Novel Rare Earth (RE)-Free Nanocomposite Magnets Derived from L10-Phase Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
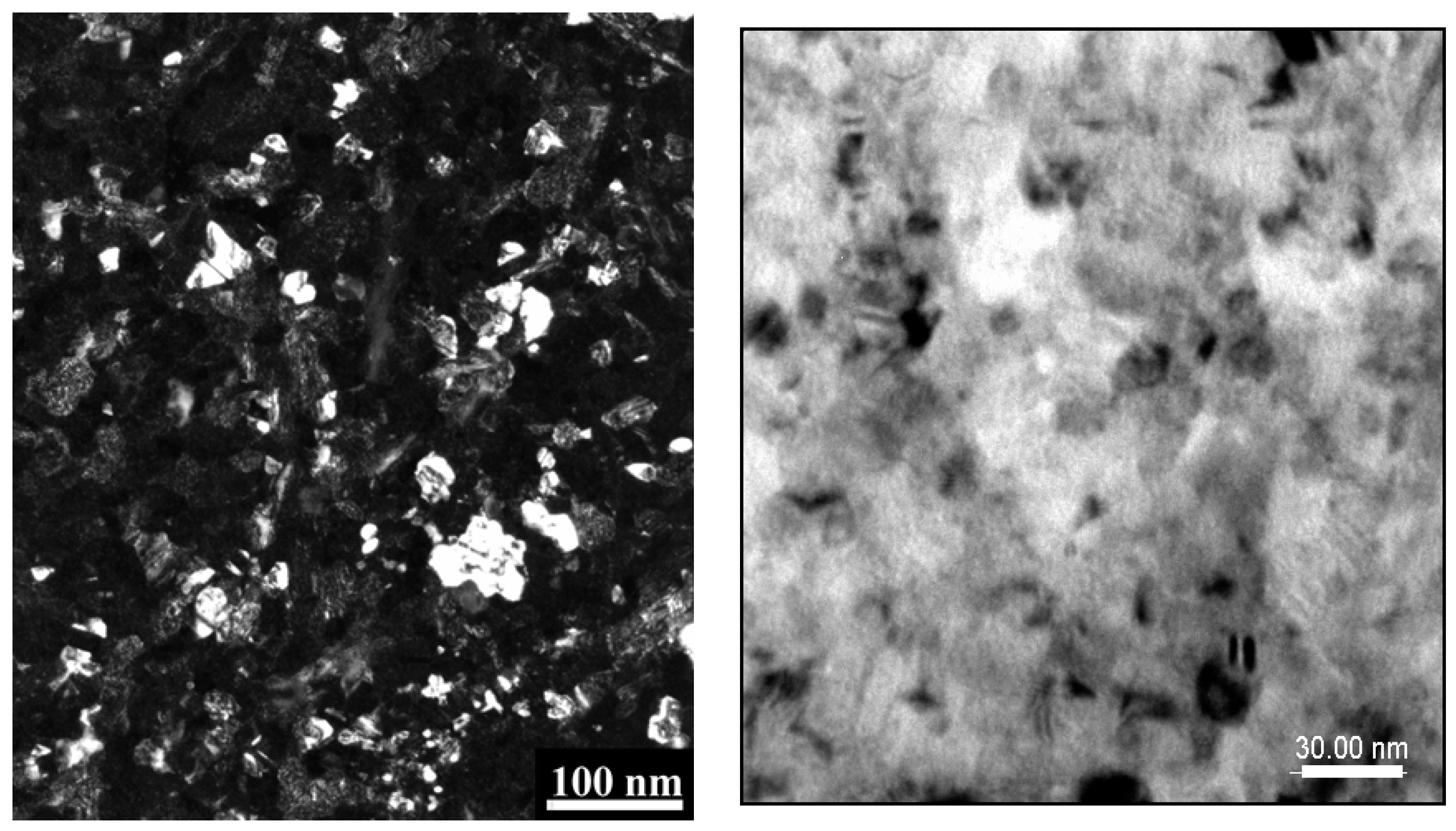
3.1. Composition and Morphology
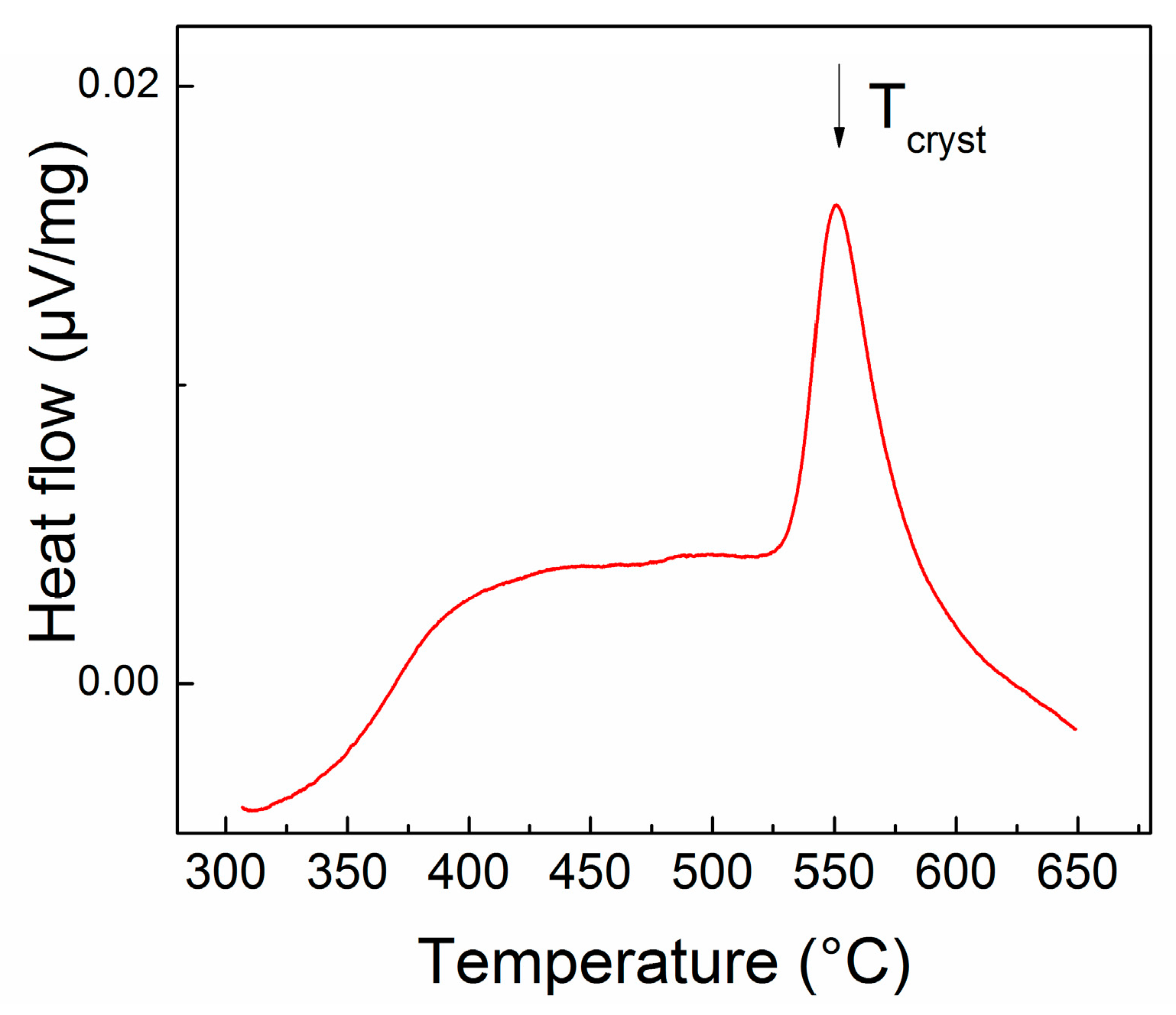
3.2. Thermal Analysis
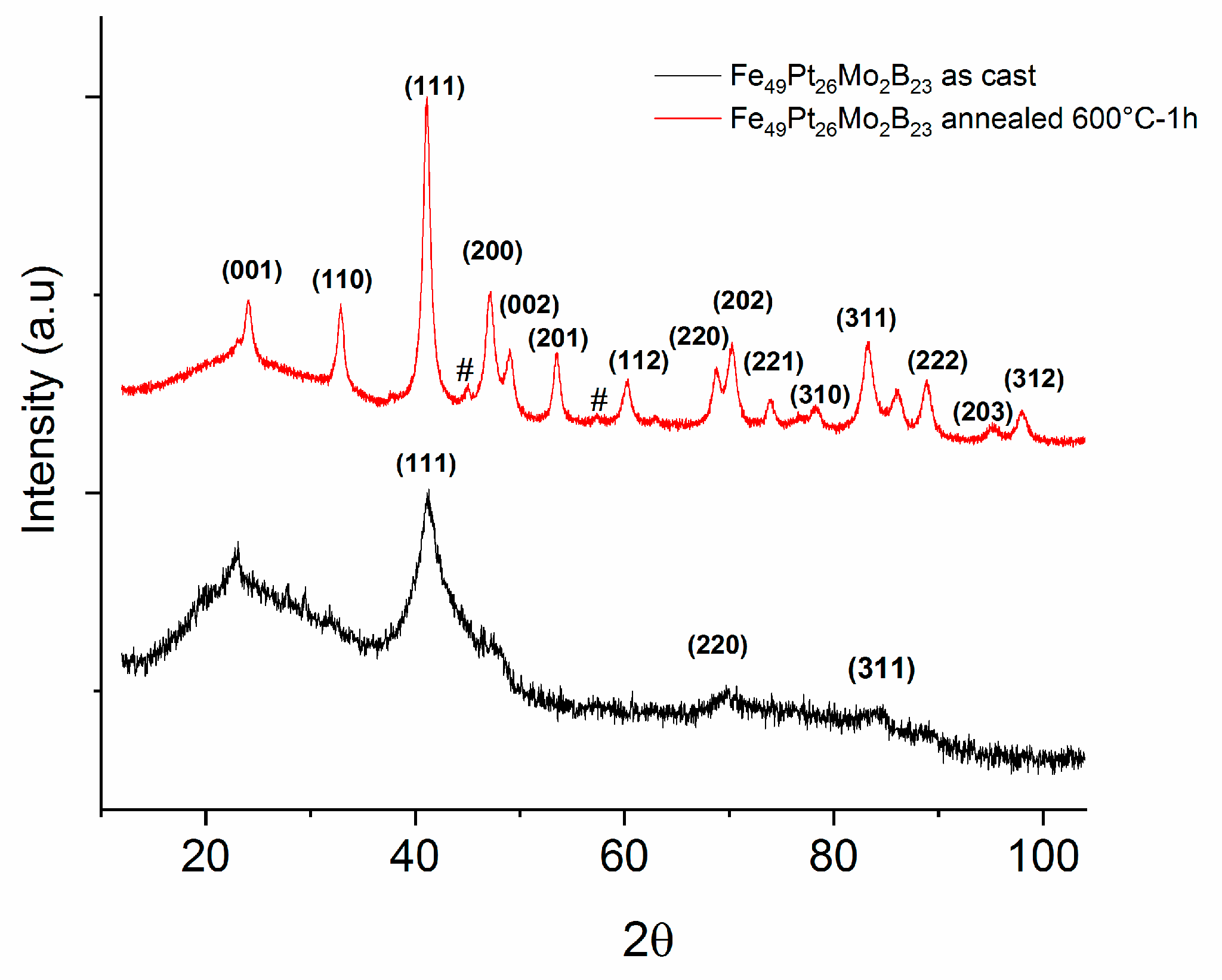
3.3. Structural Analysis
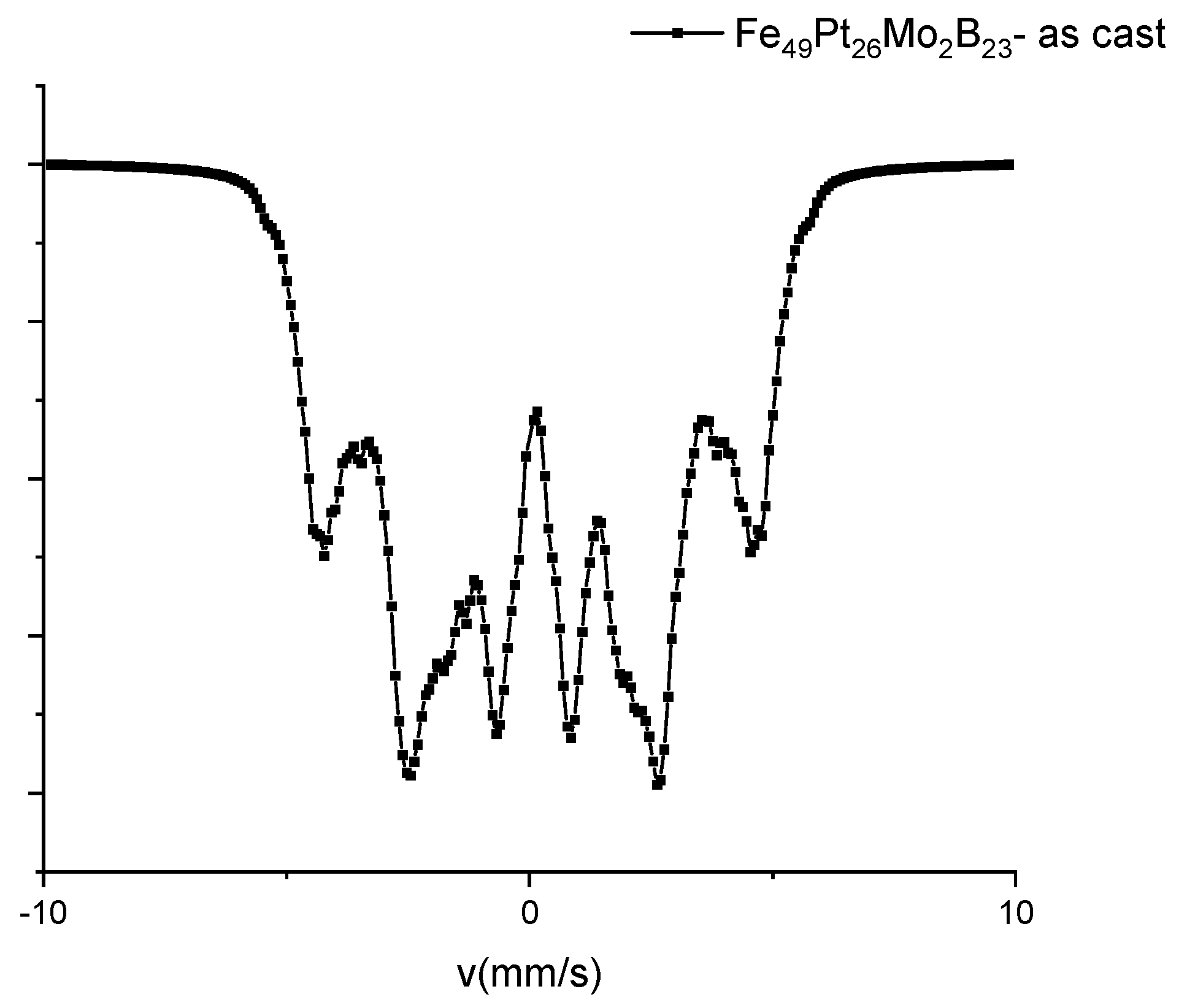
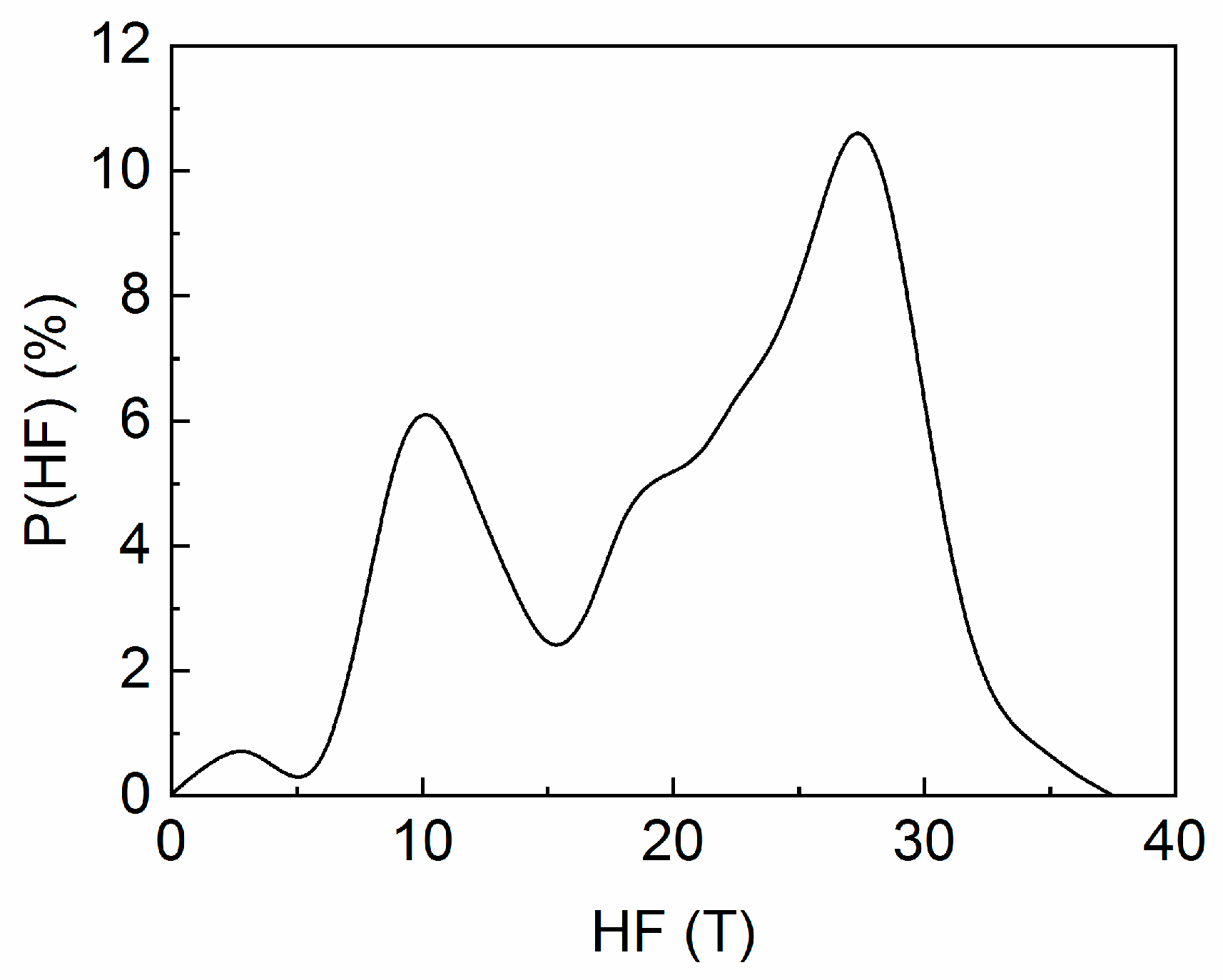
3.4. Mössbauer Analysis
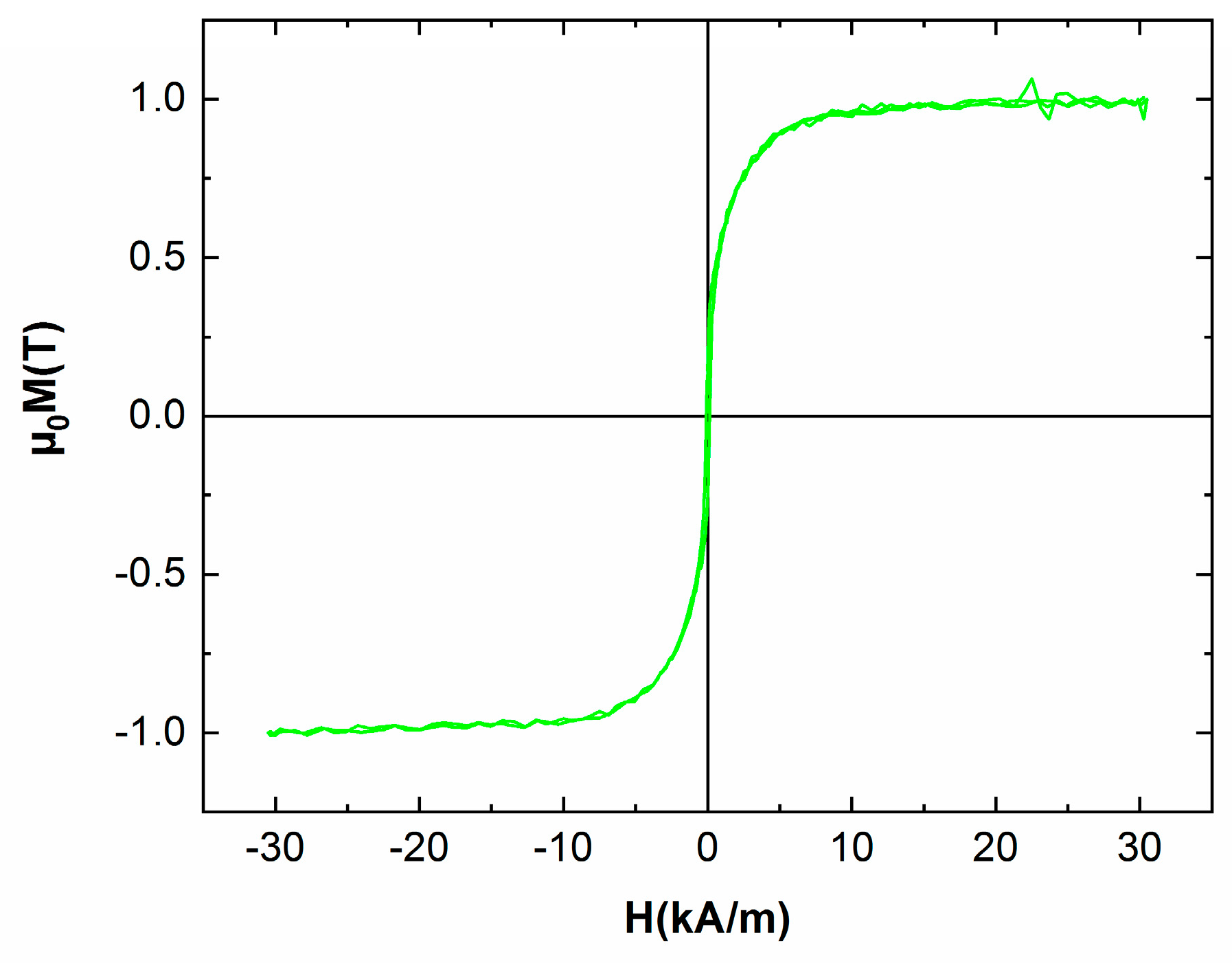
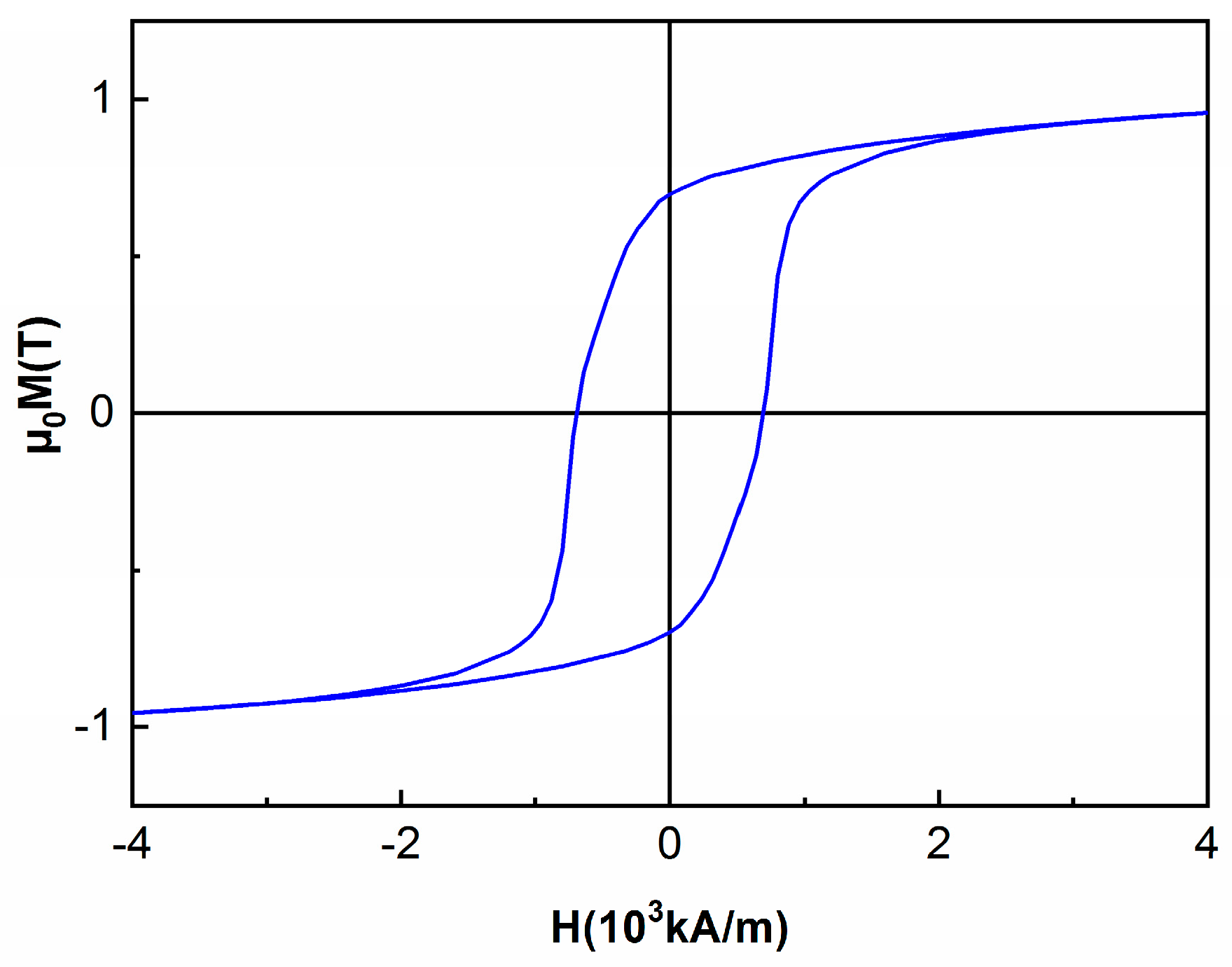
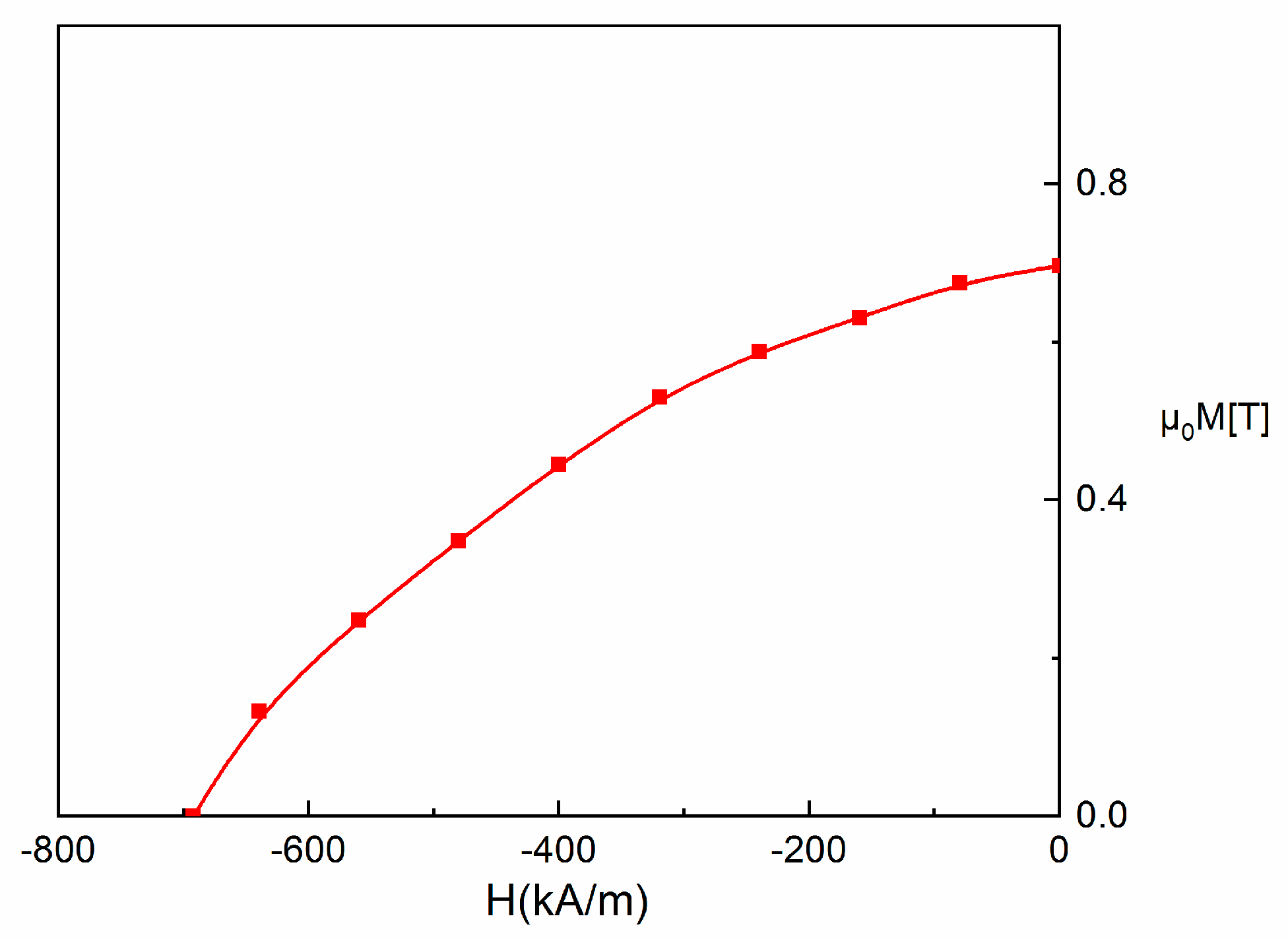
3.5. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.-H.; Pan, K.-Y.; Wei, D.-H.; Chung, R.-J. FePt nanoparticles embedded-rGO nanocomposites for magnetic fluid hyperthermia. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenosono, S.; Suzuki, T.; Saita, S. Superparamagnetic FePt nanoparticles as excellent MRI contrast agents. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, L79–L83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, A.G.; Costo, R.; Rebolledo, A.F.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Tartaj, P.; González-Carreño, T.; Morales, M.P.; Serna, C.J. Progress in the preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 224002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Ren, J.; Jiang, X. Monodisperse FePt nanoparticles as highly active electrocatalysts for methanol oxidation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48569–48573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Q. FePt-Au ternary metallic nanoparticles with the enhanced peroxidase-like activity for ultrafast colorimetric detection of H2O2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Yin, G.; Li, H.; Sun, S. Enhancing electrochemical detection of dopamine via dumbbell-like FePt–Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S. Recent advances in chemical synthesis, self-assembly, and applications of FePt nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Fujieda, S.; Shinoda, K.; Suzuki, S.; Jeyadevan, B. Low temperature synthesis of FePt alloy nanoparticles by polyol process. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 352, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedwald, U.; Han, L.; Biskupek, J.; Kaiser, U.; Ziemann, P. Preparation and characterization of supported magnetic nanoparticles prepared by reverse micelles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2010, 1, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Howard, L.E.M.; Giblin, S.R.; Tanner, B.K.; Terry, I.; Hughes, A.K.; Ross, I.M.; Serres, A.A.; Bürckstümmer, H.; Evans, J.S.O. Synthesis of monodispersed fcc and fct FePt/FePd nanoparticles by microwave irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 5136–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Loh, K.P.; Zhong, Y.L.; Lin, M.; Ding, J.; Foo, Y.L. Bifunctional FePt Core−Shell and Hollow Spheres: Sonochemical Preparation and Self-Assembly. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2566–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, S.; Kelgenbaeva, Z.; Yamamoto, K.; Chen, L.; Mashimo, T. Preparation of FePt Nanoparticles by Pulsed Plasma in Liquid Method. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 730, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, S.; Qiu, J.-M.; Wang, J.-P. Nanocomposite exchange-spring magnet synthesized by gas phase method: From isotropic to anisotropic. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 222507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Zhou, L.H.; Yang, T.T.; Gao, J.; He, P.; Jia, L.P.; Dong, F.Q.; Jia, B.; Zhang, H. Facile one-step synthesis of tunable nanochain-like Fe–Mo–B: A highly efficient and stable catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 822, 153517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, M.; Takahashi, K.; Mitomi, S.; Ohtani, H. Electron Theory Calculation of Thermodynamic Properties of Steels and Its Application to Theoretical Phase Diagram of the Fe-Mo-B Ternary System. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Fujioka, M.; Enoki, M.; Ohtani, H. Thermodynamic Analysis of the Fe-Mo-B Ternary System. Tetsu Hagane-J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2020, 106, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, O.; Labaye, Y.; Berger, L.; Coey, J.; Grenèche, J.-M. Exchange coupling effects in nanocrystalline alloys studied by Monte Carlo simulation. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Kuncser, V.; Crisan, O.; Hernando, A.; Navarro, E.; Filoti, G. A Mössbauer spectroscopy and magnetic study of FeRh. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1998, 177, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, O.; Le Breton, J.M.; Jianu, A.; Teillet, J.; Filoti, G. Structural properties of amorphous and nanocrystallized Fe-Cu-Nb-Si-B and Fe-Gd-Cu-Nb-Si-B ribbons. J. Alloys Compd. 1997, 262, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Haeften, K.; Binns, C.; Brewer, A.; Crisan, O.; Howes, P.B.; Lowe, M.P.; Sibbley-Allen, C.; Thornton, S.C. A novel approach towards the production of luminescent silicon nanoparticles: Sputtering, gas aggregation and co-deposition with H2O. Eur. Phys. J. D 2009, 52, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, A.D.; Vasiliu, F.; Nicula, R.; Bartha, C.; Mercioniu, I.; Crisan, O. Thermodynamic, structural and magnetic studies of phase transformations in MnAl nanocomposite alloys. Mater. Charact. 2018, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, O.; Crisan, A.D.; Randrianantoandro, N.; Nicula, R.; Burkel, E. Crystallization Processes and Phase Evolution in Amorphous Fe—Pt—Nb—B Alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2007, 440, L3–L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, O.; Angelakeris, M.; Flevaris, N.K.; Filoti, G. Magnetism and anisotropy in core-shell nanoparticles. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2003, 5, 959–962. [Google Scholar]
- Crisan, A.D.; Nicula, R.; Crisan, O.; Burkel, E. Thermally and pressure activated phase evolution in Fe–Pt–Nb–B melt spun ribbons. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, A.D.; Crisan, O.; Randrianantoandro, N.; Valeanu, M.; Morariu, M.; Burkel, E. Crystallization processes in Fe–Pt–Nb–B melt spun ribbons. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 1283–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, O.; Le Breton, J.M.; Crisan, A.D.; Labaye, Y.; Berger, L.; Filoti, G. Magnetism of nanocrystalline Finemet alloy: Experiment and simulation. Eur. Phys. J. B 2003, 34, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakayama, H.; Yonekura, H.; Kawai, Y. Three-Dimensional Periodically Ordered Nanohetero Metallic Materials from Self-Assembled Block Copolymer Composites. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaprasad, B.S.D.C.S.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Hono, K. Microstructure Control of L10-Ordered FePt Granular Film for Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording (HAMR) Media. JOM 2013, 65, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granz, S.D.; Kryder, M.H. Granular L10 FePt (0 0 1) thin films for Heat Assisted Magnetic Recording. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-J.; Shen, C.-Y.; Jian, S.-R.; Chang, H.-W.; Juang, J.-Y.; Liao, Y.-Y.; Fan, C.-L. Nanoindentation Study of FePt Thin Films Deposited by Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2016, 8, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, A.D.; Crisan, O. Direct formation of L10 FePt in as-cast FePt-based magnetic nanocomposite ribbons without post-synthesis annealing. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 365002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakayama, H.; Yonekura, H. Structures and magnetic properties of bulk FePt nanocomposite magnets prepared by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, H.-R.; Matthies, S.; Lutterotti, L. Texture Analysis from Diffraction Spectra. Mater. Sci. Forum 1994, 157, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, O.; Dan, I.; Palade, P.; Crisan, A.D.; Leca, A.; Pantelica, A. Magnetic Phase Coexistence and Hard–Soft Exchange Coupling in FePt Nanocomposite Magnets. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisan, O.; Crisan, A.D.; Mercioniu, I.; Nicula, R.; Vasiliu, F. Development and structural characterization of exchange-spring-like nanomagnets in (Fe,Co)-Pt bulk nanocrystalline alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 401, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nominal Composition (at.%) | Fe (at.%) | Pt (at.%) | Mo (at.%) | Measured Composition (at.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe49Pt26Mo2B23 | 47.8 | 26.8 | 2.4 | Fe47.8Pt26.8Mo2.4B23 |
| 300 K | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS (mm/s) | Γ/2 (mm/s) | QS (mm/s) | HF (T) | % | Magnetic Phase |
| 0.24 | 0.16 | 0 | 30.0 | 7 | fcc FePt A1 |
| 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 27.6 | 19 | fct FePt L10 |
| 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 27.8 | 33 | fct FePt L10 |
| 0.13 | 0.16 | 0 | 23.5 | 4 | Fe2B |
| 0.06 | 0.16 | 0 | 20.7 | 3 | Fe2B |
| 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 9.8 | 34 | Residual cubic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crisan, A.D.; Crisan, O. Novel Rare Earth (RE)-Free Nanocomposite Magnets Derived from L10-Phase Systems. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050912
Crisan AD, Crisan O. Novel Rare Earth (RE)-Free Nanocomposite Magnets Derived from L10-Phase Systems. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(5):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050912
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrisan, Alina Daniela, and Ovidiu Crisan. 2023. "Novel Rare Earth (RE)-Free Nanocomposite Magnets Derived from L10-Phase Systems" Nanomaterials 13, no. 5: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050912
APA StyleCrisan, A. D., & Crisan, O. (2023). Novel Rare Earth (RE)-Free Nanocomposite Magnets Derived from L10-Phase Systems. Nanomaterials, 13(5), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050912





