Effects of Nano-SiO2 and Nano-CaCO3 on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Cement-Based Soil Stabilizer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Stabilizer
2.2. Nano-Modifiers
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Test Procedures
3. Results and Discussions
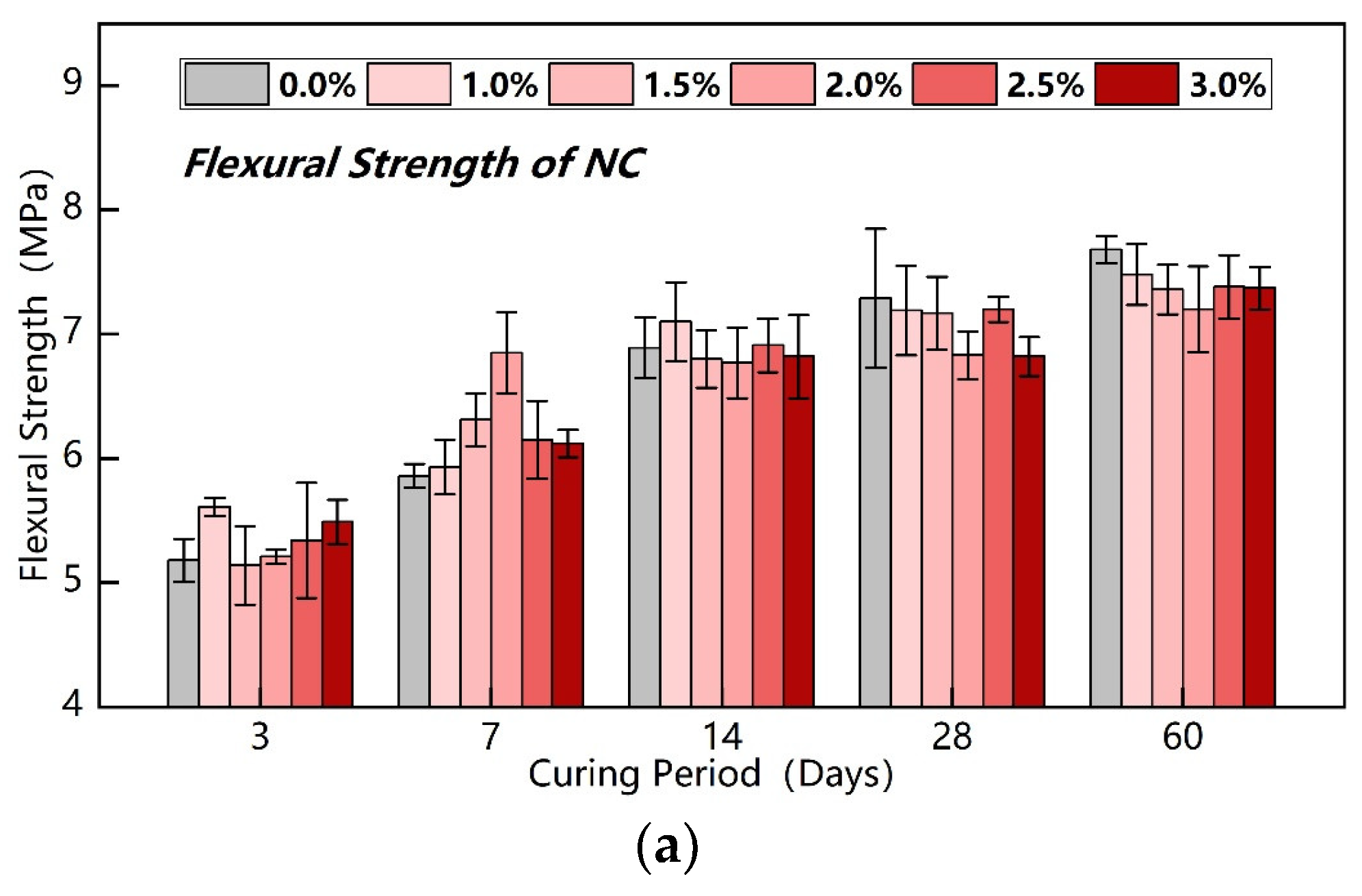
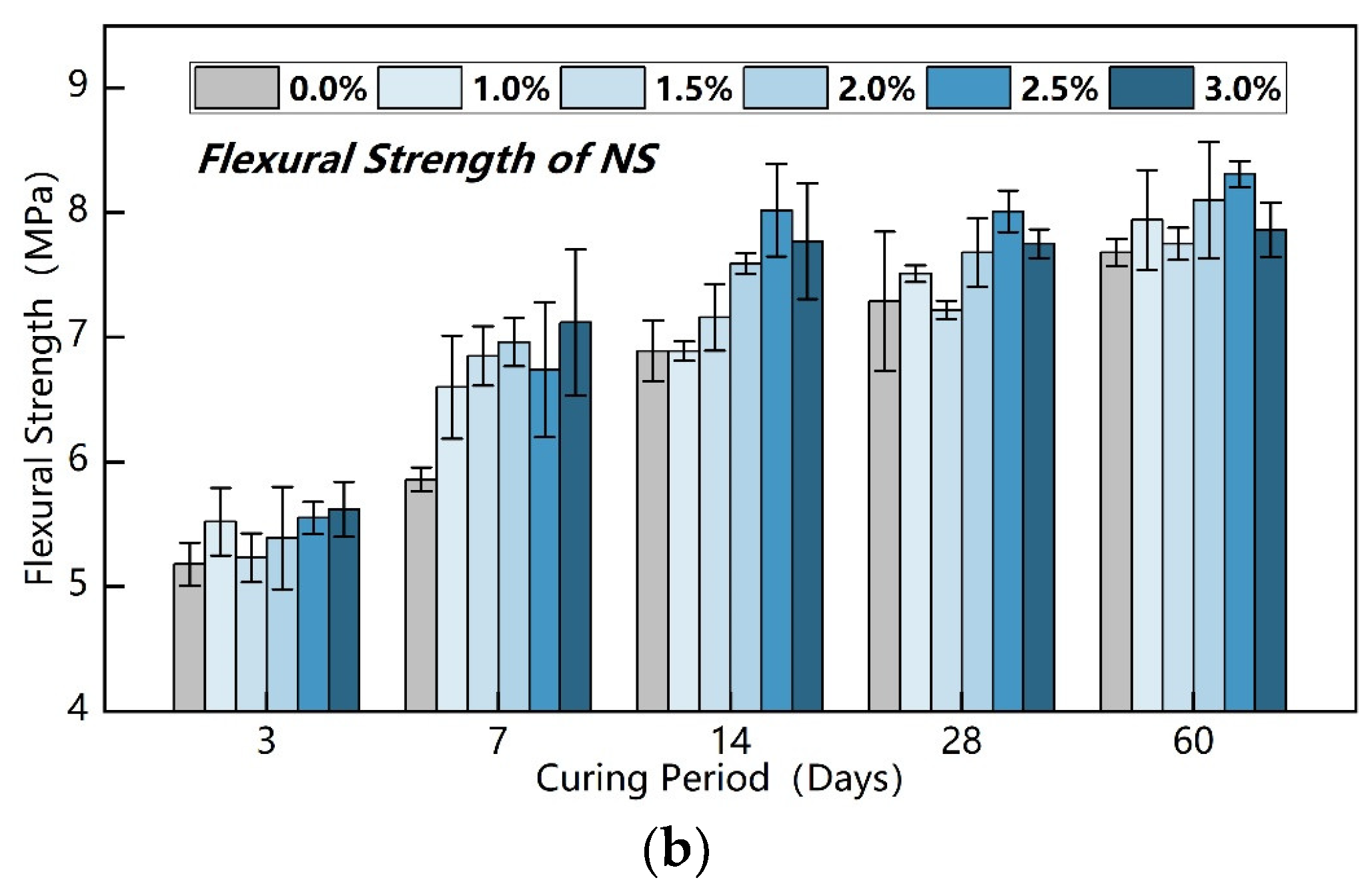
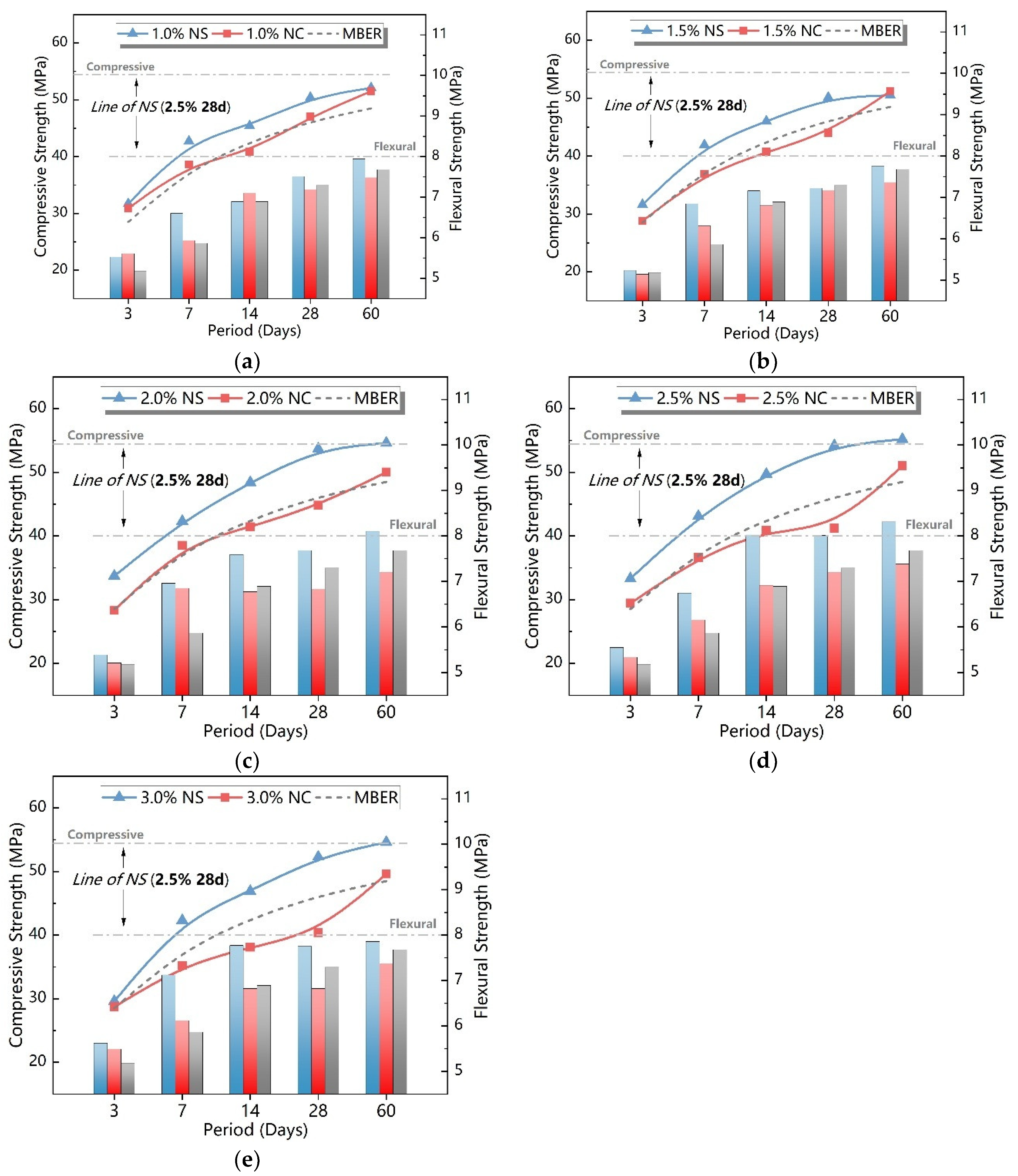
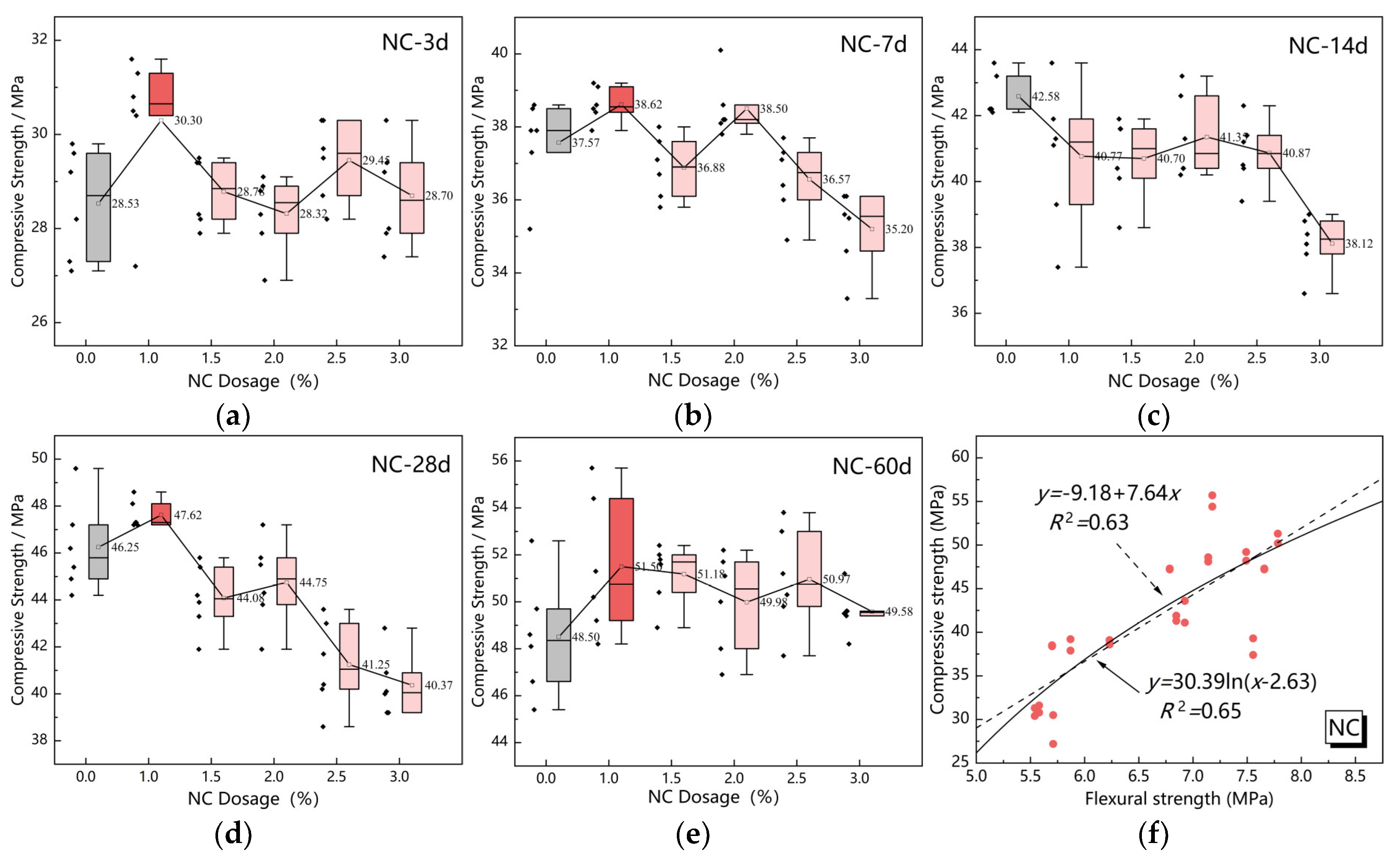
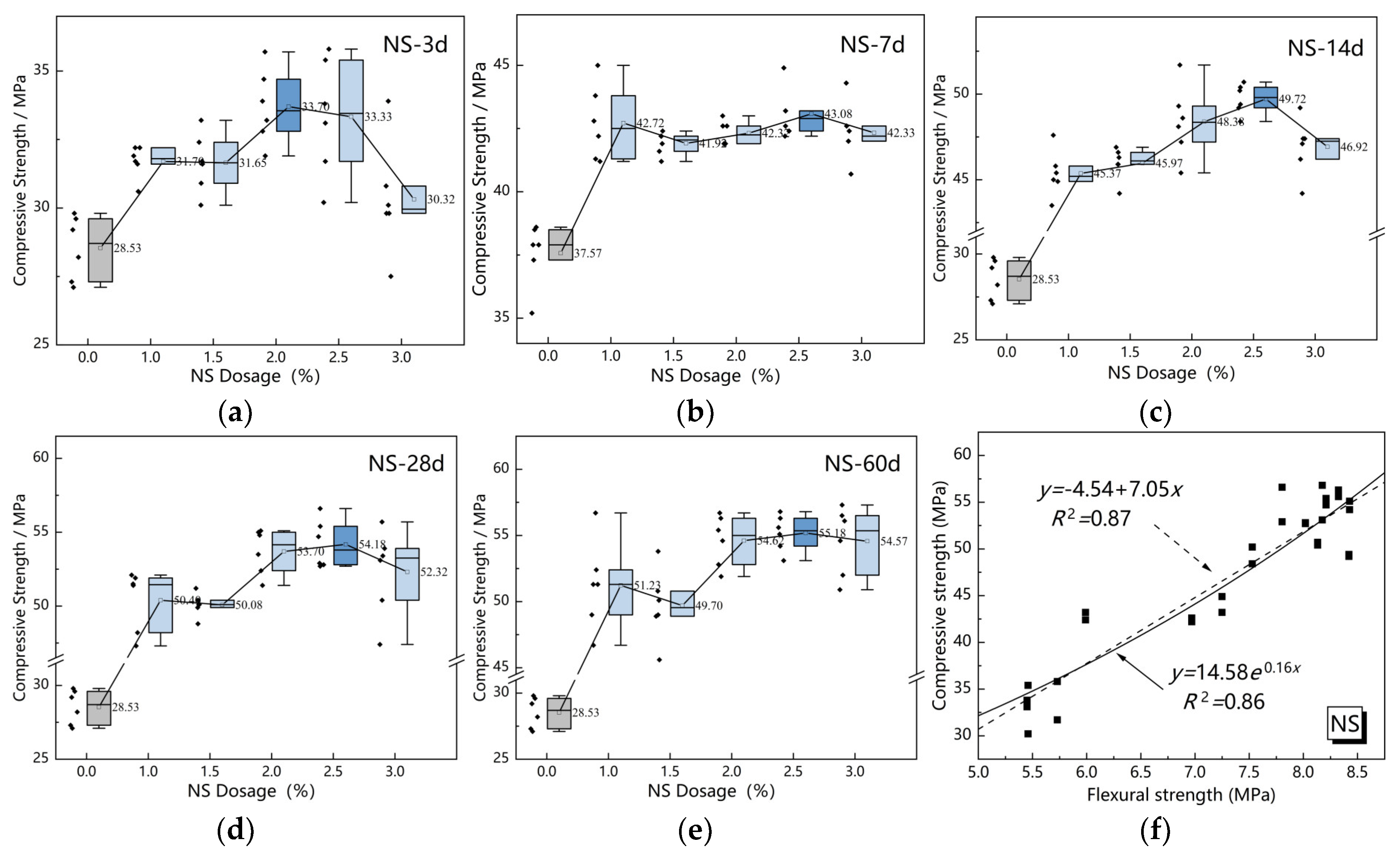
3.1. Strength of Different Cement-Based Soil Stabilizers
3.2. Correlation Analysis of Compressive and Flexural Strengths
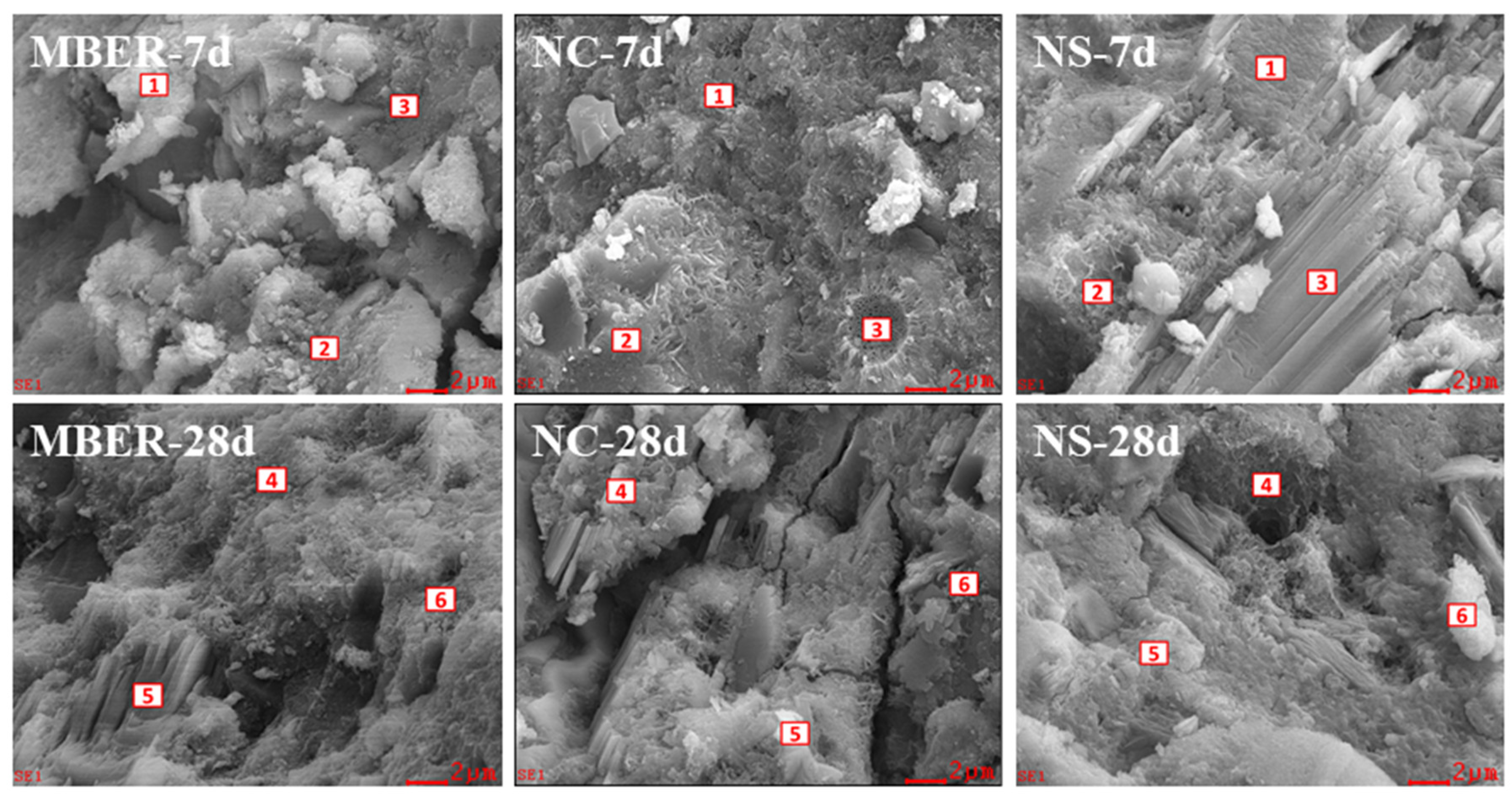
3.3. Microscopic Test Results and Analysis
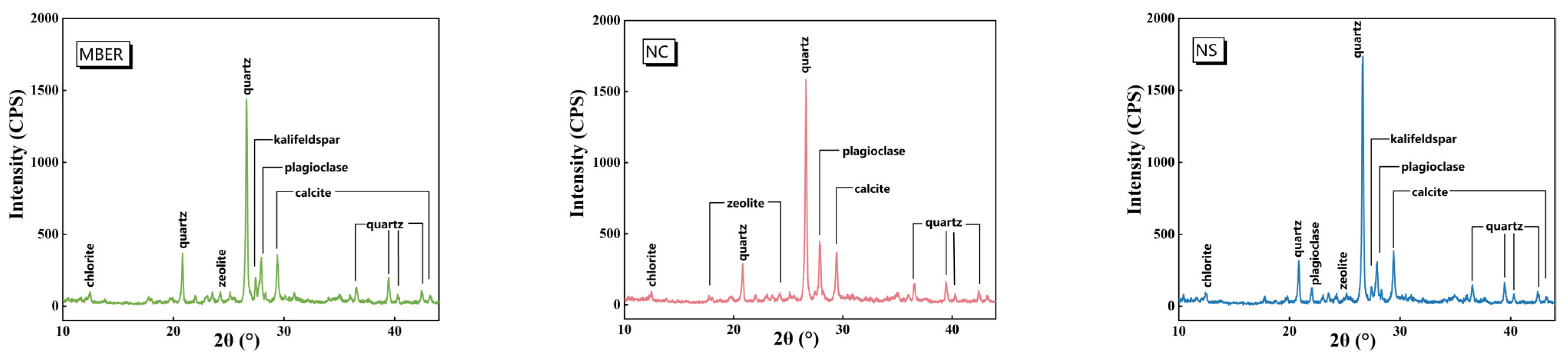
3.3.1. XRD Pattern Analysis
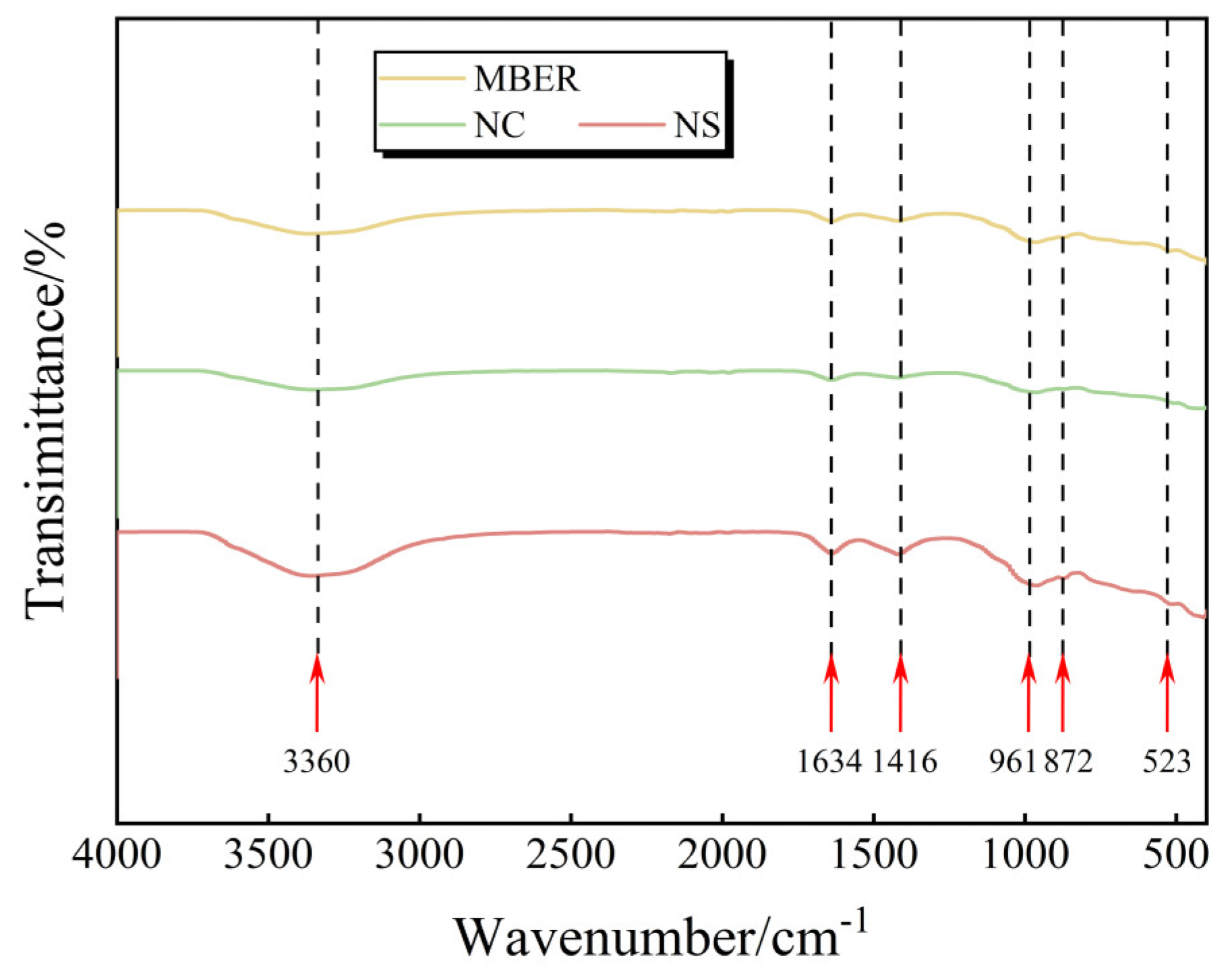
3.3.2. FT-IR Results and Analysis
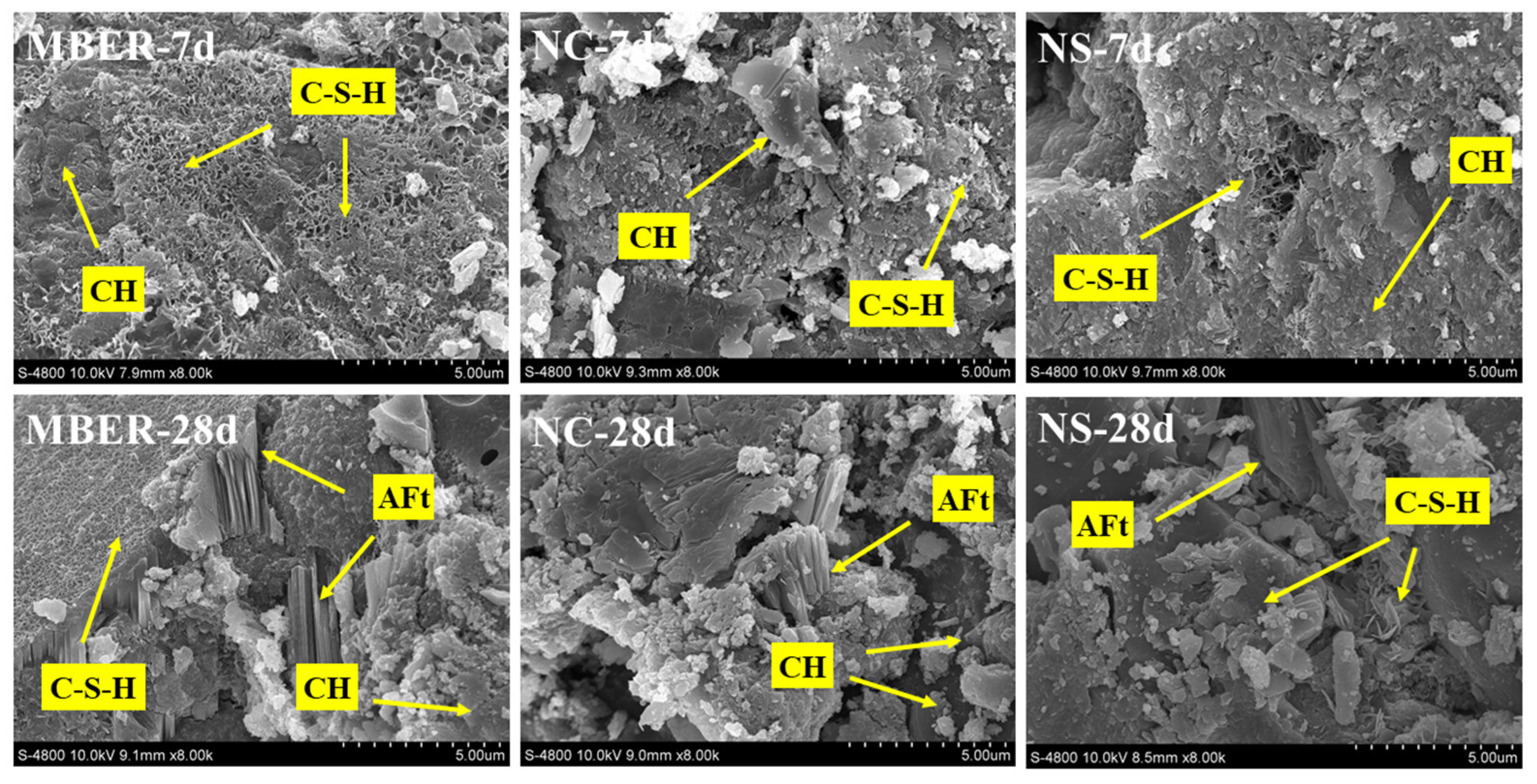
3.3.3. Microstructure Analysis
3.4. Discussions
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Mortar specimen tests under identical conditions demonstrate that NS-modified stabilizers with 1–3% dosage generally outperform NC-modified counterparts across all curing ages. This confirms NS as the superior nanomaterial for enhancing MBER-based stabilizers within this dosage range.
- (2)
- The strength enhancement of NS-modified stabilizers exhibits a parabolic trend within 1–3% dosage, peaking at 2.5% addition with strength enhancement exceeding 15%. This optimal dosage effectively improves the mechanical performance of MBER stabilizers.
- (3)
- The high reactivity and ultrafine particle characteristics of NS induce nano-activated hydration effects and strong pozzolanic activity, accelerating the hydration process. NS effectively refines calcium hydroxide (CH) crystals detrimental to strength development while promoting multi-morphology calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel formation. These gels interlock with hexagonal prismatic ettringite (AFt) crystals to establish robust three-dimensional cementitious networks, thereby optimizing interfacial microstructure and enhancing age-dependent mechanical properties.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, J.; Liang, B.; Han, B.Y.; Suo, Z.; Wang, J.-N.; Yu, H.-C. Review of soil stabilization technology in Chinese road engineering. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2023, 23, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lin, H.; Zong, T.; Xu, X.; Li, M.; Bian, X. Strength characteristics of composite early-strength soil stabilizer solidified sludge. Rock Soil Mech. 2023, 44 (Suppl. S1), 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.H.; Gao, J.E.; Wu, P.T.; Lou, Z. Physicochemical interactions in cement-based soil stabilizer solidified soils. Rock Soil Mech. 2010, 31, 3741–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.H.; Wu, P.T.; Gao, J.E.; Lou, Z.K. Microstructural characteristics of cement-based soil stabilizer solidified soils. J. Build. Mater. 2010, 13, 669–674. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.C. Development of Nano-Stabilizer Materials and Study on Soil Stabilization Performance. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Research Center of Soil and Water Conservation and Ecological Environment, Ministry of Education, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, G.; O’Kelly, B.C.; Sujatha, E.R. Geotechnical investigation of low-plasticity organic soil treated with nano-calcium carbonate. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, G.; Eskisar, T. The geomechanical properties of soils treated with nanosilica particles. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Ren, Z.; Yu, X. Experimental study of nanometer magnesium oxide-modified clay. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 2015, 52, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, N.; Farjad, A.; Sepehri, S. The use of nanoclay particles for stabilization of dispersive clayey soils. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Niu, J.; Liang, S.; Feng, D.; Luo, Q. Solidification of Nansha soft clay using cement-based composite curing agents. Adv. Cem. Res. 2020, 32, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.W.; Ju, P.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H.; Gao, J.; Sun, S. Optimization of loess stabilizer and curing liquid formulations for stabilized soils. J. Water Resour. Archit. Eng. 2024, 22, 171–179+213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Wu, W.; Feng, T. Cement-SG curing agent for solidification of mucky soils. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Gao, J.E.; Fan, H.H.; Li, X.; Gao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Long, S.; Xue, L. Experimental study on mechanical properties of nano-stabilizer reconstructed loess. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 131–137+143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Han, W.F.; Chen, W.W. Comparative study on mechanical properties between novel polymer stabilizer and cement-stabilized loess. Rock Soil Mech. 2004, 11, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, J.L. Experimental study on factors influencing unconfined compressive strength of TG stabilizer-lime soil under freeze-thaw conditions. J. Chin. Foreign Highw. 2016, 36, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Gao, J.E.; Li, X.H.; Lou, X.; Sun, S. Experimental study on effect of salt content on performance of MBER soil stabilizer solidified soil. Water Resour. Power 2015, 33, 133–135+139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zha, F. Strength and micro-structure evolution of compacted soils modified by admixtures of cement and metakaolin. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 127, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yang, G.; Li, C.; Guo, M.; Wang, T.; Jiang, L. Use of alkali-activated slag as an environment-friendly agent for high-performance stabilized soil. Materials 2023, 16, 4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumey, C. Plenty of room, plenty of history. Nat. Nanotech 2009, 4, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.A.; Mishra, A.; Benson, D.J. Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 427–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L. Experimental studies on nanomaterials for soil improvement: A review. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.P.; Mandal, J.N. Strength evaluation of soil stabilized with nano silica-cement mixes as road construction material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeri, S.M.; Valishzadeh, A. Evaluation of using different nanomaterials to stabilize the collapsible loessial soil. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 19, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.E.; Sun, S.L.; Wu, P.T. A New Type of Soil Stabilizer: China Patent No. 200410073273.5. P. Northwest Sci. -Technol. Univ. Agric. For. 2005, 6, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Asgari, H.; Ramezanianpour, A.; Butt, H.J. Effect of water and nano-silica solution on the early stages cement hydration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 129, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhilash P., P.; Nayak, D.K.; Sangoju, B.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, V. Effect of nano-silica in concrete; a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.G.; Huang, Z.H.; Zhu, J.; Kwan, A.K.H.; Chen, H.Y. Synergistic effects of micro-silica and nano-silica on strength and microstructure of mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, G.; Sujatha, E.R. A review on the choice of nano-silica as soil stabilizer. Silicon 2022, 14, 6477–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoey, F.; Zaid, O.; Martínez-García, R.; Alsharari, F.; Ahmed, M.; Arbili, M.M. Impact of Nano-silica on the hydration, strength, durability, and microstructural properties of concrete: A state-of-the-art review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Bai, Z.; Wu, J.; Long, H.; Deng, H.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, X. Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 2078–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutschera, M.; Breiner, T.; Wiese, H.; Leitl, M. Nano-modification of building materials for sustainable construction. In Nanotechnology in Construction 3: Proceedings of the NICOM3; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Du, X.; Wei, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Shah, S.P. Influence of nano-silica agglomeration on microstructure and properties of the hardened cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Qiang, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Long, S.; Gao, Z.; Fan, H. Mechanical Characterization and Constitutive Modeling of Nano-Stabilized Soil under Uniaxial Compression. Materials 2023, 16, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.P.; Hou, P.; Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S. Nano-modification of cementitious material: Toward a stronger and durable concrete. J. Sustain. Cem. -Based Mater. 2016, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, S.; Sun, S.; Han, B.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Nano-scale behavior and nano-modification of cement and concrete materials. In Advanced Research on Nanotechnology for Civil Engineering Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 28–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Unluer, C.; Yang, E.H. Low CO2 reactive magnesia cements and their applications via nano-modification. In Recent Advances in Nano-Tailored Multi-Functional Cementitious Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022; pp. 407–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Zuo, J.; He, Z. A review of recycled aggregate concrete modified by nanosilica and graphene oxide: Materials, performances and mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, A.; Wang, X. Effect of nano-CaCO3 on properties of cement paste. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z. Effect of nano-CaCO3 slurry on the mechanical properties and micro-structure of concrete with and without fly ash. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 117, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.A.S.; Rasteiro, M.G. Nanotechnology applied to chemical soil stabilization. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, P.; Taha, M.R.; Alsharef, J.; Ramalingam, K. Influence of nanolime and curing period on unconfined compressive strength of soil. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2017, 2017, 8307493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand, H.; Balachowski, L.; Parviz, R. Nano soil improvement technique using cement. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, M.R.; Taha, O.M.E. Influence of nano-material on the expansive and shrinkage soil behavior. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choobbasti, A.J.; Kutanaei, S.S. Microstructure characteristics of cement-stabilized sandy soil using nanosilica. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2017, 9, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
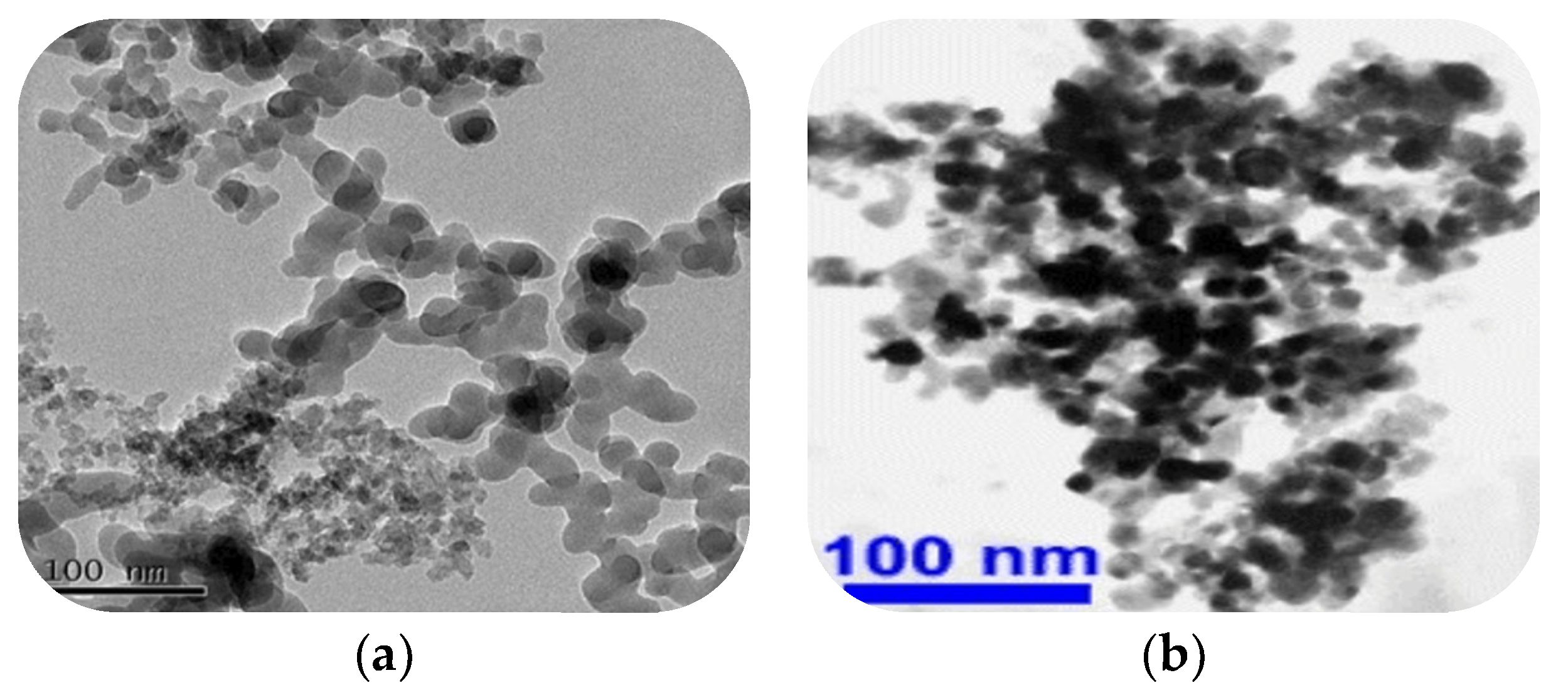
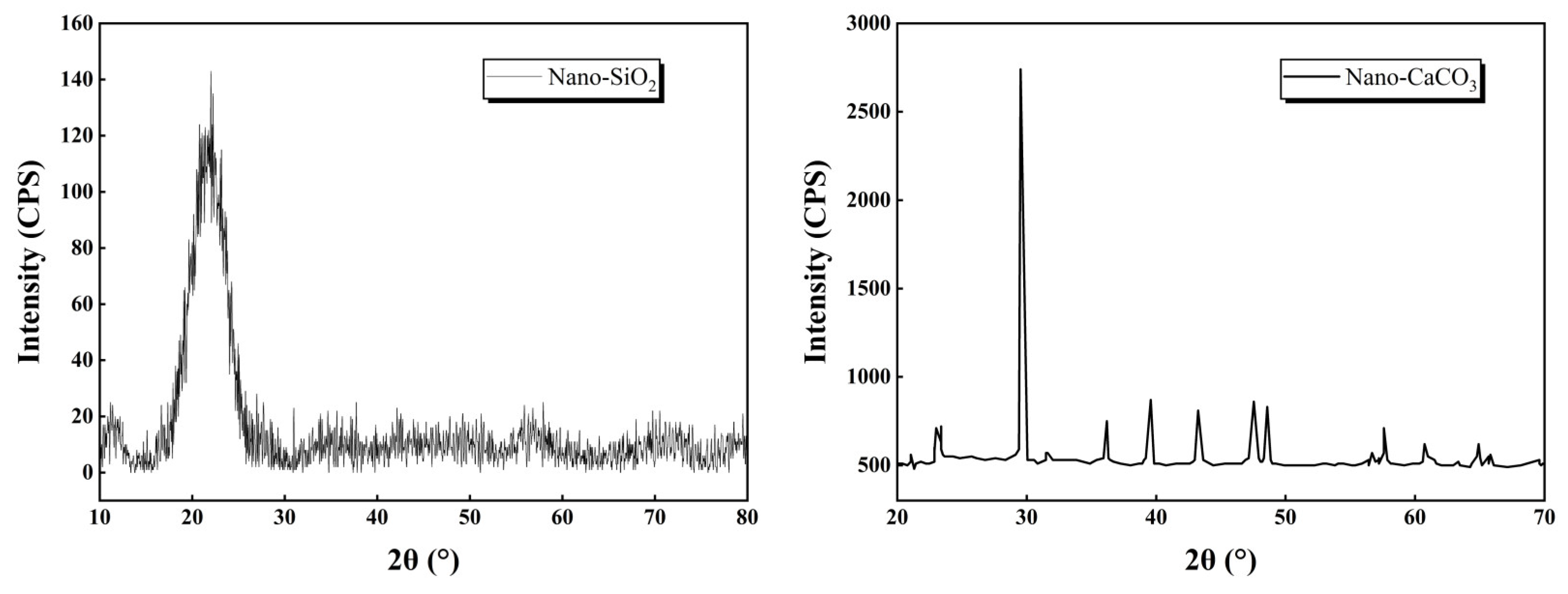



| Ingredients | Cement Clinker | Fly Ash | Gypsum | Active Agent | Soil Stabilizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content % | 85 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 100 |
| SO3 content | 2.01 | 0.26 | 1.40 | 0 | 3.67 |
| Physical Property | Purity (%) | APS (nm) | SSA (m2/g) | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | True Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano-SiO2 | 99.9% | 30 | 600 | 0.08 | 2.2~2.6 |
| Nano-CaCO3 | 99.9% | 20 | 50 | 0.30 | 5.7~5.8 |
| Sample | Point | Metering Mode | C | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | K | Ca | Fe | Mineral Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBER | 1 | Wt% | 4.58 | 41.33 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 2.75 | 18.75 | 0.68 | 1.26 | 27.32 | 1.81 | CH |
| 2 | At% | 8.35 | 56.58 | 0.71 | 0.7 | 2.23 | 14.62 | 0.46 | 0.71 | 14.93 | 0.71 | CH | |
| 3 | Wt% | 6.3 | 47.11 | 1.02 | 0.58 | 2.67 | 12.72 | 0.52 | 1.25 | 26.47 | 1.36 | C-S-H | |
| 4 | At% | 10.88 | 41.06 | 0.92 | 0.49 | 2.05 | 29.4 | 0.34 | 0.66 | 13.69 | 0.51 | C-S-H | |
| 5 | Wt% | 5.65 | 41.75 | 0.39 | 0.4 | 2.13 | 28.23 | 0.33 | 0.76 | 19.39 | 0.97 | AFt | |
| 6 | At% | 9.95 | 55.19 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 1.67 | 21.26 | 0.22 | 0.41 | 10.23 | 0.37 | C-S-H | |
| NC | 1 | Wt% | 4.35 | 41.43 | 1.15 | 1.00 | 4.17 | 10.95 | 1.09 | 1.05 | 32.12 | 2.69 | C-S-H |
| 2 | At% | 8.05 | 57.58 | 1.11 | 0.92 | 3.43 | 8.67 | 0.76 | 0.6 | 17.82 | 1.07 | CH | |
| 3 | Wt% | 4.33 | 41.48 | 0.98 | 1.11 | 4.20 | 11.22 | 1.14 | 0.96 | 32.15 | 2.43 | C-S-H | |
| 4 | At% | 8.01 | 57.58 | 0.94 | 1.02 | 3.46 | 8.87 | 0.79 | 0.55 | 17.82 | 0.97 | C-S-H | |
| 5 | Wt% | 4.17 | 41.30 | 1.07 | 0.86 | 4.27 | 11.09 | 1.13 | 1.17 | 32.46 | 2.49 | AFt | |
| 6 | At% | 7.74 | 57.58 | 1.04 | 0.79 | 3.53 | 8.81 | 0.78 | 0.67 | 18.07 | 0.99 | CH | |
| NS | 1 | Wt% | 4.74 | 38.78 | 1.13 | 0.7 | 3.46 | 13.32 | 0.78 | 1.64 | 33.4 | 2.05 | CH |
| 2 | At% | 8.9 | 54.65 | 1.11 | 0.65 | 2.89 | 10.7 | 0.55 | 0.95 | 18.79 | 0.83 | C-S-H | |
| 3 | Wt% | 4.75 | 38.93 | 1.11 | 0.62 | 3.38 | 13.27 | 0.68 | 1.58 | 33.54 | 2.15 | AFt | |
| 4 | At% | 8.91 | 54.85 | 1.09 | 0.57 | 2.82 | 10.65 | 0.48 | 0.91 | 18.86 | 0.87 | C-S-H | |
| 5 | Wt% | 4.34 | 37.99 | 0.99 | 0.63 | 3.55 | 13.11 | 0.88 | 1.71 | 33.36 | 1.99 | AFt | |
| 6 | At% | 8.29 | 54.51 | 0.99 | 0.6 | 3.02 | 10.72 | 0.63 | 1 | 19.11 | 0.82 | C-S-H |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, B.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Gao, J.; Du, Y.; Ji, Y.; Gao, Z. Effects of Nano-SiO2 and Nano-CaCO3 on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Cement-Based Soil Stabilizer. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110785
Lei B, Zhang X, Fan H, Gao J, Du Y, Ji Y, Gao Z. Effects of Nano-SiO2 and Nano-CaCO3 on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Cement-Based Soil Stabilizer. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(11):785. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110785
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Baofeng, Xingchen Zhang, Henghui Fan, Jianen Gao, Yichun Du, Yafei Ji, and Zhe Gao. 2025. "Effects of Nano-SiO2 and Nano-CaCO3 on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Cement-Based Soil Stabilizer" Nanomaterials 15, no. 11: 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110785
APA StyleLei, B., Zhang, X., Fan, H., Gao, J., Du, Y., Ji, Y., & Gao, Z. (2025). Effects of Nano-SiO2 and Nano-CaCO3 on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Cement-Based Soil Stabilizer. Nanomaterials, 15(11), 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110785






