Research on CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots-Doped Polymer Fibers and Their Gain Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
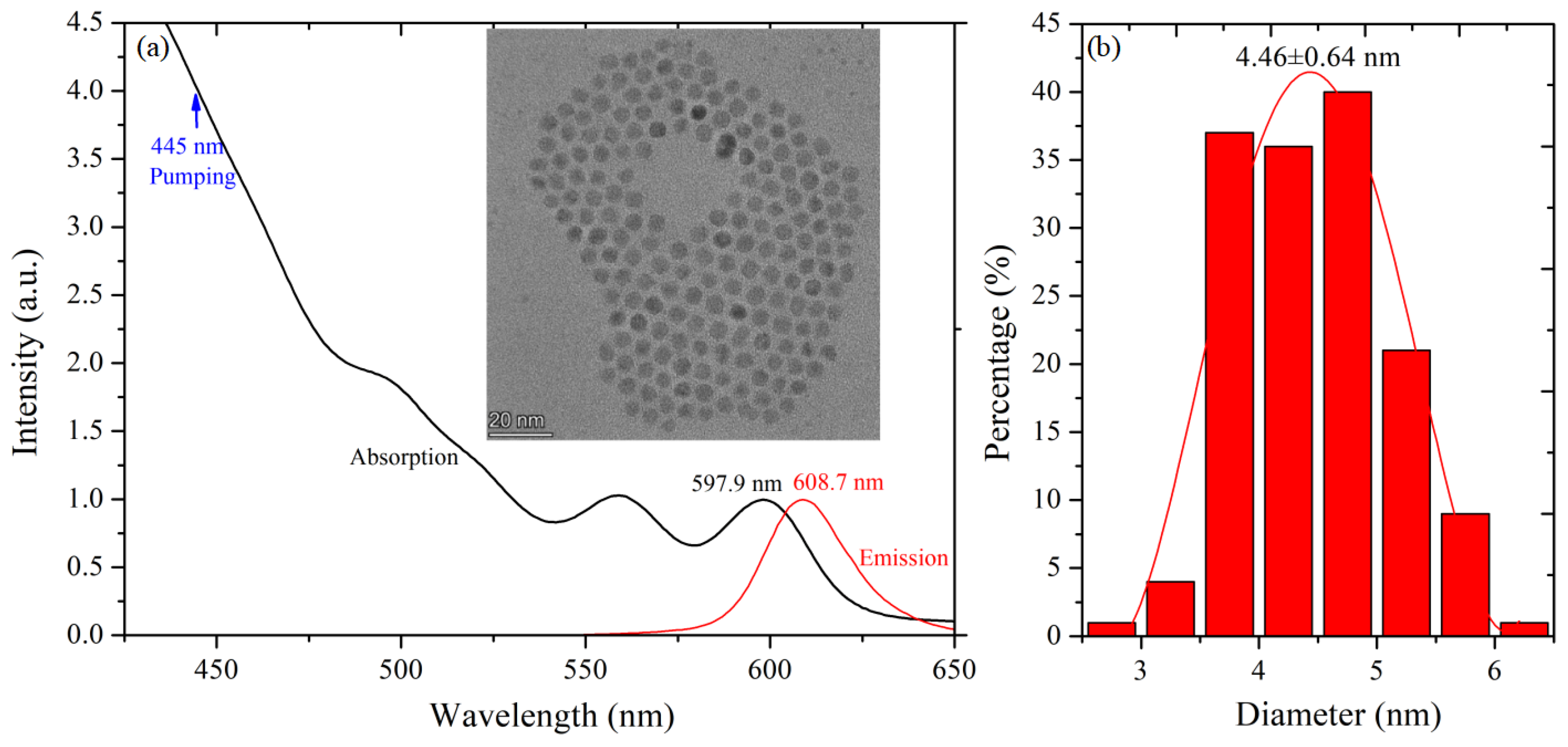
2.1. Material Characterization
2.2. Fabrication of QDs-Doped PMMA Fibers
2.2.1. Hollow Fiber Filling Method
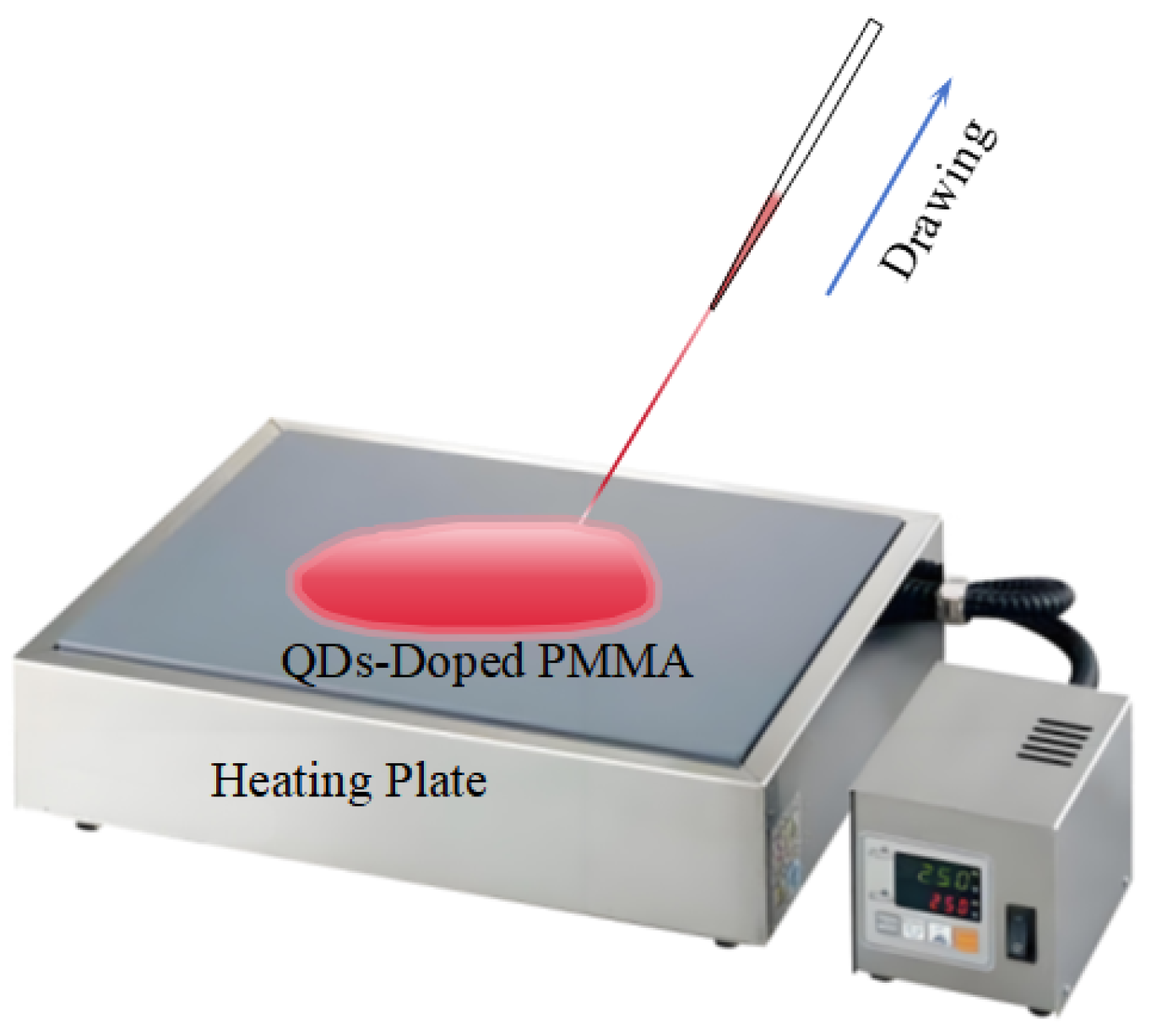
2.2.2. Melt-Drawing Method
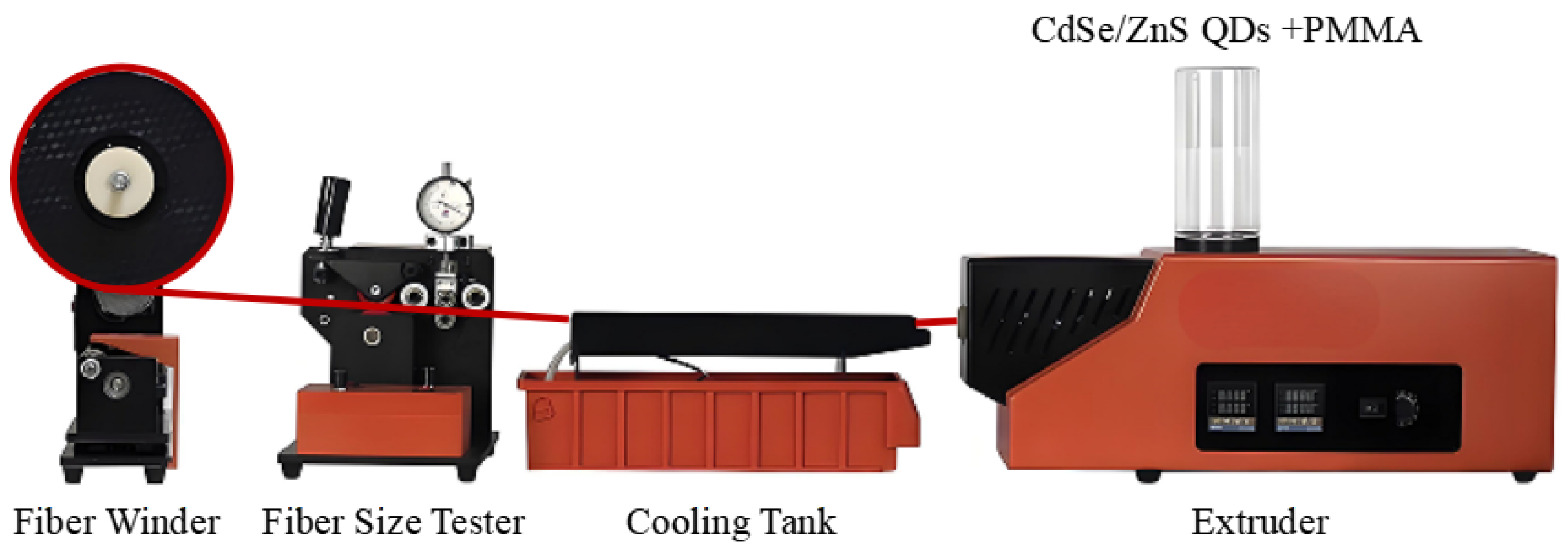
2.2.3. Melt Extrusion Method
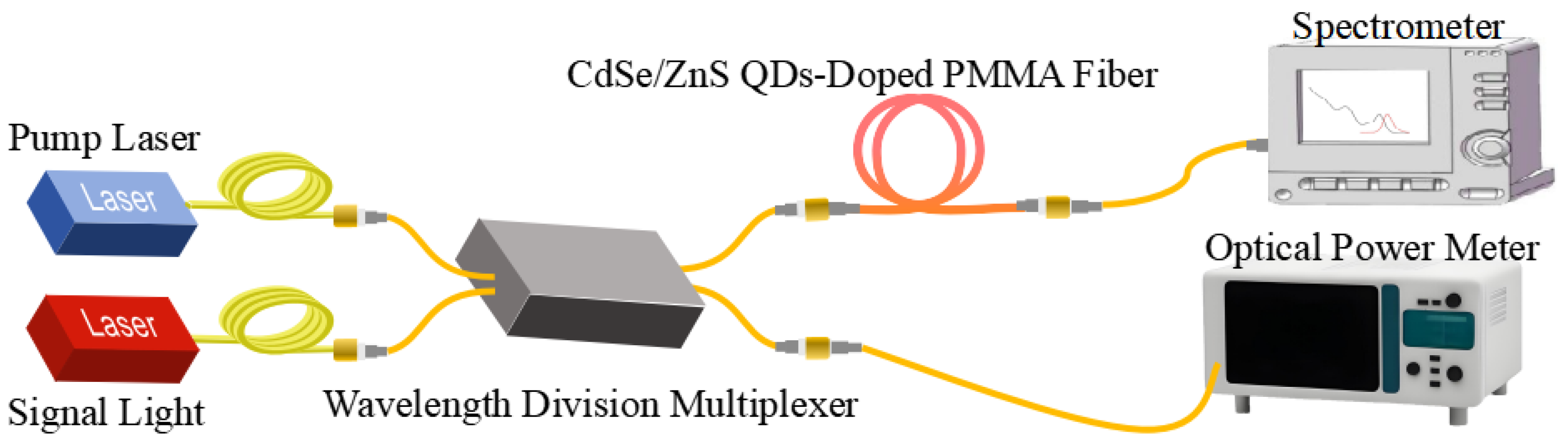
2.3. Spectral and Optical Amplification Characteristics Testing
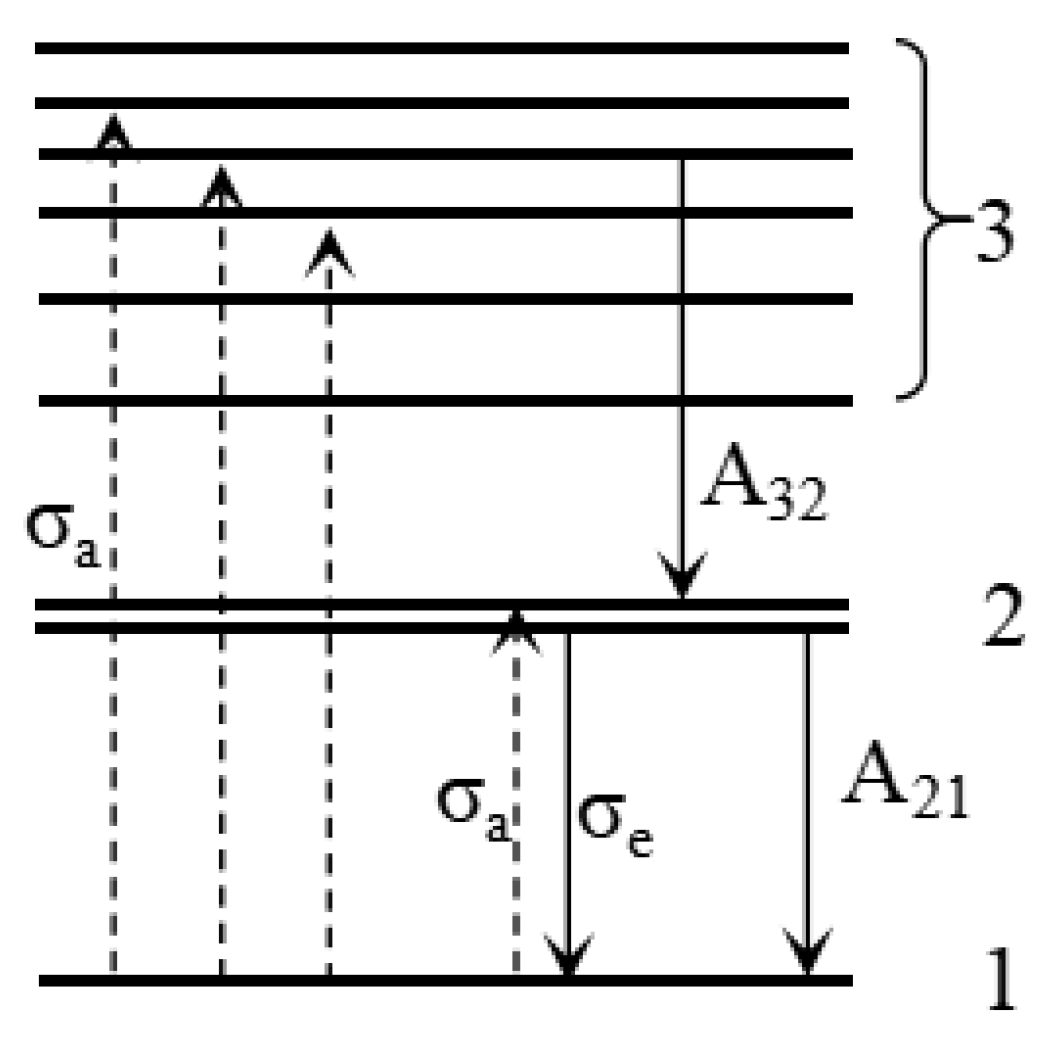
3. Theoretical Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Issues in the Fabrication of QDs-Doped PMMA Fibers
4.1.1. Advantages and Disadvantages of Hollow Fiber Filling Method
- Safety Concerns: The fabrication process involves the use of toxic solvents such as toluene and chloroform, which pose safety risks.
- Length Limitation: The length of the fabricated fibers is constrained by the length of the hollow fiber, making this method unsuitable for large-scale fiber production.
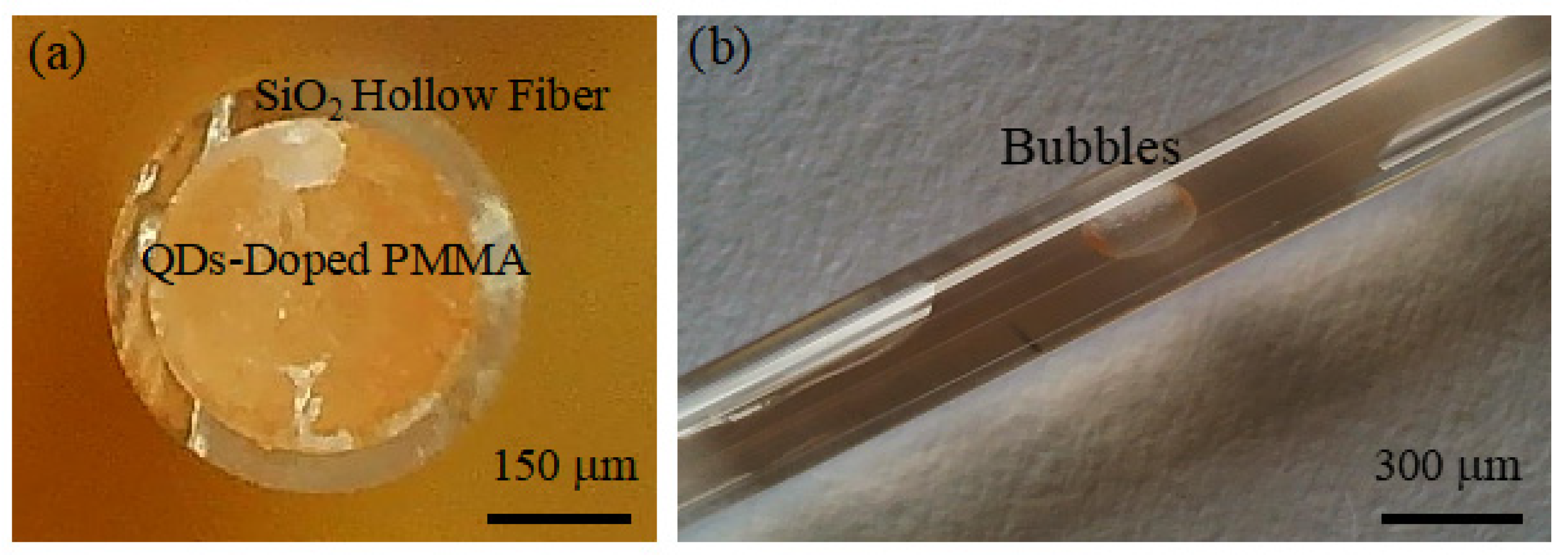
- Bubble Formation: During the mixing of PMMA powder with chloroform, numerous air bubbles can form, which will significantly impact the fiber’s performance if not effectively removed. Additionally, during the curing of the QDs-doped PMMA colloid, internal stresses can arise due to differences in materials, potentially leading to bubble formation between the fiber core and cladding (as shown in Figure 7), further affecting the optical fiber’s performance.
4.1.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Melt-Drawing Method
- Limited Fiber Length: The fibers produced using this method are typically short, limiting its suitability for large-scale production.
- Control Over Fiber Diameter and Structure: Precise control over the fiber’s diameter and structural integrity is difficult to achieve during the drawing process. The cross-sectional shape of the fibers often deviates from the ideal circular form and may include voids (as shown in Figure 8). These imperfections can adversely affect the optical performance of the fibers and present challenges in the fabrication of subsequent optical fiber jumpers.
4.1.3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Melt Extrusion Method
4.1.4. Choose of the Suitable Fabrication Method
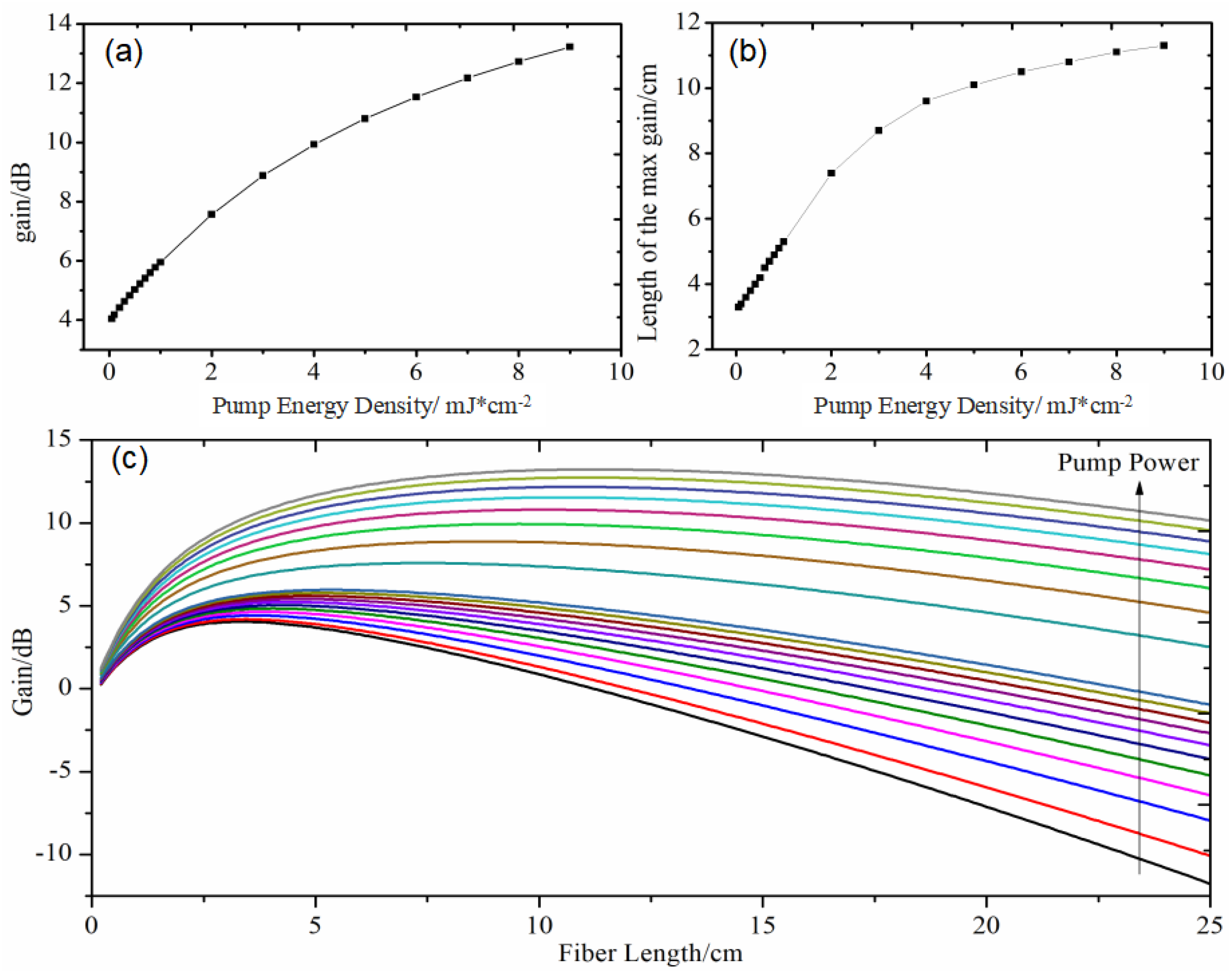
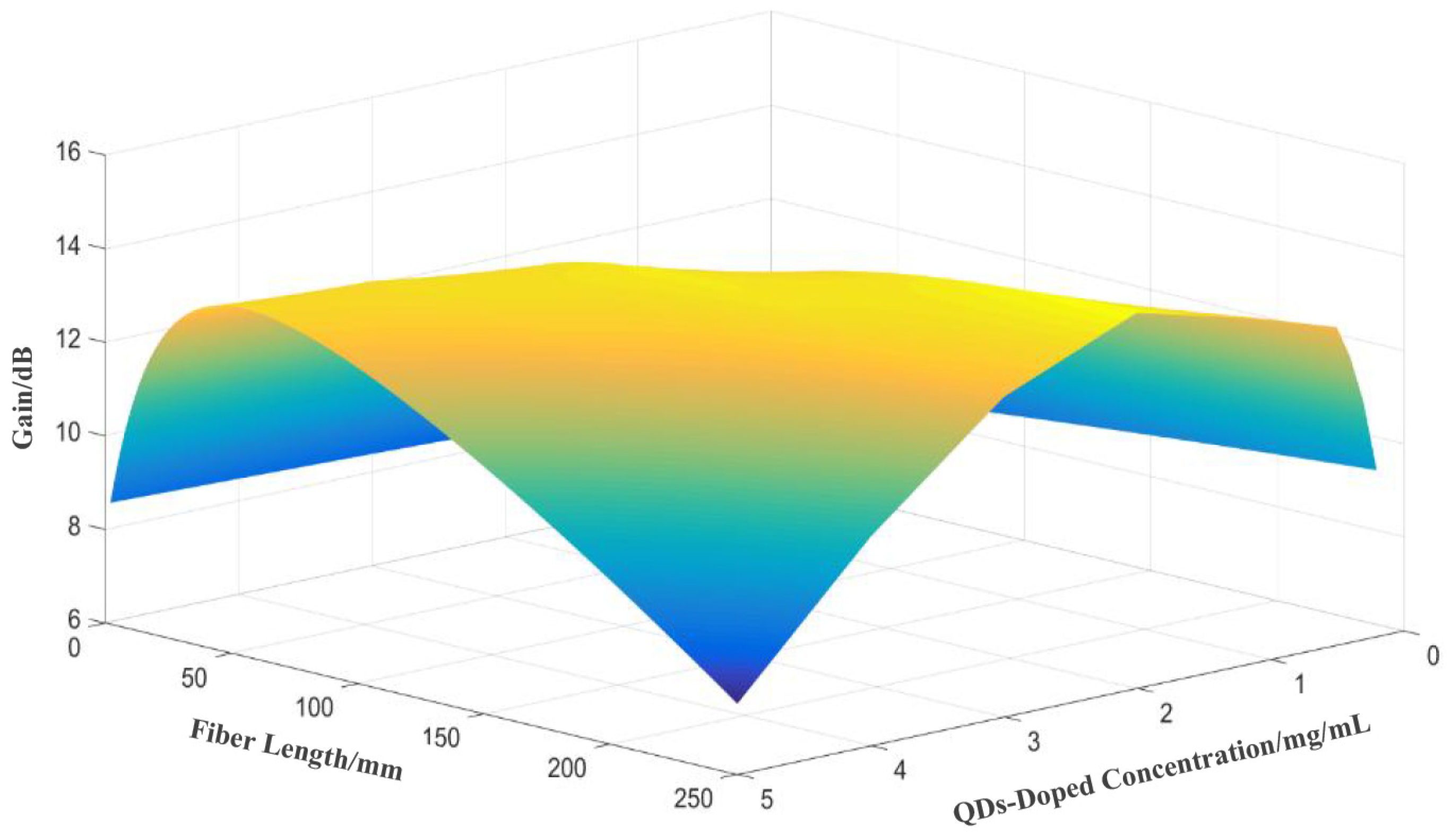
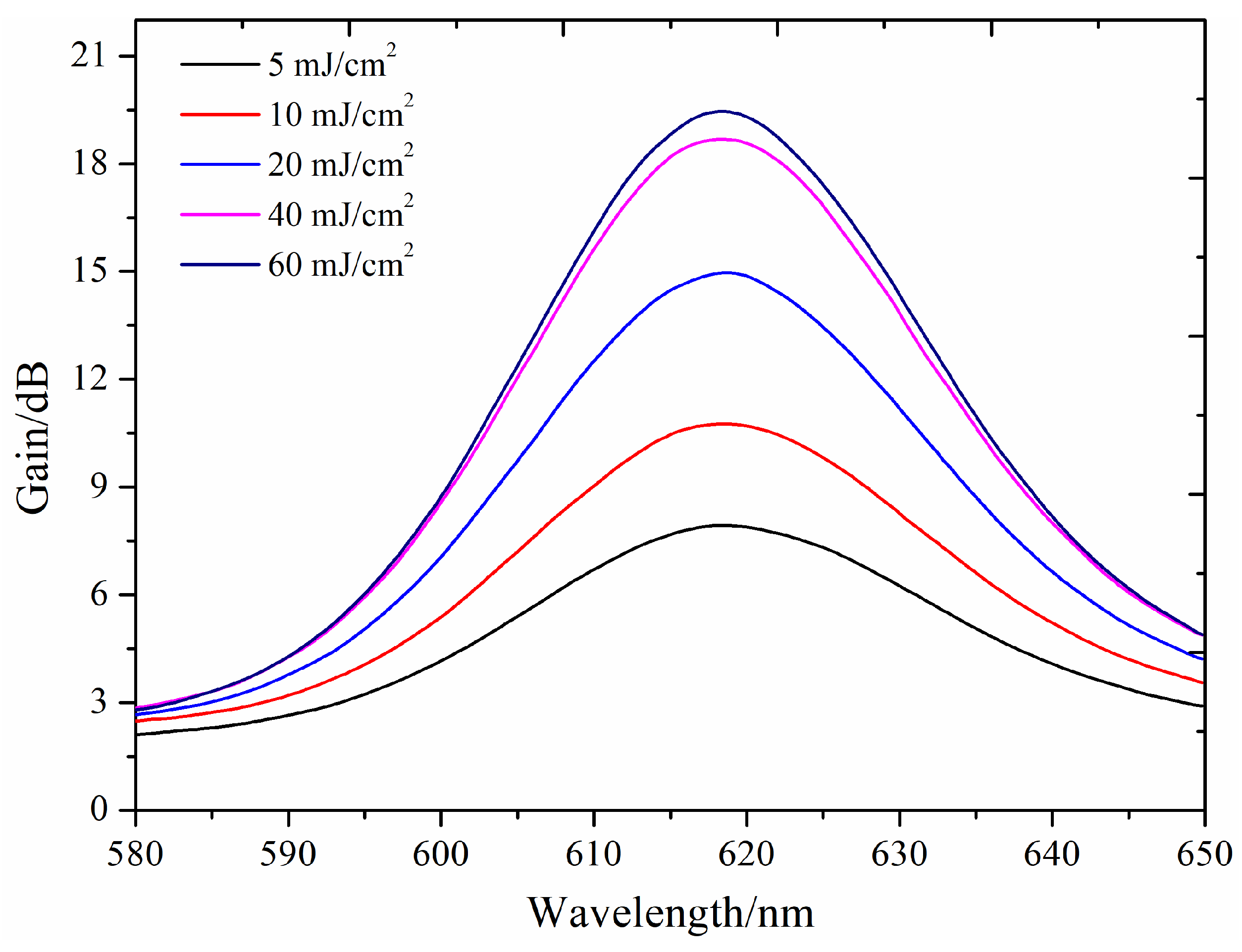
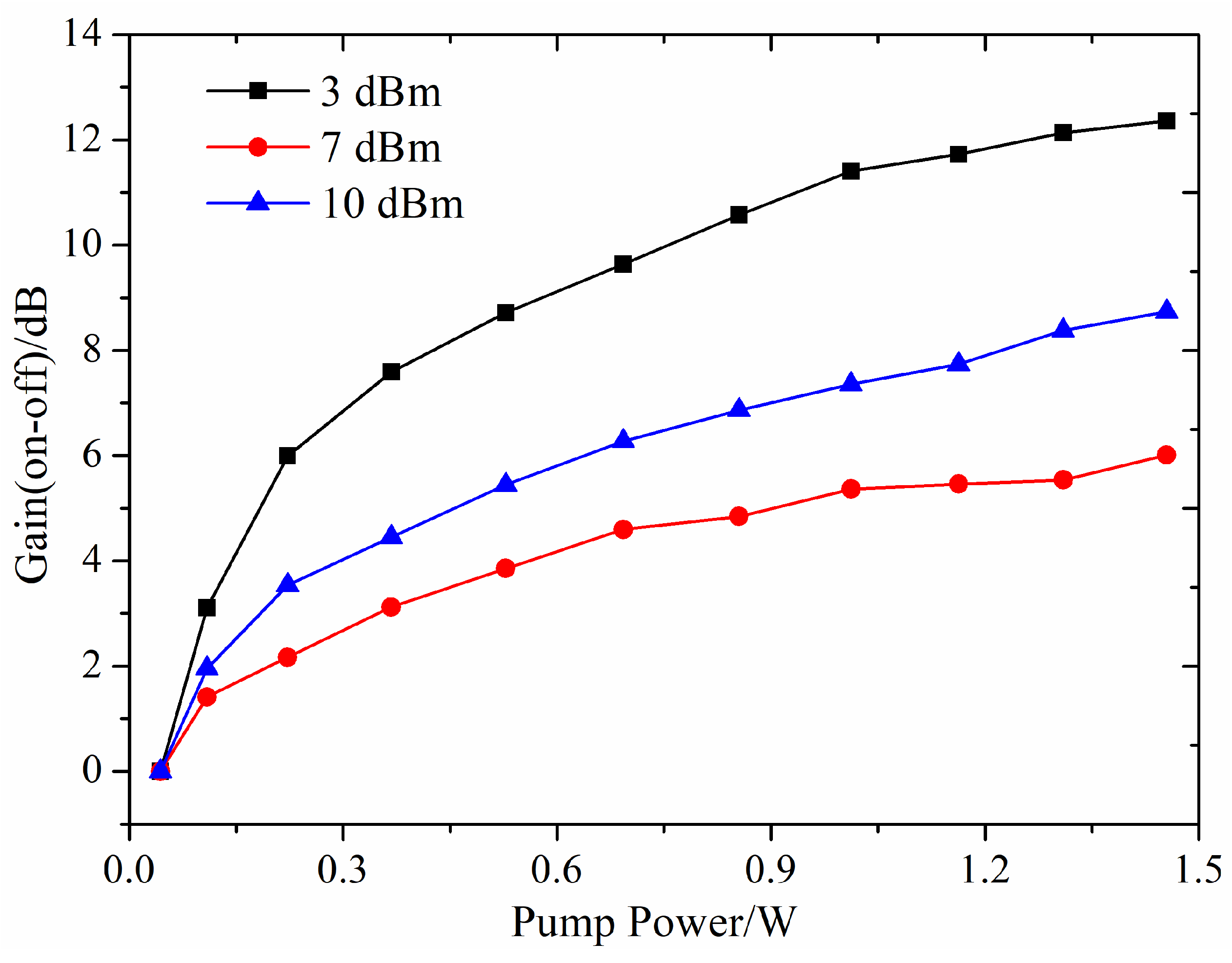
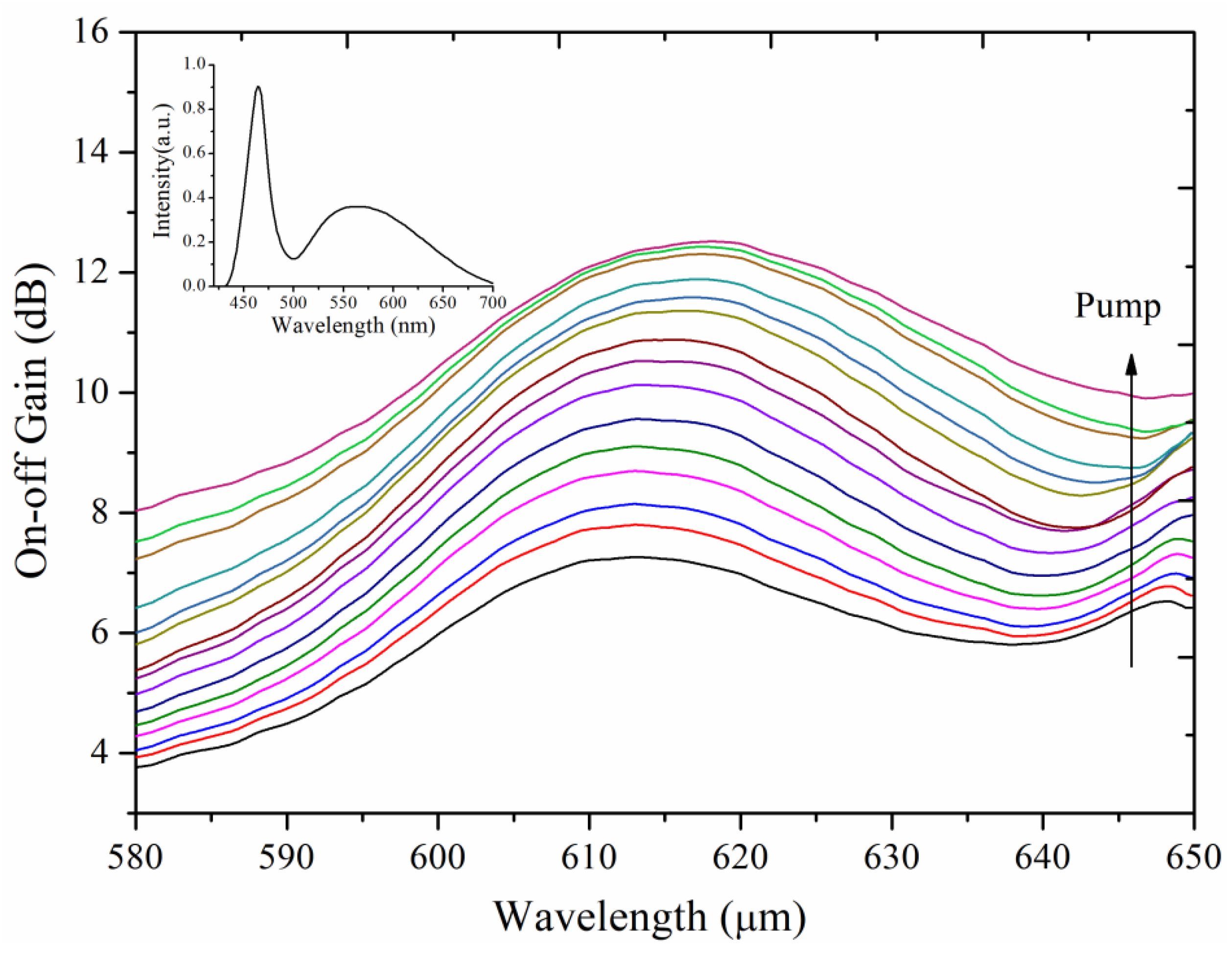
4.2. Theoretical Analysis of Spectral and Amplification Performance
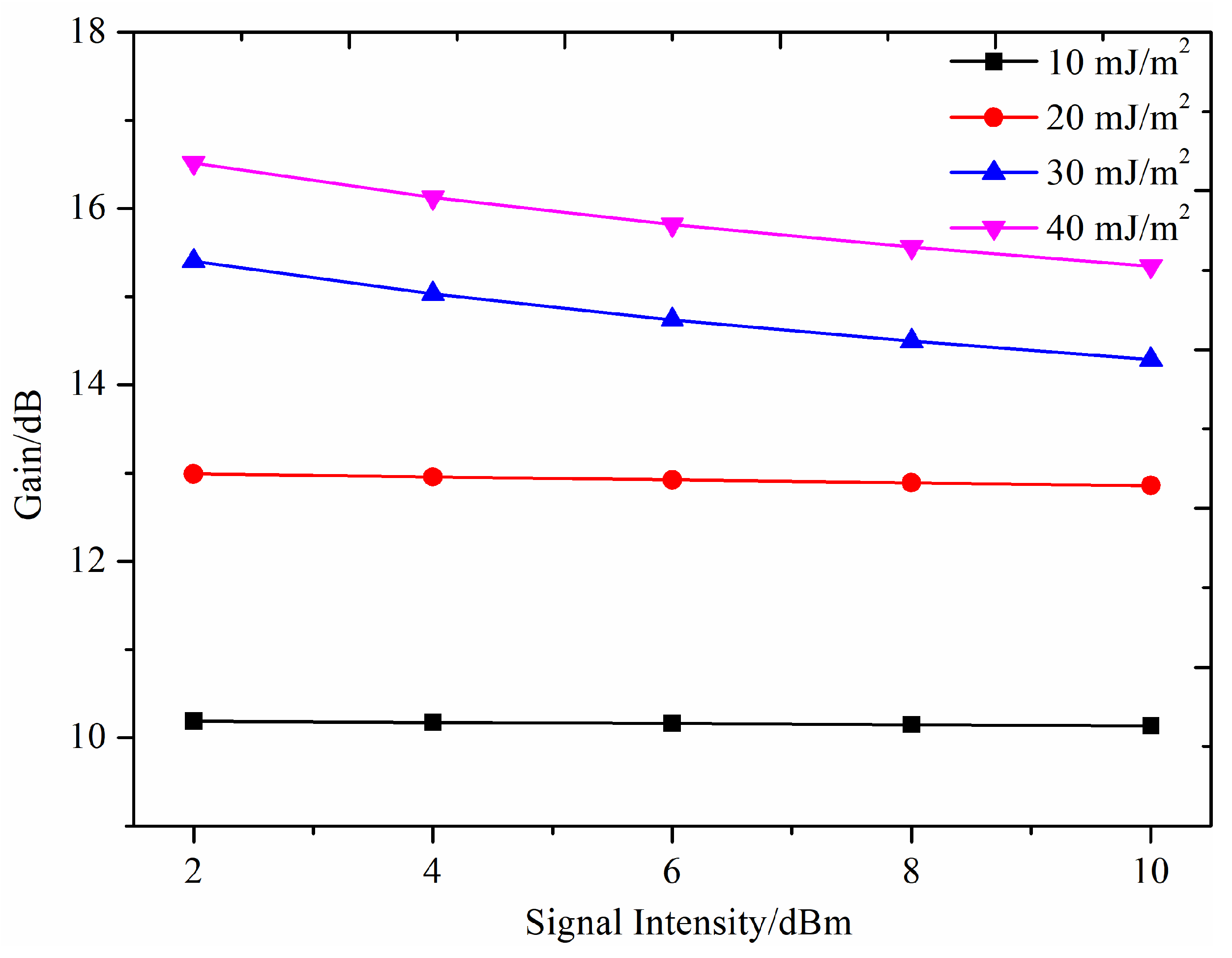
4.3. Experimental Measurement of On-Off Gain
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orfanos, V.A.; Kaminaris, S.D.; Papageorgas, P.; Piromalis, D.; Kandris, D.A. Comprehensive review of IoT networking technologies for smart home automation applications. J. Sens. Actuator. Netw. 2023, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, H.; Ji, Y. High-speed Multi-channel all-optical de-aggregator based on polarization-assisted phase-sensitive amplification in elastic optical networks. Opt. Las. Eng. 2023, 160, 109103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, Y.; Koike, K. Progress in low-loss and high-bandwidth plastic optical fibers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2015, 49, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubia, J.; Arrue, J. Plastic optical fibers: An introduction to their technological processes and applications. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2001, 7, 101–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacraz, A.; Polis, M.; Theodosiou, A.; Koutsides, C.; Kalli, K. Femtosecond Laser Inscribed Bragg Gratings in Low Loss CYTOP Polymer Optical Fiber. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surkova, G.; Kruglov, R.; Lwin, R.; Leon-Saval, S.G.; Argyros, A.; Poisel, H.; Zadorin, A. Multigigabit short-reach communication over microstructured polymer optical fiber. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2017, 34, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Ming, H.; Li, Z.; Xu, J. Optical amplification of Eu(DBM)3Phen-doped polymer optical fiber. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.J.; Qiu, W.W.; Cheng, X.S.; Luo, Y.; Qin, C.; Wu, W. Optical amplification of Eu(TTA)3Phen solution-filled hollow optical fiber. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 1902–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Tsang, K.; Pun, E.Y.B. Sm3+-doped polymer optical waveguide amplifiers. Opt. Commun. 2010, 283, 1363–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagya, S.; Teramoto, E.; Nihei, K.; Sasaki, K.; Koike, Y. High-power and High-gain Organic Dye-doped Polymer Optical Fiber Amplifiers: Novel Techiques for Preparation and Spectral Investigation. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandamparambil, R.; Mavila, S.; Karinjamanna, G. Fabrication and characterization of dye-doped polymer optical fiber as a light amplifier. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sheeba, M.; Rajesh, M.; Nampoori, V. Fabrication and characterization of dye mixture doped polymer optical fiber as a broad wavelength optical amplifier. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrue, J.; Illarramendi, M.A.; Ayesta, I.; Jimenez, F.; Zubia, J.; Tagaya, A.; Koike, Y. Laser-like Performance of Side-Pumped Dye-Doped Polymer Optical Fibers. IEEE Photon. J. 2015, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingming, S.; Pan, H.; Chu, H.; Mamat, M.; Abudurexiti, A.; Li, D. Core-shell CdSe/ZnS quantum dots polymer composite as the saturable absorber at 1.3 μm: Influence of the doped concentration. Phys. Lett. A. 2021, 400, 127307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ye, L.; Cheng, Z.; Hong, S.; Penty, R.; White, I. Random lasing action from PMMA waveguide doped with CdSe/ZnS CQDs plasmonically enhanced by Ag nanoislands. Opt. Las. Eng. 2020, 131, 106358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazes, M.; Oron, D.; Shweky, I.; Banin, U. Temperature Dependence of Optical Gain in CdSe/ZnS Quantum Rods. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2015, 111, 7898–7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.C.; Yang, Z.P.; Hwang, J.M.; Su, H.C.; Haung, J.Y.; Lin, T.N.; Shen, J.L.; Lee, M.H.; Tsai, M.T.; Lee, Y.J. Coherent and Polarized Random Laser Emissions from Colloidal CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots Plasmonically Coupled to Ellipsoidal Ag Nanoparticles. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 201600746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitinger, N.; Hohenau, A.; Köstler, S.; Krenn, J.R.; Leitner, A. Radiationless energy transfer in CdSe/ZnS quantum dot aggregates embedded in PMMA. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2011, 208, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.K.; More, P.; Bharate, B.G.; Vishwanath, A.K. Studies on light emitting CdSe quantum dots in commercial polymethylmethacrylate. J. Luminesc. 2010, 130, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, S.D.; Cheng, X.Y. CdSe/PMMA: Plastic fiber material containing CdSe quantum dots. Opt. Las. Eng. 2012, 44, 1298–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, T.; Bakhshi, R.; Petrova, D.; Pocock, R.; Imani, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Biological applications of quantum dots. Biomater. 2007, 28, 4717–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S. In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, C.A.; Perret, A.; Fortier, C.W.; Tardif, O.M.; Lamarre, S.A.; Morency, S.; Larivière, D.; Beaulieu, L.; Messaddeq, Y.; Allen, C.N. Light-generating CdSe/CdS colloidal quantum dot-doped plastic optical fibers. ACS Appl. Nano. Mater. 2020, 3, 6478–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioptsias, C.; Leontiadis, K.; Tzimpilis, E.; Tsivintzelis, I. Polypropylene nanocomposite fibers: A review of current trends and new developments. J. Plast. Film Sheet. 2021, 37, 283–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.F. Gain performance of a CdSe/ZnS quantum dot doped polymer fiber amplifier. J. Optoelectron. Laser. 2013, 24, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.F.; Wu, Z.J.; Ye, C.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W. Analysis of the Emission Features in CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dot-Doped Polymer Fibers. Photonics 2023, 10, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Hu, N.S.; Cheng, X.Y. Experimental realization of a PbSe quantum dot doped fiber amplifier with ultra-bandwidth characteristic. Opt. Commun. 2017, 382, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Xu, B.B.; Fang, Z.J.; Zhang, D.D.; Man, T.; Mo, J.Y.; Liu, X.F.; Xu, Z.S.; Liu, Y.H.; Cao, S.Y.; et al. Broadband optical amplification of PbS quantum-dot-doped glass fibers. Adv. Photonics Res. 2022, 3, 2200097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Cui, J.J.; Xu, B.B.; Man, T.; Zhang, D.D.; Tu, Y.Y.; Liu, X.F.; Qiu, J.R. PbS quantum dot doped polymer broadband optical fiber amplifier. Chin. J. Lumin. 2023, 44, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, W.; Liu, L.; Shen, D.; Liu, G.; Kost, A.R. Enhancing environmental stability of a PbS quantum dot optical fiber amplifier via rational interface design. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2018, 50, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Fang, Z.; Peng, Z.; Ma, Z.; Dong, G. Formation, element-migration and broadband luminescence in quantum dot-doped glass fibers. Opt. Express. 2017, 25, 19691–19700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philbin, J.P.; Rabani, E. Auger recombination lifetime scaling for type I and quasi-type II core/shell quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 5132–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, X.; Wu, Z.; Ding, Y. Research on CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots-Doped Polymer Fibers and Their Gain Characteristics. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171463
Peng X, Wu Z, Ding Y. Research on CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots-Doped Polymer Fibers and Their Gain Characteristics. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(17):1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171463
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Xuefeng, Zhijian Wu, and Yang Ding. 2024. "Research on CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots-Doped Polymer Fibers and Their Gain Characteristics" Nanomaterials 14, no. 17: 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171463
APA StylePeng, X., Wu, Z., & Ding, Y. (2024). Research on CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots-Doped Polymer Fibers and Their Gain Characteristics. Nanomaterials, 14(17), 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171463




