Study of the Effects on the Strengthening Mechanism and Wear Behavior of Wear-Resistant Steel of Temperature Controlling in Heat Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation Process
2.2. EBSD Observation
2.3. TEM Observation
2.4. Mechanical Property Test
2.5. Wear Resistance Test
3. Results and Discussion
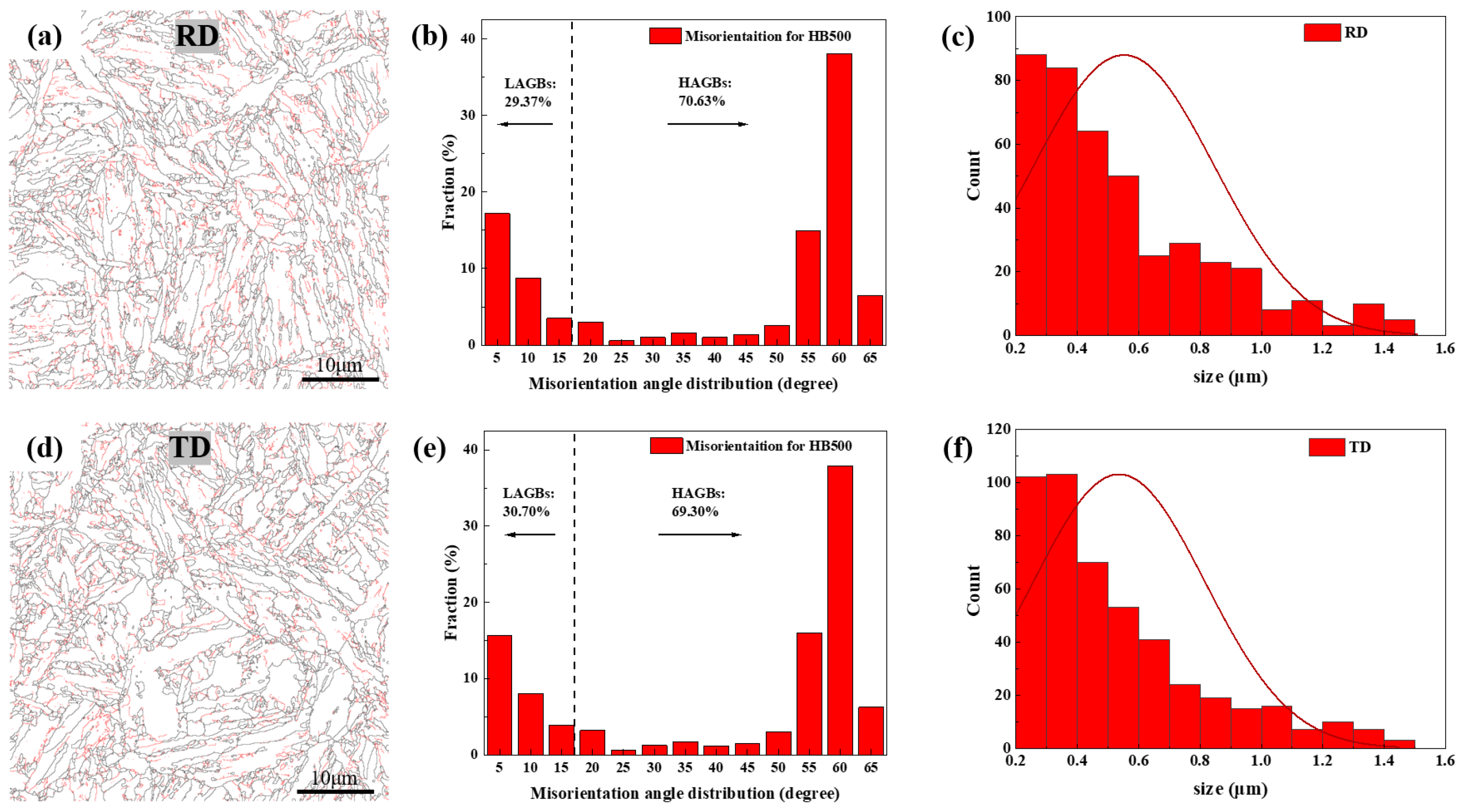
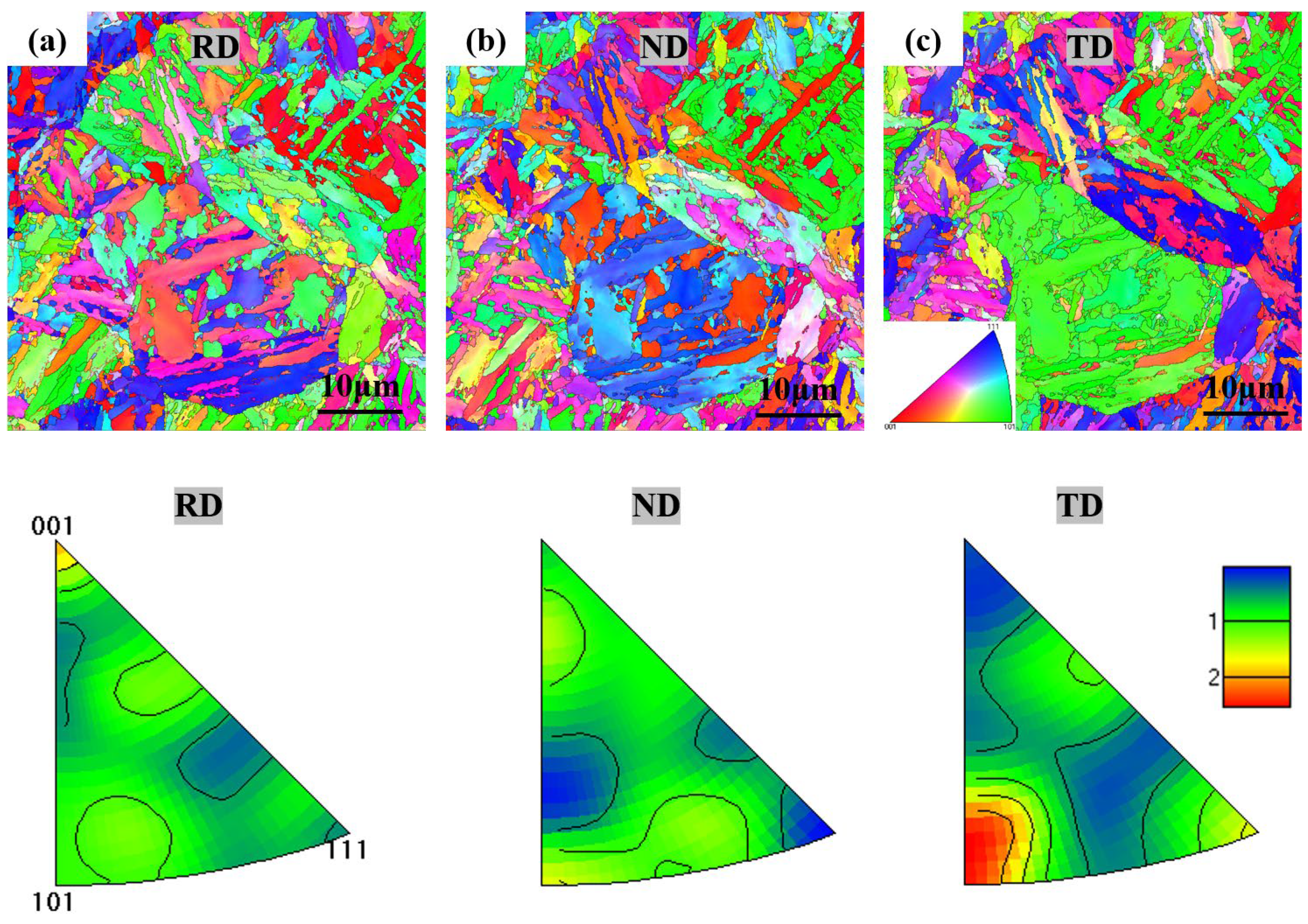
3.1. EBSD Analysis
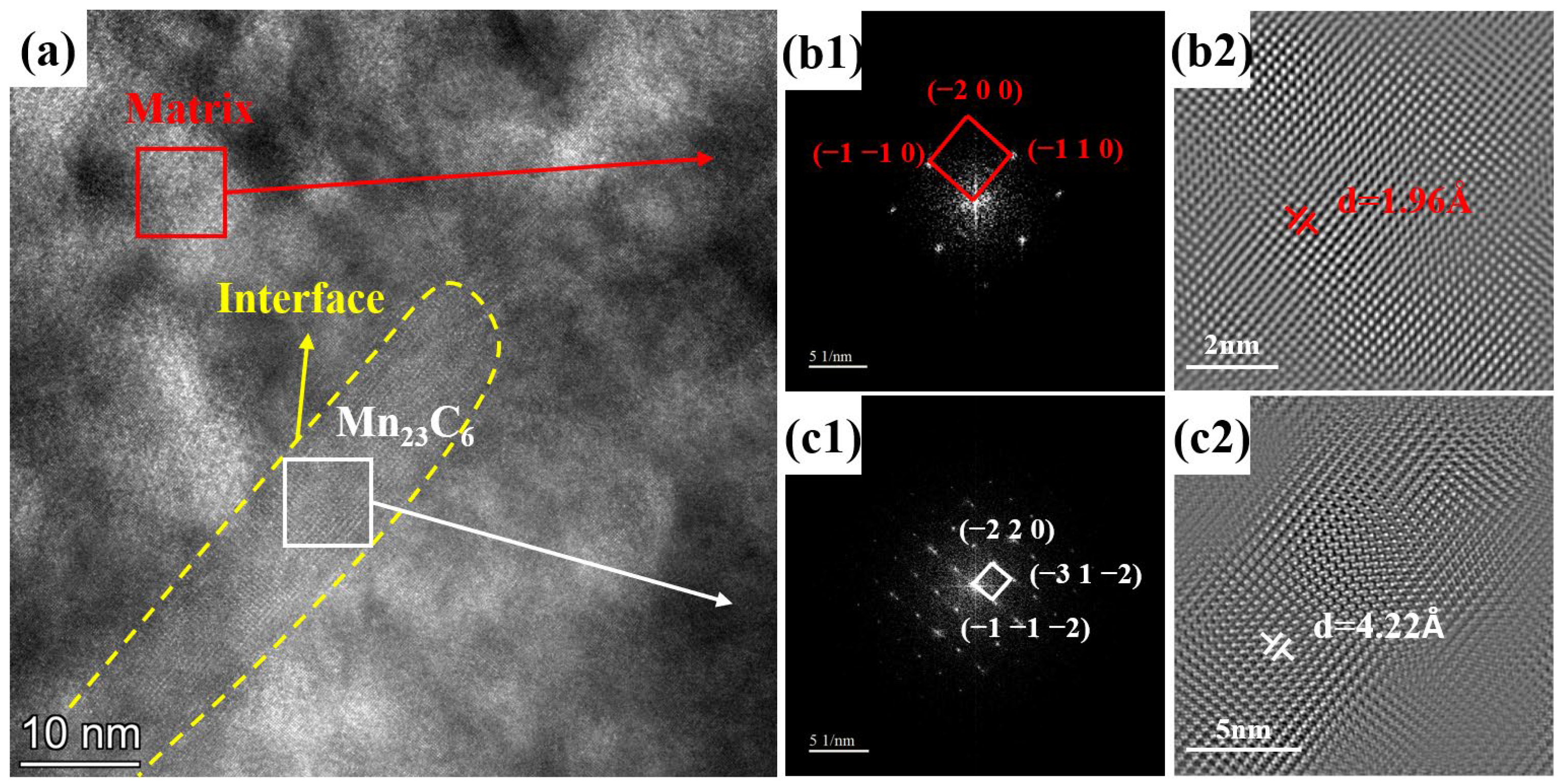
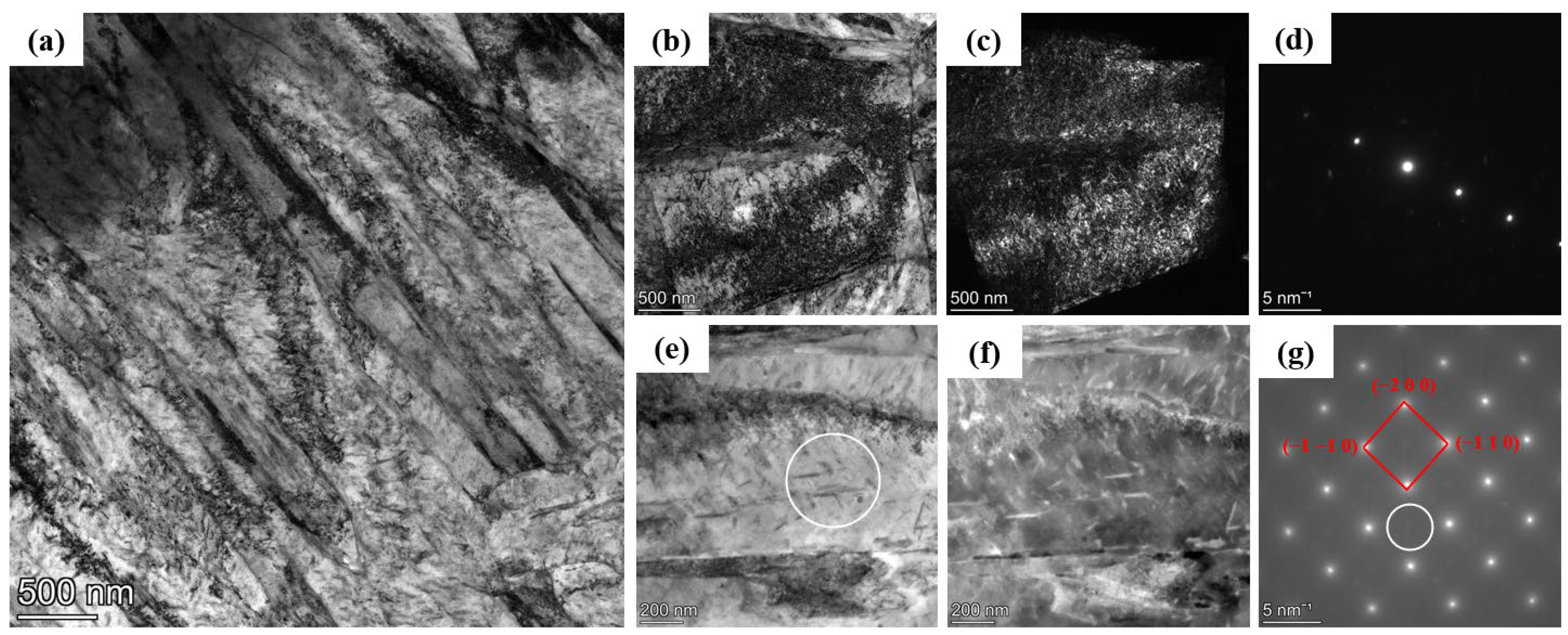
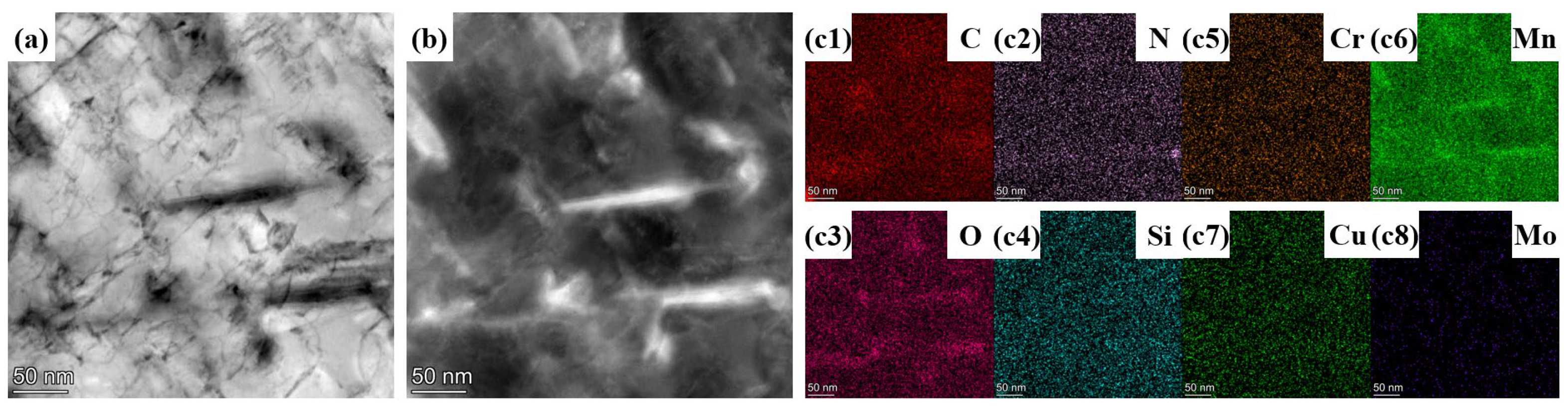
3.2. TEM Analysis
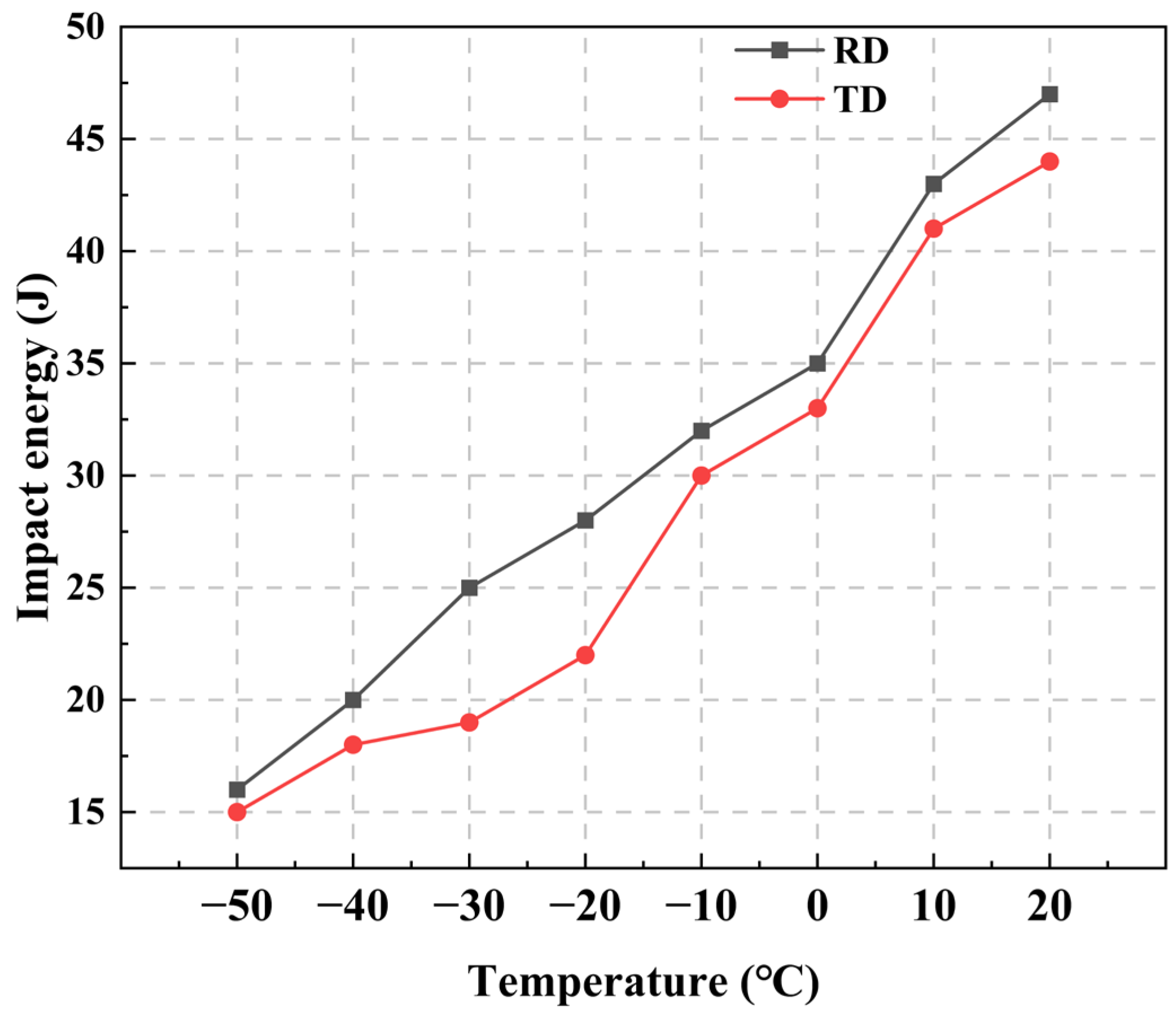
3.3. Mechanical Property Analysis
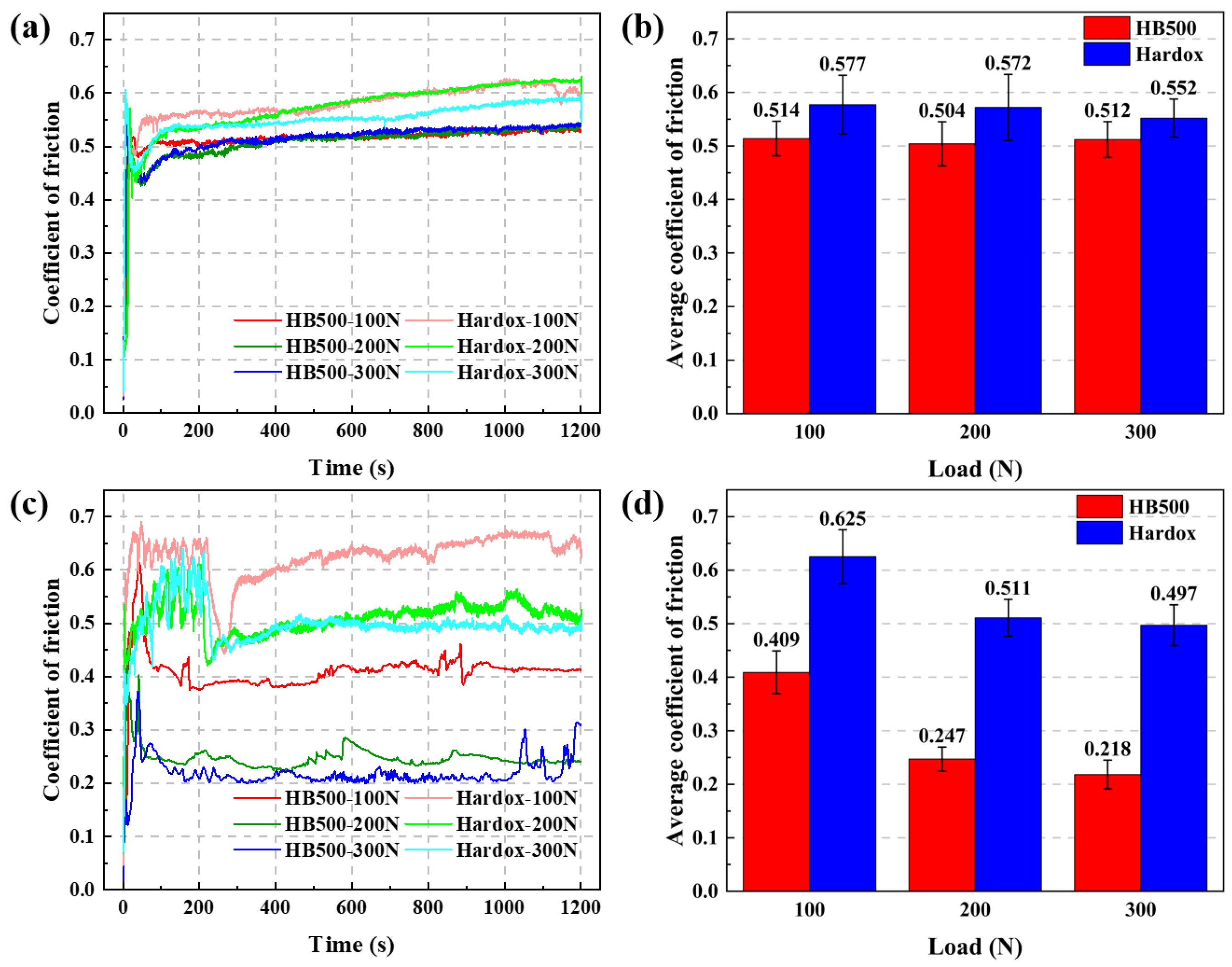
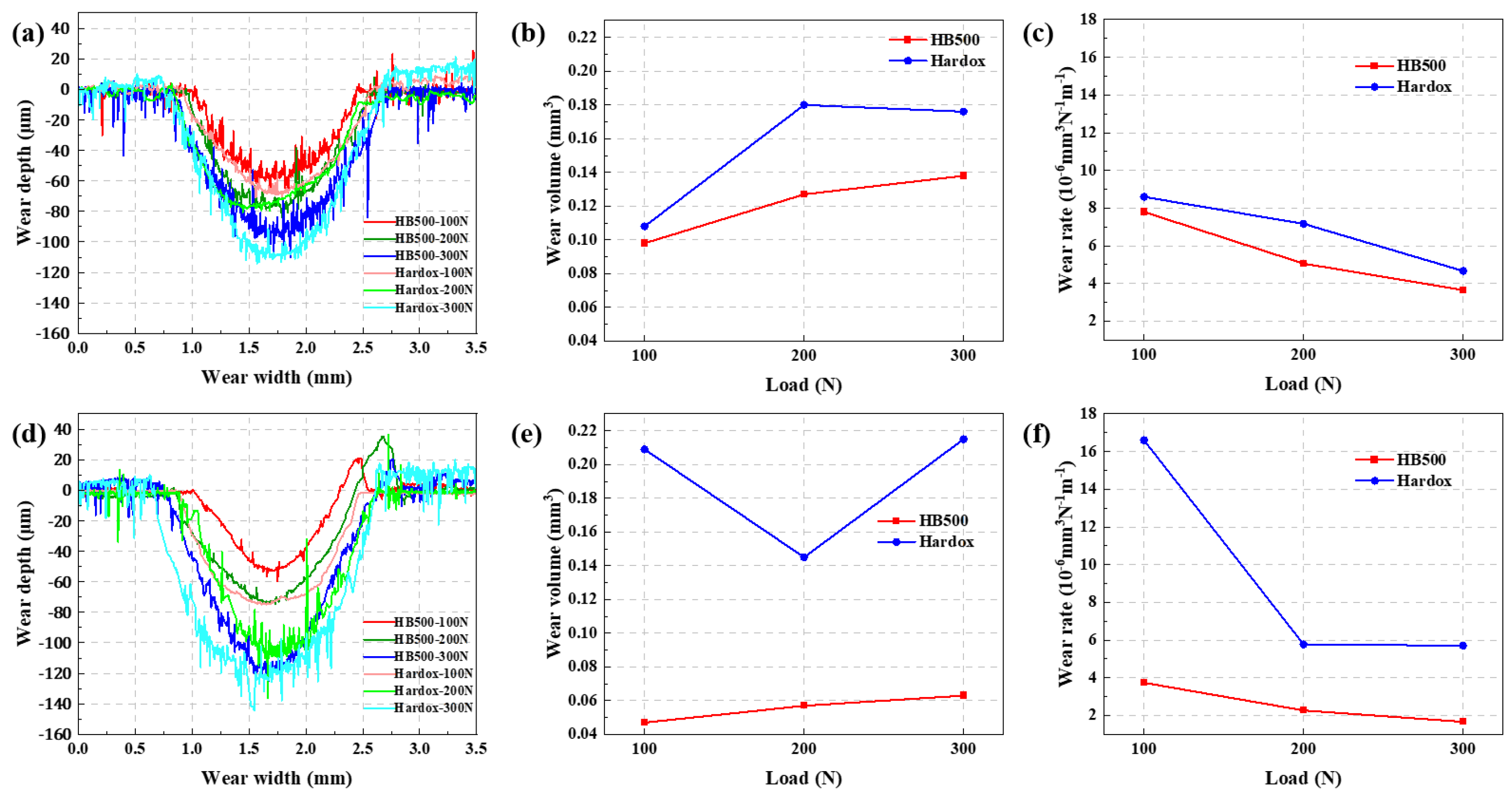
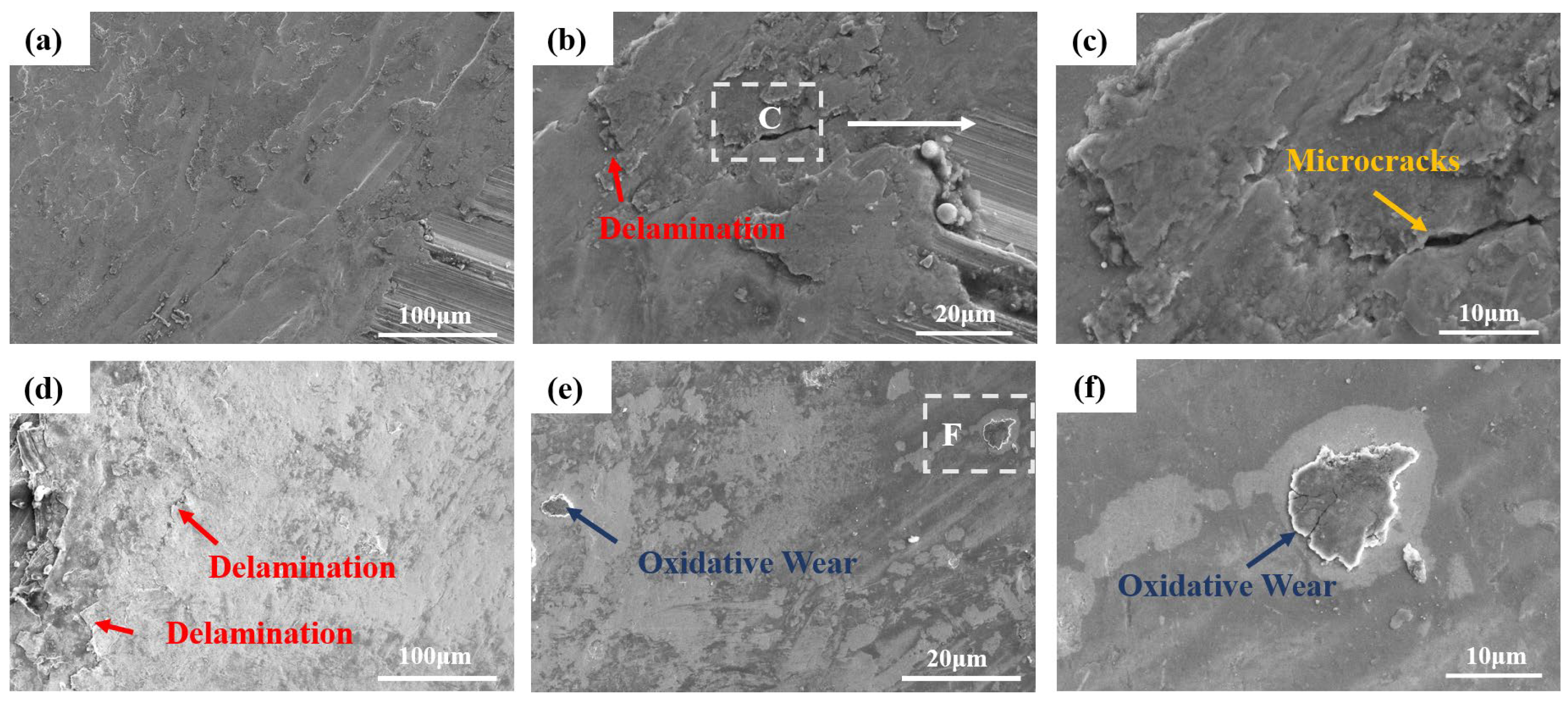
3.4. Wear Resistance Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ojala, N.; Valtonen, K.; Heino, V.; Kallio, M.; Aaltonen, J.; Siitonen, P.; Kuokkala, V.-T. Effects of composition and microstructure on the abrasive wear performance of quenched wear resistant steels. Wear 2014, 317, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojacz, H.; Katsich, C.; Kirchgaßner, M.; Kirchmayer, R.; Badisch, E. Impact-abrasive wear of martensitic steels and complex iron-based hardfacing alloys. Wear 2022, 492–493, 204183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tümer, M.; Schneider-Bröskamp, C.; Enzinger, N. Fusion welding of ultra-high strength structural steels—A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 82, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón, J.; Olsson, M. Abrasive wear resistance of some commercial abrasion resistant steels evaluated by laboratory test methods. Wear 2009, 267, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Xu, L. Review on research progress of steel and iron wear-resistant materials. Acta Met. Sin 2019, 56, 523–538. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Ding, H.; Beladi, H.; Hodgson, P.; Cai, M. Improved Mn–segregation bands and its influence on deformation behavior in a severely warm–rolled 10 Mn lightweight steel. Vacuum 2023, 216, 112428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Cao, R.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Wu, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Effect of Cr on the phase transformation and interphase nanoprecipitation behaviours of high-strength microalloyed steels. Mater. Charact. 2024, 207, 113504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Qian, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, T.; Li, K.; Wei, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, F.; Meng, J. Roles of Al in enhancing the thermal stability of reverted austenite and mechanical properties of a medium-Mn TRIP steel containing 2.7 Mn. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 167, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Cao, Y.H.; Ke, Y.B.; Yuan, X.Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Influences of Cu on microstructure and mechanical properties in Fe–Ni–Al ultra-strong maraging steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 886, 145724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, C.; Wang, R.; Zhao, C.; Wei, R.; Li, H.; Deng, R.; Bai, Q.; Liu, Y. Study on ductile iron surface laser cladding austenitic stainless steel coating heat treatment to enhance wear resistance. Tribol. Int. 2024, 191, 109202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Xiao, Q.; Fu, H. Heat treatment of multi-element low alloy wear-resistant steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 396, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecu, R. Enhancing wear resistance of R220 rail steels by quenching and partitioning (Q&P) treatment. Mater. Lett. 2024, 354, 135400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavuşoğlu, O.; Çavuşoğlu, O.; Yılmazoğlu, A.G.; Üzel, U.; Aydın, H.; Güral, A. Microstructural features and mechanical properties of 22MnB5 hot stamping steel in different heat treatment conditions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10901–10908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahany, A.N.; Saghafian, H.; Borhani, G. The effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of AISI420 martensitic stainless steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Yang, G.; Fu, Z.; Xu, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, G. Effect of low-temperature hot rolling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of air-cooling medium manganese martensitic wear-resistant steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 203, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, S.; Yue, H.; Ji, P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. Sliding wear resistance of Fe–30Mn–8Al–1.2C steel modulated by κ–carbide. Wear 2024, 546–547, 205353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, J.; Das, K.; Das, S. An investigation of mechanical property and sliding wear behaviour of 400 Hv grade martensitic steels. Wear 2020, 458, 203436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Fu, T.; Wang, Z. Three-body abrasion wear resistance of TiC-reinforced low-alloy abrasion-resistant martensitic steel under dry and wet sand conditions. Wear 2020, 452–453, 203310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Xu, T.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, Y.; Sun, W.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; et al. Achieving a superior combination of tensile properties and corrosion resistance in AISI420 martensitic stainless steel by low-temperature tempering. Corros. Sci. 2023, 225, 111551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 228.1-2021; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Room Temperature Test Method. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 229-2020; Metallic Materials—Charpy Pendulum Impact Test Method. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Sonderegger, B.; Mitsche, S.; Cerjak, H. Microstructural analysis on a creep resistant martensitic 9–12% Cr steel using the EBSD method. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 481–482, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, W.; Ruan, M.; Chen, Z. Effects of temperatures on microstructure evolution and deformation behavior of Fe–32Ni by in-situ EBSD. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 875, 145097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, A.; Miyamoto, G.; Morito, S.; Nakamura, A.; Moronaga, T.; Kitano, H.; Gutierrez-Urrutia, I.; Hara, T.; Tsuzaki, K. Substructure and crystallography of lath martensite in as-quenched interstitial-free steel and low-carbon steel. Acta Mater. 2023, 246, 118675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, H.; Sun, Z.; Yang, Y.; He, W.; Xu, J.; Xia, Y.; Yin, W. Effect of Si on the dislocation state within martensite of ultra-high strength hot-rolled medium Mn steel with good ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 869, 144825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xiao, X.; Chen, L.; Cheng, Y.; Duan, H. A hierarchical theoretical model for mechanical properties of lath martensitic steels. Int. J. Plast. 2018, 111, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialobrzeska, B.; Kostencki, P. Abrasive wear characteristics of selected low-alloy boron steels as measured in both field experiments and laboratory tests. Wear 2015, 328–329, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. A model for the microstructure behaviour and strength evolution in lath martensite. Acta Mater. 2015, 98, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W. Study on the Process Performance of Swedish Hardox500 Wear resistant Steel Plate. Technol. Enterp. 2014, 15, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raex. Raex-500. Available online: https://www.raexsteel.com/en/product-portfolio/raex-500 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Songhan. ThyssenKrupp XAR® 500 Structural Steel. Available online: https://www.lookpolymers.com/polymer_ThyssenKrupp-XAR-500-Structural-Steel.php (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Chen, K.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, F.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Gong, W.; Chen, C. Effect of quenching and tempering temperature on microstructure and tensile properties of microalloyed ultra-high strength suspension spring steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 766, 138272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihao, M.; Rongfu, X.; Peng, Q.; Feng, S.Y.; Yunshan, Z. The Effects of Quenching and Partitioning on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of High Strength Suspension Spring Steel. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, M.; Tekeli, S. The effect of martensite particle size on tensile fracture of surface-carburised AISI 8620 steel with dual phase core microstructure. Mater. Des. 2002, 23, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Tarafder, S. Geometry of dimples and its correlation with mechanical properties in austenitic stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yu, H.; Wang, S. Effect of microstructural types on toughness and microstructural optimization of ultra-heavy steel plate: EBSD analysis and microscopic fracture mechanism. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 658, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Liu, Z.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Qiao, S. Effect of martensite–austenite constituents on impact toughness of pre-tempered MnNiMo bainitic steel. Mater. Charact. 2020, 161, 110139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Liu, H.; Sun, C.; Liu, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Cai, X.; Fu, P.; Wang, P.; Li, D. Effectively improving the hardness-strength-toughness of carburized bearing steel via nanoprecipitates and fine grain structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 872, 144961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, G.; Zhao, G.; Mao, X.; Gan, X.; Yin, Q.; Yi, H. Effect of Nb on the microstructure and properties of Ti-Mo microalloyed high-strength ferritic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.I.; Kelly, A. Strengthening Methods in Crystals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1971; p. 137. [Google Scholar]
- Long, S.-L.; Liang, Y.-L.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, M.; Yi, Y.-L. Effect of quenching temperature on martensite multi-level microstructures and properties of strength and toughness in 20CrNi2Mo steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 676, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Jiang, S.; Lin, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wen, B. High-pressure quenching effect on martensitic transformation characteristics and mechanical properties of low-alloy medium-carbon steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tao, Q.; Fan, J.; Fu, L.; Shan, A. Enhanced mechanical properties of a high-carbon martensite steel processed by heavy warm rolling and tempering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 872, 144958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, G.; Kang, Y. Effect of substructure on mechanical properties and fracture behavior of lath martensite in 0.1C–1.1Si–1.7Mn steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 675, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-J.; Ren, X.-P.; Hu, Z.-L.; Xiong, Z.-P.; Zeng, J.-M.; Hou, B.-Y. Effect of tempering on microstructure and mechanical properties of 3Mn-Si-Ni martensitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Vishnu, K.G.; Titus, M.S.; Strachan, A. Uncovering the role of nanoscale precipitates on martensitic transformation and superelasticity. Acta Mater. 2022, 229, 117790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yu, B.; Misra, R.; Han, G.; Liu, S.; Shang, C. Strengthening of cobalt-free 19Ni3Mo1. 5Ti maraging steel through high-density and low lattice misfit nanoscale precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 715, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.C.; Liu, S.F.; Wu, H.H.; Luan, J.H.; Guo, J.M.; Yang, T.; Jiao, Z.B. Nanoscale precipitation, mechanical properties, and deformation behavior of NiAl-strengthened high-strength steels: Effects of Ni and Al contents and ratios. Mater. Des. 2023, 234, 112341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, L.; Peng, Z.; Huo, X.; Sun, H. On the correlation among continuous cooling transformations, interphase precipitation and strengthening mechanism in Ti-microalloyed steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Deng, X.; Wang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. Solidification and sliding wear behavior of low-alloy abrasion-resistant steel reinforced with TiC particles. Wear 2020, 458, 203444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Yang, G.; Zhao, G.; Sun, X.; Zhu, X. Strengthening mechanism and three-body impact abrasive wear behavior of the hot-rolled air-cooling martensitic wear resistant steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.P.; Ghosh, S.; Mula, S. Characterization of dry-sliding wear phenomena in a novel martensitic structure based low-carbon Nb and V alloyed steel. Tribol. Int. 2023, 189, 108959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Ji, P.; Li, B.; Zhang, G.; Ma, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Ma, M.; Liu, R. Effect of loading on microstructure and friction and wear behavior of an austenite lightweight steel. Tribol. Int. 2023, 177, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F.; Hirst, W. The wear of metals under unlubricated conditions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1956, 236, 397–410. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-I.; Lee, W.-Y.; Tokoroyama, T.; Murashima, M.; Umehara, N. Tribo-chemical wear of various 3d-transition metals against DLC: Influence of tribo-oxidation and low-shear transferred layer. Tribol. Int. 2023, 177, 107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, D.X.; Jin, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.W. Effect of boron on the microstructural evolution and wear resistance of high-hardness Fe-based alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 458, 129342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, A.; Yuan, W.; Gao, Z. Contribution of hardness and work hardening to the wear resistance of Pt-based metallic surfaces revealed by nanoscale reciprocating sliding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 614, 156178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H. A non-equiatomic Ni-Co-Fe medium-entropy alloy with excellent wear resistance and strength-ductility combination by adding Al. Mater. Charact. 2023, 205, 113305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
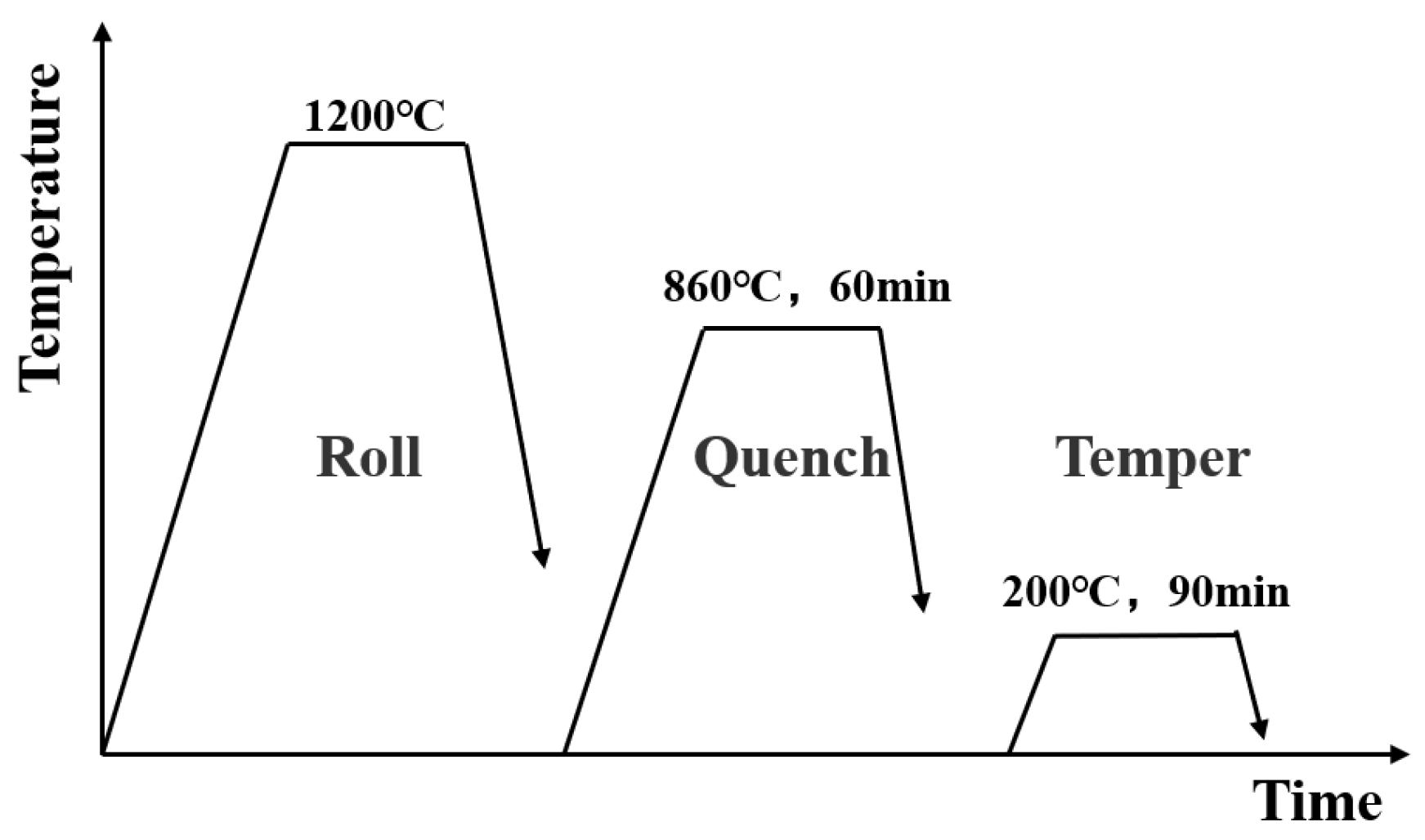
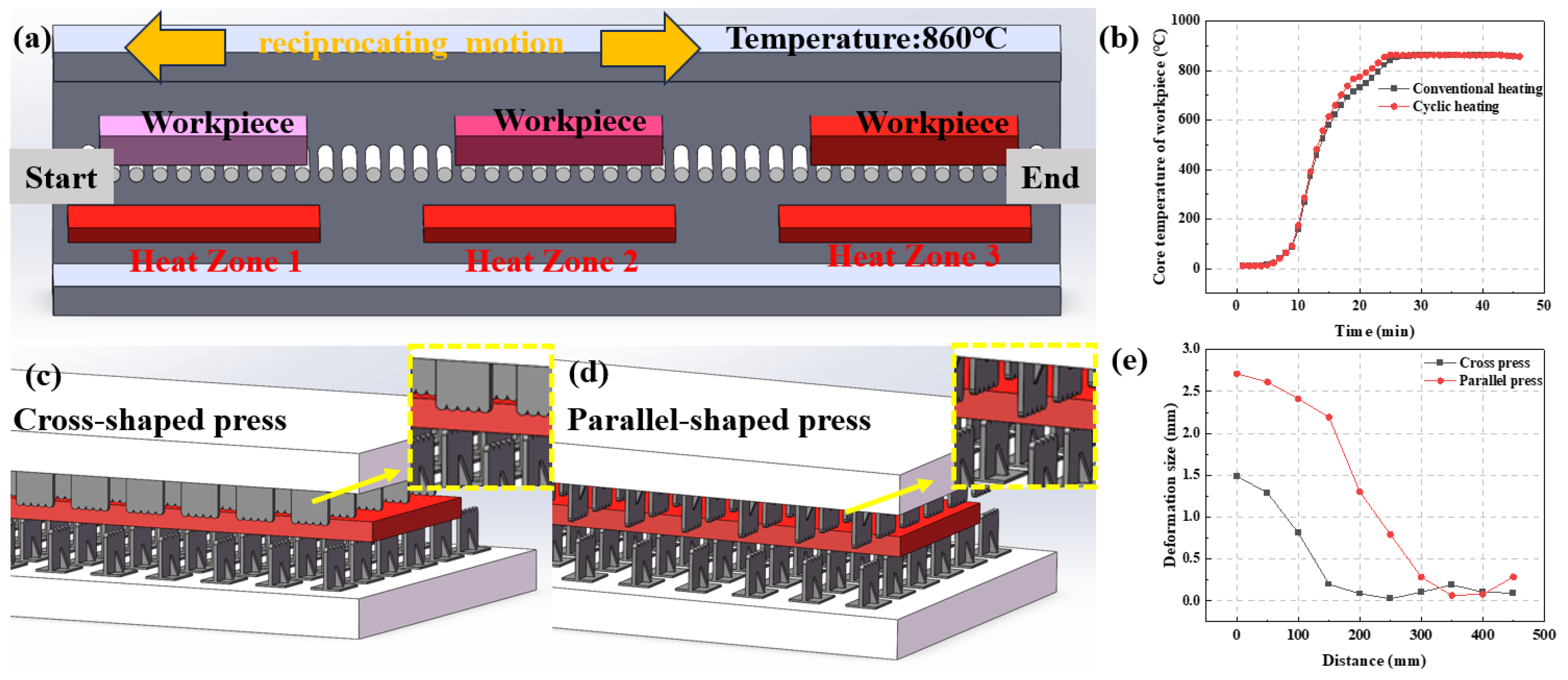
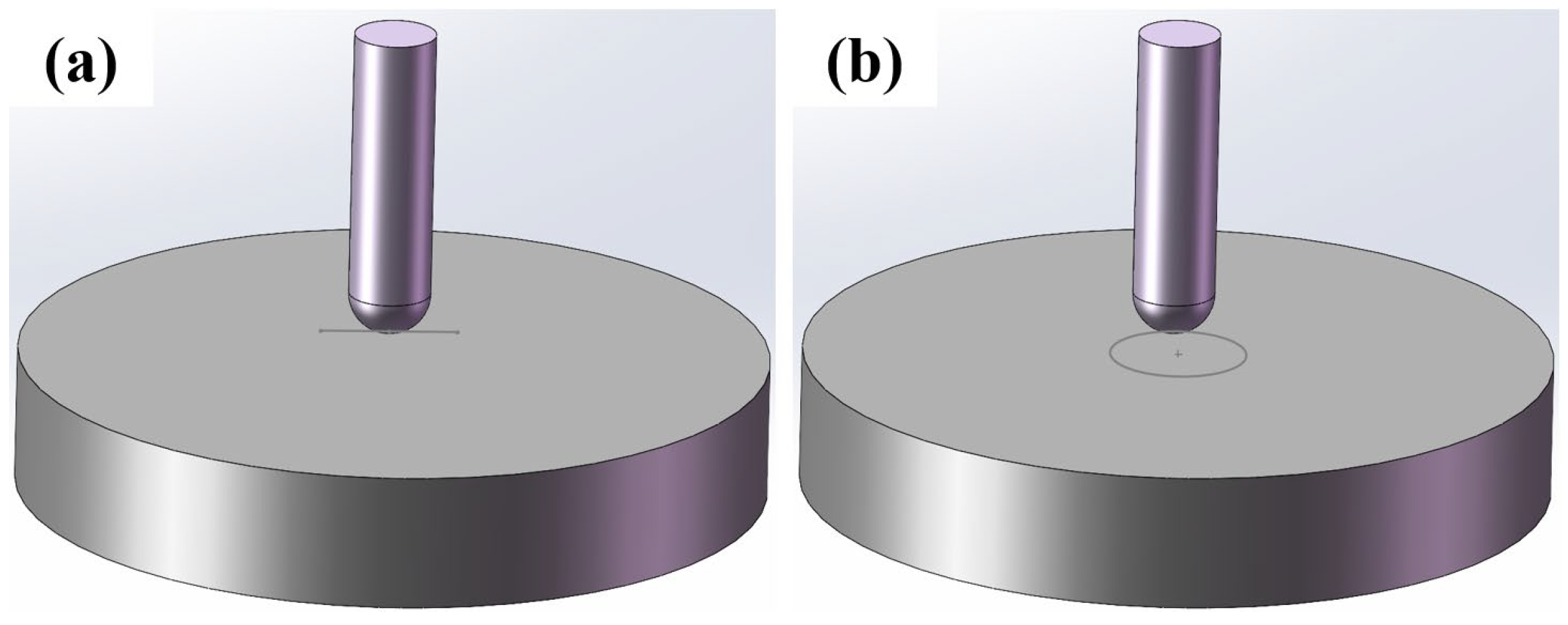
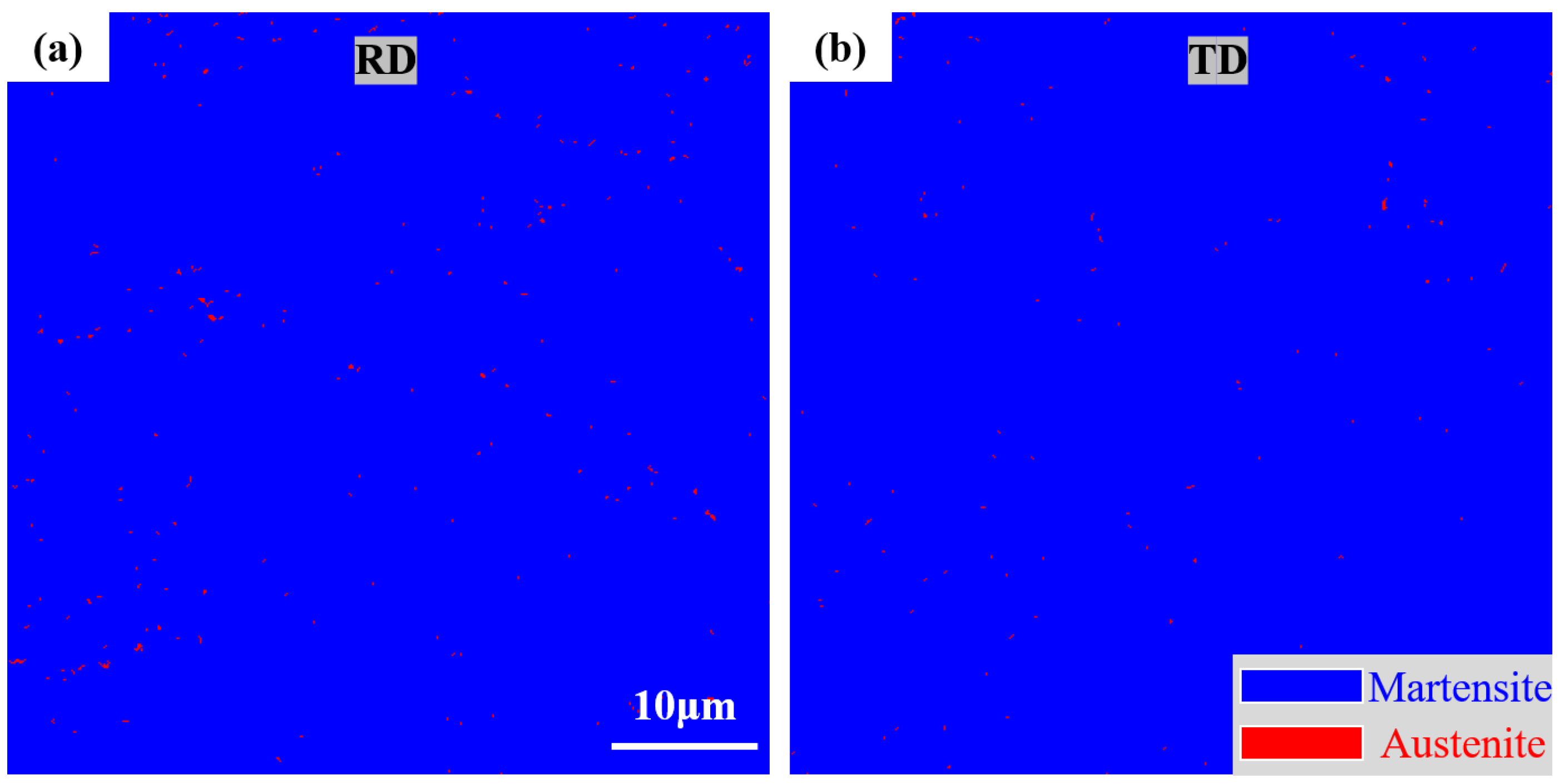



| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Cu | B | Ti | Al | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Design | 0.26–0.31 | 0.15–0.35 | 1.1–1.45 | <0.02 | <0.01 | 0.3–0.6 | <0.3 | 0.0005–0.003 | 0.018–0.05 | 0.015–0.04 | Bal. |
| Reality | 0.27 | 0.21 | 1.19 | 0.017 | 0.007 | 0.37 | 0.017 | 0.001 | 0.03 | 0.038 | Bal. |
| Thickness (mm) | 12 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 50 | 60 |
| Water consumption (L) | 5320 | 8866 | 11,083 | 13,299 | 22,166 | 26,969 |
| Spray time (s) | 64 | 106 | 132 | 160 | 266 | 320 |
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 53.4 | 52.6 | 54.8 | 52.6 | 51.7 | 53.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Lin, J.; Jiang, S.; Cao, A.; Yao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z. Study of the Effects on the Strengthening Mechanism and Wear Behavior of Wear-Resistant Steel of Temperature Controlling in Heat Treatment. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141171
Zhu X, Lin J, Jiang S, Cao A, Yao Y, Sun Y, Li S, Zhang Z. Study of the Effects on the Strengthening Mechanism and Wear Behavior of Wear-Resistant Steel of Temperature Controlling in Heat Treatment. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(14):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141171
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiaoyu, Jianghai Lin, Shaoning Jiang, Aijun Cao, Yuan Yao, Yu Sun, Sensen Li, and Zhanfeng Zhang. 2024. "Study of the Effects on the Strengthening Mechanism and Wear Behavior of Wear-Resistant Steel of Temperature Controlling in Heat Treatment" Nanomaterials 14, no. 14: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141171
APA StyleZhu, X., Lin, J., Jiang, S., Cao, A., Yao, Y., Sun, Y., Li, S., & Zhang, Z. (2024). Study of the Effects on the Strengthening Mechanism and Wear Behavior of Wear-Resistant Steel of Temperature Controlling in Heat Treatment. Nanomaterials, 14(14), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141171






