Nanostructured Solid/Liquid Acid Catalysts for Glycerol Esterification: The Key to Convert Liability into Assets
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Biorefinery Concept
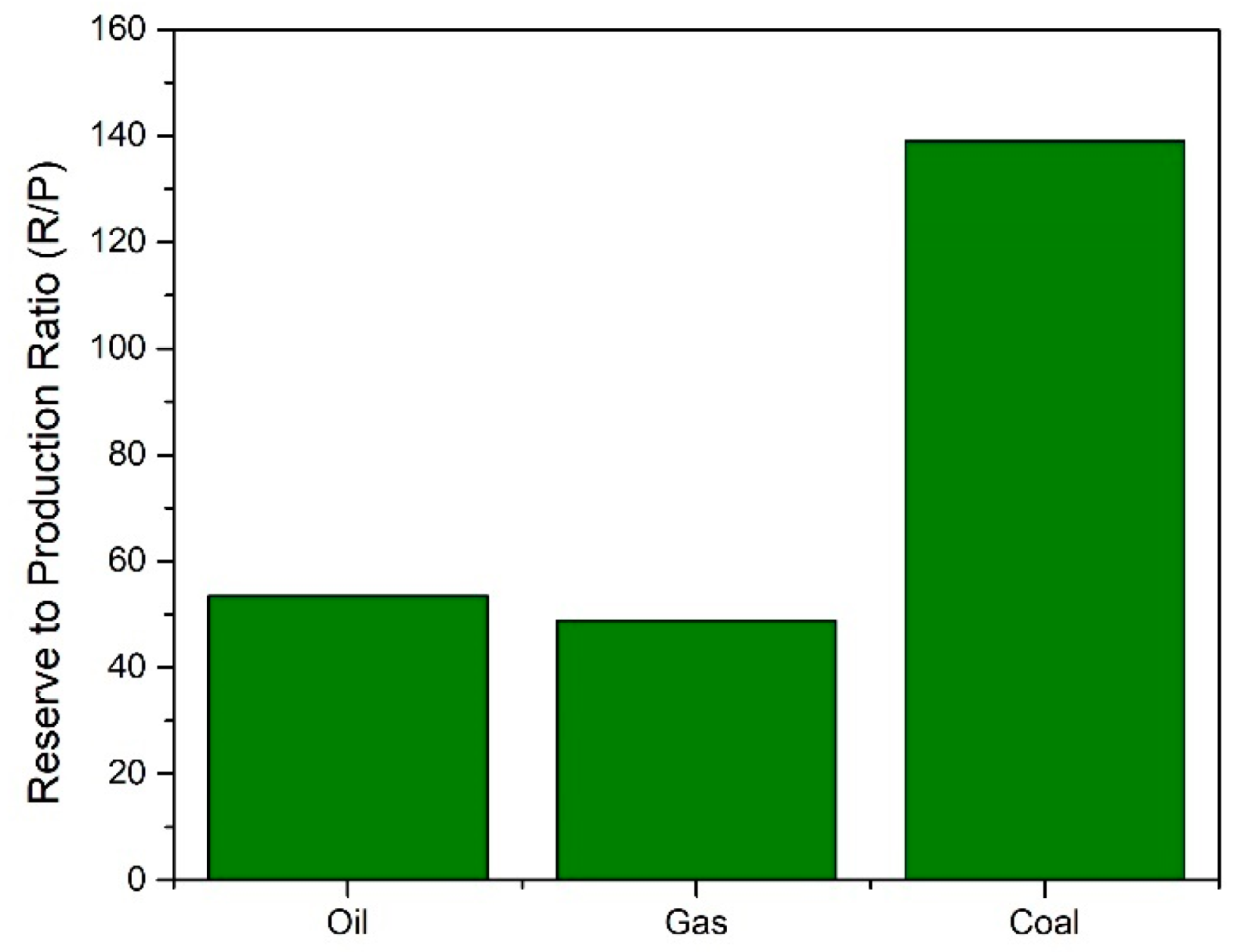
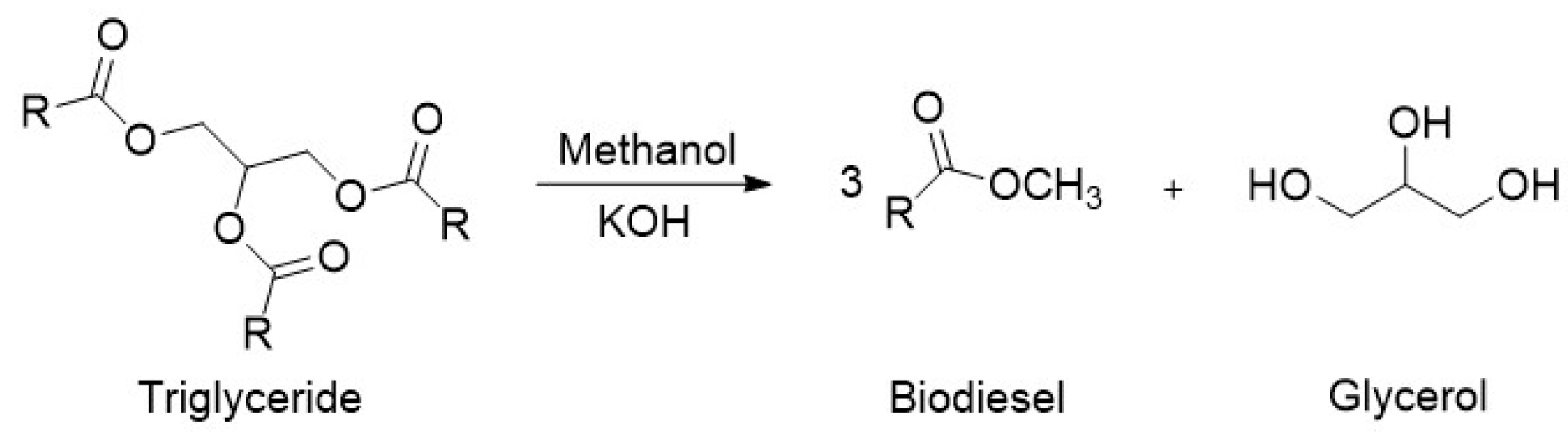
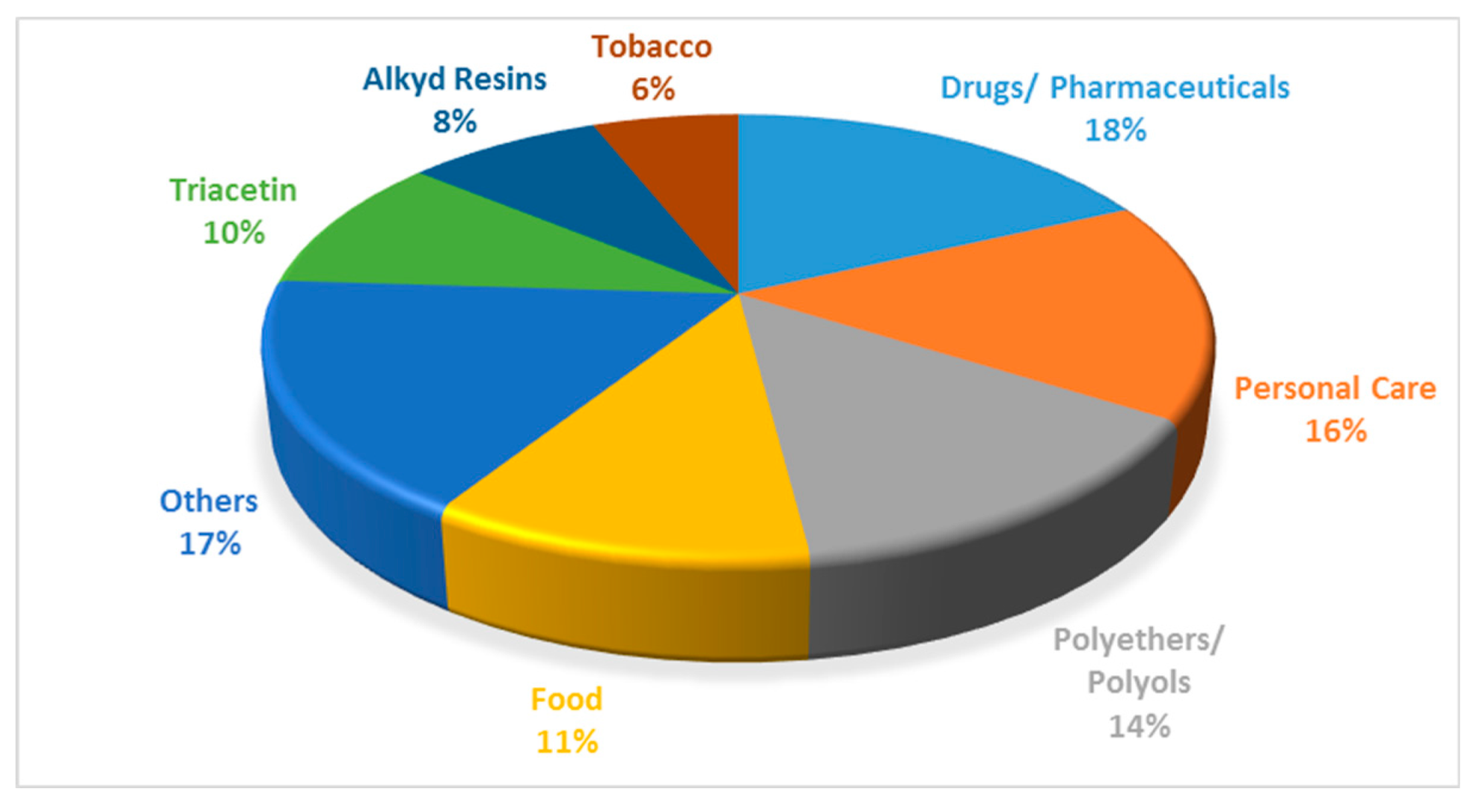
1.2. Glycerol: A Liability from Biodiesel Industry
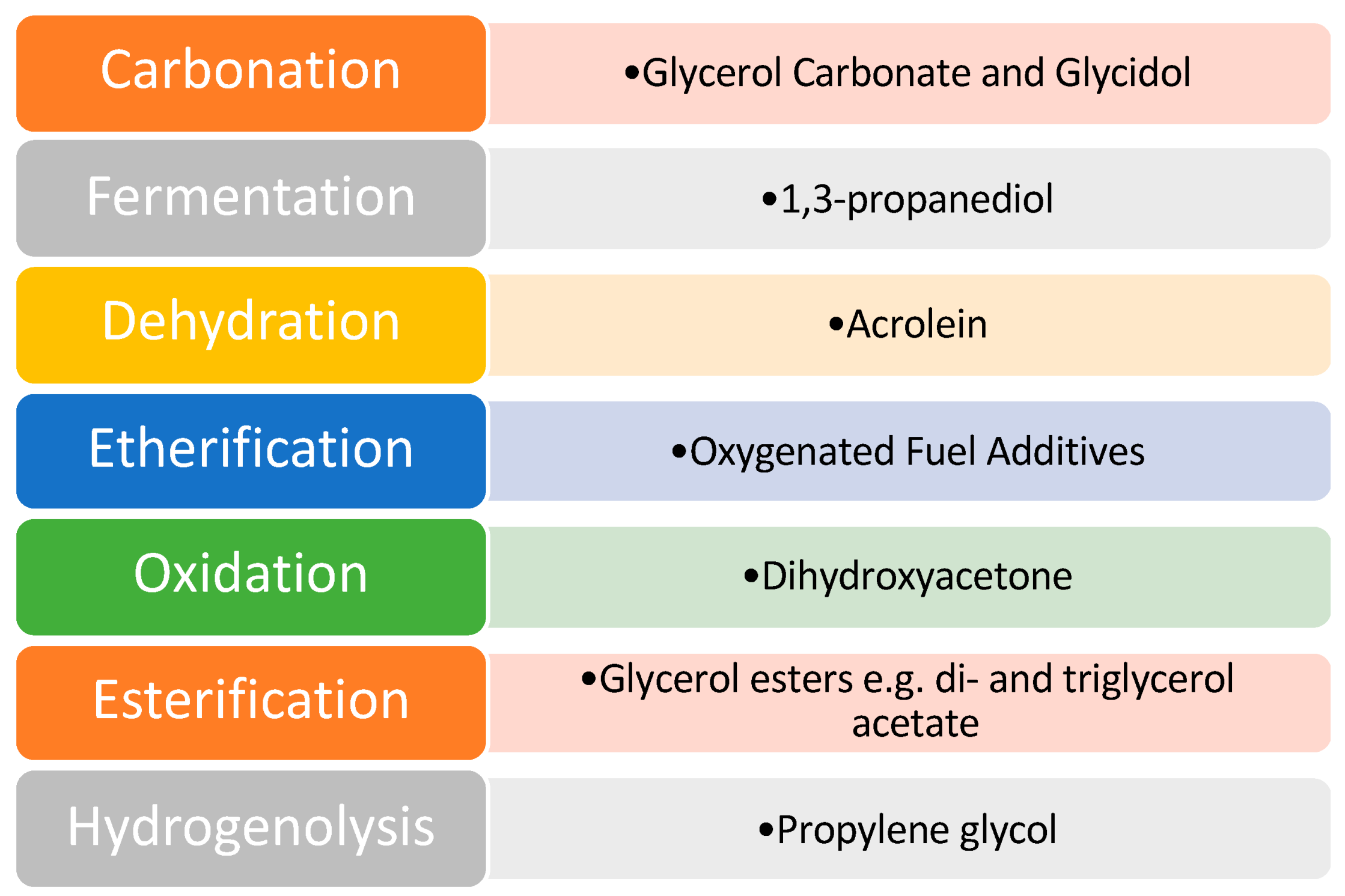
1.3. Upgrading Glycerol to Value-Added Glycerol Esters: The Key to Convert a Liability into an Asset
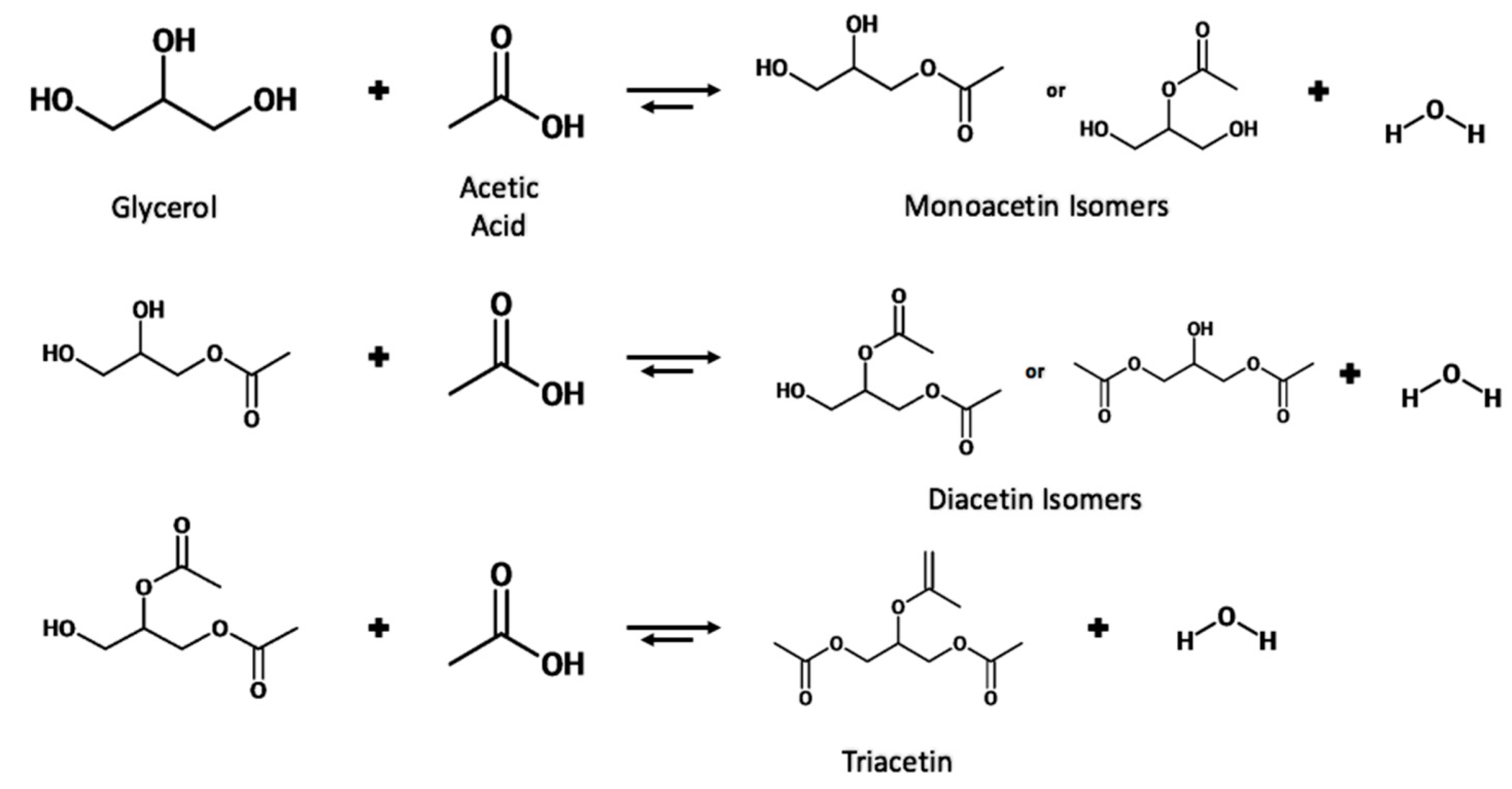
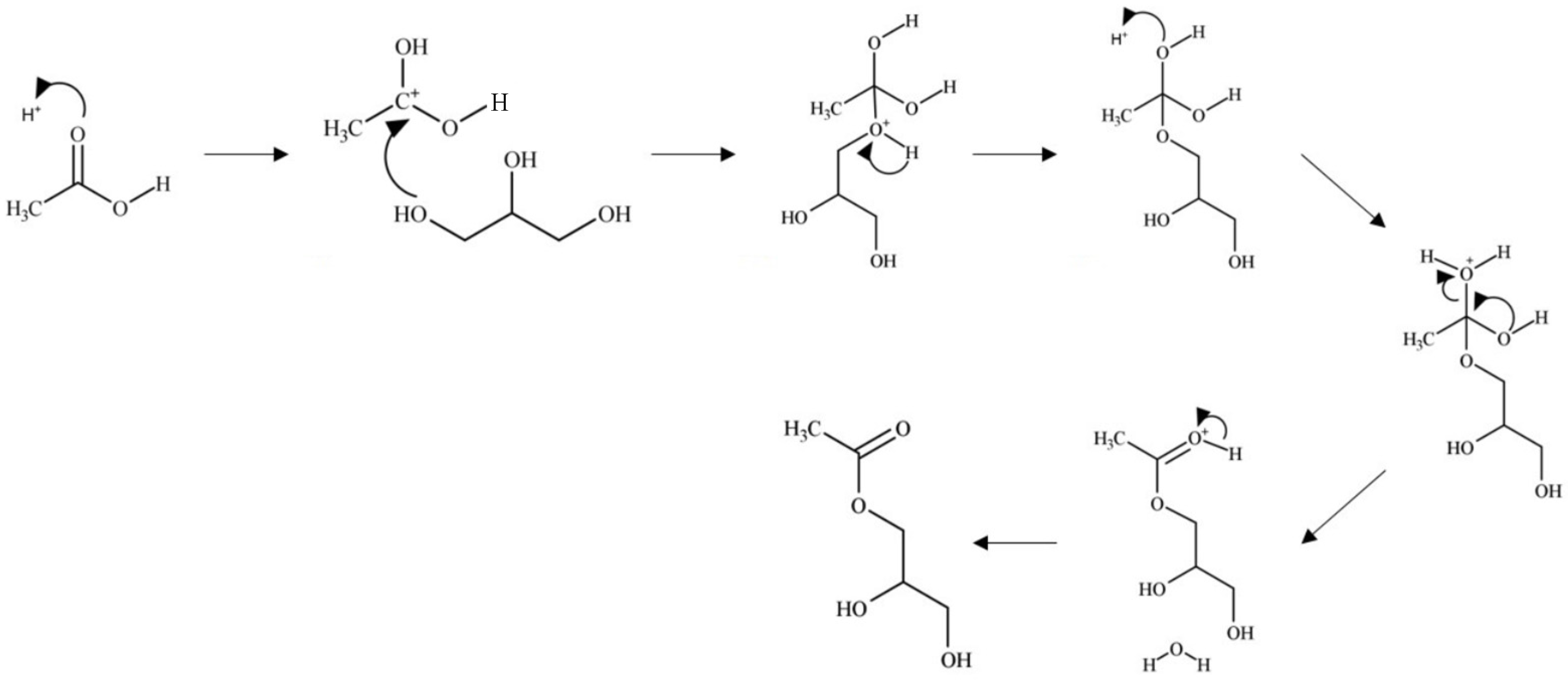
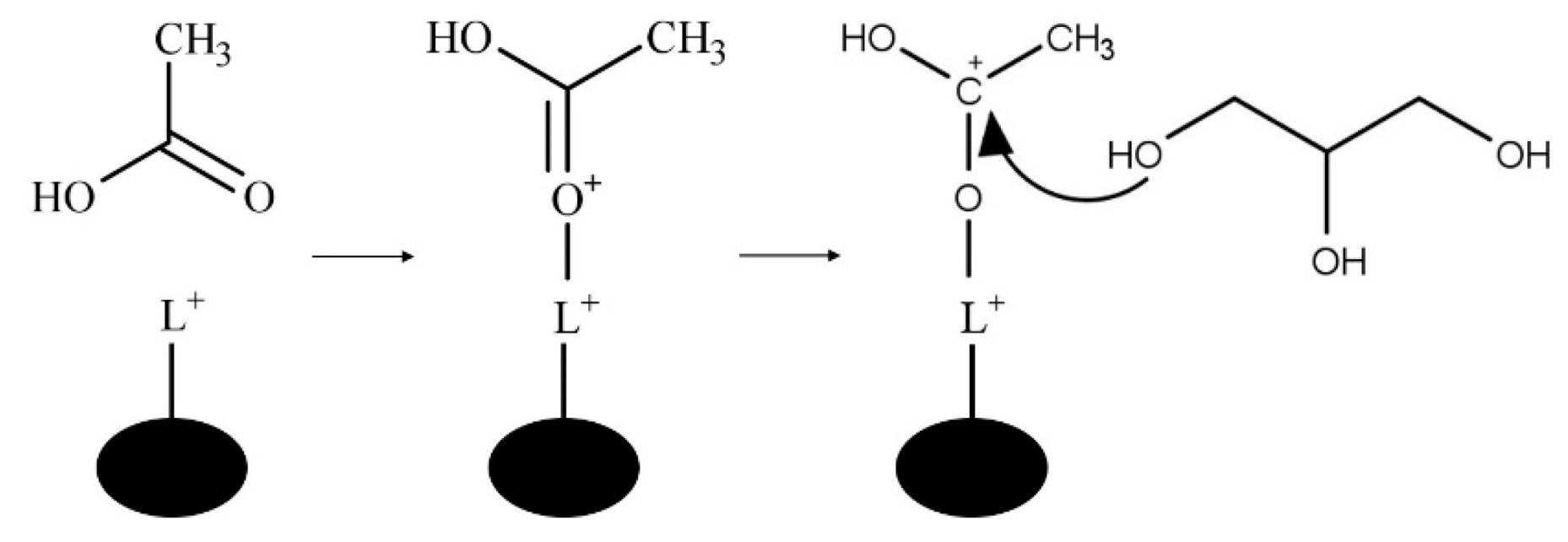
1.4. Reaction Mechanism for Esterification of Glycerol
2. Nanostructured Solid/Liquid Acid Catalysts for Glycerol Esterification
2.1. Homogeneous Catalysts Used in the Esterification of Glycerol
| Structure | Reaction Conditions | Performance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
 | T = 75 °C t = 2 h Molar ratio acetic acid:glycerol = 3:1 Catalyst = 1 mL | C = 100% S = 17.1% MA 58.8% DA 24.1% TA | [49] |
 | T = 120 °C t = 6 h Molar ratio acetic acid:glycerol = 8:1 Catalyst = 6.25 mol% | Y = 95.6% TA | [50] |
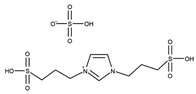 | T = 100 °C t = 30 min Molar ratio acetic acid:glycerol = 8:1 Catalyst = 0.1 mol% | C = 95.0% S = 43.1% MA 51.4% DA 5.5% TA | [51] |
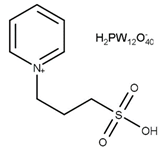 | T = 105 °C t = 6 h Molar ratio acetic acid:glycerol = 10:1 Catalyst = 2.5 mol% | C = 100% S = 2.3% MA 40.0% DA 57.7% TA | [45] |
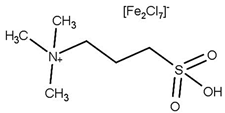 | T = Reflux t = 4 h Molar ratio acetic acid:glycerol = 5:1 Catalyst = 0.3 mol% Solvent = 30 mL toluene | Y = 98.6% TA | [53] |
2.2. Heterogeneous Catalysts Used in the Esterification of Glycerol
2.2.1. Metal Oxide Catalysts
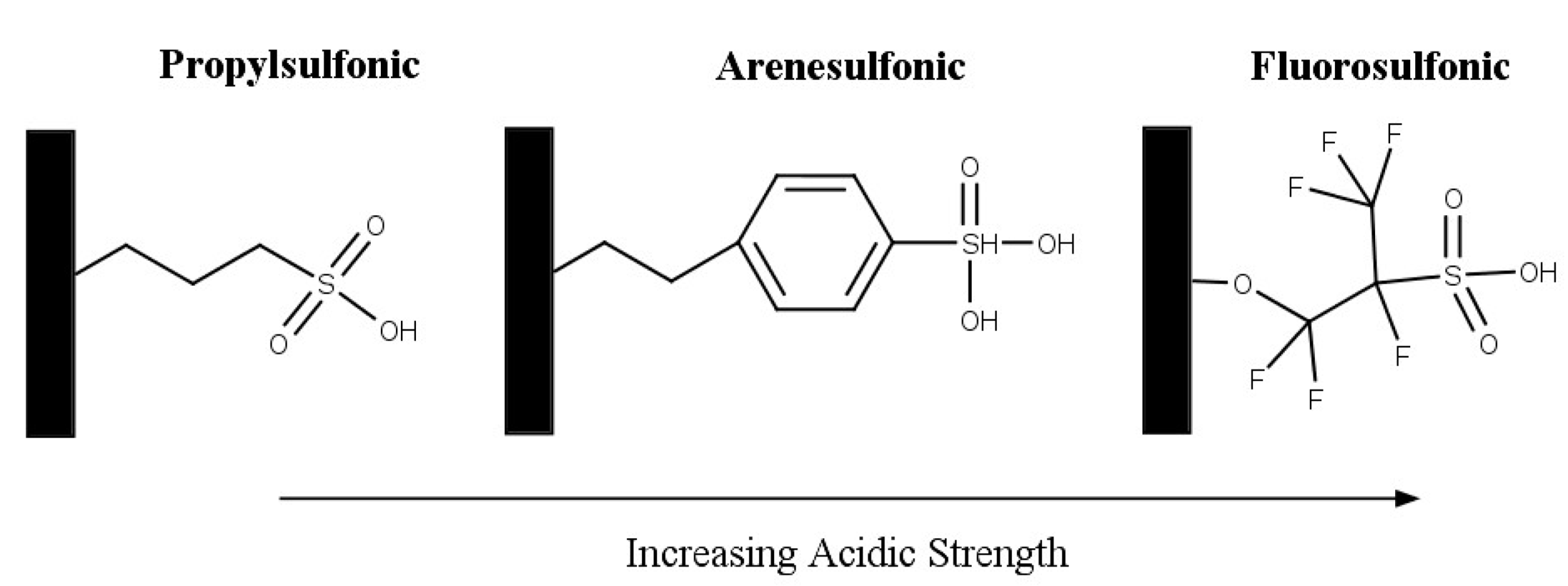
2.2.2. Ion-Exchange Resins
2.2.3. Zeolite-Based Solid Acids
2.2.4. Silica-Based Solid Acids
2.2.5. Heteropolyacids (HPAs)
2.2.6. Carbon-Based Catalysts
2.2.7. Others
2.2.8. Comparison of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysts
2.2.9. Techno-Economic Assessment and Sensitivity Analysis of Glycerol Esterification
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BP Sustainability Report. 2020. Available online: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/sustainability/group-reports/bp-sustainability-report-2020.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- BP Statistical Review of World Energy. 2019. Available online: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2019-full-report.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Cherubini, F. The biorefinery concept: Using biomass instead of oil for producing energy and chemicals. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.K.; Goswami, R. A review of production, properties and advantages of biodiesel. Biofuels 2018, 9, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, L.C.; Vidya Sagar, D.; Naik, S.N. Technical aspects of biodiesel production by transesterification—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2006, 10, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemical Book—Glycerol. Available online: https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB5339206.htm (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- PubChem—Glycerol. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Glycerin (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Morrison, L.R. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pagliaro, M.; Ciriminna, R.; Kimura, H.; Rossi, M.; Della Pina, C. From Glycerol to Value-Added Products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4434–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Pina, C.D.; Rossi, M.; Pagliaro, M. Understanding the glycerol market. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.S.; Aroua, M.K.; Daud, W.M.A.W.; Lee, H.V.; Cognet, P.; Pérès, Y. Catalytic role of solid acid catalysts in glycerol acetylation for the production of bio-additives: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68885–68905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chozhavendhan, S.; Praveen Kumar, R.; Elavazhagan, S.; Barathiraja, B.; Jayakumar, M.; Varjani, S.J. Waste to Wealth; Singhania, R.R., Agarwal, R.A., Kumar, R.P., Sukumaran, R.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Luo, X.; Wan, C.; Li, Y. Characterization of Crude Glycerol from Biodiesel Plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5915–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.T.; Taconi, K.A. The glycerin glut: Options for the value-added conversion of crude glycerol resulting from biodiesel production. Environ. Prog. 2007, 26, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inrirai, P.; Keogh, J.; Centeno-Pedrazo, A.; Artioli, N.; Manyar, H. Recent advances in processes and catalysts for glycerol carbonate production via direct and indirect use of CO2. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 80, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, J.; Deshmukh, G.; Manyar, H. Green Synthesis of Glycerol Carbonate via Transesterification of Glycerol Using Mechanochemically Prepared Sodium Aluminate Catalysts. Fuel 2022, 310, 122484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralphs, K.; Collins, G.; Manyar, H.; James, S.L.; Hardacre, C. Selective Hydrogenation of Stearic Acid Using Mechanochemically Prepared Titania-Supported Pt and Pt–Re Bimetallic Catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 6934–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, J.; Jeffrey, C.; Tiwari, M.S.; Manyar, H. Kinetic Analysis of Glycerol Esterification Using Tin Exchanged Tungstophosphoric Acid on K-10. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 19095–19103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, M.S.; Wagh, D.; Dicks, J.S.; Keogh, J.; Ansaldi, M.; Ranade, V.V.; Manyar, H.G. Solvent Free Upgrading of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) with Levulinic Acid to HMF Levulinate Using Tin Exchanged Tungstophosphoric Acid Supported on K-10 Catalyst. ACS Org. Inorg. Au 2023, 3, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumdar, N.J.; Kumar, P.; Arredondo-Arechavala, M.; Artioli, N.; Manyar, H. Structure sensitivity of Cu supported on manganese oxide catalysts in levulinic acid hydrogenation. Catal. Sci. Tech. 2023, 14, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, N.J.; Kumar, P.; Arredondo-Arechavala, M.; Artioli, N.; Manyar, H. Intensifying levulinic acid hydrogenation using mechanochemically prepared copper on manganese oxide catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyar, H.; Yadav, G.D. Synthesis of a Novel Redox Material UDCaT-3: An Efficient and Versatile Catalyst for Selective Oxidation, Hydroxylation and Hydrogenation Reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skillen, N.; Ralphs, K.; Craig, D.; McCalmont, S.; Muzio, A.F.V.; O’Rourke, C.; Manyar, H.; Robertson, P. Photocatalytic Reforming of Glycerol to H2 in a Thin Film Pt-TiO2 Recirculating Photo Reactor. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, K.; Jeffrey, C.; Keogh, J.; Tiwari, M.S.; Artioli, N.; Manyar, H. Techno-Economic Assessment and Sensitivity Analysis of Glycerol Valorization to Biofuel Additives via Esterification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 9201–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubek, T.; Ralphs, K.; Kotarba, A.; Manyar, H. Nanostructured Potassium-Manganese Oxides Decorated with Pd Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Low-Temperature Soot Oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisu, J.; Gao, N.; Quan, C.; Yanik, J.; Artioli, N. Co-Gasification of Rice Husk and Plastic in the Presence of CaO Using a Novel ANN Model-Incorporated Aspen plus Simulation. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 108, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.; Zhang, G.; Gao, N.; Su, S.; Artioli, N.; Feng, D. Behavior Study of Migration and Transformation of Heavy Metals during Oily Sludge Pyrolysis. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 8311–8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, E.L.; O’Donnell, R.; Gilmore, M.; Artioli, N.; Holbrey, J.D.; Swadźba-Kwaśny, M. Hydrophobic Functional Liquids Based on Trioctylphosphine Oxide (TOPO) and Carboxylic Acids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 24744–24763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoldi, L.; Matarrese, R.; Kubiak, L.; Daturi, M.; Artioli, N.; Pompa, S.; Lietti, L. In-Depth Insights into N2O Formation over Rh- and Pt-Based LNT Catalysts. Catal. Today 2019, 320, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilleng, M.T.; Gimba, E.C.; Ndukwe, G.I.; Bugaje, I.M.; Rooney, D.W.; Manyar, H.G. Batch to Continuous Photocatalytic Degradation of Phenol Using TiO2 and Au-Pd Nanoparticles Supported on TiO2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6382–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, R.; Ralphs, K.; Grolleau, M.; Manyar, H.; Artioli, N. Doping Manganese Oxides with Ceria and Ceria Zirconia Using a One-Pot Sol–Gel Method for Low Temperature Diesel Oxidation Catalysts. Top Catal. 2020, 63, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coney, C.; Hardacre, C.; Morgan, K.; Artioli, N.; York, A.P.E.; Millington, P.; Kolpin, A.; Goguet, A. Investigation of the oxygen storage capacity behaviour of three way catalysts using spatio-temporal analysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 258, 117918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietti, L.; Righini, L.; Castoldi, L.; Artioli, N.; Forzatti, P. Labeled 15NO study on N2 and N2O formation over Pt-Ba/Al2O3 NSR catalysts. Top. Catal. 2013, 56, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.R.; Mazumdar, N.J.; Centeno-Pedrazo, A.; Artioli, N.; Manyar, H. Recent Advances in Catalyst Design for Carboxylation Using CO2 as the C1 Feedstock. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaloni, M.; Centeno-Pedrazo, A.; Avanzi, S.; Mazumdar, N.J.; Manyar, H.; Artioli, N. Novel Ionic Liquid synthesis of highly selective catalysts for the direct hydrogenation of CO2 to short chain hydrocarbons. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilleng, M.T.; Artioli, N.; Rooney, D.; Manyar, H. Continuous Flow Photocatalytic Degradation of Phenol Using Palladium@Mesoporous TiO2 Core@Shell Nanoparticles. Water 2023, 15, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaloni, M.; Marchionni, M.; Abbá, A.; Mascia, M.; Tola, V.; Carpanese, M.P.; Bertanza, G.; Artioli, N. Exploring the Viability of Utilizing Treated Wastewater as a Sustainable Water Resource for Green Hydrogen Generation Using Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells (SOECs). Water 2023, 15, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethiraj, J.; Wagh, D.; Manyar, H. Advances in Upgrading Biomass to Biofuels and Oxygenated Fuel Additives Using Metal Oxide Catalysts. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, A.; Nabi, M.N.; Bodisco, T.A.; Hossain, F.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Ristovski, Z.D.; Brown, R.J. The effect of triacetin as a fuel additive to waste cooking biodiesel on engine performance and exhaust emissions. Fuel 2016, 182, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, A.; Ruiz, J.R.; Ramos, M.J.; Pérez, Á. Effects of Triacetin on Biodiesel Quality. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4481–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triacetin/Glyceral Triacetate Market to Reach USD 255.6 Million by 2026|Reports and Data. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2019/07/15/1882588/0/en/Triacetin-Glyceral-Triacetate-Market-To-Reach-USD-255-6-Million-By-2026-Reports-And-Data.html#:~:text=According%20to%20the%20current%20analysis,of%20glycerol%20and%20acetic%20acid (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Konwar, L.J.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Begum, P.; Kumar, N.; Thakur, A.J.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Deka, R.C.; Deka, D. Shape selectivity and acidity effects in glycerol acetylation with acetic anhydride: Selective synthesis of triacetin over Y-zeolite and sulfonated mesoporous carbons. J. Catal. 2015, 329, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebel, B.; Mittelbach, M.; Uray, G. Determination of the Composition of Acetylglycerol Mixtures by 1H NMR Followed by GC Investigation. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8712–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; An, S.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Song, D.; Shang, Q. Selective esterification of glycerol with acetic acid or lauric acid over rod-like carbon-based sulfonic acid functionalized ionic liquids. Fuel 2017, 207, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-Y.; Han, X.-X.; Hung, C.-T.; Lin, J.-C.; Wu, P.-H.; Wu, J.-C.; Liu, S.-B. Heteropolyacid-based ionic liquids as efficient homogeneous catalysts for acetylation of glycerol. J. Catal. 2014, 320, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncea, S.B.; Wuttke, S.; Kemnitz, E.; Coman, S.M.; Parvulescu, V.I. Hydroxylated magnesium fluorides as environmentally friendly catalysts for glycerol acetylation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 107, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Paul, S. Solid acids: Green alternatives for acid catalysis. Catal. Today 2014, 236, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaeezadeh, M.; Alinezhad, H. Brønsted acidic ionic liquids: Green catalysts for essential organic reactions. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 218, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Shi, F.; Beng, J.; Qiao, K. Ionic liquid as a green catalytic reaction medium for esterifications. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2001, 165, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, S.-T.; Xie, C.-X.; Liu, F.-S.; Li, H.-J. Synthesis of glycerol triacetate using functionalized ionic liquid as catalyst. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Yan, P.; Welz-Biermann, U. Esterification of glycerol with acetic acid using double SO3H-functionalized ionic liquids as recoverable catalysts. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, J.; Tiwari, M.S.; Manyar, H. Esterification of Glycerol with Acetic Acid Using Nitrogen-Based Brønsted-Acidic Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 17235–17243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, A.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Yu, S.; Xie, C.; Liu, F. Synthesis of Glycerol Triacetate Using a Brønsted–Lewis Acidic Ionic Liquid as the Catalyst. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolean, I.; Pavel, O.D.; Manyar, H.G.; Taylor, S.F.R.; Ralphs, K.; Goodrich, P.; Pârvulescu, V.I.; Hardacre, C. SCILLs as selective catalysts for the oxidation of aromatic alcohols. Catal. Today 2019, 333, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.E.; Laier, L.O.; Cardoso, A.L.; Da Silva, M.J. Bioadditive synthesis from H3PW12O40-catalyzed glycerol esterification with HOAc under mild reaction conditions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 102, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.J.; Liberto, N.A.; De Andrade Leles, L.C.; Pereira, U.A. Fe4(SiW12O40)3− catalyzed glycerol acetylation: Synthesis of bioadditives by using highly active Lewis acid catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 422, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, D.M.; Ferreira, S.O.; Chagas da Silva, R.; Natalino, R.; Da Silva, M.J. Glycerol Esterification over Sn(II)-Exchanged Keggin Heteropoly Salt Catalysts: Effect of Thermal Treatment Temperature. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7705–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Xu, J. Selective esterification of glycerol with acetic acid to diacetin using antimony pentoxide as reusable catalyst. J. Energy Chem. 2015, 24, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallesham, B.; Sudarsanam, P.; Reddy, B.M. Production of Biofuel Additives from Esterification and Acetalization of Bioglycerol over SnO2-Based Solid Acids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18775–18785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.S.; Sudarsanam, P.; Raju, G.; Reddy, B.M. Selective acetylation of glycerol over CeO2–M and SO42−/CeO2–M (M = ZrO2 and Al2O3) catalysts for synthesis of bioadditives. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.M.; Britto, P.J.; Narula, A.; Saqline, S.; Anand, D.; Bhagyalakshmi, C.; Herle, R.N. Kinetic studies on the synthesis of fuel additives from glycerol using CeO2–ZrO2 metal oxide catalyst. Biofuel Res. J. 2020, 7, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, R.; Zhao, J.; Yang, X.; Shen, L.; Wang, Z. Sulfated binary oxide solid superacids. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 80, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.S.; Sudarsanam, P.; Raju, G.; Reddy, B.M. Synthesis of bio-additives: Acetylation of glycerol over zirconia-based solid acid catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2010, 11, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosuna-Rodríguez, I.; Gaigneaux, E.M. Glycerol acetylation catalysed by ion exchange resins. Catal. Today 2012, 195, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Al-Zaini, E.; Adesina, A.A. Catalytic characteristics and parameters optimization of the glycerol acetylation over solid acid catalysts. Fuel 2013, 103, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.; Umbarkar, S.B.; Dongare, M.K.; Eckelt, R.; Armbruster, U.; Martin, A. Selective formation of triacetin by glycerol acetylation using acidic ion-exchange resins as catalyst and toluene as an entrainer. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 490, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W.-J.; Li, L.-D.; Zhang, M.-H.; Zhang, Z.-B. A swelling-changeful catalyst for glycerol acetylation with controlled acid concentration. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 142, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinoso, D.M.; Tonetto, G.M. Bioadditives synthesis from selective glycerol esterification over acidic ion exchange resin as catalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3399–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinoso, D.M.; Boldrini, D.E. Kinetic study of fuel bio-additive synthesis from glycerol esterification with acetic acid over acid polymeric resin as catalyst. Fuel 2020, 264, 116879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, I.; Bumbac, G.; Bombos, D.; Velea, S.; Gălan, A.-M.; Bozga, G. Glycerol acetylation with acetic acid over Purolite CT-275. Product yields and process kinetics. Renew. Energy 2020, 148, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, V.L.C.; Pinto, B.P.; Silva, J.C.; Mota, C.J.A. Acetylation of glycerol catalyzed by different solid acids. Catal. Today 2008, 133–135, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, M.; Lazarova, H.; Kalvachev, Y.; Todorova, T.; Szegedi, Á.; Shestakova, P.; Mali, G.; Dasireddy, V.D.B.C.; Likozar, B. Zr-modified hierarchical mordenite as heterogeneous catalyst for glycerol esterification. Catal. Commun. 2017, 100, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y. Graphene oxide as a facile solid acid catalyst for the production of bioadditives from glycerol esterification. Catal. Commun. 2015, 62, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Barman, S.; Ali, A. Catalytic performance of cerium-modified ZSM-5 zeolite as a catalyst for the esterification of glycerol with acetic acid. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2020, 18, 20200081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, J.A.; van Grieken, R.; Morales, G.; Paniagua, M. Acidic Mesoporous Silica for the Acetylation of Glycerol: Synthesis of Bioadditives to Petrol Fuel. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Yoon, J.W.; Jhung, S.H. Esterification and acetylation reactions over in situ synthesized mesoporous sulfonated silica. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 278, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejda, M.; Stawicka, K.; Dubinska, A.; Ziolek, M. Development of niobium containing acidic catalysts for glycerol esterification. Catal. Today 2012, 187, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayoon, M.S.; Triwahyono, S.; Hameed, B.H.; Jalil, A.A. Improved production of fuel oxygenates via glycerol acetylation with acetic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawicka, K.; Trejda, M.; Ziolek, M. The production of biofuels additives on sulphonated MCF materials modified with Nb and Ta—Towards efficient solid catalysts of esterification. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 467, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.; Mo, T.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. Production of bioadditives from glycerol esterification over zirconia supported heteropolyacids. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 130, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Hao, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y. Aqueous-Phase Hydrogenolysis of Glycerol to 1,3-propanediol Over Pt-H4SiW12O40/SiO2. Catal. Lett. 2012, 142, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeeswaraiah, K.; Balaraju, M.; Prasad, P.S.S.; Lingaiah, N. Selective esterification of glycerol to bioadditives over heteropoly tungstate supported on Cs-containing zirconia catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 386, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaraju, M.; Nikhitha, P.; Jagadeeswaraiah, K.; Srilatha, K.; Sai Prasad, P.S.; Lingaiah, N. Acetylation of glycerol to synthesize bioadditives over niobic acid supported tungstophosphoric acid catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.; Fonseca, I.M.; Ramos, A.M.; Vital, J.; Castanheiro, J.E. Glycerol acetylation over dodecatungstophosphoric acid immobilized into a silica matrix as catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 91, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayoon, M.S.; Hameed, B.H. Synthesis of hybrid SBA-15 functionalized with molybdophosphoric acid as efficient catalyst for glycerol esterification to fuel additives. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 433–434, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magar, S.; Mohanraj, G.T.; Jana, S.K.; Rode, C.V. Synthesis and characterization of supported heteropoly acid: Efficient solid acid catalyst for glycerol esterification to produce biofuel additives. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2020, 50, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.; Fonseca, I.M.; Ramos, A.M.; Vital, J.; Castanheiro, J.E. Esterification of glycerol with acetic acid over dodecamolybdophosphoric acid encaged in USY zeolite. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.; Fonseca, I.M.; Ramos, A.M.; Vital, J.; Castanheiro, J.E. Acetylation of glycerol over heteropolyacids supported on activated carbon. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Gao, X.; Dong, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y. Design of a highly active silver-exchanged phosphotungstic acid catalyst for glycerol esterification with acetic acid. J. Catal. 2013, 306, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandesh, S.; Manjunathan, P.; Halgeri, A.B.; Shanbhag, G.V. Glycerol acetins: Fuel additive synthesis by acetylation and esterification of glycerol using cesium phosphotungstate catalyst. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 104354–104362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Duan, X.; Tao, M.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D. Design of a Highly Efficient Indium-Exchanged Heteropolytungstic Acid for Glycerol Esterification with Acetic Acid. Catal. Surv. Asia 2016, 20, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.A.; Hernández, D.L.; Moreno, J.A.; Mondragón, F.; Fernández, J.J. Alternative carbon based acid catalyst for selective esterification of glycerol to acetylglycerols. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 405, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.-L.; Guan, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Louh, R.-F. Fabrication of sulfonated carbon catalyst from biomass waste and its use for glycerol esterification. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 138, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayoon, M.S.; Hameed, B.H. Acetylation of glycerol to biofuel additives over sulfated activated carbon catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9229–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, P.U.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Hameed, B.H. Synthesis of oxygenated fuel additives via glycerol esterification with acetic acid over bio-derived carbon catalyst. Fuel 2017, 209, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaika, A.; Kozłowski, M. Glycerol conversion towards valuable fuel blending compounds with the assistance of SO3H-functionalized carbon xerogels and spheres. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 184, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangestanifard, M.; Ghaziaskar, H.S. Arenesulfonic Acid-Functionalized Bentonite as Catalyst in Glycerol Esterification with Acetic Acid. Catalysts 2017, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Hou, Z. Esterification of glycerol with acetic acid over SO3H-functionalized phenolic resin. Fuel 2019, 255, 115842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Ji, Y.; Younas, M.; He, B. Esterification of glycerol with acetic acid using a sulfonated polyphenylene sulfide non-woven fabric as a catalyst. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2020, 18, 20200171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Molecular weight | 92.09 g mol−1 |
| Density | 1.25 g mL−1 |
| Melting point | 20 °C |
| Boiling point | 290 °C |
| Flash point | 160 °C |
| Autoignition point | 393 °C |
| Viscosity (at 25 °C) | 954 centipoises |
| pH | 5.5–8 |
| Monoacetin | Diacetin | Triacetin |
|---|---|---|
| Food additive | Oxygenate fuel additive | Oxygenate fuel additive |
| Manufacture of explosives | Plasticiser | Solvent |
| Smokeless powder | Softening agent | Food additive |
| Tanning agent | Solvent | Excipient of pharmaceutical products |
| Solvent for dyes | Plasticizer | |
| Antimicrobial and emulsifying agent in cigarette filters |
| Ion-Exchange Resin | Conversion of Acetic Acid (%) | Product Selectivity (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-MA | 2-MA | 1,3-DA | 1,2-DA | ||
| Amberlyst-15 | 95.3 | 63.4 | 7.0 | 2.0 | 0.5 |
| Amberlyst-36 | 95.6 | 62.5 | 7.8 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| Dowex 50 WX2 | 95.2 | 71.9 | 8.8 | 3.3 | 1.7 |
| Dowex 50 WX4 | 94.8 | 63.7 | 7.8 | 2.8 | 1.4 |
| Dowex 50 WX8 | 94.7 | 64.9 | 8.1 | 3.1 | 1.5 |
| Catalyst | Glycerol Conversion (%) | Product Selectivity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA | DA | TA | ||
| M | 68.2 | 33.1 | 14.6 | 52.3 |
| M1 | 89.3 | 19.3 | 17.0 | 63.7 |
| Zr/M | 74.4 | 32.2 | 24.6 | 43.2 |
| Zr/M1 | 93.5 | 18.4 | 12.4 | 69.2 |
| Catalyst | Glycerol Conversion/% | Product Selectivity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA | DA | TA | ||
| HPW | 70.3 | 59.3 | 37.7 | 3.0 |
| Ag1PW | 96.8 | 48.4 | 46.4 | 5.2 |
| Ag2PW | 82.5 | 52.7 | 43.4 | 3.9 |
| Ag3PW | 75.7 | 59.7 | 37.1 | 3.2 |
| Catalyst | Operating Parameters | Performance | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Molar Ratio of Acetic Acid to Glycerol | Catalyst Loading | |||
| Homogeneous Catalysts | ||||||
| H2SO4 | 60 | 480 | 3:1 | [H+] = 0.03 mmol | C = 98% S = 54% MA, 27% DA | [55] |
| p-TSA | C = 85% S = 86% MA, 8% DA | |||||
| 1-butylpyridinium chloride—aluminium (III) chloride | 75 | 120 | 3:1 | 1 mL | C = 100% S = 17.1% MA, 58.8% DA, 24.1% TA | [49] |
| [HSO3-pmim][HSO4] | 120 | 360 | 8:1 | 6.25 mol% | Y = 95.6% TA | [50] |
| [(HSO3-p)2im][HSO4] | 100 | 30 | 8:1 | 0.1 mol% | C = 95% S = 43.1% MA, 51.4% DA, 5.5% TA | [51] |
| PPS-TPA-HOAc | 105 | 360 | 10:1 | 2.5 mol% | C = 100% S = 2.3% MA, 40.0% DA, 57.7% TA | [45] |
| [HO3S-(CH2)3-NEt3]Cl-[FeCl3]0.67 | Reflux (Toluene) | 240 | 5:1 | 0.3 mol% | Y = 98.6% | [53] |
| H3PW12O40 | 60 | 480 | 3:1 | [H+] = 0.03 mmol | C = 96% S = 66% MA, 34% DA | [55] |
| H4SiW12O40 | 60 | 240 | 3:1 | 0.06 mol % | C = 100% S = 42% MA, 53% DA, 5% TA | [56] |
| Fe4(SiW12O40)3 | C = 100% S = 24% MA, 69% DA, 7% TA | |||||
| Sn1.5PW12O40 | 70 | 180 | 12:1 | 0.78 mol% | C = 100% S = 4% MA, 56% DA, 40% TA | [57] |
| SnCl2.H2O | 60 | 480 | 12:1 | 0.4 mmol | C = 96% S = 54% MA, 46% DA | [55] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keogh, J.; Inrirai, P.; Artioli, N.; Manyar, H. Nanostructured Solid/Liquid Acid Catalysts for Glycerol Esterification: The Key to Convert Liability into Assets. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070615
Keogh J, Inrirai P, Artioli N, Manyar H. Nanostructured Solid/Liquid Acid Catalysts for Glycerol Esterification: The Key to Convert Liability into Assets. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(7):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070615
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeogh, John, Patcharaporn Inrirai, Nancy Artioli, and Haresh Manyar. 2024. "Nanostructured Solid/Liquid Acid Catalysts for Glycerol Esterification: The Key to Convert Liability into Assets" Nanomaterials 14, no. 7: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070615
APA StyleKeogh, J., Inrirai, P., Artioli, N., & Manyar, H. (2024). Nanostructured Solid/Liquid Acid Catalysts for Glycerol Esterification: The Key to Convert Liability into Assets. Nanomaterials, 14(7), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14070615







