Controlled Multi-Dimensional Assembly of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Industrial By-Product Carbide Slag and CO2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
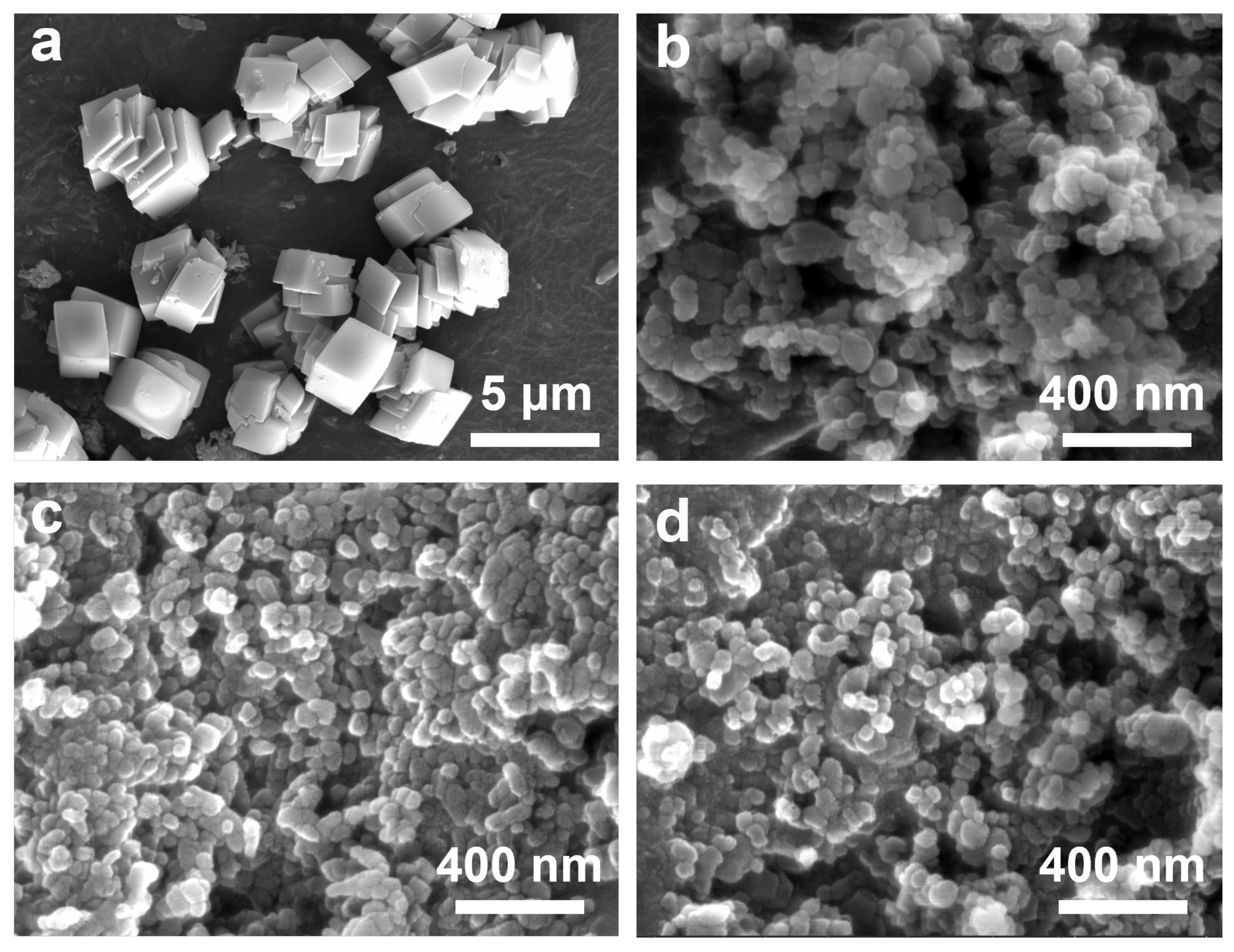
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Ye, B.; Hong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M. Uniform calcite mircro/nanorods preparation from carbide slag using recyclable citrate extractant. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Ding, Y. Carbide slag based shape-stable phase change materials for waste recycling and thermal energy storage. J. Energy Storage 2022, 10, 699–706. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, L.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z. CaO/Ca(OH)2 thermochemical heat storage of carbide slag from calcium looping cycles for CO2 capture. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 174, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Ma, L. Thermodynamic analysis of hydrogen production from carbide slag used as oxygen carrier, hydrogen carrier and in-situ carbon capture agent during the gasification of lignite. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 244, 114456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Huang, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Ji, F. Evaluation of porous calcium silicate hydrate derived from carbide slag for removing phosphate from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, G.; Zhang, F.; Sun, J. Direct aqueous mineral carbonation of carbide slag in a bubble column reactor under ambient conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Jiang, M.; Han, T.; He, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dian, B.; Zong, Y. Removal of hydrogen sulfide in the gas phase by carbide slag modified bentonite. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 20844–20855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, H.; Gao, J.; Geng, N.; Jiang, E.; Xia, F.; Xiang, M.; Jia, L.; Ning, P. High efficiency removal of NO using waste calcium carbide slag by facile KOH modification. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 139, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, H.; He, X.; Yang, W.; Deng, X. Utilization of carbide slag-granulated blast furnace slag system by wet grinding as low carbon cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Shen, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Pre-carbonation of calcium carbide slag for the preparation of eco-friendly mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 399, 132541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalas, T.; Antzaras, A.N.; Lemonidou, A.A. Evaluation of calcium-based sorbents derived from natural ores and industrial wastes for high-temperature CO2 capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 9926–9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, X.; Duan, L.; Song, H. Effect of re-carbonation on CO2 capture by carbide slag and energy consumption in the calciner. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 148, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, C.; Miao, B.; Bareille, R.; Rey, C. Preparation, physical–chemical characterisation and cytocompatibility of calcium carbonate cements. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadia, P.; Tyagi, S.; Bhagat, S.; Nair, A.; Panchal, P.; Dave, H.; Dang, S.; Singh, S. Calcium carbonate nano-and microparticles: Synthesis methods and biological applications. Biotech 2021, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Xia, Y. Performance and anti-wear mechanism of CaCO3 nanoparticles as a green additive in poly-alpha-olefin. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juuti, M.; Koivunen, K.; Silvennoinen, M.; Paulapuro, H.; Peiponen, K.-E. Light scattering study from nanoparticle-coated pigments of paper. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 352, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivula, H.; Toivakka, M.; Gane, P. Short time spreading and wetting of offset printing liquids on model calcium carbonate coating structures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 369, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.F.; Zhou, H.K.; Wang, G.Q.; Yun, J. Preparation of nano-sized precipitated calcium carbonate for PVC plastisol rheology modification. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2002, 21, 1305–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, A.; Maruyama, T.; Ohmukai, Y.; Kamio, E.; Sotani, T.; Matsuyama, H. Cross-linked DNA capsules templated on porous calcium carbonate microparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 356, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balabushevich, N.G.; Kovalenko, E.A.; Le-Deygen, I.M.; Filatova, L.Y.; Volodkin, D.; Vikulina, A.S. Hybrid CaCO3-mucin crystals: Effective approach for loading and controlled release of cationic drugs. Mater. Des. 2019, 182, 108020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Chen, L.; Cao, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y. Optimizing carbonation reaction parameters of calcium carbide slag in acidic/alkaline environment enhancing CO2 mineralization efficiency. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-L.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Yang, T.-Y.; Chatterjee, S.; Cao, M.-S.; Peng, H.-S. Facile synthesis of vaterite CaCO3 microspheres from carbon capture and solid waste utilization towards microwave absorption and dye wastewater adsorption. Carbon 2024, 226, 119199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, T.; Fang, M.; Li, Y. Preparation of calcium carbonate nanoparticles from waste carbide slag based on CO2 mineralization. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Tangchirapat, W.; Jitsangiam, P.; Nuithitikul, K.; Rattanasak, U. Carbon dioxide capture with aqueous calcium carbide residual solution for calcium carbonate synthesis and its use as an epoxy resin filler. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimoh, O.A.; Ariffin, K.S.; Hussin, H.B.; Temitope, A.E. Synthesis of precipitated calcium carbonate: A review. Carbonates Evaporites 2017, 33, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Song, B.; Tee, T.-T.; Sin, L.T.; Hui, D.; Bee, S.-T. Investigation of dynamic characteristics of nano-size calcium carbonate added in natural rubber vulcanizate. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 60, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, T.; Deng, Y.; Qi, X.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Gao, H. Hierarchical porous calcium carbonate microspheres as drug delivery vector. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2017, 27, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, F.A.; Bousserrhine, N.; Alphonse, V.; Michely, L.; Belbekhouche, S. Antibiotic loading and development of antibacterial capsules by using porous CaCO3 microparticles as starting material. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 579, 119175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, J.; You, L.; Qiu, T.; Christoforo, T.; Wei, Y. Wormwood-infused porous-CaCO3 for synthesizing antibacterial natural rubber latex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarian, M.H.; Junyusen, T.; Sutapun, W. Biogenic Vaterite Calcium Carbonate-Silver/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Film for Wound Dressing. ACS Omega 2023, 9, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hao, S.; Suonan, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y. Controllable Synthesis of Nano-Micro Calcium Carbonate Mediated by Additive Engineering. Crystals 2023, 13, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y. Rigorous recognition mode analysis of molecularly imprinted polymers—Rational design, challenges, and opportunities. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2024, 150, 101790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.-T.; Huang, F. Multiple hydrogen bonding driven supramolecular architectures and their biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 1592–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrom, H.; Goncharenko, A.A.; Fatkhutdinova, L.I.; Peltek, O.O.; Muslimov, A.R.; Koval, O.Y.; Eliseev, I.E.; Manchev, A.; Gorin, D.; Shishkin, I.I.; et al. Controllable synthesis of calcium carbonate with different geometry: Comprehensive analysis of particle formation, cellular uptake, and biocompatibility. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19142–19156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udrea, I.; Capat, C.; Olaru, E.A.; Isopescu, R.; Mihai, M.; Mateescu, C.D.; Bradu, C. Vaterite synthesis via gas–liquid route under controlled pH conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8185–8193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Cao, C.; Wang, B.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, H. The effects of impurities in carbide slag on the morphological evolution of CaCO3 during carbonation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 363, 121361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, L.; Ding, W. Preparation of calcium carbonate with microstructure and nanostructure from carbide slag for CO2 sequestration by using recyclable ammonium chloride. Particuology 2023, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Tang, X.; Liu, J. Assemblage of nano-calcium carbonate particles on palmitic acid template. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 25, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Gan, X.; Liu, J. From nano-cubic particle to micro-spindle aggregation: The control of long chain fatty acid on the morphology of calcium carbonate. Powder Technol. 2015, 270, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Choi, D.; Kim, M.H.; Park, Y. Tuning crystal polymorphisms and structural investigation of precipitated calcium carbonates for CO2 mineralization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 5, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Fu, J.; Ma, L.; Du, H.; Yue, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, C. Biomimetic synthesis of calcium carbonate under phenylalanine: Control of polymorph and morphology. Biomater. Adv. 2020, 114, 111019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-C.; Tai, C.Y.; Lee, K.C. Morphology and growth rate of calcium carbonate crystals in a gas-liquid-solid reactive crystallizer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 4171–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, M.; Hedin, N.; Bacsik, Z.; Growth, C. Spherical and porous particles of calcium carbonate synthesized with food friendly polymer additives. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 3609–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangyu, D.; Haoyang, H.; Yongsheng, H. The role of diffusion in the nucleation of calcium carbonate. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 43, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
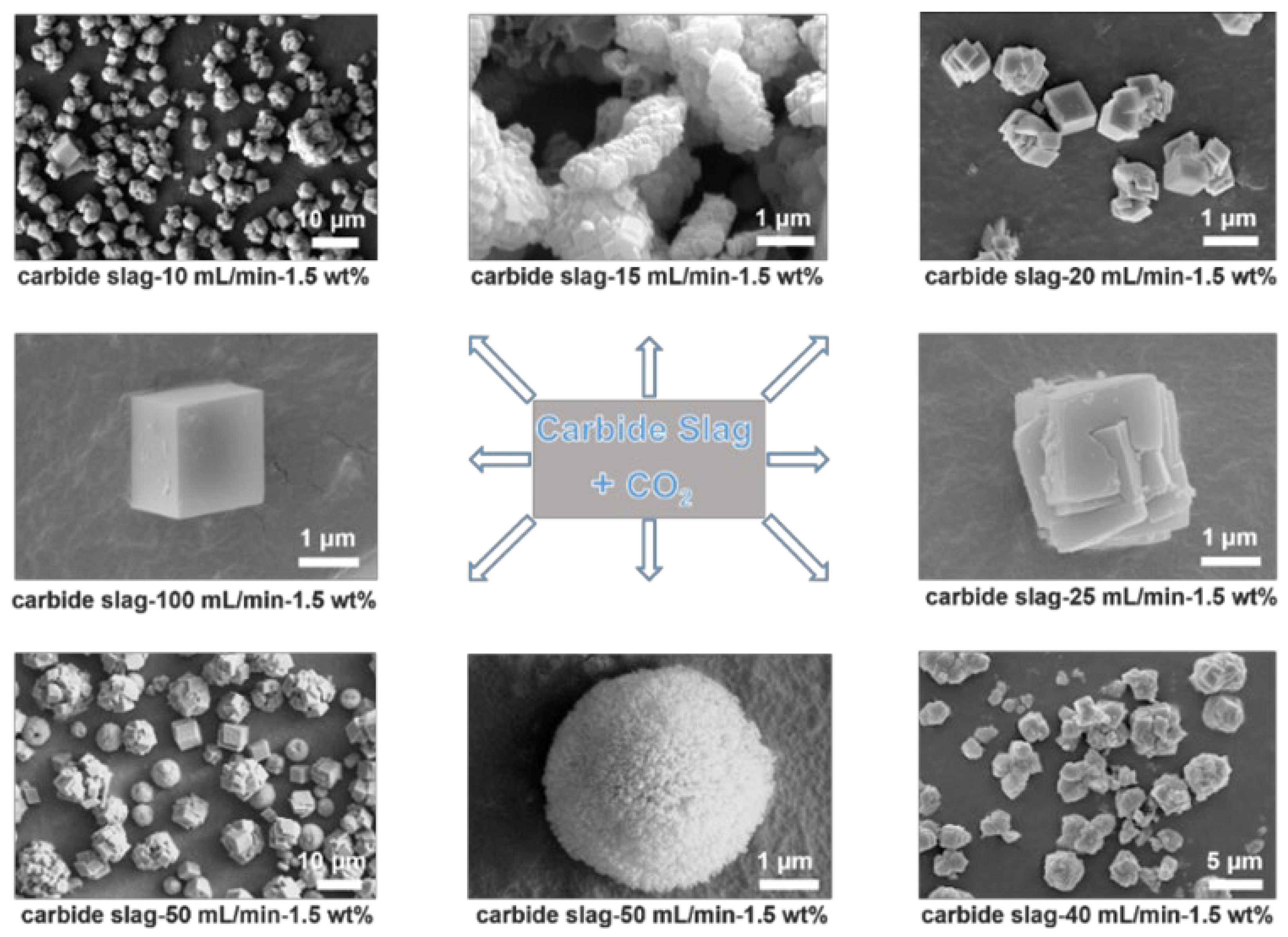
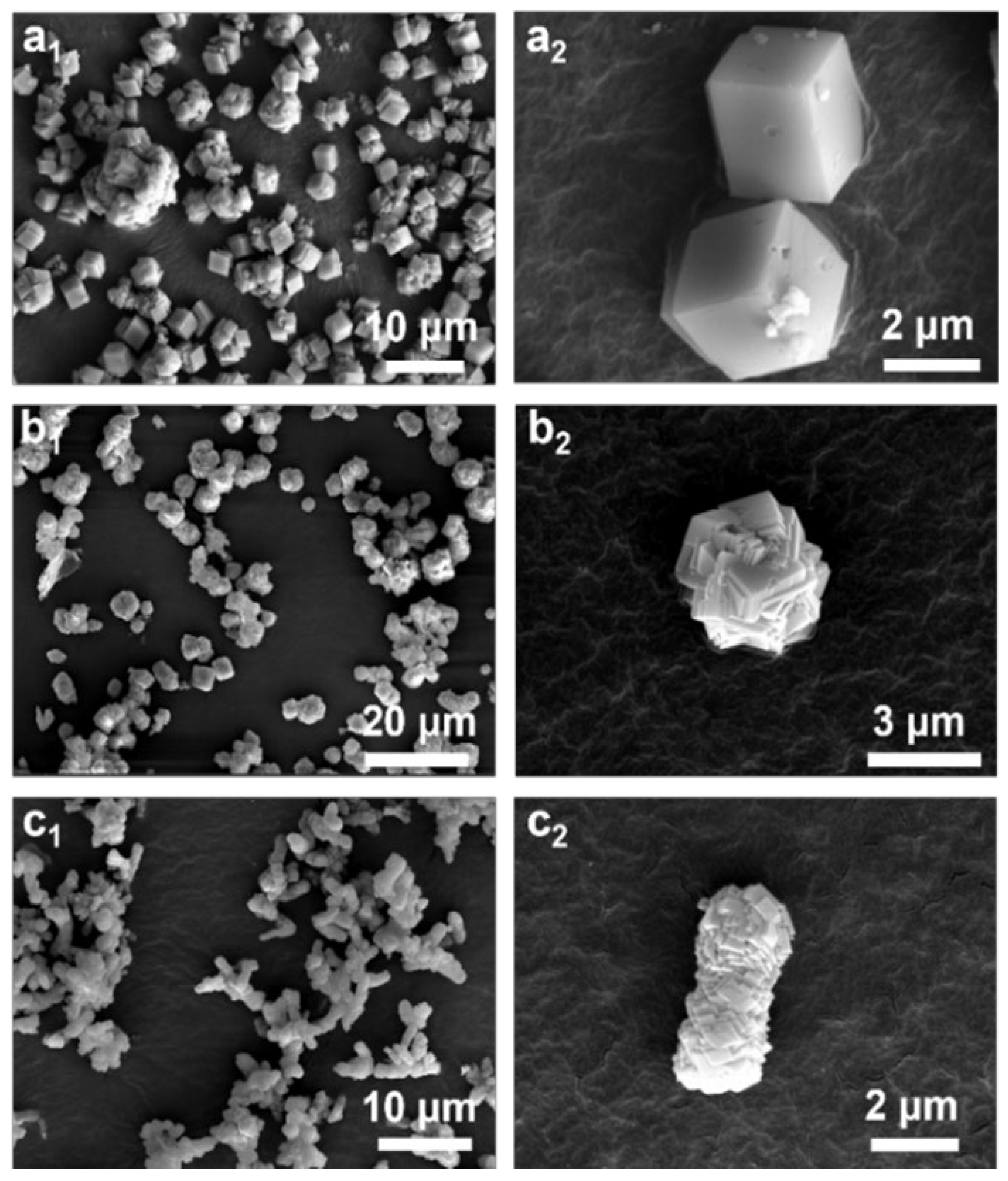
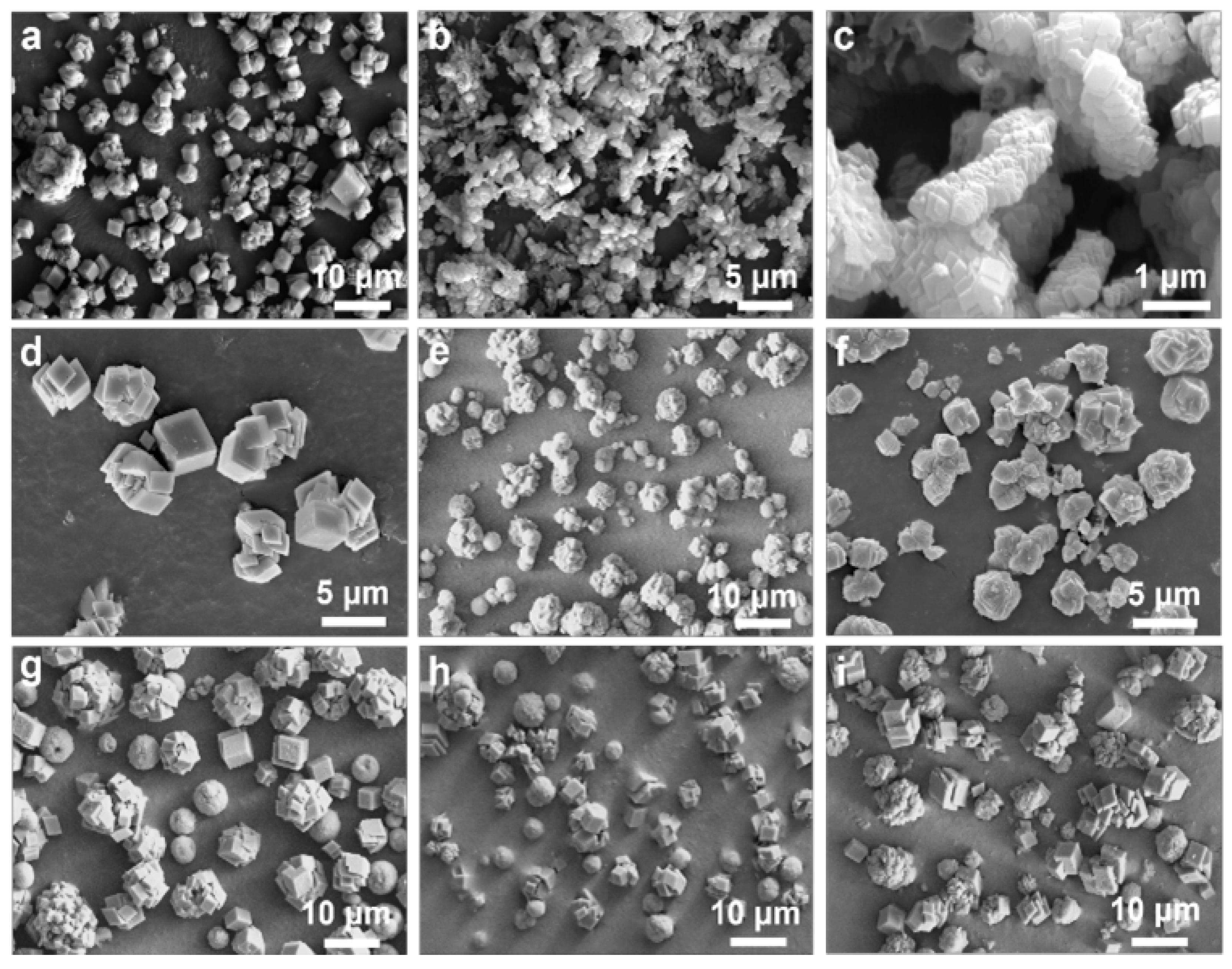
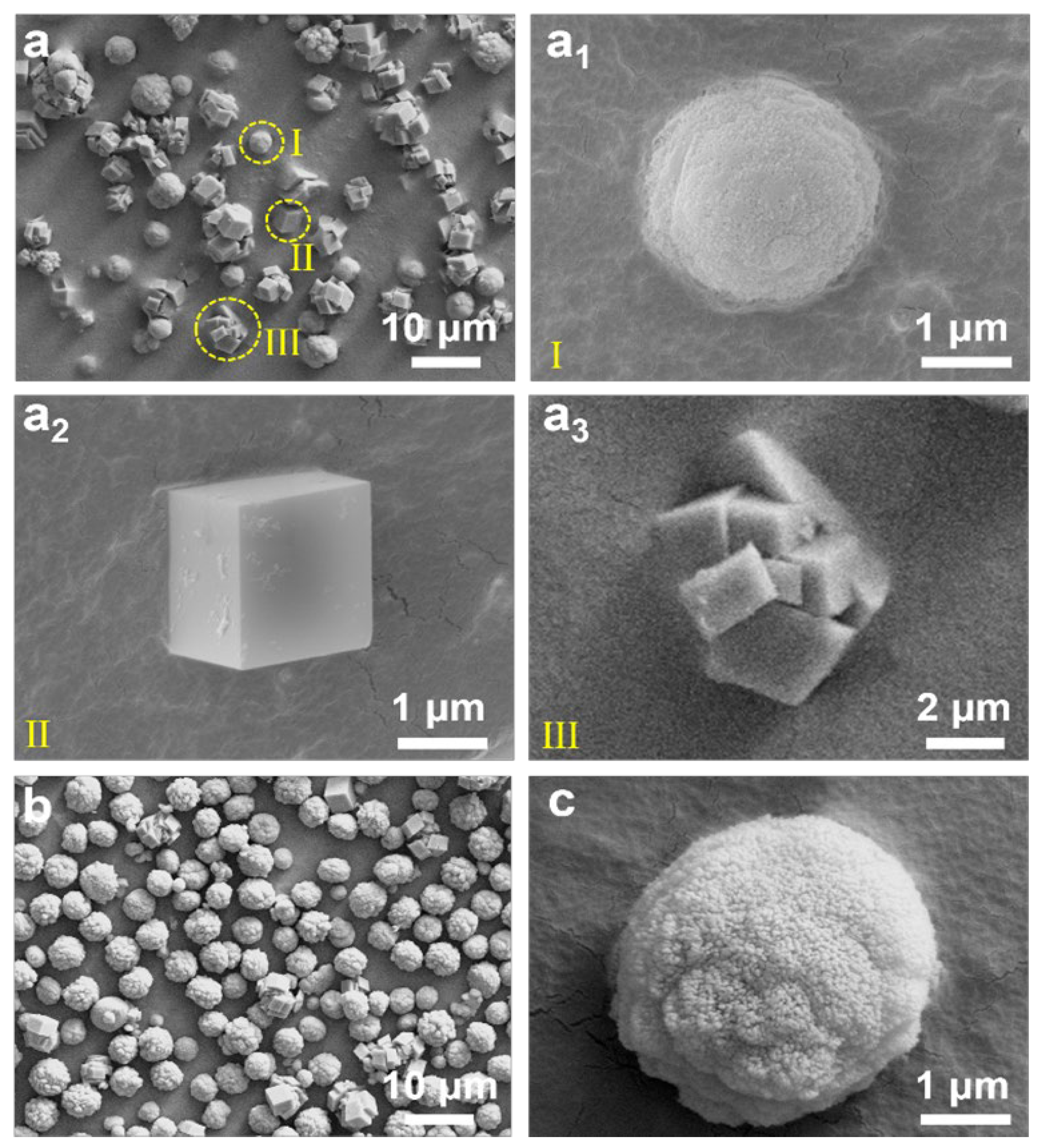
| Name | Ingredients | n(additives) (mmol) | Flow Rates of CO2 (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS-1.5wt%-10 | CS | 0.0032 | 10 |
| CS-3.0wt%-10 | CS | 0.0097 | 10 |
| CS-4.5wt%-10 | CS | 0.0129 | 10 |
| CS-1.5wt%-15 | CS | 0.0032 | 15 |
| CS-1.5wt%-20 | CS | 0.0032 | 20 |
| CS-1.5wt%-25 | CS | 0.0032 | 25 |
| CS-1.5wt%-40 | CS | 0.0032 | 40 |
| CS-1.5wt%-50 | CS | 0.0032 | 50 |
| CS-1.5wt%-100 | CS | 0.0032 | 100 |
| CS-1.5wt%-150 | CS | 0.0032 | 150 |
| Ca(OH)2-1.5wt%-100 | Ca(OH)2 | 0.0034 | 100 |
| Methods | Raw Materials | Conditions | Morphology | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 bubbling | CS + CO2 | CO2: 10, 15, 20, 25, 40, 50, 100, 150 mL/min Palmitic acid amounts: 1.5, 3.0, 4.5wt% | Spherical vaterite +cube calcite + mulberry calcite | This work |
| Ca(OH)2 + CO2 | CO2: 100 mL/min Palmitic acid amounts: 1.5wt% | Spherical vaterite +cube calcite | ||
| CO2 bubbling | CS + CO2 | Solid/liquid ratio: from1:100 to 10:100, CO2: 200 mL/min | Rod-shaped calcite | [36] |
| Ca(OH)2 + CO2 | Solid/liquid ratio: 10:100, CO2: 200, 300, 500 mL/min | Spherical calcite | ||
| CO2 bubbling ((NH4)2SO4) | CS + CO2 | CO2: 500 mL/min NH4+/Ca2+ = 2.4 | Spherical vaterite +cube calcite | [23] |
| CO2 bubbling (NH4Cl) | CS + CO2 | CO2: 60 mL/min Time: 60min | Spherical vaterite +cube calcite | [37] |
| CO2 bubbling (sodium citrate) | CS + CO2 | CO2: 0.5~1.5 L/min Terminal pH: 11 | Calcite micro-/nanorods | [1] |
| CO2 bubbling | CS + CO2 | Alkaline system: solid/liquid ratio: 1:100 Acidic system: solid/liquid ratio: 5:100, 10:100 | Cubic calcite +spindle calcite | [21] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Tang, C.; Ma, W.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P. Controlled Multi-Dimensional Assembly of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Industrial By-Product Carbide Slag and CO2. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010016
Shen Y, Jiang X, Tang C, Ma W, Cheng J, Wang H, Zhu H, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Zhao P. Controlled Multi-Dimensional Assembly of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Industrial By-Product Carbide Slag and CO2. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yuke, Xiaoli Jiang, Chengcai Tang, Wei Ma, Jianyu Cheng, Hongxu Wang, Hongyu Zhu, Lin Zhao, Yagang Zhang, and Panfeng Zhao. 2025. "Controlled Multi-Dimensional Assembly of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Industrial By-Product Carbide Slag and CO2" Nanomaterials 15, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010016
APA StyleShen, Y., Jiang, X., Tang, C., Ma, W., Cheng, J., Wang, H., Zhu, H., Zhao, L., Zhang, Y., & Zhao, P. (2025). Controlled Multi-Dimensional Assembly of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Industrial By-Product Carbide Slag and CO2. Nanomaterials, 15(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010016








