Protein Analysis of A. halleri and N. caerulescens Hyperaccumulators When Exposed to Nano and Ionic Forms of Cd and Zn
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
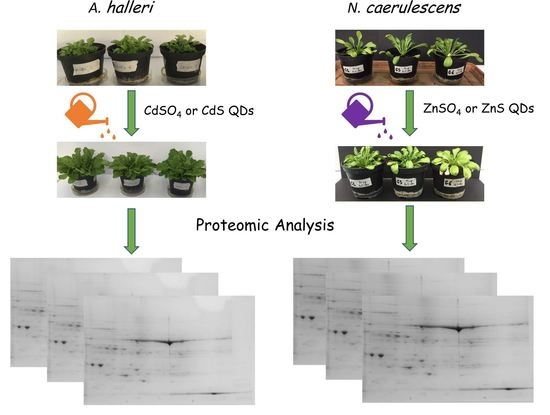
2.1. Growth Condition and Treatments
2.2. Proteins Extraction and Separation with Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (2D SDS-PAGE)
2.3. Protein Identification and Data Mining
2.4. Statistical Analysis, Data Mining, and Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plant Growth
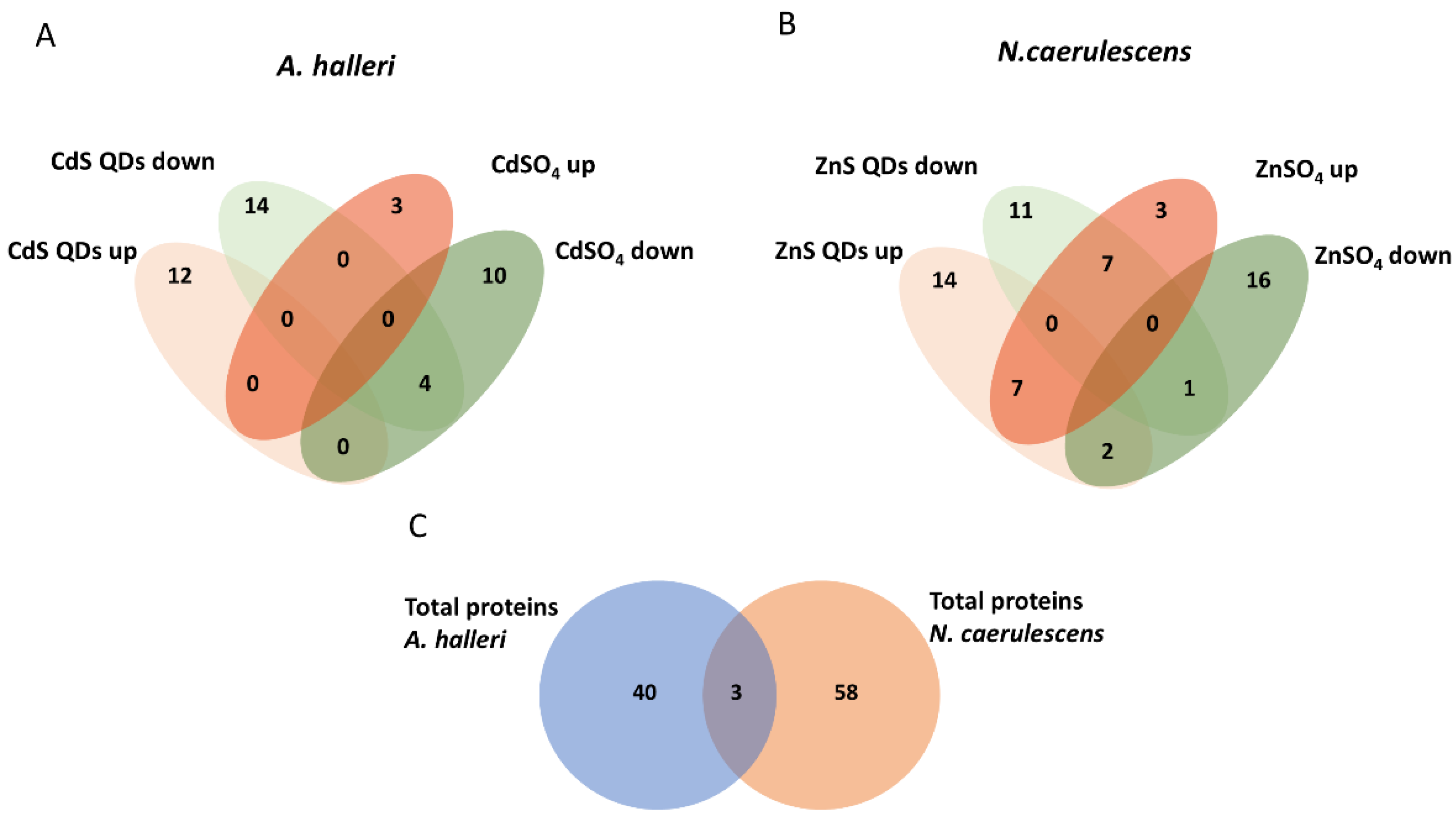
3.2. Differential Proteomic Analysis: Comparison between Plants and Treatments
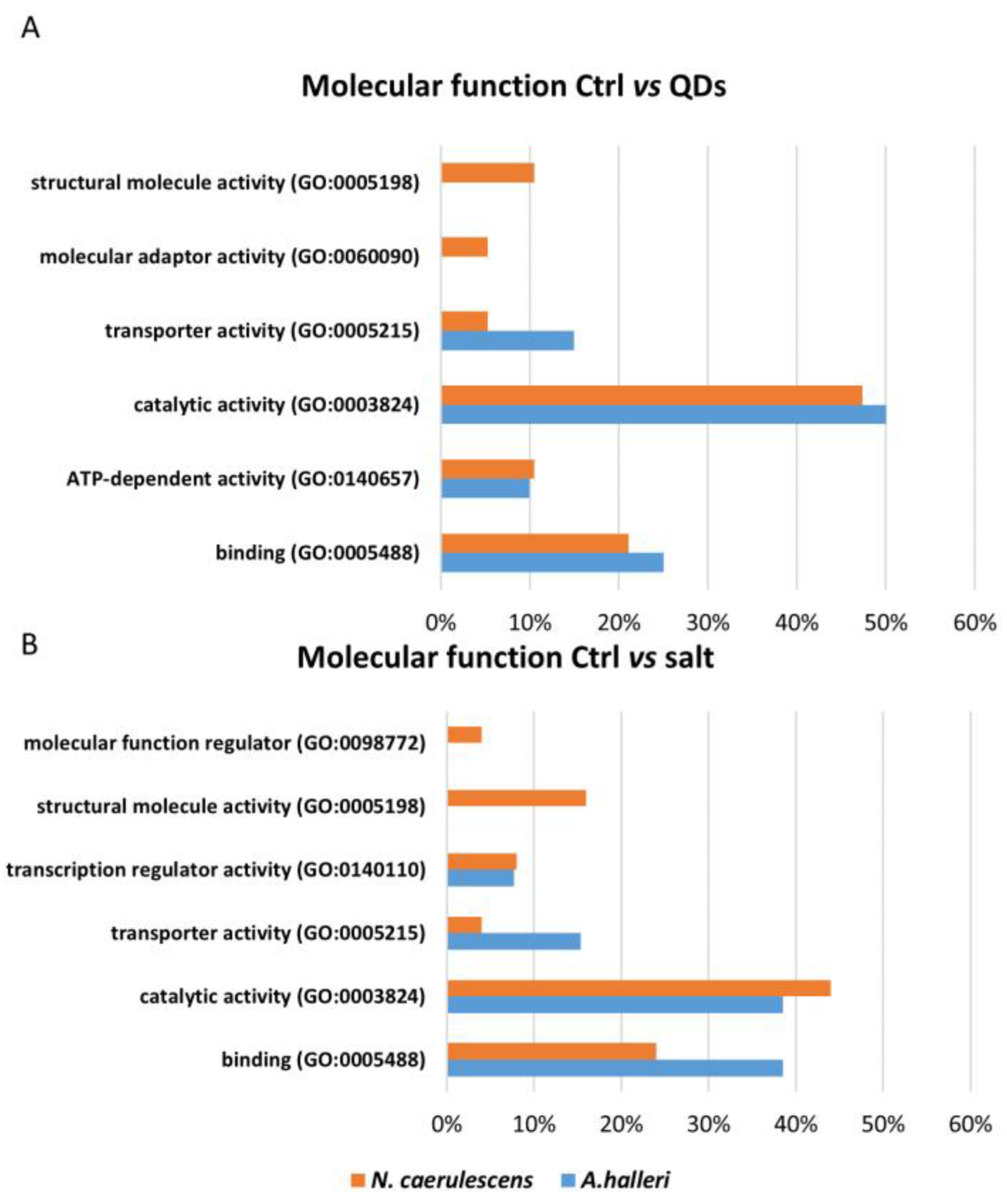
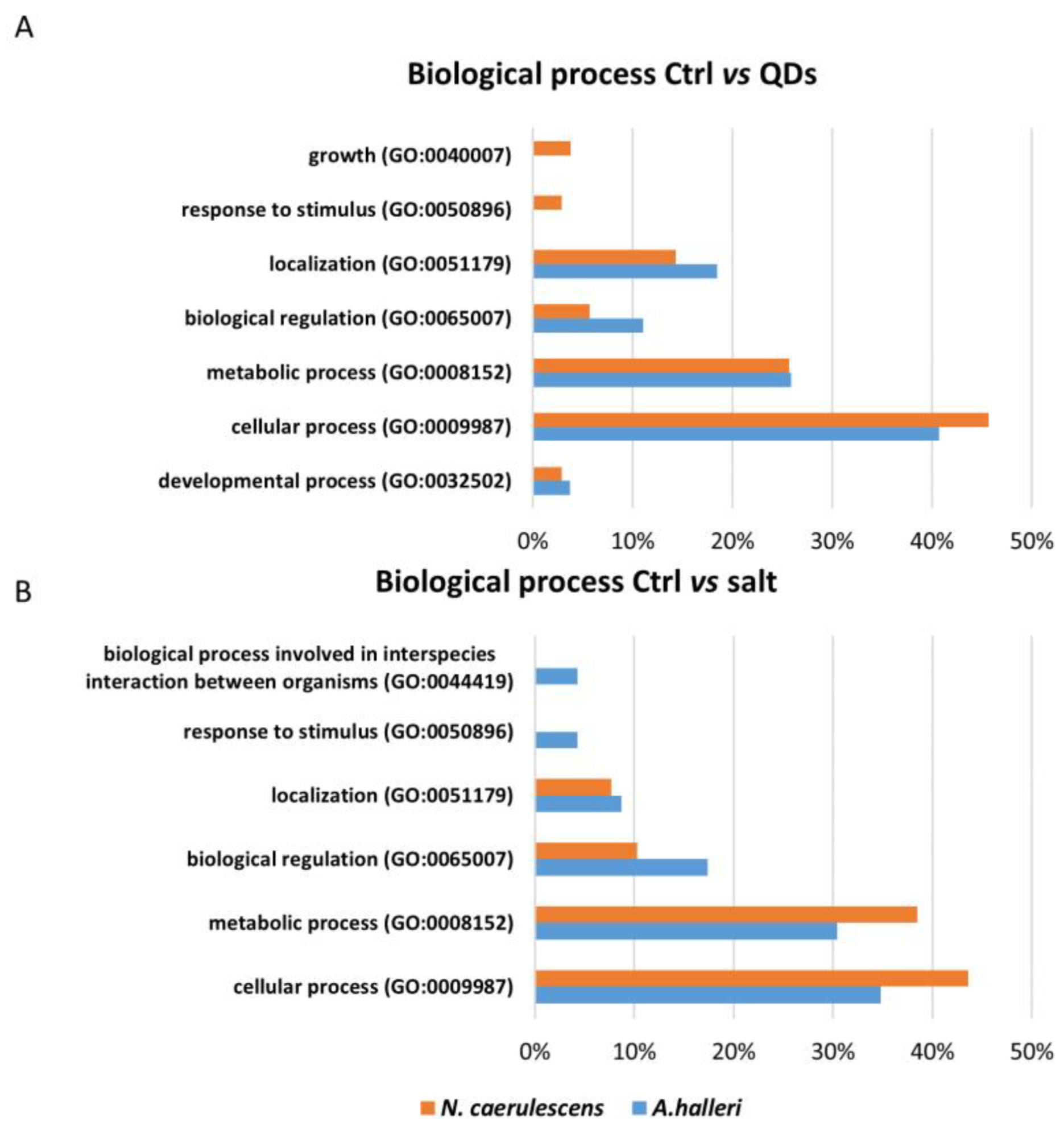
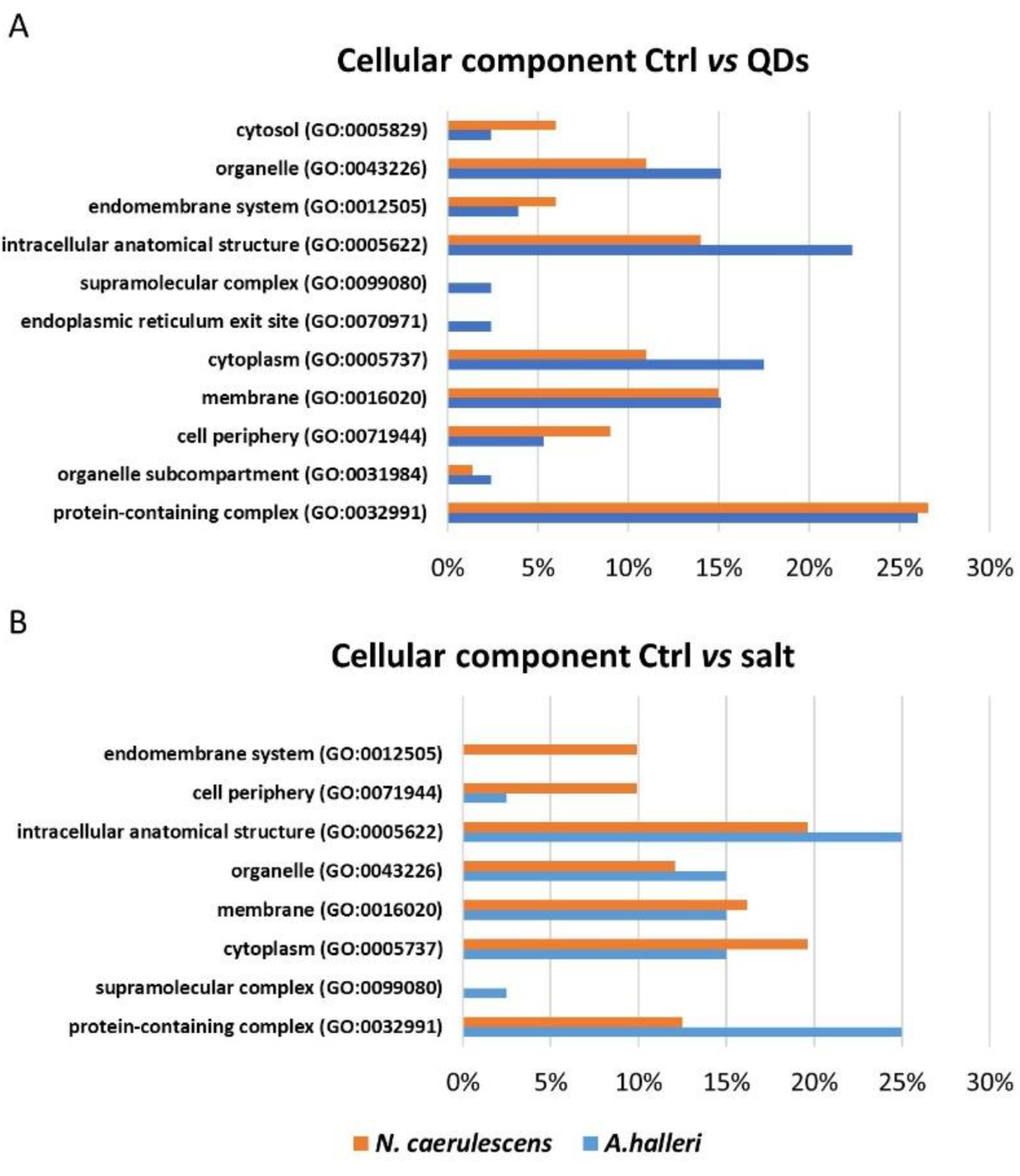
3.3. Gene Ontology Analysis
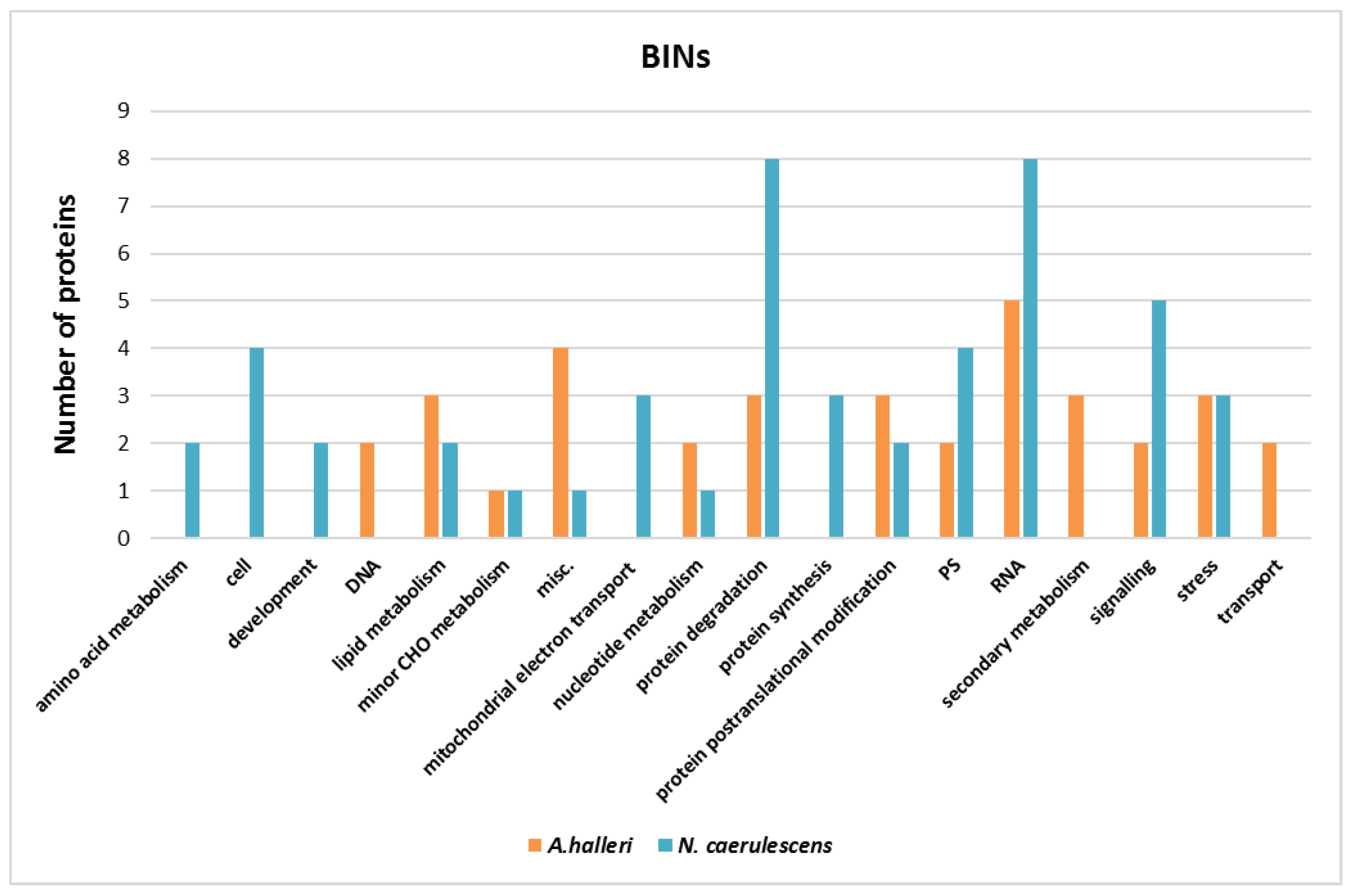
3.4. Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
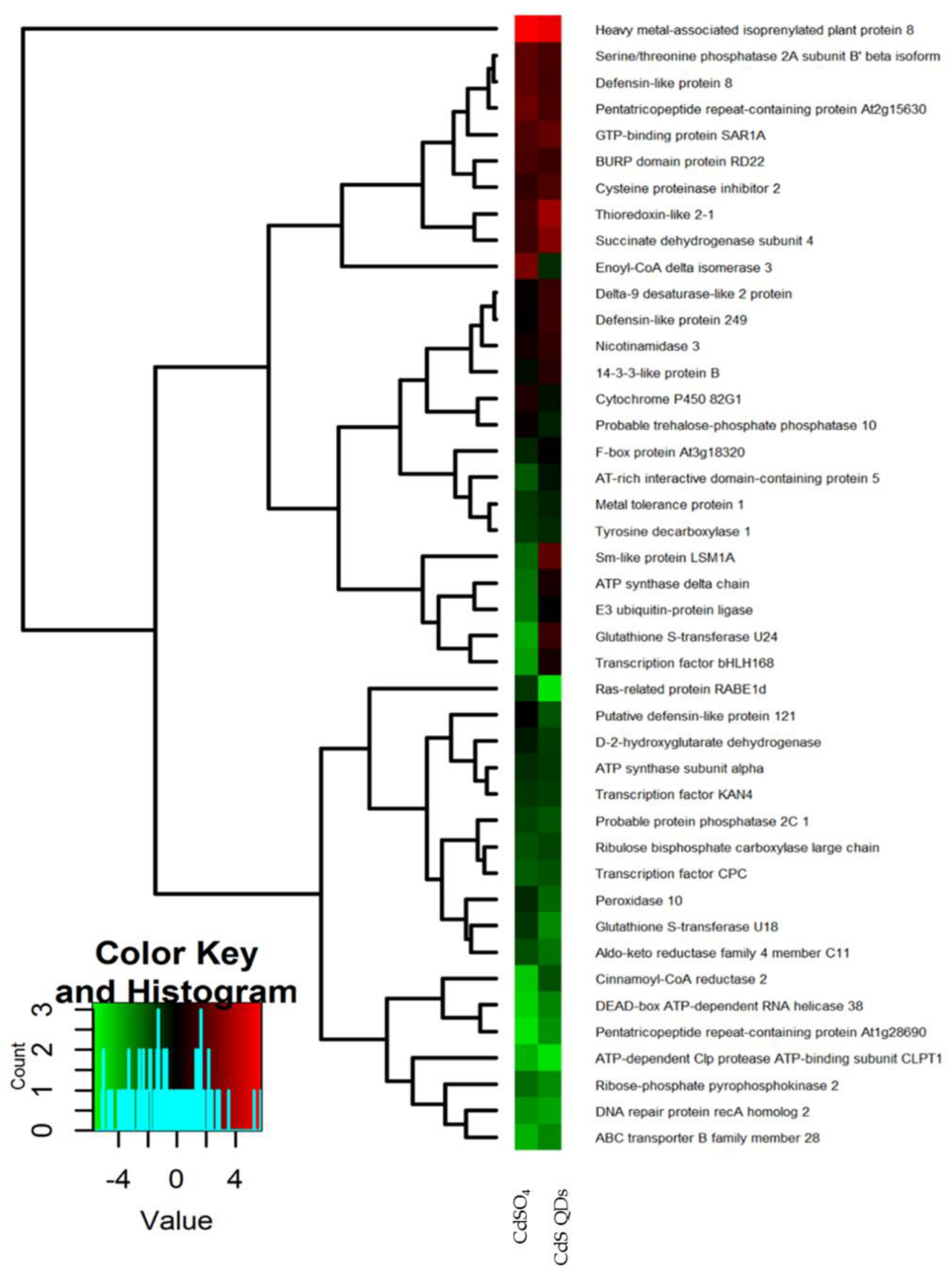
4.1. Proteomic Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins in A. halleri
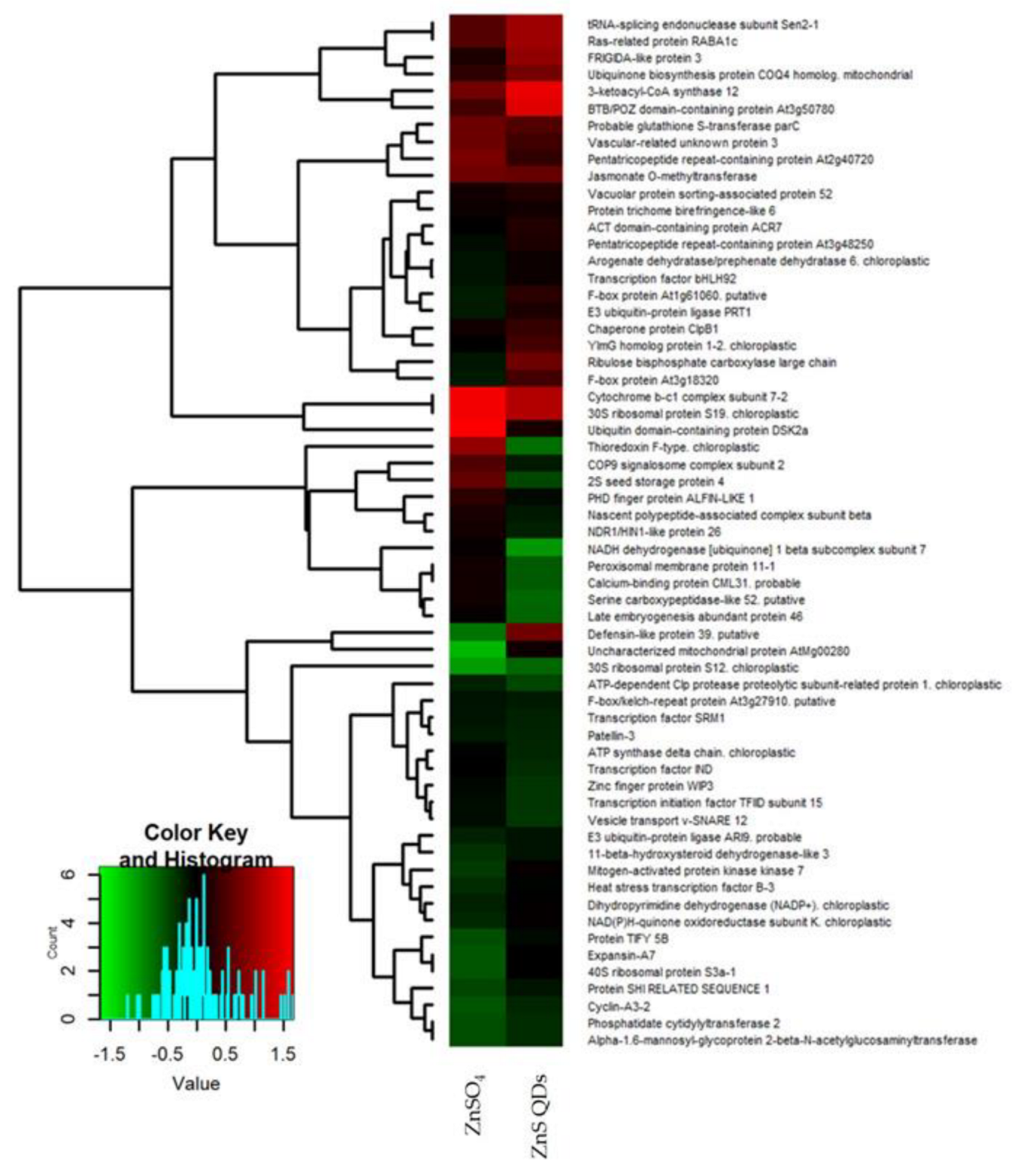
4.2. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins in N. caerulescens
4.3. Pathway Analysis
4.4. Comparison between the Two Hyperaccumulators and A. thaliana
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleiter, H. Nanostructured Materials: Basic Concepts and Microstructure. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Husen, A. Role of Nanomaterials in the Mitigation of Abiotic Stress in Plants. In Nanomaterials and Plant Potential; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 18, pp. 441–471. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, N.; Ali, L.; Ahmed, T.; Noman, M.; Adrees, M.; Shahid, M.S.; Ogunyemi, S.O.; Radwan, K.S.A.; Wang, G.; Zaki, H.E.M. Recent Advancements and Development in Nano-Enabled Agriculture for Improving Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, G.; Komatsu, S. Toxicity of Heavy Metals and Metal-Containing Nanoparticles on Plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2016, 1864, 932–944. [Google Scholar]
- Marmiroli, M.; Lepore, G.O.; Pagano, L.; d’Acapito, F.; Gianoncelli, A.; Villani, M.; Lazzarini, L.; White, J.C.; Marmiroli, N. The fate of CdS Quantum Dots in plants as revealed by Extended X-ray Absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 1150–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, J.; Uhlik, O.; Viktorova, J.; Macek, T. Phytoextraction of Heavy Metals: A Promising Tool for Clean-up of Polluted Environment? Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 871, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperiale, D.; Lencioni, G.; Marmiroli, M.; Zappettini, A.; White, J.C.; Marmiroli, N. Interaction of hyperaccumulating plants with Zn and Cd nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, U. Metal Hyperaccumulation in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behemer, S.T.; Lloyd, C.M.; Raubenheimer, D.; Stewart-Clark, J.; Knight, J.; Leighton, R.S.; Harper, F.A.; Smith, J.A.C. Metal hyperaccumulation in plants: Mechanisms of defence against insect herbivores. Funct. Ecol. 2005, 19, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fones, H.; Davis, C.A.R.; Rico, A.; Fang, F.; Smith, J.A.C.; Preston, G.M. Metal Hyperaccumulation Armors Plants against Disease. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, A.G.L.; Schat, H.; Aarts, M.G.M. Thlaspi Caerulescens, an Attractive Model Species to Study Heavy Metal Hyperaccumulation in Plants. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigola, D.; Fiers, M.; Vurro, E.; Aarts, M.G.M. The Heavy Metal Hyperaccumulator Thlaspi Caerulescens Expresses Many Species-Specific Genes, as Identified by Comparative Expressed Sequence Tag Analysis. New Phytol. 2006, 170, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, R.D.; Schwartz, C.; Morel, J.L.; Edmondson, J. Distribution and Metal-Accumulating Behavior of Thlaspi Caerulescens and Associated Metallophytes in France. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2001, 3, 145–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, V.; Lo, J.C.; Yeh, K.C. Control of Zn Uptake in Arabidopsis Halleri: A Balance between Zn and Fe. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Ent, A.; Baker, A.J.M.; Reeves, R.D.; Pollard, A.J.; Schat, H. Hyperaccumulators of Metal and Metalloid Trace Elements: Facts and Fiction. Plant Soil 2013, 362, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, G.; Marmiroli, N. The Proteomics of Heavy Metal Hyperaccumulation by Plants. J. Proteom. 2013, 79, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, H.; Narayanc, M.; Peralta-Videac, J.-R.; Lam, S.S. Exploring the significance of nanomaterials and organic amendments—Prospect for phytoremediation of contaminated agroecosystem. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 11960. [Google Scholar]
- Villani, M.; Calestani, D.; Lazzarini, L.; Zanotti, L.; Mosca, R.; Zappettini, A. Extended functionality of ZnO nanotetrapods by solution-based coupling with CdS nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperiale, D.; Lencioni, G.; Marmiroli, M.; Paesano, L.; Zappettini, A.; White, J.C.; Marmiroli, N. Data on the Interaction of Hyperaccumulating Plants with Nanoscale Metals Zn and Cd. Data Br. 2022, 42, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, V.; Zappettini, A.; Villani, M.; Marmiroli, N.; Marmiroli, M. Comparative analysis of proteins regulated during cadmium sulfide Quantum Dots response in Arabidopsis thaliana wild type and tolerant mutants. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramagli, L.S.; Rodriguez, L.V. Quantitation of Microgram Amounts of Protein in Two-dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Sample Buffer. Electrophoresis 1985, 6, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinati, S.; Dal Corso, G.; Bona, E.; Corbella, M.; Lampis, S.; Cecconi, D.; Polati, R.; Berta, G.; Vallini, G.; Furini, S. Proteomic analysis of Arabidopsis halleri shoots in response to the heavy metals cadmium and zinc and rhizosphere microorganisms. Proteomics 2009, 9, 4837–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havliš, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-Gel Digestion for Mass Spectrometric Characterization of Proteins and Proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visioli, G.; Vincenzi, S.; Marmiroli, M.; Marmiroli, N. Correlation between phenotype and proteome in the Ni hyperaccumulator Noccaea caerulescens subsp. caerulescens. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 77, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuti, N.; Kelleher, N.L. Decoding protein modifications using top-down mass spectrometry. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ma, L.; Huang, C.; Li, Q.; Nice, E.C. Proteomic Profiling of Human Plasma for Cancer Biomarker Discovery. Proteomics 2017, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Carberry, S.; Ohlendieck, K. Gel Electrophoresis-Based Proteomics of Senescent Tissues. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1048, 229–246. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Fonslow, B.R.; Shan, B.; Baek, M.-C.; Yates, J.R. Protein Analysis by Shotgun/Bottom-up Proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2343–23942345. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Fernández, R.; Davies, T.G.E.; Coleman, J.O.D.; Rea, P.A. The Arabidopsis Thaliana ABC Protein Superfamily, a Complete Inventory. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30231–30244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.P.; Skipsey, M.; Edwards, R. Roles for Glutathione Transferases in Plant Secondary Metabolism. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellmann, S.; Schnittger, A.; Kirik, V.; Wada, T.; Okada, K.; Beerman, A.; Thumfahrt, J.; Jürgens, G.; Hülskamp, M. TRIPTYCHON and CAPRICE Mediate Lateral Inhibition during Trichome and Root Hair Patterning in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5036–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Li, X.; Cui, D.; Wu, L.; Parkin, I.; Gruber, M.Y. A New Dominant Arabidopsis Transparent Testa Mutant, Sk21-D, and Modulation of Seed Flavonoid Biosynthesis by KAN4. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2010, 8, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupper, H.; Kochian, L.V. Transcriptional regulation of metal transport genes and mineral nutrition during acclimatization to cadmium and zinc in the Cd/Zn hyperaccumulator, Thlaspi caerulescens (Ganges population). New Phytol. 2010, 185, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.J.; Jiang, R.F.; Dunham, S.J.; McGrath, S.P. Cadmium uptake, translocation and tolerance in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. New Phytol. 2006, 172, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schvartzman, M.S.; Corso, M.; Fataftah, N.; Scheepers, M.; Nouet, C.; Bosman, B.; Carnol, M.; Motte, P.; Verbruggen, N.; Hanikenne, M. Adaptation to high zinc depends on distinct mechanisms in metallicolous populations of Arabidopsis halleri. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abreu-Neto, J.B.; Turchetto-Zolet, A.C.; De Oliveira, L.F.V.; Bodanese Zanettini, M.H.; Margis-Pinheiro, M. Heavy Metal-Associated Isoprenylated Plant Protein (HIPP): Characterization of a Family of Proteins Exclusive to Plants. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, V.; Srivastava, V.; Bulone, V.; Zappettini, A.; Villani, M.; Marmiroli, N.; Marmiroli, M. Proteomic analysis identifies markers of exposure to Cadmium Sulphide Quantum Dots (CdS QDs). Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, L.; Marmiroli, M.; Villani, M.; Magnani, J.; Rossi, R.; Zappettini, A.; White, J.C.; Marmiroli, N. Engineered Nanomaterial Exposure Affects Organelle Genetic Material Replication in Arabidopsis Thaliana. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmiroli, M.; Pagano, L.; Rossi, R.; La Torre-roche, R.D.; Lepore, G.O.; Ruotolo, R.; Gariani, G.; Bonanni, V.; Pollastri, S.; Puri, A.; et al. Copper Oxide Nanomaterial Fate in Plant Tissue: Nanoscale Impacts on Reproductive Tissues. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10769–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chung, K.P.; Li, B.; Lai, C.M.; Lam, S.K.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Gao, C.; Luo, M.; Wong, K.B.; et al. Unique COPII Component AtSar1a/AtSec23a Pair Is Required for the Distinct Function of Protein ER Export in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14360–14365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangoor, I.; Peled-Zehavi, H.; Levitan, A.; Pasand, O.; Danon, A. A Small Family of Chloroplast Atypical Thioredoxins. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Dauk, M.; Ramadan, H.; Yang, H.; Seamons, L.E.; Haslam, R.P.; Beaudoin, F.; Ramirez-Erosa, I.; Forseille, L. Involvement of Arabidopsis Acyl-Coenzyme A Desaturase-Like2 (At2g31360) in the Biosynthesis of the Very-Long-Chain Monounsaturated Fatty Acid Components of Membrane Lipids. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruotolo, R.; Maestri, E.; Pagano, L.; Marmiroli, M.; White, J.C.; Marmiroli, N. Plant response to metal-containing engineered nanomaterials: An omics-based perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2451–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koussevitzky, S.; Stanne, T.M.; Peto, C.A.; Giap, T.; Sjögren, L.L.E.; Zhao, Y.; Clarke, A.K.; Chory, J. An Arabidopsis Thaliana Virescent Mutant Reveals a Role for ClpR1 in Plastid Development. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 63, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiwald, D.; Dietzmann, A.; Jahns, P.; Pesaresi, P.; Joliot, P.; Joliot, A.; Levin, J.Z.; Salamini, F.; Leister, D. Knock-out of the Genes Coding for the Rieske Protein and the ATP-Synthase δ-Subunit of Arabidopsis. Effects on Photosynthesis, Thylakoid Protein Composition, and Nuclear Chloroplast Gene Expression. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; White, J.C.; Xing, B. CuO Nanoparticle Interaction with Arabidopsis Thaliana: Toxicity, Parent-Progeny Transfer, and Gene Expression. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6008–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusk, S.; Sohlberg, J.J.; Magnus Eklund, D.; Sundberg, E. Functionally Redundant SHI Family Genes Regulate Arabidopsis Gynoecium Development in a Dose-Dependent Manner. Plant J. 2006, 47, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhagen, I.; Huep, G.; Lu, G.H.; Strompen, G.; Weisshaar, B.; Sagasser, M. Weird fingers: Functional analysis of WIP domain proteins. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3116–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nover, L.; Bharti, K.; Döring, P.; Mishra, S.K.; Ganguli, A.; Scharf, K.D. Arabidopsis and the Heat Stress Transcription Factor World: How Many Heat Stress Transcription Factors Do We Need? Cell Stress Chaperones 2001, 6, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupinska, K.; Blanco, N.E.; Oetke, S.; Zottini, M. Genome Communication in Plants Mediated by Organelle–Nucleus-Located Proteins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestri, E.; Marmiroli, M.; Visioli, G.; Marmiroli, N. Metal tolerance and hyperaccumulation: Costs and trade-offs between traits and environment. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Akama, K.; Junker, V.; Beier, H. Identification of Two Catalytic Subunits of TRNA Splicing Endonuclease from Arabidopsis Thaliana. Gene 2000, 257, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmiroli, M.; Imperiale, D.; Pagano, L.; Villani, M.; Zappettini, A.; Marmiroli, M. The proteomic response of Arabidopsis thaliana to cadmium sulfide quantum dots, and its correlation with the transcriptomic response. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallo, V.; Serianni, V.M.; Imperiale, D.; Zappettini, A.; Villani, M.; Marmiroli, M.; Marmiroli, N. Protein Analysis of A. halleri and N. caerulescens Hyperaccumulators When Exposed to Nano and Ionic Forms of Cd and Zn. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234236
Gallo V, Serianni VM, Imperiale D, Zappettini A, Villani M, Marmiroli M, Marmiroli N. Protein Analysis of A. halleri and N. caerulescens Hyperaccumulators When Exposed to Nano and Ionic Forms of Cd and Zn. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(23):4236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234236
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallo, Valentina, Valentina M. Serianni, Davide Imperiale, Andrea Zappettini, Marco Villani, Marta Marmiroli, and Nelson Marmiroli. 2022. "Protein Analysis of A. halleri and N. caerulescens Hyperaccumulators When Exposed to Nano and Ionic Forms of Cd and Zn" Nanomaterials 12, no. 23: 4236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234236
APA StyleGallo, V., Serianni, V. M., Imperiale, D., Zappettini, A., Villani, M., Marmiroli, M., & Marmiroli, N. (2022). Protein Analysis of A. halleri and N. caerulescens Hyperaccumulators When Exposed to Nano and Ionic Forms of Cd and Zn. Nanomaterials, 12(23), 4236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234236