Electrochemical Sensor Based on Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Carbon Nanohorns (SWCNH) for Determination of Cr(VI) via Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry (AdCSV) in Tap Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Solutions
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Preparation of SWCNH/GCE
2.3.2. Analytical Procedure for the Determination of Cr(VI)
2.4. Sample Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of SWCNH and GC/SWCNH by SEM
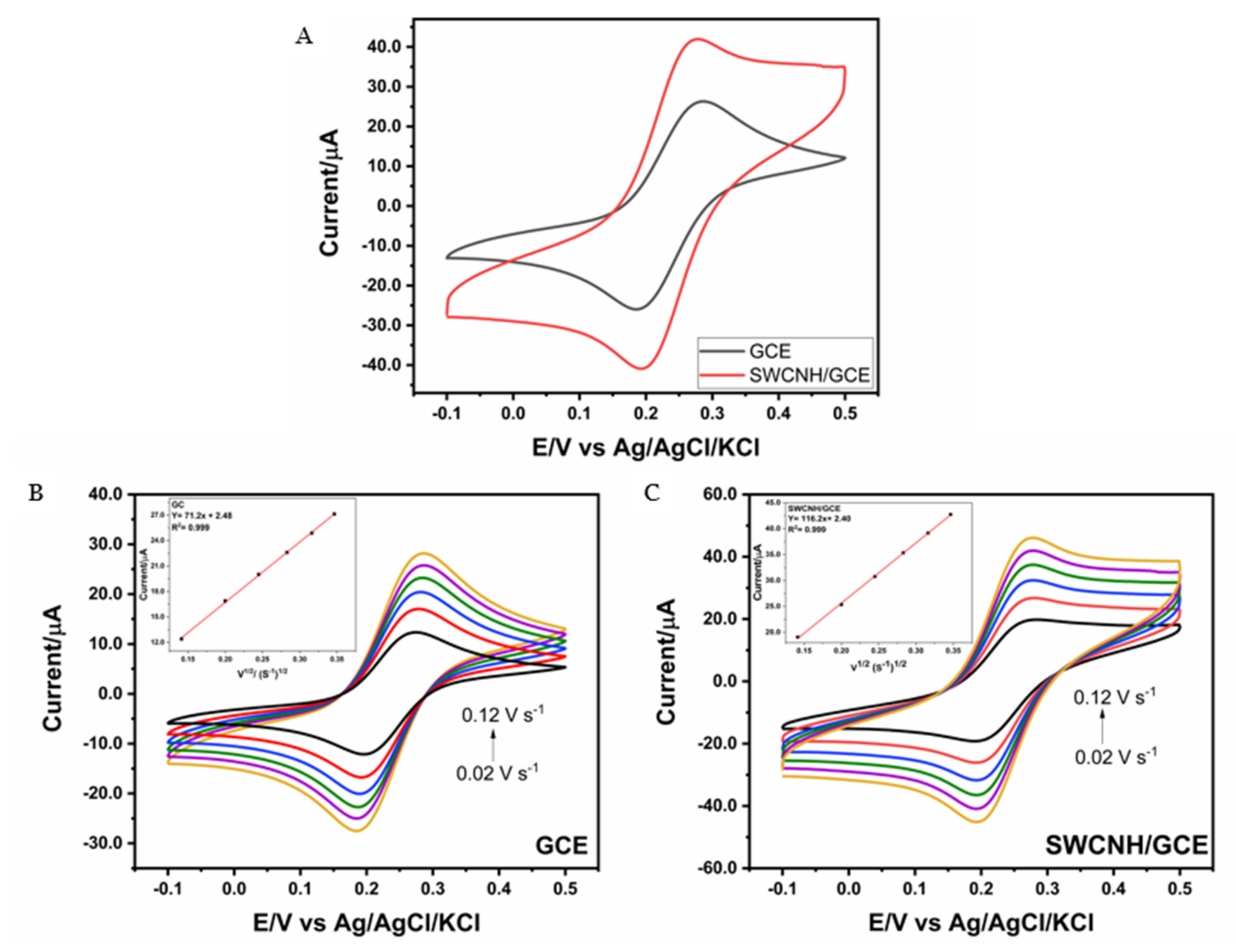
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of the GCE and SWCNH/GCE
3.3. Electrochemical Determination of Cr(VI)
3.3.1. Supporting Electrolyte Study
3.3.2. Effect of the Volume of SWCNH Suspension
3.3.3. Effect of Potential and Time of Accumulation
3.3.4. Voltammetric Response of Cr(VI)
3.4. Analytical Validation and Applications
3.4.1. Calibration Curve, Limit of Detection, and Quantification
3.4.2. Repeatability, Reproducibility, and Effect of Interferents
3.4.3. Accuracy
3.4.4. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kravkaz Kuşçu, İ.S.; Kılıç Bayraktar, M.; Tunçer, B. Determination of Heavy Metal (Cr, Co, and Ni) Accumulation in Selected Vegetables Depending on Traffic Density. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Jang, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.M.; Cho, E.-M.; Seo, Y.R. Adverse Human Health Effects of Chromium by Exposure Route: A Comprehensive Review Based on Toxicogenomic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pađan, J.; Marcinek, S.; Cindrić, A.-M.; Layglon, N.; Lenoble, V.; Salaün, P.; Garnier, C.; Omanović, D. Improved voltammetric methodology for chromium redox speciation in estuarine waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1089, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nik, V.M.; Konoz, E.; Feizbakhsh, A.; Sharif, A.A.M. Simultaneous extraction of chromium and cadmium from bean samples by SrFe12O19@CTAB magnetic nanoparticles and determination by ETAAS: An experimental design methodology. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Gan, Y.; Liang, T.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. A miniaturized electrochemical system for high sensitive determination of chromium(VI) by screen-printed carbon electrode with gold nanoparticles modification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, N.A.; Dash, S.S.; Gummadi, S.N.; Deepa, V.S. Nano-remediation of toxic heavy metal contamination: Hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Elik, A.; Altunay, N. Ultrasound-assisted supramolecular solvent dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for preconcentration and determination of Cr(VI) in waters and total chromium in beverages and vegetables. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.S.; Alamdari, P.; Chahardoli, S.; Afshari, A. Quantification of heavy metal pollution for environmental assessment of soil condition. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, Y.A.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Ghani, M. Derived N-doped carbon through core-shell structured metal-organic frameworks as a novel sorbent for dispersive solid phase extraction of Cr(III) and Pb(II) from water samples followed by quantitation through flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, M. Recent developments of heavy metals detection in traditional Chinese medicine by atomic spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Song, H.; Wang, W. Deep learning model based on urban multi-source data for predicting heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Ni, Cr) in industrial sewer networks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. SW-846 Test Method 7199: Determination of Hexavalent Chromium in Drinking Water, Groundwater, and Industrial Wastewater Effluents by Ion Chromatography; Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Berrabah, S.E.; Benchettara, A.; Smaili, F.; Tabti, S.; Benchettara, A. Electrodeposition of zinc hydroxide on carbon graphite electrode for electrochemical determination of trace copper in water samples using square wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 278, 125670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, S.; Xue, Z.-L.; Xu, L.; Gu, Y.; Miao, Y. Improved Bi film wrapped single walled carbon nanotubes for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of trace Cr(VI). Electrochim. Acta 2013, 113, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchayanukun, P.; Muncharoen, S. Chitosan coated magnetite nanoparticle as a working electrode for determination of Cr(VI) using square wave adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry. Talanta 2020, 217, 121027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadyar, A.; Al-Amoody, F.; Arachchige, D.R. Ion transfer stripping voltammetry to detect nanomolar concentrations of Cr (VI) in drinking water. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 782, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thị Hue, N.; Van Hop, N.; Thai Long, H.; Hai Phong, N.; Uyen, T.H.; Quoc Hung, L.; Nhi Phuong, N. Determination of Chromium in Natural Water by Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry Using In Situ Bismuth Film Electrode. J. Environ. Public Health 2020, 2020, 1347836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liendo, F.; de la Vega, A.P.; Jesus Aguirre, M.; Godoy, F.; Martí, A.A.; Flores, E.; Pizarro, J.; Segura, R. A simple graphene modified electrode for the determination of antimony(III) in edible plants and beverage. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, T.L.; Hung, L.C.; Phuong, T.T.B.; Ha, B.T.T.; Nguyen, B.-S.; Hai, T.D.; Nguyen, V.-H. Multiwall carbon nanotube modified by antimony oxide (Sb2O3/MWCNTs) paste electrode for the simultaneous electrochemical detection of cadmium and lead ions. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wu, H.; Ping, J. Simultaneous determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions in honey and milk samples using a single-walled carbon nanohorns modified screen-printed electrochemical sensor. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dali, M.; Zinoubi, K.; Chrouda, A.; Abderrahmane, S.; Cherrad, S.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. A biosensor based on fungal soil biomass for electrochemical detection of lead (II) and cadmium (II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 813, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Bahiraei, A. Ultra trace quantification of chromium(VI) in food and water samples by highly sensitive catalytic adsorptive stripping voltammetry with rubeanic acid. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. Structure, synthesis, and sensing applications of single-walled carbon nanohorns. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachoosangi, R.T.; Compton, R.G. Voltammetric determination of Chromium(VI) using a gold film modified carbon composite electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 178, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Li, Z.; Cui, X. Adsorptive stripping voltammetry determination of hexavalent chromium by a pyridine functionalized gold nanoparticles/three-dimensional graphene electrode. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 104022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, H.; Aslıhan Avan, A. Neutral red interlinked gold nanoparticles/multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified electrochemical sensor for simultaneous speciation and detection of chromium (VI) and vanadium (V) in water samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Garmroodi, A. A highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor for determination of Cr(VI) in the presence of Cr(III) using modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes/quercetin screen-printed electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 4972–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J. Fullerene-based anodic stripping voltammetry for simultaneous determination of Hg(II), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) in foodstuff. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, C.M.; Nekrassova, O.; Compton, R.G. Reduction of hexavalent chromium at solid electrodes in acidic media: Reaction mechanism and analytical applications. Talanta 2005, 65, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Lara, J.; Galicia, M.; Carrasco-Urrutia, K.; Torres-Pérez, J. Sensitive detection of chromium (VI) using Au-NPs/MWCNT/chitosan composite via electrochemical approach. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisiwamongkhol, K.; Batchelor-McAuley, C.; Sokolov, S.V.; Holter, J.; Young, N.P.; Compton, R.G. Optimising carbon electrode materials for adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 7, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Conceição, E.; Buffon, E.; Stradiotto, N.R. Lead signal enhancement in anodic stripping voltammetry using graphene oxide and pectin as electrode modifying agents for biofuel analysis. Fuel 2022, 325, 124906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Satpati, A.K. Fabrication of rGO/NiS/AuNCs ternary nanocomposite modified electrode for electrochemical sensing of Cr(VI) at utra-trace level. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 24, 101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, N.; Palani, Y.; Jonnalagadda, R.R.; Shanmugam, E. Covalently dual functionalized graphene oxide-based multiplex electrochemical sensor for Hg(II) and Cr(VI) detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 367, 132165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, J.; Segura, R.; Tapia, D.; Navarro, F.; Fuenzalida, F.; Jesús Aguirre, M. Inexpensive and green electrochemical sensor for the determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry in bivalve mollusks. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Electrode | Technique | μg L−1 | Sample | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineal Range | LOD | ||||
| Film of Au/polyethylene-technical carbon | LSV | 20 to 2000 | 4.4 | River water | [26] |
| Pyridine functionalized AuNPs/3D RGO/GCE | AdSV | 25 to 300 | 1.2 | Waste water | [27] |
| MWCNTs-NR-AuNPs/SPCE | LSV | 21 to 4160 | 1.3 | Tea, milk and mineral water | [28] |
| QH2/MWCNT/SPCE | DPV | 52 to 10,400 | 15.6 | Tap, Mineral and River water | [29] |
| AuNP/MWCNT-Chit/GCE | DPV | 0.003 to 0.1 | 0.007 | Tap water | [32] |
| rGO/NiS/AuNCs/GCE | SWASV | 2 to 14 | 0.09 | Ground water | [35] |
| T-GO-C/GCE | SWV | 5 to 600 | 20 | Tap and tannery water | [36] |
| SWCNH/GCE | AdCSV | 20 to 100 | 3.5 | Tap water | This work |
| Sample | Cr(VI) Concentration (µg L−1) | Recovery (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Added | Measurement | ||
| Spiked sample | 20.0 | 21.0 ± 1.8 | 105 |
| 30.0 | 33.0 ± 2.4 | 110 | |
| Samples | FAAS | AdCSV | t de Student |
|---|---|---|---|
| (μg L−1) | |||
| Tap water | ND | ND | - |
| Spiked tap water | 31.4 ± 0.7 | 33.0 ± 2.4 | 1.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liendo, F.; Pichún, B.; Vega, A.P.d.l.; Penagos, J.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M.; Pizarro, J.; Segura, R.; Aguirre, M.J. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Carbon Nanohorns (SWCNH) for Determination of Cr(VI) via Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry (AdCSV) in Tap Water. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171465
Liendo F, Pichún B, Vega APdl, Penagos J, Serrano N, Díaz-Cruz JM, Pizarro J, Segura R, Aguirre MJ. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Carbon Nanohorns (SWCNH) for Determination of Cr(VI) via Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry (AdCSV) in Tap Water. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(17):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171465
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiendo, Fabiana, Bryan Pichún, Amaya Paz de la Vega, Johisner Penagos, Núria Serrano, José Manuel Díaz-Cruz, Jaime Pizarro, Rodrigo Segura, and María Jesús Aguirre. 2024. "Electrochemical Sensor Based on Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Carbon Nanohorns (SWCNH) for Determination of Cr(VI) via Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry (AdCSV) in Tap Water" Nanomaterials 14, no. 17: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171465
APA StyleLiendo, F., Pichún, B., Vega, A. P. d. l., Penagos, J., Serrano, N., Díaz-Cruz, J. M., Pizarro, J., Segura, R., & Aguirre, M. J. (2024). Electrochemical Sensor Based on Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Carbon Nanohorns (SWCNH) for Determination of Cr(VI) via Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry (AdCSV) in Tap Water. Nanomaterials, 14(17), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171465









