Analysis of Hazy Ga- and Zr-Co-Doped Zinc Oxide Films Prepared with Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
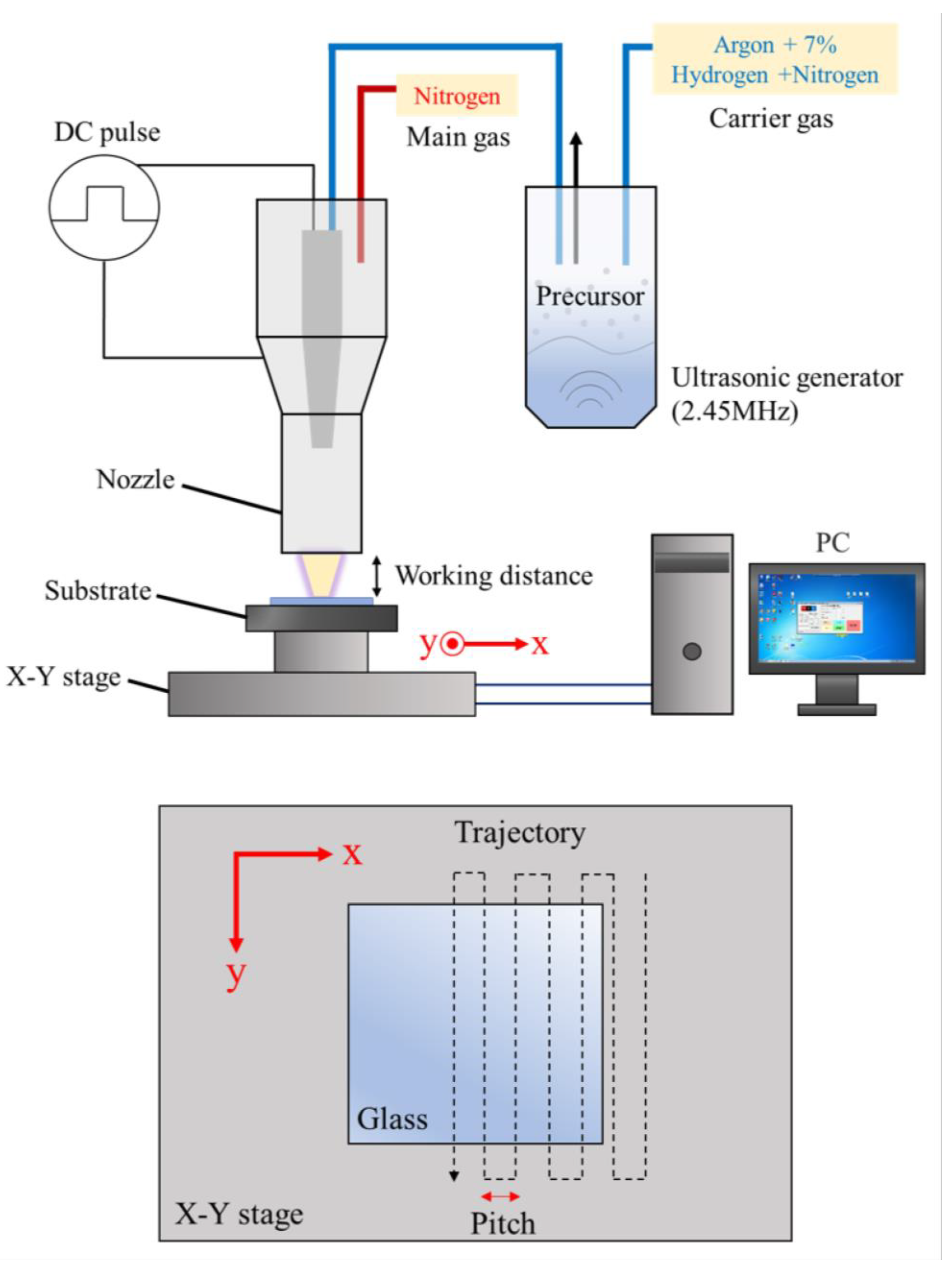
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Film Deposition
2.2. Film Characterization
3. Results
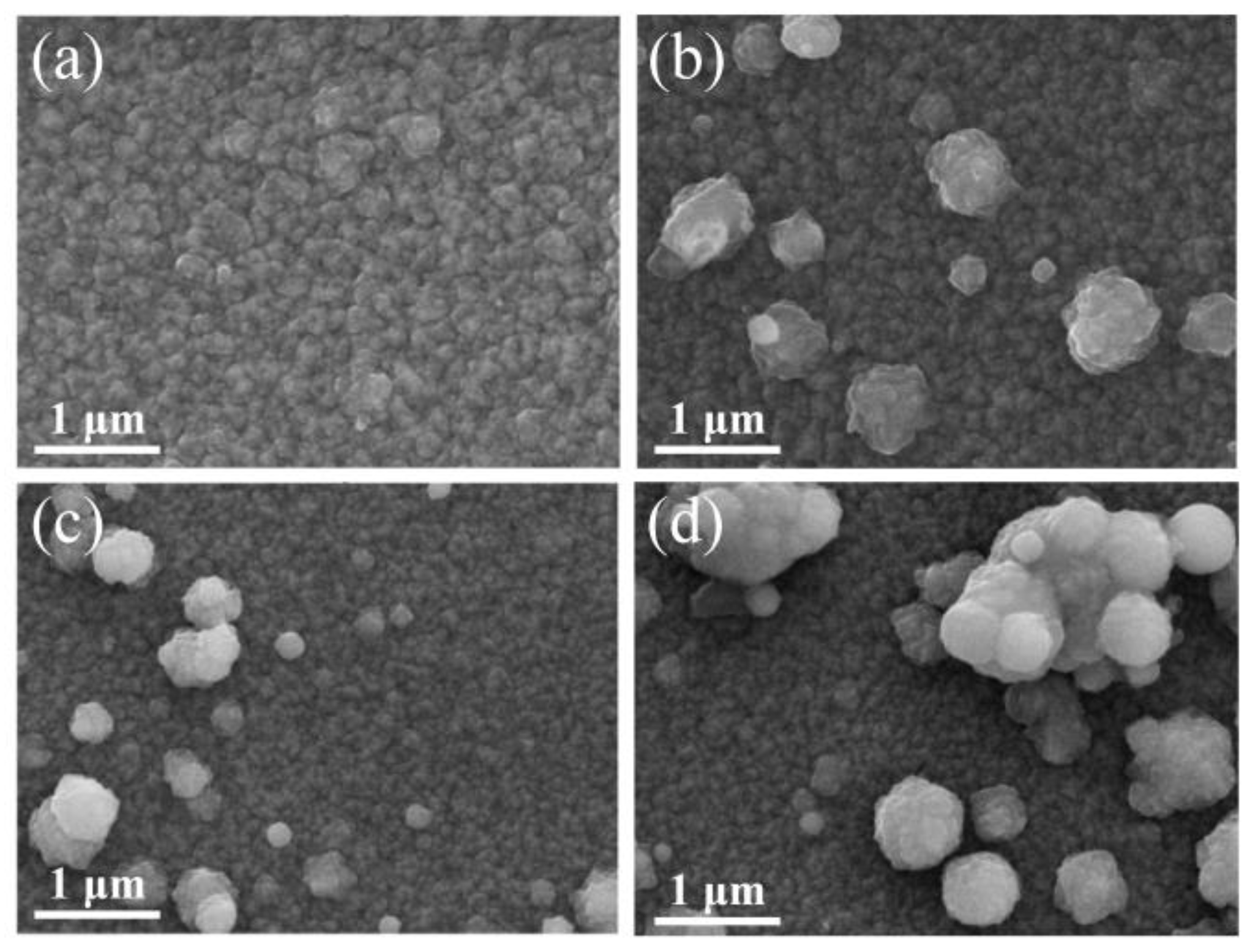
3.1. Morphological Properties
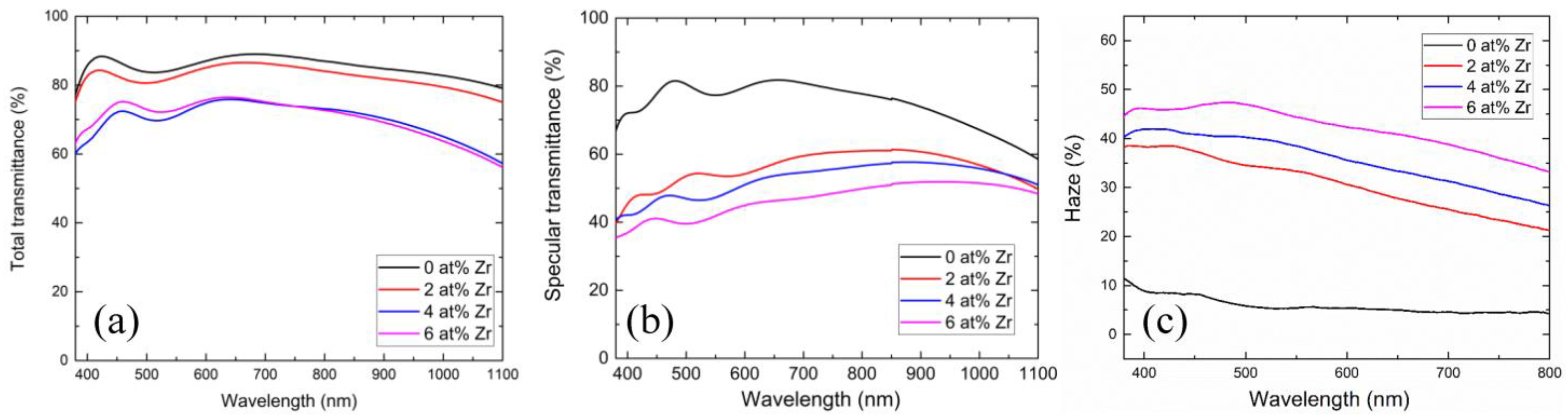
3.2. Optical Properties
3.3. EDS Analysis
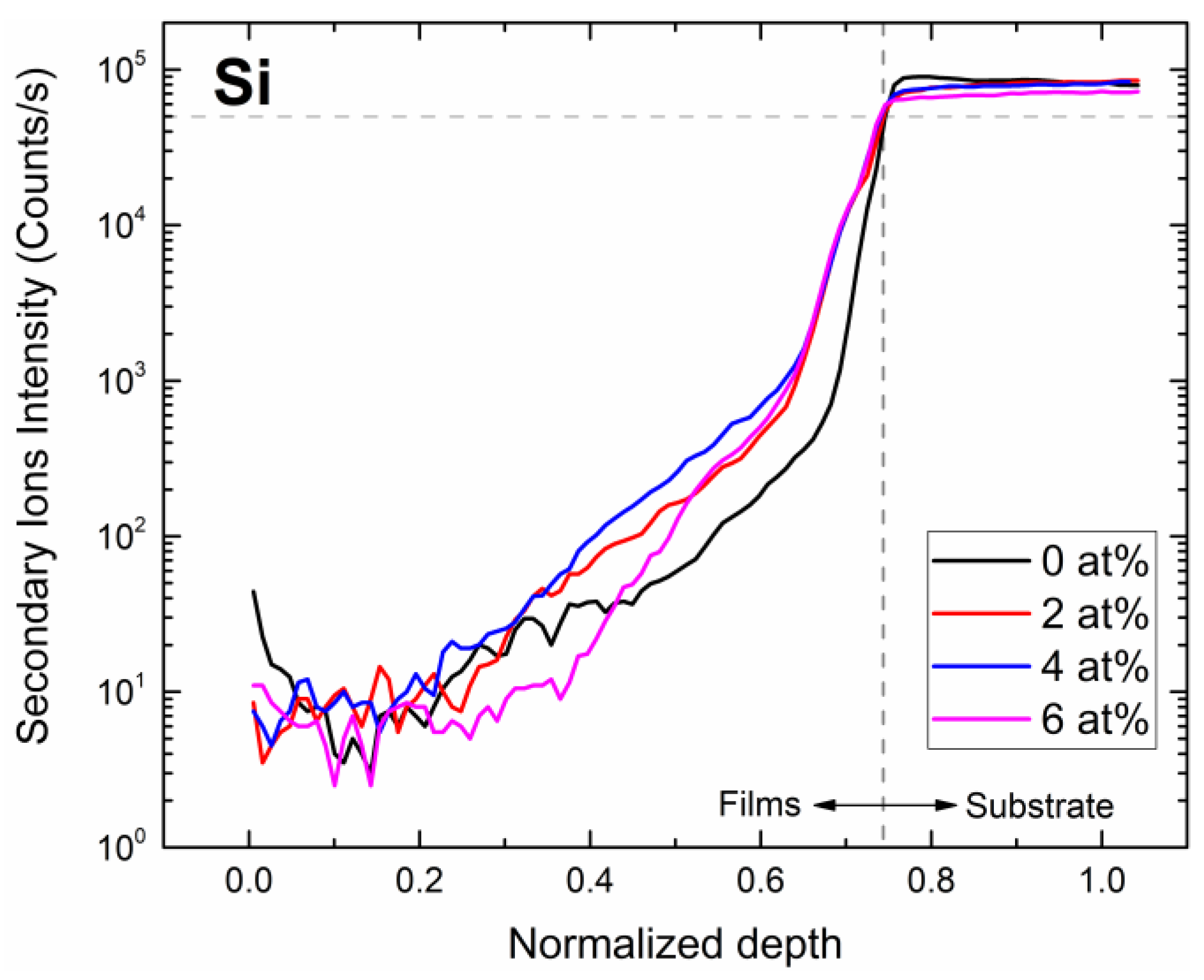
3.4. SIMS Analysis
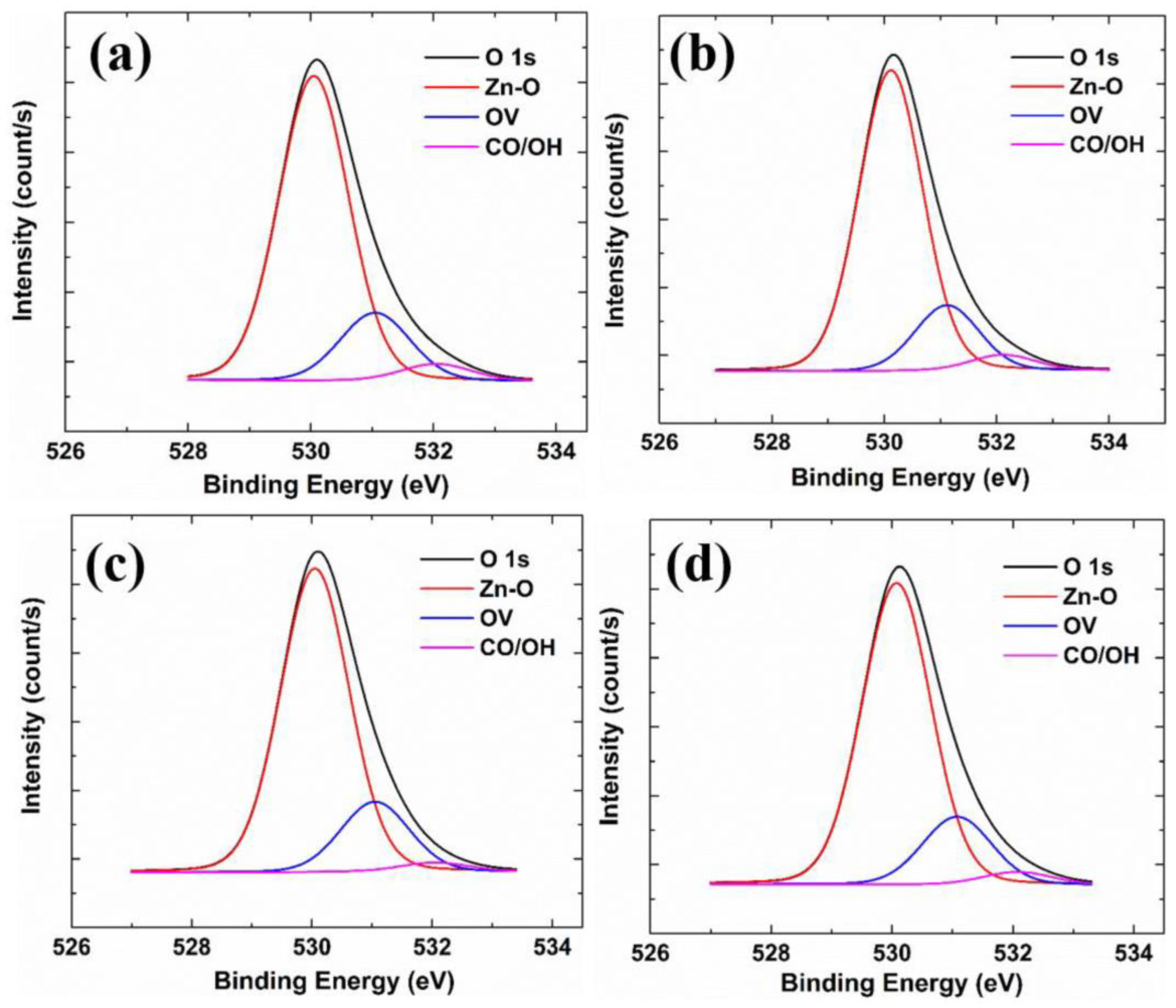
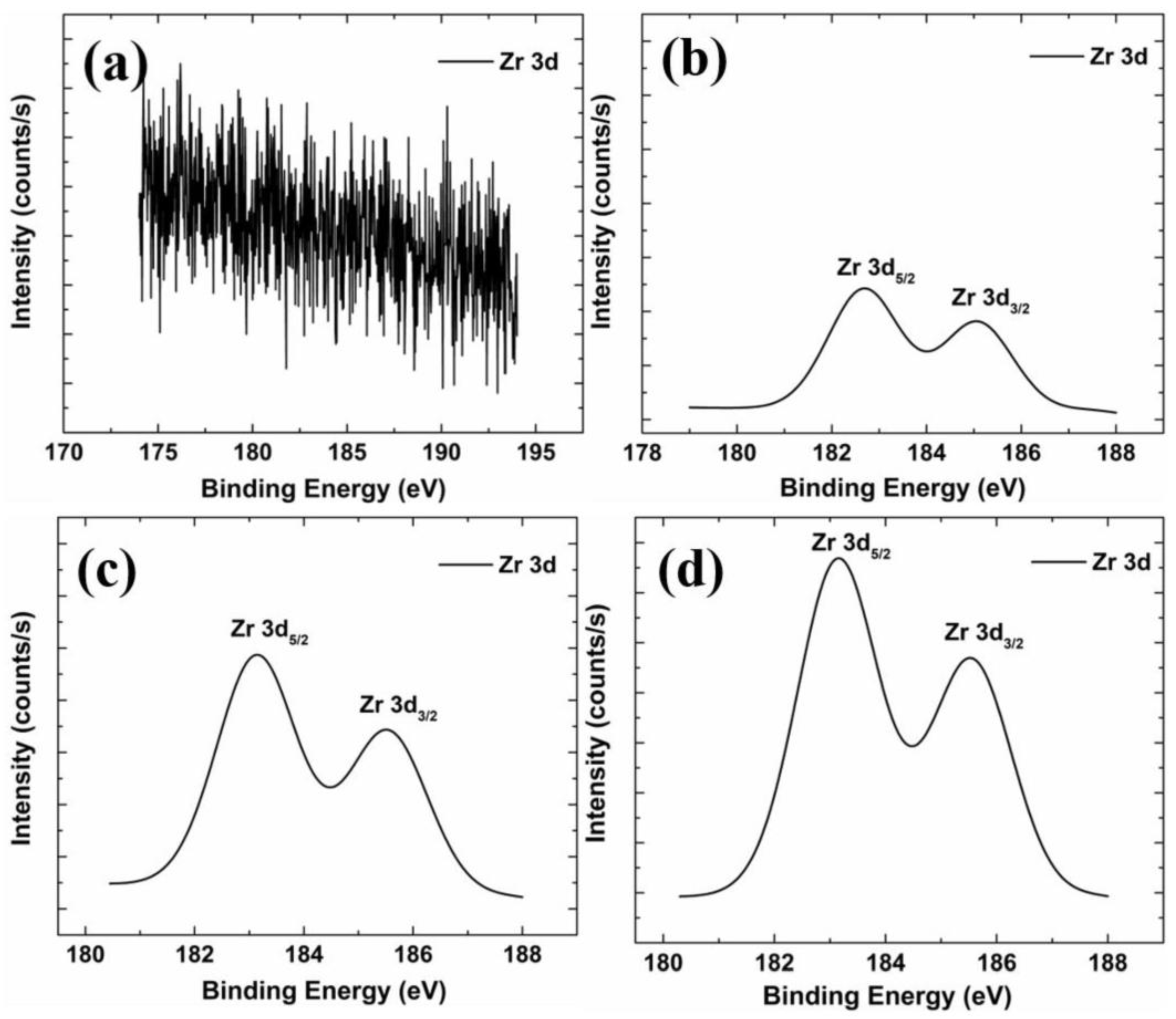
3.5. XPS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yin, T. Preparation of Ito Thin Films by Injection Ultrasound Spray Pyrolysis and Its Physical Properties. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2013, 144, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Duan, Z.; Ren, Y. Preparation of Ito Films Using a Spray Pyrolysis Solution Containing an Acetylacetone Chelating Agent. Mater. Sci. 2014, 32, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sun, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Song, J.; Hao, Z.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, X.; Shu, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Effect of Ito Target Crystallinity on the Properties of Sputtering Deposited Ito Films. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 6342–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Báez, J.; Maldonado, A.; Castañeda, L.; Delgado, G.T.; Castanedo-Pérez, R.; Olvera, M.d.l.L. On the Effect of Acetic Acid on Physical Properties of Chemically Sprayed Fluorine-Doped Zno Thin Films. Thin Solid Film. 2007, 515, 8689–8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Chiang, M.-C.; Chen, Y.-W. Temperature Dependence of Fluorine-Doped Tin Oxide Films Produced by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis. Thin Solid Film. 2009, 518, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-Z.; Wang, N.-F.; Tsai, C.-L. Fluorine-Doped Zno Transparent Conducting Thin Films Prepared by Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2010, 518, 4955–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Zhao, J.; Yu, H.; Li, N.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, D.; Liu, W.; Zheng, D.; Gao, X.; Shui, L.; et al. Light Manipulating Electrode Based on High Optical Haze Aluminum-Doped Zinc Oxide for Highly Efficient Indium-Tin-Oxide Free Organic Solar Cells with over 13% Efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 8515–8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Bai, L.; Yang, F.; Han, B.; Guo, Y.; Dai, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X. Management of Light Trapping Capability of Azo Film for Si Thin Film Solar Cells-Via Tailoring Surface Texture. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 179, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, H.; Maldonado, A.; Olvera, M.d.l.L.; Acosta, D.R. Gallium-Doped Zno Thin Films Deposited by Chemical Spray. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2005, 87, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amala Rani, A.; Ernest, S. Structural, Morphological, Optical and Compositional Characterization of Spray Deposited Ga Doped Zno Thin Film for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Application. Superlattices Microstruct. 2014, 75, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moditswe, C.; Muiva, C.M.; Juma, A. Highly Conductive and Transparent Ga-Doped Zno Thin Films Deposited by Chemical Spray Pyrolysis. Optik 2016, 127, 8317–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalisarvestani, M.; Saidur, R.; Mekhilef, S.; Javadi, F.S. Performance, Materials and Coating Technologies of Thermochromic Thin Films on Smart Windows. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2013, 26, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granqvist, C.G. Electrochromics for Smart Windows: Oxide-Based Thin Films and Devices. Thin Solid Film. 2014, 564, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; Choi, D.; Jin, M.J.; Kim, I.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, S.W. Mechanically Powered Transparent Flexible Charge-Generating Nanodevices with Piezoelectric Zno Nanorods. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2185–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Makino, H.; Osone, S.; Ujihara, A.; Ito, T.; Hokari, H.; Maruyama, T.; Yamamoto, T. Development of Ga-Doped Zno Transparent Electrodes for Liquid Crystal Display Panels. Thin Solid Film. 2012, 520, 4131–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuili, M.; El Hallani, G.; Fazouan, N.; El Makarim, H.A.; Atmani, E.H. First-Principles Calculation of (Al,Ga) Co-Doped Zno. Comput. Condens. Matter 2019, 21, e00426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Masis, M.; Rucavado, E.; Monnard, R.; Barraud, L.; Holovsky, J.; Despeisse, M.; Boccard, M.; Ballif, C. Highly Conductive and Broadband Transparent Zr-Doped In2o3 as Front Electrode for Solar Cells. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2018, 8, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.H. Efficient and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells Based on Inorganic Hole Transport Materials. Nanomaterials 2021, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K.; Klein, A.; Rech, B. Transparent Conductive Zinc Oxide: Basics and Applications in Thin Film Solar Cells; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume xiii, 443p. [Google Scholar]
- Ellmer, K. Past Achievements and Future Challenges in the Development of Optically Transparent Electrodes. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, A.; Basak, D. Revisiting the Electrical and Optical Transmission Properties of Co-Doped Zno Thin Films as N-Type Tcos. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 96, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Chiu, L.-C.; Juang, J.-Y. High Haze Ga and Zr Co-Doped Zinc Oxide Transparent Electrodes for Photovoltaic Applications. J. Alloy Compd. 2022, 901, 163678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüpkes, J.; Owen, J.I.; Pust, S.E.; Bunte , E. Chemical Etching of Zinc Oxide for Thin-Film Silicon Solar Cells. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Li, W.; Aberle, A.G.; Venkataraj, S. Investigation of the Thickness Effect on Material and Surface Texturing Properties of Sputtered Zno:Al Films for Thin-Film Si Solar Cell Applications. Vacuum 2016, 123, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-L.; Huang, K.-C.; Yeh, C.-H.; Hung, C.-I.; Houng, M.-P. Investigation of Textured Al-Doped Zno Thin Films Using Chemical Wet-Etching Methods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 127, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-C.; Juang, J.-Y. Facile Preparation of Hazy Ga-Doped Zno Electrodes by Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 580, 152232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, J.Y.; Lin, H.T.; Liang, C.T.; Li, P.R.; Chen, W.K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Pan, K.L. Effect of Ambient Air Flow on Resistivity Uniformity of Transparent Ga-Doped Zno Film Deposited by Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet. J. Alloy Compd. 2018, 766, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P.-H.; Huang, J.-C.; Pan, K.-L.; Juang, J.-Y. Enhancement of Electrical Conductivity of Transparent Ga-Doped Zinc Oxide Films Via Quench Reduction in an Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 12, 034050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, P.C.; Xu, L.; Juang, J.Y. Simultaneous Enhancement of Electrical Conductivity, Uniformity, and near-Infrared Transmittance Via Laser Annealing on Zno:Ga Films Deposited by Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet. J. Alloy Compd. 2021, 857, 157697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-M.; Kuo, Y.-L.; Lin, C.-M.; Lee, S.-F. One-Step Fabrication of Tetragonal Zro2 Particles by Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet. Powder Technol. 2014, 267, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.A.; Mangal, S.; Singh, U.P. Impact of Rapid Thermal Annealing on Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of Dc Sputtered Doped and Co-Doped Zno Thin Film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 288, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, G.; Consonni, V.; Puyoo, E.; Bellet, D. High Performance Zno-Sno2:F Nanocomposite Transparent Electrodes for Energy Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14096–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-T.; Foldyna, M.; Roussel, H.; Consonni, V.; Pernot, E.; Schmidt-Mende, L.; Rapenne, L.; Jiménez, C.; Deschanvres, J.-L.; Muñoz-Rojas, D.; et al. Tuning the Properties of F:Sno2 (Fto) Nanocomposites with S:Tio2 Nanoparticles–Promising Hazy Transparent Electrodes for Photovoltaics Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, D.B.; Powell, M.J.; Parkin, I.P.; Carmalt, C.J. Aluminium/Gallium, Indium/Gallium, and Aluminium/Indium Co-Doped Zno Thin Films Deposited Via Aerosol Assisted Cvd. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seid, E.T.; Dejene, F.B. Gallium and Indium Co-Doping Effects on Structural, Optical and Luminescence Properties of Zno Nanostructures. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Xiu, X.; Pang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Ye, L.; Cheng, C.; Han, S. Structural, Electrical and Optical Properties of Zirconium-Doped Zinc Oxide Films Prepared by Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2008, 516, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, P.; Zou, Z.; Mayr, S.; Diebold, U.; Schmid, M. Using Photoelectron Spectroscopy to Observe Oxygen Spillover to Zirconia. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 17613–17620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
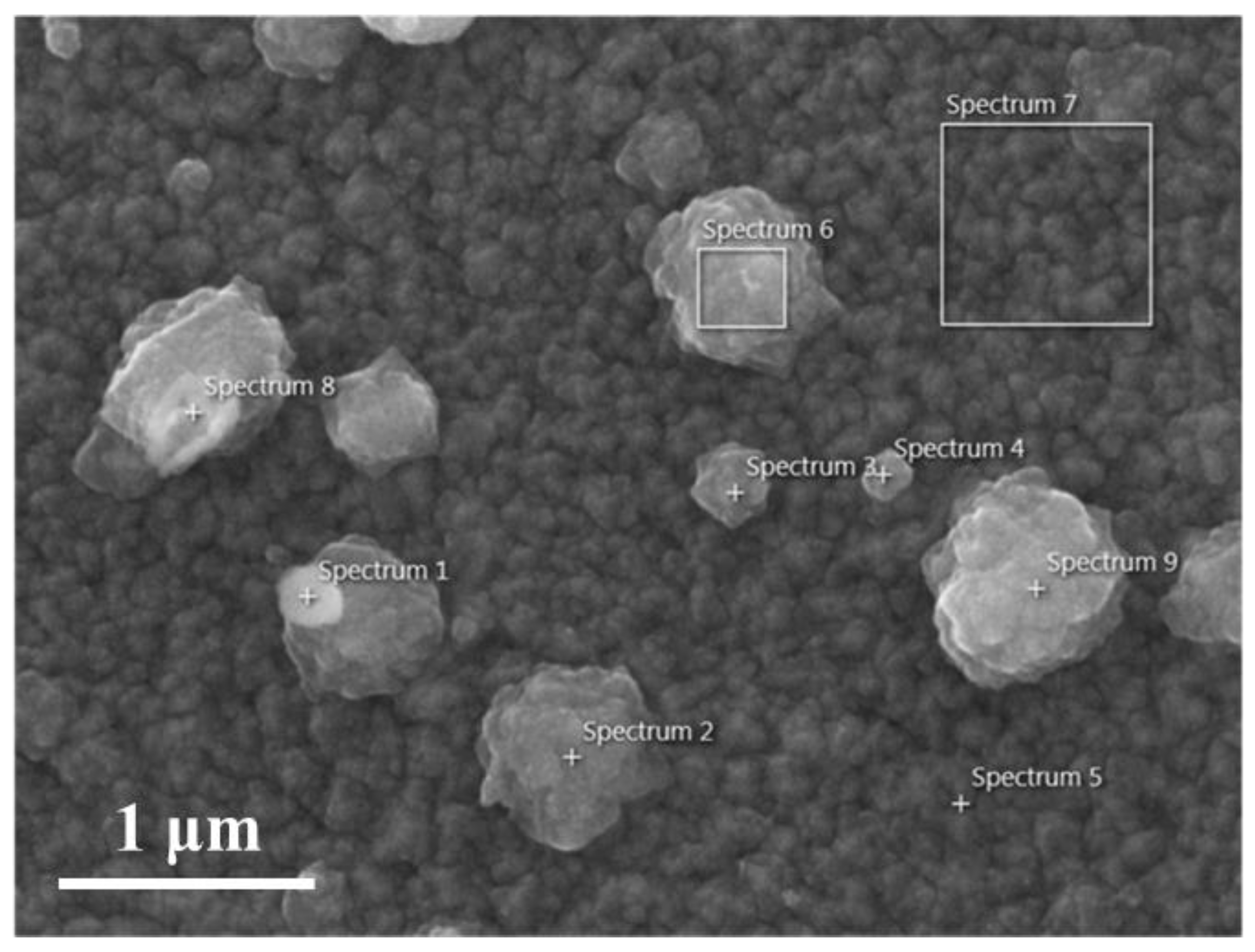


| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O (at%) | 50.4 | 45.2 | 47.8 | 47.2 | 42.4 | 45.6 | 45.6 | 46.1 | 45.4 |
| Zn (at%) | 17.3 | 24.9 | 23.5 | 21.4 | 31.6 | 23.7 | 27.7 | 18.6 | 20.8 |
| Ga (at%) | 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.4 |
| Zr (at%) | 3.6 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 1.3 | N/A | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 0.3 |
| Ga-Ga | Ga/Zn | Ga-O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GZO | 2.4% | 78.3% | 19.3% |
| GZO:Zr (2 at%) | 4.1% | 75.9% | 20.0% |
| GZO:Zr (4 at%) | 3.7% | 75.7% | 20.6% |
| GZO:Zr (6 at%) | 4.9% | 74.7% | 20.4% |
| Zn-O | OV | CO/OH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GZO | 78.2% | 17.4% | 4.3% |
| GZO:Zr (2 at%) | 78.9% | 17.1% | 4.0% |
| GZO:Zr (4 at%) | 79.4% | 18.3% | 2.3% |
| GZO:Zr (6 at%) | 78.9% | 17.8% | 3.3% |
| Zr 3d5/2 (eV) | Zr 3d3/2 (eV) | Area under Zr 3d | Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GZO | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| GZO:Zr (2 at%) | 182.7 | 185.1 | 518.4 | 1 |
| GZO:Zr (4 at%) | 183.1 | 185.5 | 1000.1 | 1.9 |
| GZO:Zr (6 at%) | 183.1 | 185.5 | 1519.3 | 2.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.-T.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chiu, L.-C.; Juang, J.-Y. Analysis of Hazy Ga- and Zr-Co-Doped Zinc Oxide Films Prepared with Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Systems. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192691
Luo Y-T, Zhou Z, Wu C-Y, Chiu L-C, Juang J-Y. Analysis of Hazy Ga- and Zr-Co-Doped Zinc Oxide Films Prepared with Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Systems. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(19):2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192691
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yu-Tang, Zhehan Zhou, Cheng-Yang Wu, Li-Ching Chiu, and Jia-Yang Juang. 2023. "Analysis of Hazy Ga- and Zr-Co-Doped Zinc Oxide Films Prepared with Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Systems" Nanomaterials 13, no. 19: 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192691
APA StyleLuo, Y.-T., Zhou, Z., Wu, C.-Y., Chiu, L.-C., & Juang, J.-Y. (2023). Analysis of Hazy Ga- and Zr-Co-Doped Zinc Oxide Films Prepared with Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet Systems. Nanomaterials, 13(19), 2691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192691








