Calcium Ion Sensors with Unrivaled Stability and Selectivity Using a Bilayer Approach with Ionically Imprinted Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
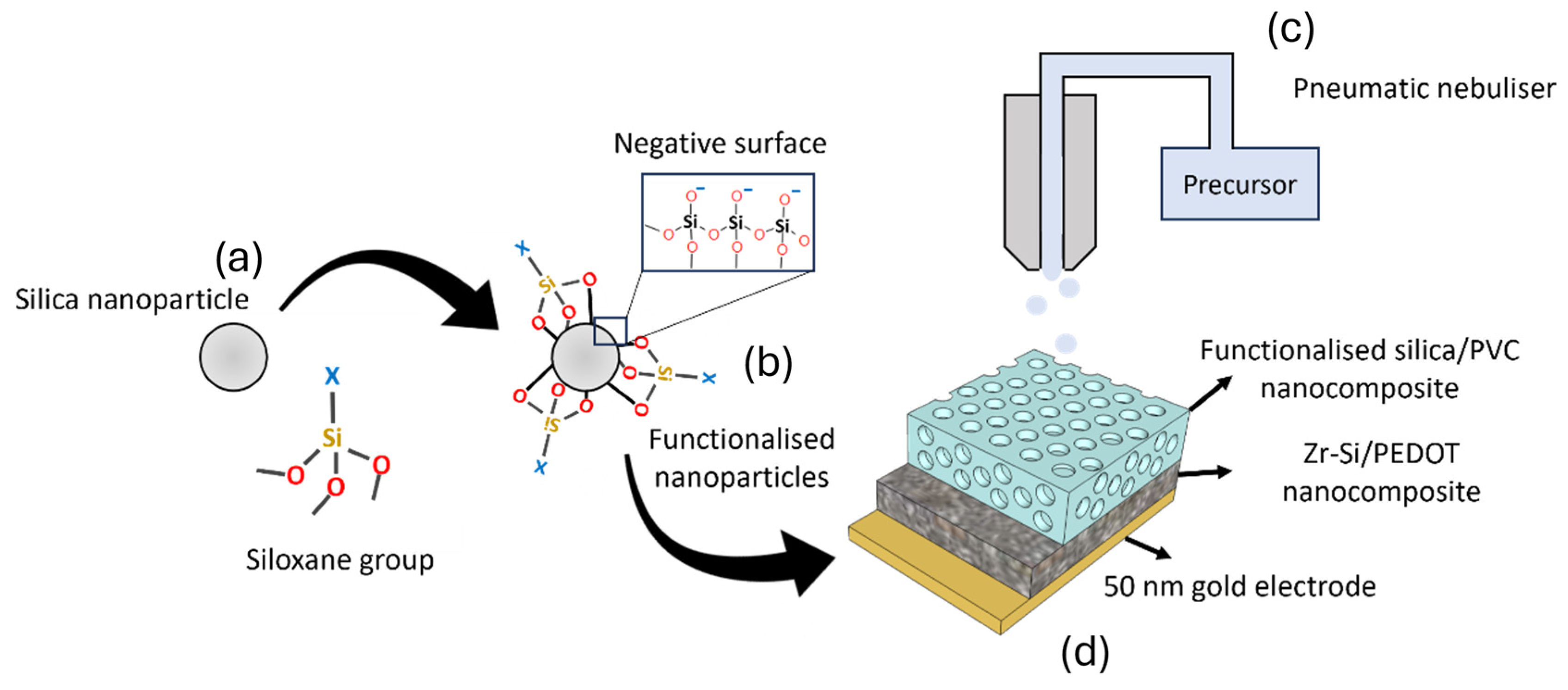
2.2. Functionalization of Silica Nanoparticles
2.3. Synthesis of Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Nanoparticles
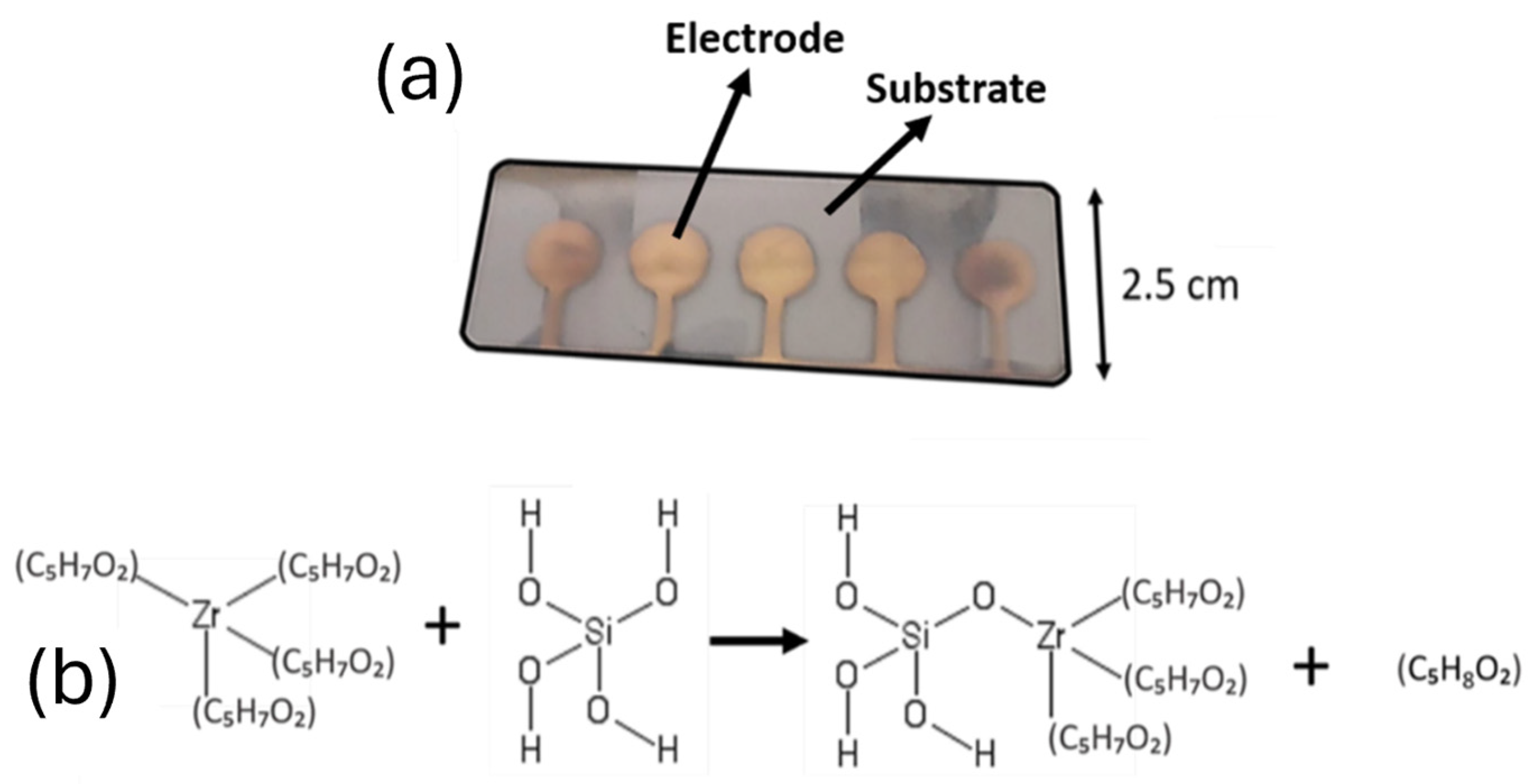
2.4. Synthesis of Nanoporous Zirconium Silicate ZrSiOx Nanoparticles
2.5. Device Fabrication
2.6. Device Configuration
2.7. Electrochemical Characterization of Films
2.8. Quartz Microbalance Characterisation
2.9. Density Functional Theory Simulation of Materials
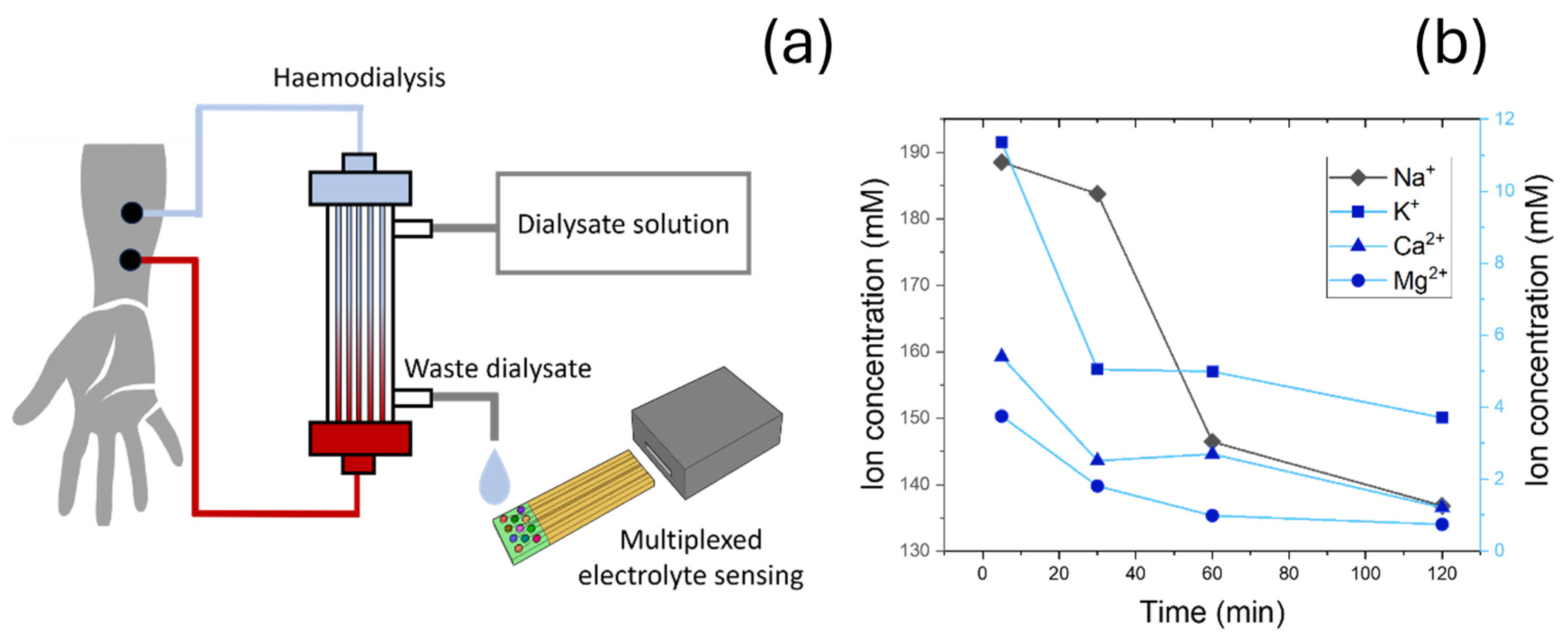
2.10. Development of Electrolyte Sensors for Dialysate Sample Characterisation
2.11. Dialysate Collection and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
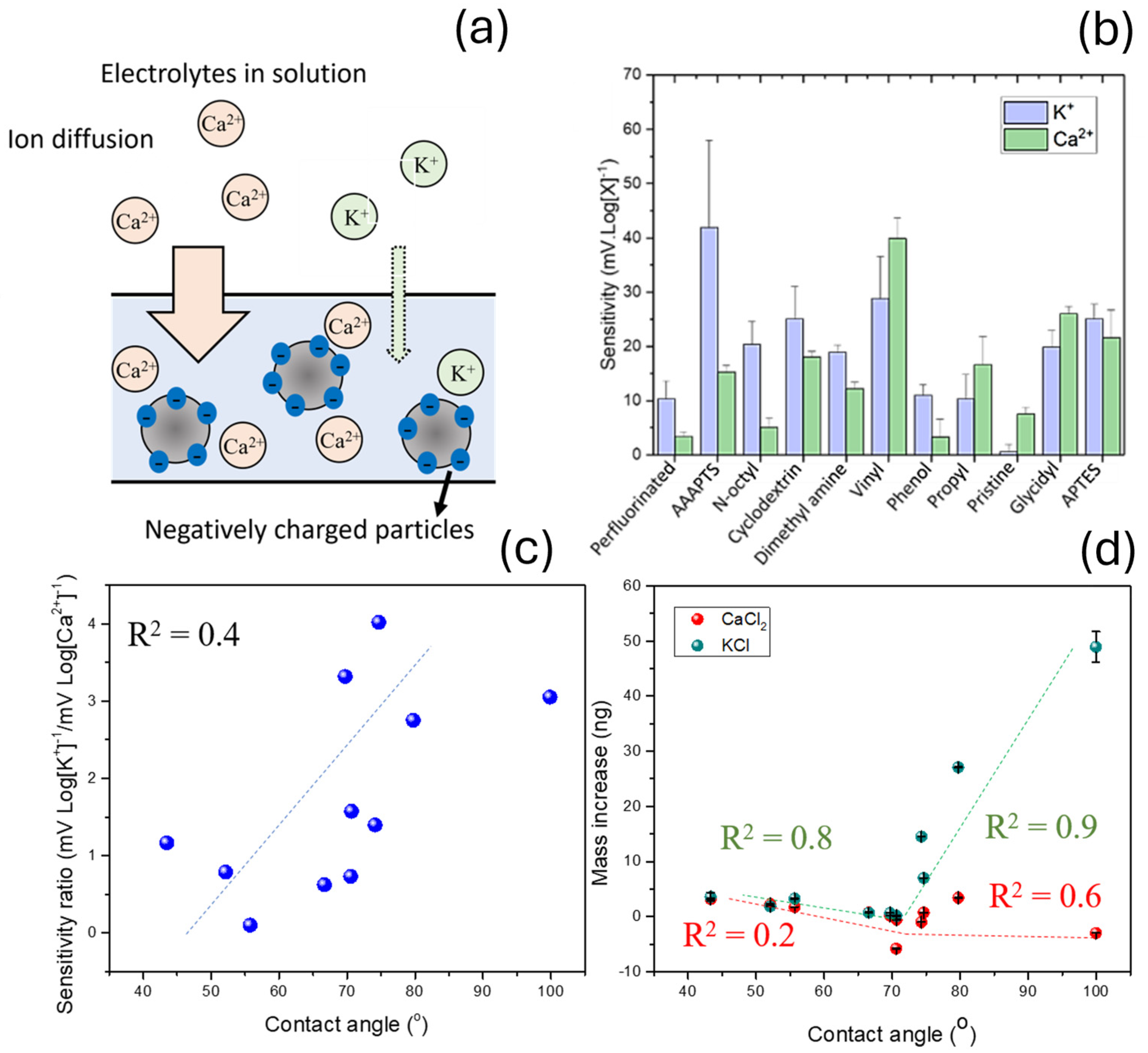
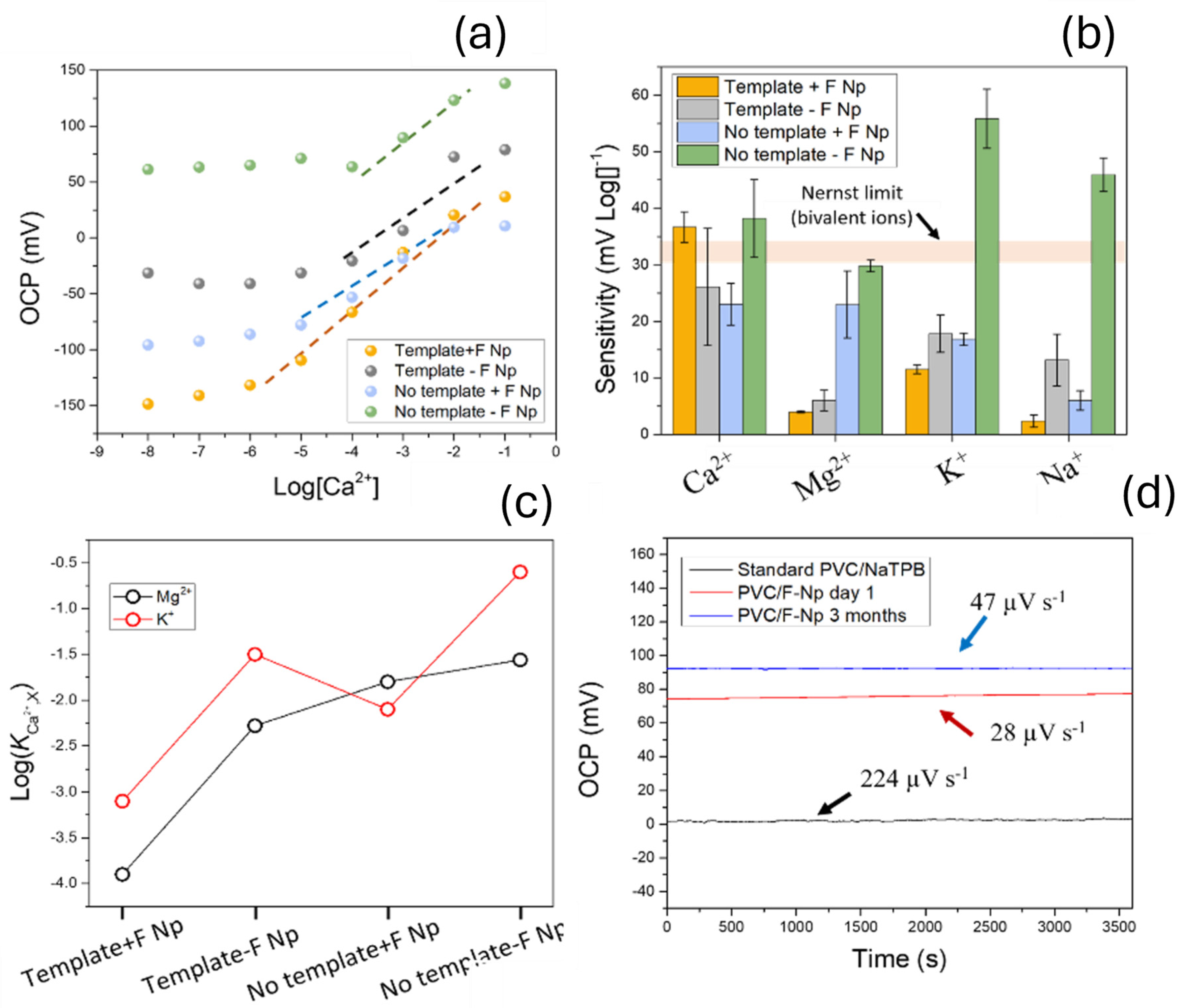
3.1. Study of the Sensitivity and Selectivity of the Ion Sensors
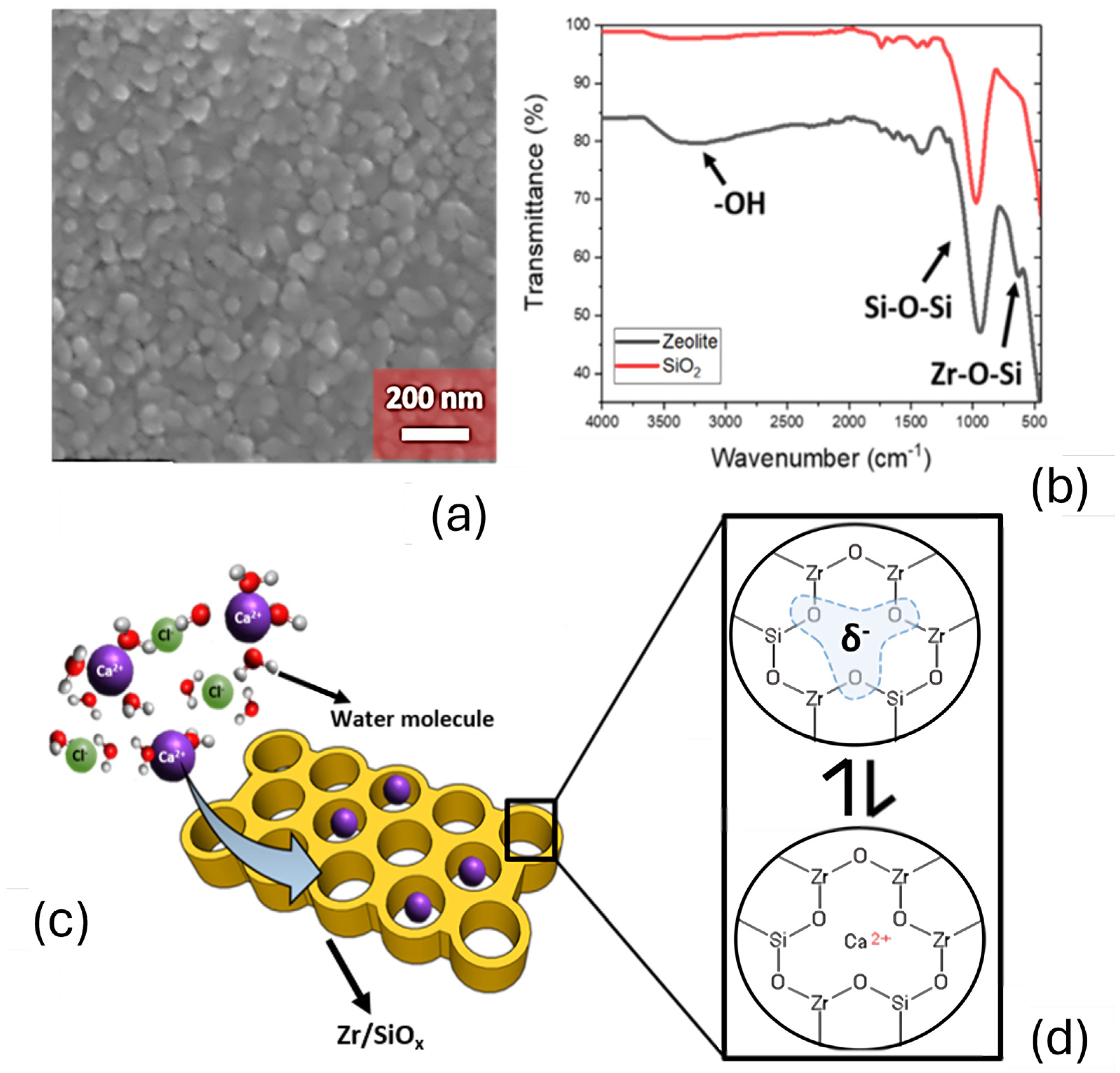
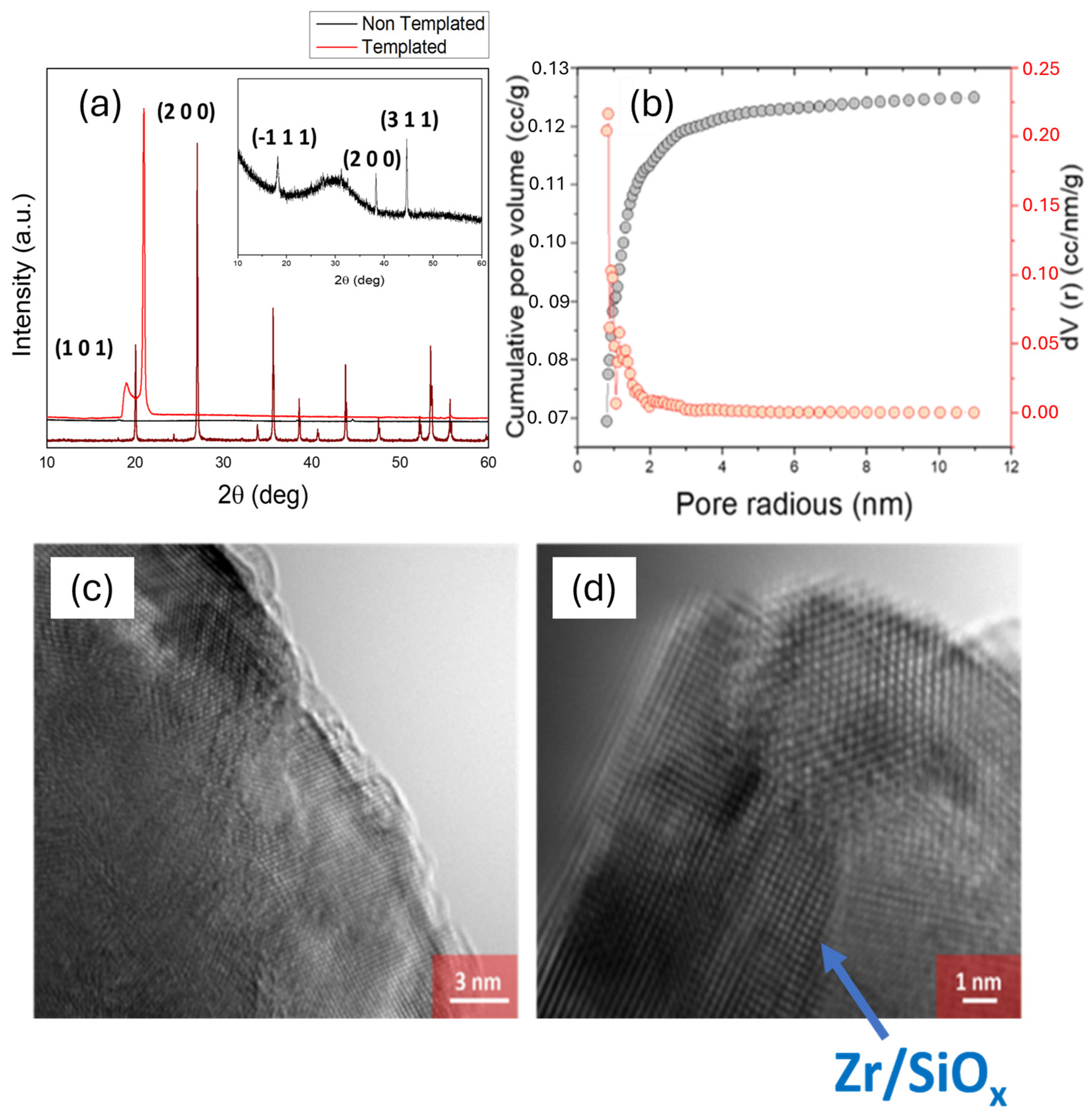
3.2. ZrSiOx Particle Characterization
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization of the Ion Sensing Devices
3.4. Clinical Testing in Dialysate Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reid, I.R.; Birstow, S.M.; Bolland, M.J. Calcium and Cardiovascular Disease. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 32, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leurs, L.J.; Schouten, L.J.; Mons, M.N.; Goldbohm, R.A.; van den Brandt, P.A. Relationship between tap water hardness, magnesium, and calcium concentration and mortality due to is-chemic heart disease or stroke in The Netherlands. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, P. Potential health impacts of hard water. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 866–875. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, A.; Chao, S.-J.; Lin, W.-T. Effects of Leaching Behavior of Calcium Ions on Compression and Durability of Cement-Based Materials with Mineral Admixtures. Materials 2013, 6, 1851–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.J.; Broadley, M.R. Calcium in Plants. Ann. Bot. 2003, 92, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.; New, A.; Gavalas, V.; Bachas, L.G. Polymeric plasticizer extends the lifetime of PVC-membrane ion-selective electrodes. Analyst 2014, 139, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morf, W.; Simon, W. Estimation of alkali and alkaline earth ion selectivity of electrically neutral carrier-antibiotics and model compounds. Helv. Chim. Acta 1971, 54, 2683–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zheng, W.; Cao, A.-M.; Mao, L. In Vivo Measurement of Calcium Ion with Solid-State Ion-Selective Electrode by Using Shelled Hollow Carbon Nanospheres as a Transducing Layer. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4421–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attiyat, A.S.; Christian, G.D.; Hallman, J.L.; Bartsch, R.A. A comparative study of the effect of o-nitrophenyl octyl ether and o-nitrophenyl pentyl ether as plasticizers on the response and selectivity of carrier-based liquid membrane ion-selective electrodes. Talanta 1988, 35, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurina, J.; López-Aviles, E.; Le Moal, A.; Hernández-Cassou, S. Determination of calcium and total hardness in natural waters using a potentiometric sensor array. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 464, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.M.; Paeng, K.-J.; Badr, I.H.A.; Hume, D.; Lynn, B.C.; Johnson, R.D.; Bachas, L.G. Correlating the potentiometric selectivity of cyclosporin-based electrodes with binding patterns obtained from electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Analyst 2017, 142, 3241–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühlmann, P.; Umezawa, Y.; Rondinini, S.; Vertova, A.; Pigliucci, A.; Bertesago, L. Lifetime of Ion-Selective Electrodes Based on Charged Ionophores. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girija, A.R. 12-Medical Applications of Polymer/Functionalized Nanoparticle Systems. In Polymer Composites with Functionalized Nanoparticles; Pielichowski, K., Majka, T.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 381–404. [Google Scholar]
- Arvand, M.; Moghimi, M.; Bagherinia, M.A. Zeolite-Modified Sol-Gel Electrode as an Electrochemical Sensor for Potentiometric Determination of Cesium Ions in Water Samples. Anal. Lett. 2009, 42, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavros, F.; Yang, A.; Leon, A.; Nuttall, M.; Rasmussen, H.S. Characterization of Structure and Function of ZS-9, a K+ Selective Ion Trap. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, B.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y. Mechanism Exploration of Ion Transport in Nanocomposite Cation Exchange Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13491–13499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbar, Y.; Hammache, Z.E.; Bensaadi, S.; Soukeur, R.; Amara, M.; Van der Bruggen, B. Effect of functionalized silica nanoparticles on sulfonated polyethersulfone ion exchange membrane for removal of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solutions. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 32, 100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Gonzalez, A.; Choy, K.L. Highly selective and robust nanocomposite-based sensors for potassium ions detection. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 23, 101008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhondup, T.; Qian, Q. Acid-Base and Electrolyte Disorders in Patients with and without Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update. Kidney Dis. 2017, 3, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenepoel, P.; Jørgensen, H.S.; Bover, J.; Davenport, A.; Bacchetta, J.; Haarhaus, M.; Hansen, D.; Gracia-Iguacel, C.; Ketteler, M.; McAlister, L.; et al. Recommended calcium intake in adults and children with chronic kidney disease—A European consensus statement. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 39, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, S.M. Calcium as a cardiovascular toxin in CKD-MBD. Bone 2017, 100, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.-F.; Chen, W.-H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, S.-X.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. Charge-reversal plug gate nanovalves on peptide-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5723–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-L.; Li, G.-Y.; Chau, L.-K.; Hon, Y.-S. Single-step approach to β-cyclodextrin-bonded silica as monolithic stationary phases for CEC. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, T.; Tzompantzi, F.; Hernández-Ventura, J.; Gómez, R.; Bokhimi, X.; Pecchi, G.; Reyes, P. Effect of Zirconia Precursor on the Properties of ZrO2 SiO2 Sol-Gel Oxides. J. Sol.-Gel. Sci. Technol. 2002, 24, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavodinsky, V.G. The mechanism of ionic conductivity in stabilized cubic zirconia. Phys. Solid State 2004, 46, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gao, M.; Liu, X.; Xie, Y.; Yi, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Shen, X. Monolithic zirconia aerogel from polyacetylacetonatozirconium precursor and ammonia hydroxide gel initiator: Formation mechanism, mechanical strength and thermal properties. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41603–41611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Gonzalez, A.; Choy, K.-L. Integration of an Aerosol-Assisted Deposition Technique for the Deposition of Functional Biomaterials Applied to the Fabrication of Miniaturised Ion Sensors. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereczki, R.; Takács, B.; Langmaier, J.; Neely, M.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Tóth, K.; Nagy, G.; Lindner, E. How To Assess the Limits of Ion-Selective Electrodes: Method for the Determination of the Ultimate Span, Response Range, and Selectivity Coefficients of Neutral Carrier-Based Cation Selective Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazvini, S.F.; Nikolaevna, E.I. Kinetic analysis of monomolecular cracking of normal Alkanes (C4C6) over Brønsted Acid site of Zeolitic type catalyst with energetic evaluation of transition states using Quantum-Chemical modeling. Fuel Commun. 2024, 19, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumbimuni-Torres, K.Y.; Calvo-Marzal, P.; Wang, J.; Bakker, E. Electrochemical Sample Matrix Elimination for Trace-Level Potentiometric Detection with Polymeric Membrane Ion-Selective Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6114–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareh, M.; Elgendy, K.; Keshk, A.; Zaky, M.; Abd-Alhady, A. Preparation of Cu-PVC membrane electrochemical membrane sensor based on β-Cyclodextrin. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 21123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanei-Motlagh, M.; Taher, M. Novel imprinted polymeric nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel technique for electrochemical detection of toxic cadmium(II) ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.G.; Crespo, G.A.; Bakker, E. Direct Ion Speciation Analysis with Ion-Selective Membranes Operated in a Sequential Potentiometric/Time Resolved Chronopotentiometric Sensing Mode. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8813–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veder, J.-P.; De Marco, R.; Patel, K.; Si, P.; Grygolowicz-Pawlak, E.; James, M.; Alam, M.T.; Sohail, M.; Lee, J.; Pretsch, E.; et al. Evidence for a Surface Confined Ion-to-Electron Transduction Reaction in Solid-Contact Ion-Selective Electrodes Based on Poly(3-octylthiophene). Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10495–10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, Y.; Aparicio, M.; Moreno, R.; Durán, A. Silica-Zirconia Sol–Gel Coatings Obtained by Different Synthesis Routes. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2005, 35, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillippi, C.M.; Mazdiyasni, K.S. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Zirconia Polymorphs. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1971, 54, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Condrate, R.A. The infrared and Raman spectra of ZrO2-SiO2 glasses prepared by a sol-gel process. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 23, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiauchawal, T.; Mungchamnankit, A.; Sujinnapram, S.; Kaewkhao, J.; Limsuwan, P. The Effect of Heat Treatment on Crystal Structure in Zircon Monitored by ESR and XRD. Procedia Eng. 2012, 32, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, L.; Mecartney, M.; Krumdieck, S. Nanocrystalline ZrO2 thin films on silicon fabricated by pulsed-pressure metalorganic chemical vapor deposition (PP-MOCVD). J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudasama, C.D.; Sebastian, J.; Jasra, R.V. Pore-Size Engineering of Zeolite A for the Size/Shape Selective Molecular Sep-aration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate: A Review in Hyperkalaemia. Drugs 2018, 78, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hardan, N.H.; Hamid, M.A.A.; Ahmed, N.M.; Jalar, A.; Shamsudin, R.; Othman, N.K.; Keng, L.K.; Chiu, W.; Al-Rawi, H.N. High Sensitivity pH Sensor Based on Porous Silicon (PSi) Extended Gate Field-Effect Transistor. Sensors 2016, 16, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Gonzalez, A.; Huang, J.; Xun, C.; Chhabra, R.; Lee, R.; Yizhong, H.; Davenport, A.; Li, B.; Palgrave, R.; Choy, K.L. Ultrasensitive and miniaturized ion sensors using ionically imprinted nanostructured films. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 29, 101600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, G.J.; Oke, R.B.; Thomas, J.D.R. A calcium-sensitive electrode based on a liquid ion exchanger in a poly(vinyl chloride) matrix. Analyst 1970, 95, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindfors, T.; Szücs, J.; Sundfors, F.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Polyaniline Nanoparticle-Based Solid-Contact Silicone Rubber Ion-Selective Electrodes for Ultratrace Measurements. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9425–9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-Z.; Fierke, M.A.; Stein, A.; Bühlmann, P. Ion-Selective Electrodes with Three-Dimensionally Ordered Macroporous Carbon as the Solid Contact. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4621–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuartero, M.; Pankratova, N.; Cherubini, T.; Crespo, G.A.; Massa, F.; Confalonieri, F.; Bakker, E. In Situ Detection of Species Relevant to the Carbon Cycle in Seawater with Submersible Potentiometric Probes. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedlechowicz, I.; Maj-Żurawska, M.; Sokalski, T.; Hulanicki, A. Effect of a plasticizer on the detection limit of calcium-selective electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2002, 537, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-A.; Ou, S.-M.; Lin, C.-C. Influence of Dialysis Membranes on Clinical Outcomes: From History to Innovation. Membranes 2022, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, G.L. Chapter 194-Serum Sodium. In Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; Walker, H.W., Hurst, J.W., Eds.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rastegar, A. Chapter 195-Serum Potassium. In Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; Walker, H.W., Hurst, J.W., Eds.; Butterworths: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Micke, O.; Vormann, J.; Kraus, A.; Kisters, K. Serum magnesium: Time for a standardized and evidence-based reference range. Magnes. Res. 2021, 34, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, E.W. Ionized calcium in normal serum, ultrafiltrates, and whole blood determined by ion-exchange electrodes. J. Clin. Investig. 1970, 49, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidoo, V.Y.A.; Cara, K.C.; Dickinson, S.L.; Brown, A.W.; Wallace, T.C.; Chung, M.; Gletsu-Miller, N. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis to Estimate a Reference Range for Circulating Ionized Magnesium Concentrations in Adult Populations. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 3458–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pun, P.H.; Horton, J.R.; Middleton, J.P. Dialysate calcium concentration and the risk of sudden cardiac arrest in hemodialy-sis patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Gonzalez, A.; Chhabra, R.; Cao, X.; Huang, Y.; Davenport, A.; Choy, K.-L. Calcium Ion Sensors with Unrivaled Stability and Selectivity Using a Bilayer Approach with Ionically Imprinted Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100741
Ruiz-Gonzalez A, Chhabra R, Cao X, Huang Y, Davenport A, Choy K-L. Calcium Ion Sensors with Unrivaled Stability and Selectivity Using a Bilayer Approach with Ionically Imprinted Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(10):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100741
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Gonzalez, Antonio, Roohi Chhabra, Xun Cao, Yizhong Huang, Andrew Davenport, and Kwang-Leong Choy. 2025. "Calcium Ion Sensors with Unrivaled Stability and Selectivity Using a Bilayer Approach with Ionically Imprinted Nanocomposites" Nanomaterials 15, no. 10: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100741
APA StyleRuiz-Gonzalez, A., Chhabra, R., Cao, X., Huang, Y., Davenport, A., & Choy, K.-L. (2025). Calcium Ion Sensors with Unrivaled Stability and Selectivity Using a Bilayer Approach with Ionically Imprinted Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials, 15(10), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15100741






