Fabrication of PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibers Reinforced with ZnO Nanoparticles and In Vitro Degradation Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization Techniques
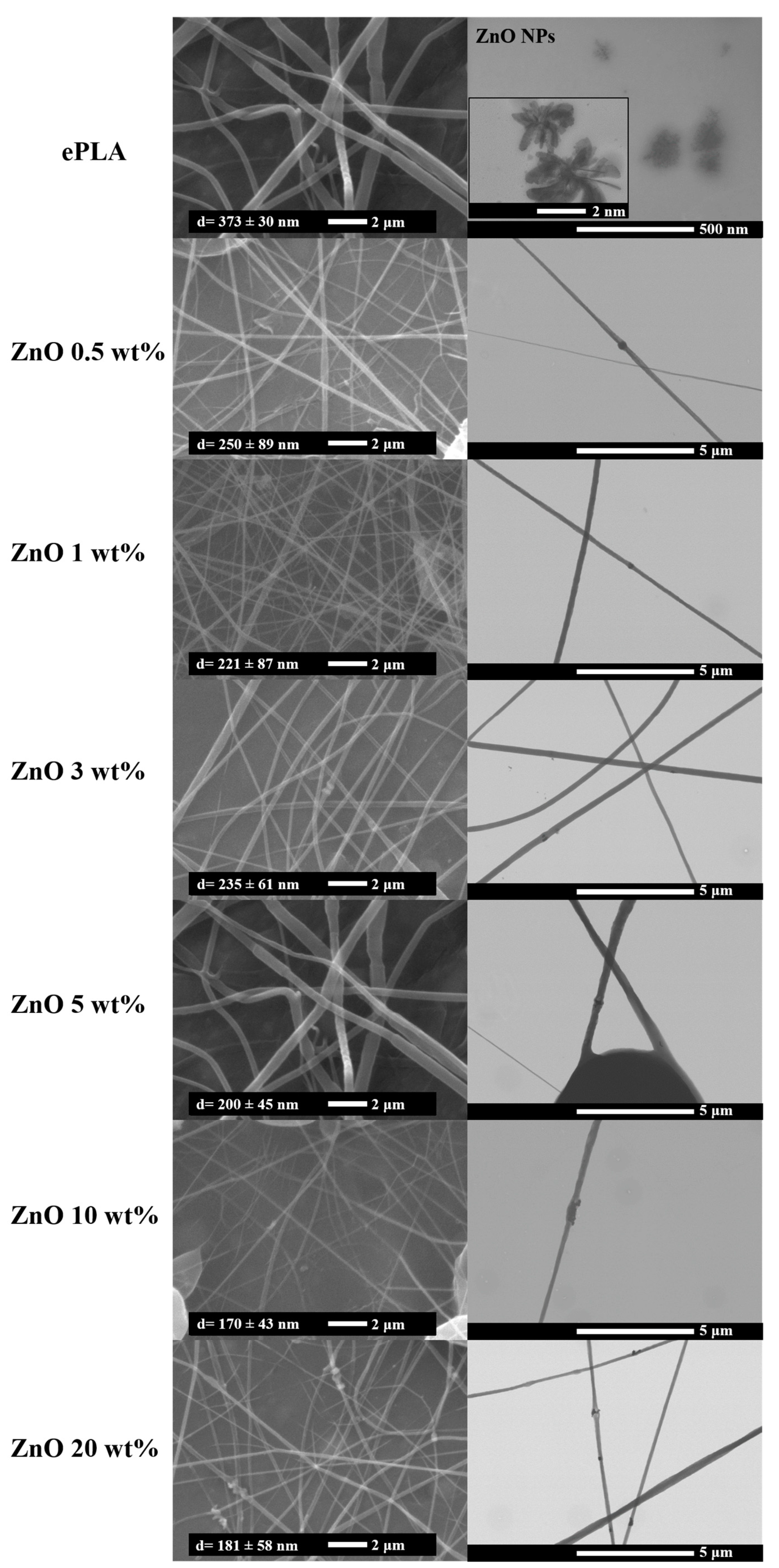
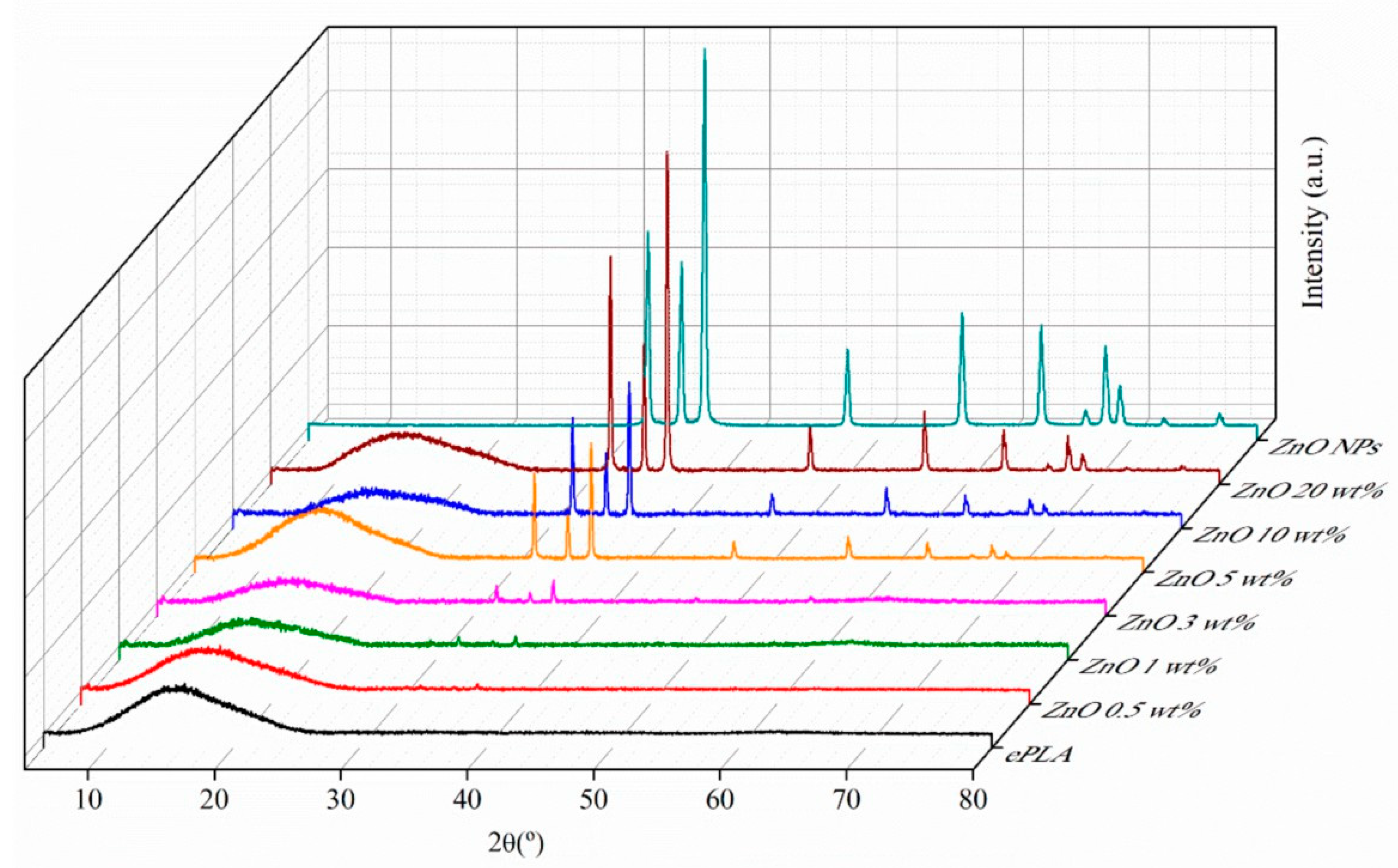
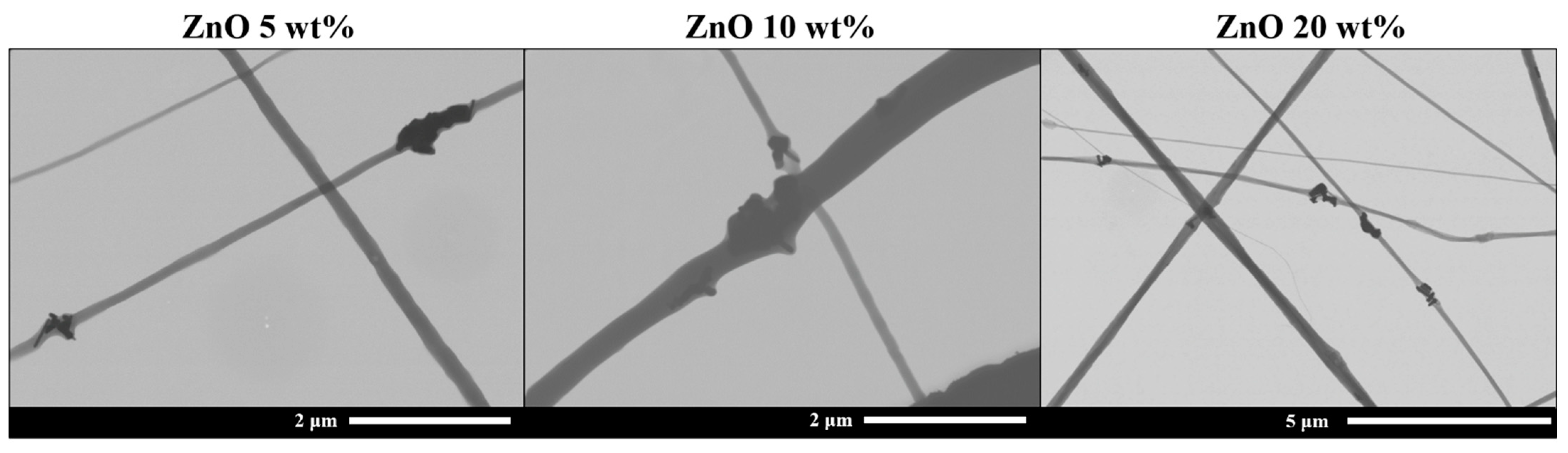
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ang, B.C.; Andriyana, A.; Afifi, A.M. A review on fabrication of nanofibers via electrospinning and their applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Cornejo-Bravo, J.M.; Vera-Graziano, R.; Grande, D. Electrospinning as a powerful technique for biomedical applications: A critically selected survey. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Lu, S.; Cai, R.; Tan, W. Multifunctional Shape Memory Films for a Flexible Electrical Sensor. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gough, C.R.; Deng, Q.; Gu, Z.; Wang, F.; Hu, X. Recent advances in electrospun sustainable composites for biomedical, environmental, energy, and packaging applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, R.S.; Bachu, R.D.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Bhaduri, S. Biomedical applications of electrospun nanofibers: Drug and nanoparticle delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriello, M.; Afsari, M.; Shon, H.K.; Tijing, L.D. Progress on the fabrication and application of electrospun nanofiber composites. Membranes 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taib, N.A.A.B.; Rahman, M.R.; Huda, D.; Kuok, K.K.; Hamdan, S.; Bakri, M.K.B.; Julaihi, M.R.M.B.; Khan, A. A Review on Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) as a Biodegradable Polymer; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 80, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Saniei, H.; Mousavi, S. Surface modification of PLA 3D-printed implants by electrospinning with enhanced bioactivity and cell affinity. Polymer 2020, 196, 122467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardhono, E.Y.; Kanani, N.; Alfirano; Rahmayetty. Development of polylactic acid (PLA) bio-composite films reinforced with bacterial cellulose nanocrystals (BCNC) without any surface modification. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Shah, S.R.; Walker, J.L.; Mikos, A.G. Poly(lactic acid) nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, V.; Khan, S.; Tabada, A. Applications of PLA in modern medicine. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrández-Montero, A.; Lieblich, M.; González-Carrasco, J.L.; Benavente, R.; Lorenzo, V.; Detsch, R.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Ferrari, B. Development of biocompatible and fully bioabsorbable PLA/Mg films for tissue regeneration applications. Acta Biomater. 2019, 98, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peponi, L.; Puglia, D.; Torre, L.; Valentini, L.; Kenny, J.M. Processing of nanostructured polymers and advanced polymeric based nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 85, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonés, A.; Peponi, L.; Fiori, S.; Lieblich, M. Effect of the Addition of MgO Nanoparticles on the Thermally-Activated Shape Memory Behavior of Plasticized PLA Electrospun Fibers. Polymers 2022, 14, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazibt, N.; Kaci, M.; Dehouche, N.; Ragoubi, M. Effect of Filler Content on the Morphology and Physical Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid)-Hydroxyapatite Composites. Materials 2023, 16, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.R.; Yu, J.; Choi, S.J. Fate determination of ZnO in commercial foods and human intestinal cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Jakaj, G.; Lin, H. Polymeric Membranes Incorporated With ZnO Nanoparticles for Membrane Fouling Mitigation: A Brief Review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrone, E.; Araneo, R.; Notargiacomo, A.; Pea, M.; Rinaldi, A. ZnO nanostructures and electrospun ZnO–polymeric hybrid nanomaterials in biomedical, health, and sustainability applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Synthesis, characterization, electrical and sensing properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2010, 21, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Malik, H.N.; Singhal, D.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Malakar, D.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Electrospun polycaprolactone/ZnO nanocomposite membranes as biomaterials with antibacterial and cell adhesion properties. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorov, E.; Luna-Bárcenas, G.; Limón, J.M.Y.; Sánchez, A.G.; Kovalenko, Y. Chitosan-zno nanocomposites assessed by dielectric, mechanical, and piezoelectric properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, K.; Koutsos, V.; Cheung, R.; Mastropaolo, E. PDMS-ZnO piezoelectric nanocomposites for pressure sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonato, R.C.; Mei, L.H.I.; Bonse, B.C.; Leal, C.V.; Levy, C.E.; Oliveira, F.A.; Delarmelina, C.; Duarte, M.C.T.; Morales, A.R. Nanocomposites of PLA/ZnO nanofibers for medical applications: Antimicrobial effect, thermal, and mechanical behavior under cyclic stress. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharova, D.A.; Bolbasov, E.N.; Nemoykina, A.L.; Aljulaih, A.A.; Tverdokhlebova, T.S.; Kulinich, S.A.; Svetlichnyi, V.A. Structure and properties of biodegradable PLLA/ZnO composite membrane produced via electrospinning. Materials 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tobías, H.; Morales, G.; Grande, D. Improvement of mechanical properties and antibacterial activity of electrospun poly(D,L-lactide)-based mats by incorporation of ZnO-graft-poly(D,L-lactide) nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 182, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsah, A.H.; Cartmell, S.H.; Richardson, S.M.; Bosworth, L.A. Material Characterization of PCL: PLLA Electrospun Fibers Following Six Months Degradation In Vitro. Polymers 2020, 12, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque-Monrós, M.C.; Vidaurre, A.; Gil-Santos, L.; Gironés Bernabé, S.; Monleón-Pradas, M.; Más-Estellés, J. Study of the degradation of a new PLA braided biomaterial in buffer phosphate saline, basic and acid media, intended for the regeneration of tendons and ligaments. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Dolan, K.; Soto-Valdez, H.; Selke, S. Effect of nanoparticles on the hydrolytic degradation of PLA-nanocomposites by water-ethanol solutions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 146, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri, S.E.; Mousavi, S.R.; Khakestani, M.; Mozaffari, S.; Ajami, N.; Khonakdar, H.A. Electrospun nanofibers of poly (lactic acid)/poly (ε-caprolactone) blend for the controlled release of levetiracetam. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 4070–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lan, W.; Ji, T.; Sameen, D.E.; Ahmed, S.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y. Development of polylactic acid/ZnO composite membranes prepared by ultrasonication and electrospinning for food packaging. Lwt 2021, 135, 110072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, S.; Liu, G.; Cheng, W.; Han, G.; Bai, L. Electrospun Poly(lactic acid)-Based Fibrous Nanocomposite Reinforced by Cellulose Nanocrystals: Impact of Fiber Uniaxial Alignment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarani, E.; Pušnik Črešnar, K.; Zemljič, L.F.; Chrissafis, K.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Lambropoulou, D.; Zamboulis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Terzopoulou, Z. Cold crystallization kinetics and thermal degradation of pla composites with metal oxide nanofillers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, L.; Cao, Y.; Lan, T.; Chen, H.; Qin, Y. Effects of PLA film incorporated with ZnO nanoparticle on the quality attributes of fresh-cut apple. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, T.S.; Vshivkov, S.A. Effect of Fe nanoparticles on the structure and optical properties of polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite films. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 519, 119452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Wang, L.F.; Rhim, J.W. Incorporation of zinc oxide nanoparticles improved the mechanical, water vapor barrier, UV-light barrier, and antibacterial properties of PLA-based nanocomposite films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, M.; Doumbia, A.; Bonnaud, L.; Dechief, A.L.; Paint, Y.; Ferreira, M.; Campagne, C.; Devaux, E.; Dubois, P. High-performance polylactide/ZnO nanocomposites designed for films and fibers with special end-use properties. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalwa, K.; Thakur, A.; Sharma, N. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and its application in adsorption. Adv. Mater. Proc. 2021, 2, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Peng, W.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. Effects of Size and Aggregation/Agglomeration of Nanoparticles on the Interfacial/Interphase Properties and Tensile Strength of Polymer Nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, E.; Cocchi, D.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Brugo, T.M.; Giorgini, L.; Zucchelli, A. How Nanofibers Carry the Load: Toward a Universal and Reliable Approach for Tensile Testing of Polymeric Nanofibrous Membranes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, D.A.; Piñones, N.; Saavedra, M.; Loyo, C.; Palza, H.; Peponi, L.; Leonés, A.; Baier, R.V.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Grünelwald, A.; et al. Fabrication and assessment of bifunctional electrospun poly(L-lactic acid) scaffolds with bioglass and zinc oxide nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitole, A.A.; Raut, P.W.; Sharma, N.; Giram, P.; Khandwekar, A.P.; Garnaik, B. Electrospun polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite/ZnO nanofibers as potential biomaterials for bone tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaris, V.; López, D.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. Hydrolytic Degradation and Bioactivity of Electrospun PCL-Mg-NPs Fibrous Mats. Molecules 2023, 28, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Viswanathan, K.; Kasi, G.; Sadeghi, K.; Thanakkasaranee, S.; Seo, J. Poly (Lactic Acid)/ZnO Bionanocomposite Films with Positively Charged ZnO as Potential Antimicrobial Food Packaging Materials. Polymers 2019, 11, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaba, N.F.; Jaafar, M. A review on degradation mechanisms of polylactic acid: Hydrolytic, photodegradative, microbial, and enzymatic degradation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2061–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the in vitro degradation of electrospun polycaprolactone membranes in simulated body fluid. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2016, 65, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalkarim, S.Y.H.; Yu, H.Y.; Song, M.L.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Ni, Q.Q. In vitro degradation and possible hydrolytic mechanism of PHBV nanocomposites by incorporating cellulose nanocrystal-ZnO nanohybrids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, R.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, X. Fabrication of Al2O3-NaCl composite heat storage materials by one-step synthesis method. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2016, 31, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, A.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R.; Tayebi, L.; Mostafavi, E. Polylactic acid piezo-biopolymers: Chemistry, structural evolution, fabrication methods, and tissue engineering applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawy, M.A.; Kim, K.H.; Park, J.W.; Deep, A. Hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid (PLA) and its composites. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.A.; Galceran, J.; Rey-Castro, C.; Puy, J.; Companys, E.; Salvador, J.; Monné, J.; Wallace, R.; Vakourov, A. Dissolution kinetics and solubility of ZnO nanoparticles followed by AGNES. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 11758–11767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonés, A.; Salaris, V.; Ramos Aranda, I.; Lieblich, M.; López, D.; Peponi, L. Thermal Properties and In Vitro Biodegradation of PLA-Mg Filaments for Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers 2023, 15, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
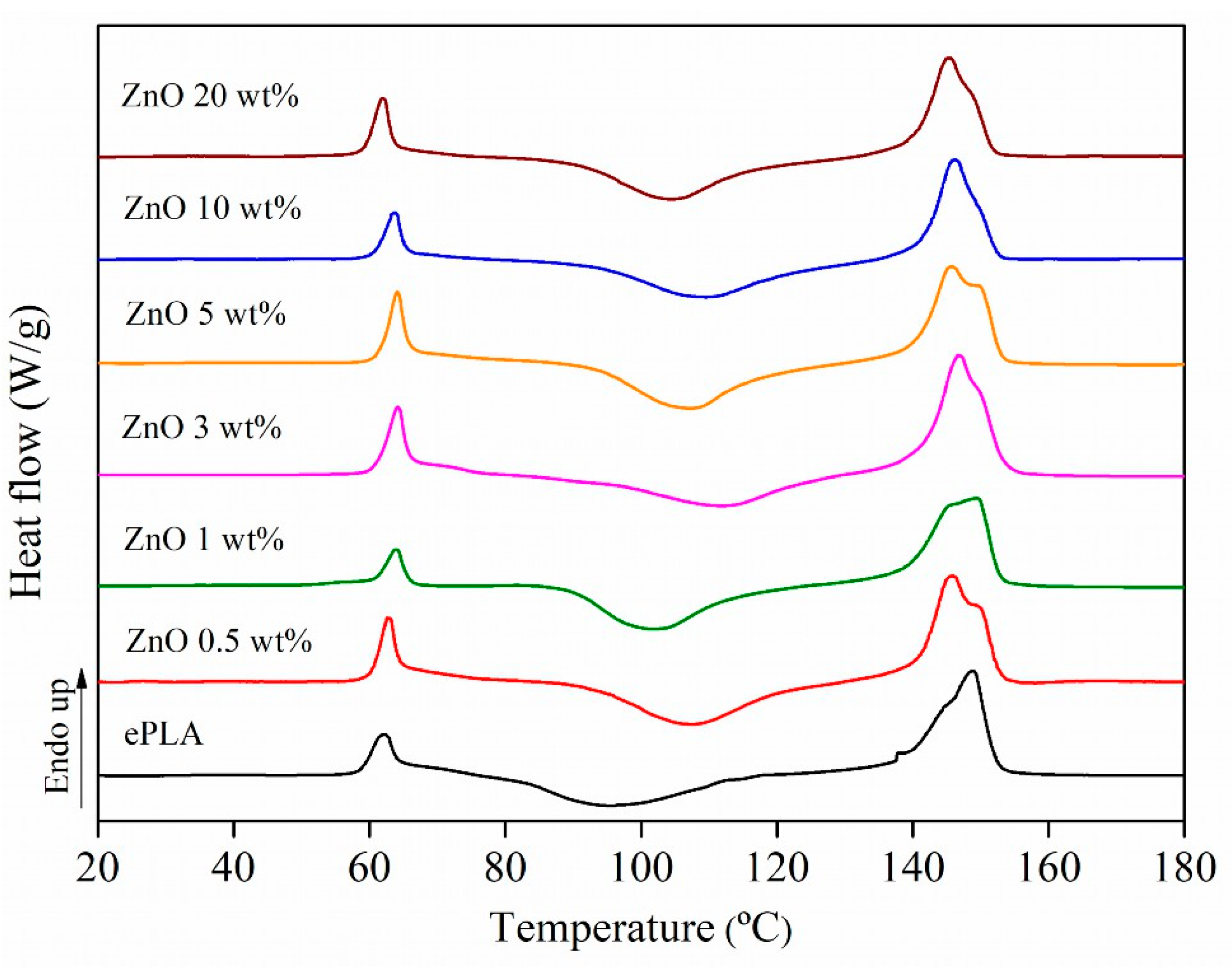

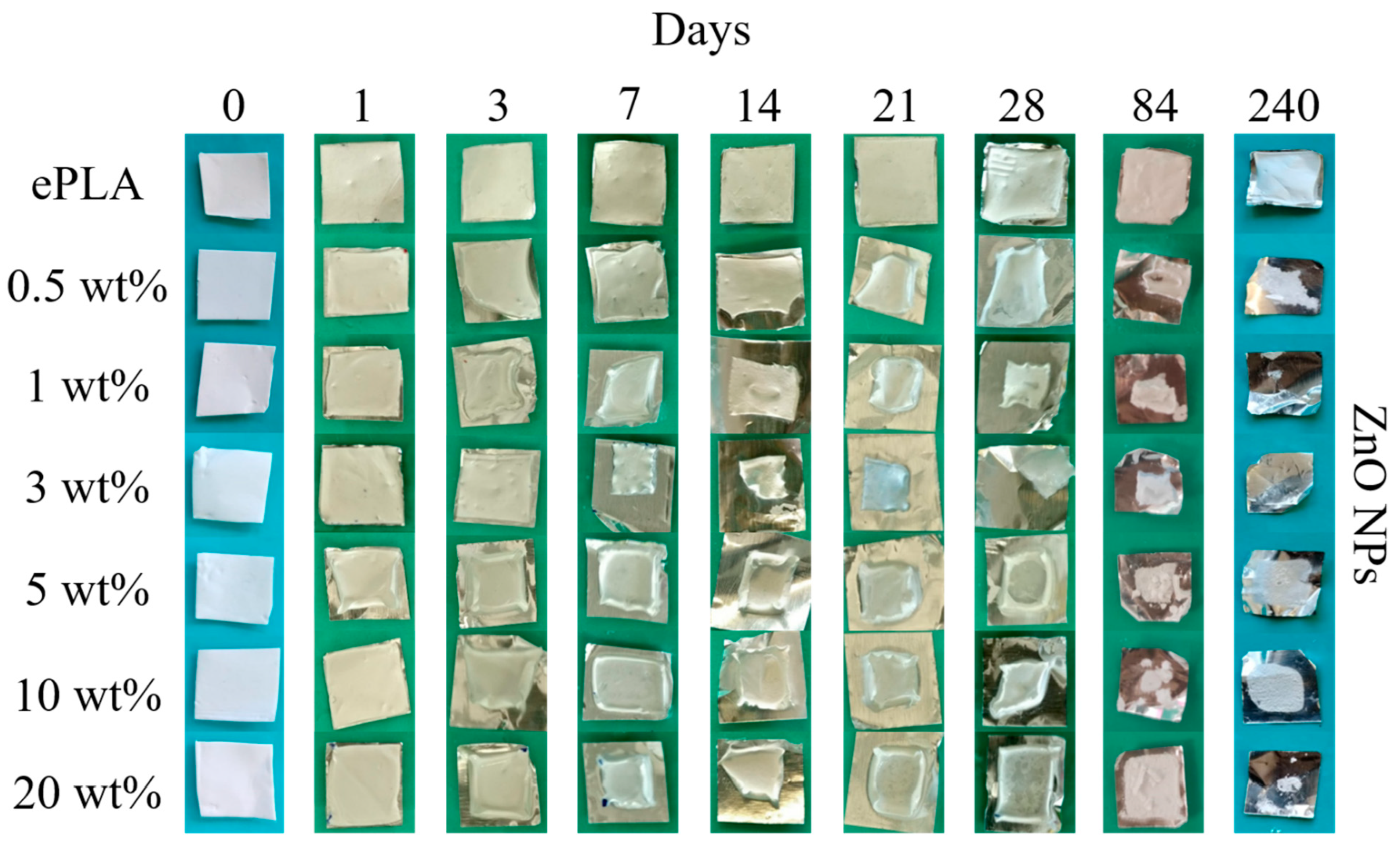


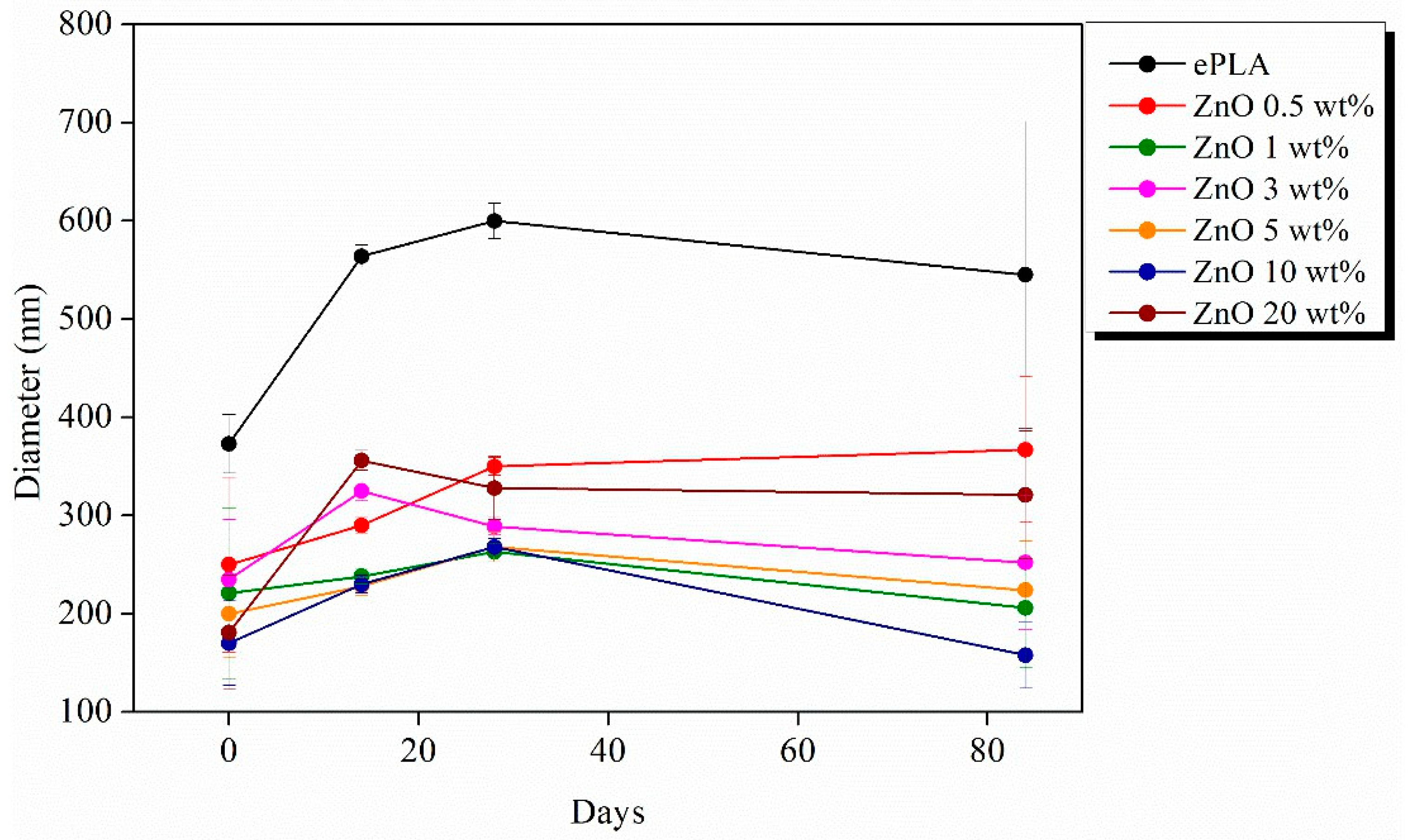
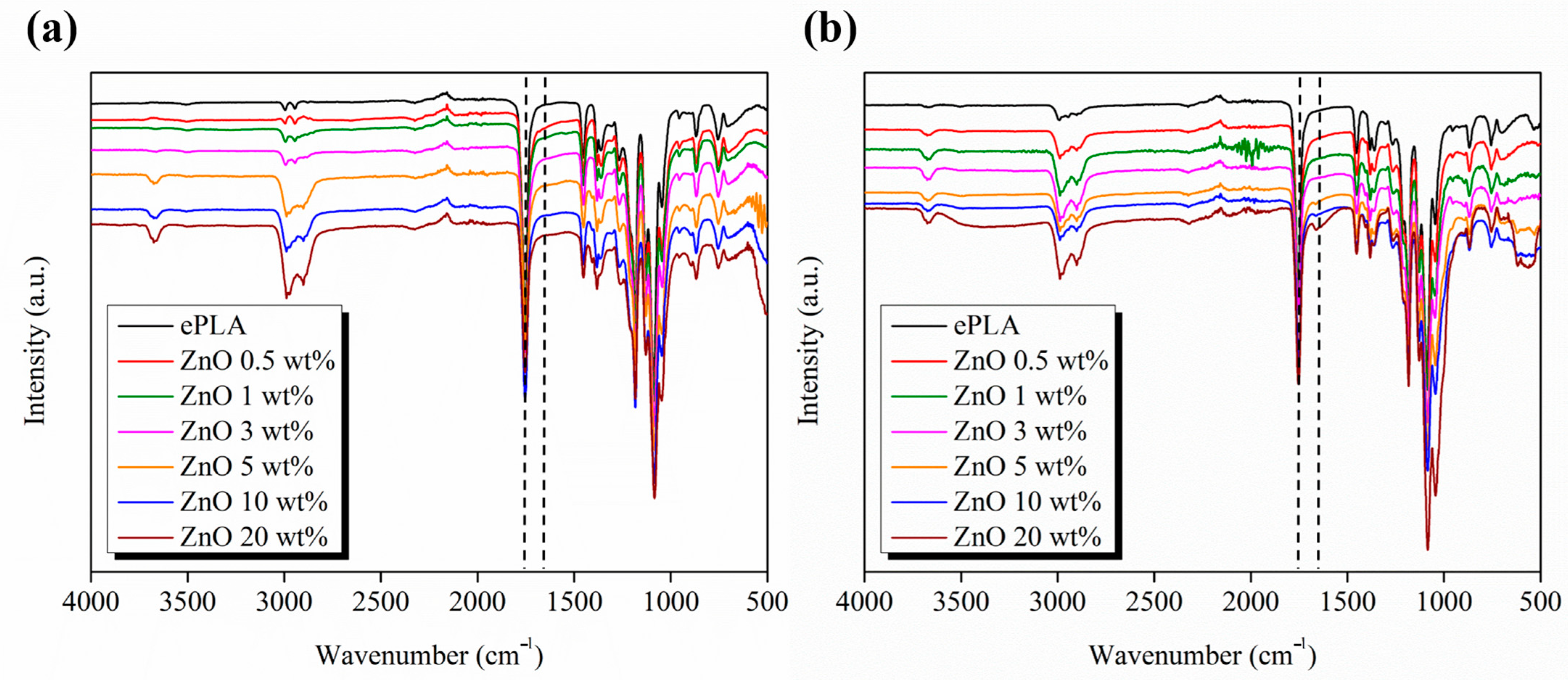
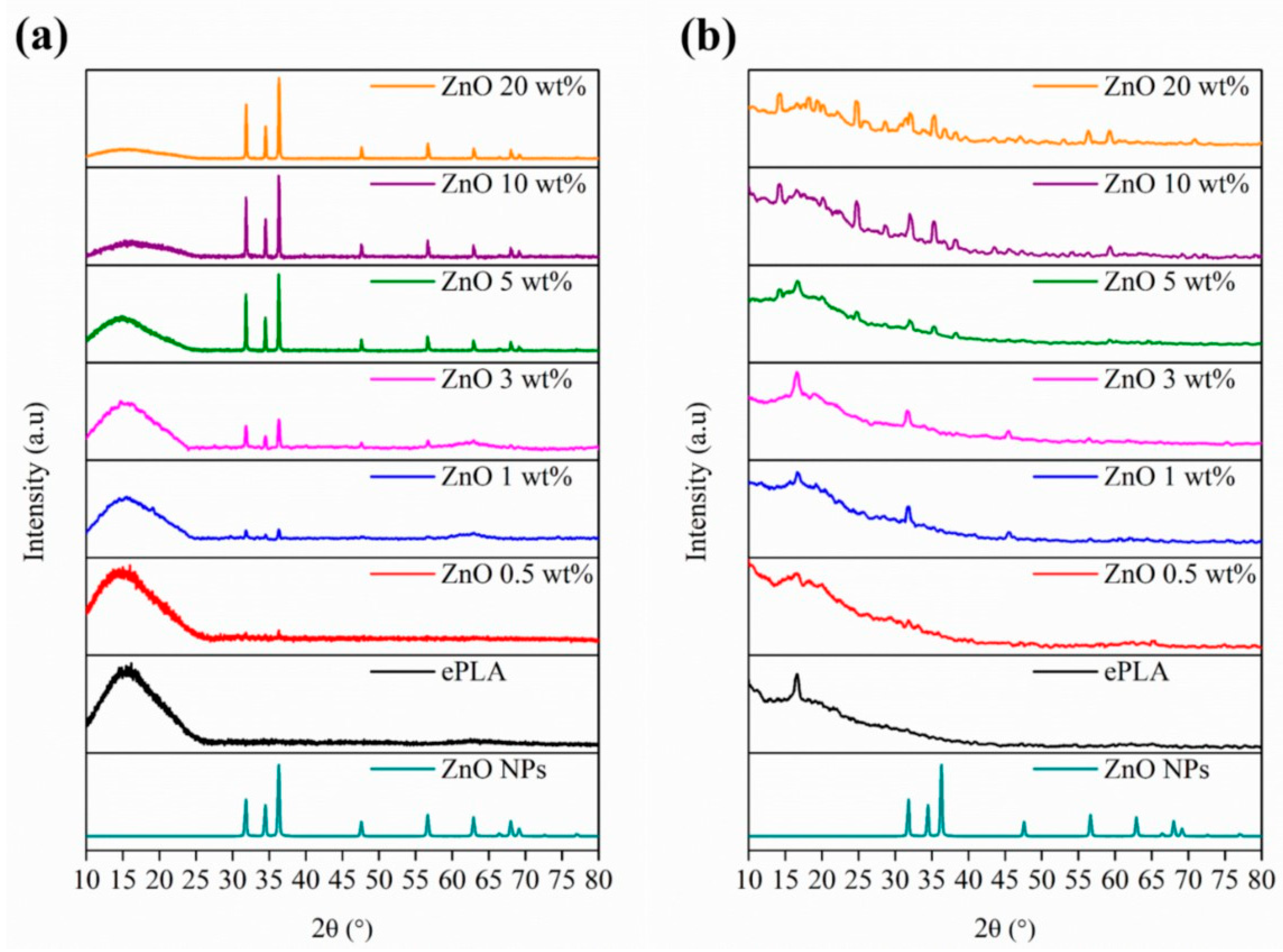
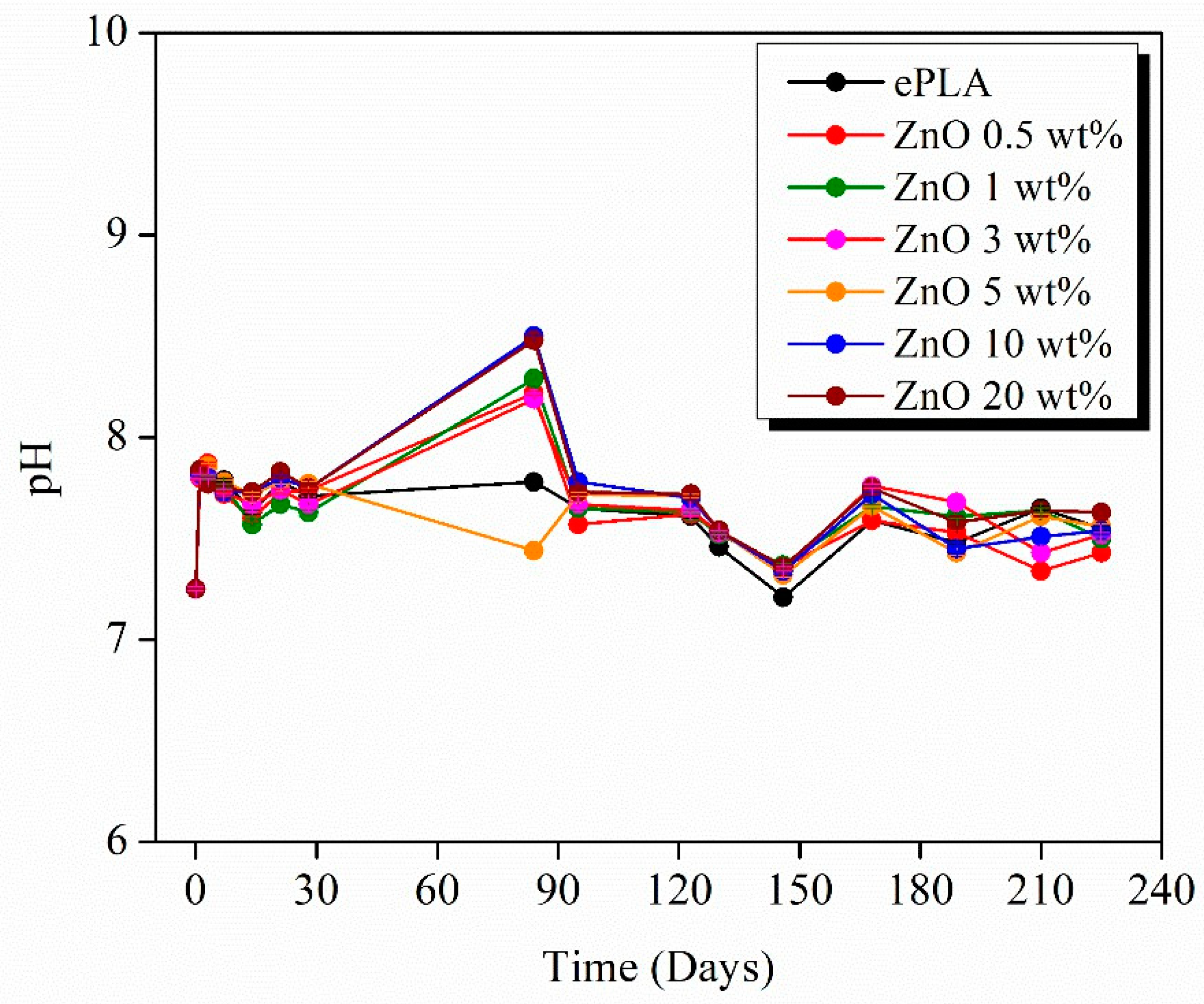
| Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | Tm (°C) | Xc (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ePLA | 60 | 96 | 149 | 3 |
| ePLA + ZnO 0.5 wt% | 61 | 107 | 145/149 | 5 |
| ePLA + ZnO 1 wt% | 61 | 102 | 146/149 | 4 |
| ePLA + ZnO 3 wt% | 62 | 112 | 146 | 10 |
| ePLA + ZnO 5 wt% | 62 | 107 | 146/149 | 2 |
| ePLA + ZnO 10 wt% | 61 | 109 | 146 | 3 |
| ePLA + ZnO 20 wt% | 59 | 105 | 145 | 4 |
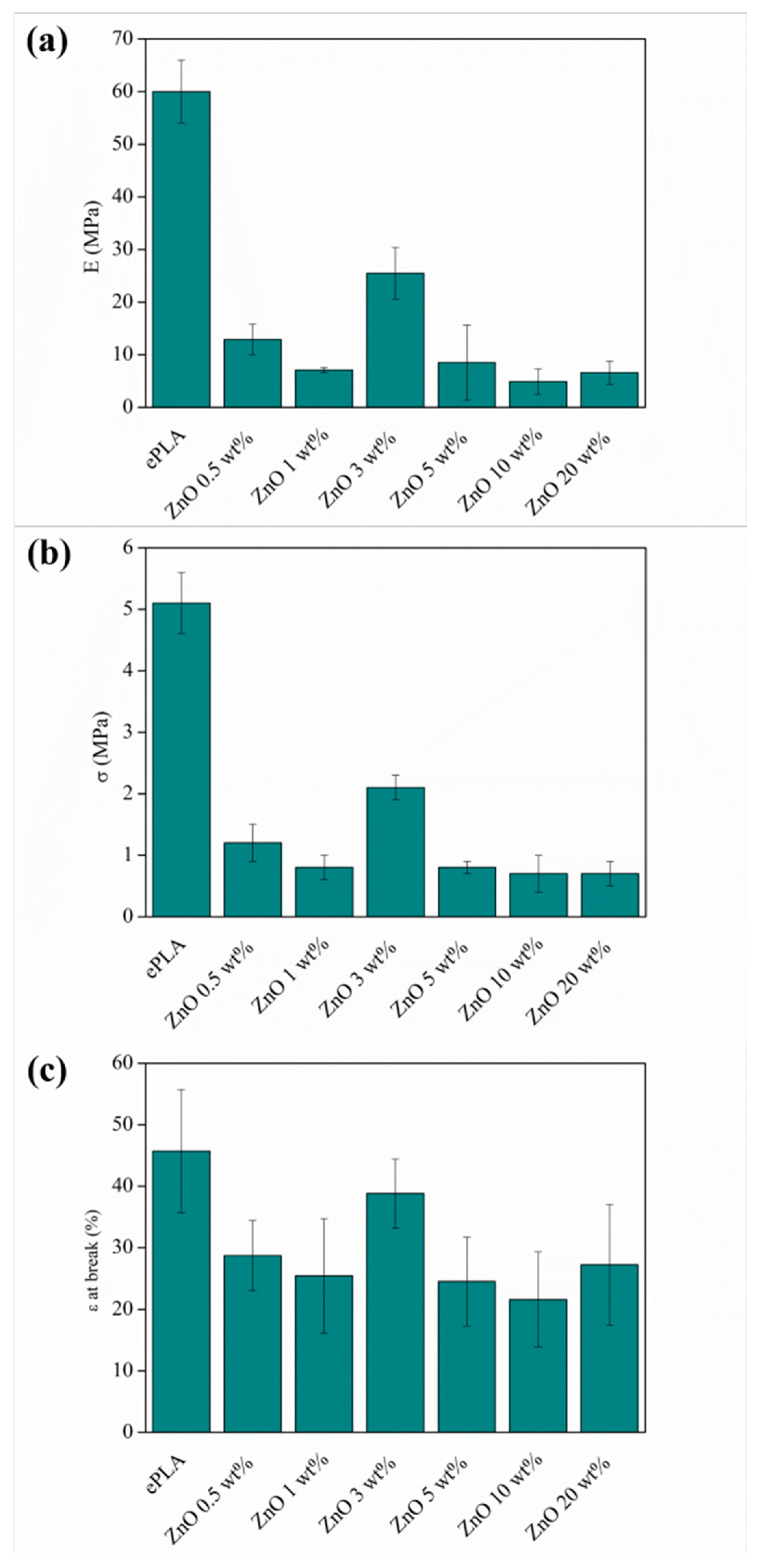
| Sample | E (MPa) | σ (MPa) | ε at Break (%) | Porosity % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ePLA | 60 ± 5 a | 5.1 ± 0.5 a | 45.7 ± 10 a | 18 |
| ePLA + ZnO 0.5 wt% | 11.6 ± 2.9 c | 1.2 ± 0.3 b | 28.7 ± 5.7 b | 30 |
| ePLA + ZnO 1 wt% | 5.5 ± 1.9 c,d | 0.8 ± 0.2 b | 25.4 ± 9.3 b | 38 |
| ePLA + ZnO 3 wt% | 21.5 ± 4 b | 2.1 ± 0.2 c | 38.8 ± 5.6 a | 29 |
| ePLA + ZnO 5 wt% | 7.2 ± 3.8 c,d | 0.8 ± 0.1 b | 24.5 ± 7.2 b | 27 |
| ePLA + ZnO 10 wt% | 4.9 ± 2 d | 0.7 ± 0.3 b | 21.6 ± 7.7 b | 33 |
| ePLA + ZnO 20 wt% | 4.2 ± 1.4 d | 0.7 ± 0.2 b | 27.2 ± 9.8 b | 37 |
| F ratio | 191.19 | 125.48 | 8.35 | |
| p-Value | 0.0000 * | 0.0000 * | 0.0000 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salaris, V.; San Félix García-Obregón, I.; López, D.; Peponi, L. Fabrication of PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibers Reinforced with ZnO Nanoparticles and In Vitro Degradation Study. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152236
Salaris V, San Félix García-Obregón I, López D, Peponi L. Fabrication of PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibers Reinforced with ZnO Nanoparticles and In Vitro Degradation Study. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(15):2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152236
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalaris, Valentina, Iñaki San Félix García-Obregón, Daniel López, and Laura Peponi. 2023. "Fabrication of PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibers Reinforced with ZnO Nanoparticles and In Vitro Degradation Study" Nanomaterials 13, no. 15: 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152236
APA StyleSalaris, V., San Félix García-Obregón, I., López, D., & Peponi, L. (2023). Fabrication of PLA-Based Electrospun Nanofibers Reinforced with ZnO Nanoparticles and In Vitro Degradation Study. Nanomaterials, 13(15), 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13152236








