides drought endurance in Eleucine coracana. Environ. Sci. Nano 2024, 11, 3412–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, K.; Zhou, R.; Hui, T.P.; Liu, Y.N.; Zhang, X.R.; Li, W.K.; Lei, P.; Gao, Y.Q.; Ma, Z.Q. Preparation and biological activity of hollow mesoporous silica loaded tebuconazole nano sustained release granules. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2024, 26, 559–569. [Google Scholar]
- Thabet, A.F.; Boraei, H.A.; Galal, O.A.; El-Aziz, A.A.; Soliman, E.H.; Fouda, M.A. Silica nanoparticles as pesticide against insects of different feeding types and their non-target attraction of predators. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14484. [Google Scholar]
- Barik, T.K.; Sahu, B.; Swain, V. Nanosilica-from medicine to pest control. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Tang, G.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Yu, X.; Luo, L.; et al. Carrier-free small molecular self-assembly based on berberine and curcumin incorporated in submicron particles for improving antimicrobial activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10055–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangguan, W.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, P.; Cao, C.; Yu, M.; Cao, Y.; Cao, L. Making the complicated simple: A minimizing carrier strategy on innovative nano-pesticides. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.H.; Ren, Y.P.; Xue, H.J. Fabrication and application of carrier-free and carrier-based nanopesticides in pest management. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2024, 116, e22124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Yin, Q.; Shangguan, W.; Cao, C.; Huang, Q.; Cao, L. An organic solvent-free self-assembly strategy for scalable preparation of nanobiopesticides with enhanced insecticidal activity against houseflies. Nanoscale 2025, 17, 9363–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yao, J.; Cai, M.; Chai, H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J.; Chandankere, R.; Masakorala, K. Synthesis of a novel nano-pesticide and its potential toxic effect on soil microbial activity. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chi, Y.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z. Fabrication of a controllable nano-pesticide system with magnetic collectability. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cao, L.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, C.; Li, F.; Huang, Q. Emulsion-based synchronous pesticide encapsulation and surface modification of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with carboxymethyl chitosan for controlled azoxystrobin release. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sahu, B.K.; Cao, L.; Bindra, P.; Kaur, K.; Chandel, M.; Koratkar, N.; Huang, Q.; Shanmugam, V. Porous nanomaterials: Main vein of agricultural nanotechnology. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 121, 100812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Niu, S.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Shan, Y.; Huang, Q. Positive-charge functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers for controlled 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid sodium salt release. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6594–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xue, L.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.; Kang, Z. Sustainable pest management with hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with β-cypermethrin. Agronomy 2025, 15, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Shi, T.; Tang, T.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y. Preparation and characterization of nano-sized calcium carbonate as controlled release pesticide carrier for validamycin against Rhizoctonia solani. Microchim. Acta 2011, 173, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, G.; Rebora, M.; Piersanti, S.; Saitta, V.; Kovalev, A.; Gorb, E.; Gorb, S. Reduction in insect attachment caused by different nanomaterials used as particle films (kaolin, zeolite, calcium carbonate). Sustainability 2021, 13, 8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, Z.; He, K.; Jing, D. Graphene oxide as a multifunctional synergist of insecticides against lepidopteran insect. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, Z.; He, K. Graphene oxide as a pesticide delivery vector for enhancing acaricidal activity against spider mites. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zeng, Z.; Cui, H.; Verheggen, F. Polymer-based nanoinsecticides: Current developments, environmental risks and future challenges. A review. Biotechnol. Agron. Société Environ. 2020, 24, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, F.; Wang, L.; Yan, P.; Guo, X.; Zhao, R.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. Redox-responsive nano-pesticides based on natural polymers for environmentally safe delivery of pesticides with enhanced foliar dispersion and washout resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 20343–20353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bhanjana, G.; Sharma, A.; Sidhu, M.C.; Dilbaghi, N. Synthesis, characterization and on field evaluation of pesticide loaded sodium alginate nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.E.S.; Grillo, R.; Mello, N.F.S.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Application of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanoparticles containing atrazine herbicide as an alternative technique to control weeds and reduce damage to the environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuruzzaman, M.D.; Rahman, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Nanoencapsulation, nano-guard for pesticides: A new window for safe application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1447–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cui, B.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Z.; Cui, H. Progress on categories and synergistic mechanism of nano-pesticides. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2020, 22, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, L.T.M.; Rocha, B.L.; Teixeira, C.C.; Martins, H.C.; Silveira, M.C.A.; Albuquerque, B.; Cangussu, A.S.R.; He, P.; Aguiar, R.W.S.; Maia, A.M.S.; et al. Preparation of β-myrcene-chitosan nanoparticles and their uptake and toxicity in Aedes aegypti larvae. Insects 2024, 15, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, Z.; He, C.; Yao, W.; Zhang, C.; Gu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Du, F. Facile--prepared size-controllable nanogels for enhancing bidirectional translocation, control efficiency, and security of nano-pesticide. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2410555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Shang, X.F.; Yang, L.; Shi, Y.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Li, J.C.; Yang, G.Z.; Yang, C.J. Engineering of peglayted camptothecin into nanomicelles and supramolecular hydrogels for pesticide combination control. Front. Chem. 2020, 7, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Peng, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. A nanocarrier pesticide delivery system with promising benefits in the case of dinotefuran: Strikingly enhanced bioactivity and reduced pesticide residue. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H. Light and temperature dual responsive pesticide release system based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified by dopamine. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 29, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, J.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Qian, K. A pH- and enzymatic-responsive nano-pesticide to control pea aphids and reduce toxicity for earthworms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Tang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Niu, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A simple preparation process for an efficient nano-formulation: Small molecule self-assembly based on spinosad and sulfamic acid. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 4882–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tang, G.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, G.; Hu, G.; Yan, W.; Li, J.; Cao, Y. Carrier-free self-assembled nanoparticles based on prochloraz and fenhexamid for reducing toxicity to aquatic organism. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 943, 173821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Li, X.; Yan, W.; Hu, G.; Tang, G.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, G.; et al. Carrier-free codelivery of an insecticidal nanosystem based on thiamethoxam and lambda-cyhalothrin for sustainable pest management. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 8792–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wan, M.; Feng, W.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, X.; Luo, Y.; Shen, J. Environmentally friendly Zr-based MOF for pesticide delivery: Ultrahigh loading capacity, pH-responsive release, improved leaf affinity, and enhanced antipest activity. Langmuir 2022, 38, 10867–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y. Pesticide formulation and dose transfer. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 1999, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Cheng, X.; Huang, G.; Zhao, P.; Cao, C.; Cao, L.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, Q. Research progress in target dose transfer and regulation of pesticides deposition by foliar spray diluted with water. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2022, 24, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Neinhuis, C.; Barthlott, W. Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Ann. Bot. 1997, 79, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super--hydrophobic surfaces: From natural to artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cao, C.; Xu, B.; Ran, G.; Cao, L.; Li, F.; Zhao, P.; Huang, Q. Research progress on bouncing behavior and control technology of pesticide droplets at plant leaf surface. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2019, 21, 895–907. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Gao, F.; Sun, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhan, S.; Li, X.; Cui, H.; Duan, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Self-assembly of 1-triacontanol onto layered doubled hydroxide nano-carriers toward sustainable growth regulation of maize. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Gao, F.; Cui, B.; Wang, T.; Chen, F.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhou, X.; Cui, H. Improving the stability, foliar utilization and biological activity of imidacloprid delivery systems: Size effect of nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Sun, C.; Xue, Y.; Liu, C.; Qiu, D.; Cui, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.; Zeng, Z. Tannic acid-based nano-pesticides coating with highly improved foliage adhesion to enhance foliar retention. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27096–27104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Qiu, L.; Liu, Q.; He, Y. Preparation of an environmentally friendly nano-insecticide through encapsulation in polymeric liposomes and its insecticidal activities against the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Insects 2022, 13, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Huang, J.; Tang, H.; He, F.; Yuan, J.; Wan, S.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Q.; Feng, Y.; Yu, G.; et al. Fabricating network-link acetamiprid-loading micelles based on dopamine-functionalized alginate and alkyl polyglucoside to enhance folia deposition and retention. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3596–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Peng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Du, X.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. A star polyamine-based nanocarrier delivery system for enhanced avermectin contact and stomach toxicity against green peach aphids. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.C.; Yang, C.M.; Meng, Z.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Fan, T.L.; Cui, J.J. Nano-carrier hollow mesoporous silica improving uptake ability of tetrachlorantraniliprole. Agrochemicals 2022, 61, 803–807. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Lin, Y.M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cui, X.; Yang, Y. Effective translocation of rigid nanoparticles across leaf surfaces by deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 146395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Xu, Y.; He, Y.; Nikolic, M.; Nikolic, N.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, Z. Silicon nanoparticles in sustainable agriculture: Synthesis, absorption, and plant stress alleviation. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1393458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Peng, M.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. Nanocarrier-loaded imidaclothiz promotes plant uptake and decreases pesticide residue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, D.; Zhao, M.; Fan, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X. Uptake and translocation properties of rotenone nano-pesticide mediated by hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles in cucumber plant. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2022, 43, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Hou, R. Optimizing the size of mesoporous silica nano-delivery system enhances the absorption, transport, and retention of pesticides in tea plants. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 227, 120789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Cao, S.H.; Yin, S.Y.; Zhou, C.G.; Gao, S.K.; Jia, C.Y.; Ji, Y.C.; Liu, Y.X. Self-assembled bovine serum albumin nanoparticles as pesticide delivery vectors for controlling trunk-boring pests. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Gao, F.; Cui, B.; Du, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, X.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H. The key factors of solid nanodispersion for promoting the bioactivity of abamectin. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 201, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Yuan, F.; Song, B.; Teng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, T. A nanoformulation that enhance the efficiency of camptothecin against lepidopteran pests by controlled release and ‘poison bait’ strategies. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 486, 150358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Jing, M.; Liu, S.; Feng, J.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z. Self-assembled mixed micelle loaded with natural pyrethrins as an intelligent nano-insecticide with a novel temperature-responsive release mode. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, H.; Li, N.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H. Dinotefuran nano-pesticide with enhanced valid duration and controlled release properties based on a layered double hydroxide nano-carrier. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 3202–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, S.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Liang, P.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Gao, X. Nanodelivery system alters an insect growth regulator’s action mode: From oral feeding to topical application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 35105–35113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Patra, P. Relative larvicidal property of common oxide nanostructures against Culex quinquefasciatus. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Ma, X.; Shi, H.; Ma, T.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Luo, K.; Cai, L.; et al. Green synthesis of an alginate-coated silver nanoparticle shows high antifungal activity by enhancing its cell membrane penetrating ability. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4087–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. A nano-delivery system expands the insecticidal target of thiamethoxam to include a devastating pest, the fall armyworm. Insect Sci. 2023, 30, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wei, J.; Yin, M.; Du, X.; Shen, J. Simple osthole/nanocarrier pesticide efficiently controls both pests and diseases fulfilling the need of green production of strawberry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 36350–36360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chao, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. Visualization of the process of a nanocarrier-mediated gene delivery: Stabilization, endocytosis and endosomal escape of genes for intracellular spreading. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, P.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced insecticidal activity of chlorfenapyr against Spodoptera frugiperda by reshaping the intestinal microbial community and interfering with the metabolism of iron-based metal–organic frameworks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 36036–36051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Chen, D.; Che, L.; Gu, N.; Yin, M.; Du, X.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. Biotoxicity evaluation of a cationic star polymer on a predatory ladybird and cooperative pest control by polymer-delivered pesticides and ladybird. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6083–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Tang, T.; Lin, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Kah, M.; Li, L. Environmental risks and the potential benefits of nano-pesticides: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2097–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Majumdar, D.; Biswas, H.; Chowdhury, A.; Podder, S. Nano-biopesticide formulation comprising of silver nanoparticles anchored to Ocimum sanctum: A sustainable approach to pest control in jute farming. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Elbehery, H.H.; Samy, A. The efficacy of green silica nanoparticles synthesized from rice straw in the management of Callosobruchus maculatus (Col., Bruchidae). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; Ayoub, H.A.; Rashwan, F.A.; Abdel-Hafez, H.F. Sea urchin-like calcium borate microspheres and synergistic action with cholinesterase-inhibiting insecticides for ecofriendly Spodoptera littoralis control. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2021, 23, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwesh, O.M.; Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; El-Bakry, A.M. Nano-chitosan as a bio-enhancer for improving insecticide formulations: A study on indoxacarb and methomyl against cotton leafworm. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalakannan, M.; Rajendran, D.; Thomas, J.; Chandrasekaran, N. Synergistic impact of nanoplastics and nanopesticides on Artemia salina and toxicity analysis. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 3119–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, Z.; Sadeghi, Z.; Khorrami, F.; Ojaghi Aghbash, K.; Moridi Farimani, M. Salvia abrotanoides methanolic extract Fe3O4@Carbon nanocomposite as biological approach for protection against the Potato Tuber Moth. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, R.; Shakil, N.A.; Sarkar, D.J.; Chander, S. Evaluation of fipronil nanoformulations for effective management of brown plant hopper (Nilaparvata lugens) in rice. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2019, 65, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.B.; Wang, J.; Yuan, J.J.; Tao, M.; Wang, A.Q.; Li, N.J.; Wu, Q.J. Evaluation of the field efficacy of three controlled release nano-pesticides against Thrips tabaci Lindeman. J. Environ. Entomol. 2022, 44, 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Taktak, N.E.M.; Badawy, M.E.I.; Awad, O.M.; Abou El-Ela, N.E.; Abdallah, S.M. Enhanced mosquitocidal efficacy of pyrethroid insecticides by nanometric emulsion preparation towards Culex pipiens larvae with biochemical and molecular docking studies. J. Egypt. Public. Health. Assoc. 2021, 96, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; An, S.; Yin, X. Nanochitin whisker enhances insecticidal activity of chemical pesticide for pest insect control and toxicity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaud, M.; Souto, E.B.; Zielinska, A.; Severino, P.; Batain, F.; Oliveira-Junior, J.; Alves, T. Nanopesticides in agriculture: Benefits and challenge in agricultural productivity, toxicological risks to human health and environment. Toxics 2021, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, F. Opportunities and limitations of nanoagrochemicals. Helv. Chim. Acta 2022, 106, e202200136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.A.; Biraku, X.; Nielsen, E.; Ozketen, A.C.; Ozketen, A.A.; Hakki, E.E. Agricultural nanotechnology for a safe and sustainable future: Current status, challenges, and beyond. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 3159–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, M.; Machinski, P.; Koerner, P.; Tiede, K.; Hofmann, T.; Tappin, A.D.; Jex, L.M. Analysing the fate of nanopesticides in soil and the applicability of regulatory protocols using a polymer-based nanoformulation of atrazine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11699–11707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhardi, J.A.; Fraceto, L.F.; Wilkinson, K.J.; Ghoshal, S. Soil enzyme activities as an integral part of the environmental risk assessment of nanopesticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8514–8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhao, K.; Liu, S.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Song, R.; Gu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Du, F. Promising nanocarriers endowing non-systemic pesticides with upward translocation ability and microbial community enrichment effects in soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojtová, D.; Vašíčková, J.; Grillo, R.; Bílková, Z.; Šimek, Z.; Neuwirthová, N.; Kah, M.; Hofman, J. Nanoformulations can significantly affect pesticide degradation and uptake by earthworms and plants. Environ. Chem. 2019, 16, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; Yin, J.; Wang, Z.; Shen, J.; Liu, S.; Deng, X.; Yan, S. Differential ecotoxicity of nanoencapsulated metamifop and its active ingredient in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Insights from transcriptome and metabolome analysis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 208, 106506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, A.; El-Mehasseb, I.; Saad Allah, M.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; Alsharif, K.F.; Ahmed, M.S.; Derbalah, A.S. Advanced oxidation processes using zinc oxide nanocatalyst for detoxification of some highly toxic insecticides in an aquatic system combined with improving water quality parameters. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 807290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Masarawy, M.S.; El-Bendary, H.M.; El-Helaly, A.M.A. The effect of using imidacloprid and chlorpyrifos and their nanoforms on certain characteristics of honeybee Apis mellifera L. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, M.; Zhao, C.; Akhtar, S.; Ahmad, I.; Jilong, P.; Zhang, S. Assessment of nano-formulated conventional insecticide-treated sugar baits on mosquito control and the effect on non-target Aphidophagous Coccinella septempunctata. Insects 2024, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Tao, M.; Xu, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Z. Impacts of nano-acetamiprid pesticide on faba bean root metabolic response and soil health. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; He, J.; Yu, T.; Sun, C.; Shi, D.; Jiang, Y.; Xianyu, Y.; Shao, Y. Dietary exposure of copper and zinc oxides nanoparticles affect the fitness, enzyme activity, and microbial community of the model insect, silkworm Bombyx mori. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihegwuagu, N.; Sha’Ato, R.; Tor-Anyiin, T.A.; Nnamonu, L.A.; Buekes, P.; Sone, B.; Maaza, M. Facile formulation of starch–silver-nanoparticle encapsulated dichlorvos and chlorpyrifos for enhanced insecticide delivery. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Wu, J.; Yan, W.; Zhu, S.; Miao, X.; Wang, R.; Huang, S.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z. Green synthesis of a chlorfenapyr chitosan nanopesticide for maize root application: Reducing environmental pollution and risks to nontarget organisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said-Elbahr, R.; Nasr, M.; Alhnan, M.A.; Taha, I.; Sammour, O. Simultaneous pulmonary administration of celecoxib and naringin using a nebulization-friendly nanoemulsion: A device-targeted delivery for treatment of lung cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Li, Y. A comparative study of the controllable release and insecticidal efficacy for two typical carrier methods on diamide insecticide delivery system. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2025, 208, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhuang, K.; Du, J.; Duan, H.; Gao, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; et al. Sustainable lignin-modified epoxy nanocarriers for enhanced foliar insecticide efficacy and food safety. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, D.; Yurdusen, A.; Mouchaham, G.; Nouar, F.; Serre, C. Large-scale production of metal–organic frameworks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2309089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rodrigues, S.; Tsyusko, O.V.; Unrine, J.M. Comparing plant–insect trophic transfer of Cu from lab-synthesised nano-Cu(OH)2 with a commercial nano-Cu(OH)2 fungicide formulation. Environ. Chem. 2019, 16, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, E.S.; Olisah, C.; Malloum, A.; Adegoke, K.A.; Ighalo, J.O.; Conradie, J.; Ohoro, C.R.; Amaku, J.F.; Oyedotun, K.O.; Maxakato, N.W.; et al. Ecotoxicological impact of dinotefuran insecticide and its metabolites on non-targets in agroecosystem: Harnessing nanotechnology- and bio-based management strategies to reduce its impact on non-target ecosystems. Environ. Res. 2024, 243, 117870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, H.; Hou, R.; Zhou, J.; Lin, S.; Zhao, K.; Wang, R.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Z. Nano-pesticide carrier O-carboxymethyl chitosan is indigestible in Apis cerana cerana and affects intestinal flora. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, J.P.; Fang, H.; Wang, M.C.; Wang, Q.W.; Zhou, B.S. Coexposure to environmental concentrations of cis-bifenthrin and graphene oxide: Adverse effects on the nervous system during metamorphic development of Xenopus laevis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Gu, N.; Peng, M.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, E.; Li, Z.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Du, X.; Dong, M. A preparation method of nano-pesticide improves the selective toxicity toward natural enemies. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Du, X.; Yan, S.; Dong, M. Star polymer-based nanodelivery system for pesticides: Enhanced broad-spectrum toxicity and selective toxicity. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 41595–41602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ji, C.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J. Chronic exposure to the star polycation (SPc) nanocarrier in the larval stage adversely impairs life history traits in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Martínez, A.C.; Parra-Cota, F.I.; De Los Santos-Villalobos, S. Beneficial microorganisms in sustainable agriculture: Harnessing microbes’ potential to help feed the world. Plants 2022, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, A.P.B.; Sastry, T.P.; Manigandan, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Environmental benignity of a pesticide in soft colloidal hydrodispersive nanometric form with improved toxic precision towards the target organisms than non-target organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, R.; Ping, Y.; Ma, M.; Gao, Y.; He, C.; Wu, T.; Ma, Y.; et al. Salinity-driven interface self-assembly of a biological amphiphilic emulsifier to form stable Janus core–shell emulsion for enhancing agrichemical delivery. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 9486–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, S.; Henriques, I.; Loureiro, S. Long-term effects of Cu(OH)2 nano-pesticide exposure on soil microbial communities. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Wu, M.; Qian, X.; Lin, D.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Zeng, T.; Yao, W.; Filser, J.; et al. Potential environmental risks of nano-pesticides: Application of Cu(OH)2 nano-pesticides to soil mitigates the degradation of neonicotinoid thiacloprid. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubeen, B.; Hasnain, A.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Naqvi, S.A.H.; Prasad, R.; Rehman, A.U.; Sohail, M.A.; Hassan, M.Z.; Farhan, M.; et al. Current progress and open challenges for combined toxic effects of manufactured nano-sized objects (MNO’s) on soil biota and microbial community. Coatings 2023, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, P.; Zhou, H.; Hao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X. pH/redox dual responsive from natural polymer-based nanoparticles for on-demand delivery of pesticides. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, M.; Yu, C.; Li, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, J.; Mo, Z.; Qin, C.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Redox and near-infrared light-responsive nanoplatform for enhanced pesticide delivery and pest control in rice: Construction, efficacy, and potential mechanisms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 41351–41361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Ma, N.; He, L.X.; Xu, P.; Wang, F.; You, C.Q. High deposition and precise stimulus-response release performance of lignin-coated dendritic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for efficient pesticide utilization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Du, J.; Wang, R.; Luo, J.; Jing, T.F.; Li, B.X.; Mu, W.; Liu, F.; Hou, Y.M. Core/shell dual-responsive nanocarriers via iron-mineralized electrostatic self-assembly for precise pesticide delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, P.; Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; Lu, W.; Li, D.; Yin, X.; Lian, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Z. Rational design of multi-stimuli-responsive polymeric nanoparticles as a ‘Trojan horse’ for targeted pesticide delivery. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 193, 116182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, W.; Huang, Q.; Cao, L. ‘Microscopic engineering vehicles’ for plants under stress combination. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.M.; Zaki, A.H.; Farghali, A.A.; Abdel-Rahim, E.F. Sodium titanate-Bacillus as a new nanopesticides for cotton leaf-worm. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 11, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.A.; Camara, M.C.; de Oliveira, J.L.; Campos, E.V.R.; Carvalho, L.B.; de Freitas Proença, P.L.; Guilger-Casagrande, M.; Lima, R.; do Nascimento, J.; Gonçalves, K.C.; et al. Zein based-nanoparticles loaded botanical pesticides in pest control: An enzyme stimuli-responsive approach aiming sustainable agriculture. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.A.; Ferreira-Sá, P.S.; Garcia, M.D.N.; Pereira, V.L.P.; Carvalho, J.C.T.; Rocha, L.; Fernandes, C.P.; Souto, R.N.P.; Araújo, R.S.; Botas, G.; et al. Nano-emulsions of the essential oil of Baccharis reticularia and its constituents as eco-friendly repellents against Tribolium castaneum. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 162, 113282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott-Fordsmand, J.J.; Fraceto, L.F.; Amorim, M.J.B. Nano-pesticides: The lunch-box principle-deadly goodies (semio-chemical functionalised nanoparticles that deliver pesticide only to target species). J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, X.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. Recent advances in nanoparticle-mediated co-delivery system: A promising strategy in medical and agricultural field. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Li, M.; Jiang, Q.; Li, M.; Hu, M.; Shi, X.; Liang, P.; Yin, M.; Gao, X.; Shen, J.; et al. Self-assembled co-delivery nanoplatform for increasing the broad-spectrum susceptibility of fall armyworm toward insecticides. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.H.; Zhao, P.; Ning, X.Y.; Xie, Y.Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.X. Nanomaterial-encapsulated dsRNA-targeting chitin pathway-a potential efficient and eco-friendly strategy against cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 20905–20917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Yan, S.; Li, H. Construction of a nontoxic nano-pesticide and its co-application with natural predators for perfect cooperative pest management: An innovative strategy for pesticide reduction. Environ. Sci. Nano 2024, 11, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Xia, Z.; Sun, Z.; Mu, Q.; Huang, C.; Song, F.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Li, H.; et al. Perfect cooperative pest control via nano-pesticide and natural predator: High predation selectivity and negligible toxicity toward predatory stinkbug. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Active Ingredient (AI) | Nano-Formulation Type | Target Pest | Nano-Insecticide vs. Traditional Insecticide LC50/Mortality | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I: nanoscale active ingredients | ||||
| Silver (Ag) | Metallic NPs (Ag NPs) | Spilosoma obliqua | Nano: LC50 93.21 mg/L; Traditional crude leaf extract: LC50 1590.74 mg/L; Efficiency: 17.07× | [110] |
| Silica (Si) | Non-metallic NPs (nano-silica) | Callosobruchus maculatus | Nano LC50: 88.170 mg/L | [111] |
| CaB2O4 | Non-metallic NPs (sea urchin-like calcium borate microspheres CB-A) | Spodoptera littoralis | Nano CB-A: LC50 207 mg/L; Traditional microblocks: LC50 406 mg/L; Efficiency: 1.96× | [112] |
| Purslane oil | Non-metallic (nano-emulsion) | Aphis gossypii | Nano: LC50 72.74 mg/L; Traditional Emulsion: LC50 85.02 mg/L; Efficiency: 1.17× | [26] |
| Radish oil | Nano: LC50 453.91 mg/L; Traditional Emulsion: LC50 555.42 mg/L; Efficiency: 1.22× | |||
| Rosemary oil | Nano: LC50 72.45 mg/L; Traditional Emulsion: LC50 869.64 mg/L; Efficiency: 12× | |||
| Type II: nanocarrier-loaded insecticides | ||||
| Methomyl | Organic carrier (nano-chitosan) | Spodoptera littoralis | Nano: LC50 4.97 mg/L; Traditional insecticides: LC50 20.82 mg/L; Efficiency: 4.19× | [113] |
| β-cyfluthrin | Organic carrier (graphene oxide) | Ostrinia furnacalis | Nano: LC50 0.62 mg/L; Traditional insecticide: LC50 1.32 mg/L; Efficiency: 2.13× | [61] |
| Imidacloprid | Nano: LC50 2.31 mg/L; Traditional insecticide: LC50 4.23 mg/L; Efficiency: 1.83× | |||
| Permethrin | Organic carrier (SLN) | Artemia salina | Nano: LC50 3.127 mg/L; Traditional Emulsion: LC50 4.536 mg/L; Efficiency: 1.45× | [114] |
| Salvia abrotanoides extract | Hybrid carrier (Fe3O4@Carbon) | Phthorimaea operculella | Nano: LC50 355.30 mg/L; Traditional pure extract: LC50 660.02 mg/L; Efficiency: 1.86× | [115] |
| Aspect | Conventional Pesticides | Nano-Enabled Pesticides |
|---|---|---|
| Soil residue and degradation |
| |
| Aquatic pollution risk |
| |
| Impact on non-target organisms (NTOs) |
|
|
| Volatility and atmospheric pollution | ||
| Application efficiency and loss | ||
| Bioaccumulation and long-term risk |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, M.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Gao, L.; Yan, S. Nano-Enabled Insecticides for Efficient Pest Management: Definition, Classification, Synergistic Mechanism, and Safety Assessment. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131050
Wei Y, Chen J, Dong M, Yin M, Shen J, Gao L, Yan S. Nano-Enabled Insecticides for Efficient Pest Management: Definition, Classification, Synergistic Mechanism, and Safety Assessment. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(13):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131050
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Ying, Jingyi Chen, Min Dong, Meizhen Yin, Jie Shen, Le Gao, and Shuo Yan. 2025. "Nano-Enabled Insecticides for Efficient Pest Management: Definition, Classification, Synergistic Mechanism, and Safety Assessment" Nanomaterials 15, no. 13: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131050
APA StyleWei, Y., Chen, J., Dong, M., Yin, M., Shen, J., Gao, L., & Yan, S. (2025). Nano-Enabled Insecticides for Efficient Pest Management: Definition, Classification, Synergistic Mechanism, and Safety Assessment. Nanomaterials, 15(13), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15131050






