One-Pot Synthesis of Lamellar Fe-Cu Bimetal-Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Enhanced Removal of Cr(VI) from Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Reagents
2.2. Experimental Instruments
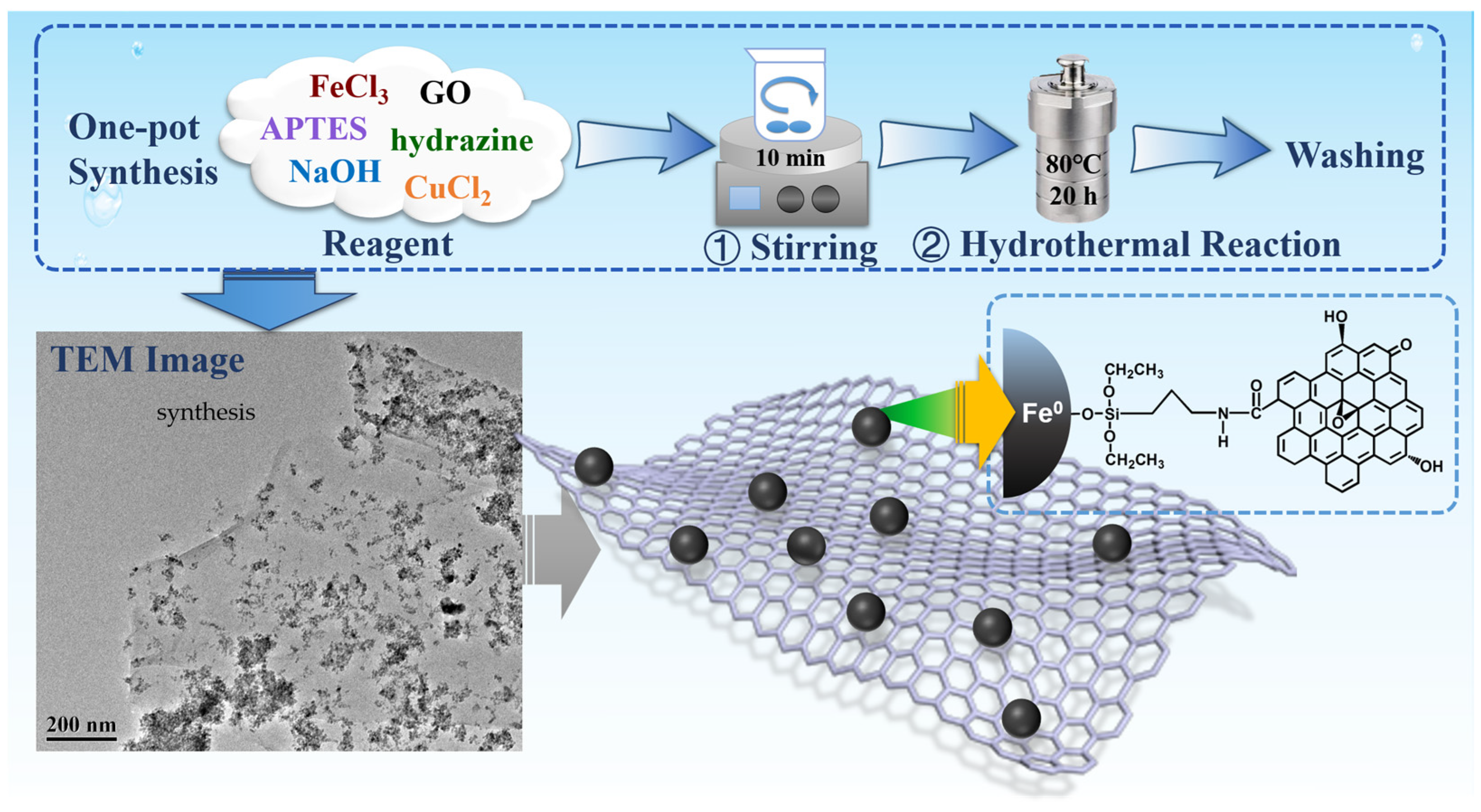
2.3. Nanocomposite Fabrication
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Removal of Cr(VI) Experiment
2.5.1. Batch Experiments
2.5.2. Cr(VI) Determination and Calculation
2.5.3. Kinetic Experiment and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
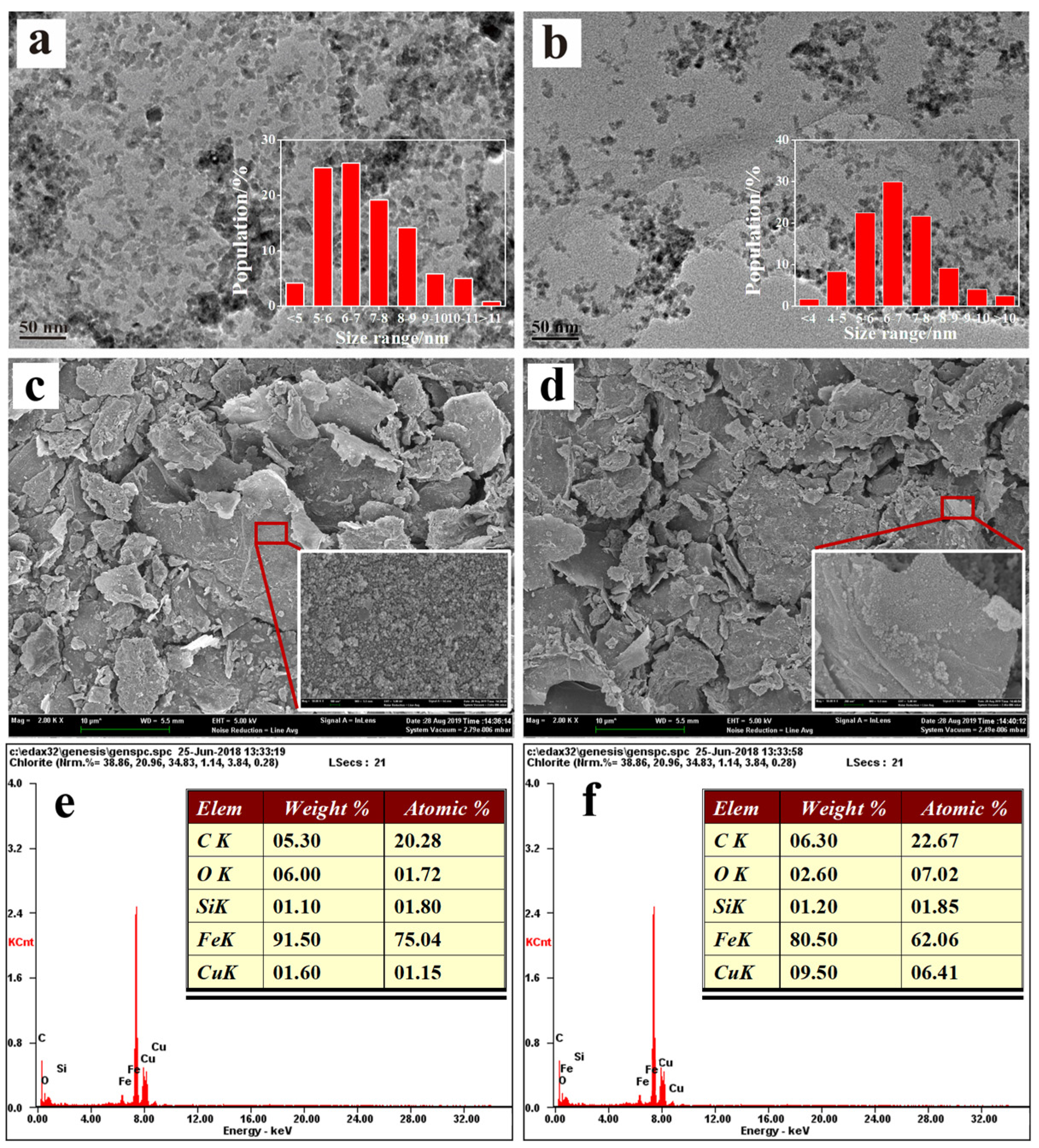
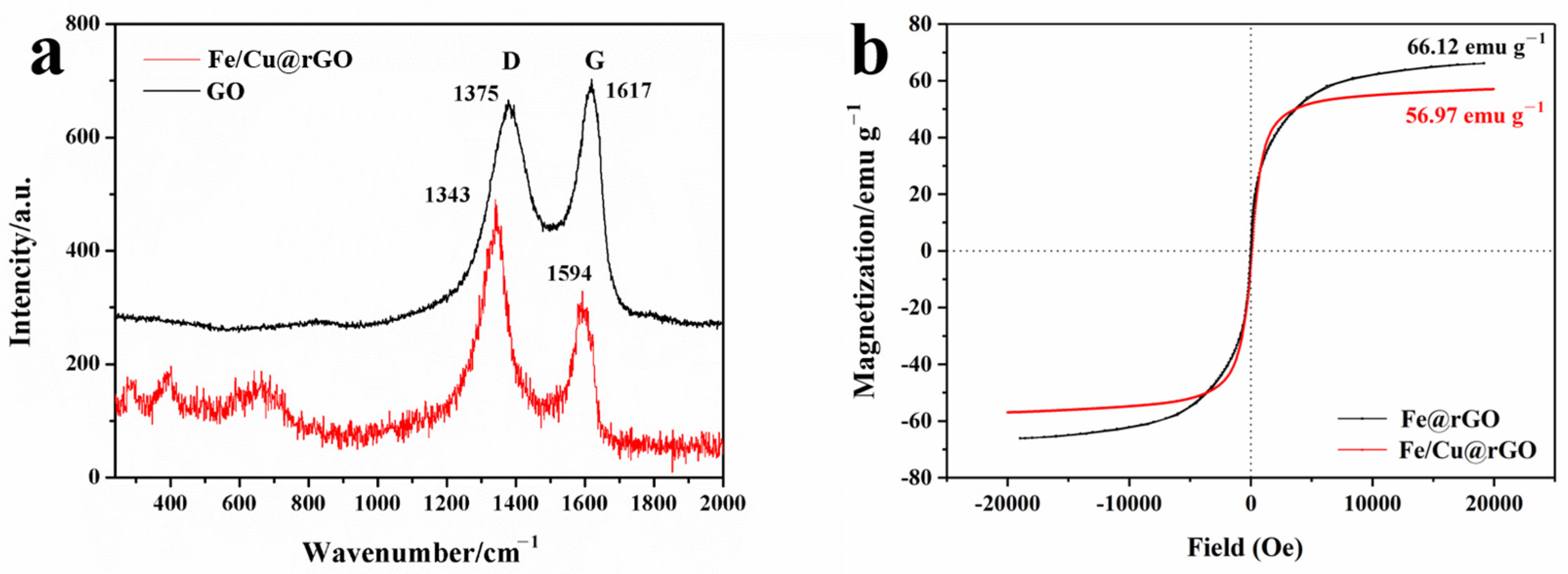
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Investigation of Factors Affecting Cr(VI) Removal
3.2.1. The Effect of Cu Addition and rGO Amount
3.2.2. The Effect of pH
3.2.3. The Effect of Initial Concentration
3.2.4. The Effect of Ionic Strength
3.2.5. The Effect of HA
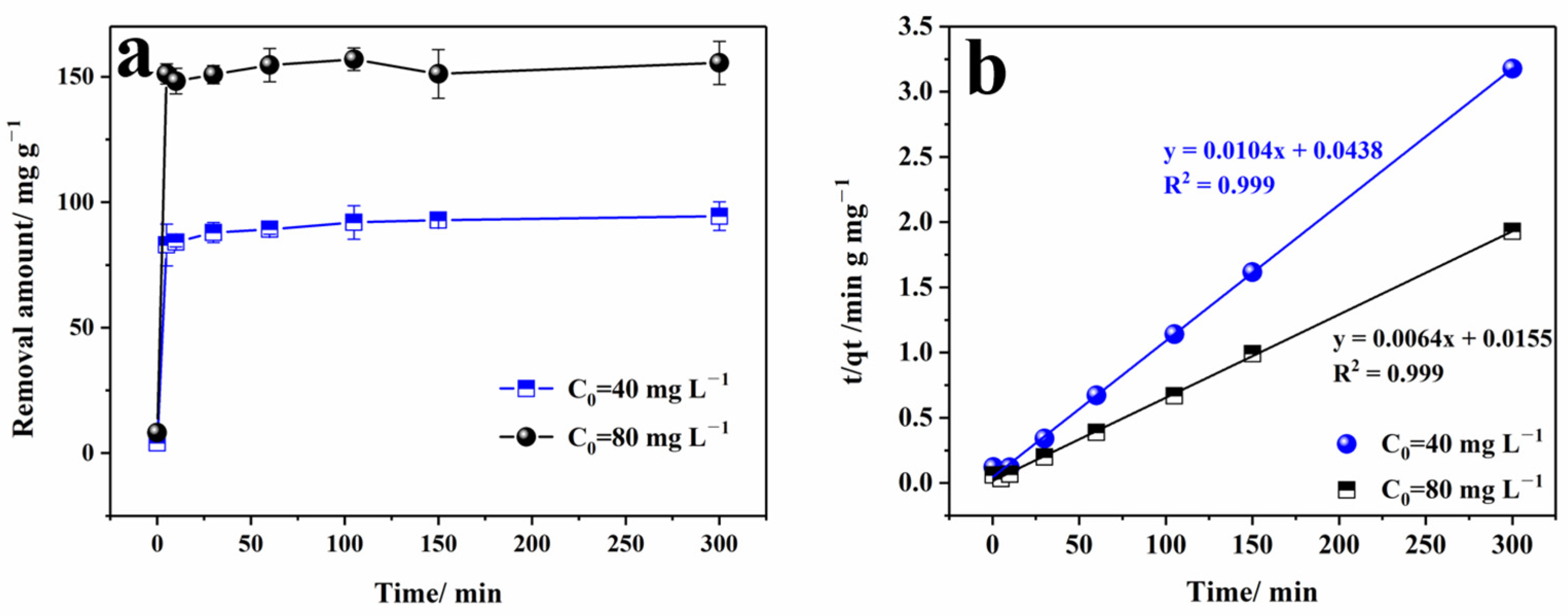
3.3. Kinetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, Z.Y.; Gao, H.; Hu, Z.L.; Jia, X.D.; Wen, D.S. Ni–Fe/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for hexavalent chromium reduction in an aqueous environment. Acs Omega 2022, 7, 4041–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, X.Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.H.; Leng, L.J.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zeng, G.M. Facile synthesis of polypyrrole decorated reduced graphene oxide-Fe3O4 magnetic composites and its application for the Cr(VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukhurebor, K.E.; Aigbe, U.O.; Onyancha, R.B.; Nwankwo, W.; Osibote, O.A.; Paumo, H.K.; Ama, O.M.; Adetunji, C.O.; Siloko, I.U. Effect of hexavalent chromium on the environment and removal techniques: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Liu, W.T.; Chi, Z.F. Reduced graphene oxide supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI/rGO) for in-situ remediation of Cr(VI)/nitrate-polluted aquifer. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.T.; Bai, J.; Chi, Z.F.; Ren, L.M.; Dong, J. An in-situ reactive zone with xanthan gum modified reduced graphene oxide supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (XG-nZVI/rGO) for remediation of Cr(VI)-polluted aquifer: Dynamic evolutions of Cr(VI) and environmental variables. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillham, R.W.; O’Hannesin, S.F. Enhanced degradation of halogenated aliphatics by zero-valent iron. Groundwater 1994, 32, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.S.; Qin, X.F.; Wang, K.F.; Peng, Y.Y.; Wang, P.; Jiang, G.M. Nanoscale zero valent iron supported on MgAl-LDH-decorated reduced graphene oxide: Enhanced performance in Cr(VI) removal, mechanism and regeneration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, R.W.; Powell, R.M.; Paul, C.J.; Blowes, D. Groundwater remediation of chromium using zero-valent iron in a permeable reactive barrier. In Innovative Subsurface Remediation; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; Volume 725, pp. 182–194. [Google Scholar]
- Ponder, S.M.; Darab, J.G.; Mallouk, T.E. Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported, nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2564–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.X.; Li, J.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhao, D.C. Iron-based magnetic nanomaterials and their environmental applications. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tec. 2016, 46, 783–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, R.A.; Scott, T. The removal of uranium onto carbon-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.F.; Cheng, Y.L.; Shih, Y.H. Removal of trichloroethylene by zerovalent iron/activated carbon derived from agricultural wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 129, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, R.A.; Scott, T.B. Nanoscale zero-valent iron: Future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, B.L. Adsorption and coadsorption of organic pollutants and a heavy metal by graphene oxide and reduced graphene materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sharma, P. Novel insights into adsorption of heavy metal ions using magnetic graphene composites. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersan, G.; Apul, O.G.; Perreault, F.; Karanfil, T. Adsorption of organic contaminants by graphene nanosheets: A review. Water Res. 2017, 126, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.C.; Ahmed, F.; Gutierrez, K.M.; Frigi Rodrigues, D. A comparative study of lysozyme adsorption with graphene, graphene oxide, and single-walled carbon nanotubes: Potential environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Miao, S.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.P.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption properties of magnetic Fe3O4@graphene nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 184, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Wang, L.; Yuan, L.Y.; Xiao, C.L.; Mei, L.; Zheng, L.R.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.H.; Zhao, Y.L.; Zhu, Z.T.; et al. Efficient removal of uranium from aqueous solution by zero-valent iron nanoparticle and its graphene composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 290, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.Q.; Weerasooriya, R.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, X. Tea polyphenols mediated Zero-valent Iron/Reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for electrochemical determination of Hg2+. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 917, 116428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Kim, A.Y.; Woo, J.C.; Cho, H.S.; Youk, J.H. Study on preparation methodology of zero-valent iron decorated on graphene oxide for highly efficient sonocatalytic dye degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, M.; Elkady, M.; Kamal, A.; Elessawy, N.; Zaki, S.; Eltarahony, M. Novel biosynthesis of graphene-supported zero-valent iron nanohybrid for efficient decolorization of acid and basic dyes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Bai, H.; Wen, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Guo, L. Highly efficient adsorption and mechanism of alkylphenols on magnetic reduced graphene oxide. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, B.; Mehmood, T.; Wang, Z.; Chofreh, A.G.; Shen, A.; Yang, B.; Yuan, J.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W.; et al. Next-generation graphene oxide additives composite membranes for emerging organic micropollutants removal: Separation, adsorption and degradation. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.; Boo, C.; Song, I.H.; Park, C. Investigating the potential of ammonium retention by graphene oxide ceramic nanofiltration membranes for the treatment of semiconductor wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, T.; Bibi, F.; Arif, S.; Waseem, M.; Haq, S.; Azra, M.N.; Liblik, T.; Zekker, I. Adsorption and kinetics studies of Cr (VI) by graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide-zinc oxide nanocomposite. Molecules 2022, 27, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Song, H.; Li, Q.; Li, A. Fe/Cu bimetallic catalysis for reductive degradation of nitrobenzene under oxic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Lai, B.; Yang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, S. Comparative study on the reactivity of Fe/Cu bimetallic particles and zero valent iron (ZVI) under different conditions of N2, air or without aeration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J. Removal of p-nitrophenol (PNP) in aqueous solution by the micron-scale iron–copper (Fe/Cu) bimetallic particles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Tosco, T. Transport and retention of high concentrated nano-Fe/Cu particles through highly flow-rated packed sand column. Water Res. 2013, 47, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaomin, N.; Xiaobo, S.; Huagui, Z.; Dongen, Z.; Dandan, Y.; Qingbiao, Z. Studies on the one-step preparation of iron nanoparticles in solution. J. Cryst. Growth. 2005, 275, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, D.; Arai, Y.; Fu, X.; Li, X.; Huang, W. Kinetics and mechanisms of debromination of tetrabromobisphenol A by Cu coated nano zerovalent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubair, T.; Eljamal, O.; Khalil, A.M.E.; Tahara, A.; Matsunaga, N. Novel application of nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic nano-Fe/Cu particles for the treatment of cesium contaminated water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4253–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubair, T.; Eljamal, O.; Khalil, A.M.E.; Matsunaga, N. Multilayer system of nanoscale zero valent iron and Nano-Fe/Cu particles for nitrate removal in porous media. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 193, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 7467-87; Water Quality-Determination of Chromium(Ⅵ)-1,5 Diphenylcarbohydrazide Spectrophotometric Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1987.
- Jiang, Y.; Du, L.; Cheng, Q.; Jin, Z.; Hui, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xu, L. Nanoscale zero-valent iron alters physiological, biochemical, and transcriptomic response of nonylphenol-exposed algae (Dictyosphaerium sp.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 20711–20720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Q.; You, W.H.; Qiao, S.; Ma, Y.H.; Ren, Z.Y. Comprehensive understanding of adsorption and reduction on 2,4-DCP and Cr(VI) removal process by NZVI-rGO: Performance and mechanism. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Huang, C.; Yan, S.; Li, X.J.; Pan, S.Y. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption properties of magnetite/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. Talanta 2015, 144, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Li, D.; Ni, X.; Zheng, H. A facile chemical reduction route to the preparation of single-crystalline iron nanocubes. Chem. Lett. 2007, 36, 722–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.X. Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: An overview. J. Nanopart. Res. 2003, 5, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hu, E.; Yang, S.; Gong, L.; He, F. Chromium(VI) removal by mechanochemically sulfidated zero valent iron and its effect on dechlorination of trichloroethene as a co-contaminant. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 650, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, B. Macroscopic and Spectroscopic Investigations of the adsorption of nitroaromatic compounds on graphene oxide, reduced graphene oxide, and graphene Nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6181–6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Li, J.; Xiong, Z.; Lai, B. Enhanced reactivity of microscale Fe/Cu bimetallic particles (mFe/Cu) with persulfate (PS) for p-nitrophenol (PNP) removal in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.F.; Guo, J.M.; Ma, J.C.; Chen, E.Q.; Pang, J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Hao, H.D.; Wu, D.L.; Wang, S.B. Effective removal of hexavalent chromium with magnetically reduced graphene oxide bentonite. Clay Miner. 2023, 58, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fana, M.J.; Li, M.; Liu, X. Cr(VI) removal from groundwater using double surfactant-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Effects of materials in different status. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 717, 137112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-C.; Shu, H.Y.; Hsieh, W.P.; Wang, M.C. Using nanoscale zero-valent iron for the remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soil. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, D.; Cui, J. Necklace-like core-shell structural mesoporous silica-coated nanoscale zero-valent iron for efficient remediation Cd-contaminated water and soil. Water Air Soil Poll. 2023, 234, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yan, B. Charged nanoplastics differentially affect the conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Sci. Nano, 2023, in press.
- Waghmare, A.; Rathore, R.; Pandey, A.; Chandra, V. Graphene-oxide-coated, polypyrrole-supported, nano zerovalent iron nanocomposites for adsorption of hexavalent chromium from wastewater. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202204410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Material | Atomic Percentage/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Cr | O | C | Cu | |
| Fe/Cu@rGO before reaction | 19 | 2.36 | 39.73 | 34.72 | 4.19 |
| Fe/Cu@rGO (pH 2) after reaction | 16.81 | 3.73 | 47.84 | 30.37 | 1.25 |
| Fe/Cu@rGO (pH 7) after reaction | 15.78 | 5.02 | 44.06 | 28.96 | 6.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Fan, M.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, M. One-Pot Synthesis of Lamellar Fe-Cu Bimetal-Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Enhanced Removal of Cr(VI) from Water. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13202745
Li J, Fan M, Yuan Z, Liu F, Li M. One-Pot Synthesis of Lamellar Fe-Cu Bimetal-Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Enhanced Removal of Cr(VI) from Water. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(20):2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13202745
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jing, Mingjie Fan, Ziting Yuan, Fang Liu, and Miao Li. 2023. "One-Pot Synthesis of Lamellar Fe-Cu Bimetal-Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Enhanced Removal of Cr(VI) from Water" Nanomaterials 13, no. 20: 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13202745
APA StyleLi, J., Fan, M., Yuan, Z., Liu, F., & Li, M. (2023). One-Pot Synthesis of Lamellar Fe-Cu Bimetal-Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Enhanced Removal of Cr(VI) from Water. Nanomaterials, 13(20), 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13202745





