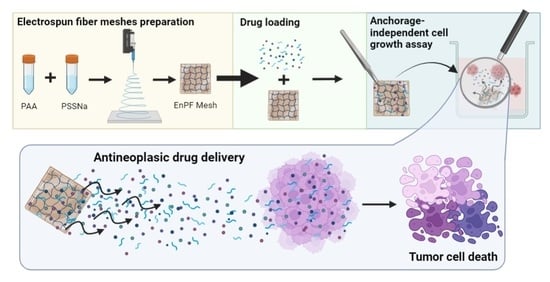
Electrospun Poly(acrylic acid-co-4-styrene sulfonate) as Potential Drug-Eluting Scaffolds for Targeted Chemotherapeutic Delivery Systems on Gastric (AGS) and Breast (MDA-Mb-231) Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactants
2.2. Synthesis of Homo- and Copolymers
2.3. Preparation of Electrospun Fiber Meshes by Electrospinning
2.4. Caracterización de EPnF Meshes
2.4.1. Spectroscopic Characterization
2.4.2. Contact Angle and Surface Tension of EPnF Meshes
- σL: Surface tension DMEM
- σs: Solid surface tension
- θ: Contact angle between the surface of the solid and water
- m: Drop mass
- g: Gravitational acceleration (9.8 m/s2)
- γ: Surface tension at the droplet-air interface
- 2 · π · r: Wet perimeter
2.4.3. Morphological Analysis
2.5. Biological Evaluation
2.5.1. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
2.5.2. Colony Formation Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spectroscopic Characterization of PAA, PSS Homopolymers, and P(AA-co-SS) Copolymers
3.2. Characterization of EPnF Meshes
3.2.1. Contact Angle and Surface Tension of EPnF Meshes
3.2.2. Optical and Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.3. Biological Evaluation
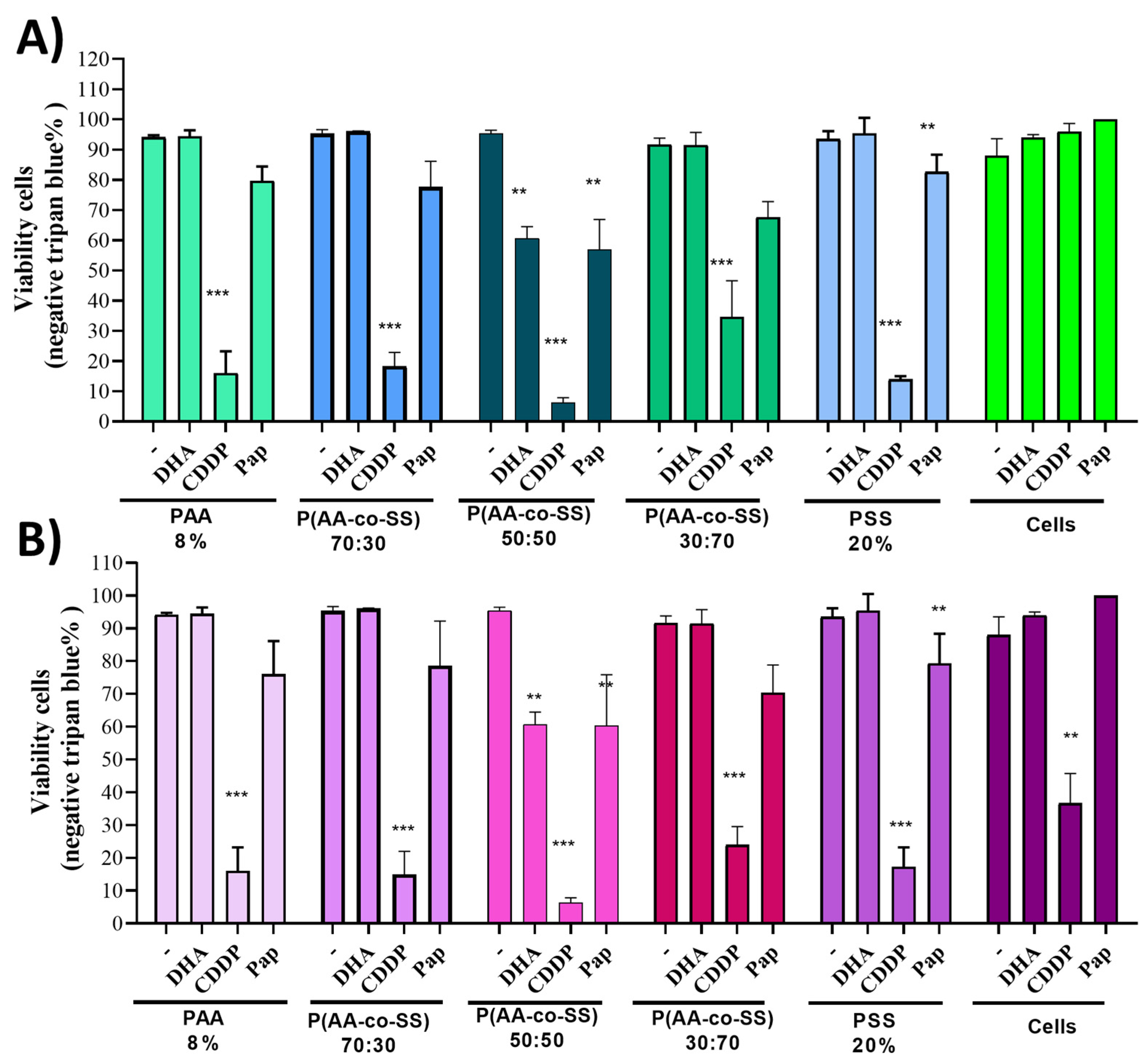
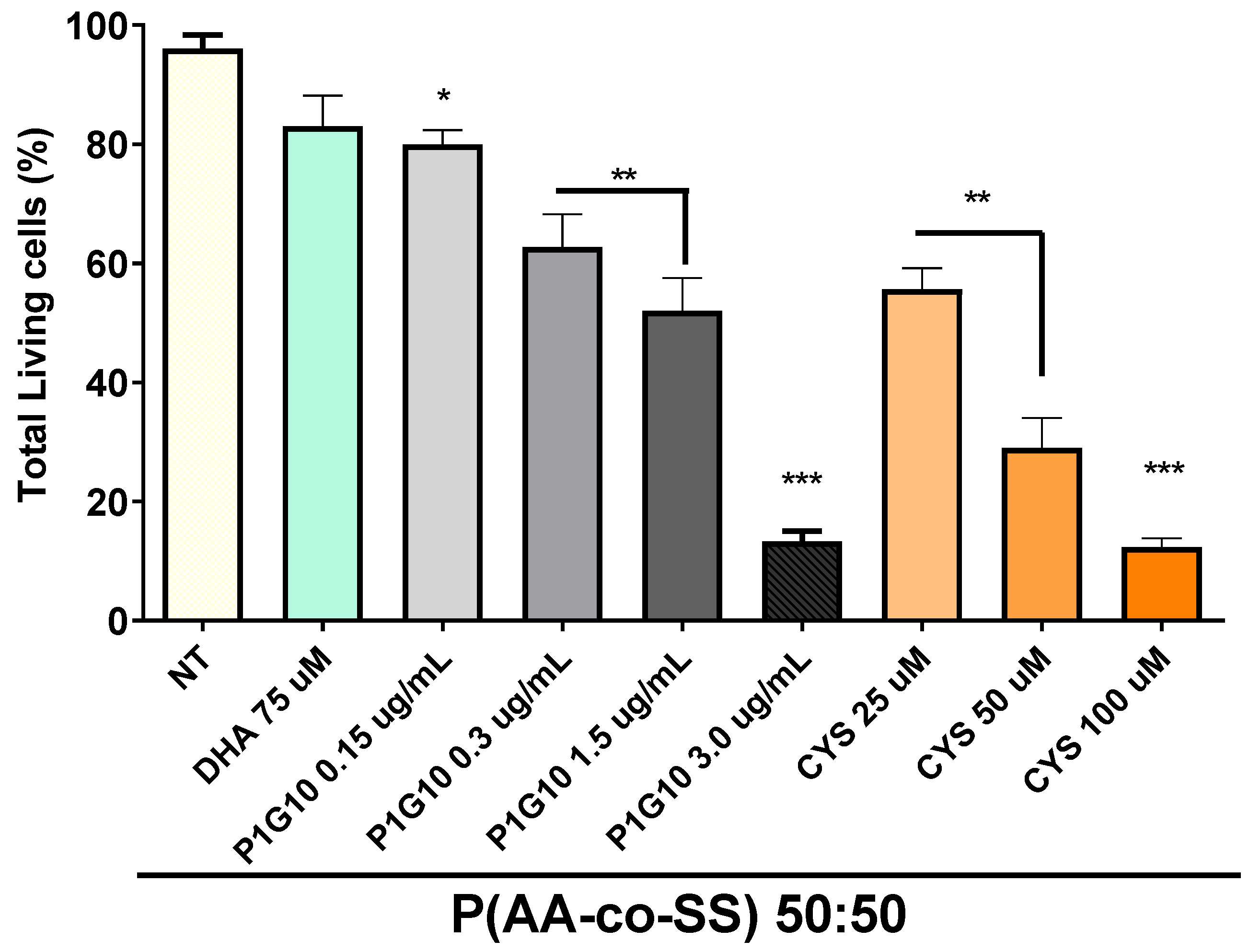
3.3.1. Viability Assay in Gastric Cancer Cells Assays of EPnF Meshes
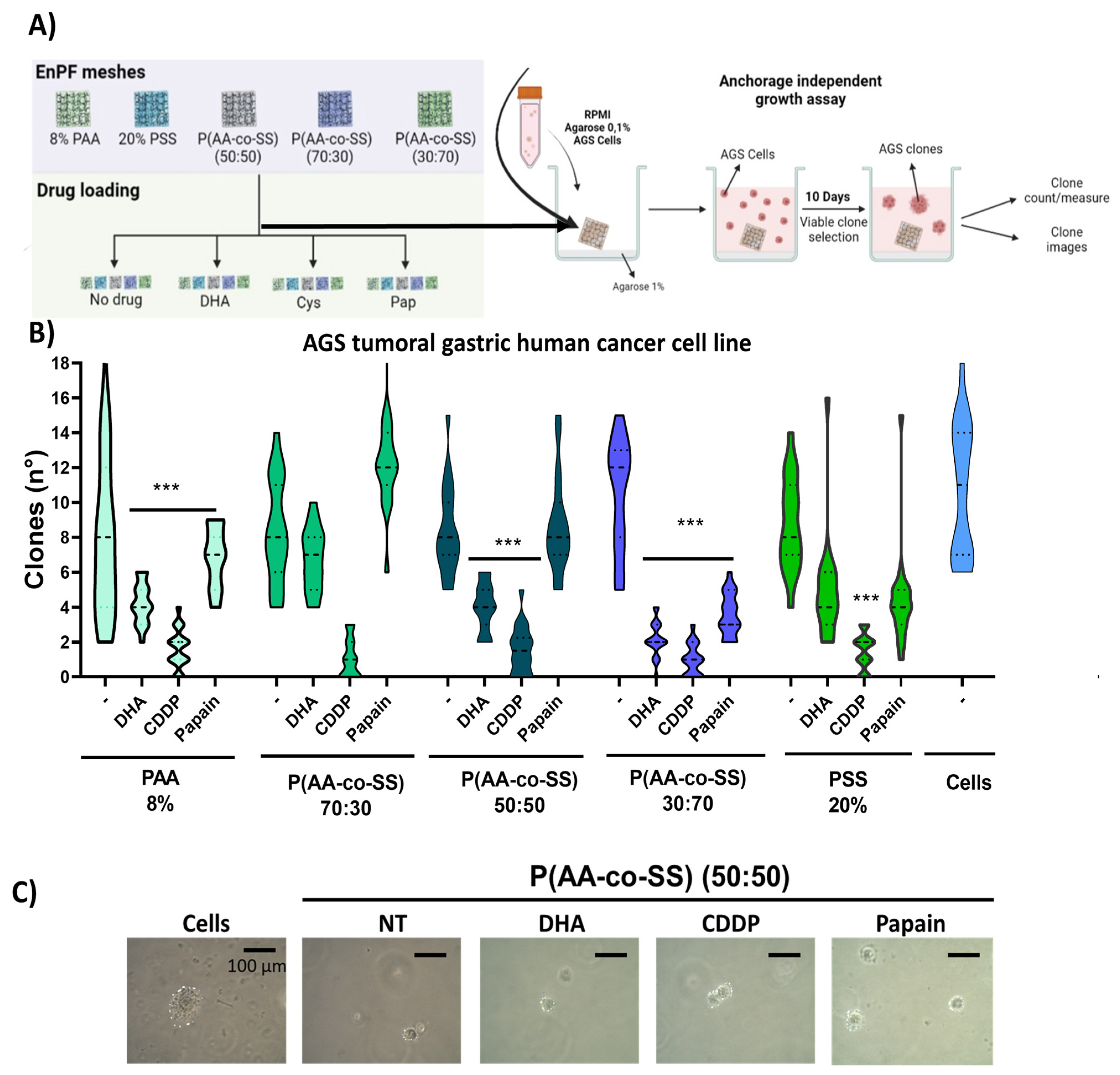
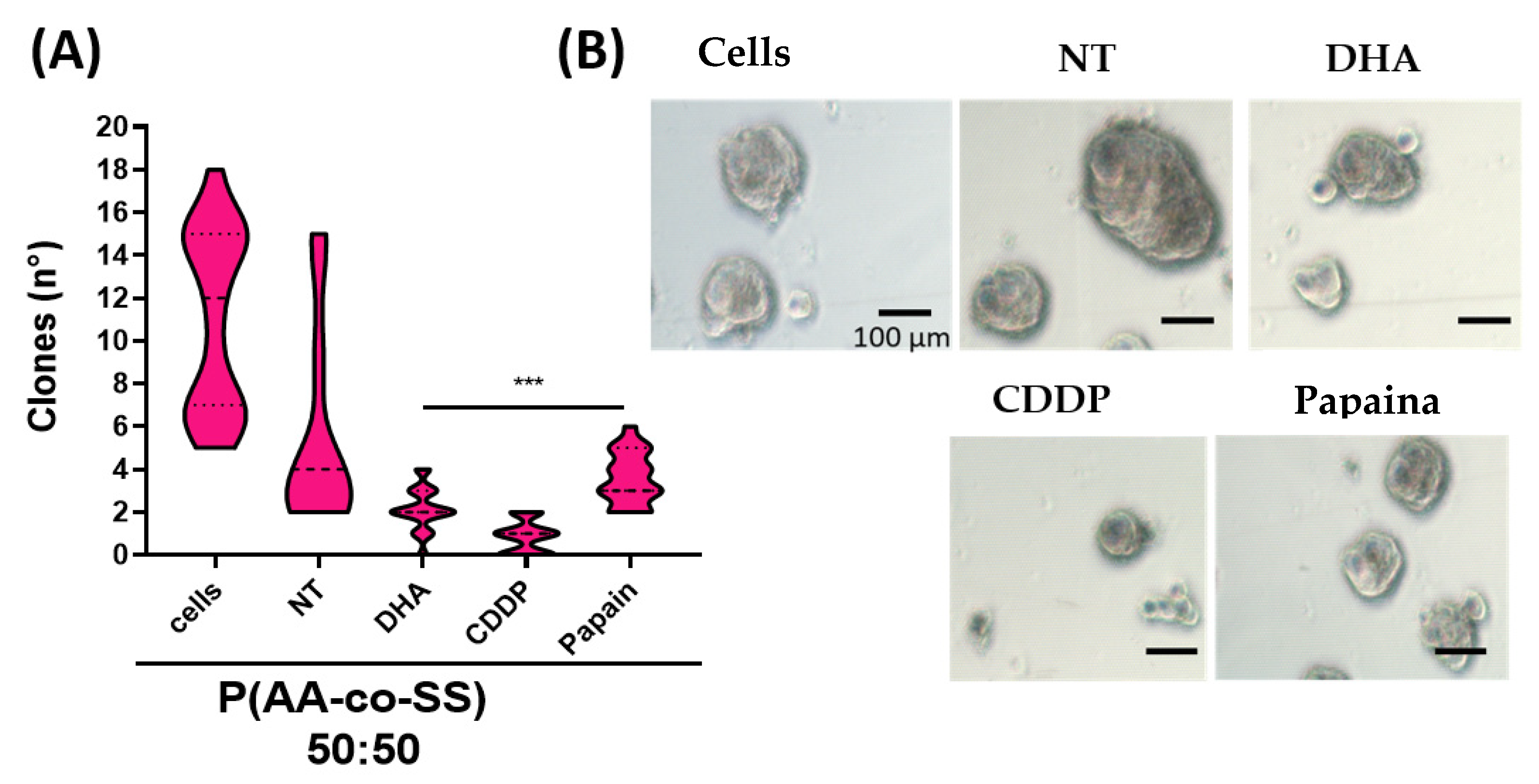
3.3.2. Clonogenic Assay in Gastric and Breast Cancer Cells Using EPnF Meshes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumbar, S.; Laurencin, C.; Deng, M. Natural and Synthetic Biomedical Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Newnes: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Lin, T. Needleless Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Technology and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, P.H.; Cho, J.Y. Myocardial Tissue Engineering Using Electrospun Nanofiber Composites. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, R.; Srinadhu, E.S.; Subramanian, B.; Nallani, S. β-PVDF Based Electrospun Nanofibers—A Promising Material for Developing Cardiac Patches. Med. Hypotheses 2019, 122, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, A.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. Electrospun Nanofibers for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Boda, S.K.; Batra, S.K.; Li, X.; Xie, J. Emerging Roles of Electrospun Nanofibers in Cancer Research. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1701024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, O.S.; Olafson, K.N.; Pillai, P.S.; Mitchell, M.J.; Langer, R. Advances in Biomaterials for Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1705328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, C.M.; Harris, M.; Choi, L.; Murali, V.P.; Guerra, F.D.; Jennings, J.A. Stimuli-Responsive Drug Release from Smart Polymers. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Zhang, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Liu, X. pH-Sensitive Biomaterials for Drug Delivery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, A.A.; Dalmoro, A.; de Santis, F.; Lamberti, G. Synthesis and Characterization of P(MMA-AA) Copolymers for Targeted Oral Drug Delivery. Polym Bull. 2009, 62, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Jana, S. Functional Biomaterials. Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alkekhia, D.; Hammond, P.T.; Shukla, A. Layer-by-layer biomaterials for drug delivery. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 22, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Wright, S.L. Solute Diffusion in Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly (Acrylic Acid) Interpenetrating Networks. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 8798–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacík, I.; Stach, M.; Kasák, P.; Semak, V.; Uhelská, L.; Chovancová, A.; Reinhold, G.; Kilz, P.; Delaittre, G.; Charleux, B.; et al. SEC Analysis of Poly(Acrylic Acid) and Poly(Methacrylic Acid). Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Poly(Acrylic Acid) Nanocomposites: Design of Advanced Materials. J. Plast. Film Sheeting 2021, 37, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, K.; Zuchora, M.; Sencadas, V.; Tehei, M.; Lerch, M.; Thorpe, N.; Rosenfeld, A.; Dou, S.X.; Liu, H.K.; Konstantinov, K. Synthesis of Methotrexate-Loaded Tantalum Pentoxide–Poly(Acrylic Acid) Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Release Applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 538, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, B.C.; Bourne, N.; Marcellino, D.; Kirkpatrick, R.; Strauss, D.M.; Zaneveld, L.J.D.; Waller, D.P.; Anderson, R.A.; Chany, C.J.; Barham, B.J.; et al. Poly(Sodium 4-Styrene Sulfonate): An Effective Candidate Topical Antimicrobial for the Prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattananuwat, P.; Tagaya, M.; Kobayashi, T. Controllable Nanoporous Fibril-like Morphology by Layer-by- Layer Self-Assembled Films of Bioelectronics Poly(Pyrrole-co-Formyl Pyrrole)/Polystyrene Sulfonate for Biocompatible Electrode. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 99, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranti, A.S.; Schander, A.; Bödecker, A.; Lang, W. PEDOT: PSS Coating on Gold Microelectrodes with Excellent Stability and High Charge Injection Capacity for Chronic Neural Interfaces. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 275, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamizar-Sarmiento, M.G.; Molina-Soto, E.F.; Guerrero, J.; Shibue, T.; Nishide, H.; Moreno-Villoslada, I.; Oyarzun-Ampuero, F.A. A New Methodology to Create Polymeric Nanocarriers Containing Hydrophilic Low Molecular-Weight Drugs: A Green Strategy Providing a Very High Drug Loading. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2892–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, R.E.; Zhong, X.; Youle, P.J.; Wang, Q.G.; Wimpenny, I.; Downes, S.; Hoyland, J.A.; Watts, D.C.; Gough, J.E.; Budd, P.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(Vinylphosphonic Acid-co-Acrylic Acid) Copolymers for Application in Bone Tissue Scaffolds. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 2656–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.G.; Wimpenny, I.; Dey, R.E.; Zhong, X.; Youle, P.J.; Downes, S.; Watts, D.C.; Budd, P.M.; Hoyland, J.A.; Gough, J.E. The Unique Calcium Chelation Property of Poly(Vinyl Phosphonic Acid-co-Acrylic Acid) and Effects on Osteogenesis in Vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2018, 106, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Gwon, G.; Ha, J.H.; Kim, D.; Eom, K.J.; Park, J.H.; Kang, S.J.; Kwak, B.; Hong, J.L.; Lee, S.; et al. Enhancing the Conductivity of PEDOT:PSS Films for Biomedical Applications via Hydrothermal Treatment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, A.; Venkatesan, J.K.; Castner, D.G.; Cucchiarini, M.; Migonney, V. Analysis of Early Cellular Responses of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Fibroblasts Seeded on Different Molecular Weight Polycaprolactone Films Functionalized by a Bioactive Poly(Sodium Styrene Sulfonate) Polymer. Biointerphases 2019, 14, 041004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Yang, X.; Che, X.; Yang, M.; Zhai, G. Biomedical Application and Controlled Drug Release of Electrospun Fibrous Materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajdič, S.; Planinšek, O.; Gašperlin, M.; Kocbek, P. Electrospun Nanofibers for Customized Drug-Delivery Systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, M.; Romero, C.; Butto, N.; Neira-Carrillo, A. Use of Electrospun PCL meses for 3D Cell Cultures of Epithelial. In Proceedings of the 1st National Congress of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, Santiago, Chile, 6–7 November 2017; Lambert Academic Publishing (LAP): Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Subedi, D.P. Contact Angle Measurement for the Surface Characterization of Solids. Himal. Phys. 2011, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, M.E. Young-dupre revisited. Langmuir 1995, 11, 3585–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Herrero, M.; Gómez-Tejedor, J.A.; Vallés-Lluch, A. PLA/PCL Electrospun Membranes of Tailored Fibres Diameter as Drug Delivery Systems. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, J.R.; Esteban, B. A Simple Laboratory Experiment to Measure the Surface Tension of a Liquid in Contact with Air. Eur. J. Phys. 2014, 35, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.B.; Ravindra, P.; Chan, E.S. New Drop Weight Analysis for Surface Tension Determination of Liquids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 332, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobos-González, L.; Silva, V.; Araya, M.; Restovic, F.; Echenique, J.; Oliveira-Cruz, L.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Briones, M.; Villegas, J.; Villota, C.; et al. Targeting Antisense Mitochondrial ncRNAs Inhibits Murine Melanoma Tumor Growth and Metastasis through Reduction in Survival and Invasion Factors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58331–58350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio, D.A.; Urbano, B.F.; Rivas, B.L. Water-Soluble Polymers with the Ability to Remove Amoxicillin as Emerging Pollutant from Water. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carees, F.O.; Sivadasan, K.; Somasundaran, P.; Turro, N.J. Interpolymer Complexation of Poly(Acrylic Acid) and Poly (Acrylamide): Structural and Dynamic Studies by Solution-and Solid-State NMR. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin, J.E.; Reisch, A.; Markarian, M.Z.; Schlenoff, J.B. Sulfonation of Polystyrene: Toward the “Ideal” Polyelectrolyte. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 2416–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Bakar, N.F.A.; Ling, T.H.; Ideris, N.; Zain, Z.H.M.; Radacsi, N. Morphology and Conductivity Evaluation of Electrospun Polyacrylic Acid (PAA) Microfiber. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 17, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, S.; Schmid, R.; Wieland, A.; Strissel, P.L.; Strick, R.; Fischer, L.; Thievessen, I.; Kataev, E.; Arkudas, A.; Horch, R.E.; et al. Role of Fiber Thickness and Surface Treatment of Electrospun Polycaprolactone Matrices on the Growth of Different Breast Cancer-Associated Cells. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrame, J.M.; Guindani, C.; Novy, M.G.; Felipe, K.B.; Sayer, C.; Pedrosa, R.C.; Hermes De Araújo, P.H. Covalently Bonded N-Acetylcysteine-Polyester Loaded in PCL Scaffolds for Enhanced Interactions with Fibroblasts. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2021, 4, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, T.A.; Tolba, E.; Gaffer, H.; Kamel, S. Development of Electrospun Nanofibrous-Walled Tubes for Potential Production of Photoluminescent Endoscopes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 10044–10055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Guo, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. A Negatively Charged Loose Nanofiltration Membrane by Blending with Poly (Sodium 4-Styrene Sulfonate) Grafted SiO2 via SI-ATRP for Dye Purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 146, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luraghi, A.; Peri, F.; Moroni, L. Electrospinning for Drug Delivery Applications: A Review. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Kuang, H.; You, Z.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. Electrospun Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering with Drug Loading and Release. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug Solubility: Importance and Enhancement Techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidaurre, S.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Burzio, V.A.; Briones, M.; Villota, C.; Villegas, J.; Echenique, J.; Oliveira-Cruz, L.; Araya, M.; Borgna, V.; et al. Down-Regulation of the Antisense Mitochondrial Non-Coding RNAs (NcRNAs) Is a Unique Vulnerability of Cancer Cells and a Potential Target for Cancer Therapy. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27182–27198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, L.; Lobos-González, L.; Reyna-Jeldes, M.; Cerda, D.; de la Fuente-Ortega, E.; Castro, P.; Bernal, G.; Coddou, C. The Ω-3 Fatty Acid Docosahexaenoic Acid Selectively Induces Apoptosis in Tumor-Derived Cells and Suppress Tumor Growth in Gastric Cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 896, 173910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Bernard Tchounwou, P. Cisplatin in Cancer Therapy: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Eur, J. Pharmacol 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedeszko, C.; Sloane, B.F. Cysteine Cathepsins in Human Cancer. Biol. Chem. 2004, 385, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Dong, H.; Yang, S.; Guo, H. Cathepsins in Digestive Cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41690–41700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, S.; Pandit, A. Multi-modal delivery of therapeutics using biomaterial scaffolds. J. Mater. Chem B 2014, 2, 6692–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, W.W.; Du, N.R.; Chan, C.H.; Silva, E.A.; Mooney, D.J. Mimicking nature by codelivery of stimulant and inhibitor to create temporally stable and spatially restricted angiogenic zones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17933–17938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Stem Cells in Tissues, Organoids, and Cancers. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 4043–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomokiyo, A.; Wada, N.; Maeda, H. Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells: Regenerative Potency in Periodontium. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolios, G.; Moodley, Y. Introduction to Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine. Respiration 2012, 85, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, S.; Domingues, A.; Ratajczak, J.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Potential Clinical Applications of Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine. In Stem Cells; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
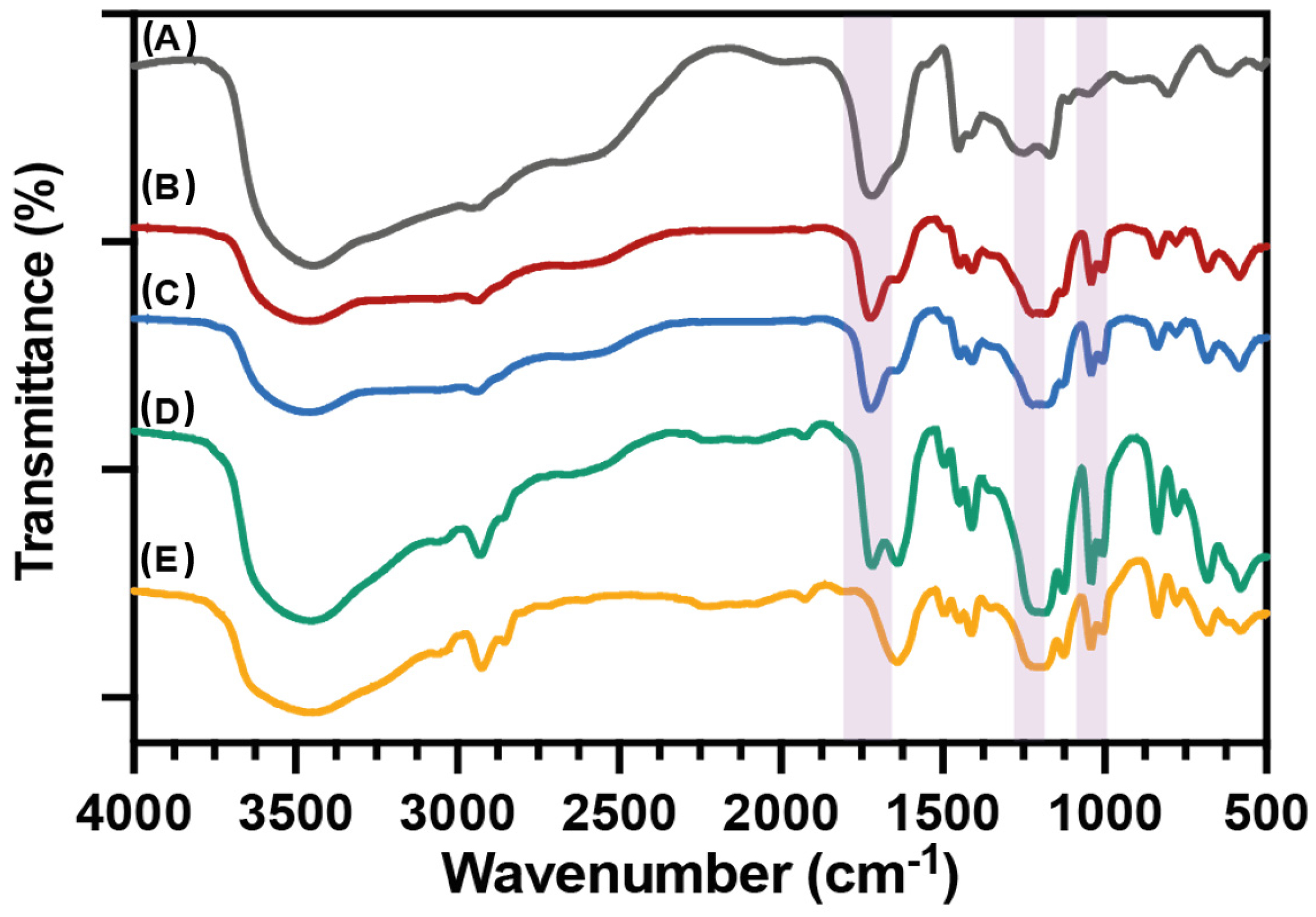
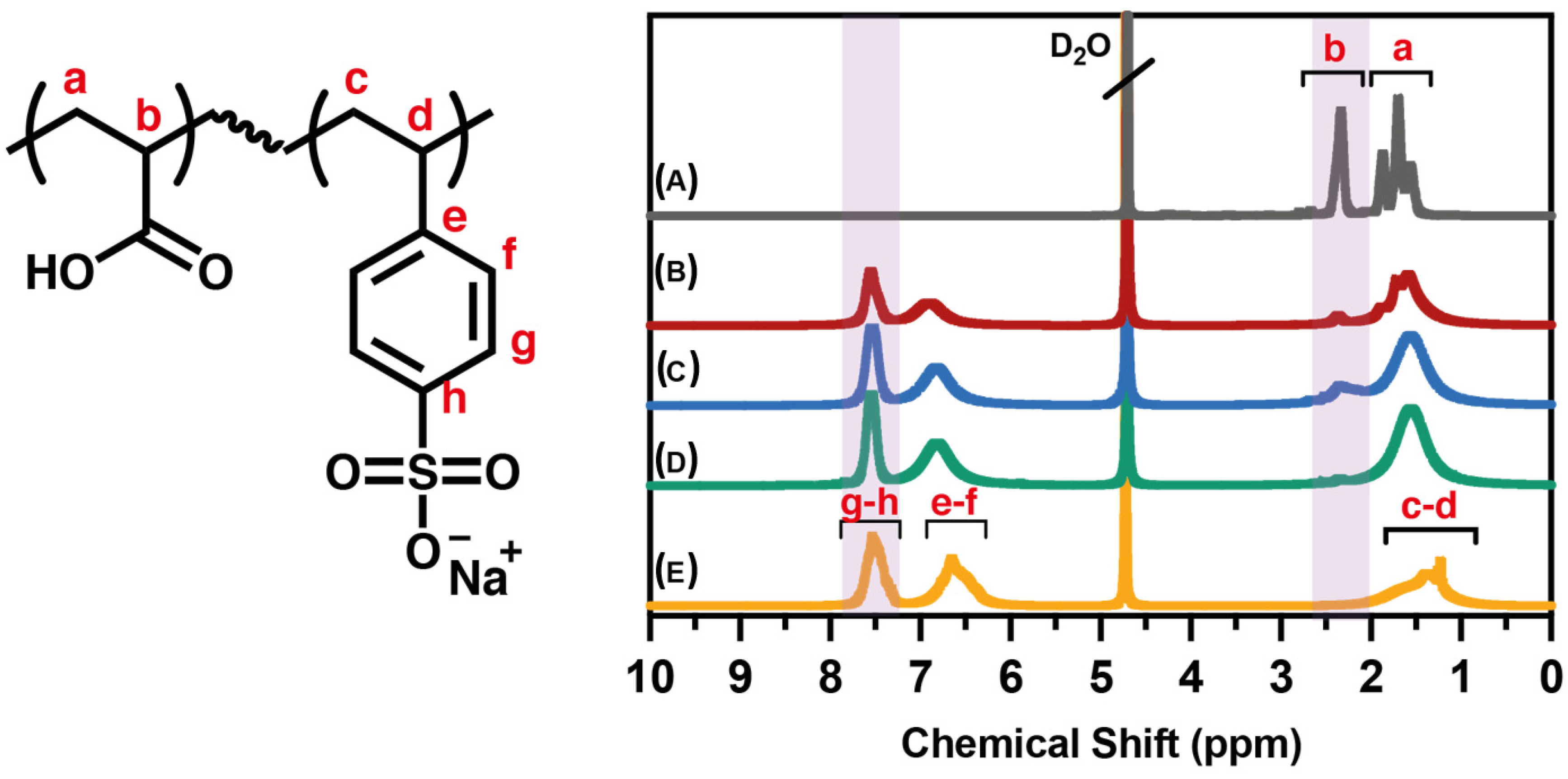

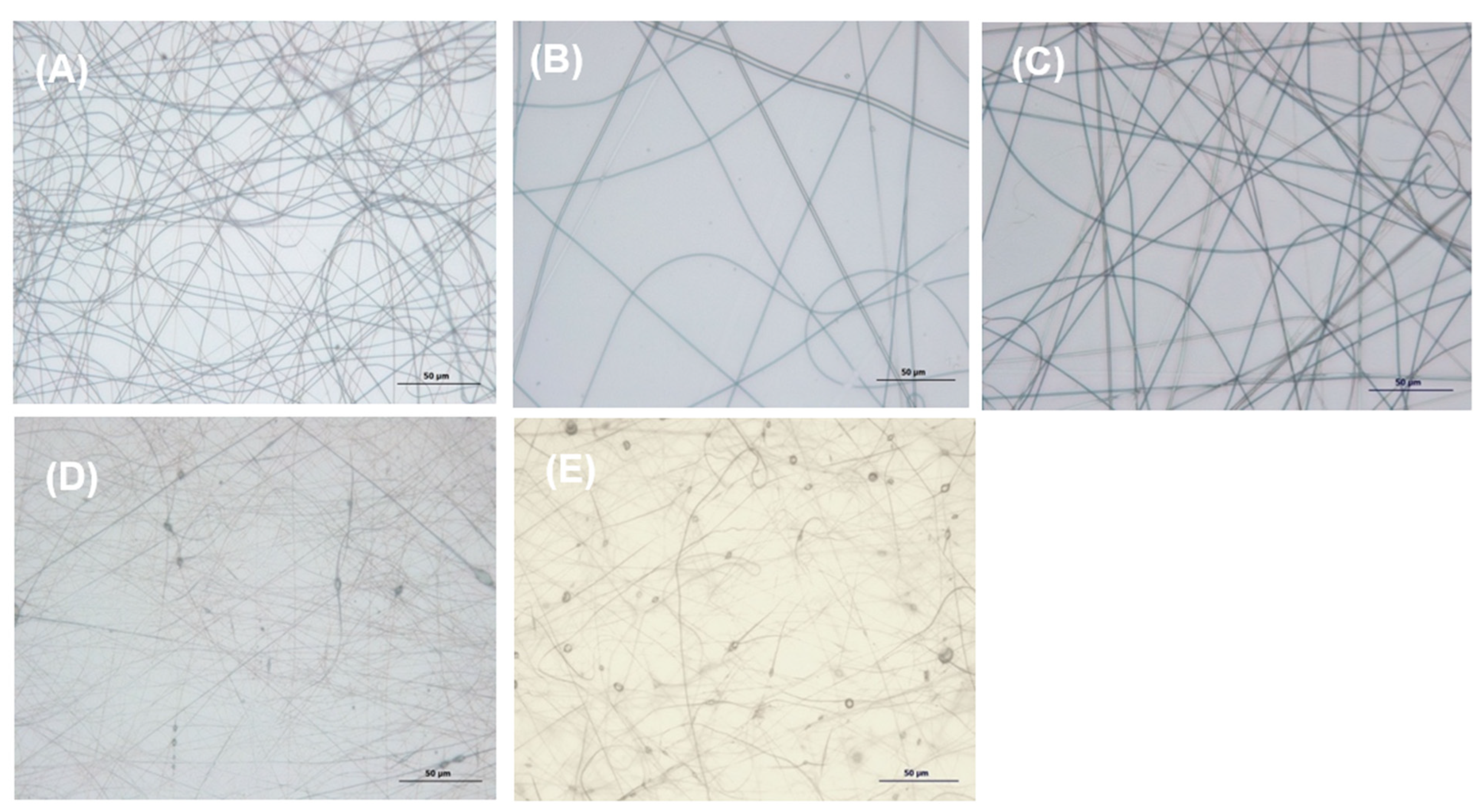


| Surface Tension σL | PAA | PAA:PSS (70:30) | PAA:PSS 50:50) | PAA:PSS (30:70) | PSSNa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σL a | 52.3 | 45.9 | 44.6 | 66.9 | 67.5 |
| σL * | 55.0 | 47.8 | 47.2 | 67.3 | 68.6 |
| σL b | 57.5 | 49.6 | 49.8 | 67.7 | 69.1 |
| Radio (m) | Density (kg/m3) | Drop Mass (kg) | Drop Volume (m3) | F | Surface Tension DMEM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00194641 | 1001 | 5.61 × 10−5 | 5.60 × 10−8 | 0.5096 | 0.649196026 | 69.28 |
| Sample | %C | %O | %S | %Na | Total wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAA | 55.8 | 44.2 | - | - | 100 |
| PAA:PSS (70:30) | 59.2 | 32.4 | 4.8 | 3.7 | 100 |
| PAA:PSS (50:50) | 59.6 | 33.2 | 3.3 | 3.9 | 100 |
| PAA:PSS (30:70) | 55.1 | 30.5 | 7.5 | 6.8 | 100 |
| PSSNa | 55.7 | 21.7 | 15.1 | 7.5 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neira-Carrillo, A.; Zárate, I.A.; Nieto, E.; Butto-Miranda, N.; Lobos-González, L.; Del Campo-Smith, M.; Palacio, D.A.; Urbano, B.F. Electrospun Poly(acrylic acid-co-4-styrene sulfonate) as Potential Drug-Eluting Scaffolds for Targeted Chemotherapeutic Delivery Systems on Gastric (AGS) and Breast (MDA-Mb-231) Cancer Cell Lines. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12213903
Neira-Carrillo A, Zárate IA, Nieto E, Butto-Miranda N, Lobos-González L, Del Campo-Smith M, Palacio DA, Urbano BF. Electrospun Poly(acrylic acid-co-4-styrene sulfonate) as Potential Drug-Eluting Scaffolds for Targeted Chemotherapeutic Delivery Systems on Gastric (AGS) and Breast (MDA-Mb-231) Cancer Cell Lines. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(21):3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12213903
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeira-Carrillo, Andrónico, Ignacio A. Zárate, Eddie Nieto, Nicole Butto-Miranda, Lorena Lobos-González, Matias Del Campo-Smith, Daniel A. Palacio, and Bruno F. Urbano. 2022. "Electrospun Poly(acrylic acid-co-4-styrene sulfonate) as Potential Drug-Eluting Scaffolds for Targeted Chemotherapeutic Delivery Systems on Gastric (AGS) and Breast (MDA-Mb-231) Cancer Cell Lines" Nanomaterials 12, no. 21: 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12213903
APA StyleNeira-Carrillo, A., Zárate, I. A., Nieto, E., Butto-Miranda, N., Lobos-González, L., Del Campo-Smith, M., Palacio, D. A., & Urbano, B. F. (2022). Electrospun Poly(acrylic acid-co-4-styrene sulfonate) as Potential Drug-Eluting Scaffolds for Targeted Chemotherapeutic Delivery Systems on Gastric (AGS) and Breast (MDA-Mb-231) Cancer Cell Lines. Nanomaterials, 12(21), 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12213903