Biological Effects of Green Synthesized Al-ZnO Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract from Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze on Living Organisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Anisomeles Indica Leaf Extracts
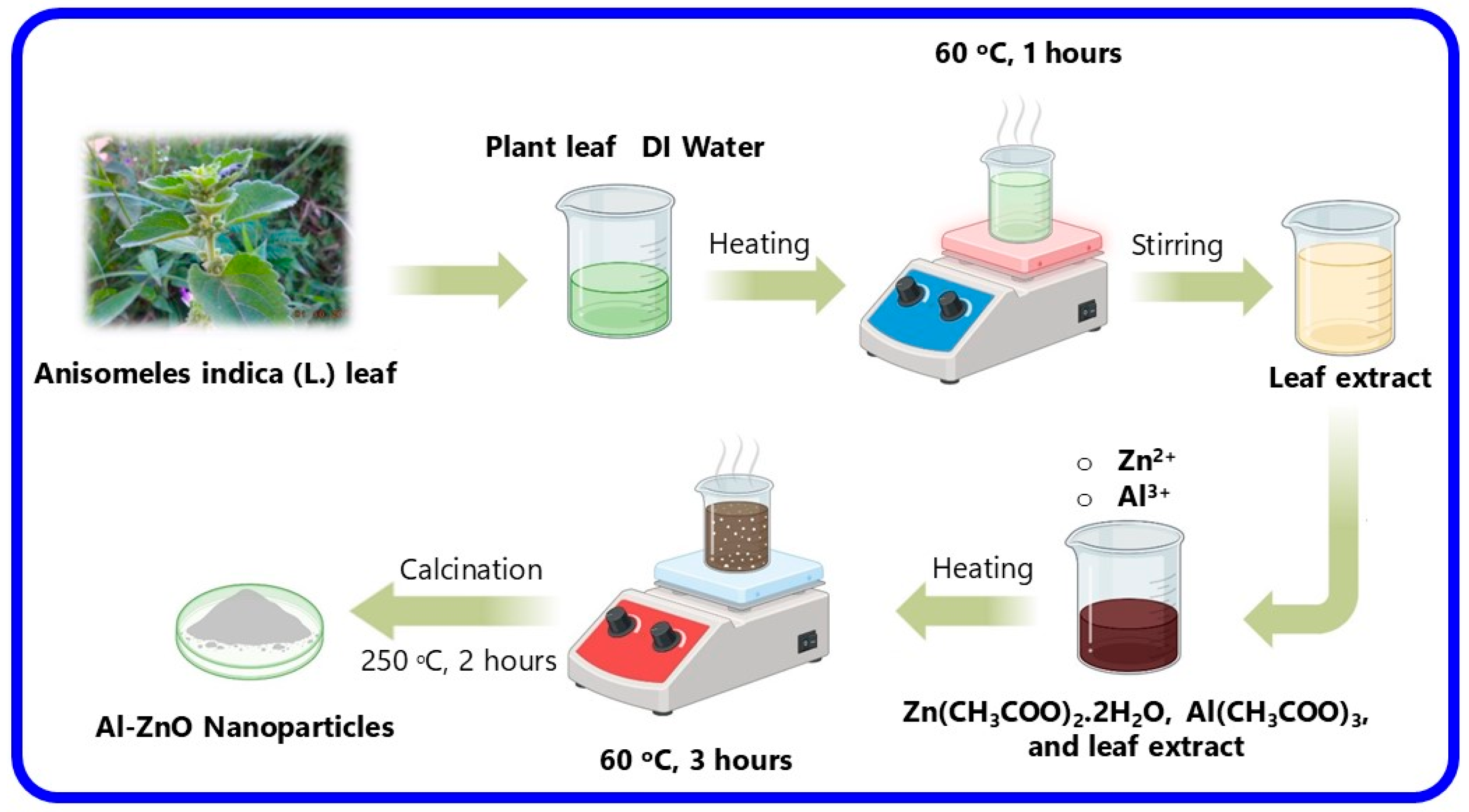
2.3. Green Synthesis of Al-ZnO Nanoparticles
2.4. Characterization of Al-ZnO Nanoparticles
2.5. Microbial Assay
2.5.1. Test Microorganisms
2.5.2. Zone of Inhibition Assay
2.5.3. Evaluated Methods
2.5.4. Agar Diffusion Well Variant
2.6. Antioxidant Studies of Al-ZnO Nanoparticles
2.6.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.6.2. Determination of IC50 Value
2.6.3. MTT Assay
2.7. In Vitro Anti-Diabetic Activity of Al-ZnO Nanoparticles
2.7.1. α-Amylase Inhibition Assay
2.7.2. α-Glycosidase Inhibition Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Studies of Al-ZnO Nanoparticles Using Anisomeles indica (L.) Leaf Extract
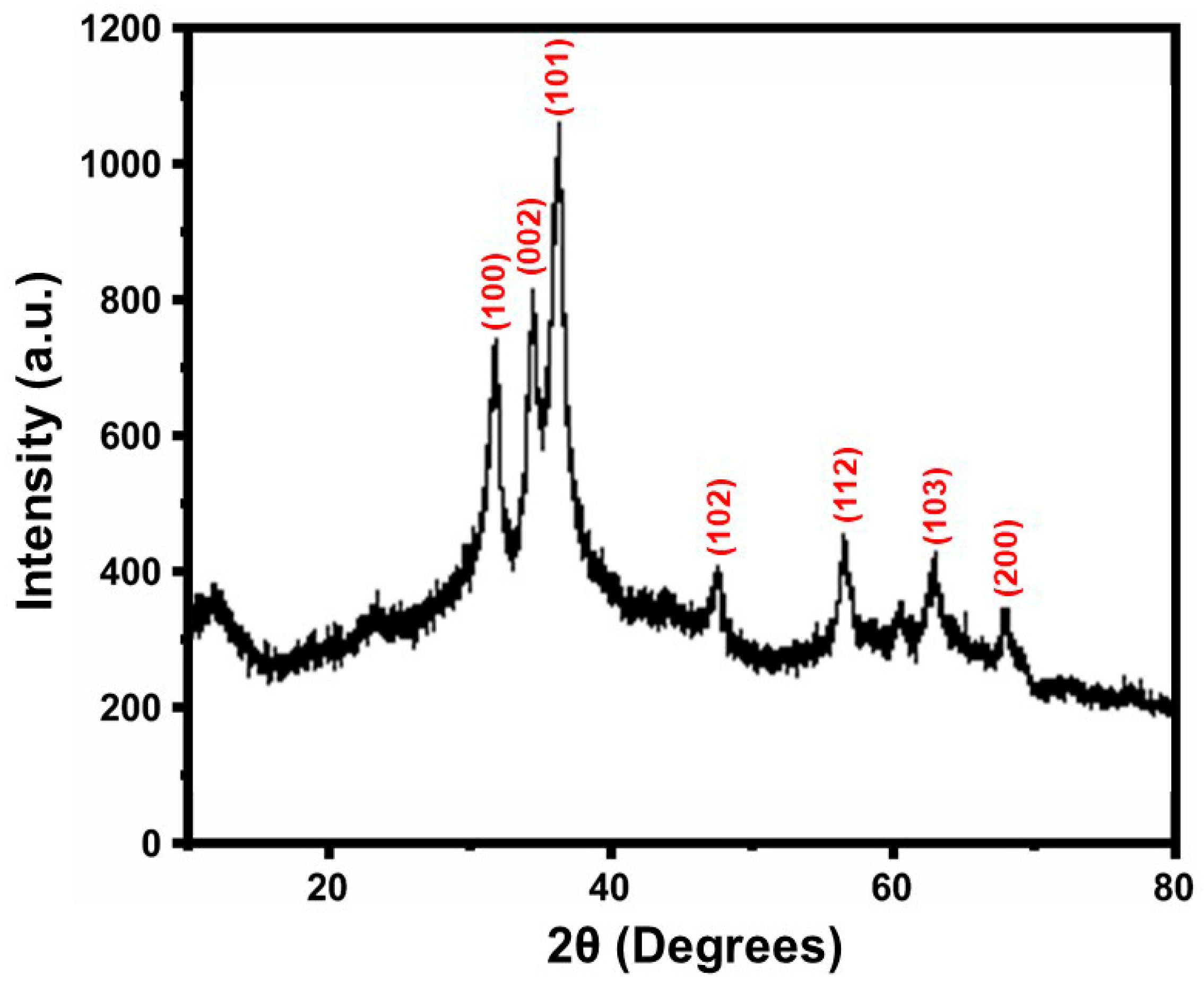
3.1.1. XRD Analysis
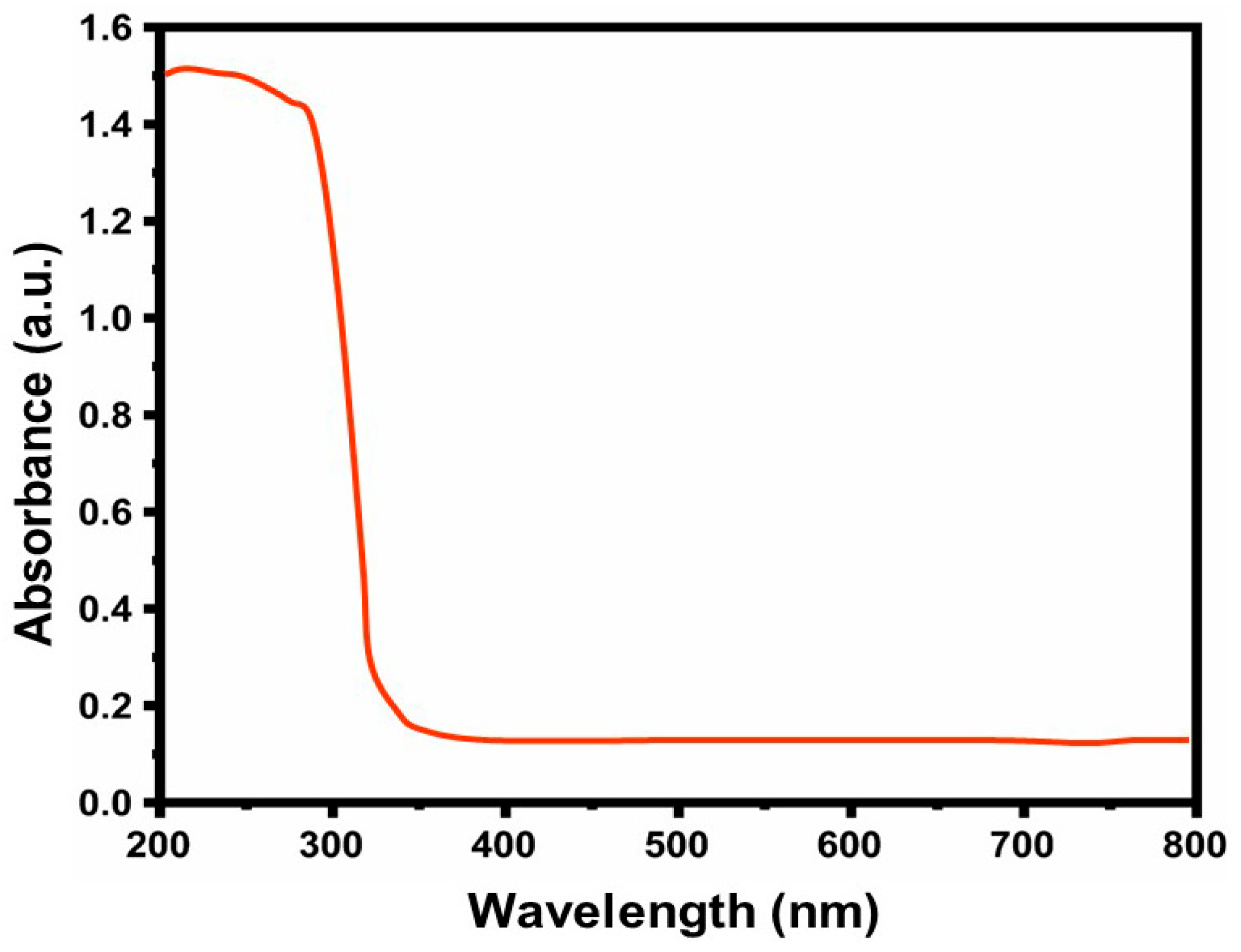
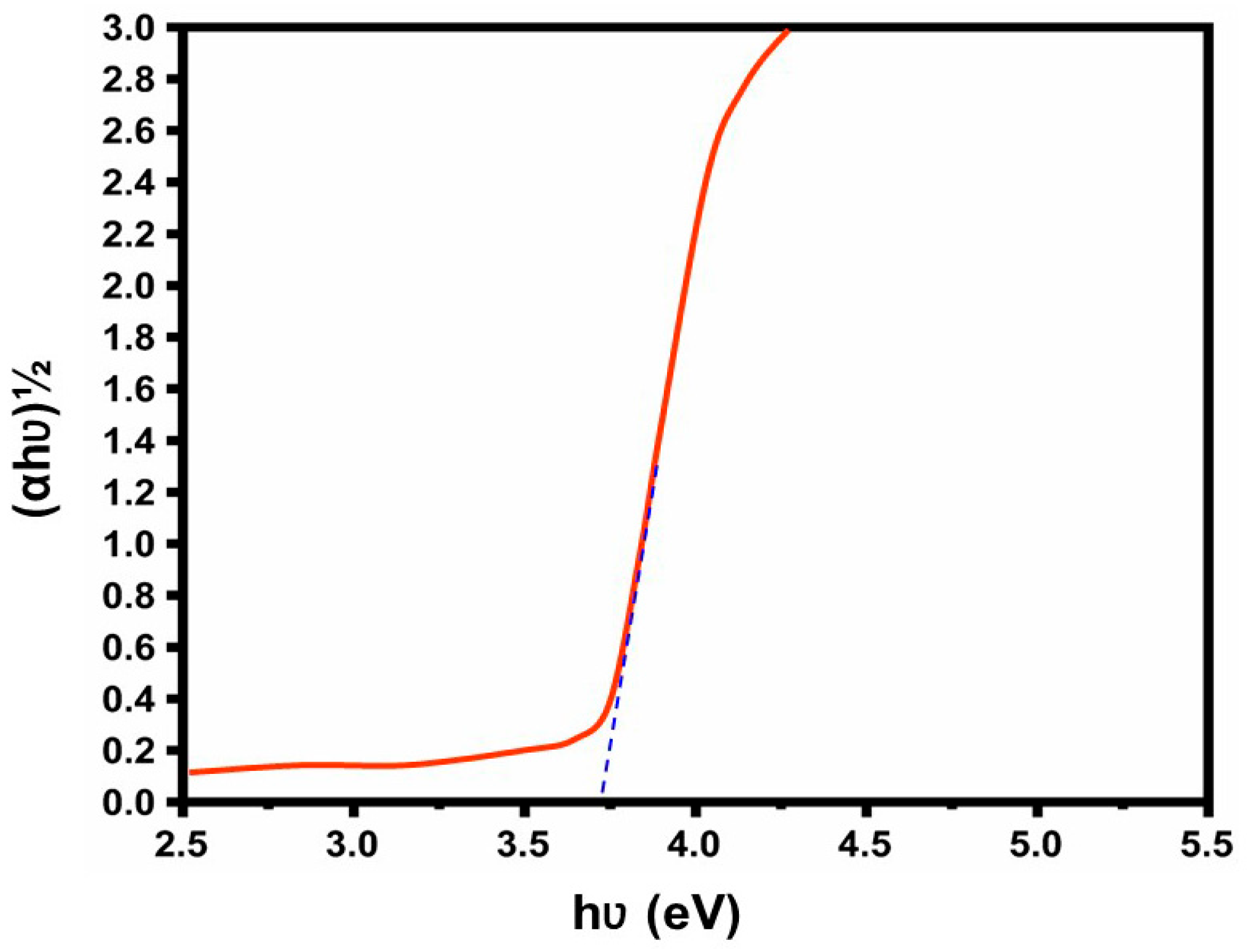
3.1.2. UV–Vis Studies
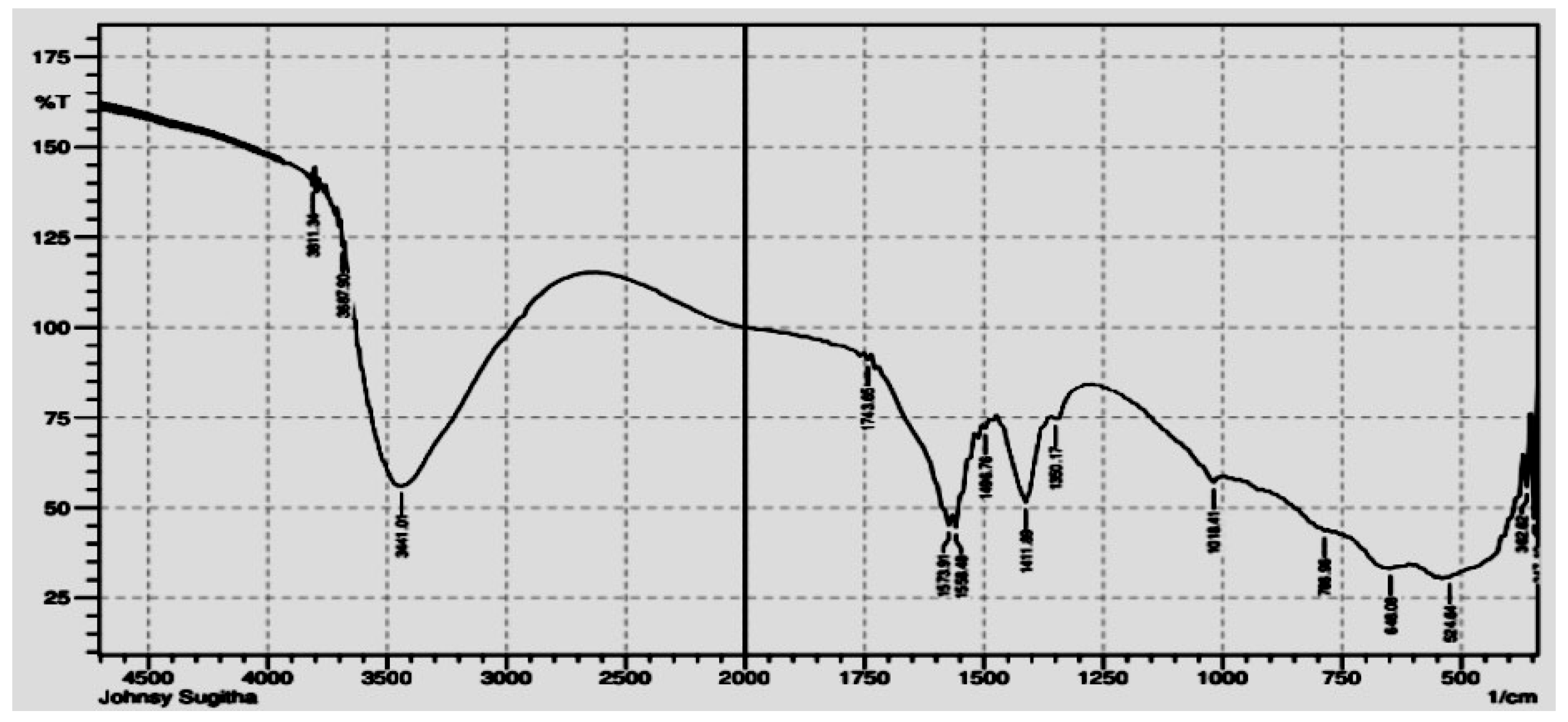
3.1.3. FTIR Analysis
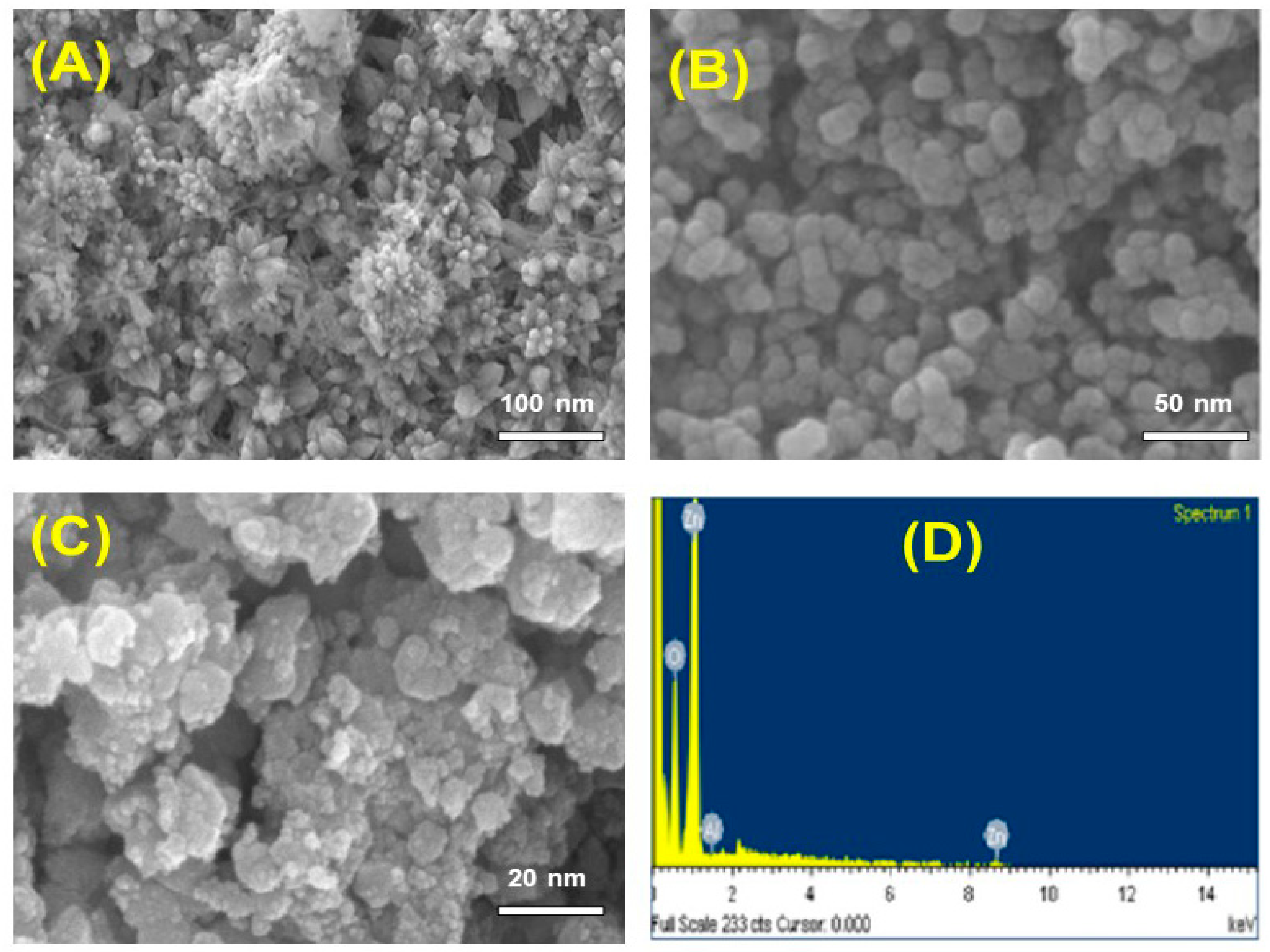
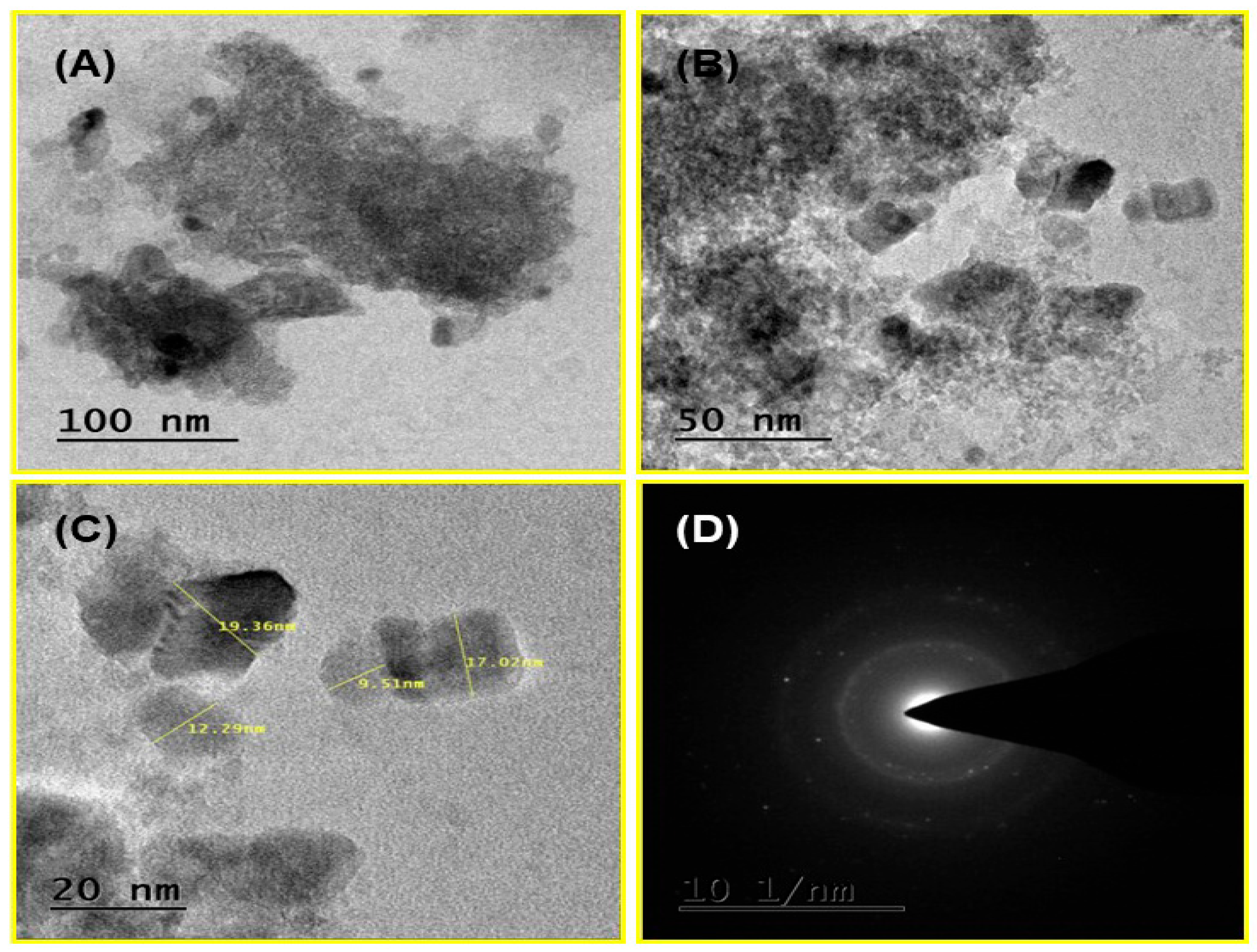
3.1.4. Morphological Studies
3.2. Biological Studies of Al-ZnO Nanoparticles
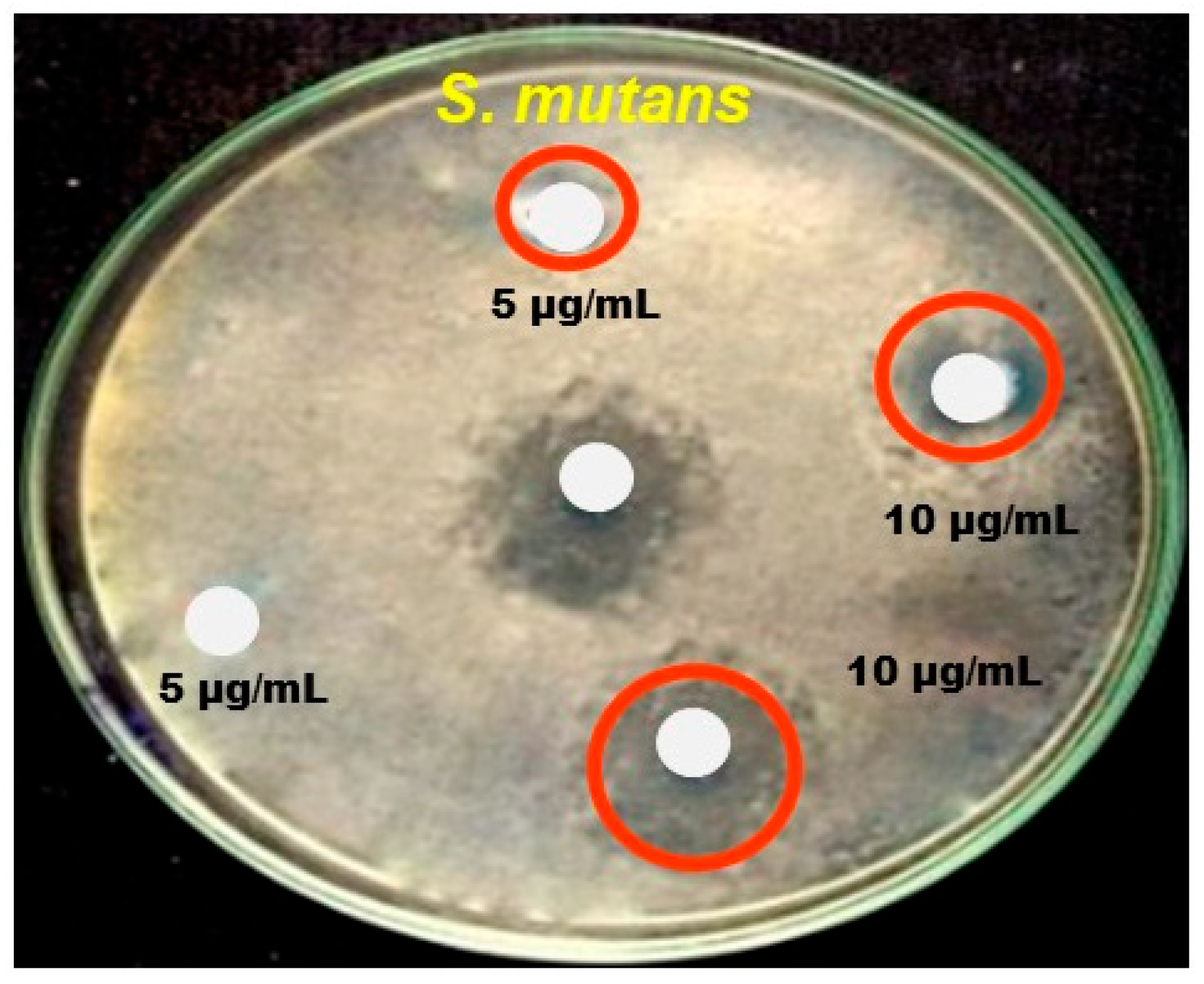
3.2.1. Antibacterial Activity
3.2.2. Antifungal Activity
3.2.3. Antioxidant Studies
3.2.4. Anticancer Studies
3.3. Anti-Diabetic Studies of Al-ZnO Nanoparticles
3.3.1. α-Amylase Activity
3.3.2. α-Glucosidase Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Nanotechnology: A revolution in modern industry. Molecules 2023, 28, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C. Application of nanomaterials in biomedical imaging and cancer therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambzickaite, G.; Talaikis, M.; Dobilas, J.; Stankevic, V.; Drabavicius, A.; Niaura, G.; Mikoliunaite, L. Microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of nanocrystallite-derived magnetite spheres. Materials 2022, 15, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, B.; Singh, P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Budhwar, V. Eco-friendly greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzeid, H.M.; Julien, C.M.; Zhu, L.; Hashem, A.M. Green synthesis of nanoparticles and their energy storage, environmental, and biomedical applications. Crystals 2023, 13, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Plant-based green synthesis of nanoparticles: Production, characterization and applications. Biomolecules 2021, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kafshgari, M.H.; Meunier, M. Optical properties and applications of plasmonic-metal nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavali, M.S.; Nikolova, M.P. Metal oxide nanoparticles and their applications in nanotechnology. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, S.; Donga, S.; Pande, J. Green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles: A review of antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic and photocatalytic properties. In Zinc Oxide: Production, Properties and Applications; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Shao, W.Z.; Li, W.J.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhen, L.; Li, Y. Suppressing the agglomeration of ZnO nanoparticles in air by doping with lower electronegativity metallic ions: Implications for Ag/ZnO electrical contact composites. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 10809–10817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, O.; Ray, A.; Gadnayak, A.; Champati, B.B.; Jena, S.; Sahoo, A.; Das, P.K.; Kamila, P.K.; Nayak, S.; Panda, P.C. Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze leaf essential oil ameliorates LPS-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 cells: An integrated approach of network pharmacology and experimental validation. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 169, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, A.; Murugan, P.J.; Paularokiadoss, F. Biological synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) from Anisomeles malabarica. Vietnam J. Chem. 2022, 60, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Jiang, W.-P.; Deng, J.-S.; Chou, Y.-N.; Wu, Y.-B.; Liang, H.-J.; Lin, J.-G.; Huang, G.-J. Anisomeles indica Extracts and their constituents suppress the protein expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 In Vivo and In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayegowda, S.B.; Sarma, G.; Gadilingappa, M.N.; Alghamdi, S.; Aslam, A.; Refaat, B.; Almehmadi, M.; Allahyani, M.; Alsaiari, A.A.; Aljuaid, A.; et al. Green-synthesized nanoparticles and their therapeutic applications: A review. Green Process. Synth. 2023, 12, 20230001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veera Kumar, K.; Govindarajan, M. Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Anisomeles indica and their mosquito efficacy. Int. J. Zool. Anim. Biol. 2019, 2, 000176. [Google Scholar]
- Antil, R.; Singh, L.; Gahlawat, D.K.; Dahiya, P. Investigation of chemical composition of methanolic extract of Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze by using FTIR and GC-MS. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Mahomoodally, M.F.; Protab, K.; Aumeeruddy, M.Z. Medicinal plants brought by Indian indentured immigrants: A comparative review of ethnopharmacological uses between Mauritius and India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 234, 245–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nateq, M.H.; Ceccato, R. Enhanced sol–gel route to obtain a highly transparent and conductive aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin film. Materials 2019, 12, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, S.; Sasani Ghamsari, M.; Lee, C.; Han, W.; Park, H.H.; Tafreshi, M.J.; Afarideh, H.; Ara, M.H.M. Preparation and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghurabi, M.N.A.K.; Mahmood, R.S.; Salim, E.T.; Alhasan, S.F.H.; Khalid, F.G. Structure, optical, and morphological investigations of nano copper oxide prepared using RPLD at different laser wavelength effects. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 2497–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, V.; Hasan, A.; Sharma, S.; Pandey, L.M. Edible oil nanoemulsion: An organic nanoantibiotic as a potential biomolecule delivery vehicle. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2018, 67, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehana, D.; Mahendiran, D.; Kumar, R.S.; Rahiman, A.K. In vitro antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Pandey, V.; Husain, M.S.; Munjal, S. Structural and spectroscopic analysis of pure phase hexagonal wurtzite ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, J.; Alam, T. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their antibacterial properties using plant extract of aristolochia elegans, Asian J. Chem. 2020, 32, 2589–2593. [Google Scholar]
- Disha, S.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Habib, M.L.; Ahmed, S. Calculation of crystallite sizes of pure and metals doped hydroxyapatite engaging Scherrer method, Halder-Wagner method, Williamson-Hall model, and size-strain plot. Results Mater. 2024, 21, 100496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, A.; Assem, E.E.; Shaaban, E.R. Investigation of dilute aluminum doped zinc oxide thin films: Structural and morphological properties for varies applications. J. Ovonic Res. 2022, 18, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarroum, M.; Alfarraj, N.S.; Al-Qurainy, F.; Al-Hashimi, A.; Khan, S.; Nadeem, M.; Salih, A.M.; Shaikhaldein, H.O. Improving the production of secondary metabolites via the application of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles in the calli of Delonix elata: A potential medicinal plant. Metabolites 2023, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porrawatkul, P.; Nuengmatcha, P.; Kuyyogsuy, A.; Pimsen, R.; Rattanaburi, P. Effect of Na and Al doping on ZnO nanoparticles for potential application in sunscreens. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2023, 240, 112668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, H.; Yakuphanoglu, F.; Aydın, C. Al-doped ZnO as a multifunctional nanomaterial: Structural, morphological, optical and low-temperature gas sensing properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.G.; Velu, A.S. Synthesis, structural and optical properties of pure ZnO and Co doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by the co-precipitation method. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2016, 10, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Jan, H.; Shah, S.A.; Shah, S.; Khan, A.; Akbar, M.T.; Rizwan, M.; Jan, F.; Wajidullah, A.N.; Khattak, A.; et al. Green synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using aqueous fruit extracts of Myristica fragrans: Their characterizations and biological and environmental applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9709–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekha, S.M.; Neelamana, H.V.; Bhat, S.V. Recent advances in solution-processed zinc oxide thin films for ultraviolet photodetectors. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 4051–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, V.; Kumar, M.; Shukla, D.K.; Choudhary, R.J.; Phase, D.M.; Kumar, R.; Joshi, B.C. Structural, optical and electronic structure studies of Al doped ZnO thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 2015, 83, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.A.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The chemistry of reactive oxygen species (ROS) revisited: Outlining their role in biological macromolecules (DNA, lipids and proteins) and induced pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Tai, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z. Nanomedicine-induced programmed cell death enhances tumor immunotherapy. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 62, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanag, F.M.; Bayrami, A.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Pouran, S.R. A comprehensive study on antidiabetic and antibacterial activities of ZnO nanoparticles biosynthesized using Silybum marianum L seed extract. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashtoh, H.; Baek, K.H. New insights into the Latest advancement in α-amylase inhibitors of plant origin with anti-diabetic effects. Plants 2023, 12, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
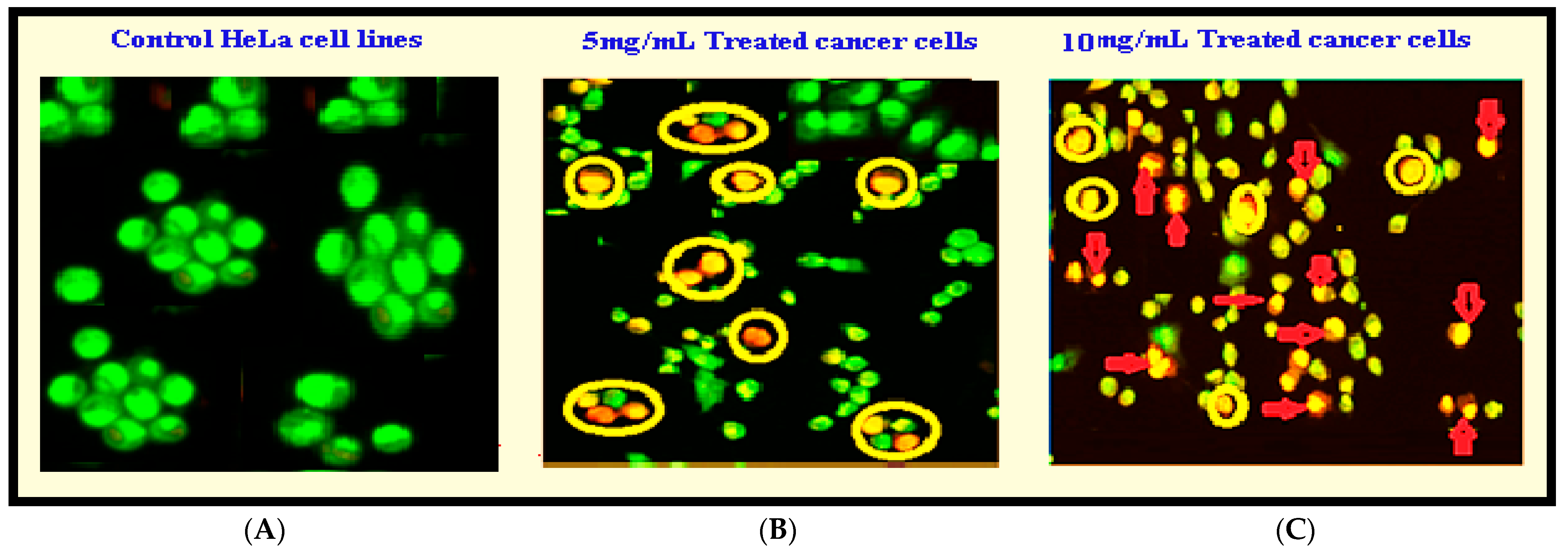
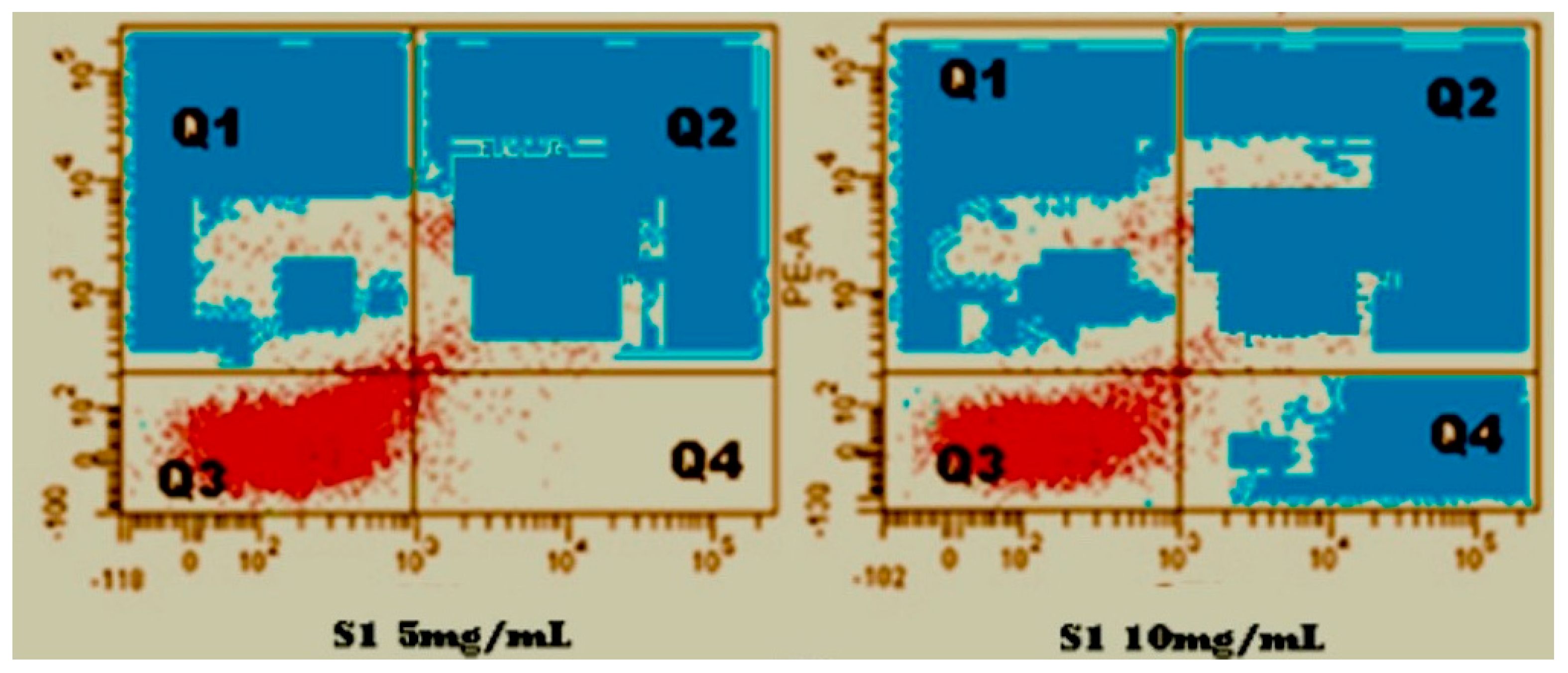
| Name of the Organisms | Zone of Inhibition (mm-cm) | Positive Control | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg/mL | 10 mg/mL | ||
| K. pneumonea | 1.64 ± 0.21 | 2.45 ± 0.01 | 4.63 ± 0.11 |
| E. coli | 3.17 ± 0.02 | 4.01 ± 0.02 | 2.10 ± 0.01 |
| V. cholera | 2.00 ± 0.45 | 4.40 ± 0.02 | - |
| B. subtilis | 1.62 ± 0.21 | 2.32 ± 0.02 | 3.25 ± 0.91 |
| S. aureus | 1.92 ± 0.25 | 2.74 ± 0.05 | - |
| S. mutans | 3.00 ± 0.06 | 5.74 ± 0.07 | 4.22 ± 0.03 |
| Name of the Organisms | Zone of Inhibition (mm-cm) | Positive Control | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg/mL | 10 mg/mL | ||
| Aspergillus flavus | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 1.89 ± 0.01 | 2.00 ± 0.10 |
| Candida albicans | - | - | 3.22 ± 0.15 |
| S. No | Concentration (mg/mL) | IC50 Value (µM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 0.2 | 18.00 ± 0.10 |
| 2. | 0.4 | 20.13 ± 0.37 |
| 3. | 0.6 | 24.11 ± 0.71 |
| 4. | 0.8 | 30.72 ± 1.52 |
| 5. | 1.0 | 41.58 ± 1.23 |
| 6. | IC50 value mg/mL | 23.52 ± 0.03 |
| S. No | Concentration (mg/mL) | IC50 Value (µM) | Inhibition (%) | IC50 mg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1.0 | 0.411 ± 0.02 | 32.65 | 23.61 |
| 2. | 2.5 | 0.155 ± 0.02 | 59.65 | |
| 3. | 5.0 | 0.226 ± 0.03 | 70.76 | |
| 4. | 10.0 | 0.213 ± 0.03 | 80.39 |
| Concentration (mg/mL) | Absorbant Value of α-Amylase | Absorbant Value of α-Glucosidase | Average | Enzyme Activity (mg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Amylase | α-Glucosidase | ||||
| 0.2 | 18.65 | 19.07 | 18.86 ± 0.40 | 36.38 | 13.70 |
| 0.4 | 20.13 | 20.28 | 20.25 ± 0.20 | 39.06 | 18.72 |
| 0.6 | 24.11 | 23.11 | 23.61 ± 0.71 | 45.55 | 21.07 |
| 0.8 | 30.72 | 31.08 | 30.90 ± 0.28 | 59.61 | 28.98 |
| 1.0 | 39.58 | 38.64 | 39.11 ± 0.37 | 75.45 | 34.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sugitha, S.K.J.; Latha, R.G.; Venkatesan, R.; Vetcher, A.A.; Ali, N.; Kim, S.-C. Biological Effects of Green Synthesized Al-ZnO Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract from Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze on Living Organisms. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171407
Sugitha SKJ, Latha RG, Venkatesan R, Vetcher AA, Ali N, Kim S-C. Biological Effects of Green Synthesized Al-ZnO Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract from Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze on Living Organisms. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(17):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171407
Chicago/Turabian StyleSugitha, S. K. Johnsy, R. Gladis Latha, Raja Venkatesan, Alexandre A. Vetcher, Nemat Ali, and Seong-Cheol Kim. 2024. "Biological Effects of Green Synthesized Al-ZnO Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract from Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze on Living Organisms" Nanomaterials 14, no. 17: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171407
APA StyleSugitha, S. K. J., Latha, R. G., Venkatesan, R., Vetcher, A. A., Ali, N., & Kim, S.-C. (2024). Biological Effects of Green Synthesized Al-ZnO Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract from Anisomeles indica (L.) Kuntze on Living Organisms. Nanomaterials, 14(17), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171407










