Surfalize: A Python Library for Surface Topography and Roughness Analysis Designed for Periodic Surface Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Surfalize Description
2.1. Operations
- Interpolation of non-measured points;
- Plane leveling;
- Spatial filtering;
- Rotation;
- Texture alignment;
- Cropping;
- Profile extraction;
- Outlier removal;
- Thresholding based on areal material ratio curve.
2.2. Quantitative Characterization
- Height parameters: Sa, Sq, Sz, Sv, Sp, Sku, Ssk;
- Hybrid parameters: Sdq, Sdr;
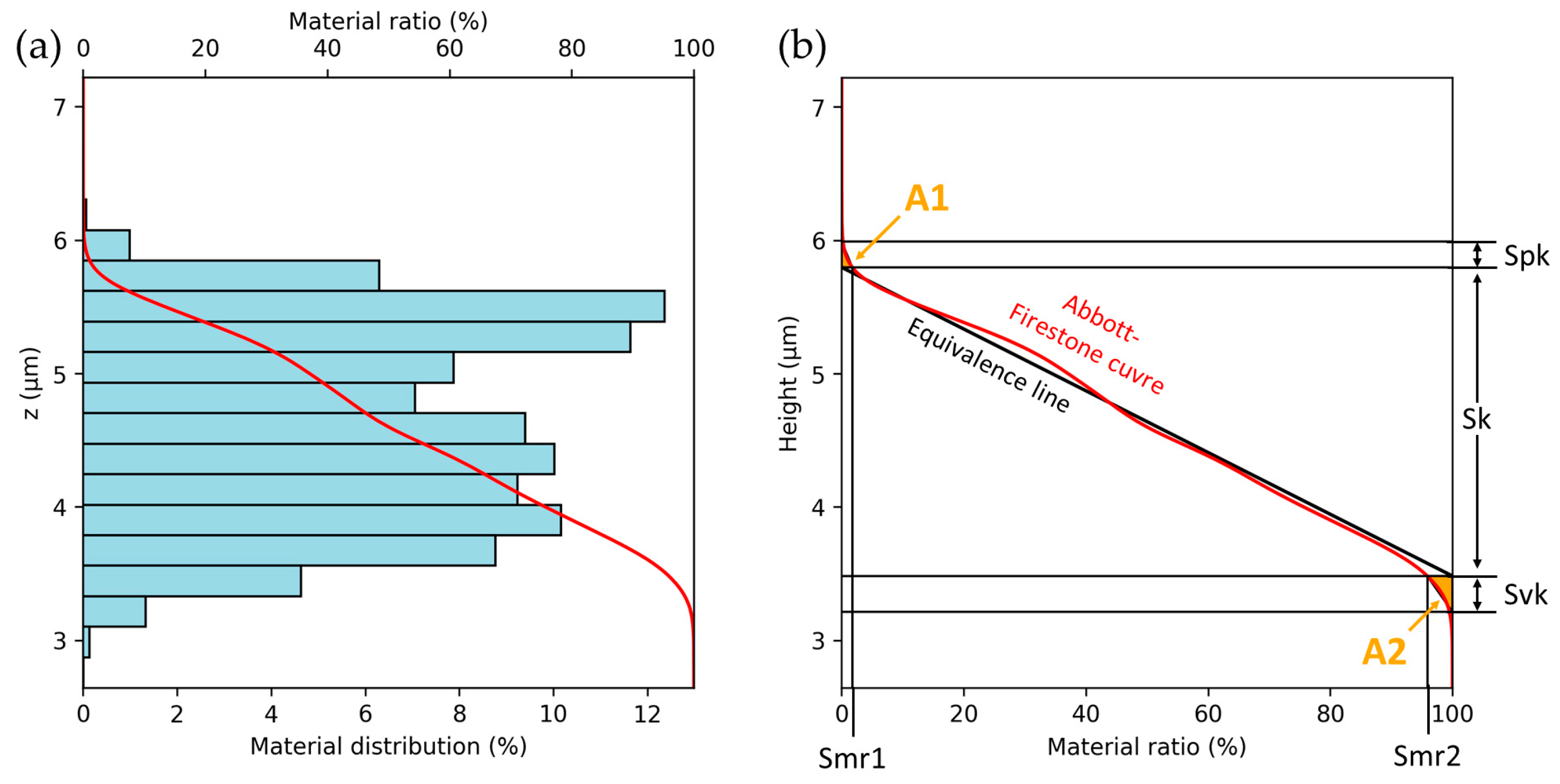
- Functional parameters: Sk, Spk, Svk, Smr1, Smr2, Sxp, Smr(c), Smc(mr);
- Functional volume parameters: Vmp, Vmc, Vvc, Vvv;
- Spatial parameters: Sal, Str;
- Period texture parameters: spatial period, structure depth, aspect ratio, orientation, homogeneity.
2.3. Plotting
- Plotting surface topography in 2d;
- Plotting the Fourier transform;
- Plotting the autocorrelation function;
- Plotting of the Abbott–Firestone curve;
- Plotting of the visual parameter study of the functional parameters.
2.4. Batch Processing
2.5. File Formats
3. Implementation
3.1. ISO 25178 Surface Roughness Parameters
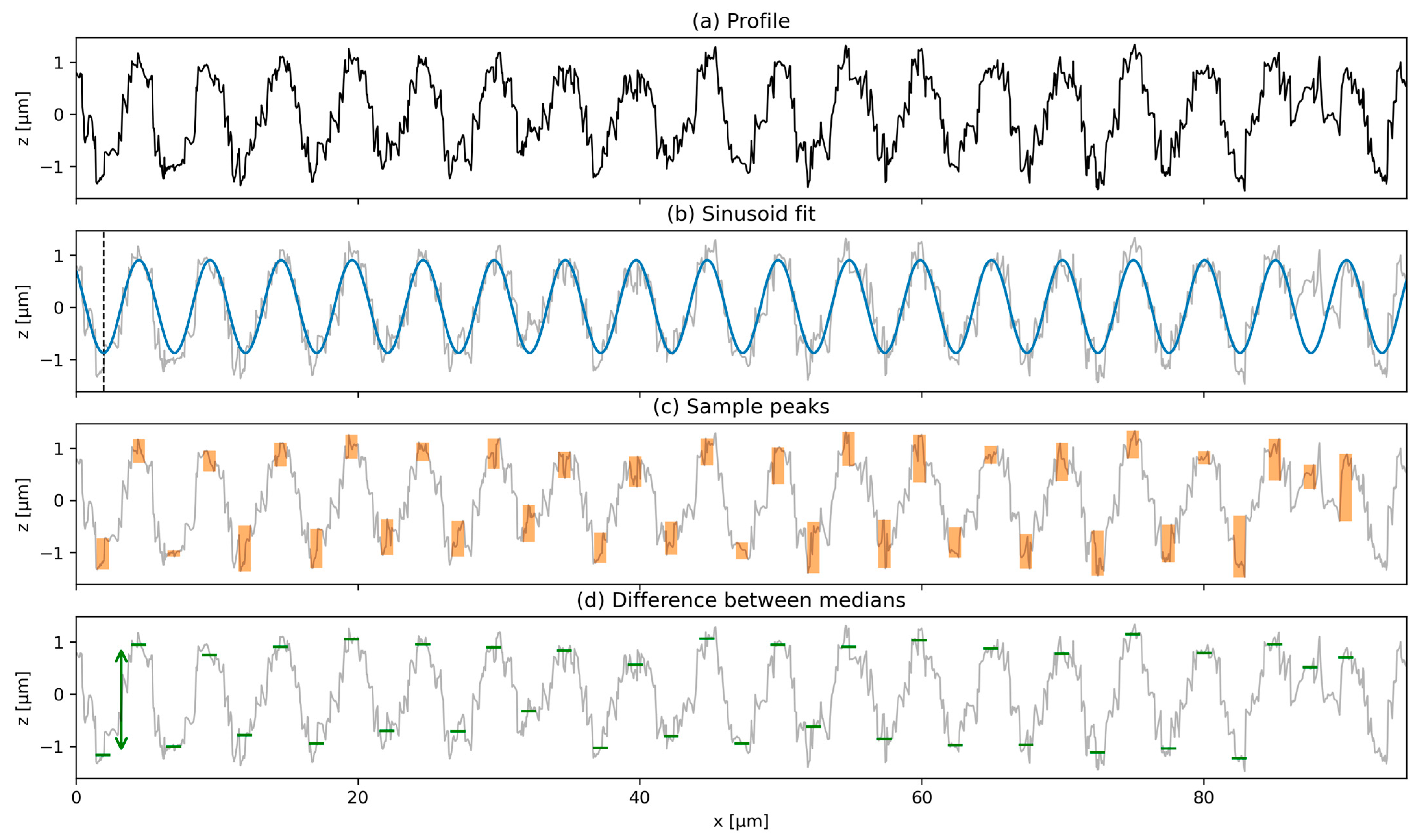
3.2. Surface Texture Period
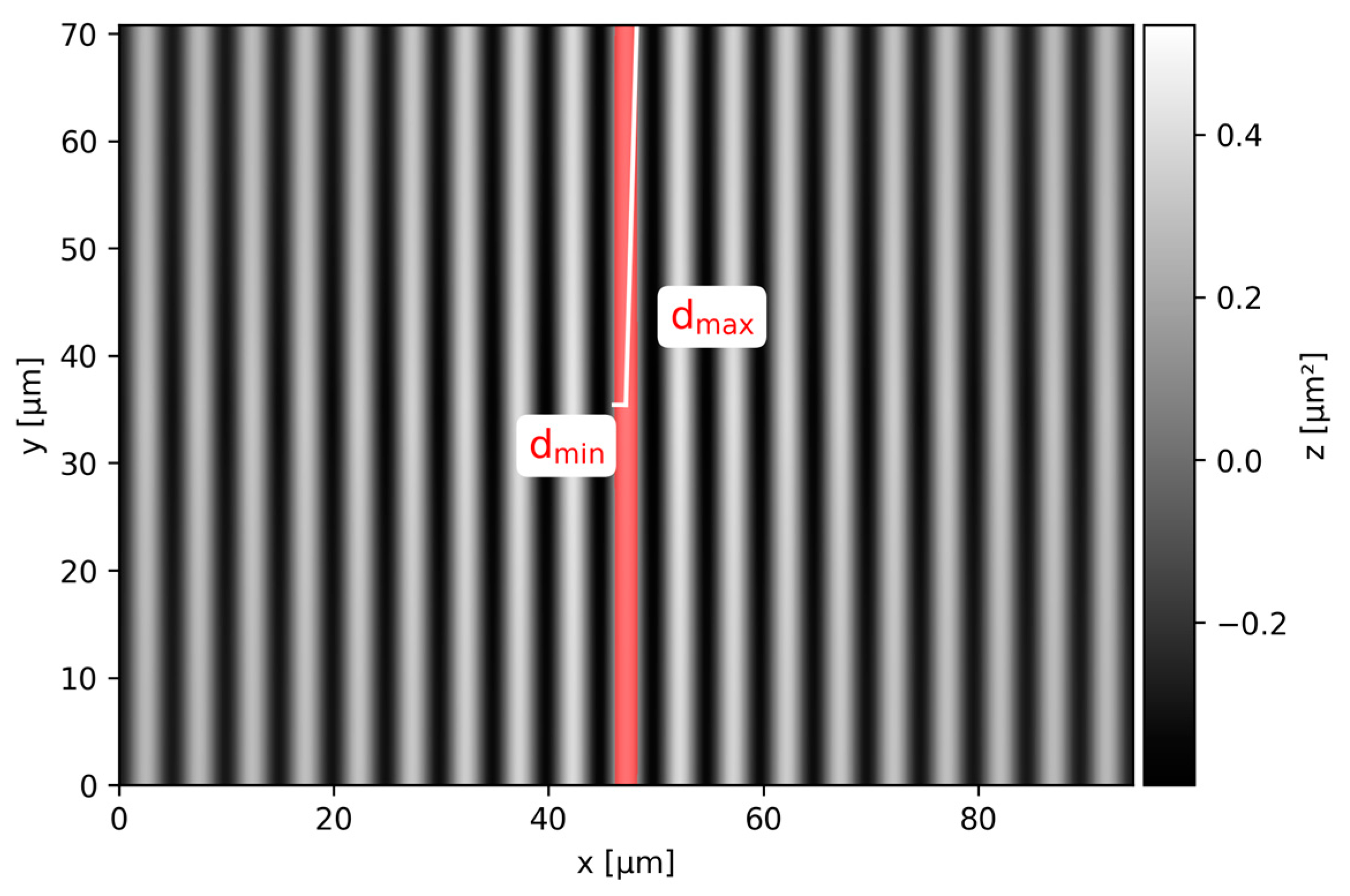
3.3. Texture Depth
3.4. Orientation of the Periodic Structure
3.5. Texture Homogeneity
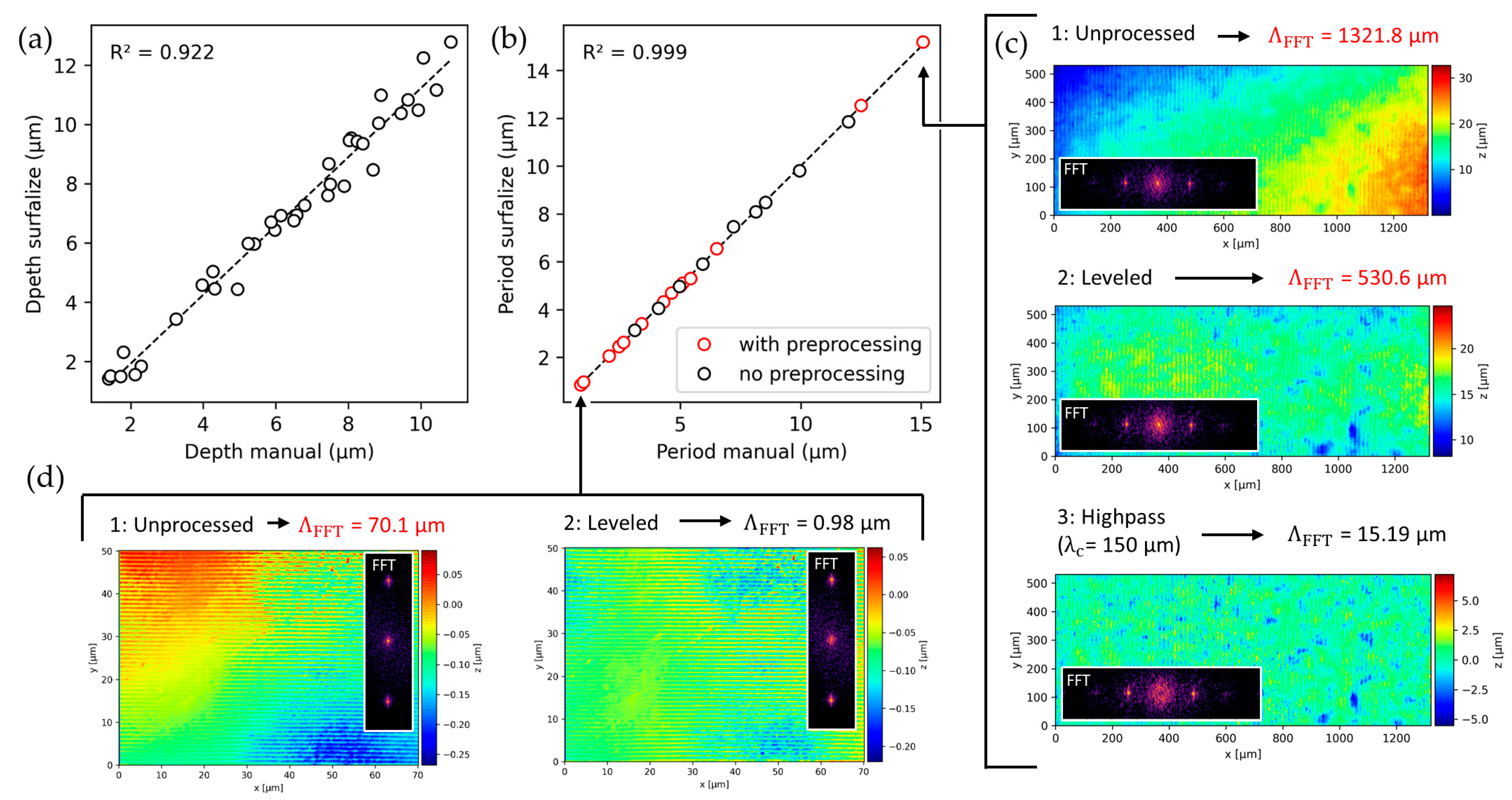
4. Validation
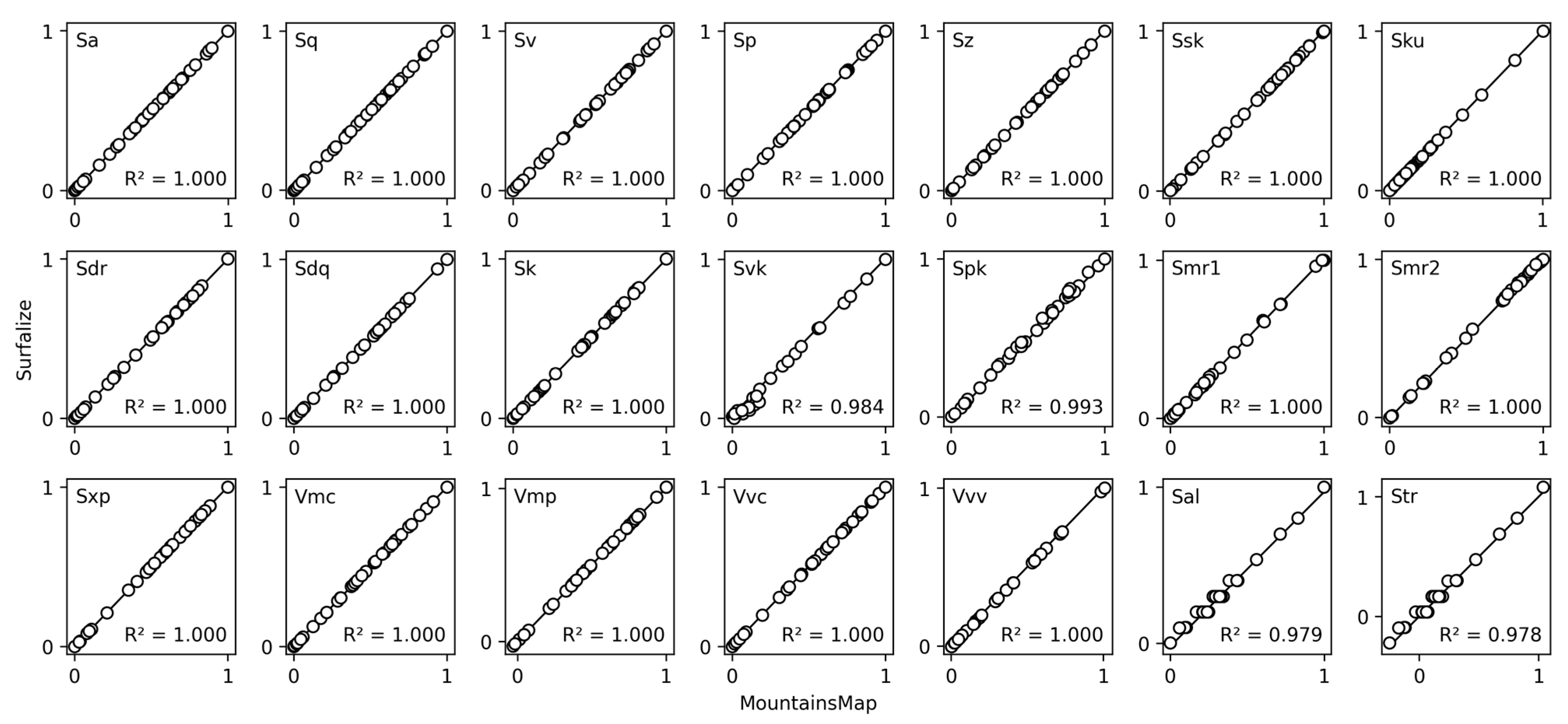
4.1. Validation of Roughness Parameter Calculations
4.2. Validation of Structure Period and Peak-to-Valley Depth Estimation
4.3. Alignment
4.4. Homogeneity Validation
5. Application Example
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, C.A.; Hansen, H.N.; Jiang, X.J.; Blateyron, F.; Berglund, J.; Senin, N.; Bartkowiak, T.; Dixon, B.; Le Goïc, G.; Quinsat, Y.; et al. Multiscale Analyses and Characterizations of Surface Topographies. CIRP Ann. 2018, 67, 839–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlus, P.; Reizer, R.; Wieczorowski, M. Functional Importance of Surface Texture Parameters. Materials 2021, 14, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, H.I.; Mohammed, K.S.; Rahmat, A.; Uday, M.B. The Influence of the Surface Roughness on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of 6061 Aluminium Alloy Using Friction Stir Welding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 270, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Effects of Titanium Surface Topography on Bone Integration: A Systematic Review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso, M.G.; Méndez-Vilas, A.; Bruque, J.M.; González-Martin, M.L. On the Relationship between Common Amplitude Surface Roughness Parameters and Surface Area: Implications for the Study of Cell–Material Interactions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 59, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.Y.; Schwartz, Z.; Hummert, T.W.; Schraub, D.M.; Simpson, J.; Lankford, J.; Dean, D.D.; Cochran, D.L.; Boyan, B.D. Effect of Titanium Surface Roughness on Proliferation, Differentiation, and Protein Synthesis of Human Osteoblast-like Cells (MG63). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariharan, A.; Goldberg, P.; Schell, F.; Hempel, U.; Striggow, F.; Hantusch, M.; Medina-Sánchez, M.; Lasagni, A.F.; Gebert, A. Single- and Multiscale Laser Patterning of 3D Printed Biomedical Titanium Alloy: Toward an Enhanced Adhesion and Early Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2310607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larena, A.; Millán, F.; Pérez, G.; Pinto, G. Effect of Surface Roughness on the Optical Properties of Multilayer Polymer Films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 187, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Sidpara, A.; Bandyopadhyay, P.P. Understanding the Role of Surface Roughness on the Tribological Performance and Corrosion Resistance of WC-Co Coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 378, 125080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, L.; Robotti, F.; Dialameh, M.; Calignano, F.; Manfredi, D.; Chiavazzo, E.; Asinari, P. Rough Surfaces with Enhanced Heat Transfer for Electronics Cooling by Direct Metal Laser Sintering. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 75, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongru, A.; Xiangqin, L.; Shuyan, S.; Ying, Z.; Tianqing, L. Measurement of Wenzel Roughness Factor by Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7052–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN ISO 25178-2:2012; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Areal; Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters (ISO 25178-2:2012). 2012. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/74591.html (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Marinello, F.; Pezzuolo, A. Application of ISO 25178 Standard for Multiscale 3D Parametric Assessment of Surface Topographies. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 275, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlus, P.; Reizer, R.; Wieczorowski, M.; Krolczyk, G. Material Ratio Curve as Information on the State of Surface Topography—A Review. Precision Eng. 2020, 65, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todhunter, L.D.; Leach, R.K.; Lawes, S.D.A.; Blateyron, F. Industrial Survey of ISO Surface Texture Parameters. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2017, 19, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranav, C.; Do, M.-T.; Tsai, Y.-C. Analysis of High-Friction Surface Texture with Respect to Friction and Wear. Coatings 2021, 11, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shareef, I.; Castiblanco, O. White Light Interferometry and MountainsMap®—Case Studies in Static Load Capacity of Bearings and Surface Finish Optimisation of Orthotic Knee Joints. IJSURFSE 2018, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, A.; Yates, B.; Takacs, P. Using MountainsMap (Digital Surf) Surface Analysis Software as an Analysis Tool for X-ray Mirror Optical Metrology Data; Assoufid, L., Takacs, P.Z., Asundi, A.K., Eds.; Proceedings of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering: San Diego, CA, USA, 15 October 2012; p. 850106. [Google Scholar]
- Buchenau, T.; Brüning, H.; Amkreutz, M. Post-Processing of Surface Topography Data for as-Built Metal Additive Surface Texture Characterization. J. Addit. Manuf. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; Maalouf, M.; Claudel, P.; Sedao, X.; Di Maio, Y.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Thomas, M.; Guignandon, A.; Dumas, V. Key Topographic Parameters Driving Surface Adhesion of Porphyromonas Gingivalis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečas, D.; Klapetek, P. Gwyddion: An Open-Source Software for SPM Data Analysis. Open Phys. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millman, K.J.; Aivazis, M. Python for Scientists and Engineers. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 13, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roitero, E.; Lasserre, F.; Anglada, M.; Mücklich, F.; Jiménez-Piqué, E. A Parametric Study of Laser Interference Surface Patterning of Dental Zirconia: Effects of Laser Parameters on Topography and Surface Quality. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, e28–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschwitz, P.; Jagdheesh, R.; Alamri, S.; Rostohar, D.; Kunze, T.; Brajer, J.; Kopeček, J.; Mocek, T. Fabrication of Functional Superhydrophobic Surfaces on Carbon Fibre Reinforced Plastics by IR and UV Direct Laser Interference Patterning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 144817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raillard, B.; Rémond, J.; Ramos-Moore, E.; Souza, N.; Gachot, C.; Mücklich, F. Wetting Properties of Steel Surfaces Modified by Laser Interference Metallurgy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2013, 15, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.M.; Buchberger, G.; Stifter, D.; Duchoslav, J.; Hertwig, A.; Bonse, J.; Heitz, J.; Schwibbert, K. Spatial Period of Laser-Induced Surface Nanoripples on PET Determines Escherichia Coli Repellence. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechthaler, B.; Pauly, C.; Mücklich, F. Objective Homogeneity Quantification of a Periodic Surface Using the Gini Coefficient. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldera, M.; Reichel, C.; Kuisat, F.; Lasagni, A.F. Topography Analysis and Homogeneity Quantification of Laser-Patterned Periodic Surface Structures. JLMN 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Morales, A.I.; Alamri, S.; Kunze, T.; Lasagni, A.F. Influence of Processing Parameters on Surface Texture Homogeneity Using Direct Laser Interference Patterning. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 107, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluyver, T.; Ragan-Kelley, B.; Pérez, F.; Granger, B.; Bussonnier, M.; Frederic, J.; Kelly, K.; Hamrick, J.; Grout, J.; Corlay, S.; et al. Jupyter Notebooks—A Publishing Format for Reproducible Computational Workflows. In Positioning and Power in Academic Publishing: Players, Agents and Agendas—Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Electronic Publishing; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 87–90. ISBN 978-1-61499-649-1. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, F.; Granger, B.E. IPython: A System for Interactive Scientific Computing. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnel, S.; Bradshaw, R.; Citro, C.; Dalcin, L.; Seljebotn, D.S.; Smith, K. Cython: The Best of Both Worlds. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 13, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, K.J. (Ed.) Development of Methods for the Characterisation of Roughness in Three Dimensions; Rev. reprint; Penton: London, UK, 2000; ISBN 978-1-85718-023-7. [Google Scholar]
- De Battisti, F.; Porro, F.; Vernizzi, A. The Gini Coefficient and the Case of Negative Values. Electron. J. Appl. Stat. Anal. 2019, 12, 85–107. [Google Scholar]
- Schell, F.; Chukwudi Okafor, R.; Steege, T.; Alamri, S.; Ghevariya, S.; Zwahr, C.; Lasagni, A.F. Increasing Heat Transfer from Metal Surfaces through Laser-Interference-Induced Microscopic Heat Sinks. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todhunter, L.; Leach, R.; Lawes, S.; Harris, P.; Blateyron, F. Mathematical Approach to the Validation of Field Surface Texture Parameter Software. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2020, 8, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Manufacturer | Formats | Loading | Saving |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keyence | .vk4 | Yes | No |
| Keyence | .vk6 | Yes | No |
| Keyence | .vk7 | Yes | No |
| Sensofar | .plu | Yes | No |
| Sensofar | .plux | Yes | No |
| Digital Surf | .sur (uncompressed) .sur (compressed) | Yes | Yes |
| Digital Surf | .sdf (ascii) .sdf (binary) | Yes | Yes |
| KLA | .zmg | Yes | No |
| Wyko | .opd | Yes | No |
| Nanofocus | .nms | Yes | No |
| General | .xyz | Yes | No |
| Alicona | .al3d | Yes | Yes |
| Gwyddion | .gwy | Yes | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schell, F.; Zwahr, C.; Lasagni, A.F. Surfalize: A Python Library for Surface Topography and Roughness Analysis Designed for Periodic Surface Structures. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14131076
Schell F, Zwahr C, Lasagni AF. Surfalize: A Python Library for Surface Topography and Roughness Analysis Designed for Periodic Surface Structures. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(13):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14131076
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchell, Frederic, Christoph Zwahr, and Andrés F. Lasagni. 2024. "Surfalize: A Python Library for Surface Topography and Roughness Analysis Designed for Periodic Surface Structures" Nanomaterials 14, no. 13: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14131076
APA StyleSchell, F., Zwahr, C., & Lasagni, A. F. (2024). Surfalize: A Python Library for Surface Topography and Roughness Analysis Designed for Periodic Surface Structures. Nanomaterials, 14(13), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14131076






