Time-Dependent Size and Shape Evolution of Gold and Europium Nanoparticles from a Bioproducing Microorganism, a Cyanobacterium: A Digitally Supported High-Resolution Image Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Exemplary TEM Images with Nanoparticles
3.2. Particle Size Distributions (PSDs)
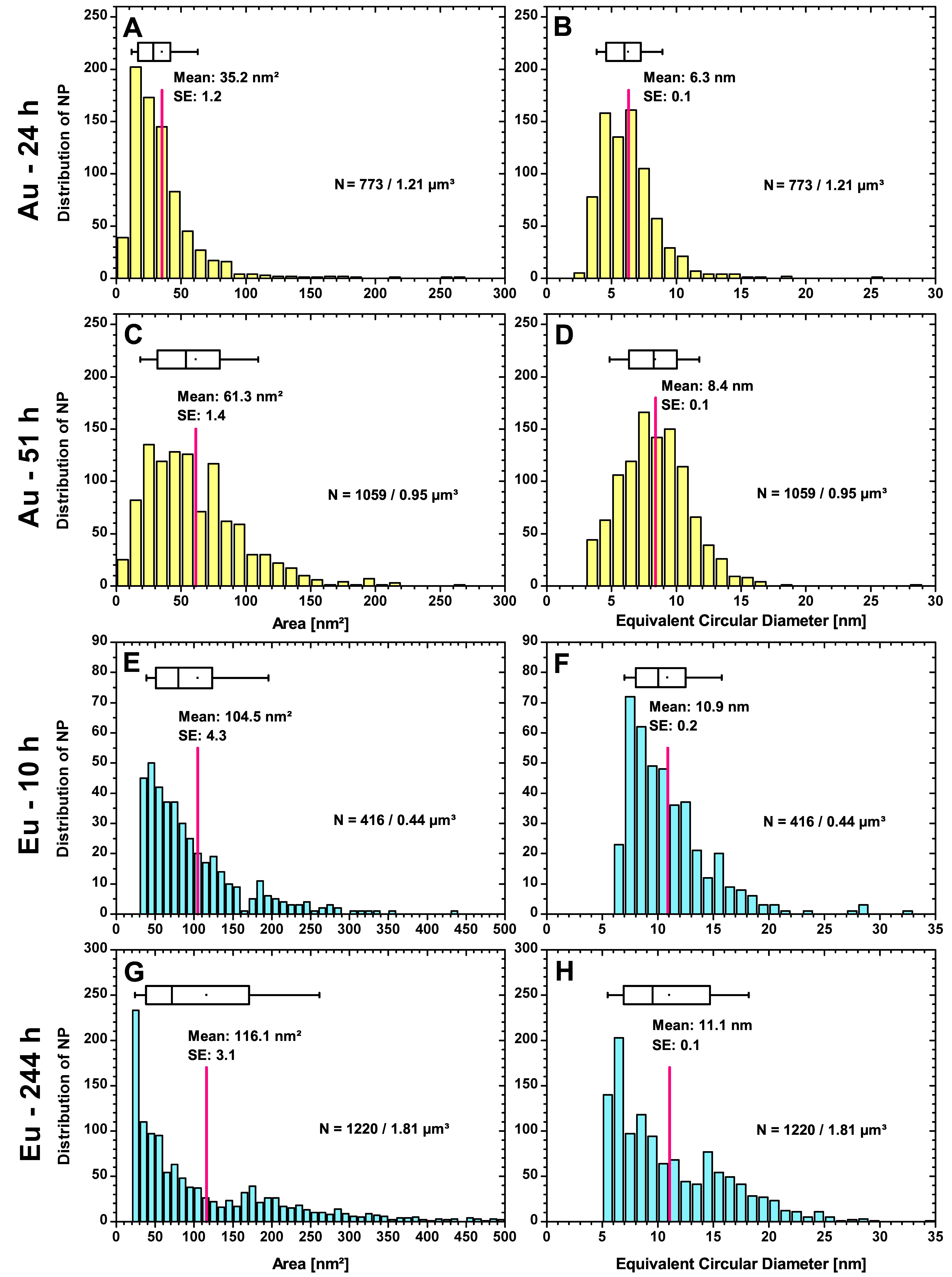
3.2.1. PSDs of all NPs in Complete Cells
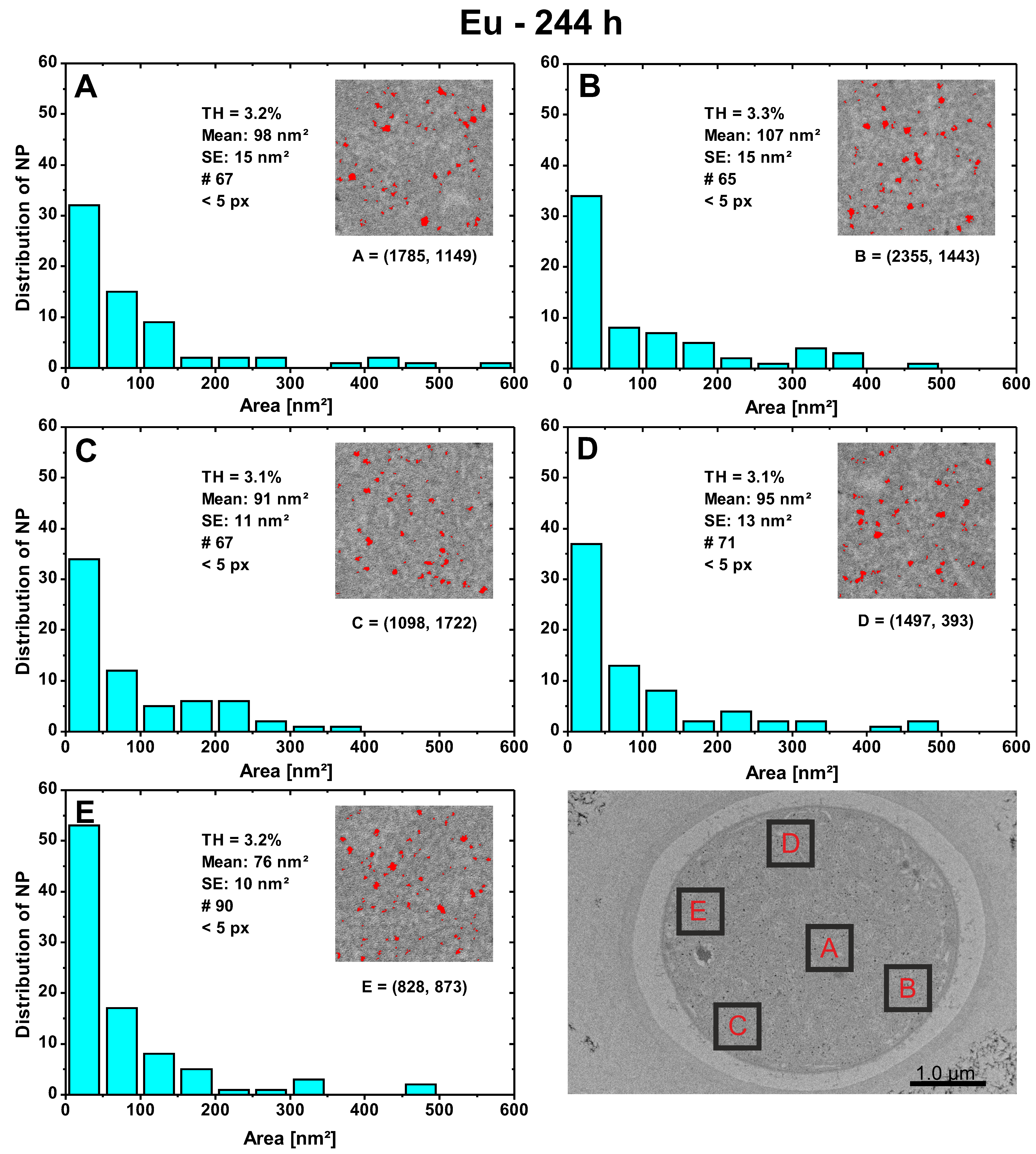
3.2.2. High-Resolution (HR)-PSD of Cell Sections
3.2.3. Local PSDs within an Exemplary Cell
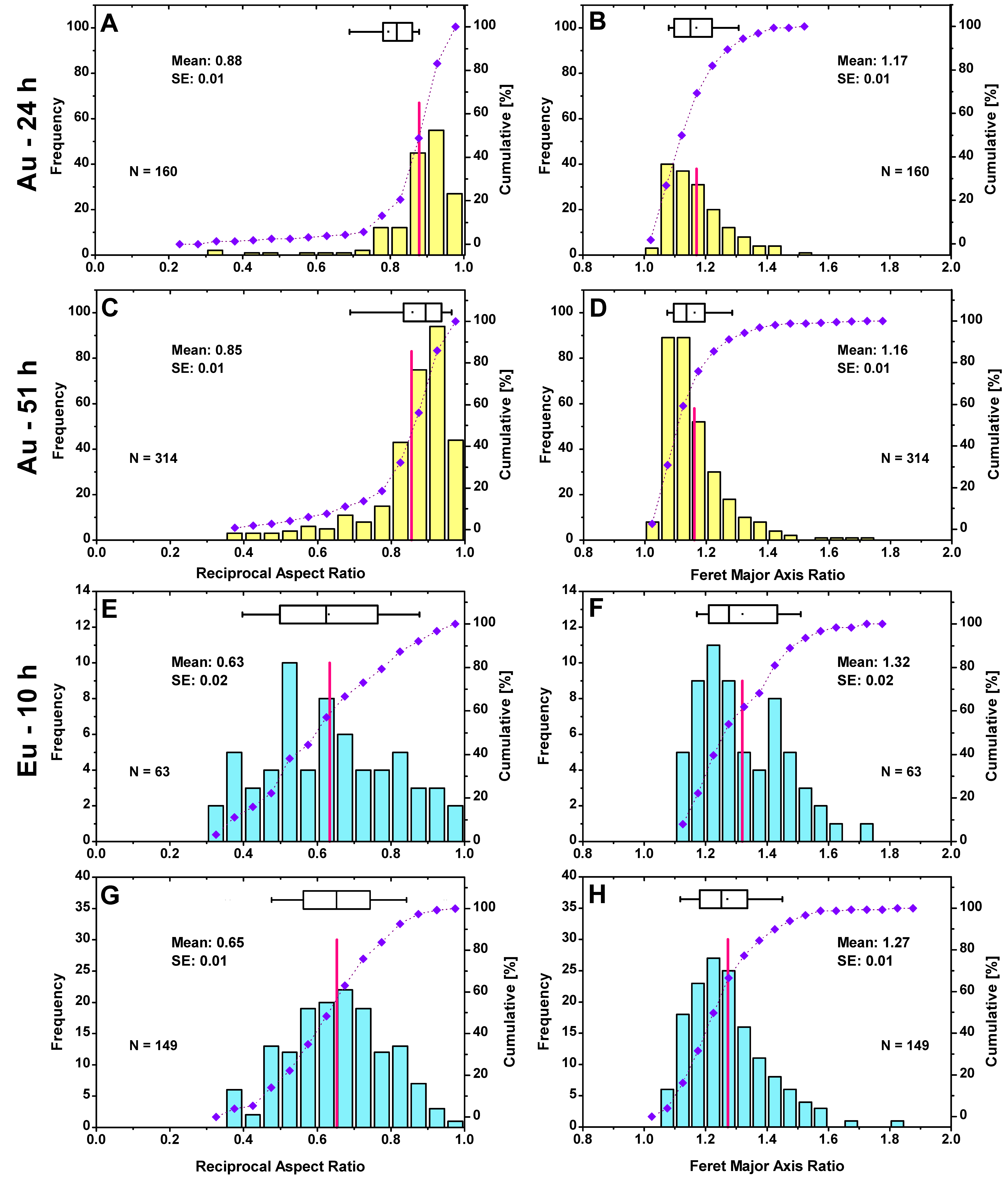
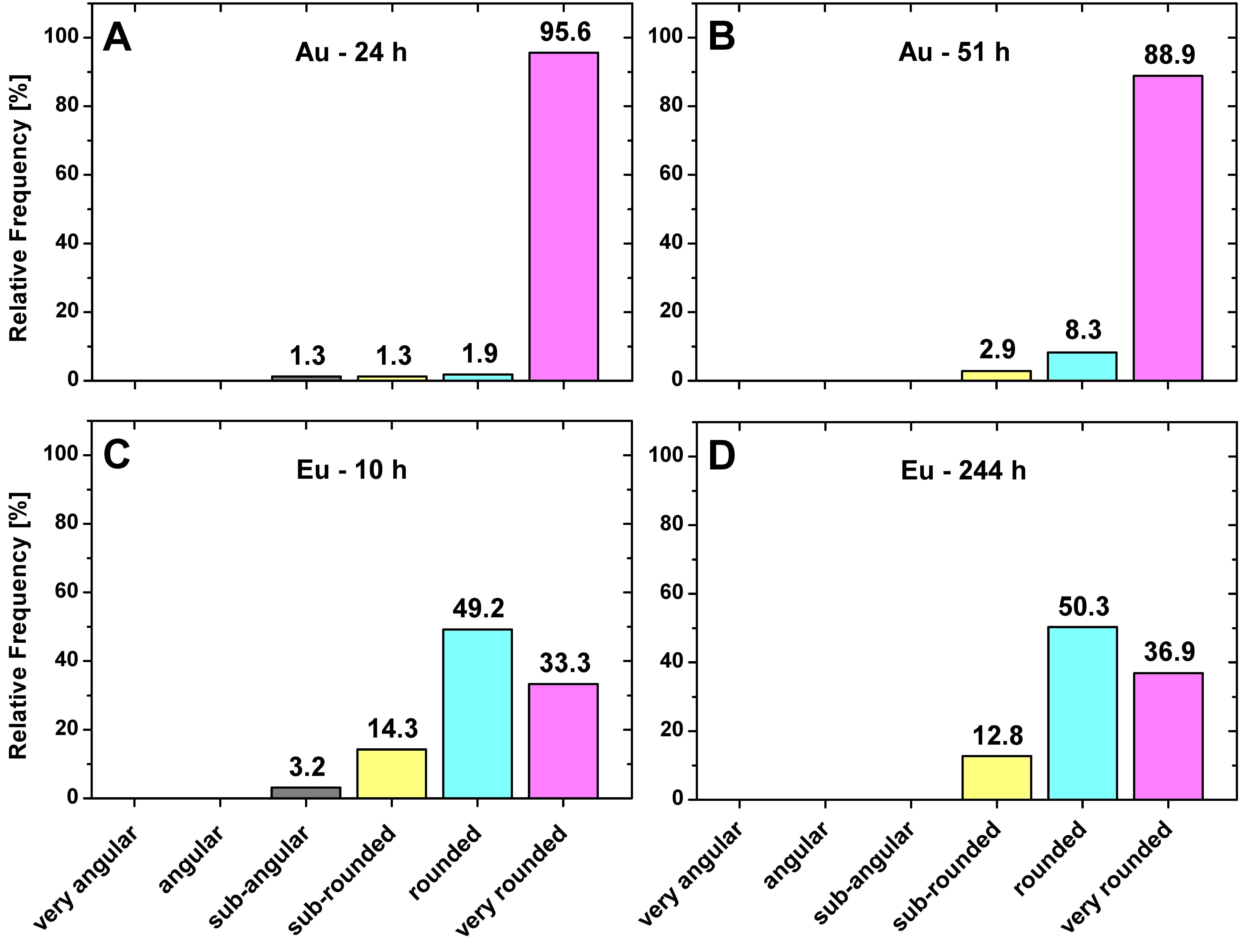
3.3. Shape Classification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh, S.; Ahmad, R.; Banerjee, K.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Rahman, S. Mechanistic Aspects of Microbe-Mediated Nanoparticle Synthesis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Ping, H.; Tan, T.; Lei, L.; Xie, H.; Yang, X.Y.; Fu, Z. Bioprocess-inspired fabrication of materials with new structures and functions. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 105, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, D.; Volesky, B. Advances in the biosorption of heavy metals. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.H.S.F.; Volesky, B. Biosorption: A solution to pollution? Int. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadogan, E.I.; Lee, C.H.; Popuri, S.R.; Lin, H.Y. Efficiencies of chitosan nanoparticles and crab shell particles in europium uptake from aqueous solutions through biosorption: Synthesis and characterization. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 95, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Makuvara, Z.; Marumure, J. Rare earth elements: Human exposure, risk factors, and health risks (Chapter 15). In Emerging Contaminants in the Terrestrial-Aquatic-Atmosphere Continuum. Occurrence, Health Risks, and Mitigation; Gwenzi, W., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Jally, B.; Laubie, B.; Tang, Y.-T.; Simonnot, M.-O. Processing of Plants to Products: Gold, REEs and Other Elements. In Agromining: Farming for Metals: Extracting Unconventional Resources Using Plants, 2nd ed.; van der Ent, A., Baker, A.J.M., Echevarria, G., Simonnot, M.-O., Morel, J.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleke, M.; Valverde, A.; Gomez-Arias, A.; Cason, E.D.; Vermeulen, J.G.; Coetsee-Hugo, L.; Swart, H.; van Heerden, E.; Castillo, J. Anaerobic reduction of europium by a Clostridium strain as a strategy for rare earth biorecovery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, R.R.; Ilyas, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.; Trinh, H.B.; Ghauri, M.A.; Ilyas, N. Biotechnological recycling of critical metals from waste printed circuit boards. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2796–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, V.; Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Bel, G. Surge in Global E-Waste, up 21 Per Cent in 5 Years. The Global E-waste Monitor 2020. 2020. Available online: https://api.globalewaste.org/publications/file/271/The-Global-E-waste-Monitor-2020-Quantities-flows-and-the-circular-economy-potential.zip (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Kammerlander, K.K.K.; Köhler, L.; Huittinen, N.; Bok, F.; Steudtner, R.; Oschatz, C.; Vogel, M.; Stumpf, T.; Brunner, E. Sorption of europium on diatom biosilica as model of a “green” sorbent for f-elements. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 126, 104823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadogan, E.I.; Lee, C.H.; Popuri, S.R. Facile synthesis of chitosan derivatives and Arthrobacter sp. biomass for the removal of europium(III) ions from aqueous solution through biosorption. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, D.D.; Ortiz, M.; Rayson, G.D. Spectroscopic Comparison of Eu(III) Binding to Various Biosorbents. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.B.; Seo, J.M.; Kim, G.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, T.J. In vivo synthesis of europium selenide nanoparticles and related cytotoxicity evaluation of human cells. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2016, 95, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösken, L.M.; Cappel, F.; Körsten, S.; Fischer, C.B.; Schönleber, A.; van Smaalen, S.; Geimer, S.; Beresko, C.; Ankerhold, G.; Wehner, S. Time-dependent growth of crystalline Au0-nanoparticles in cyanobacteria as self-reproducing bioreactors: 2. Anabaena cylindrical. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösken, L.M.; Körsten, S.; Fischer, C.B.; Schönleber, A.; van Smaalen, S.; Geimer, S.; Wehner, S. Time-dependent growth of crystalline Au0-nanoparticles in cyanobacteria as self-reproducing bioreactors: 1. Anabaena sp. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, S.; Li, C.; Lu, X.; Chen, S.; Yin, B. Technology Microalgal extracellular polymeric substances and their interactions with metalloids: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1769–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahoumane, S.A.; Yéprémian, C.; Djédiat, C.; Couté, A.; Fiévet, F.; Coradin, T.; Brayner, R. A global approach of the mechanism involved in the biosynthesis of gold colloids using micro-algae. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenartowicz, M.; Marek, P.H.; Madura, I.D.; Lipok, J. Formation of Variously Shaped Gold Nanoparticles by Anabaena laxa. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 3035–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Kaur, A.; Goyal, D. Algae-based metallic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and applications. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2019, 163, 105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahoumane, S.A.; Yéprémian, C.; Djédiat, C.; Couté, A.; Fiévet, F.; Coradin, T.; Brayner, R. Improvement of kinetics, yield, and colloidal stability of biogenic gold nanoparticles using living cells of Euglena gracilis microalga. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.Á.; Ballester, A. Exploring the possibilities of biological fabrication of gold nanostructures using orange peel extract. Metals 2015, 5, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramrakhiani, L.; Ghosh, S. Metallic nanoparticle synthesised by biological route: Safer candidate for diverse applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S. Advances in nanoscale alloys and intermetallics: Low temperature solution chemistry synthesis and application in catalysis. Dalt. Trans. 2015, 44, 18692–18717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetchinkina, E.; Loshchinina, E.; Kupryashina, M.; Burov, A.; Nikitina, V. Shape and Size Diversity of Gold, Silver, Selenium, and Silica Nanoparticles Prepared by Green Synthesis Using Fungi and Bacteria. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 17207–17218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klekotko, M.; Brach, K.; Olesiak-Banska, J.; Samoc, M.; Matczyszyn, K. Popcorn-shaped gold nanoparticles: Plant extract-mediated synthesis, characterization and multiphoton-excited luminescence properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 229, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Bhatnagar, A.; Lima, E.C. Adsorption of rare earth metals: A review of recent literature. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahoumane, S.A.; Wujcik, E.K.; Jeffryes, C. Noble metal, oxide and chalcogenide-based nanomaterials from scalable phototrophic culture systems. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2016, 95, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochert, A.S.; Rösken, L.M.; Fischer, C.B.; Schönleber, A.; Ecker, D.; van Smaalen, S.; Geimer, S.; Wehner, S. Bioselective synthesis of gold nanoparticles from diluted mixed Au, Ir, and Rh ion solution by Anabaena cylindrica. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.B.; Körsten, S.; Rösken, L.M.; Cappel, F.; Beresko, C.; Ankerhold, G.; Schönleber, A.; Geimer, S.; Ecker, D.; Wehner, S. Cyanobacterial promoted enrichment of rare earth elements europium, samarium and neodymium and intracellular europium particle formation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32581–32593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayner, R.; Claude, Y.; Djediat, C.; Coradin, T.; Livage, J.; Fi, F.; Cout, A. Photosynthetic Microorganism-Mediated Synthesis of Akaganeite (β -FeOOH) Nanorods. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10062–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaisen, K.; Hahn, A.; Valdebenito, M.; Moslavac, S.; Samborski, A.; Maldener, I.; Wilken, C.; Valladares, A.; Flores, E.; Hantke, K.; et al. The interplay between siderophore secretion and coupled iron and copper transport in the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2010, 1798, 2131–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahoumane, S.A.; Mechouet, M.; Wijesekera, K.; Filipe, C.D.M.; Sicard, C.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Jeffryes, C. Algae-mediated biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials as a promising route in nanobiotechnology-a review. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 552–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, B.; Morais, T.; Cardoso, C.E.D.; Freitas, R.; Viana, T.; Ferreira, N.; Fabre, E.; Pinheiro-Torres, J.; Pereira, E. Can the recycling of europium from contaminated waters be achieved through living macroalgae? Study on accumulation and toxicological impacts under realistic concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, E.S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igathinathane, C.; Pordesimo, L.O.; Columbus, E.P.; Batchelor, W.D.; Methuku, S.R. Shape identification and particles size distribution from basic shape parameters using ImageJ. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 63, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, M.; Körsten, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; Lv, Y.; Liu, M.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. High-resolution particle size and shape analysis of the first Samarium nanoparticles biosynthesized from aqueous solutions via cyanobacteria Anabaena cylindrical. NanoImpact 2022, 26, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Karishma, S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Jeevanantham, S.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; George, C.S. A review on biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles and its environmental applications. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Nawaz, K.; Khan, A.K.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H.; Anjum, S. An overview of the algae-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Poonia, A.K.; Yadav, D.; Jin, J.O. Microbe-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles: Applications and future prospects. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, P.; Bhattacharya, A.; Dasgupta, A.; Pal, R. Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticle using fractioned cellular components from eukaryotic algae and cyanobacteria. Phycol. Res. 2016, 64, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, N.; Banerjee, A.; Lahiri, S.; Panda, A.; Gosh, A.N.; Pal, R. Biorecovery of gold using cyanobacteria and an eukaryotic alga with special reference to nanogold formation—A novel phenomenon. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalah, J.; Espina, G.; Blamey, L.; Muñoz-Ibacache, S.A.; Blamey, J.M. Advantages of using extremophilic bacteria for the biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles and its potential for rare earth element recovery. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ion Contact Time | Cell No. | Zoom | Range [px] | Scale Ratio [px/µm] | Threshold [%] | Counts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au—24 h | 1 | ×8.0 k | 5–500 | 736 | 0.2 | 178 |
| 2 | ×8.0 k | 10–inf | 732 | 0.2 | 30 | |
| 3 | ×15.0 k | 10–inf | 1374 | 0.2 | 194 | |
| 4 | ×10.0 k | 10–300 | 917 | 0.2 | 371 | |
| Au—51 h | 5 | ×8.0 k | 5–inf | 734 | 0.4 | 552 |
| 6 | ×7.0 k | 10–1000 | 639 | 0.5 | 507 | |
| Eu—10 h | 7 | ×7.0 k | 15–500 | 643 | 1.4 | 416 |
| Eu—244 h | 8 | ×5.0 k | 5–100 | 458 | 0.5 | 742 |
| 9 | ×7.0 k | 20–400 | 639 | 1.3 | 258 | |
| 10 | ×6.0 k | 40–300 | 496 | 1.4 | 220 |
| Class | Very Angular | Angular | Sub- Angular | Sub-Rounded | Rounded | Very Rounded |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAR value | 0.12–0.17 | 0.17–0.25 | 0.25–0.35 | 0.35–0.49 | 0.49–0.70 | 0.70–1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fritz, M.; Körsten, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; Lv, Y.; Liu, M.; Wehner, S.; Fischer, C.B. Time-Dependent Size and Shape Evolution of Gold and Europium Nanoparticles from a Bioproducing Microorganism, a Cyanobacterium: A Digitally Supported High-Resolution Image Analysis. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13010130
Fritz M, Körsten S, Chen X, Yang G, Lv Y, Liu M, Wehner S, Fischer CB. Time-Dependent Size and Shape Evolution of Gold and Europium Nanoparticles from a Bioproducing Microorganism, a Cyanobacterium: A Digitally Supported High-Resolution Image Analysis. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(1):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13010130
Chicago/Turabian StyleFritz, Melanie, Susanne Körsten, Xiaochen Chen, Guifang Yang, Yuancai Lv, Minghua Liu, Stefan Wehner, and Christian B. Fischer. 2023. "Time-Dependent Size and Shape Evolution of Gold and Europium Nanoparticles from a Bioproducing Microorganism, a Cyanobacterium: A Digitally Supported High-Resolution Image Analysis" Nanomaterials 13, no. 1: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13010130
APA StyleFritz, M., Körsten, S., Chen, X., Yang, G., Lv, Y., Liu, M., Wehner, S., & Fischer, C. B. (2023). Time-Dependent Size and Shape Evolution of Gold and Europium Nanoparticles from a Bioproducing Microorganism, a Cyanobacterium: A Digitally Supported High-Resolution Image Analysis. Nanomaterials, 13(1), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13010130










