A Novel Nanoporous Adsorbent for Pesticides Obtained from Biogenic Calcium Carbonate Derived from Waste Crab Shells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining the Adsorbent Powder
2.2. Characterization of the Adsorbent Powder
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Chromatographic Analysis of Acetamiprid
3. Results
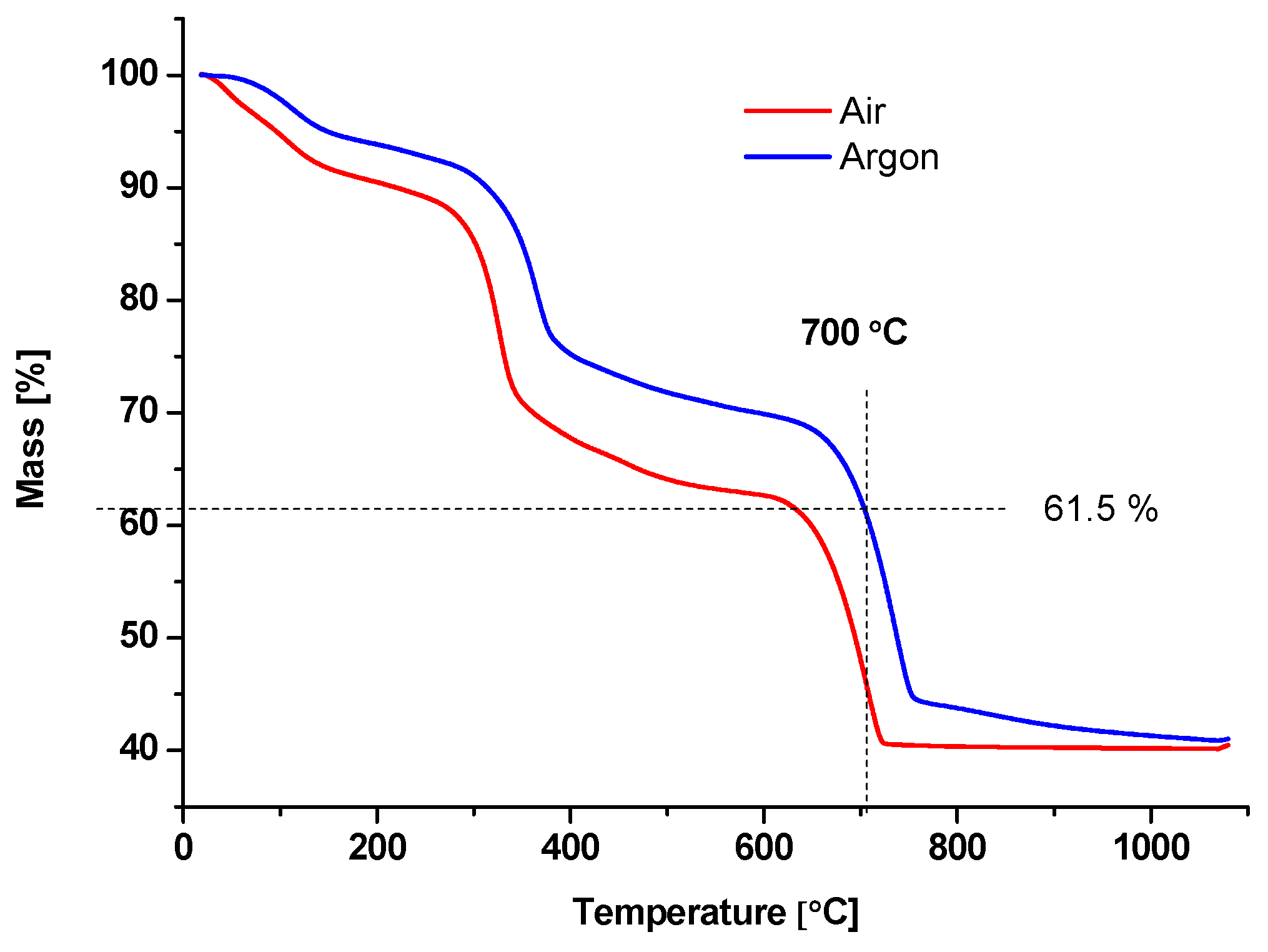
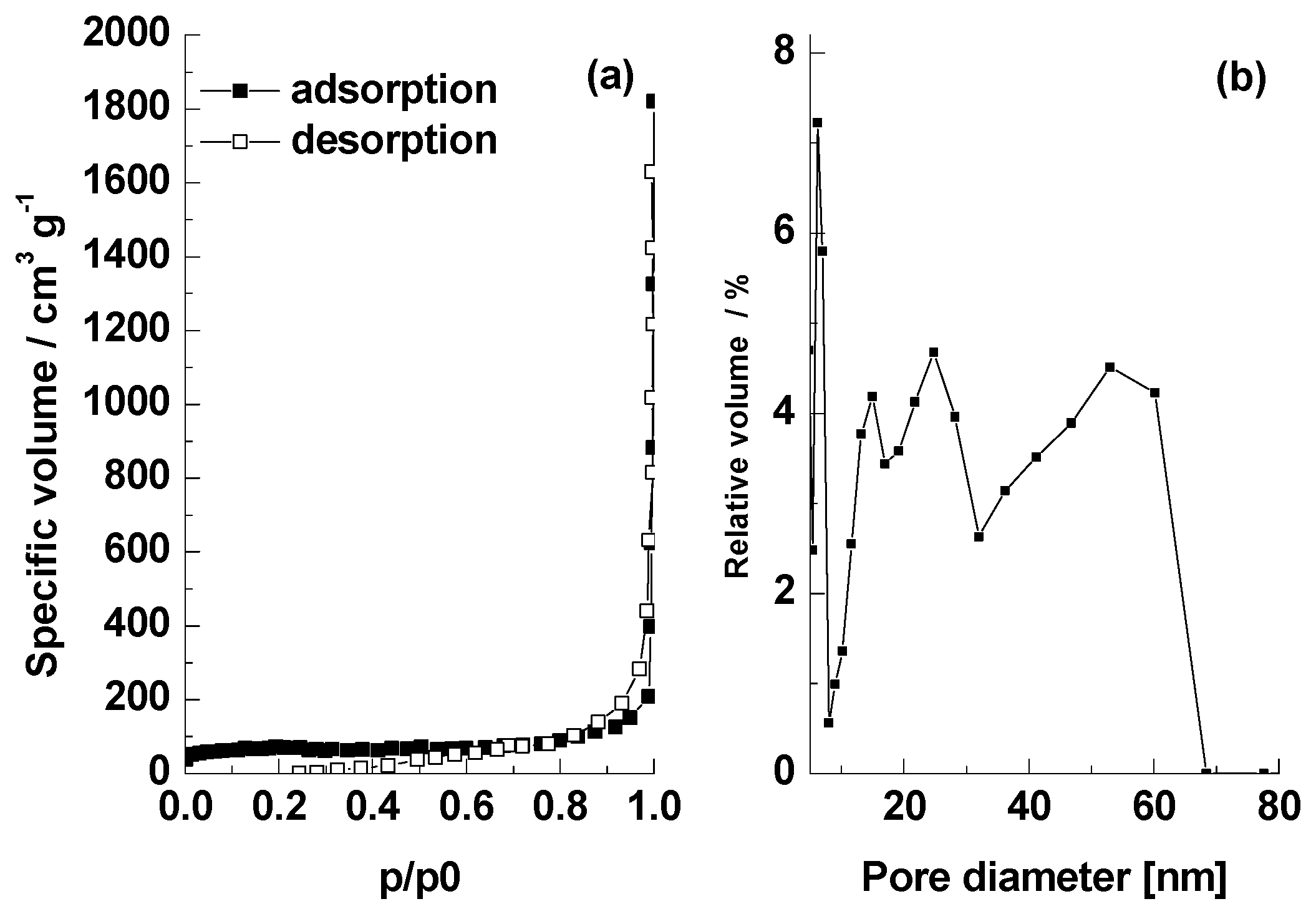
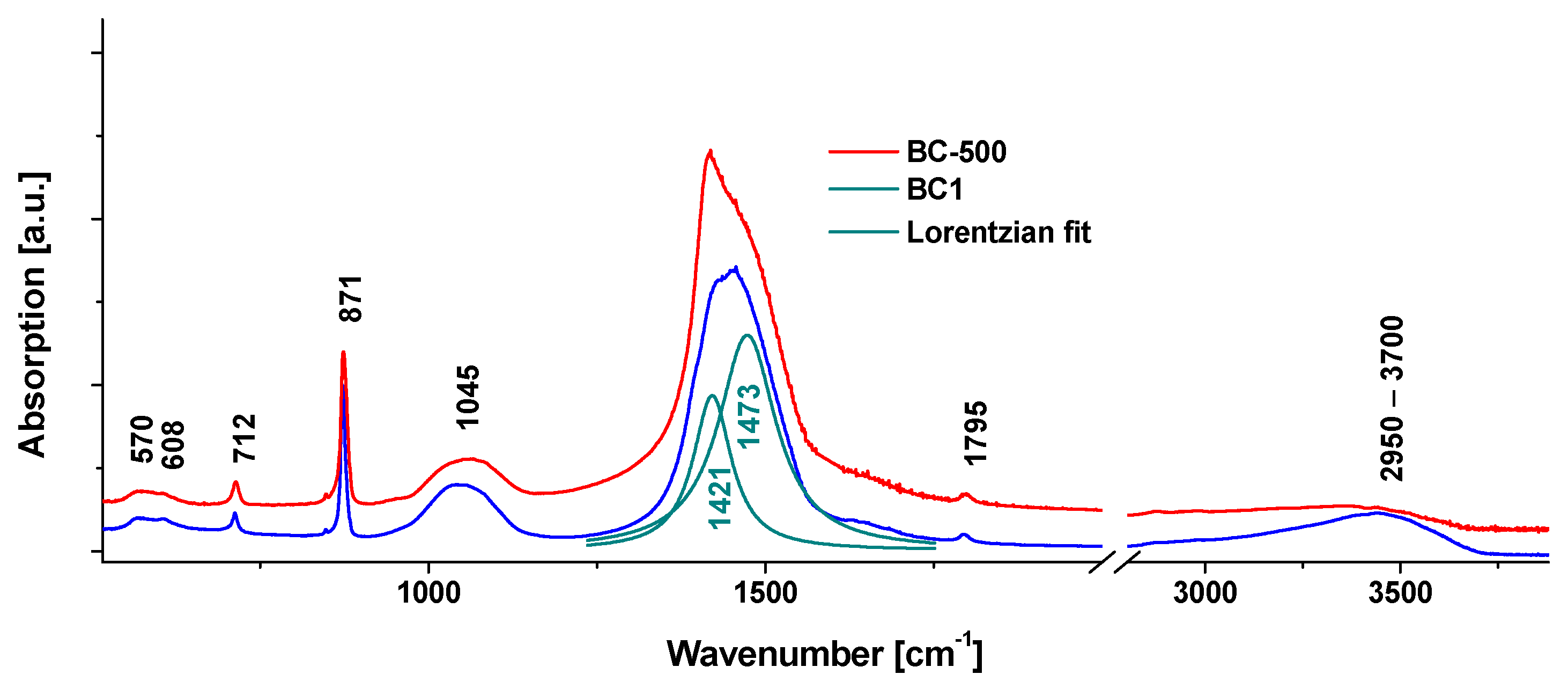
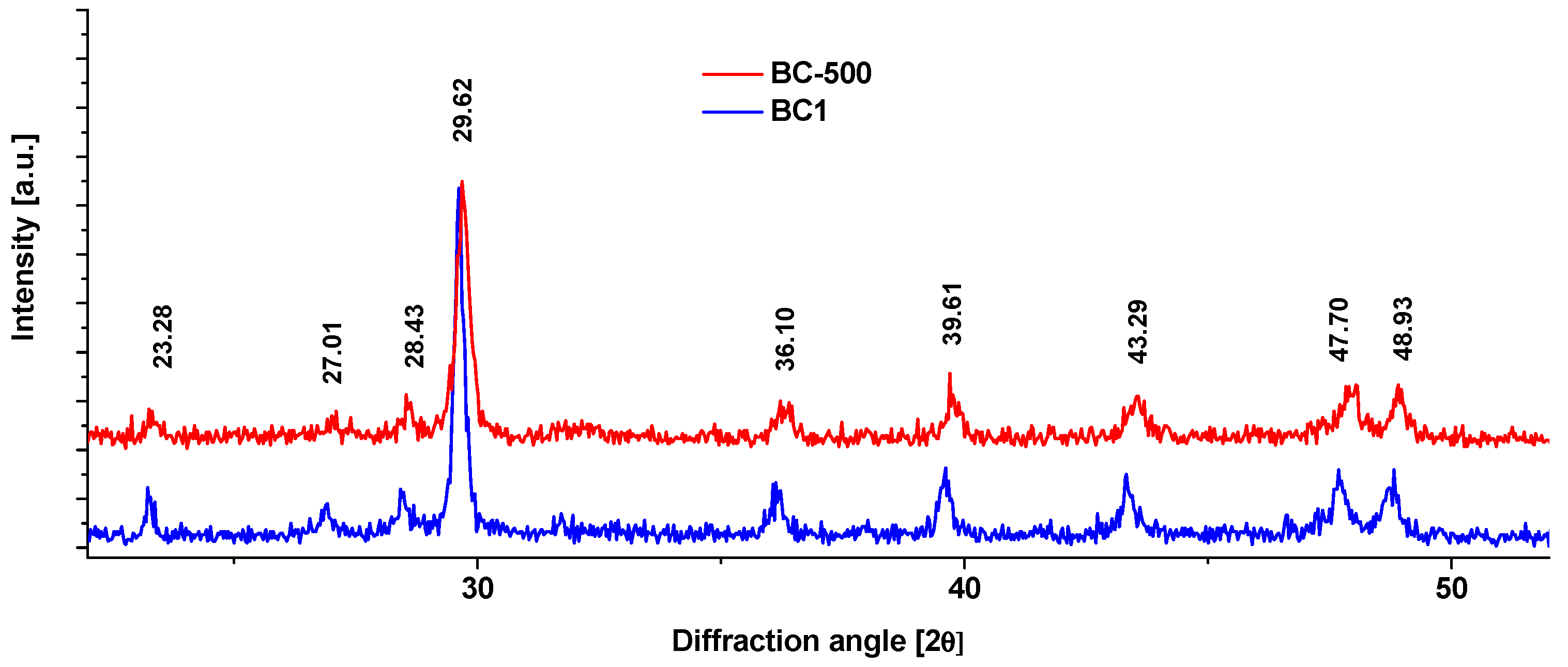
3.1. Obtaining the Adsorbent BC1 and Its Physical and Chemical Properties
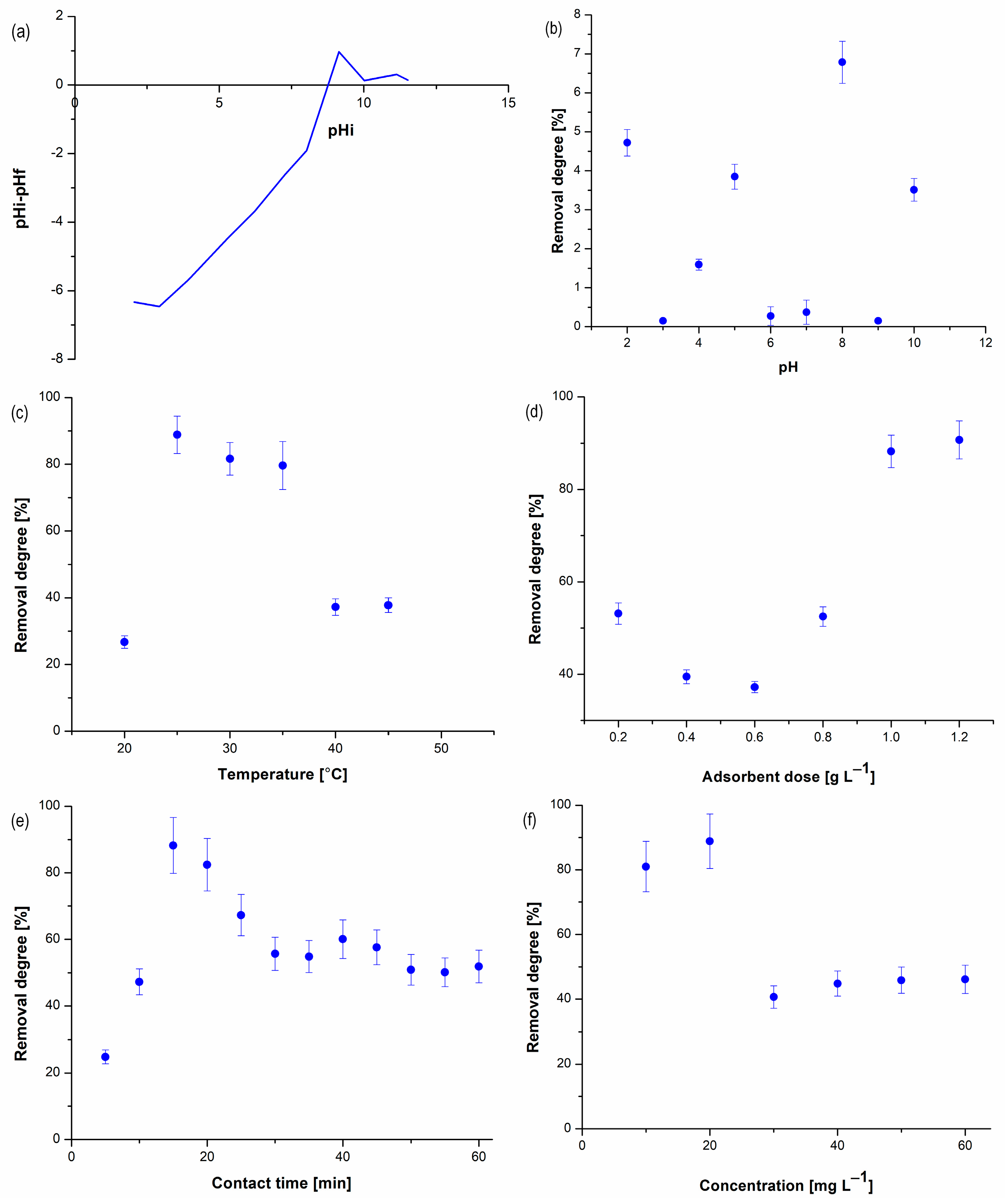
3.2. Investigation of Acetamiprid Adsorption on BC1
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torrinha, A.; Oliveira, T.M.B.F.; Ribeiro, F.W.P.; Correia, A.N.; Lima-Neto, P.; Morais, S. Application of nanostructured carbon-based electrochemical (bio)sensors for screening of emerging pharmaceutical pollutants in waters and aquatic species: A review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Xue, Y.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, S.; Fan, J. Recent advances in carbon-based materials for adsorptive and photocatalytic antibiotic removal. Nanomaterials 2022, 13, 4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangu, K.K.; Maddila, S.; Mukkamala, S.B.; Joonnalagadda, S.B. A review on contemporary metal–organic framework materials. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2016, 446, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Agboola, O.S.; Ogunmodede, J.; Araoye, A.O.; Bello, O.S. Metal-organic frameworks as adsorbents for sequestering organic pollutants from wastewater. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 253, 123246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, M.; Foroughi, M.M.; Ebrahimoor, N.; Jahani, S.; Omidi, A.; Khatami, M. A review on metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis and applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Lenaerts, S.; Symes, M.D.; Yang, X.-Y. Hierarchical design in nanoporous metals. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kianfar, E.; Savadi, H. Recent advances in properties and applications of nanoporous materials and porous carbons. Carbon Lett. 2022, 32, 1645–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topić-Popović, N.; Lorencin, V.; Strunjak-Perovic, I.; Coz-Rakovac, R. Shell waste management and utilization: Mitigating organic pollution and enhancing sustainability. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.; Kim, D.; Kim, T. Exceptional properties of hyper-resistant armor of a hydrothermal vent crab. Sci. Rep.-UK 2022, 12, 11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zheng, G.; Li, W.; McDowell, M.T.; Seh, Z.W.; Liu, N.; Lu, Z.; Cui, Y. Crab shells as sustainable templates from nature for nanostructured battery electrodes. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3385–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekvapil, F.; Pinzaru, S.C.; Barbu–Tudoran, L.; Suciu, M.; Glamuzina, B.; Tamas, T.; Chis, V. Color-specific porosity in double pigmented natural 3d-nanoarchitectures of blue crab shell. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Karlsson, A. Image analyses of two crustacean exoskeletons and implications of the exoskeletal microstructure on the mechanical behavior. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 2854–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, G.; Nekvapil, F.; Hirian, R.; Glamuzina, B.; Tamas, T.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Pinzaru, S.C. Novel drug carrier: 5-Fluorouracil formulation in nanoporous biogenic Mg-calcite from blue crab shells—Proof of concept. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 27781–27790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa, M.E.A.; Gadelha de Sousa, K.S.M.; Clericuzi, G.Z.; Ferreir, A.L.O.; Soares, M.C.S.; Neto, J.C.Q. Adsorption of reactive dye onto uçá crab shell (Ucides cordatus): Scale-up and comparative studies. Energies 2021, 14, 5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekvapil, F.; Mihet, M.; Lazar, G.; Cinta Pinzaru, S.; Gavrilovic, A.; Ciorita, A.; Levei, E.; Tamas, T.; Soran, M.-L. Comparative analysis of composition and porosity of the biogenic powder obtained from wasted crustacean exoskeletons after carotenoids extraction for the blue bioeconomy. Water 2023, 15, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Paris, O.; Terrill, N.J.; Gupta, H.S. Uncovering three [1]dimensional gradients in fibrillar orientation in an impact-resistant biological armour. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, G.; Nekvapil, F.; Glamuzina, B.; Tamas, T.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Suciu, M.; Cinta Pinzaru, S. pH-dependent behavior of novel 5-FU delivery system in environmental conditions comparable to the gastro-intestinal tract. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekvapil, F.; Ganea, I.-V.; Ciorita, A.; Hirian, R.; Tomsic, S.; Martonos, I.M.; Cinta Pinzaru, S. A new biofertilizer formulation with enriched nutrients content from wasted algal biomass extracts incorporated in biogenic powders. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeynaike, A.; Wang, L.; Jones, M.I.; Patterson, D.A. Pyrolysed powdered mussel shells for eutrophication control: Effect of particle size and powder concentration on the mechanism and extent of phosphate removal. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 6, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.I.; Wang, L.Y.; Abeynaike, A.; Patterson, D.A. Utilisation of waste Mmaterial for environmental applications: Calcination of mussel shells for waste water treatment. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2011, 110, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladoja, N.A.; Adelagun, R.O.A.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ololade, I.A. Phosphorus recovery from aquaculture wastewater using thermally treated gastropod shell. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 98, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.C.; Santos, E.B.H.; Marques, C.R. First study on oyster-shell-based phosphorous removal in saltwater—A proxy to effluent bioremediation of marine aquaculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Tan, F.; Li, H.; Zhu, N.; He, M.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, G.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J. Calcium-rich biochar from the pyrolysis of crab shell for phosphorus removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 198, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhu, W.; He, L.; Tan, F.; Zhu, N.; Zhou, Q.; He, M.; Hu, G. Calcium-rich biochar from crab shell: An unexpected super adsorbent for dye removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Feng, P.; Wen, L.; Huang, G.; Xu, C.; Lin, B. Highly efficient and ultra-rapid adsorption of malachite green by recyclable crab shell biochar. J. Industr. Eng. Chem. 2022, 113, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizal, A.N.M.; Putra, N.R.; Zaini, M.A.A. Scylla Sp. shell: A potential green adsorbent for wastewater treatment. Toxin Rev. 2022, 41, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.C.; Wang, C.I.; Sye, W.F. Applications of chitosan beads and porous crab shell powder for the removal of 17 organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in water solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.; Sneddon, J. Use of crustacean shells for uptake and removal of metal ions in solution. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2011, 46, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londono-Zuluaga, C.; Jameel, H.; Gonzalez, R.W.; Lucia, L. Crustacean shell-based biosorption water remediation platforms: Status and perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 231, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA—United States Environmental Protection Agency, Pesticide Re-evaluation Division. Acetamiprid: Proposed Interim Registration Review Decision Case Number 7617; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Alonso-Muñoz, S.; Garcia-Muina, F.E.; Medina-Salgado, M.-S.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, R. Towards circular economy practices in food waste management: A retrospective overview and a research agenda. Br. Food J. 2022, 12, 478–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunadasa, K.S.P.; Manoratne, C.H.; Pitawala, H.M.T.G.A.; Rajapakse, R.M.G. Thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate (calcite polymorph) as examined by in-situ high-temperature X-ray powder diffraction. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 134, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koll, P.; Borchers, G.; Metzger, J.O. Thermal degradation of chitin and cellulose. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1991, 19, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, H.F.G.; Francisco, D.S.; Ferreira, A.P.G.; Cavalheiro, E.T.G. A new look towards the thermal decomposition of chitins and chitosans with different degrees of deacetylation by coupled TG-FTIR. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, F.A.; Brecevic, L. Infrared spectra of amorphous and crystalline calcium carbonate. Acta Chem. Scand. 1991, 1989, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanienda-Pilecki, K.J. The importance of Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy in the identification of carbonate phases differentiated in magnesium content. Spectroscopy 2015, 34, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Galvan-Ruiz, M.; Banos, L.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M.E. Lime characterization as a food additive. Sens. Instrumen. Food Qual. 2007, 1, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Tahir, H.; Sultan, M.; Akhtar, N. Synthesis and characterization of cupric oxide (CuO) nanoparticles and their application for the removal of dyes. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 6650–6660. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hosney, H.A.; Grassian, V.H. Carbonic Acid: An Important Intermediate in the Surface Chemistry of Calcium Carbonate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8068–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, J.; Lorusso, M. Dissolution Behaviour of Calcium Carbonate in Mildly Acidic Conditions. In The Science of Papermaking, Proceedings of the 12th Fundamental Research Symposium Oxford, UK, 17–21 September 2001; Baker, C.F., Ed.; FRC: Manchester, UK, 2001; pp. 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto, B.; Martos, C.; Pena, J.L.; Rodriguez, R.; Pastor, G. Effects in the solubility of CaCO3: Experimental study and model description. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2012, 324, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, I.; Soran, M.L.; Stegarescu, A.; Opris, O.; Gutoiu, S.; Leostean, C.; Lazar, M.D.; Kacso, I.; Silipas, T.D.; Porav, A.S. Evaluation of CNT-COOH/MnO2/Fe3O4 nanocomposite for ibuprofen and paracetamol removal from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbert, F.; Morin-Crini, N.; Renault, F.; Badot, P.M.; Crini, G. Adsorption isotherm models for dye removal by cationized starch-based material in a single component system: Error analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, H.R.; Ibrahim, S.M.; El-Molla, S.A. Textile dye removal from aqueous solutions using cheap MgO nanomaterials: Adsorption kinetics, isotherm studies and thermodynamics. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Alves, D.C.; Healy, B.; de Almeida Pinto, L.A.; Cadaval, T.R.S., Jr.; Breslin, C.B. Recent developments in chitosan-based adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from aqueous environments. Molecules 2021, 26, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbricino, M.; Pontoni, L. Use of non-treated shrimp-shells for textile dye removal from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4100–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissouli, L.; Benicha, M.; Chafik, T.; Chabbi, M. Decontamination of water polluted with pesticide using biopolymers: Adsorption of glyphosate by chitin and chitosan. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 8, 4544–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthapanya, X.; Wu, S.; Han, Z.; Zeng, G.; Wu, M.; Yang, C. Adsorptive removal of anionic dye using calcined oyster shells: Isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 5944–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, L.; Xu, D.; Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Metal–organic framework preparation using magnetic graphene oxide–β-cyclodextrin for neonicotinoid pesticide adsorption and removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, S.G.; Ahmed, S.M.; Amr, A.E.E.; Kamel, A.H. Porous activated carbon from lignocellulosic agricultural waste for the removal of acetamiprid pesticide from aqueous solutions. Molecules 2020, 25, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahraoui, N.; Tassalit, D.; Rekhila, G.; Chekir, N. Laboratory studies on the adsorption of acetamiprid to activated carbon from pomegranate waste. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikhaow, A.; Chaengsawang, W.; Kiatsiriroat, T.; Kajitvichyanukul, P.; Smith, S.M. Adsorption kinetics of imidacloprid, acetamiprid and methomyl pesticides in aqueous solution onto eucalyptus woodchip derived biochar. Minerals 2022, 12, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
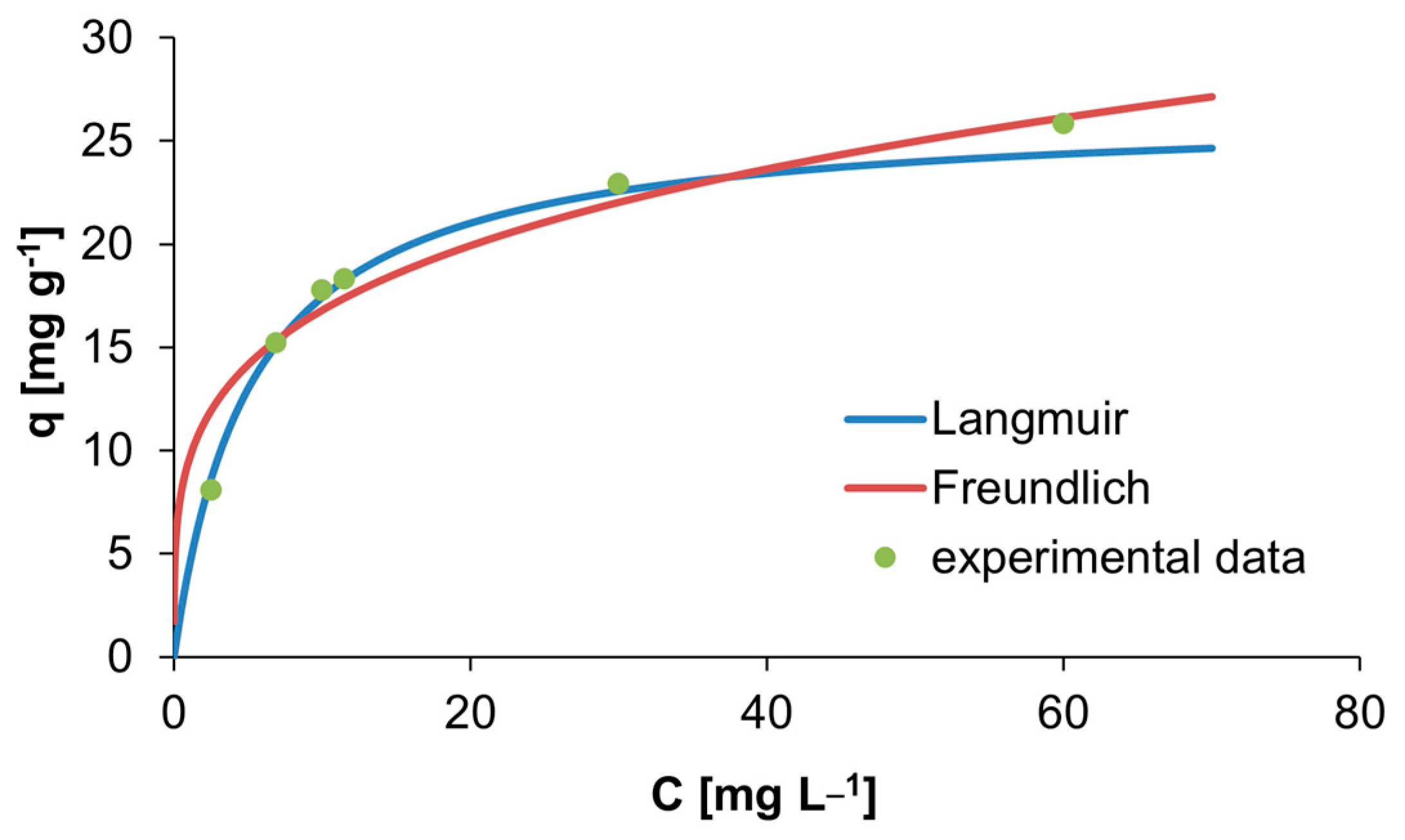
| Isotherm Model | Constants | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm [mg g−1] | 26.4550 |
| KL [L g−1] | 0.1927 | |
| R2 | 0.9123 | |
| Freundlich | KF [L mg−1] | 9.5258 |
| 1/n | 0.2463 | |
| R2 | 0.5862 |
| Starting Material | Composition | Pollutant | Adsorption Capacity (mg g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oyster shells | CaCO3 | Acid green | 33.3 | [45] |
| Uca crab | Native shell (CaCO3 and chitin) | Reactive blue 222 | 4.19 | [14] |
| Unspecified crab shell stock | biochar | Phosphorus | n.r. | [23] |
| Unspecified crab shell stock | Biochar | Malachite green; Congo red | 12,501.98; 20,317.47 | [24] |
| Unspecified crab shell stock | Biochar | Malachite green | 6142.5 | [25] |
| Unspecified crab shell stock | Native shell (CaCO3 and chitin) | Organochlorine pesticides | 0.001 to 0.0015 for 4,4’-DDE | [27] |
| Graphene oxide-β-cyclodextrin metal–organic framework (MOF) | Magnetic MOF | Acetamiprid | 2.96 | [49] |
| Tangerine peel | Activated carbon | Acetamiprid | 35.7 | [50] |
| Pomegranate waste | Activated carbon | Acetamiprid | 27.62 | [51] |
| Eucalyptus woodchip | Biochar | Acetamiprid | 4.87 | [52] |
| BC1 | CaCO3 | Acetamiprid | 26.45 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nekvapil, F.; Stegarescu, A.; Lung, I.; Hirian, R.; Cosma, D.; Levei, E.; Soran, M.-L. A Novel Nanoporous Adsorbent for Pesticides Obtained from Biogenic Calcium Carbonate Derived from Waste Crab Shells. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13233042
Nekvapil F, Stegarescu A, Lung I, Hirian R, Cosma D, Levei E, Soran M-L. A Novel Nanoporous Adsorbent for Pesticides Obtained from Biogenic Calcium Carbonate Derived from Waste Crab Shells. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(23):3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13233042
Chicago/Turabian StyleNekvapil, Fran, Adina Stegarescu, Ildiko Lung, Razvan Hirian, Dragoș Cosma, Erika Levei, and Maria-Loredana Soran. 2023. "A Novel Nanoporous Adsorbent for Pesticides Obtained from Biogenic Calcium Carbonate Derived from Waste Crab Shells" Nanomaterials 13, no. 23: 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13233042
APA StyleNekvapil, F., Stegarescu, A., Lung, I., Hirian, R., Cosma, D., Levei, E., & Soran, M.-L. (2023). A Novel Nanoporous Adsorbent for Pesticides Obtained from Biogenic Calcium Carbonate Derived from Waste Crab Shells. Nanomaterials, 13(23), 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13233042






