Hybrid Chitosan–TiO2 Nanocomposite Impregnated in Type A-2186 Maxillofacial Silicone Subjected to Different Accelerated Aging Conditions: An Evaluation of Color Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
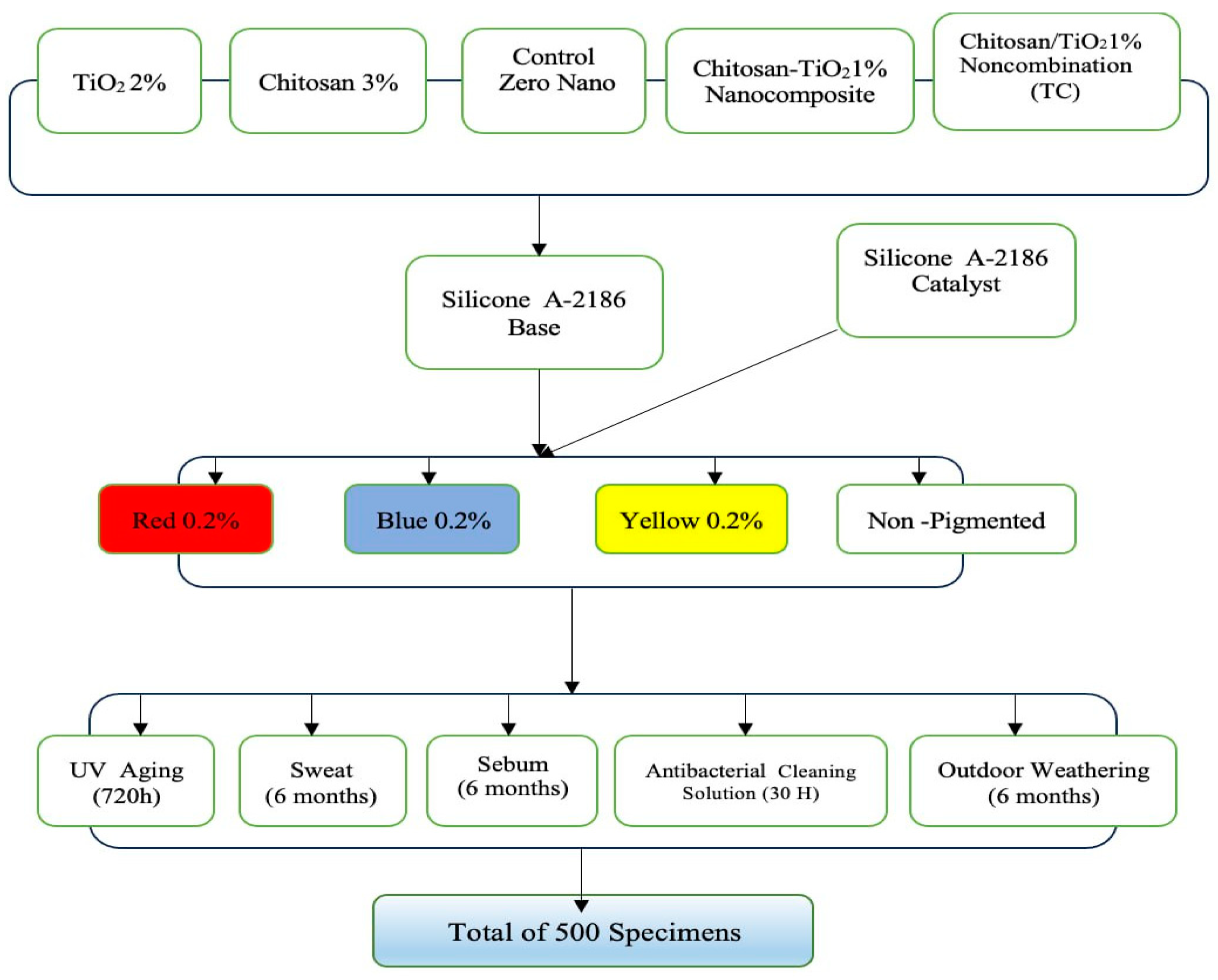
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Pilot Study
2.2.2. Preparation of the Nanocomposite
2.2.3. Preparation of the Control Group Specimens
2.2.4. Preparation of the Experimental Group Specimens
2.2.5. Preparation of the Experimental Group Specimens Reinforced with the Synthesized Chitosan–TiO2 Nanocomposite
2.2.6. Color Stability Test
2.2.7. Conditioning Modes
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Characteristics
3.1.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
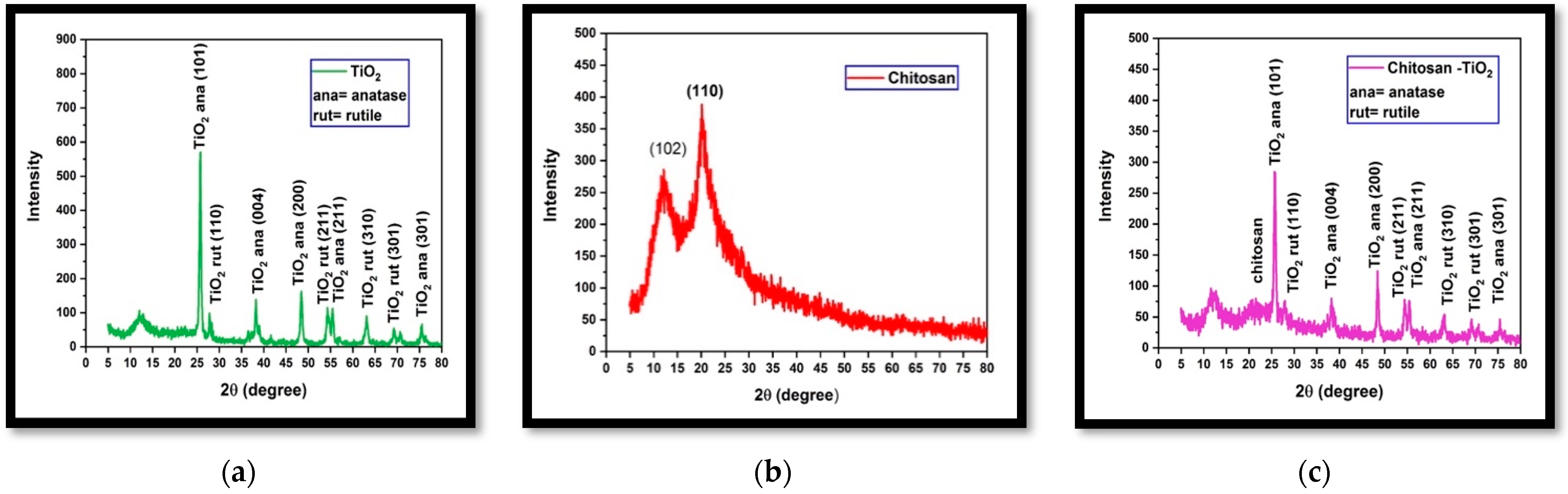
3.1.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
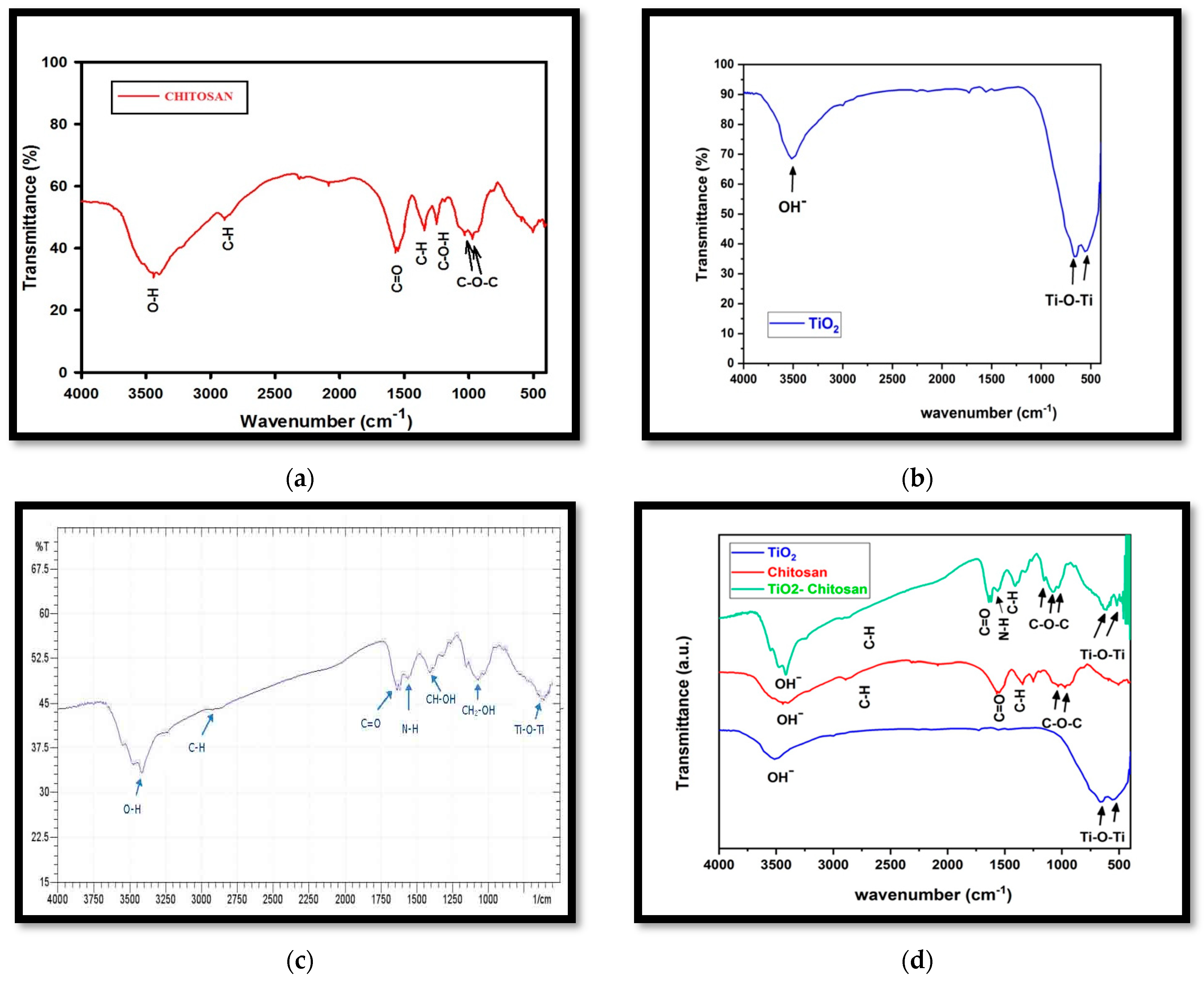
3.1.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
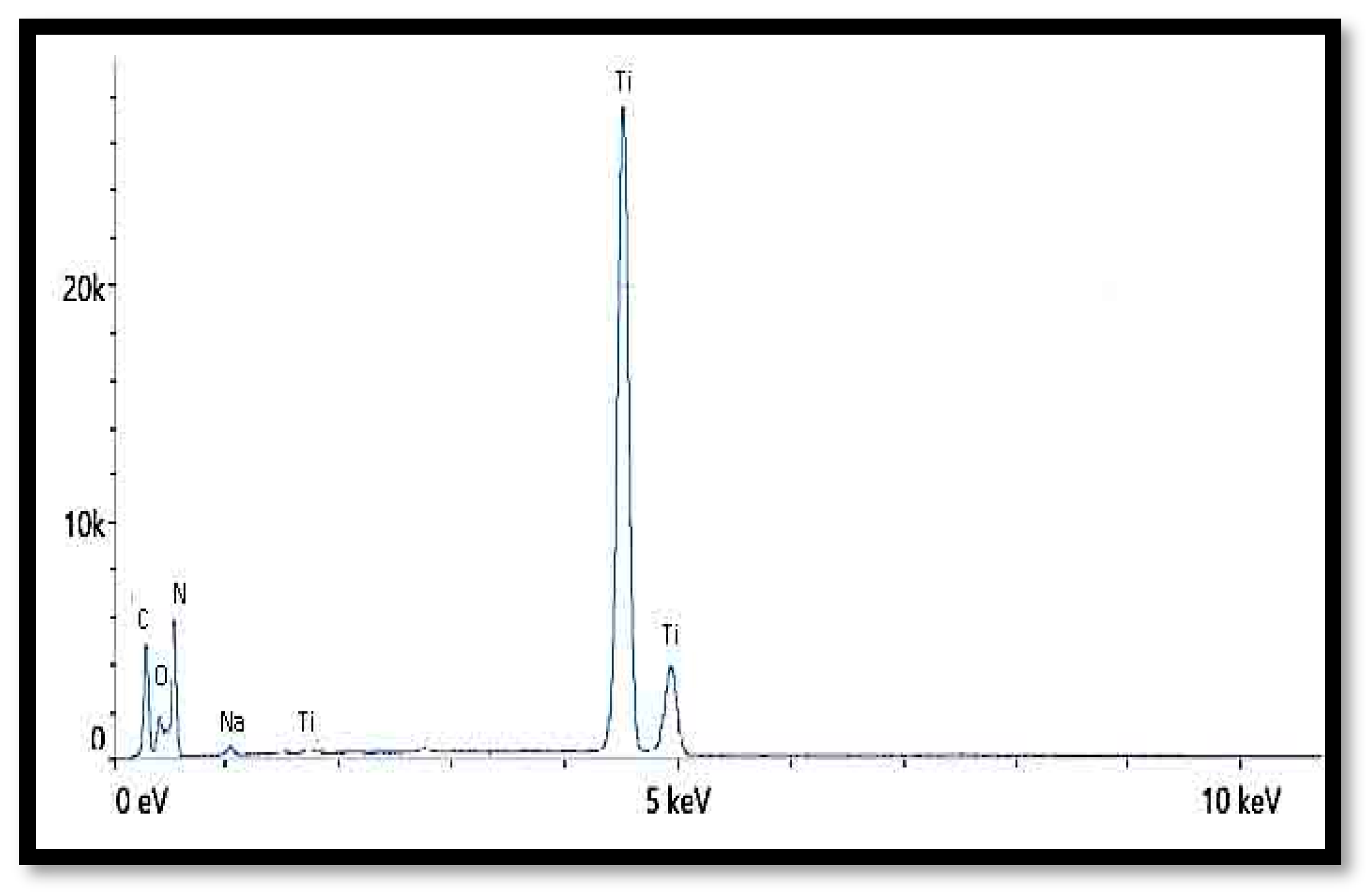
3.1.4. Energy-Dispersive X-ray (EDX)
3.2. Pilot Study
3.3. Color Stability Results
3.3.1. The Red Color
| Groups | Brilliant Red ΔE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% Chitosan–TiO2 | 1% TC | 2% TiO2 | 3% Chitosan | Control (Zero Nanocomposite) | p-Value | |
| Sweat (6 months) | 6.66 ± 3.60 | 6.14 ± 0.38 | 5.45 ± 0.58 | 5.01 ± 2.02 | 5.15 ± 1.43 | 0.561 |
| Antibacterial cleaning solution (30 h) | 3.31 ± 1.67 | 1.35 ± 0.49 c,d | 1.03 ± 0.98 c,d | 4.62 ± 2.39 | 4.66 ± 1.11 | 0.000 |
| Outdoor weather (6 months) | 16.61 ± 6.32 | 21.19 ±1.70 | 19.74 ± 2.95 | 20.87 ± 1.03 | 18.91 ± 9.90 | 0.695 |
| UV weather (1 month 720 h) | 27.93 ± 1.24 a,c | 31.38 ± 0.6 b,c | 27.36 ± 0.71 c | 41.19 ± 2.6 | 40.84 ± 7.15 | 0.000 |
| Sebum (6 months) | 6.24 ± 1.66 d | 7.48 ± 1.66 d | 6.25 ± 2.34 d | 9.26 ± 1.85 d | 14.44 ± 2.36 | 0.000 |
| p-value | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | |
3.3.2. The Blue Color
| Groups | Blue ΔE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% Chitosan-TiO2 | 1% TC a | 2% TiO2 b | 3% Chitosan | Control (Zero Nanocomposite) | p-Value | |
| Sweat (6 months) | 3.49 ± 2.57 | 1.18 ± 0.82 c | 0.96 ± 0.26 c | 3.46 ± 1.02 d | 1.50 ± 0.55 | 0.001 |
| Antibacterial cleaning solution (30 h) | 1.21 ± 0.67 | 1.37 ± 0.93 | 0.74 ± 0.43 c | 2.94 ± 1.39 | 1.32 ± 0.31 | 0.001 |
| Outdoor weather (6 months) | 9.08 ± 1.44 d | 8.92 ± 0.59 d | 10.65 ± 0.25 d,c | 7.73 ± 0.66 d | 5.71 ± 1.57 | 0.000 |
| UV weather 1 month (720 h) | 3.73 ± 0.89 d | 2.67 ± 0.58 | 2.67 ± 0.37 | 3.63 ± 0.93 d | 1.88 ± 0.86 | 0.005 |
| Sebum (6 months) | 4.21 ± 1.79 | 2.84 ± 1.34 c | 3.09 ± 1.36 c | 5.76 ± 2.19 | 4.85 ± 1.26 | 0.018 |
| p-value | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | |
3.3.3. The Yellow Color
| Groups | Yellow ΔE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% Chitosan–TiO2 | 1% TC a | 2% TiO2 | 3% Chitosan | Control (Zero Nanocomposite) | p-Value | |
| Sweat (6 months) | 1.34 ± 0.48 b | 1.69 ± 0.85 b | 0.48 ± 0.23 c,d | 1.5 ± 0.60 | 2.21 ± 1.24 | 0.006 |
| Antibacterial cleaning solution (30 h) | 1.84 ± 0.50 | 1.14 ± 0.35 | 0.86 ± 0.38 | 1.41 ± 0.74 | 1.45 ± 0.78 | 0.103 |
| Outdoor weather (6 months) | 2.61 ± 0.56 | 2.64 ± 0.63 | 2.72 ± 0.74 | 2.72 ± 0.40 | 3.04 ± 0.61 | 0.803 |
| UV weather (1 month; 720 h) | 0.95 ± 0.26 | 0.7 ± 0.26 | 1.02 ± 0.16 | 0.89 ± 0.32 | 1.13 ± 0.43 | 0.267 |
| Sebum (6 months) | 1.07 ± 0.36 | 1.49 ± 0.87 | 1.38 ± 0.50 | 1.32 ± 0.40 | 1.6 ± 1.29 | 0.788 |
| p-value | 0.000 * | 0.002 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.035 * | |
3.3.4. The Non-Pigmented Group
| Groups | Non-Pigmented ΔE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% Chitosan–TiO2 | 1% TC | 2% TiO2 | 3% Chitosan | Control (Zero Nanocomposite) | p-Value | |
| Sweat (6 months) | 1.12 ± 0.41 c | 1.70 ± 0.99 c | 1.26 ± 0.59 c | 7.63 ± 3.5 d | 1.39 ± 0.46 | 0.000 |
| Antibacterial cleaning solution (30 h) | 1.24 ± 0.48 | 1.10 ± 0.37 | 0.76 ± 0.37 | 1.17 ± 0.32 | 0.95 ± 0.39 | 0.294 |
| Outdoor weather (6 months) | 7.77 ± 0.36 a,b,c,d | 3.42 ± 0.45 | 4.11 ± 0.93 | 3.13 ± 1.61 | 4.67 ± 2.54 | 0.000 |
| UV weather (1 month 720 h) | 3.81 ± 0.35 a,b,d | 2.00 ± 0.51 c | 1.8 ± 0.34 c | 5.04 ± 1.21 d | 1.88 ± 0.99 | 0.000 |
| Sebum (6 months) | 4.81 ± 0.92 b | 4.84 ± 0.92 b | 2.55 ± 0.52 d | 5.5 ± 4.28 | 9.02 ± 3.96 | 0.009 |
| p-value | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.014 * | 0.000 * | |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rangel Goulart, D.; Sigua-Rodriguez, E.A.; Alvarez-Pinzón, N.; Rocha Fernandes, A.Ú.; Queiroz, E. Quality of life of patients with facial prosthesis. Rev. Fac. Odontol. 2017, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, P.C.; Kiat-Amnuay, S. Survey of currently used materials for fabrication of extraoral maxillofacial prostheses in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 19, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.H.; Hodges, J.S. Effects of processing parameters on physical properties of the silicone maxillofacial prosthetic materials. Dent. Mater. 1999, 15, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotra, R.; Malhotra, P.; Yadav, B.; Bhardwaj, H.; Yadav, T. Color in Maxillofacial Prosthetics. Indian J. Health Sci. Care 2016, 3, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleni, P.N.; Krokida, M.K.; Polyzois, G.L.; Bisharat, G.I. Color stability of facial silicon prosthetic elastomer after artificial weathering. Dent. Res. J. 2008, 5, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, M. Industrial applications of colour science. Phys. Technol. 1988, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Barman, A.; Farook, T.H.; Jamayet, N.B.; Yhaya, M.F.B.; Alam, M.K. Factors affecting color stability of maxillofacial prosthetic silicone elastomer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Elastomers Plast. 2020, 53, 698–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, M.W.; Mahanna, G.K.; Dick, K.; Jia, W. Color changes in dry-pigmented maxillofacial elastomer resulting from ultraviolet light exposure. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1995, 74, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiat-amnuay, S.; Lemon, J.C.; Powers, J.M. Effect of opacifiers on color stability of pigmented maxillofacial silicone A-2186 subjected to artificial aging. J. Prosthodont. 2002, 11, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, R.N.; Guttal, S.S. Effect of Incorporation of Nano-Oxides on Color Stability of Maxillofacial Silicone Elastomer Subjected to Outdoor Weathering. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 24, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Kiat-amnuay, S.; Powers, J.M.; Zhao, Y. Effect of nano-oxide concentration on the mechanical properties of a maxillofacial silicone elastomer. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 100, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, C.; Powers, J.M.; Kiat-amnuay, S. Color stability of pigmented maxillofacial silicone elastomer: Effects of nano-oxides as opacifiers. J. Dent. 2010, 38 (Suppl. S2), e100–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prameshwari, F.; Karlina, E.; Hasratiningsih, Z. Synthesis of Ca-Psz nanoparticles using sol-gel technique with chitosan as a dispersant for raw materials restoration and dental rehabilitation equipment. Padjadjaran J. Dent. 2013, 25, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, T.; Pisulkar, S.; Kambala, S. Evaluation of antifungal effect of maxillofacial silicone after incorporation of chitosan nanoparticles: Evidence in pharmaceutical therapeutics. J. Datta Meghe Inst. Med. Sci. Univ. 2020, 15, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya-Esparza, L.M.; Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M.; Maytorena-Verdugo, C.I.; González-Silva, N.; Romero-Toledo, R.; Aguilera-Aguirre, S.; Pérez-Larios, A.; Montalvo-González, E. Chitosan-TiO2: A Versatile Hybrid Composite. Materials 2020, 13, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, M.; Dodero, A.; Scarfi, S.; Mirata, S.; Pozzolini, M.; Tassara, E.; Sionkowska, A.; Adamiak, K.; Alloisio, M.; Vicini, S. Chitosan&Collagen Electrospun Nanofibers Loaded with Curcumin as Wound-Healing Patches. Polymers 2023, 15, 2931. [Google Scholar]
- Sonnahalli, N.K.; Chowdhary, R. Effect of nanoparticles on color stability and mechanical and biological properties of maxillofacial silicone elastomer: A systematic review. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2020, 20, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.H.J.; Al-Judy, H.J. Mechanical properties of chitosan incorporated in maxillofacial silicone and its anti candidal activity in vitro. J. Res. Med. Dent. Sci. 2018, 6, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, K.; Sarkar, S.; Jagajjanani Rao, K.; Paria, S. Core/shell nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 8–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, D.S.; Sethuraman, R. Comparative evaluation of tensile strength, tear strength, color stability and hardness of conventional and 1% trisnorbornenylisobutyl polyhedralsilsesquioxane modified room temperature vulcanizing maxillofacial silicone after a six month artificial aging period. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2022, 22, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, M.M.; Polyzois, G.L.; Nuseir, A.; Hatamleh, K.; Alnazzawi, A. Mechanical Properties and Simulated Aging of Silicone Maxillofacial Elastomers: Advancements in the Past 45 Years. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 25, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Saratchandran, S. Comparative Evaluation of Color Stability of Maxillofacial Silicones Following Accelerated Aging Conditions. Face 2022, 3, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, M.M.; Polyzois, G.L.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Effect of extraoral aging conditions on mechanical properties of maxillofacial silicone elastomer. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 20, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, D.M.; Goiato, M.C.; Moreno, A.; Pesqueira, A.A.; Haddad, M.F. Influence of pigments and opacifiers on color stability of an artificially aged facial silicone. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 20, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, T.; Kheur, M.; Coward, T.; Patel, N. Change in color of a maxillofacial prosthetic silicone elastomer, following investment in molds of different materials. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2015, 15, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzois, G.L. Color stability of facial silicone prosthetic polymers after outdoor weathering. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 82, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, D.; Goiato, M.; Dekon, S.; Gennari-Filho, H. Visual evaluation of color stability after accelerated aging of pigmented and nonpigmented silicones to be used in facial prostheses. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2009, 20, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiat-amnuay, S.; Johnston, D.A.; Powers, J.M.; Jacob, R.F. Color stability of dry earth pigmented maxillofacial silicone A-2186 subjected to microwave energy exposure. J. Prosthodont. 2005, 14, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamaria, A.; Aras, M.A.; Chitre, V.; Rajagopal, P. Effect of Chemical Disinfectants on the Color Stability of Maxillofacial Silicones: An In Vitro Study. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, e869–e872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, H.E.; Ahmad, M.A.; Moustafa, N.A. Evaluation of intrinsic color stability of Facial silicone elastomer reinforced with Different nanoparticles. Alex. Dent. J. 2016, 41, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalqadir, M.; Faraj, S.; Azhdar, B. An evaluation of a technique to improve the mechanical properties of maxillofacial silicone elastomers with zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 128, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, M.W.; Mahanna, G.K.; Jia, W. Ultraviolet radiation-induced color shifts occurring in oil-pigmented maxillofacial elastomers. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 82, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiat-Amnuay, S.; Mekayarajjananonth, T.; Powers, J.M.; Chambers, M.S.; Lemon, J.C. Interactions of pigments and opacifiers on color stability of MDX4-4210/type A maxillofacial elastomers subjected to artificial aging. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2006, 95, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiat-amnuay, S.; Beerbower, M.; Powers, J.M.; Paravina, R.D. Influence of pigments and opacifiers on color stability of silicone maxillofacial elastomer. J. Dent. 2009, 37 (Suppl. S1), e45–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantola, R.; Lassila, L.V.; Tolvanen, M.; Valittu, P.K. Color stability of thermochromic pigment in maxillofacial silicone. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2013, 5, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kheur, M.G.; Kakade, D.; Trevor, C.J.; Lakha, T.A.; Sethi, T. Effect of newly developed pigments and ultraviolet absorbers on the color change of pigmented silicone elastomer. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2017, 17, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, P.; Yildirim-Bicer, A.Z. Effect of different types of disinfection solution and aging on the hardness and colour stability of maxillofacial silicone elastomers. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldorai, Y.; Shim, J.-J. Novel chitosan-TiO2 nanohybrid: Preparation, characterization, antibacterial, and photocatalytic properties. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, A.; Sherriff, M.; Coward, T. Color stability of nonpigmented and pigmented maxillofacial silicone elastomer exposed to 3 different environments. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, M.M.; Watts, D.C. Effect of extraoral aging conditions on color stability of maxillofacial silicone elastomer. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 19, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzois, G.L.; Tarantili, P.A.; Frangou, M.J.; Andreopoulos, A.G. Physical properties of a silicone prosthetic elastomer stored in simulated skin secretions. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2000, 83, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefaniak, A.B.; Harvey, C.J. Dissolution of materials in artificial skin surface film liquids. Toxicol. Vitro 2006, 20, 1265–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 105-E04:1996; Textiles–Tests for Color Fastness. Part E04: Color Fastness to Perspiration. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- ASTM G7-97; Standard Practice for Atmospheric Environmental Exposure Testing of Nonmetallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1997.
- Al-Harbi, F.A.; Ayad, N.M.; Saber, M.A.; ArRejaie, A.S.; Morgano, S.M. Mechanical behavior and color change of facial prosthetic elastomers after outdoor weathering in a hot and humid climate. J Prosthet Dent 2015, 113, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, M.G.; Ganji, K.K.; Aldajani, A.M.; Sonune, S. Colour Stability of Two Commercially Available Maxillofacial Prosthetic Elastomers after Outdoor Weathering in Al Jouf Province. Materials 2023, 16, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotprasert, N.; Shrestha, B.; Sipiyaruk, K. Effects of Disinfection Methods on the Color Stability of Precolored and Hand-Colored Maxillofacial Silicone: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Biomater. 2022, 2022, 7744744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, M.A.; Mari, M.; Munoz-Espi, R. Synthetic Strategies in the Preparation of Polymer/Inorganic Hybrid Nanoparticles. Materials 2014, 7, 4057–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, D.M.; Goiato, M.C.; Sinhoreti, M.A.; Fernandes, A.U.; Ribeiro Pdo, P.; Dekon, S.F. Color stability of polymers for facial prosthesis. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2010, 21, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishal, A.K.; Wee, A.G.; Barao, V.A.R.; Yuan, J.C.; Landers, R.; Sukotjo, C.; Takoudis, C.G. Color stability of maxillofacial prosthetic silicone functionalized with oxide nanocoating. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangera, B.S.; Guttal, S.S. Evaluation of varying concentrations of nano-oxides as ultraviolet protective agents when incorporated in maxillofacial silicones: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrega Malavazi, E.; Dos Santos, D.M.; de Moraes Melo Neto, C.L.; Pereira de Caxias, F.; Freitas da Silva, E.V.; Bannwart, L.C.; Pesqueira, A.A.; de Melo Moreno, A.L.; de Magalhaes Bertoz, A.P.; Goiato, M.C. Influence of Different Pigmentations and Accelerated Aging on the Hardness and Tear Strength of the A-2186 and MDX4-4210 Silicones. Int. J. Dent. 2020, 2020, 8492091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, S.P.; Moore, B.K.; Andres, C.J. Color stability and colorant effect on maxillofacial elastomers. Part II: Weathering effect on physical properties. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Date (2022) | Temperature °C | Average Humidity % | Pressure (mbar) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Average | |||
| February | 15.2 | 5.4 | 10.3 | 64.0 | 917.4 |
| March | 15.3 | 6.4 | 10.8 | 59.6 | 915.9 |
| April | 26.2 | 14.6 | 20.4 | 43.5 | 914.5 |
| May | 28.2 | 17.3 | 22.8 | 41.8 | 913.2 |
| June | 37.4 | 24.6 | 31.0 | 28.3 | 910.1 |
| July | 40.7 | 26.8 | 33.7 | 24.2 | 906.4 |
| August | 42.1 | 28.0 | 35.0 | 23.9 | 908.5 |
| Element | Weight % | Atomic % |
|---|---|---|
| C | 12.9 | 22.0 |
| N | 3.7 | 5.4 |
| O | 42.9 | 54.8 |
| Na | 1.3 | 1.1 |
| Si | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Ti | 38.8 | 16.5 |
| Groups | Brilliant Red ΔE (Pilot Study) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% Chitosan–TiO2 | 1.5% Chitosan–TiO2 | 0.5% Chitosan–TiO2 | p-Value | |
| Sweat (6 months) | 6.66 ± 3.60 | 5.20± 0.36 | 4.12± 0.87 | 0.305 |
| Antibacterial cleaning solution (30 h) | 3.31 ± 1.67 | 2.99 ± 2.02 | 1.28 ± 0.64 | 0.179 |
| Outdoor weather (6 months) | 16.62 ± 6.32 b | 17.59 ± 1.68 b | 24.64 ± 0.68 | 0.035 |
| UV weather (1 month; 720 h) | 27.92 ± 1.24 | 26.45 ± 1.11 | 25.61 ± 2.64 | 0.162 |
| Sebum (6 months) | 6.24 ± 1.66 a,b | 10.09 ± 2.96 | 11.14 ± 0.92 | 0.01 |
| p-value | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Kadi, F.K.; Abdulkareem, J.F.; Azhdar, B.A. Hybrid Chitosan–TiO2 Nanocomposite Impregnated in Type A-2186 Maxillofacial Silicone Subjected to Different Accelerated Aging Conditions: An Evaluation of Color Stability. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162379
Al-Kadi FK, Abdulkareem JF, Azhdar BA. Hybrid Chitosan–TiO2 Nanocomposite Impregnated in Type A-2186 Maxillofacial Silicone Subjected to Different Accelerated Aging Conditions: An Evaluation of Color Stability. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(16):2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162379
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Kadi, Faten K., Jwan F. Abdulkareem, and Bruska A. Azhdar. 2023. "Hybrid Chitosan–TiO2 Nanocomposite Impregnated in Type A-2186 Maxillofacial Silicone Subjected to Different Accelerated Aging Conditions: An Evaluation of Color Stability" Nanomaterials 13, no. 16: 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162379
APA StyleAl-Kadi, F. K., Abdulkareem, J. F., & Azhdar, B. A. (2023). Hybrid Chitosan–TiO2 Nanocomposite Impregnated in Type A-2186 Maxillofacial Silicone Subjected to Different Accelerated Aging Conditions: An Evaluation of Color Stability. Nanomaterials, 13(16), 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162379








