Comparative Study of Water Flow in Nanopores with Different Quartz
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models and Methods
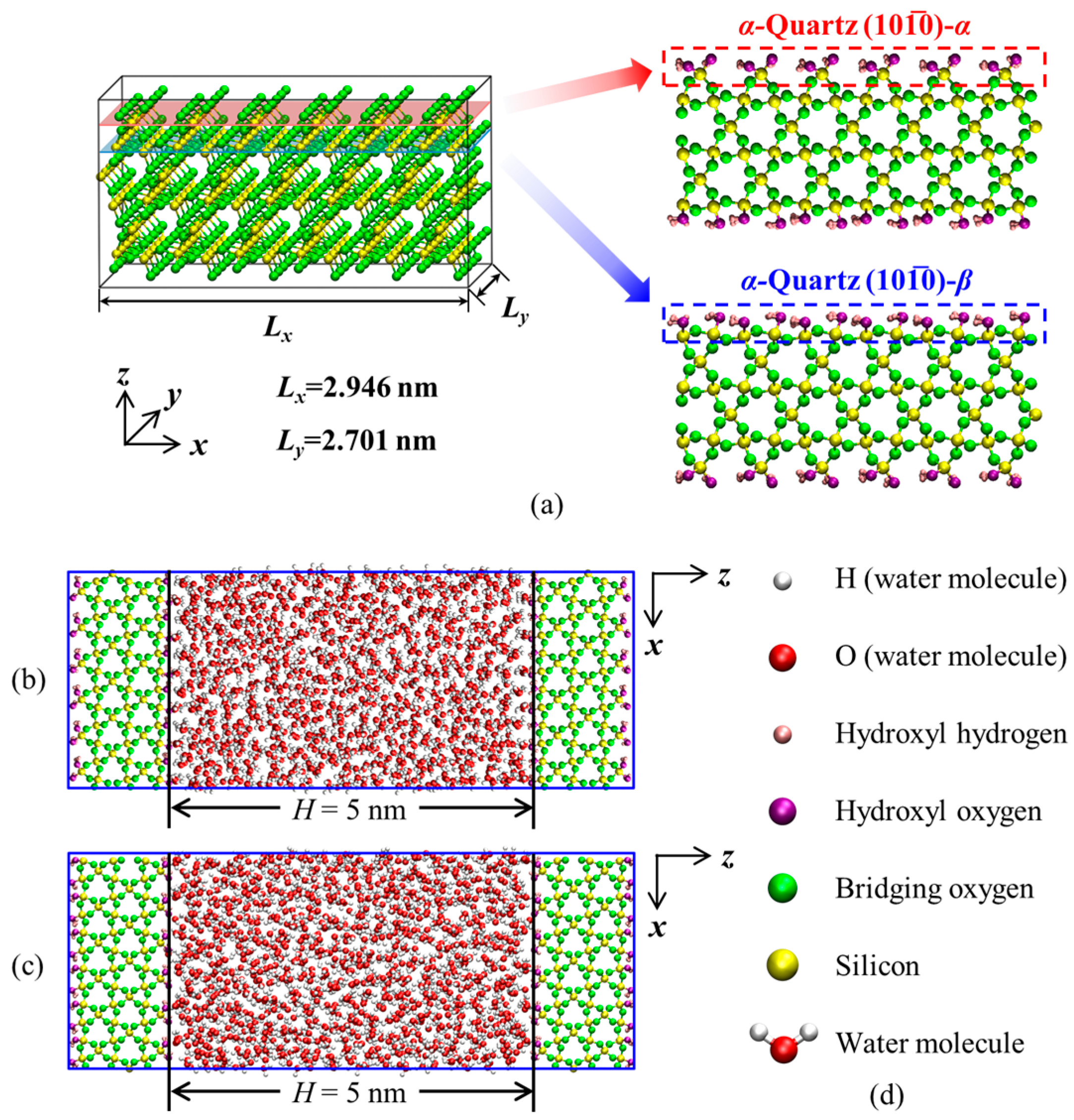
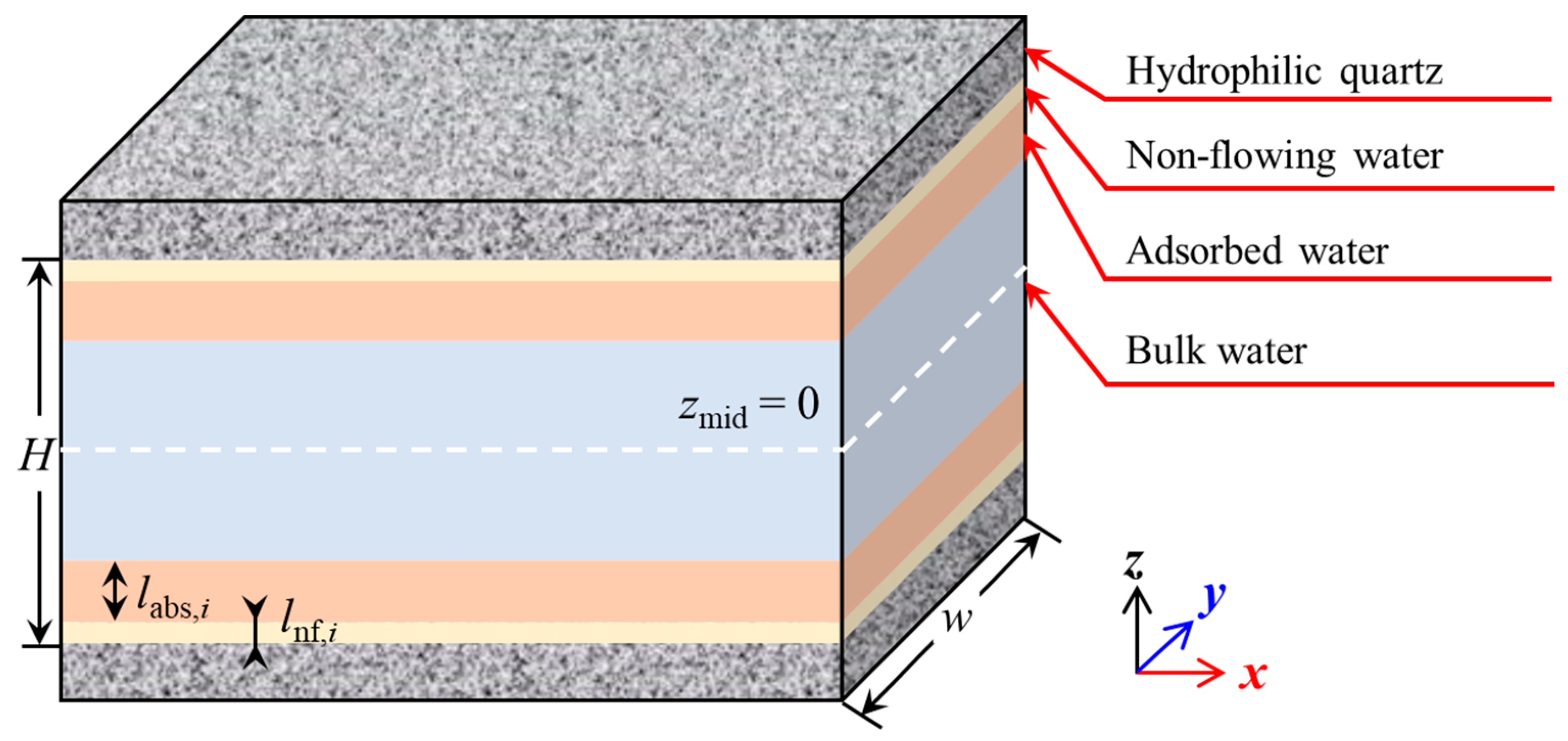
2.1. Molecular Models
2.2. Simulation Methods and Details
3. Results and Discussions
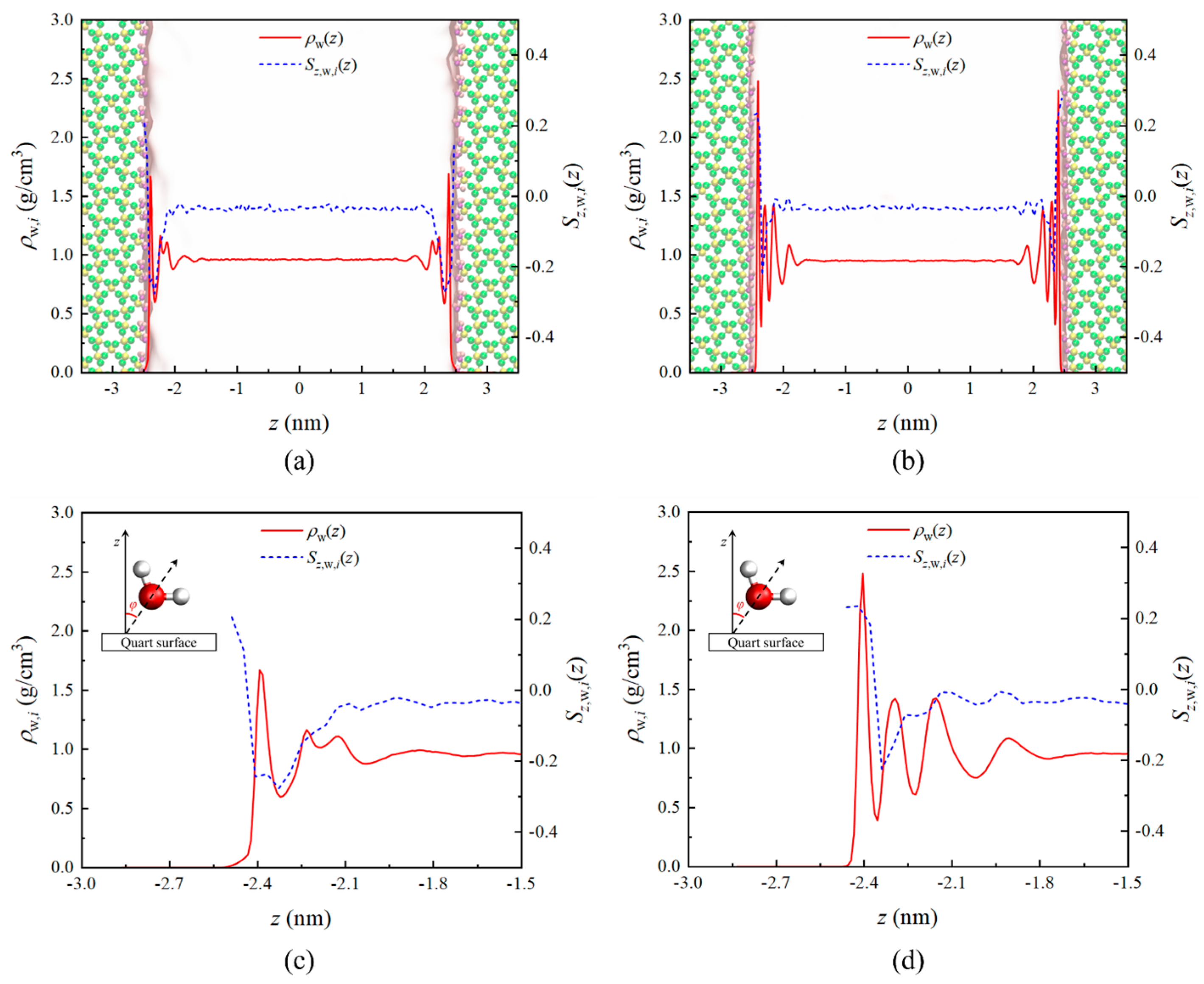
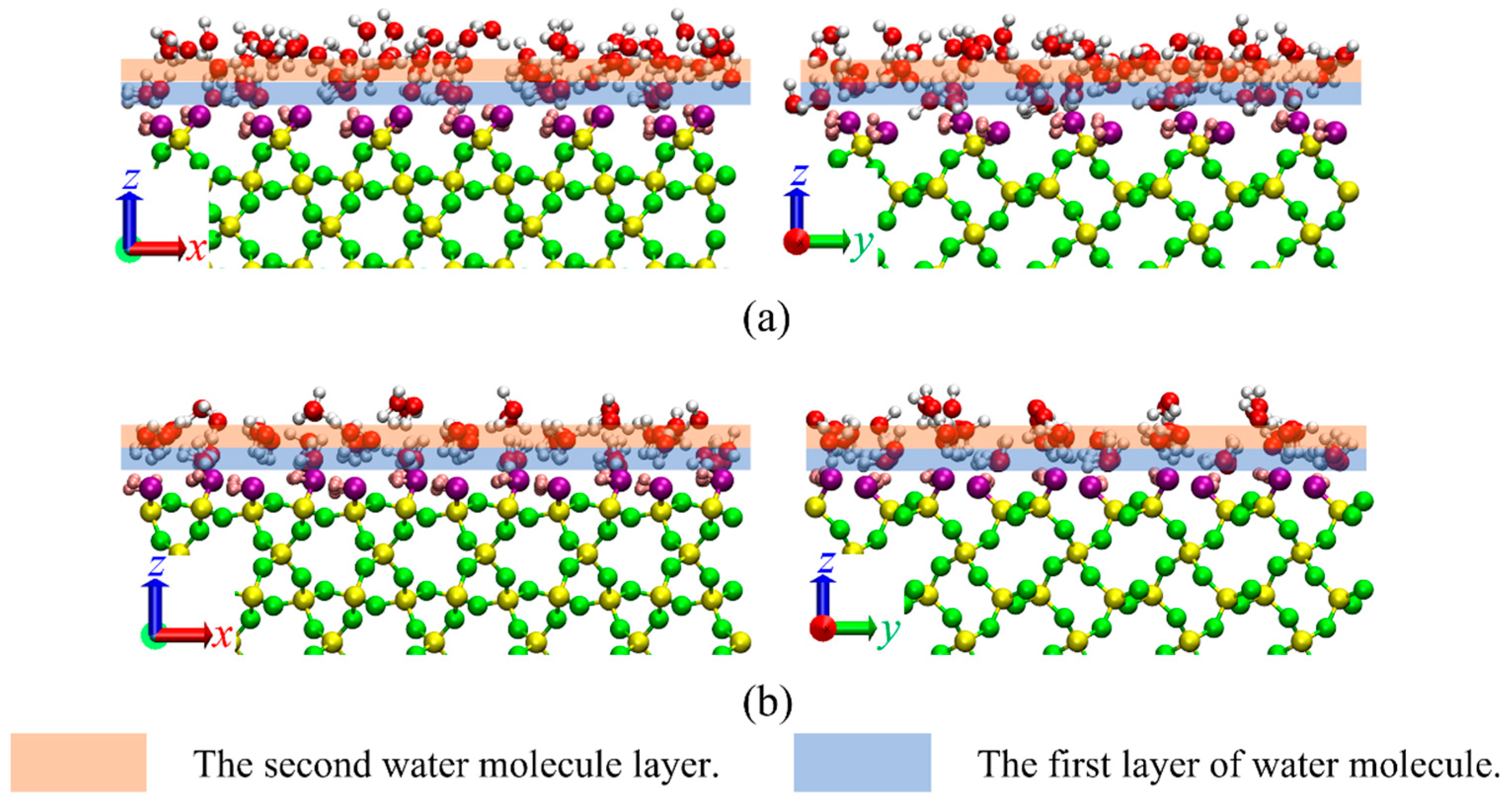
3.1. Density Profile and Orientation Parameter
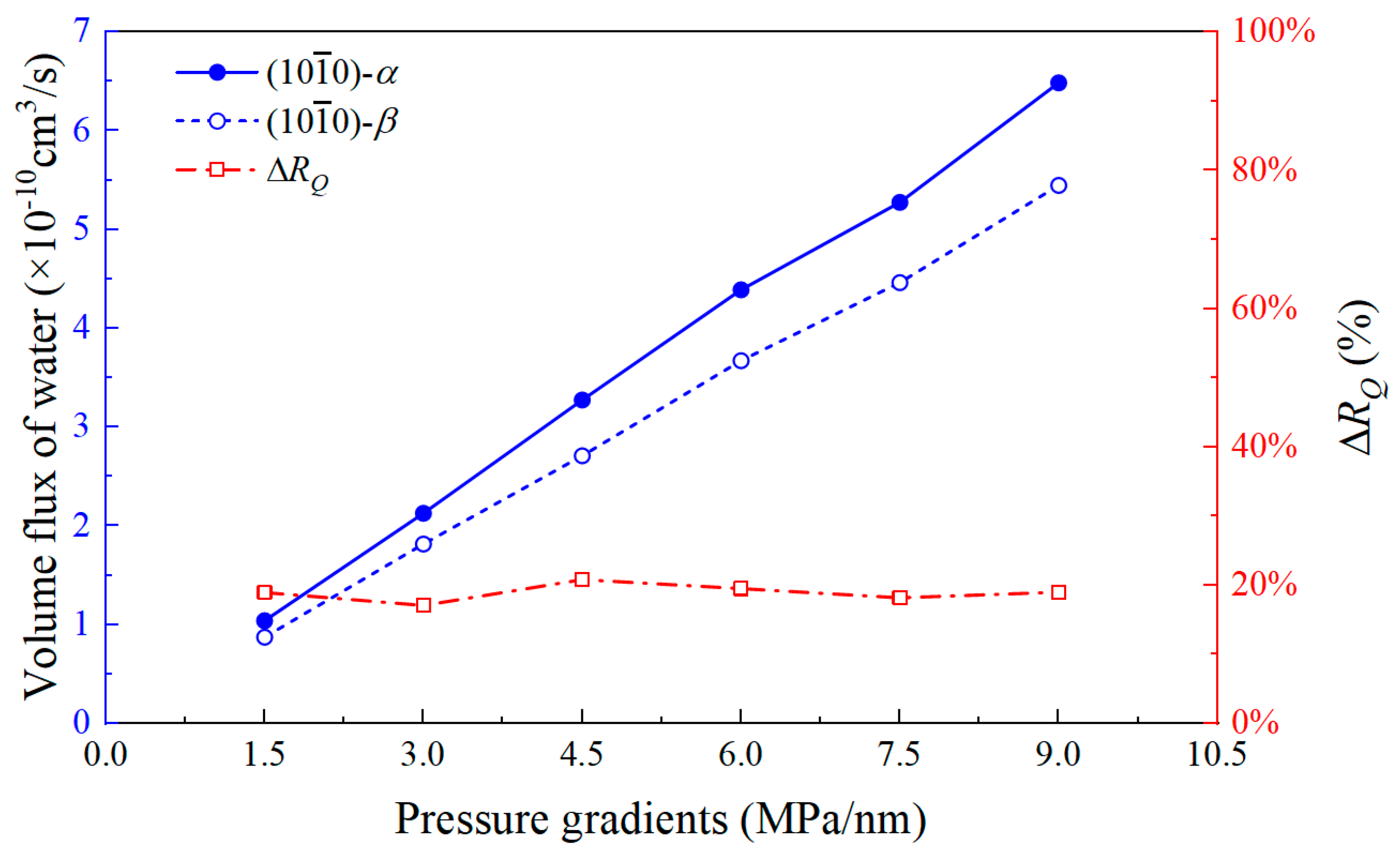
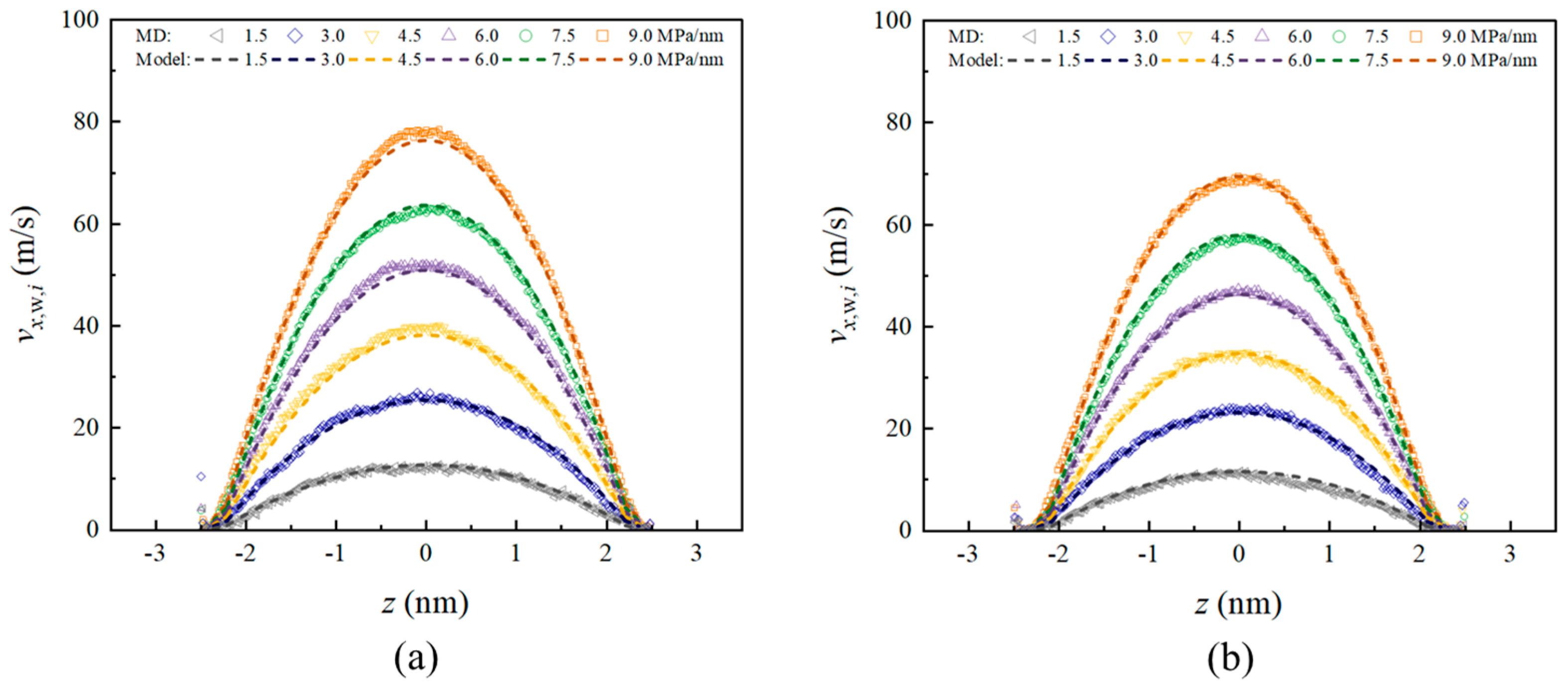
3.2. Velocity Profile and Volume Flux
3.3. Water Flow Theoretical Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salygin, V.; Guliev, I.; Chernysheva, N.; Sokolova, E.; Toropova, N.; Egorova, L. Global shale revolution: Successes, challenges, and prospects. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Wang, B.; Chen, X.; Tan, P. Reservoir stimulation for unconventional oil and gas resources: Recent advances and future perspectives. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2024, 13, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Deng, S.; Sun, Y. Recent advances on shale oil and gas exploration and development technologies. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2024, 11, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.R.; Solano, N.; Bustin, R.M.; Bustin, A.; Chalmers, G.R.; He, L.; Melnichenko, Y.B.; Radliński, A.; Blach, T.P. Pore structure characterization of North American shale gas reservoirs using USANS/SANS, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion. Fuel 2013, 103, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Song, Z.; Wang, S.; Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Xia, J. Characterizing the pore structure in the Silurian and Permian shales of the Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 61, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Xu, S.; Xing, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S. Advances and challenges in shale oil development: A critical review. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2020, 4, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Su, Y.; Wang, W. A new fractal approach for describing induced-fracture porosity/permeability/compressibility in stimulated unconventional reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 179, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Su, Y.; Zhan, S.; Meng, F.; Zhao, G. Fully coupled fluid-solid numerical simulation of stimulated reservoir volume (SRV)-fractured horizontal well with multi-porosity media in tight oil reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 174, 757–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fan, D.; Sheng, G.; Chen, Z.; Su, Y. A review of analytical and semi-analytical fluid flow models for ultra-tight hydrocarbon reservoirs. Fuel 2019, 256, 115737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S. Vapor-liquid equilibrium and criticality of CO2 and n-heptane in shale organic pores by the Monte Carlo simulation. Fuel 2021, 299, 120909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riewchotisakul, S.; Akkutlu, I.Y. Adsorption-enhanced transport of hydrocarbons in organic nanopores. SPE J. 2016, 21, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnyakov, A.; Neimark, A.V. Studies of Liquid-Vapor equilibria, criticality, and spinodal transitions in nanopores by the gauge cell Monte Carlo simulation method. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 7009–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Bao, J.; Ning, S.; Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Effect of surface roughness on methane adsorption in shale organic nanopores from the perspective of molecular simulations. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Ning, S.; Bao, J.; Jing, W.; Zhang, M.; Cui, J.; Duan, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Comparative study on adsorption behaviors of CH4/CO2 and CH4/H2S in quartz nanopores from molecular perspectives: Implication for EGR in shale reservoirs. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 712, 136419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Zhao, S. A review of experimental nanofluidic studies on shale fluid phase and transport behaviors. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 86, 103745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojabaei, B.; Johns, R.T.; Chu, L. Effect of capillary pressure on phase behavior in tight rocks and shales. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2013, 16, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Li, W.; Jin, Z. Slip length of methane flow under shale reservoir conditions: Effect of pore size and pressure. Fuel 2020, 259, 116237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Bao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Su, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z. A comparative study of shale oil transport behavior in graphene and kerogen nanopores with various roughness via molecular dynamics simulations. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, P.; Toghraie, D.; Karimipour, A.; Hajian, M. Molecular dynamics simulation of fluid flow passing through a nanochannel: Effects of geometric shape of roughnesses. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 275, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Su, Y.; Jin, Z.; Wang, W.; Cai, M.; Li, L.; Hao, Y. Molecular insight into the boundary conditions of water flow in clay nanopores. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 311, 113292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jiang, H.; Liu, X.; Hu, X. Observation and analysis of water transport through graphene oxide interlamination. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, K.; Shi, J.; Zhang, T.; Feng, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Mao, S.; Li, X. Effect of pore geometry on nanoconfined water transport behavior. AIChE J. 2019, 65, e16613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M. A universal model of water flow through nanopores in unconventional reservoirs: Relationships between slip, wettability and viscosity. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 26–28 September 2016; p. D021S027R009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Fan, J.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, H. Multiscale gas transport behavior in heterogeneous shale matrix consisting of organic and inorganic nanopores. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 75, 103139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hatcherian, J.; Hackley, P.C.; Pomerantz, A.E. Nanoscale geochemical and geomechanical characterization of organic matter in shale. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, H.; Su, K.; Shu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, T. Dissolution of marine shales and its influence on reservoir properties in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 102, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.J.; Bustin, R.M. The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ostadhassan, M. Microstructural and geomechanical analysis of Bakken shale at nanoscale. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 153, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Rai, C.; Sondergeld, C.; Devegowda, D. Rock typing in eagle ford, barnett, and woodford formations. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2018, 21, 654–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ostadhassan, M.; Zhou, J.; Gentzis, T.; Rezaee, R. Nanoscale pore structure characterization of the Bakken shale in the USA. Fuel 2017, 209, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Rao, S.; Liang, Y.; Lu, H. Crystal face dependent wettability of α-quartz: Elucidation by time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry techniques combined with molecular dynamics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, Z.; Rao, S.; Zheng, H.; Huang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Lu, H. Mechanism for the effects of surface chemical composition and crystal face on the wettability of α-quartz surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 633, 157559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Firoozabadi, A. Water Film Structure and Wettability of Different Quartz Surfaces: Hydrogen Bonding Across Various Cutting Planes. Langmuir 2024, 40, 4635–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Dong, X. Wettability effect on nanoconfined water flow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, 3358–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.A.; Papavassiliou, D.V.; Lee, L.L.; Striolo, A. Liquid water can slip on a hydrophilic surface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2011, 108, 16170–16175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsharpoor, A.; Javadpour, F. Liquid slip flow in a network of shale noncircular nanopores. Fuel 2016, 180, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Wang, W.; Sheng, G.; Li, H.; Zafar, A. Enhanced water flow and apparent viscosity model considering wettability and shape effects. Fuel 2019, 253, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Wang, W.; Sheng, G. Hydrodynamic resistance model of oil flow in nanopores coupling oil–wall molecular interactions and the pore-throat structures effect. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 209, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Sun, S.; Qiao, R. Structure, thermodynamics, and dynamics of thin brine films in oil–brine–rock systems. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10341–10353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, M.L.; Nagy, K.L.; Fenter, P.; Sturchio, N.C. Structures of quartz (100)-and (101)-water interfaces determined by x-ray reflectivity and atomic force microscopy of natural growth surfaces. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 3037–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, A.; Wesolowski, D.J.; Cummings, P.T. Investigating the quartz (1010)/water interface using classical and ab initio molecular dynamics. Langmuir 2011, 27, 8700–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, A.; Fenter, P.; Kubicki, J.D.; Wesolowski, D.J.; Cummings, P.T. Simulations of the quartz (1011)/water interface: A comparison of classical force fields, ab initio molecular dynamics, and X-ray reflectivity experiments. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 2076–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, B. Unveiling the hydroxyl-dependent viscosity of water in graphene oxide nanochannels via molecular dynamics simulations. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 778, 138808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Javadpour, F.; Feng, Q. Molecular dynamics simulations of oil transport through inorganic nanopores in shale. Fuel 2016, 171, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhan, S.; Wang, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, H. Molecular dynamics simulations of two-phase flow of n-alkanes with water in quartz nanopores. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.B.; Walsh, T.R. Facet selectivity of binding on quartz surfaces: Free energy calculations of amino-acid analogue adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 2933–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koretsky, C.M.; Sverjensky, D.A.; Sahai, N. A model of surface site types on oxide and silicate minerals based on crystal chemistry; implications for site types and densities, multi-site adsorption, surface infrared spectroscopy, and dissolution kinetics. Am. J. Sci. 1998, 298, 349–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Striolo, A.; Cole, D.R. Propane simulated in silica pores: Adsorption isotherms, molecular structure, and mobility. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 121, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cygan, R.T.; Liang, J.-J.; Kalinichev, A.G. Molecular models of hydroxide, oxyhydroxide, and clay phases and the development of a general force field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neek-Amal, M.; Peeters, F.M.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Geim, A.K. Commensurability effects in viscosity of nanoconfined water. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3685–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Yin, X.; Qiao, R. Interfacial CO2-mediated nanoscale oil transport: From impediment to enhancement. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 23057–23063. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.A.; McGaughey, A.J. Reassessing fast water transport through carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsi, M. Comparative assessment of the ELBA coarse-grained model for water. Mol. Phys. 2014, 112, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Su, Y.; Jin, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, L. Effect of water film on oil flow in quartz nanopores from molecular perspectives. Fuel 2020, 262, 116560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yao, J.; Kou, J. Mixture composition effect on hydrocarbon–water transport in shale organic nanochannels. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 4291–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Qi, C.; Zhao, X.; Teng, G.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhan, K.; Shi, J. Nanoscale two-phase flow of methane and water in shale inorganic matrix. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 26671–26679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, K.; Sedlmeier, F.; Joly, L.; Netz, R.R.; Bocquet, L. Ultralow liquid/solid friction in carbon nanotubes: Comprehensive theory for alcohols, alkanes, OMCTS, and water. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14261–14272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Su, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Hao, Y.; Li, L. Study of liquid-liquid two-phase flow in hydrophilic nanochannels by molecular simulations and theoretical modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucaba-Piętal, A.; Walenta, Z.; Peradzyński, Z. Molecular dynamics computer simulation of water flows in nanochannels. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2009, 57, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lemmon, E.W.; McLinden, M.O.; Friend, D.G. Thermophysical Properties of Fluid Systems by in NIST Chemistry WebBook; NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69; Linstrom, P.J., Mallard, W.G., Eds.; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA; Volume 20899. Available online: http://webbook.nist.gov (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Jin, Z.; Firoozabadi, A. Methane and carbon dioxide adsorption in clay-like slit pores by Monte Carlo simulations. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2013, 360, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botan, A.; Rotenberg, B.; Marry, V.; Turq, P.; Noetinger, B. Hydrodynamics in clay nanopores. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 16109–16115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B. Determining the shear viscosity of model liquids from molecular dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Dong, X.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Jia, X. Manipulating the flow of nanoconfined water by temperature stimulation. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 8568–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, Y.; Wang, W.; Lu, M.; Sheng, G. Apparent permeability for liquid transport in nanopores of shale reservoirs: Coupling flow enhancement and near wall flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 115, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Sheng, G.; Zhan, S. Relative permeability model of oil-water flow in nanoporous media considering multi-mechanisms. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 183, 106361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Feng, D.; Miao, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z. An analytical model for relative permeability in water-wet nanoporous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 174, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, P.; Bao, J.; Zhan, S.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Lan, B.; Liu, Z.
Comparative Study of Water Flow in Nanopores with Different Quartz
Zhou P, Bao J, Zhan S, Wang X, Li S, Lan B, Liu Z.
Comparative Study of Water Flow in Nanopores with Different Quartz
Zhou, Peng, Junyao Bao, Shiyuan Zhan, Xingjian Wang, Shaopeng Li, Baofeng Lan, and Zhanbo Liu.
2025. "Comparative Study of Water Flow in Nanopores with Different Quartz
Zhou, P., Bao, J., Zhan, S., Wang, X., Li, S., Lan, B., & Liu, Z.
(2025). Comparative Study of Water Flow in Nanopores with Different Quartz








