Mixed Metal Oxide W-TiO2 Nanopowder for Environmental Process: Synergy of Adsorption and Photocatalysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis Procedure
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
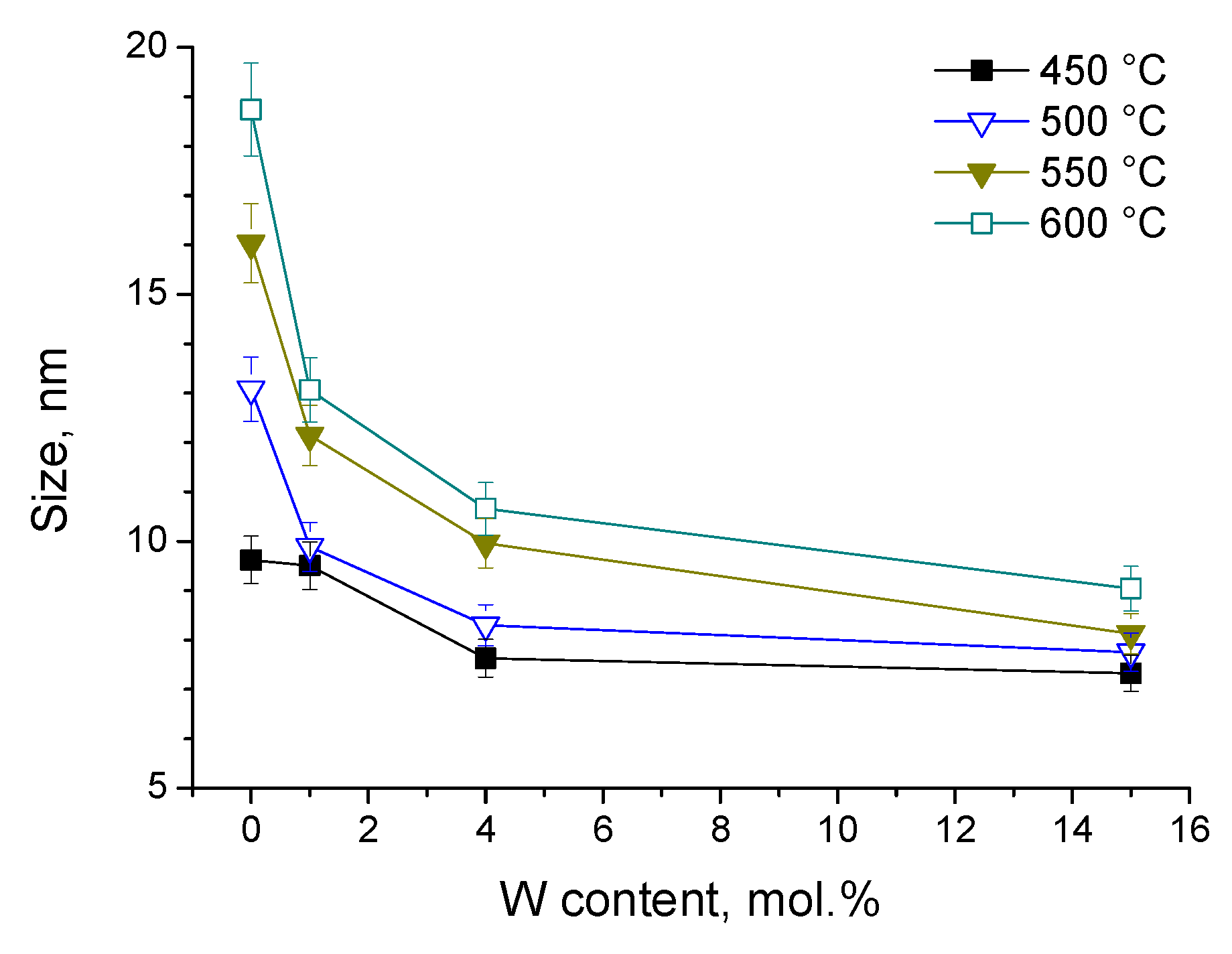
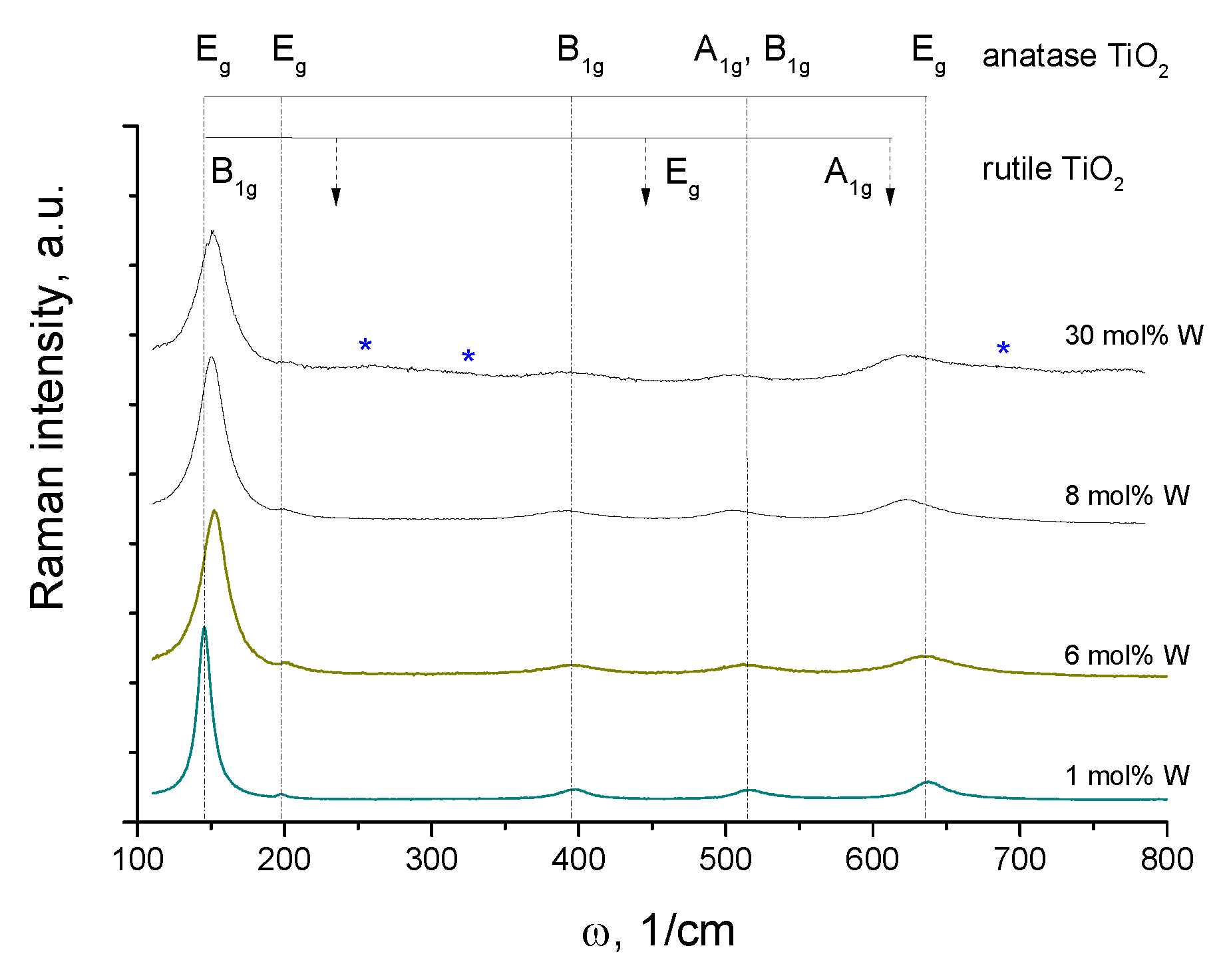
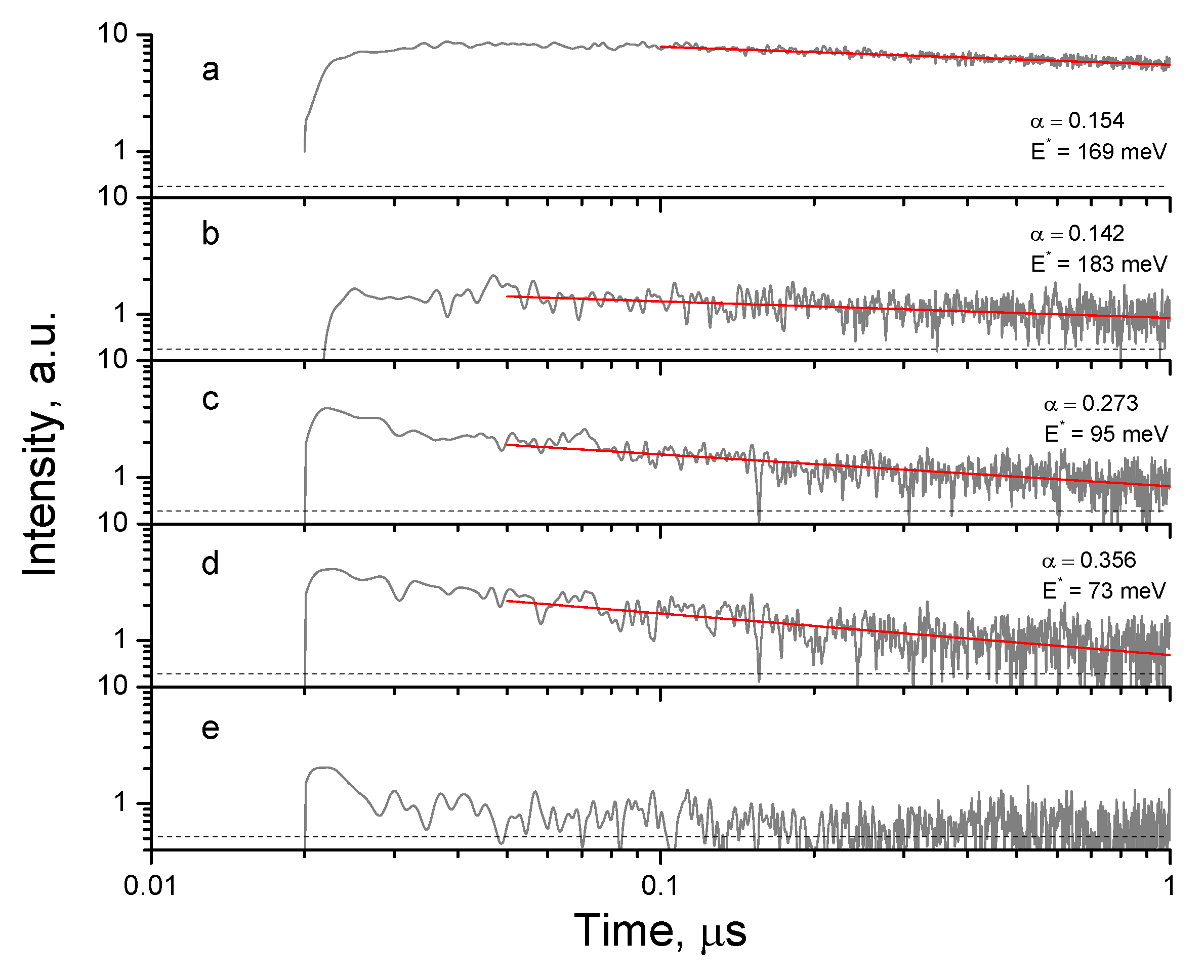
3.1. Structural Properties
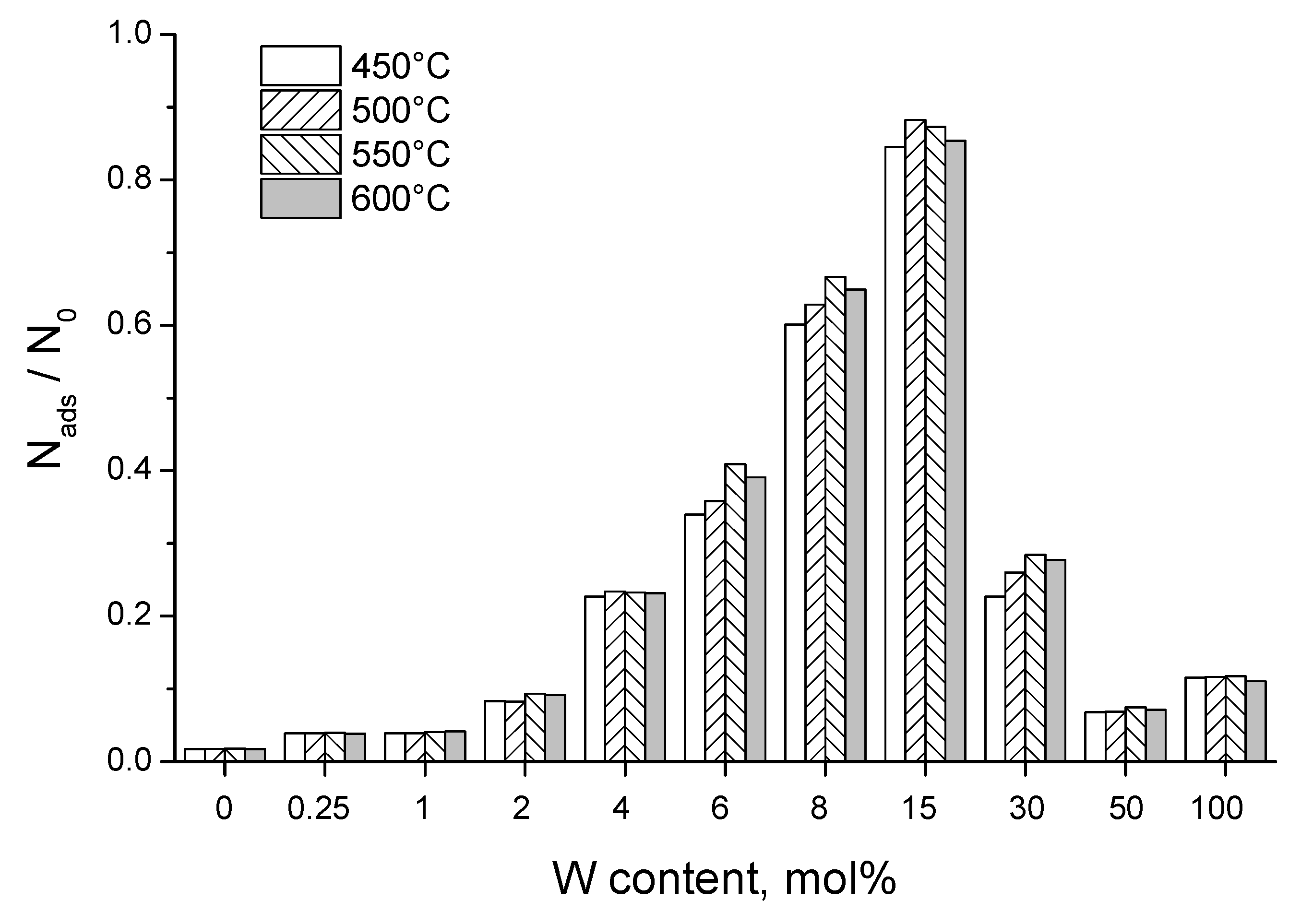
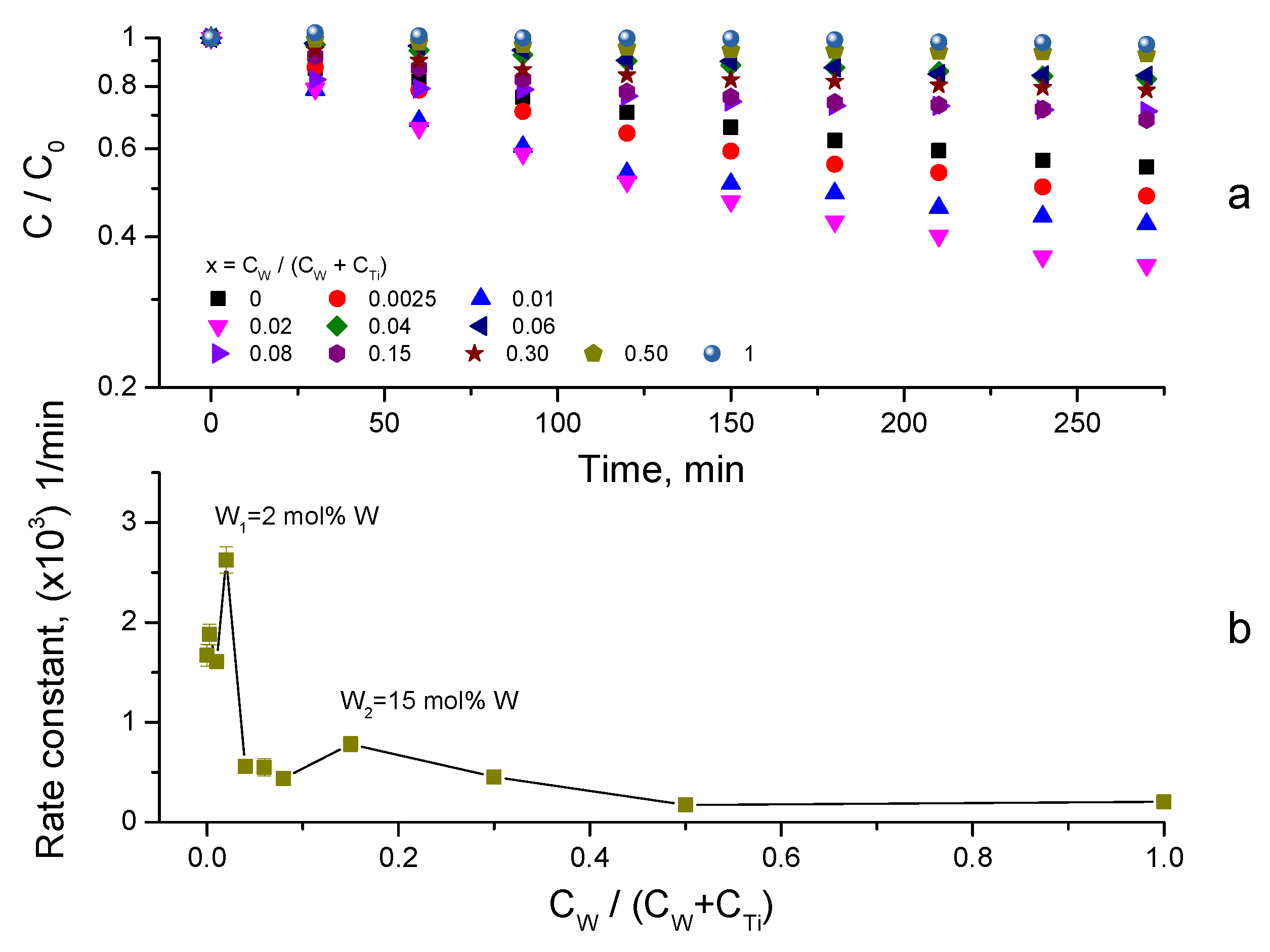
3.2. Adsorption Capacity
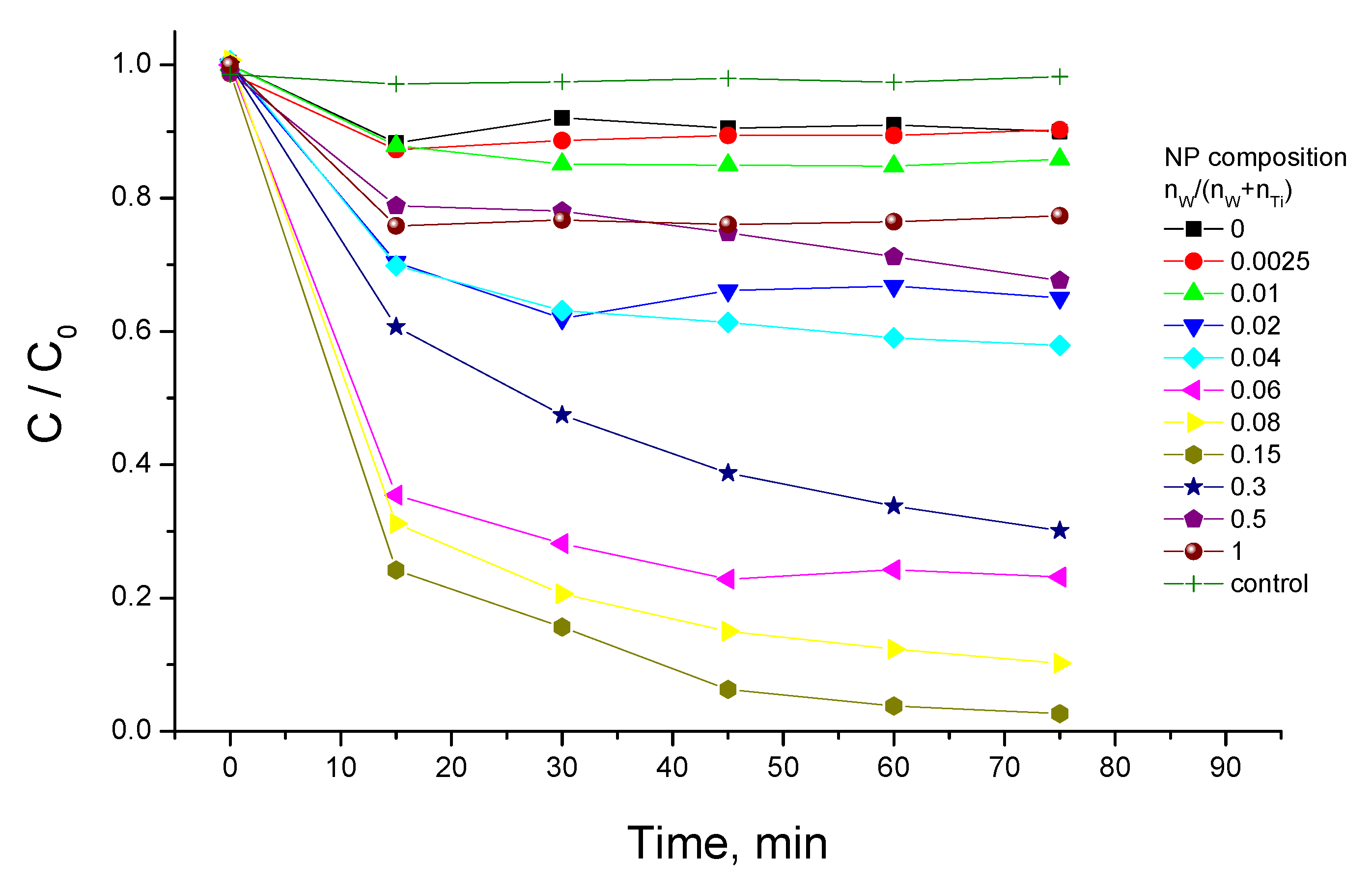
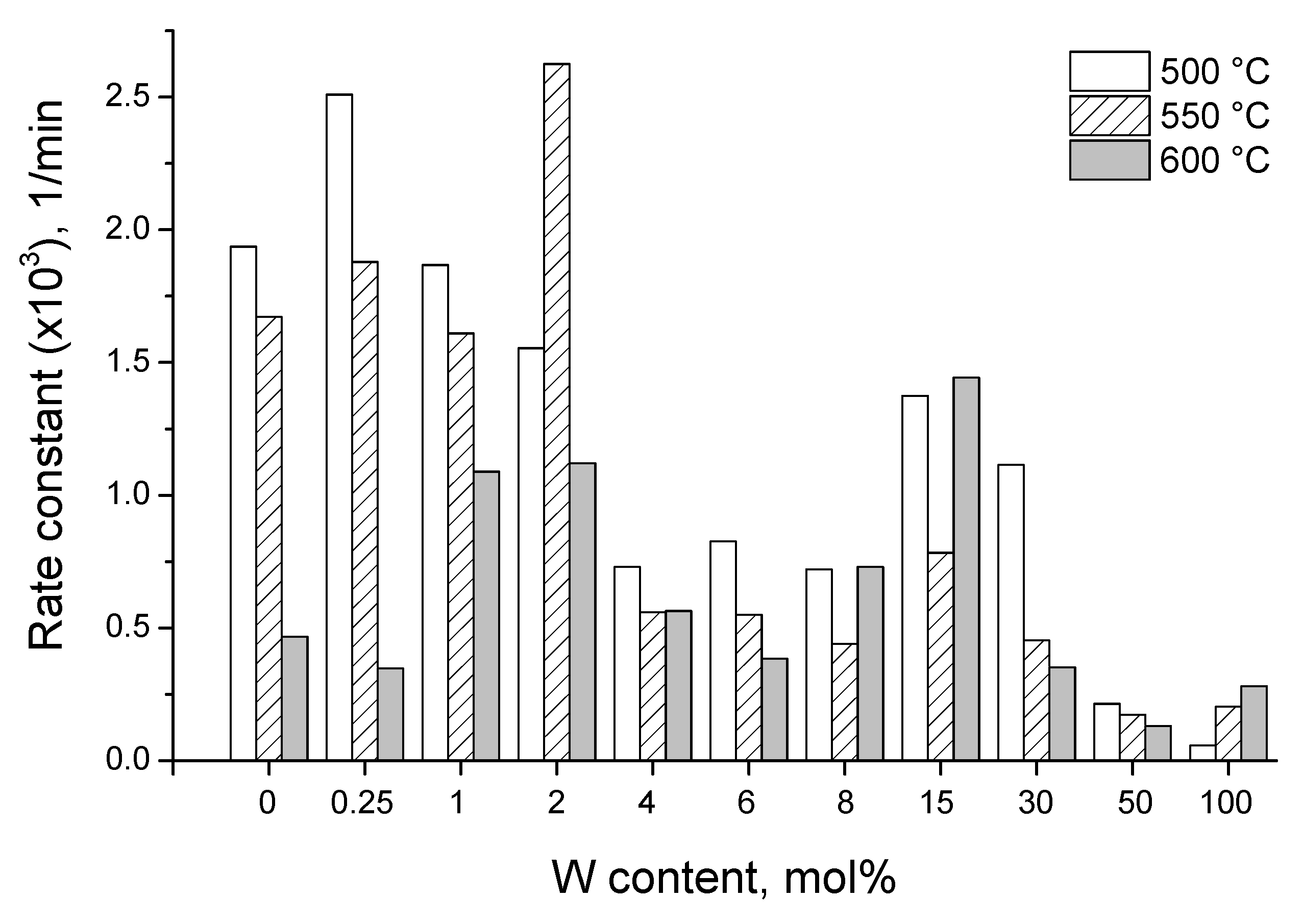
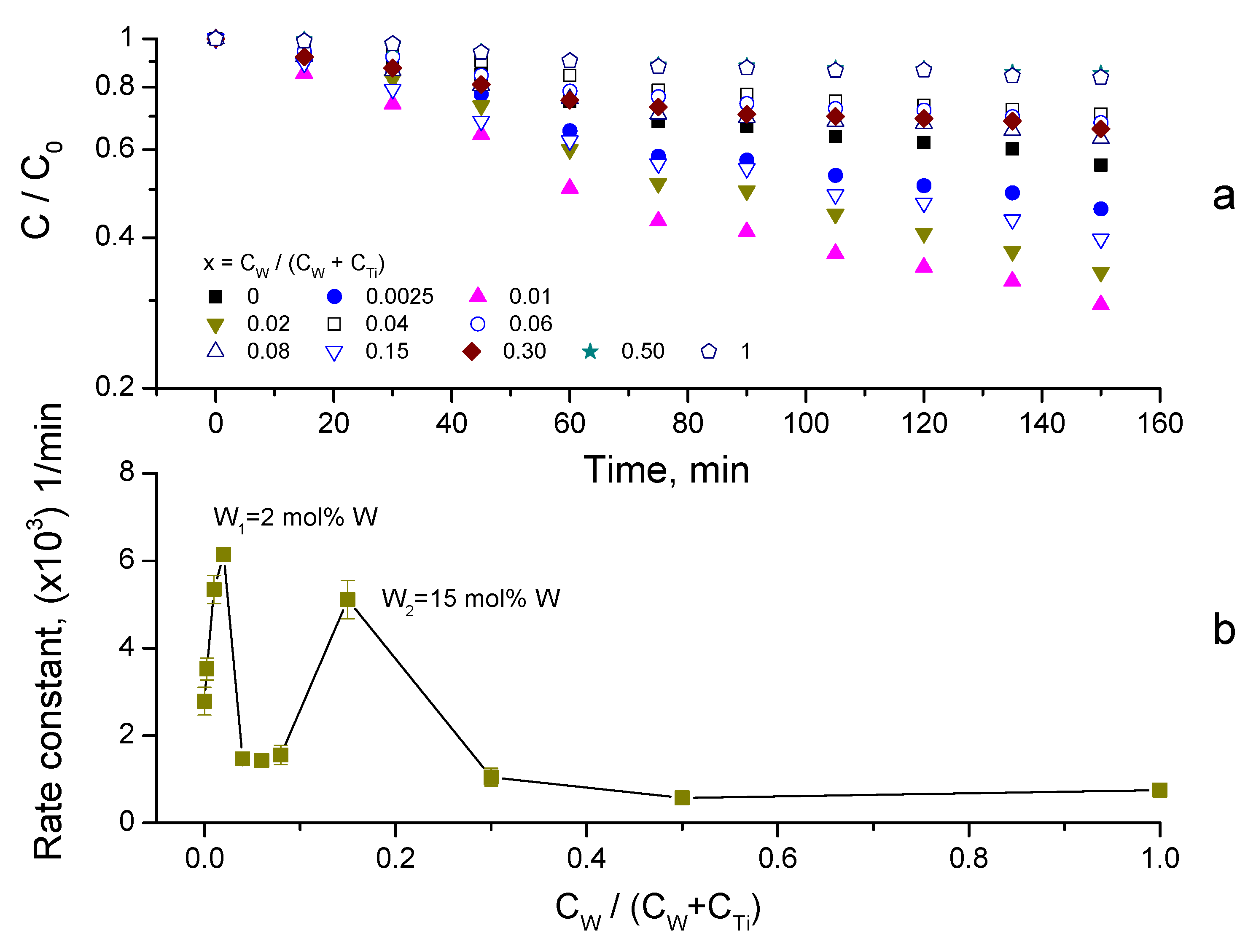
3.3. Photocatalytic Activity
3.4. Synergy of Adsorption and Photocatalysis
- –
- kNORM was greatly different for 0 ≤ CW/(CW + CTi) ≤ 0.02 and 0.04 ≤ CW/(CW + CTi) ≤ 1;
- –
- kNORM was stronger under sunlight illumination compared to UV-A, attaining the peak value at 15 mol% W.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishima, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Watanabe, T. TiO2 Photocatalysis: Fundamentals and Applications; BKC: Tokyo, Japan, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, K.; Irie, H.; Fujishima, A. TiO2 photocatalysis: A historical overview and future prospects. Jap. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 8269–8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Zhang, J.; Horiuchi, Y.; Anpo, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: Mechanisms and materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9919–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, K.; Ochiai, T.; Murakami, T.; Fujishima, A. Photoenergy conversion with TiO2 photocatalysis: New materials and recent applications. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharma, H.N.C.; Jaafar, J.; Widiastuti, N.; Matsuyama, H.; Rajabsadeh, S.; Othman, M.H.D.; Rahman, M.A.; Jafri, N.N.M.; Suhaimin, N.S.; Nasir, A.M.; et al. A review of titanium dioxide (TiO2)-based photocatalyst for oilfield-produced water treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baia, L.; Orbán, E.; Fodor, S.; Hampel, B.; Kedves, E.Z.; Saszet, K.; Székely, I.; Karácsonyi, É.; Réti, B.; Berki, P.; et al. Preparation of TiO2/WO3 composite photocatalysts by the adjustment of the semiconductors’ surface charge. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process 2016, 42, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. TiO2 photocatalysis: Design and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2012, 13, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Xiang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, X. High surface area, high catalytic activity titanium dioxide aerogels prepared by solvothermal crystallization. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 47, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.J.; Jameel, Z.N.; Al-Hussaini, I.H.M. Review on: Titanium dioxide applications. Energy Procedia 2019, 157, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Park, S.-J. TiO2 photocatalyst for water treatment applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X.; Tryk, D.A. TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2008, 63, 515–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, N.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Huo, S.; Cheng, P.; Peng, P.; Zhang, R.; et al. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using TiO2-based photocatalysts: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapertot, M.; Pichat, P.; Parra, S.; Guillard, C.; Pulgarin, C. Photocatalytic degradation of p-halophenols in TiO2 aqueous suspensions: Halogen effect on removal rate, aromatic intermediates and toxicity variations. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2006, 41, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadei, M.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mahvi, A.H.; Rabbani, S.; Naddafi, K. A comprehensive systematic review of photocatalytic degradation of pesticides using nano TiO2. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 13055–13071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Q.Y.; Li, H. Photocatalytic degradation of plastic waste: A mini review. Micromachines 2021, 12, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizama, C.; Bravo, C.; Caneo, C.; Ollino, M. Photocatalytic degradation of surfactants with immobilized TIO2: Comparing two reaction systems. Environ. Technol. 2005, 26, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peral, J.; Ollis, D.F. TiO2 photocatalyst deactivation by gas-phase oxidation of heteroatom organics. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1997, 115, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.D.; Tang, J.; Bi, X.G. Preparation of WO3-TiO2 photo-anode and its performance of photocatalytic hydrogen production by water splitting. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 8513–8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.-T.; Yap, P.-S.; Srinivasan, M.; Fane, A.G. TiO2/AC composites for synergistic adsorption-photocatalysis processes: Present challenges and further developments for water treatment and reclamation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 1173–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozzi, M.V.; Marzorati, S.; Longhi, M.; Coduri, M.; Artiglia, L.; Selli, E. Photocatalytic activity of TiO2-WO3 mixed oxides in relation to electron transfer efficiency. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 186, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Mendez, M.; Lemarchand, A.; Traore, M.; Perruchot, C.; Sassoye, C.; Selmane, M.; Nikravech, M.; Ben Amar, M.; Kanaev, A. Photocatalytic activity of nanocoatings based on mixed oxide V-TiO2 nanoparticles with controlled composition and size. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Chhor, K.; Passarello, J.-P.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Kanaev, A. Photocatalytic nanoparticulate ZrxTi1−xO2 coatings with controlled homogeneity of elemental composition. Chem. Select 2018, 3, 11118–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieng, S.; Kanaev, A.; Chhor, K. New homogeneously doped Fe(III)-TiO2 photocatalyst for gaseous pollutant degradation. Appl. Catal. A 2011, 399, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingmongkol, Y.; Trinh, D.T.T.; Channei, D.; Khanitchaidecha, W. Decomposition of dye pigment via photocatalysis process using CuO-TiO2 nanocomposite. Mater. Today Proceed. 2021, 47, 3441–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, P.; Nawaz, S.; Shafiq, I.; Nazir, A. Efficient visible light assisted photocatalysis using ZnO/TiO2 nanocomposites. Mol. Catal. 2023, 535, 112896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Hao, X.D.; Zhang, Y.X. Facile biphasic synthesis of TiO2-MnO2 nanocomposites for photocatalysis. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 19425–19428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, S.; Sivasankar, T.; Lana-Villarreal, T. Synthesis of TiO2/WO3 nanoparticles via sonochemical approach for the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under visible light illumination. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1964–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Rigamonti, M.G.; Patience, G.S.; Boffito, D.C. Spray dried TiO2/WO3 heterostructure for photocatalytic applications with residual activity in the dark. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 226, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaddad, M.; Ismail, A.A.; Alkhatham, N.; Alghamdi, Y.G. Co3O4 nanoparticles accommodated mesoporous TiO2 framework as an excellent photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic properties. Opt. Mater. 2022, 131, 112643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.B.; Nabi, G.; Rafique, M.; Khalid, N.R. Nanostructured-based WO3 photocatalysts: Recent development, activity enhancement, perspectives and applications for wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 2519–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Silveira, C.M.; Elangovan, E.; Neto, J.P.; Nunes, D.; Pereira, L.; Martins, R.; Viegas, J.; Moura, J.J.G.; Todorovic, S.; et al. Synthesis of WO3 nanoparticles for biosensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.C. Structure and properties of WO3 thin films for electrochromic device application. J. Non-Oxide Glass. 2013, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stapinski, T.; Marszalek, K.; Swatowska, B.; Stanco, A. Characterisation and application of WO3 films for electrochromic devices. In Proceedings of the SPIE 8902, Conference on Electron Technology, Ryn Castle, Poland, 16–20 April 2013; p. 890224. [Google Scholar]
- Riboni, F.; Bettini, L.G.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Selli, E. WO3-TiO2 vs. TiO2 photocatalysts: Effect of the W precursor and amount on the photocatalytic activity of mixed oxides. Catal. Today 2013, 209, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboni, F.; Dozzi, M.V.; Paganini, M.C.; Giamello, E.; Selli, E. Photocatalytic activity of TiO2-WO3 mixed oxides in formic acid oxidation. Catal. Today 2017, 287, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Xie, D.; Gao, L.; Cao, L.; Du, F. Synthesis and characterization of TiO2/WO3 composite nanotubes for photocatalytic applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Delgado, N.A.; Gracia-Pinilla, M.A.; Maya-Treviño, L.; Hinojosa-Reyes, L.; Guzman-Mar, J.L.; Hernández-Ramírez, A. Solar photocatalytic activity of TiO2 modified with WO3 on the degradation of an organophosphorus pesticide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrocinio, A.O.T.; Paula, L.F.; Paniago, R.M.; Freitag, J.; Bahnemann, D.W. Layer-by-layer TiO2/WO3 thin films as efficient photocatalytic self-cleaning surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16859–16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arce-Sarria, A.; Machuca-Martínez, F.; Bustillo-Lecompte, C.; Hernández-Ramírez, A.; Colina-Márquez, J. Degradation and loss of antibacterial activity of commercial amoxicillin with TiO2/WO3-assisted solar photocatalysis. Catalysts 2018, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Hu, X.; Wong, K.S.; Yu, J.C. WO3/TiO2 microstructures for enhanced photocatalytic oxidation. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2012, 91, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žerjav, G.; Arshad, M.S.; Djinović, P.; Zavašnik, J.; Pintar, A. Electron trapping energy states of TiO2-WO3 composites and their influence on photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 209, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinguu, H.; Bhuiyan, M.M.H.; Ikegami, T.; Ebihara, K. Preparation of TiO2/WO3 multilayer thin film by PLD method and its catalytic response to visible light. Thin Solid Films 2006, 506–507, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Silva, E.; Longo, C. Electrochemical and photocatalytic properties of TiO2/WO3 photoelectrodes. In Proceedings of the SPIE 7770, Solar Hydrogen and Nanotechnology V, San Diego, CA, USA, 24 August 2010; p. 777006. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.H.; Lee, W.I. Preparation of highly ordered cubic mesoporous WO3/TiO2 films and their photocatalytic properties. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akurati, K.K.; Vital, A.; Dellemann, J.P.; Michalow, K.; Graule, T.; Ferri, D.; Baiker, A. Flame-made WO3/TiO2 nanoparticles: Relation between surface acidity, structure and photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 79, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, M.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, H.; Sun, Z.; Shao, Q.; Guo, X.; Hao, L.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Heterostructured TiO2/WO3 nanocomposites for photocatalytic degradation of toluene under visible light. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, H1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.B.; Farman, S.; Rafique, M.; Shakil, M.; Khan, M.I.; Ijaz, M.; Mubeen, I.; Ashraf, M.; Riaz, K.N. Photocatalytic performance of hybrid WO3/TiO2 nanomaterials for the degradation of methylene blue under visible light irradiation. Int. J. Environ. Analyt. Chem. 2021, 101, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaritkaun, N.; Wootthikanokkhan, J.; Piewnuan, C.; Ngaotrakanwiwat, P.; Chiarakorn, S. Inducing catalytic activity in the dark of TiO2/WO3 mixed metal oxides by using an in situ polymerized semiconductive polymeric binder. Synth. React. Inorg. Metal-Org. Nano-Metal Chem. 2016, 46, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.A.; Madras, G. Photocatalytic degradation with combustion synthesized WO3 and WO3-TiO2 mixed oxides under UV and visible light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 105, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, W.I. Photocatalytic WO3/TiO2 nanoparticles working under visible light. J. Electroceram. 2006, 17, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Ouyang, H.; Tao, X.; Liu, C. One-pot synthesis of TiO2-WO3 composite nanocrystallites with improved photocatalytic properties under natural sunlight irradiation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 25, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohćević-Mitrović, Z.; Stojadinović, S.; Lozzi, L.; Aškrabić, S.; Rosić, M.; Tomić, N.; Paunović, N.; Lazović, S.; Nikolić, M.G.; Santucci, S. WO3/TiO2 composite coatings: Structural, optical and photocatalytic properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 83, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Liu, B.; Terashima, C.; Katsumata, K.I.; Suzuki, N.; Fujishima, A.; Sakai, H.; Nakata, K. Fabrication of efficient visible-light-responsive TiO2-WO3 hollow particle photocatalyst by electrospray method. Chem. Lett. 2017, 46, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B.; Vijayan, B.L.; Krishnan, S.G.; Harilal, M.; Basirun, W.J.; Lowe, A.; Yusoff, M.M.; Jose, R. Hydrothermal syntheses of tungsten doped TiO2 and TiO2/WO3 composite using metal oxide precursors for charge storage applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 740, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirvelan, J.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Thomas, A. Ethylene detection using TiO2-WO3 composite sensor for fruit ripening applications. Sens. Rev. 2017, 37, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, J. TiO2/WO3 photoanodes with enhanced photocatalytic activity for air treatment in a polymer electrolyte cell. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2012, 16, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Chen, Y.-W. Anticorrosion of WO3-modified TiO2 thin film prepared by peroxo sol-gel method. Mod. Res. Catal. 2020, 9, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Liang, C.; Shao, G. Construction of solid-state z-scheme carbon-modified TiO2/WO3 nanofibers with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production. J. Pow. Sour. 2016, 328, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaraldo, T.T.; Gonçales, V.R.; Silva, B.F.; de Torresi, S.I.C.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Hydrogen production and simultaneous photoelectrocatalytic pollutant oxidation using a TiO2/WO3 nanostructured photoanode under visible light irradiation. J. Electroanalyt. Chem. 2016, 765, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Gil, K.R.; Stephens, Z.D.; Stavila, V.; Robinson, D.B. Composite WO3/TiO2 nanostructures for high electrochromic activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Gan, W.; Qiu, Z.; Zhan, X.; Qiang, T.; Li, J. Preparation of heterostructured WO3/TiO2 catalysts from wood fibers and its versatile photodegradation abilities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M.; Shangguan, W. Photocatalytic energy storage ability of TiO2-WO3 composite prepared by wet-chemical technique. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaotrakanwiwat, P.; Tatsuma, T.; Saitoh, S.; Ohko, Y.; Fujishima, A. Charge-discharge behavior of TiO2-WO3 photocatalysis systems with energy storage ability. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 3234–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuma, T.; Takeda, S.; Saitoh, S.; Ohko, Y.; Fujishima, A. Bactericidal effect of an energy storage TiO2-WO3 photocatalyst in dark. Electrochem. Commun. 2003, 5, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, S.; Rocha, K.O.; Rodrigues, J.A.J.; Longo, E. Soft-chemical synthesis, characterization and humidity sensing behavior of WO3/TiO2 nanopowders. Sens. Actuat. B 2014, 190, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmas, S.; Castresana, P.A.; Mais, L.; Vacca, A.; Mascia, M.; Ricci, P.C. TiO2-WO3 nanostructured systems for photoelectrochemical applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 101671–101682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boga, B.; Székely, I.; Pap, Z.; Baia, L.; Baia, M. Detailed spectroscopic and structural analysis of TiO2/WO3 composite semiconductors. J. Spectrosc. 2018, 2018, 6260458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Deng, F.; Min, L.; Luo, S.; Guo, B.; Zeng, G.; Au, C. Facile one-step synthesis of inorganic-framework molecularly imprinted TiO2/WO3 nanocomposite and its molecular recognitive photocatalytic degradation of target contaminant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7404–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, G.; Zhang, H. The photocatalytic applications of TiO2-WO3 heterostructure in methylene blue. Am. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2019, 61, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Paula, L.F.; Hofer, M.; Lacerda, V.P.B.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Patrocinio, A.O.T. Unraveling the photocatalytic properties of TiO2/WO3 mixed oxides. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 2469–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce-Sarria, A.; Caicedo-Rosero, C.L.; Lara-Ramos, J.A.; Diaz-Angulo, J.; Machuca-Martínez, F. Experimental data on synthesis and characterization of WO3/TiO2 as catalyst. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Li, R.; Li, M.; Pei, J.; Guo, F.; Zhang, S. Photocatalytic efficiencies of WO3/TiO2 nanoparticles for exhaust decomposition under UV and visible light irradiation. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 095029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shi, R.; Zhang, K.; Hu, Y.; Tang, A.; Li, X. Synthesis of WO3/TiO2 nanocomposites via sol-gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 398, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.T.; Ni, H.W.; Chen, R.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.W.; Li, J.H. One-step hydrothermal preparation of TiO2/WO3 nanocomposite films on anodized stainless steel for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Thin Solid Films 2013, 548, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, V.; Mokaya, R.; Puma, G.L. Novel one step hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2/WO3 nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem. Commun. 2007, 45, 4749–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugunthan, E.; Saidutta, M.B.; Jagadeeshbabu, P.E. Visible light assisted photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac using TiO2-WO3 mixed oxide catalysts. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monitor. Manag. 2018, 10, 322–330. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, L.; Alves, A. Photocatalytic properties of TiO2 and TiO2/WO3 films applied as semiconductors in heterogeneous photocatalysis. Mater. Lett. 2018, 211, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, D.; Fuentes, S.; Castro-Alvarez, A.; Chavez-Angel, E. Review on sol-gel synthesis of perovskite and oxide nanomaterials. Gels 2021, 7, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saepurahman, A.M.A.; Abdullah, M.A.; Chong, F.K. Dual-effects of adsorption and photodegradation of methylene blue by tungsten-loaded titanium dioxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couselo, N.; Einschlag, F.S.G.; Candal, R.J.; Jobbagy, M. Tungsten-doped TiO2 vs. pure TiO2 photocatalysts: Effects on photobleaching kinetics and mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azouani, R.; Soloviev, A.; Benmami, M.; Chhor, K.; Bocquet, J.-F.; Kanaev, A. Stability and growth of titanium-oxo-alcoxy TixOy(OiPr)z clusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 16243–16248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbeau-Justin, C.; Kunst, M.; Huguenin, D. Structural influence on charge-carrier lifetimes in TiO2 powders studied by microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Chhor, K.; Kanaev, A. Solvent effect on nucleation-growth of titanium-oxo-alkoxy nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 672, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Mendez, M.; Jia, Z.; Traore, M.; Ben Amar, M.; Nikravech, M.; Kanaev, A. Nucleation and growth of mixed vanadium-titanium oxo-alkoxy nanoparticles in sol-gel synthesis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 610, 125636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribb, A.A.; Banfield, J.F. Particle size effects on transformation kinetics and phase stability in nanocrystalline TiO2. Am. Miner. 1997, 82, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Wang, S.; Yu, W.; Huang, T.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, C.; Chen, X.; Hao, J.; Dai, N. Ultrasensitive ppb-level H2S gas sensor at room temperature based on WO3/rGO hybrids. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 5008–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, J.; Real, C. Mechanism of the inhibiting effect of phosphate on the anatase → rutile transformation induced by thermal and mechanical treatment of TiO2. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1983, 79, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdennouri, M.; Elmoubarki, R.; Elmhammedi, A.; Galadi, A.; Baâlala, M.; Bensitel, M.; Boussaoud, A.; El Hafiane, Y.; Smith, A.; Barka, N. Influence of tungsten on the anatase-rutile phase transition of sol-gel synthesized TiO2 and on its activity in the photocatalytic degradation of pesticides. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 953–960. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H.Q.; Huynh, T.T.; Bich, H.N.; Pham, T.M.; Nguyen, S.T.; Lu, L.T.; Ho, V.T.T. Tungsten-doped titanium-dioxide-supported low-Pt-loading electrocatalysts for the oxidation reaction of ethanol in acidic fuel cells. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2019, 22, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, S.; Bhachu, D.S.; Lu, Y.; Chadwick, N.; Althabaiti, S.A.; Alyoubi, A.O.; Basahel, S.N.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P. Tungsten doped TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic and optoelectrical properties via aerosol assisted chemical vapor deposition. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, R.; Khan, S. Fabrication of WO3-reduced graphene oxide (WO3-G) nanocomposite for enhanced optical and electrical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 8370–8384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Sarukawa, K.; Tokieda, K.; Matsumura, M. Morphology of a TiO2 photocatalyst (Degussa, P-25) consisting of anatase and rutile crystalline phases. J. Catal. 2001, 203, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y. Adsorption of methylene blue by coal-based activated carbon in high-salt wastewater. Water 2022, 14, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largitte, L.; Pasquier, R. A review of the kinetics adsorption models and their application to the adsorption of lead by an activated carbon. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-Y.; Léonard, A.; Lemaire, A.; Tian, G.; Su, B.-L. Self-formation phenomenon to hierarchically structured porous materials: Design, synthesis, formation mechanism and applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2763–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouslama, M.; Amamra, M.C.; Jia, Z.; Ben Amar, M.; Brinza, O.; Chhor, K.; Abderrabba, M.; Vignes, J.-L.; Kanaev, A. New nanoparticulate TiO2-Al2O3 photocatalytic media: Effect of particle size and polymorphism on photocatalytic activity. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, B. Titania photocatalysis beyond recombination: A critical review. Catalysts 2013, 3, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Q.; Miao, T.; Wang, H.; Tang, J. Insight on shallow trap states-introduced photocathodic performance in n-type polymer photocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | Optimal W Loading mol% | Illumination | Enhancement | Pollutant (1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sol–gel | 3 | UV-A | 2.1 | Formic acid | [35] |
| Hydrothermal | 1 | Sunlight | ~3 | Rhodamine B | [52] |
| Sol–gel | 2 | Sunlight | 2.1 | Malathion pesticide | [38] |
| Physical mixing | 10–15 | UV-A/visible | 2.0 | Methylene blue and orange G | [50] |
| Sol–gel | 1 | UV-A | 2.5 | Formic acid | [36] |
| Sol–gel | 0.02–1 | UV-A | 2.3 | Cr2O72− | [21] |
| Ultrasound- assisted | 5.4 | Visible | 3.9 | Methylene blue | [28] |
| PLD | - (2) | Visible | - | Methylene blue | [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, K.; Heng, S.; Tieng, S.; David, F.; Dine, S.; Haddad, O.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Traore, M.; Kanaev, A. Mixed Metal Oxide W-TiO2 Nanopowder for Environmental Process: Synergy of Adsorption and Photocatalysis. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090765
Cheng K, Heng S, Tieng S, David F, Dine S, Haddad O, Colbeau-Justin C, Traore M, Kanaev A. Mixed Metal Oxide W-TiO2 Nanopowder for Environmental Process: Synergy of Adsorption and Photocatalysis. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(9):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090765
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Khley, Socheata Heng, Siteng Tieng, Ford David, Sarah Dine, Oriana Haddad, Christophe Colbeau-Justin, Mamadou Traore, and Andrei Kanaev. 2024. "Mixed Metal Oxide W-TiO2 Nanopowder for Environmental Process: Synergy of Adsorption and Photocatalysis" Nanomaterials 14, no. 9: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090765
APA StyleCheng, K., Heng, S., Tieng, S., David, F., Dine, S., Haddad, O., Colbeau-Justin, C., Traore, M., & Kanaev, A. (2024). Mixed Metal Oxide W-TiO2 Nanopowder for Environmental Process: Synergy of Adsorption and Photocatalysis. Nanomaterials, 14(9), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090765







