Preparation of Hybrid Nanopigments with Excellent Environmental Stability, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties Based on Monascus Red and Sepiolite by One-Step Grinding Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Hybrid Nanopigments
2.3. Preparation of Hybrid Nanopigments@fluoro POS Coatings
2.4. Thermal Stability of Hybrid Nanopigments
2.5. DPPH Scavenging Activity
2.6. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
2.7. Reducing Power
2.8. Antibacterial Activity of Hybrid Nanopigments
2.9. Characterization Methods
3. Results
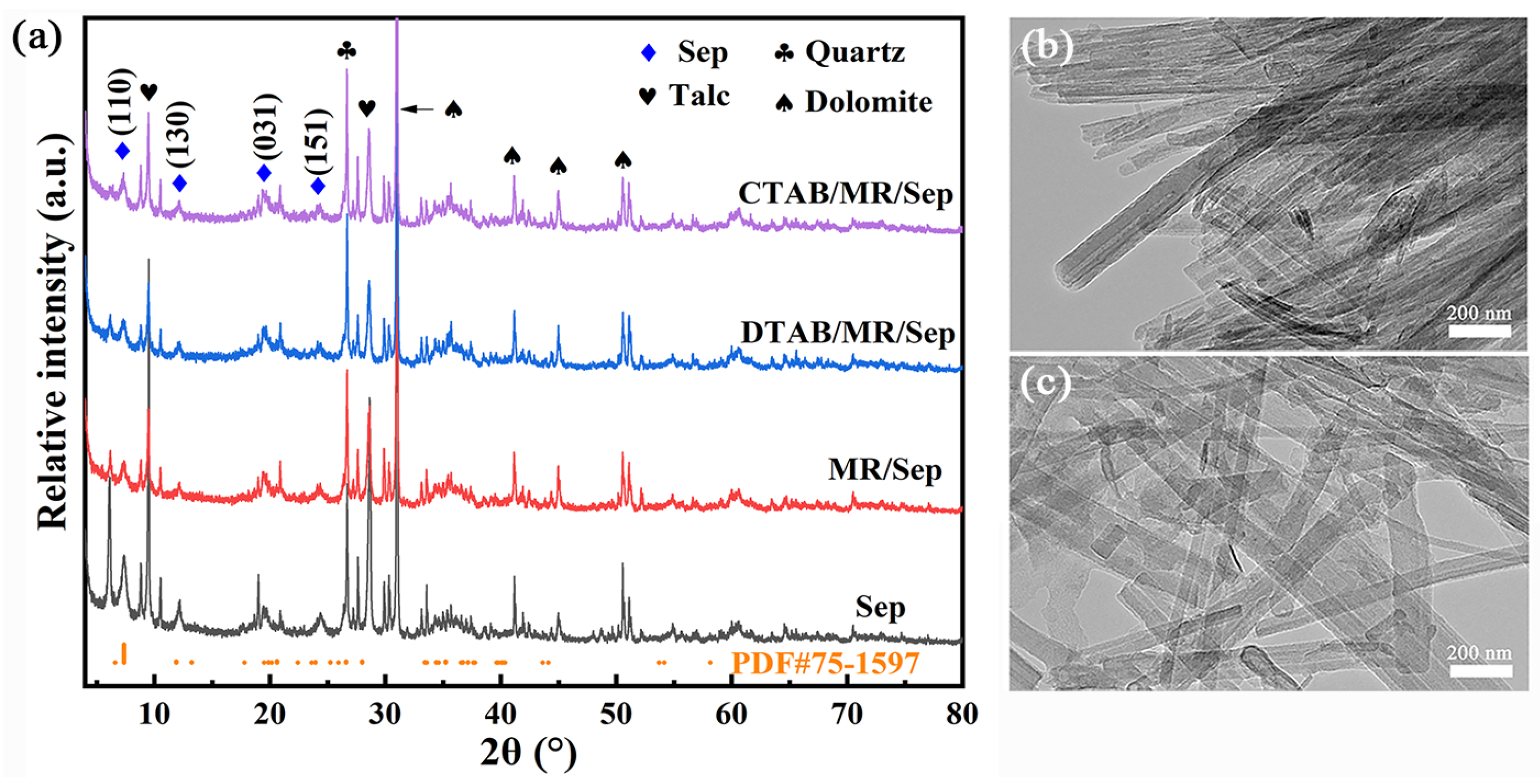
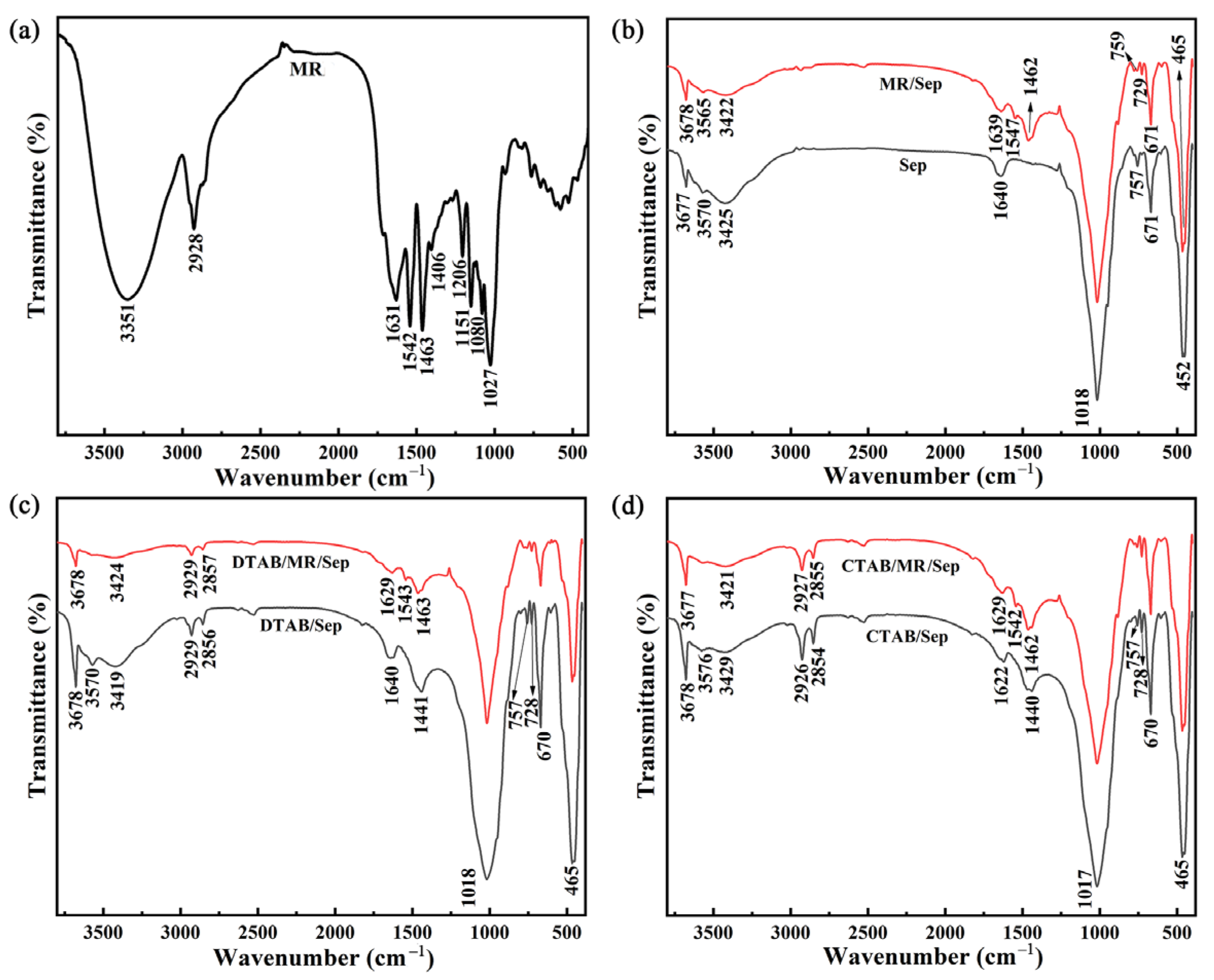
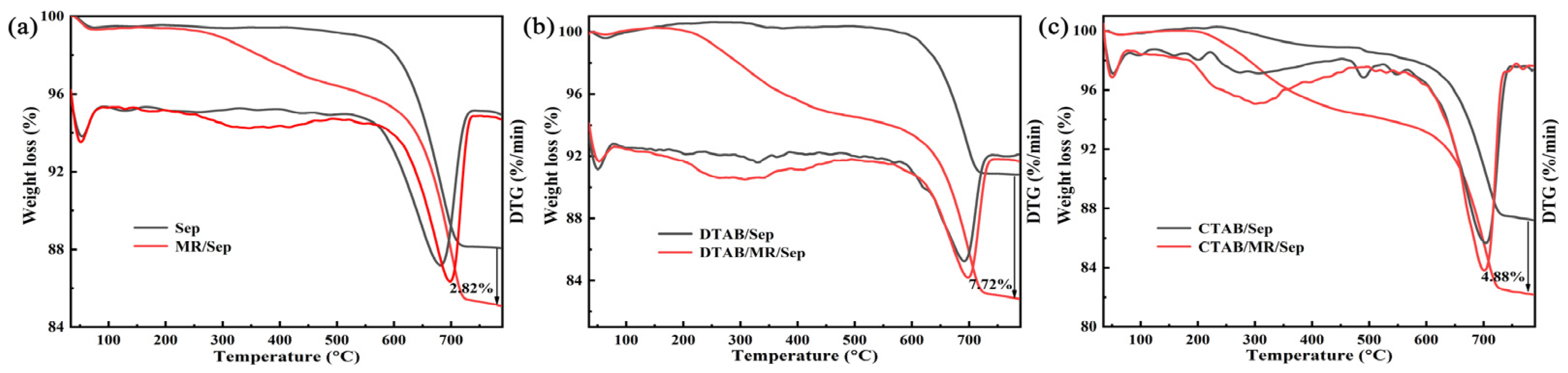
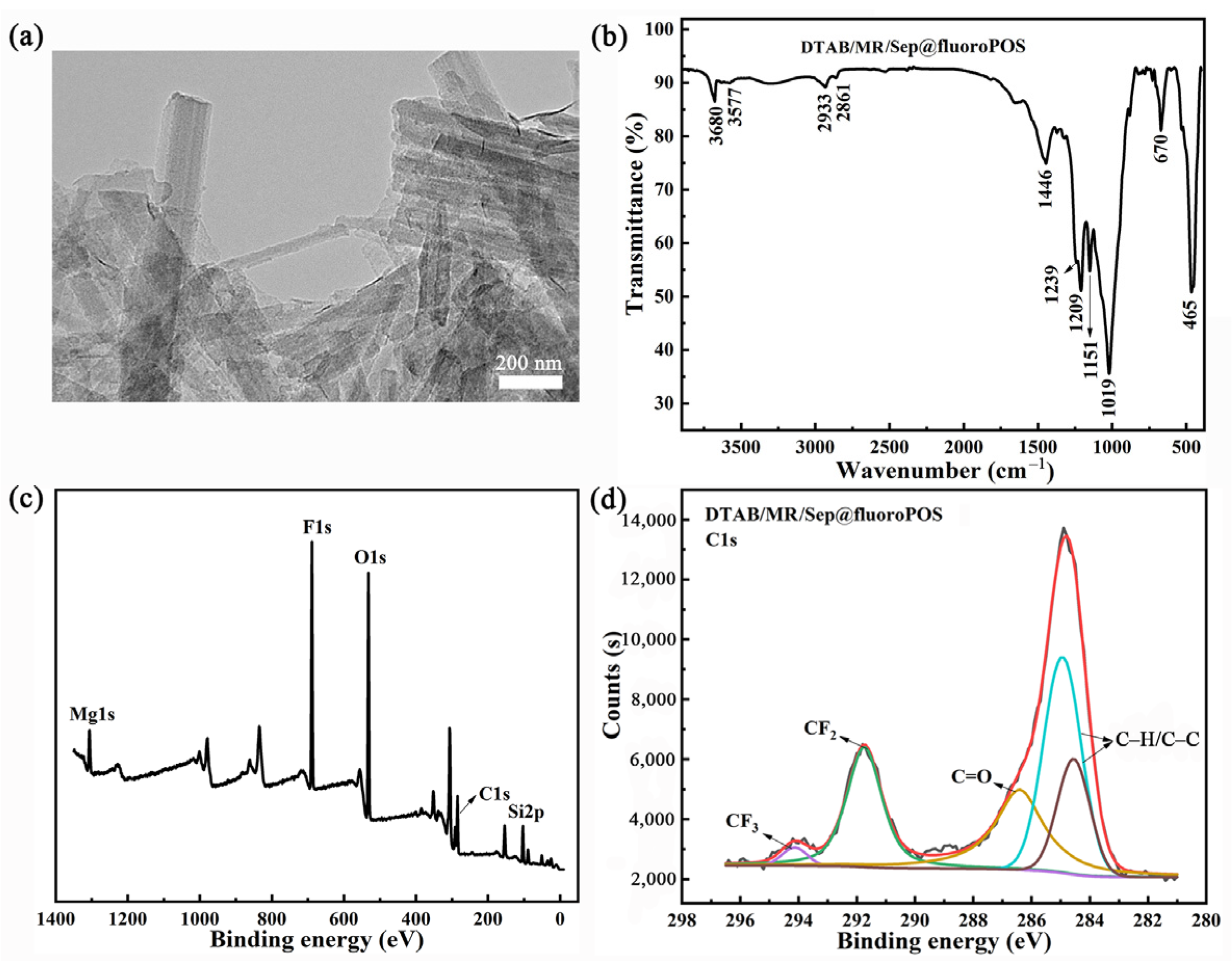
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Hybrid Nanopigments
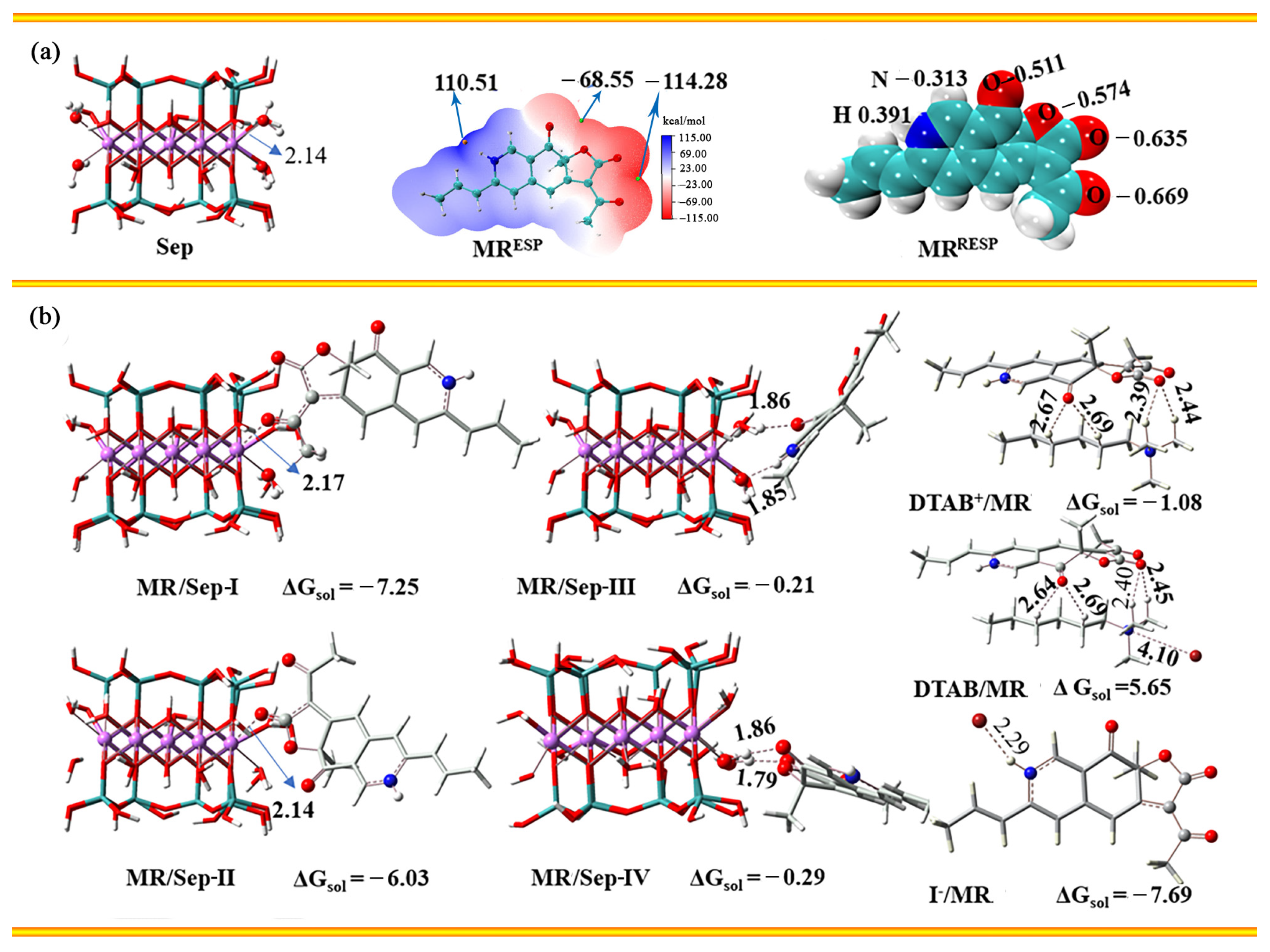
3.2. The Possible Interaction between DTAB, MRP and Sep
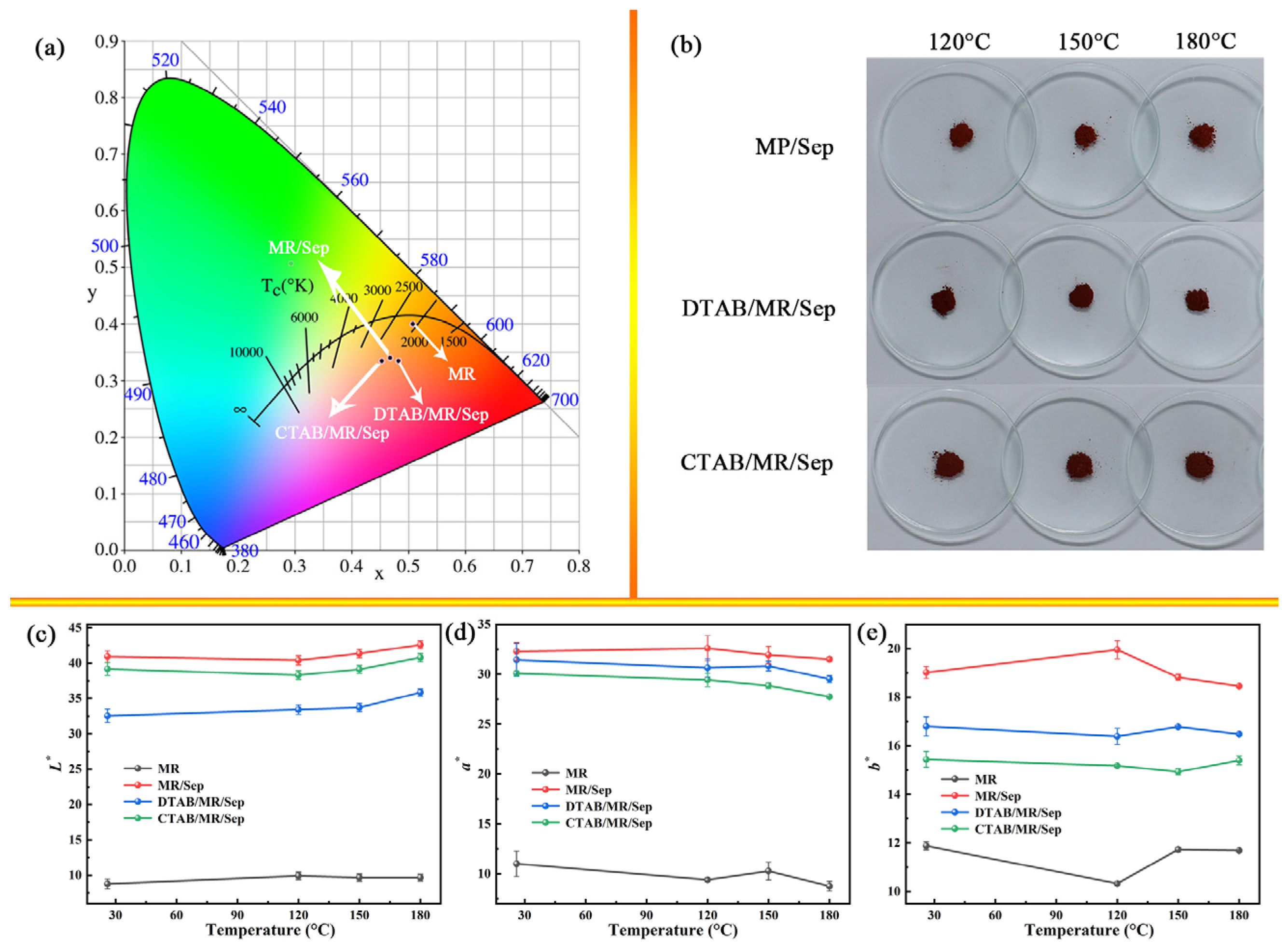
3.3. Color and Environmental Stability of Hybrid Nanopigments
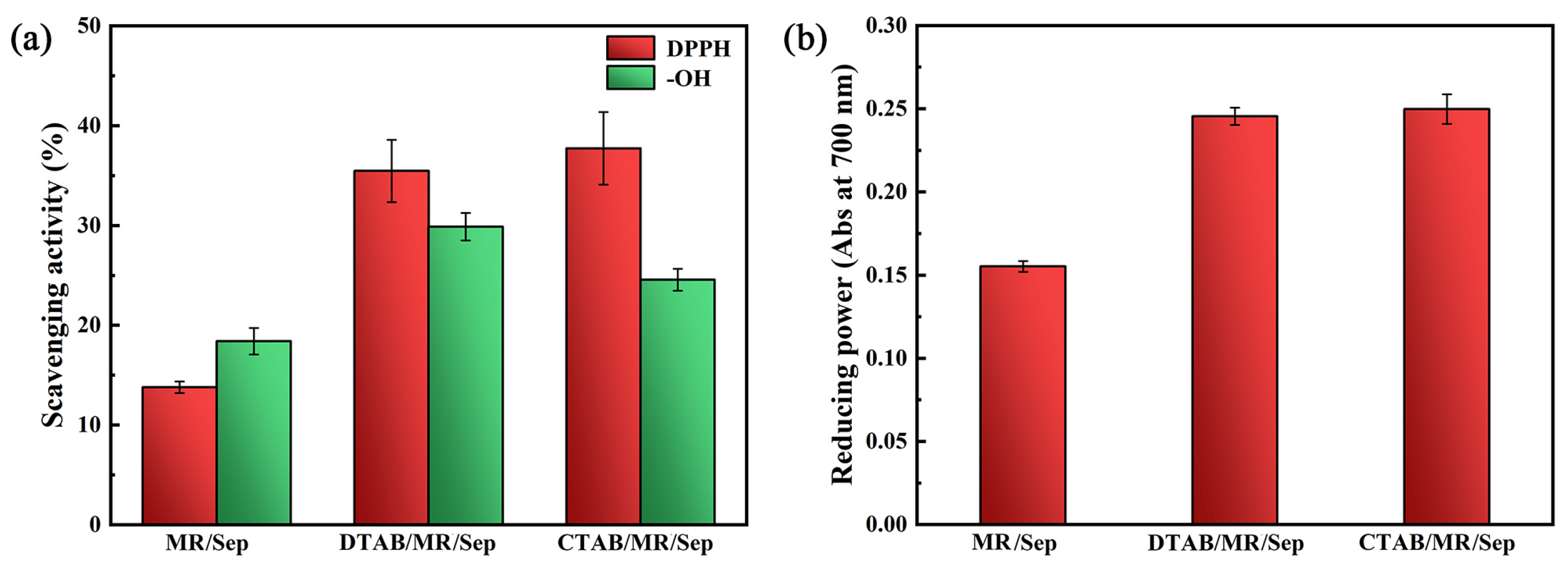
3.4. Antioxidant Activity of Hybrid Nanopigments
3.5. Antioxidant Activity of Hybrid Nanopigments
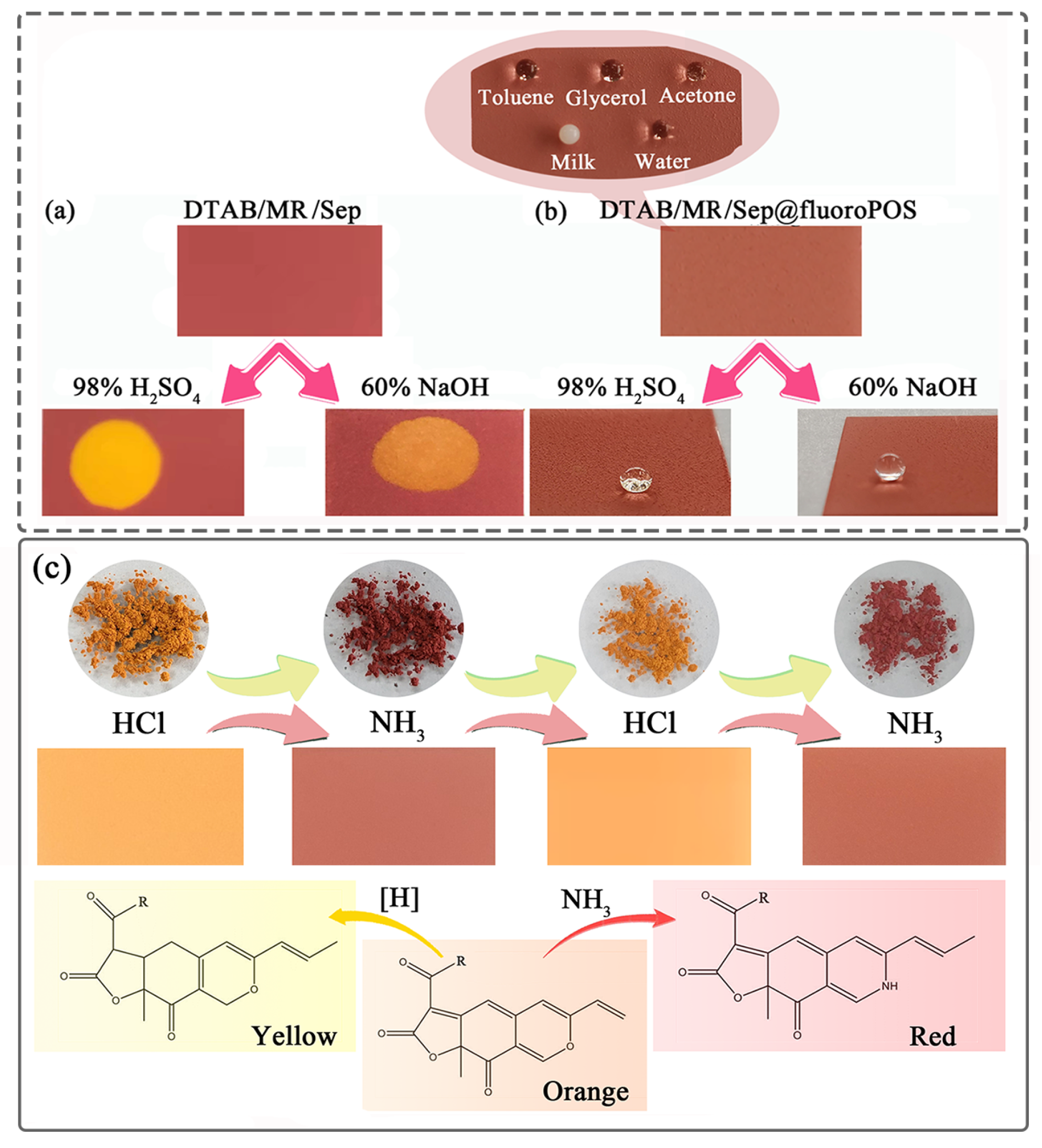
3.6. Application for Reversible Allochroic Superamphiphobic Coatings
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fabre, C.E.; Santerre, A.L.; Loret, M.O.; Baberian, R.; Pareilleux, A.; Goma, G.; Blanc, P.J. Production and food applications of the red Pigments of Monascus ruber. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.P.; Feng, Y.L.; Molnar, I.; Chen, F.S. Nature and nurture: Confluence of pathway determinism with metabolic and chemical serendipity diversifies Monascus azaphilone pigments. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.L.; Tu, X.; He, K.; Wang, C.T.; Yin, S.; Zhou, Y.X.; Chen, W.P. Monascorubrin and rubropunctatin: Preparation and reaction characteristics with amines. Dyes Pigments 2019, 170, 107629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.P.; Chen, R.F.; Liu, Q.P.; He, Y.; He, K.; Ding, X.L.; Kang, L.J.; Guo, X.X.; Xie, N.N.; Zhou, Y.X.; et al. Orange, red, yellow: Biosynthesis of azaphilone pigments in Monascus fungi. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 4917–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juzlova, P.; Martinkova, L.; Kren, V. Secondary metabolites of the fungus Monascus: A review. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 1996, 16, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, S.T.; Daroit, D.J.; Sant’Anna, V.; Brandelli, A. Stability Modeling of Red Pigments Produced by Monascus purpureus in Submerged Cultivations with Sugarcane Bagasse. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2013, 6, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, W.J.; Sun, Y.M.; Wu, J.Y. Improving the water solubility of Monascus pigments under acidic conditions with gum arabic. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2926–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Fujimoto, Y.; Shibata, M.; Tomita, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Fukuhara, C. Effect of stabilizers on the stability enhancement of naturally occurring dye incorporated in clay interlayer. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 163, 110546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, B.; Kuang, W.X.; Moser, A.; Facey, G.A.; Detellier, C. Structural study of Maya Blue: Textural, thermal and solidstate multinuclear magnetic resonance characterization of the palygorskite-indigo and sepiolite-indigo adducts. Clay. Clay Miner. 2003, 51, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech-Carbo, A.; Valle-Algarra, F.M.; Domenech-Carbo, M.T.; Domine, M.E.; Osete-Cortina, L.; Gimeno-Adelantado, J.V. Redox tuning and species distribution in Maya Blue-type materials: A reassessment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8134–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Zhang, Z.P.; Zhuang, G.Z.; Jiang, R. A new method to prepare ‘Maya red’ pigment from sepiolite and Basic red 46. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 174, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.; Ferraz, E.; Santarén, J.; Gamelas, J.A.F. Comparison of surface properties of sepiolite and palygorskite: Surface energy and nanoroughness. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.L.; Vinokurov, V.; Kopitsyn, D.; Shchukin, D.G. Sepiolite nanocarriers as a matrix for controlled thermal energy storage. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25828–25834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustetto, R.; Wahyudi, O.; Corazzari, I.; Turci, F. Chemical stability and dehydration behavior of a sepiolite/indigo Maya Blue pigment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 52, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovarlez, S.; Giulieri, F.; Chaze, A.M.; Delamare, F.; Raya, J.; Hirschinger, J. The incorporation of indigo molecules in sepiolite tunnels. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 11326–11332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szadkowski, B.; Rogowski, J.; Maniukiewicz, W.; Beyou, E.; Marzec, A. New natural organic–inorganic pH indicators: Synthesis and characterization of pro-ecological hybrid pigments based on anthraquinone dyes and mineral supports. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 105, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.T.M.; da Silva, K.M.; Silva, C.P.; Rodrigues, A.C.B.; Oake, J.; Gehlen, M.H.; Bohne, C.; Quina, F.H. Highly fluorescent hybrid pigments from anthocyanin- and red wine pyranoanthocyanin-analogs adsorbed on sepiolite clay. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Gao, M.L. Gemini surfactant modified organo-clays for removal of organic pollutants from water: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, S.H.; Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Ranjbari, S. Substantial improvement in the adsorption behavior of montmorillonite toward Tartrazine through hexadecylamine impregnation. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinayaa, R.; Jeevitha, G.; Mangalaraj, D.; Ponpandian, N.; Meena, P. Toxic influence of pristine and surfactant modified halloysite nanotubes on phytopathogenic bacteria. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 174, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, C.X.; Jiang, C.J.; Liao, Y.; Xiong, H.; Zhao, Q. Complexation with whey protein fibrils and chitosan: A potential vehicle for curcumin with improved aqueous dispersion stability and enhanced antioxidant activity. Food Hydrocolloid. 2020, 104, 105729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, J.Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Li, W.D.; Xing, Y.H.; Wang, Y.R. Monascus pigment-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Catalytic, antioxidant, and antibacterial activity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Wang, M.X.; Sun, D.J.; Li, Y.J.; Wu, T. Effective removal of emulsified oil from oily wastewater using surfactant-modified sepiolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 157, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.F.; Xu, Y.T.; Ye, Q.Q.; Li, J.Z.; Fang, Z. Marine Sponge-Inspired Organic–Inorganic Double-Network Strategy to Produce Magnesium Oxychloride Cement with Integrated Water Resistance and Compressive Strength. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 15514–15524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, Z.X.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.P. Adsorption properties and mechanism of sepiolite modified by anionic and cationic surfactants on oxytetracycline from aqueous solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.A.; Ciuffi, K.J.; Rives, V.; Vicente, M.A.; Trujillano, R.; Gil, A.; Korili, S.A.; de Faria, E.H. Effect of chemical modification of palygorskite and sepiolite by 3-aminopropyltriethoxisilane on adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.F.; Jia, G.G.; Wang, C.L.; Chen, M.H.; Xie, F.J.; Nepovinnykh, N.V.; Douglas Goff, H.; Guo, Q.B. Structural characterisation and immunomodulatory activity of exopolysaccharides from liquid fermentation of Monascus purpureus (Hong Qu). Food Hydrocolloid. 2020, 103, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, W.J.; Tao, H.W.; Zhu, W.M.; Qi, X.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Li, H.Y.; Zhao, C.Q.; Yang, Y.P.; Hou, Y.J.; et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by the mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. Y16. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8179–8184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credico, B.D.; Tagliaro, I.; Cobani, E.; Conzatti, L.; D’Arienzo, M.; Giannini, M.; Mascotto, S.; Scotti, R.; Stagnaro, P.; Tadiello, L. A green approach for preparing high-loaded sepiolite/polymer biocomposites. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largo, F.; Haounati, R.; Akhouairi, S.; Ouachtak, H.; El Haouti, R.; El Guerdaoui, A.; Hafid, N.; Santos, D.M.F.; Akbal, F.; Kuleyin, A.; et al. Adsorptive removal of both cationic and anionic dyes by using sepiolite clay mineral as adsorbent: Experimental and molecular dynamic simulation studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Tang, F.Y.; Hao, F.; Zhao, H.; Liu, W.Y.; Lv, Y.; Liu, P.L.; Xiong, W.; Luo, H. Tuning the electron density of metal nickel via interfacial electron transfer in Ni/MCM-41 for efficient and selective catalytic hydrogenation of halogenated nitroarenes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 2947–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, F.D.; Brandão Lima, L.C.; Silva-Filho, E.C.; Fonseca, M.G.; Jaber, M. Through alizarin-hectorite pigments: Influence of organofunctionalization on fading. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 587, 124323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladysz-Plaska, A.; Majdan, M.; Tarasiuk, B.; Sternik, D.; Grabias, E. The use of halloysite functionalized with isothiouronium salts as an organic/inorganic hybrid adsorbent for uranium(VI) ions removal. J. Hazard Mater. 2018, 354, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volle, N.; Giulieri, F.; Burr, A.; Pagnotta, S.; Chaze, A.M. Controlled interactions between silanol groups at the surface of sepiolite and an acrylate matrix: Consequences on the thermal and mechanical properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.M.; Park, Y.; Zheng, S.L.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L. Thermal stability and hot-stage Raman spectroscopic study of Ca-montmorillonite modified with different surfactants: A comparative study. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 569, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.Y.; Hou, Z.Q.; Yuan, Y.H.; Wang, S.J.; Cao, Y.P.; Sun, B.G. Effect of carrier agents on the physical properties and morphology of spray-dried Monascus pigment powder. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koli, S.H.; Suryawanshi, R.K.; Mohite, B.V.; Patil, S.V. Prospective of monascus pigments as an additive to commercial sunscreens. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19894095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, E.C.A.; Isom, G.L.; Rooke, J.L.; Pullela, K.; Icke, C.; Yang, Z.; Boelter, G.; Jones, A.; Warner, I.; Da Costa, R.; et al. Loss of YhcB results in dysregulation of coordinated peptidoglycan, LPS and phospholipid synthesis during Escherichia coli cell growth. PLos Genet. 2021, 17, e1009586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.C.; Wang, H.; Bai, H.T.; Zhang, P.B.; Liu, L.B.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.L. Tuning Antibacterial Activity of Cyclodextrin-Attached Cationic Ammonium Surfactants by a Supramolecular Approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 31657–31666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Xu, X.H.; Zhang, J.P.; Wang, A.Q. Colorful Superamphiphobic Coatings with Low Sliding Angles and High Durability Based on Natural Nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Hu, T.; Li, B.C.; Wei, J.F.; Zhang, J.P. Totally Waterborne and Highly Durable Superamphiphobic Coatings for Anti-Icing and Anticorrosion. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1901255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, F.; Rocha, I.L.D.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Ventura, S.P.M.; dos Santos, A.G.; Crevelin, E.J.; Ebinuma, V.D.S. Identification of azaphilone derivatives of Monascus colorants from Talaromyces amestolkiae and their halochromic properties. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.T.; Jia, M.X.; Li, W.; Deng, J.; Ren, J.L.; Luo, F.J.; Bai, J.; Liu, J. Toward improvements for enhancement the productivity and color value of Monascus pigments: A critical review with recent updates. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7139–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision A.1; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal Solvation Model Based on Solute Electron Density and on a Continuum Model of the Solvent Defined by the Bulk Dielectric Constant and Atomic Surface Tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F.W. Quantitative analysis of molecular surface based on improved Marching Tetrahedra algorithm. J. Mol. Graph. Model 2012, 38, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayly, C.I.; Cieplak, P.; Cornell, W.D.; Kollman, P.A. A well-behaved electrostatic potential based method using charge restraints for deriving atomic charges: The RESP Model. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 10269–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.D.A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semichem, I. GaussView 6.0.16 Program. Semichem, Inc. Available online: http://gaussian.com/gaussview6/ (accessed on 25 November 2019).
- Parrish, R.M.; Burns, L.A.; Smith, D.G.A.; Simmonett, A.C.; DePrince, A.E.; Hohenstein, E.G.; Bozkaya, U.; Sokolov, A.Y.; Di Remigio, R.; Richard, R.M.; et al. Psi4 1.1: An Open-Source Electronic Structure Program Emphasizing Automation, Advanced Libraries, and Interoperability. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 3185–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamian, S.; Lu, T.; Kruse, H.; Emamian, H. Exploring Nature and Predicting Strength of Hydrogen Bonds: A Correlation Analysis Between Atoms-in-Molecules Descriptors, Binding Energies, and Energy Components of Symmetry-Adapted Perturbation Theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2019, 40, 2868–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | SBET (m2/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) | Zeta Potentials (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MR | - | - | −35.20 ± 1.63 |
| Sep | 31.09 ± 0.90 | 0.0516 ± 0.0011 | −12.63 ± 0.46 |
| MR/Sep | 19.63 ± 1.63 | 0.0631 ± 0.0062 | −16.53 ± 0.38 |
| DTAB/Sep | 30.57 ± 1.97 | 0.0760 ± 0.0014 | −12.43 ± 0.31 |
| DTAB/MR/Sep | 13.27 ± 2.41 | 0.0389 ± 0.0100 | −20.67 ± 0.21 |
| CTAB/Sep | 20.77 ± 5.31 | 0.0605 ± 0.0074 | −2.05 ± 0.34 |
| CTAB/MR/Sep | 7.70 ± 1.33 | 0.0260 ± 0.0123 | −19.57 ± 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Yan, P.; Mu, B.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A. Preparation of Hybrid Nanopigments with Excellent Environmental Stability, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties Based on Monascus Red and Sepiolite by One-Step Grinding Process. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111792
Li S, Yan P, Mu B, Kang Y, Wang A. Preparation of Hybrid Nanopigments with Excellent Environmental Stability, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties Based on Monascus Red and Sepiolite by One-Step Grinding Process. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(11):1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111792
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shue, Penji Yan, Bin Mu, Yuru Kang, and Aiqin Wang. 2023. "Preparation of Hybrid Nanopigments with Excellent Environmental Stability, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties Based on Monascus Red and Sepiolite by One-Step Grinding Process" Nanomaterials 13, no. 11: 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111792
APA StyleLi, S., Yan, P., Mu, B., Kang, Y., & Wang, A. (2023). Preparation of Hybrid Nanopigments with Excellent Environmental Stability, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties Based on Monascus Red and Sepiolite by One-Step Grinding Process. Nanomaterials, 13(11), 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111792








