Inverted Pyramid Nanostructures Coupled with a Sandwich Immunoassay for SERS Biomarker Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
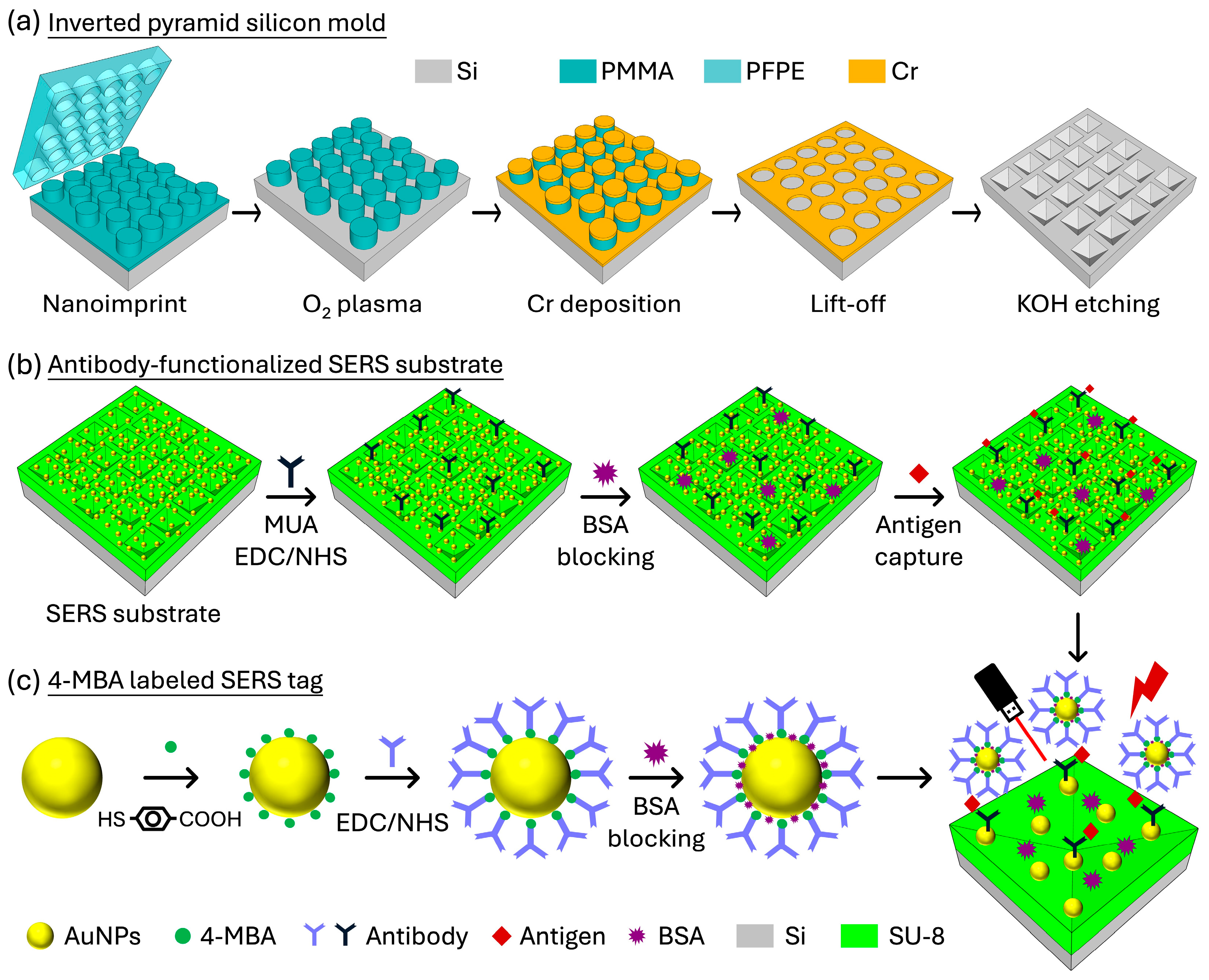
2.2. Nanoimprint Process
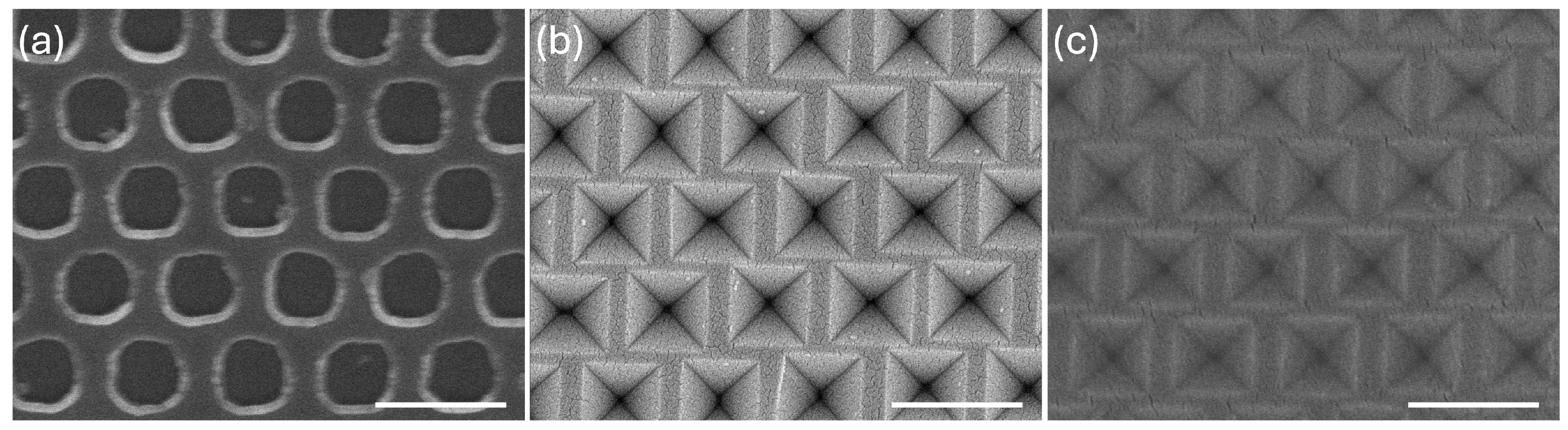
2.3. Fabrication of Si Master Molds with Inverted Pyramid Nanostructures
2.4. Synthesis of AuNPs
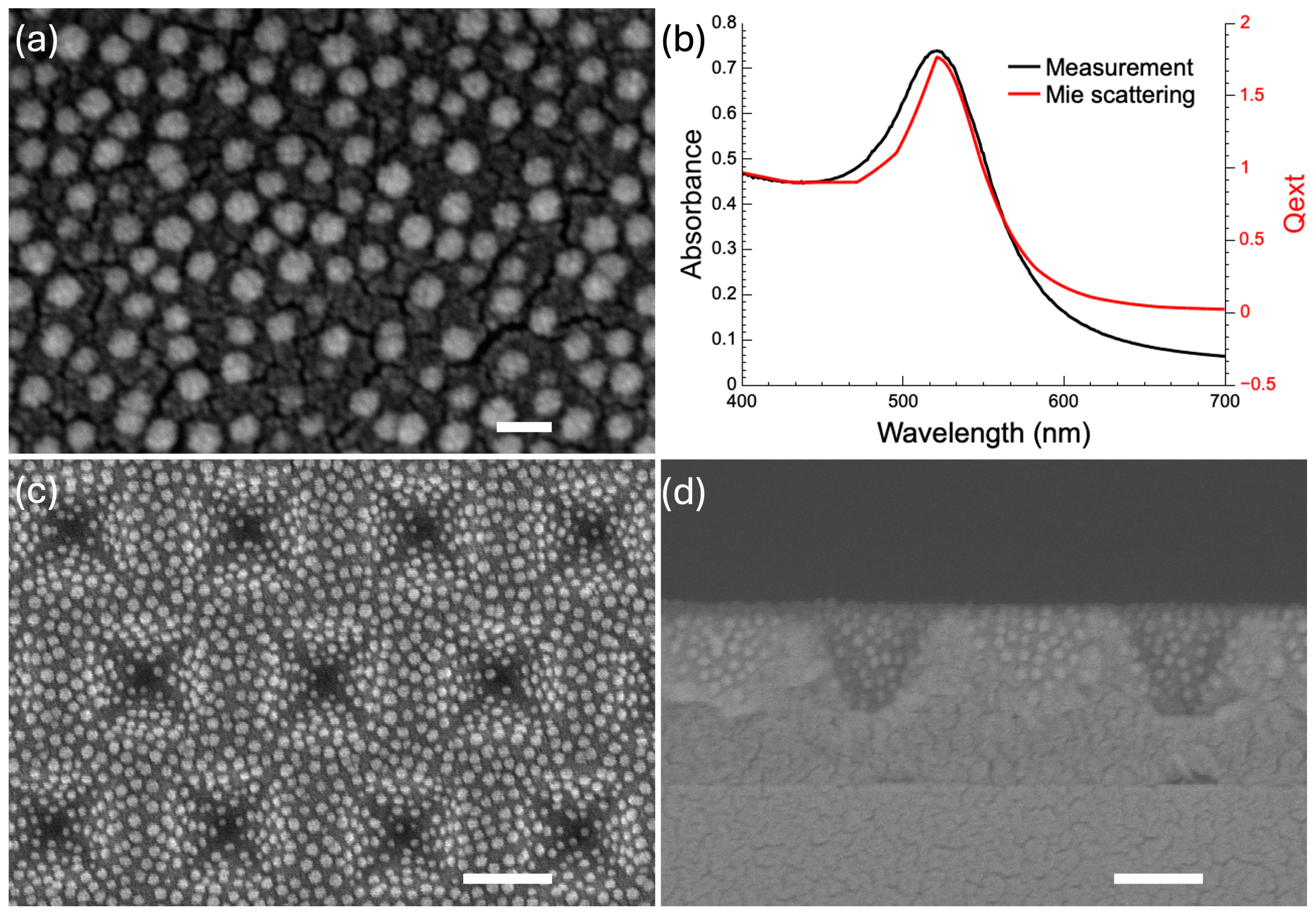
2.5. Self-Assembled AuNPs on APTES-Functionalized Nanostructured Surface
2.6. Antibody Functionalized to the SERS Substrate
2.7. Preparation of 4-MBA-Labeled SERS Tags
2.8. Sandwich Immunoassay for HA Molecule Detection
2.9. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of SU-8 Inverted Pyramid Nanostructures
3.2. APTES-Directed Self-Assembly of AuNPs on SU-8 Inverted Pyramids for SERS Substrate
3.3. Performance Testing of SERS Substrate Using MG as Analyte
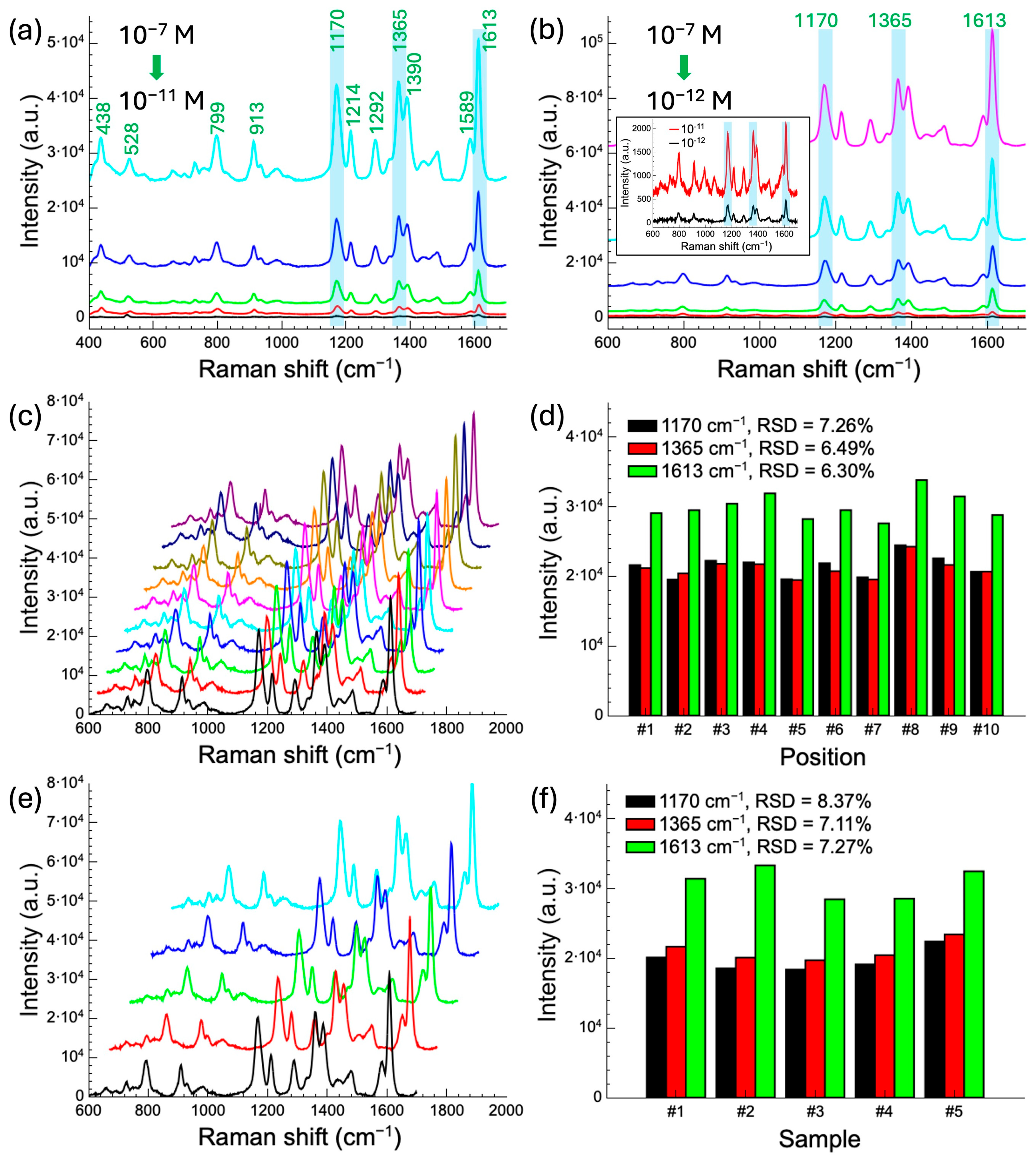
3.4. Application of SERS Substrate in HA Molecule Detection
3.4.1. Preparation of Antibody-Functionalized SERS Substrates and 4-MBA-Labeled SERS Tags
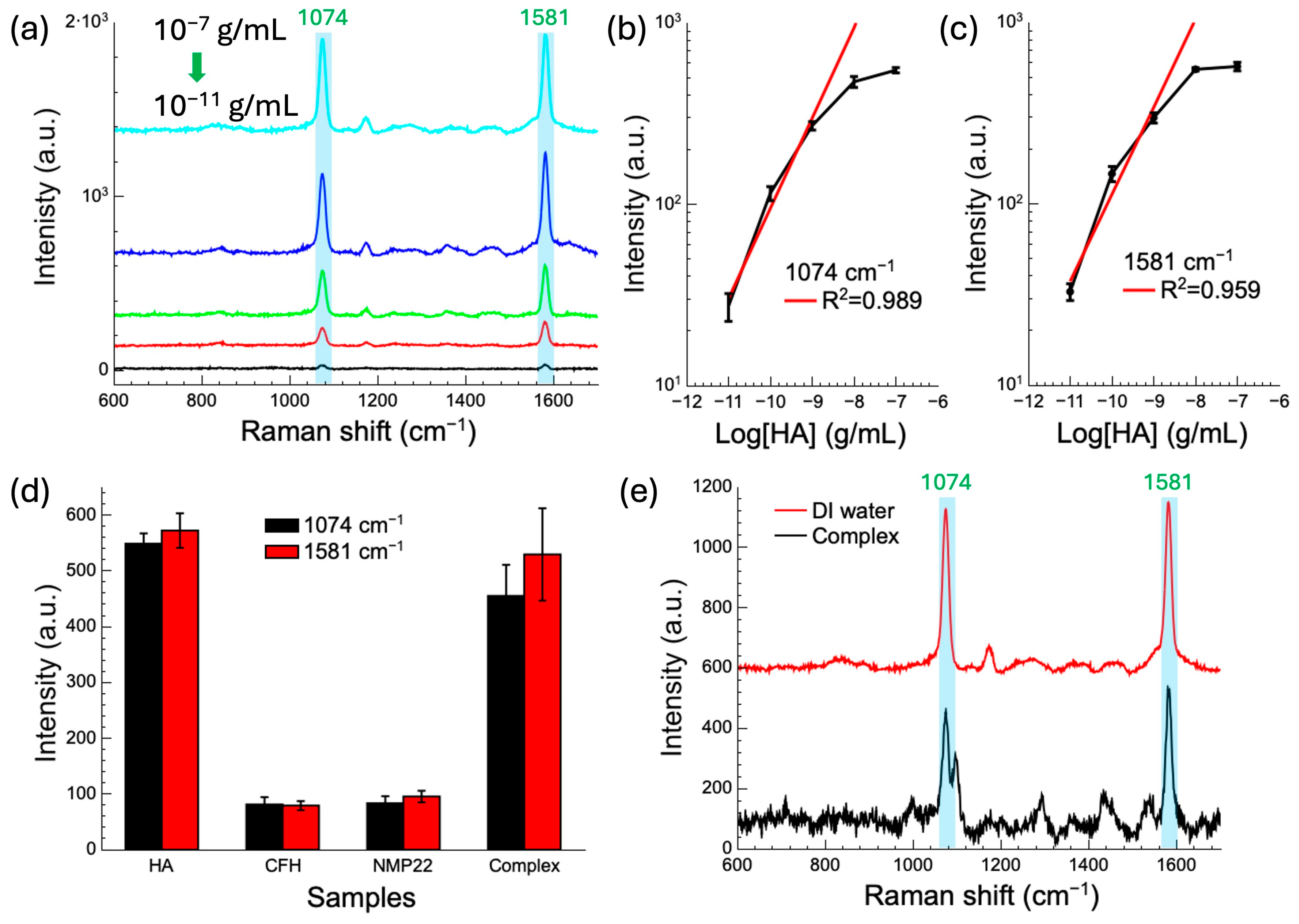
3.4.2. HA Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matthews, H.K.; Bertoli, C.; de Bruin, R.A. Cell cycle control in cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of cancer: New dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Wang, Z.; Stebbing, J.; Yu, Z. Novel immunotherapeutic drugs for the treatment of lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2022, 34, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.; Scheckel, C.; Jensen, C.J.; Orme, J.; Williams, C.; Shah, N.; Leventakos, K.; Adjei, A.A. Trends in Prices of Drugs Used to Treat Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer in the US From 2015 to 2020. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2144923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigrossi, A.; Hong, L.K.; Ekyalongo, R.C.; Cruz-Alvarez, C.; Gornick, E.; Diamond, A.M.; Kastrati, I. SELENOF is a new tumor suppressor in breast cancer. Oncogene 2022, 41, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Peng, R.; Min, Q.; Hui, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; Qin, S. Bisindole natural products: A vital source for the development of new anticancer drugs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 243, 114748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Gu, Y.; Li, Z.; Ge, S.; Mao, Y.; Gu, Y.; Lu, D. A SERS microfluidic chip for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of SCCA and CYFRA21-1 in serum based on Au nanobowl arrays and hybridization chain reaction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 375, 132894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Bao, C.; Liu, X.; Feng, J.; Wu, D.; Ma, H.; Wang, H.; Wei, Q.; Du, B. Facile fabrication of visible light photoelectrochemical immunosensor for SCCA detection based on BiOBr/Bi2S3 heterostructures via self-sacrificial synthesis method. Talanta 2019, 198, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er, E.; Sánchez-Iglesias, A.; Silvestri, A.; Arnaiz, B.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Prato, M.; Criado, A. Metal nanoparticles/MoS2 surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based sandwich immunoassay for α-fetoprotein detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 8823–8831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roointan, A.; Mir, T.A.; Wani, S.I.; Hussain, K.K.; Ahmed, B.; Abrahim, S.; Savardashtaki, A.; Gandomani, G.; Gandomani, M.; Chinnappan, R. Early detection of lung cancer biomarkers through biosensor technology: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medetalibeyoglu, H.; Kotan, G.; Atar, N.; Yola, M.L. A novel sandwich-type SERS immunosensor for selective and sensitive carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1139, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fass, L. Imaging and cancer: A review. Mol. Oncol. 2008, 2, 115–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, H.; Mao, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Luo, P.; Xue, J.; et al. Liquid biopsy for human cancer: Cancer screening, monitoring, and treatment. MedComm (2020) 2024, 5, e564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Fujita, M. Whole genome sequencing analysis for cancer genomics and precision medicine. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokeshwar, V.B.; ÖBek, C.; Pham, H.T.; Wei, D.; Young, M.J.; Duncan, R.C.; Soloway, M.S.; Block, N.L. Urinary hyaluronic acid and hyaluronidase: Markers for bladder cancer detection and evaluation of grade. J. Urol. 2000, 163, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azab, M.Y.; Hameed, M.F.O.; Obayya, S.S.A. Overview of Optical Biosensors for Early Cancer Detection: Fundamentals, Applications and Future Perspectives. Biology 2023, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-Y.; Chang, W.-H.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-H. Noninvasive Detection of Bladder Cancer Markers Based on Gold Nanomushrooms and Sandwich Immunoassays. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 5557–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, W.-T. Plasmonic phase transition and phase retardation: Essential optical characteristics of localized surface plasmon resonance. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9950–9956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, H.-W.; Chen, H.; Kang, W.; Xu, X.-D. Highly Selective and Sensitive Detection of Hyaluronic Acid Based on a Pyrene-Cored Cationic Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.R.M.; Passerotti, C.C.; Maciel, R.M.B.; Sampaio, L.O.; Dietrich, C.P.; Nader, H.B. Practical determination of hyaluronan by a new noncompetitive fluorescence-based assay on serum of normal and cirrhotic patients. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 319, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, L.; Ding, S.; Wang, G.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. SERS-based test strips: Principles, designs and applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.L.; Yang, J.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Shieh, J.; Fang Huang, Y.; Ho, Y.H.; Ko, T.S.; Hsu, C.C.; Ostrikov, K. Plasma-Etched Nanograss Surface without Lithographic Patterning to Immobilize Water Droplet for Highly Sensitive Raman Sensing. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2300291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Chang, W.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H. Direct synthesis of monolayer gold nanoparticles on epoxy based photoresist by photoreduction and application to surface-enhanced Raman sensing. Mater. Des. 2021, 197, 109211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Wu, L.; Zhu, D.; Cui, Y. Sers-Activated Platforms for Immunoassay: Probes, Encoding Methods, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7910–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Dong, Q.; Pu, H. Multiplex Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering: An Emerging Tool for Multicomponent Detection of Food Contaminants. Biosensors 2023, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, E.; Jenczyk, J.; Miłosz, Z.; Henzie, J.; Latsunskyi, I.; Florczak, P.; Andrzejewska, W.; Lewandowski, M.; Wiesner, M. Polarized-SERS of non-isotropic molecules on thermally-induced corrugated plasmonic surface supporting a NIR-SPP mode. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 659, 159821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-W.; Hung, Y.-H.; Chung, C.-S.; Yeh, S.-J.; Lee, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Nanotransfer Printed Dual-Layer Metasurfaces for Infrared Cut-off Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 25593–25602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Chang, W.-H.; Lin, C.-H. Selective Growth of Patterned Monolayer Gold Nanoparticles on SU-8 through Photoreduction for Plasmonic Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 4, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastús, N.G.; Comenge, J.; Puntes, V. Kinetically controlled seeded growth synthesis of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: Size focusing versus Ostwald ripening. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11098–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laven, P. MiePlot. 2021. Available online: http://www.philiplaven.com/mieplot.htm (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Miao, J.; Lai, K. Selective recognition and determination of malachite green in fish muscles via surface-enhanced Raman scattering coupled with molecularly imprinted polymers. Food Control. 2021, 130, 108367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Khosla, R.; Soni, M.; Deva, D.; Sharma, S.K. A highly sensitive, flexible SERS sensor for malachite green detection based on Ag decorated microstructured PDMS substrate fabricated from Taro leaf as template. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, W.P.; Dang, H.; Lee, S.; Choo, J. Electrochemical surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy analysis of malachite green on gold substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 649, 159163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammi, M.I.; Oikari, S.; Pasonen-Seppänen, S.; Rilla, K.; Auvinen, P.; Tammi, R.H. Activated hyaluronan metabolism in the tumor matrix—Causes and consequences. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokeshwar, V.B.; Öbek, C.; Soloway, M.S.; Block, N.L. Tumor-associated hyaluronic acid: A new sensitive and specific urine marker for bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morera, D.S.; Hennig, M.S.; Talukder, A.; Lokeshwar, S.D.; Wang, J.; Garcia-Roig, M.; Ortiz, N.; Yates, T.J.; Lopez, L.E.; Kallifatidis, G. Hyaluronic acid family in bladder cancer: Potential prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hefnawy, A.S.; Rizk, E.M.A.E.A.; Al Demerdash Khamis, N.M.; Barakat, M.A.A.; Khater, S.M.; Shokeir, A.A. Urinary hyaluronic acid: A versatile marker of bladder cancer. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wallwiener, M.; Rudolph, A.; Ćuk, K.; Eilber, U.; Celik, M.; Modugno, C.; Trumpp, A.; Heil, J.; Marmé, F.; et al. Plasma hyaluronic acid level as a prognostic and monitoring marker of metastatic breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghcheli, K.; Parsian, H.; Qujeq, D.; Talebi, M.; Mosapour, A.; Khalilipour, E.; Islami, F.; Semnani, S.; Malekzadeh, R. Serum hyaluronic acid and laminin as potential tumor markers for upper gastrointestinal cancers. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarmoutsos, I.; Skarmoutsos, A.; Katafigiotis, I.; Tataki, E.; Giagini, A.; Adamakis, I.; Alamanis, C.; Duvdevani, M.; Sitaras, N.; Constantinides, C. Hyaluronic acid and hyaluronidase as possible novel urine biomarkers for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Med. Oncol. 2018, 35, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orasan, O.H.; Ciulei, G.; Cozma, A.; Sava, M.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Hyaluronic acid as a biomarker of fibrosis in chronic liver diseases of different etiologies. Clujul Med. 2016, 89, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, A.; Cláudia, N.; Salette, R. Hyaluronic Acid: A Key Ingredient in the Therapy of Inflammation. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokeshwar, V.B.; Block, N.L. Ha-Haase Urine Test: A Sensitive and Specific Method for Detecting Bladder Cancer and Evaluating Its Grade. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 27, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowman, M.K.; Lee, H.G.; Schwertfeger, K.L.; McCarthy, J.B.; Turley, E.A. The Content and Size of Hyaluronan in Biological Fluids and Tissues. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.Y.; Kim, W.S.; Heo, I.S.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, S. Extraction of Hyaluronic Acid (Ha) from Rooster Comb and Characterization Using Flow Field-Flow Fractionation (Flfff) Coupled with Multiangle Light Scattering (Mals). J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3530–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, P.; Alberto, M. Caution Should be Used in Long-Term Treatment with Oral Compounds of Hyaluronic Acid in Patients with a History of Cancer. Clin. Drug Investig. 2015, 35, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Han, D.; Pang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, L. Charge Transfer in an Ordered Ag/Cu2s/4-Mba System Based on Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 5599–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwiche, F.; Parekh, D.J.; Gonzalgo, M.L. Biomarkers for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Current Tests and Future Promise. Indian J. Urol. 2015, 31, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Zhou, R.; Takei, K.; Hong, M. Toward Flexible Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Sensors for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Sadique, M.A.; Ranjan, P.; Kumar, N.; Singhal, A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Khan, R. SERS Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Point-of-Care Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 2974–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Cheng, T.-C.; Shieh, J.; Lin, H.-H. Nanoimprinting of Flexible Polycarbonate Sheets with a Flexible Polymer Mold and Application to Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1500030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Lin, H.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Cheng, T.-C. Direct imprinting on a polycarbonate substrate with a compressed air press for polarizer applications. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 2026–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaphan, K.; Wongravee, K.; Nhujak, T.; Dissayabutra, T.; Srisa-Art, M. Online preconcentration and determination of chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate and hyaluronic acid in biological and cosmetic samples using capillary electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2867–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Hernández, L.A.; Camacho-Ruíz, R.M.; Arriola-Guevara, E.; Padilla-Camberos, E.; Kirchmayr, M.R.; Corona-González, R.I.; Guatemala-Morales, G.M. Validation of an Analytical Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Hyaluronic Acid Concentration and Molecular Weight by Size-Exclusion Chromatography. Molecules 2021, 26, 5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmita, H.; Hayun, H.; Geofani, M.H. Quantification of hyaluronic acid and methylsulfonylmethane in dietary supplements. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2020, 12, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perk, B.; Büyüksünetçi, Y.T.; Anık, Ü. Gold nanoparticle deposited electrochemical sensor for hyaluronic acid detection. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 4319–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B.; Liu, S.P. Resonance Rayleigh scattering study of interaction of hyaluronic acid with ethyl violet dye and its analytical application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Qin, J.; Lv, J.; Yang, J.; Yan, G. “Turn on” room-temperature phosphorescent biosensors for detection of hyaluronic acid based on manganese-doped ZnS quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2873–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Verde, G.; Sasso, A.; Rusciano, G.; Capaccio, A.; Fusco, S.; Mayol, L.; Biondi, M.; Silvestri, T.; Netti, P.A.; La Commara, M.; et al. Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid-Coated PLGA Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaneckova, T.; Bezdekova, J.; Han, G.; Adam, V.; Vaculovicova, M. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers as artificial receptors for imaging. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Raman Shift (cm−1) | Peak Assignment | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 438 | Phenyl-C-phenyl out-of-plane bending | [32] |
| 528 | Phenyl-C-phenyl out-of-plane bending | [33] |
| 799 | Ring C–H out-of-plane bending | [32,33,34] |
| 913 | Ring C–H out-of-plane bending or ring breathing | [32,33,34] |
| 1170 | Ring C–H in-plane bending | [32,33,34] |
| 1214 | Ring C–H rocking | [33,34] |
| 1292 | Ring C–C stretching | [33] |
| 1365 | N-phenyl stretching | [32,33,34] |
| 1390 | N-phenyl stretching, ring C–H in-plane bending, and ring C–C stretching | [33,34] |
| 1589 | Ring C–C stretching | [33,34] |
| 1613 | Ring C–C stretching | [32,33] |
| Method | Detection Limit (g/mL) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Capillary electrophoresis | 10−6 | [54] |
| Size-exclusion HPLC | 1.2 × 10−5 | [55] |
| HPLC with fluorescence detection | 3.55 × 10−6 | [56] |
| Electrochemistry | 3.4 × 10−8 | [57] |
| Resonance Rayleigh scattering | 9.6 × 10−8 | [58] |
| Phosphorescence | 3 × 10−8 | [59] |
| Fluorescence | 6.9 × 10−9 | [20] |
| Fluorescence-based immunoassay | 2 × 10−10 | [21] |
| ELISA | 10−9 | [16] |
| LSPR-based refractive index immunoassay | 8.3 × 10−12 | [18] |
| SERS-based immunoassay | 10−11 | this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, W.-H.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Inverted Pyramid Nanostructures Coupled with a Sandwich Immunoassay for SERS Biomarker Detection. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010064
Chang W-H, Zhang S-Q, Yang Z-Y, Lin C-H. Inverted Pyramid Nanostructures Coupled with a Sandwich Immunoassay for SERS Biomarker Detection. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(1):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010064
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Wen-Huei, Shao-Quan Zhang, Zi-Yi Yang, and Chun-Hung Lin. 2025. "Inverted Pyramid Nanostructures Coupled with a Sandwich Immunoassay for SERS Biomarker Detection" Nanomaterials 15, no. 1: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010064
APA StyleChang, W.-H., Zhang, S.-Q., Yang, Z.-Y., & Lin, C.-H. (2025). Inverted Pyramid Nanostructures Coupled with a Sandwich Immunoassay for SERS Biomarker Detection. Nanomaterials, 15(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010064







