Biofilm Degradation by Seashell-Derived Calcium Hydroxide and Hydrogen Peroxide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
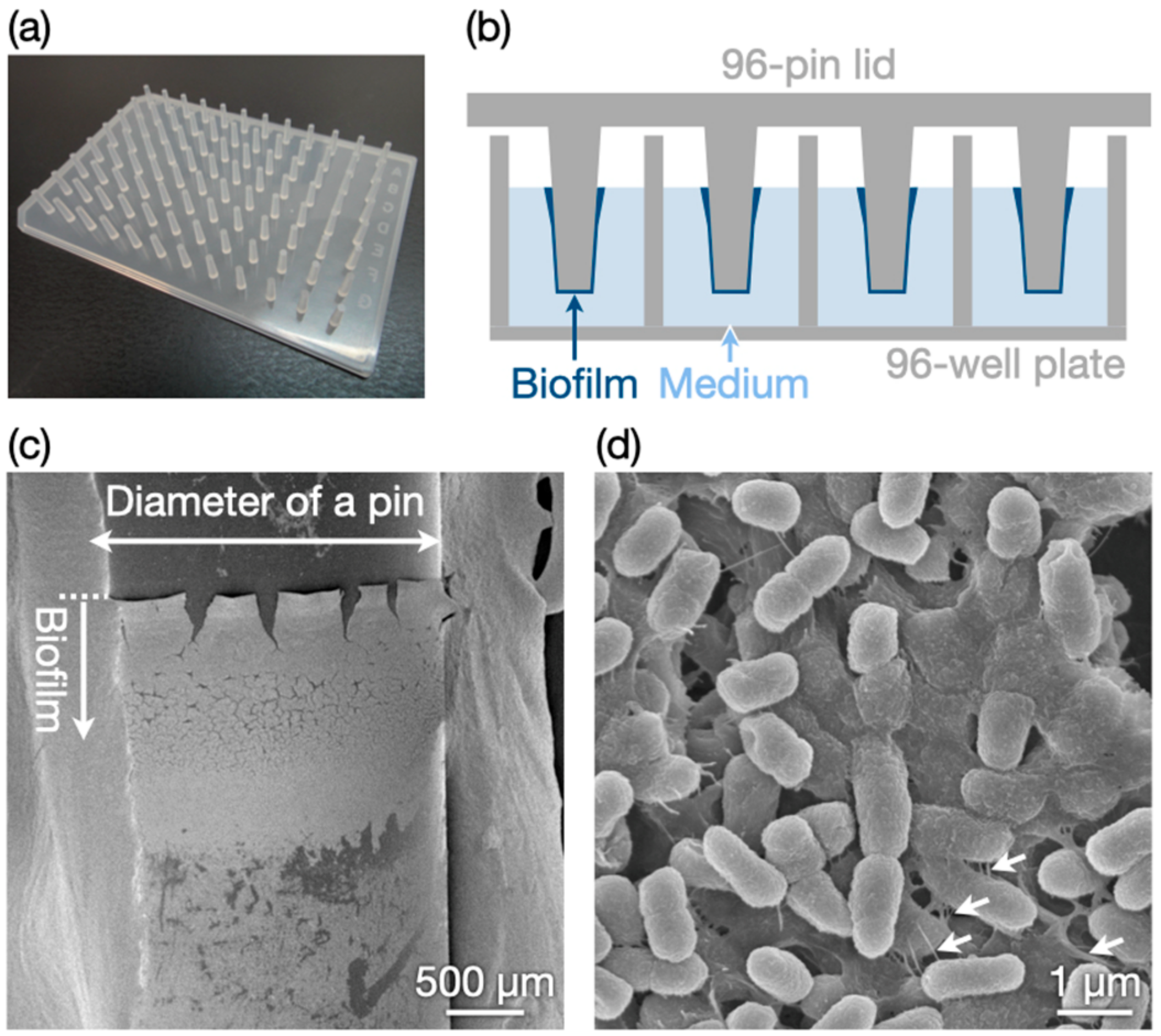
2.2. Preparation of Biofilms
2.3. Degradation and Semi-Quantification of Biofilms
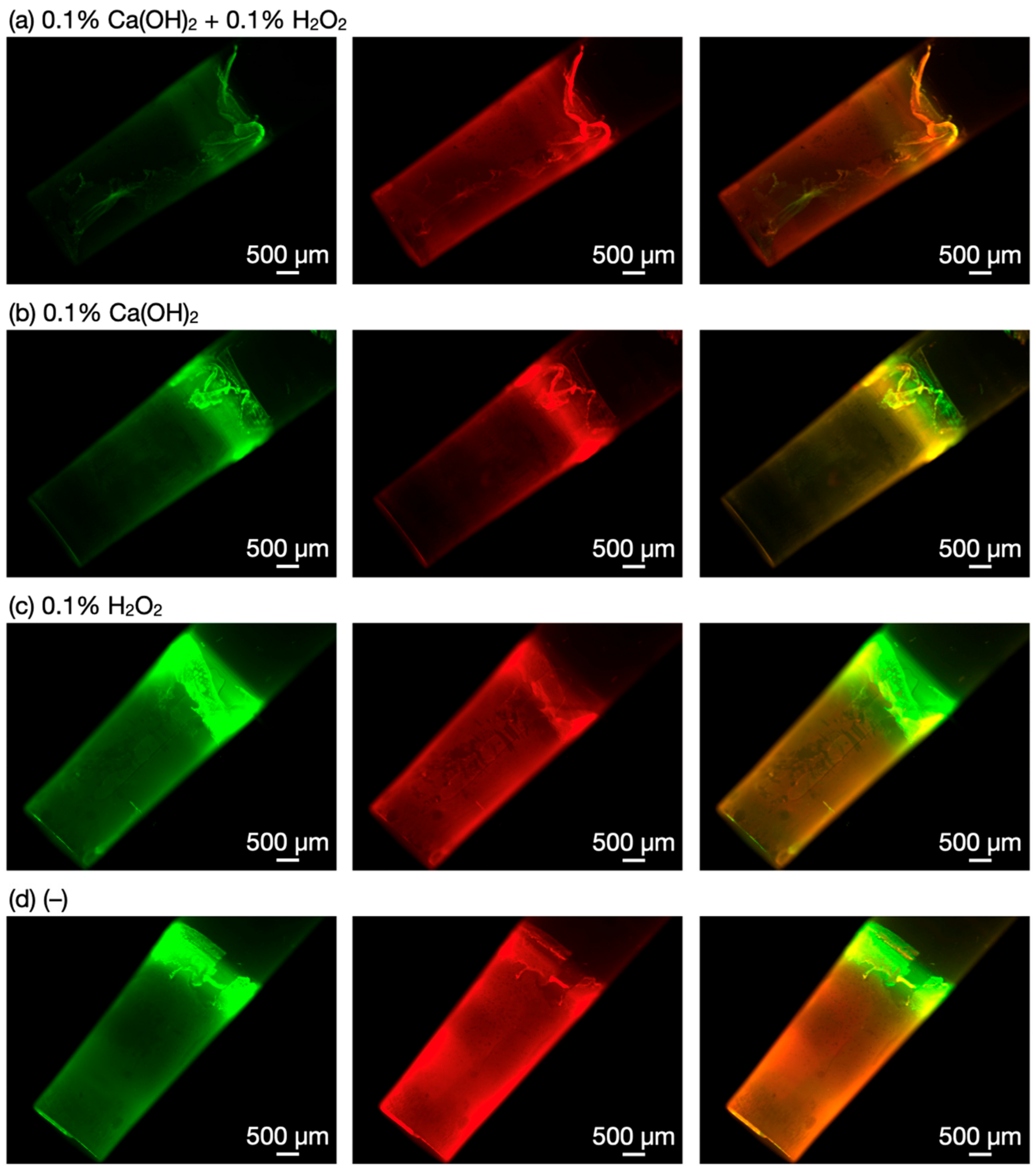
2.4. Microscopic Observations of Biofilms
2.5. Characterization of Ca(OH)2–H2O2 Solutions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biofilm Preparation
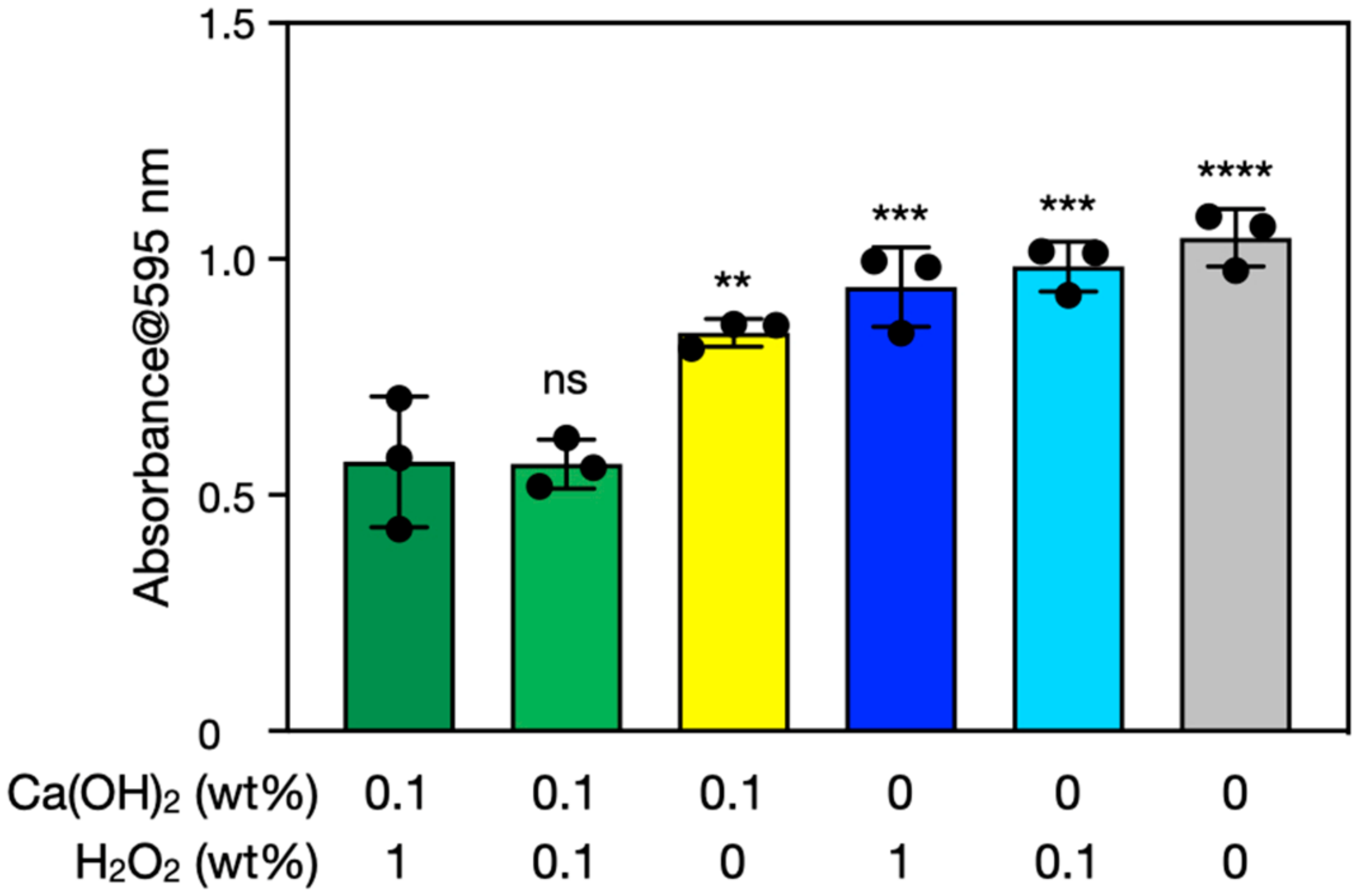
3.2. Biofilm Degradation by Ca(OH)2–H2O2
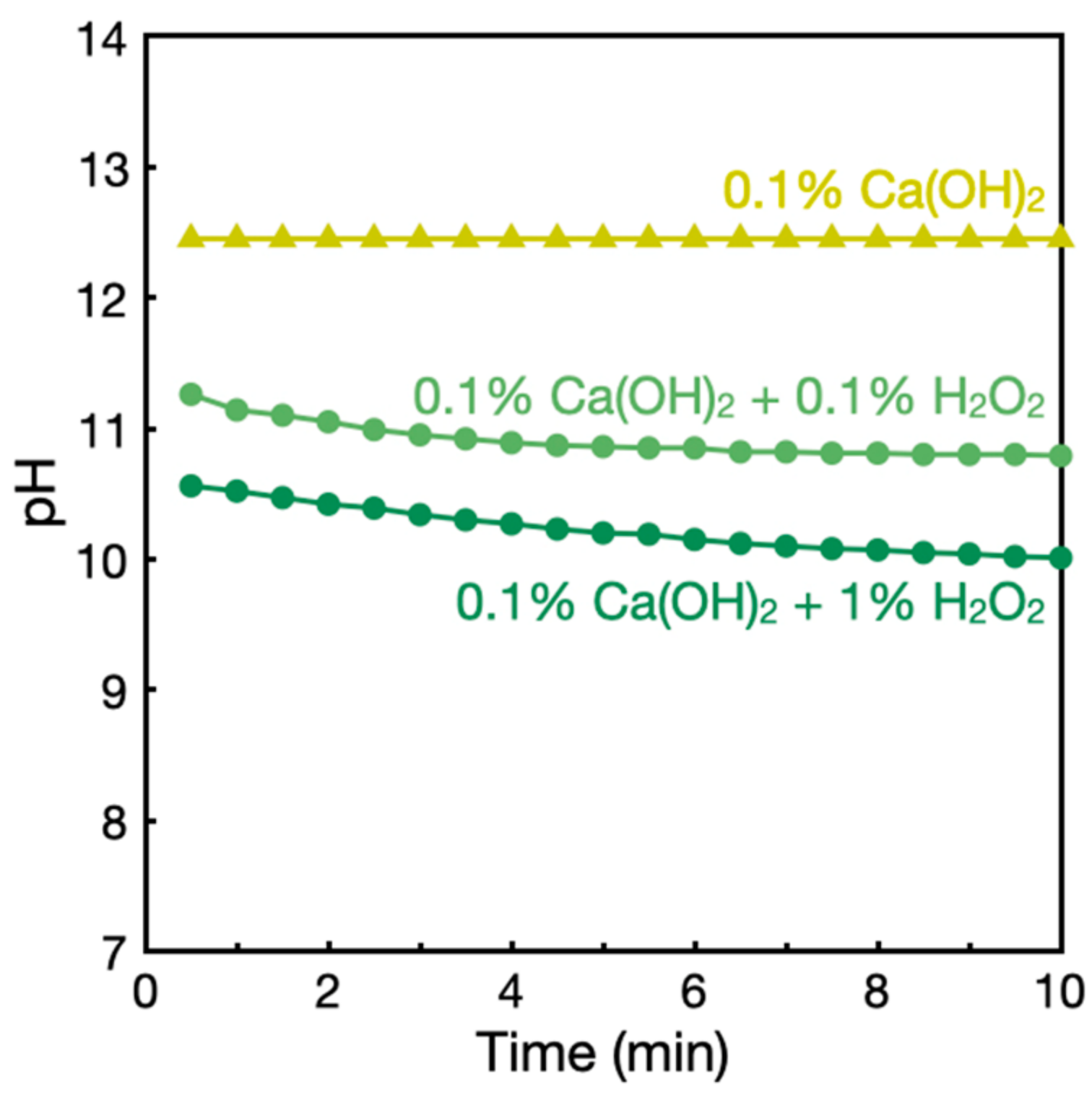
3.3. Investigations into Ca(OH)2–H2O2 Solutions
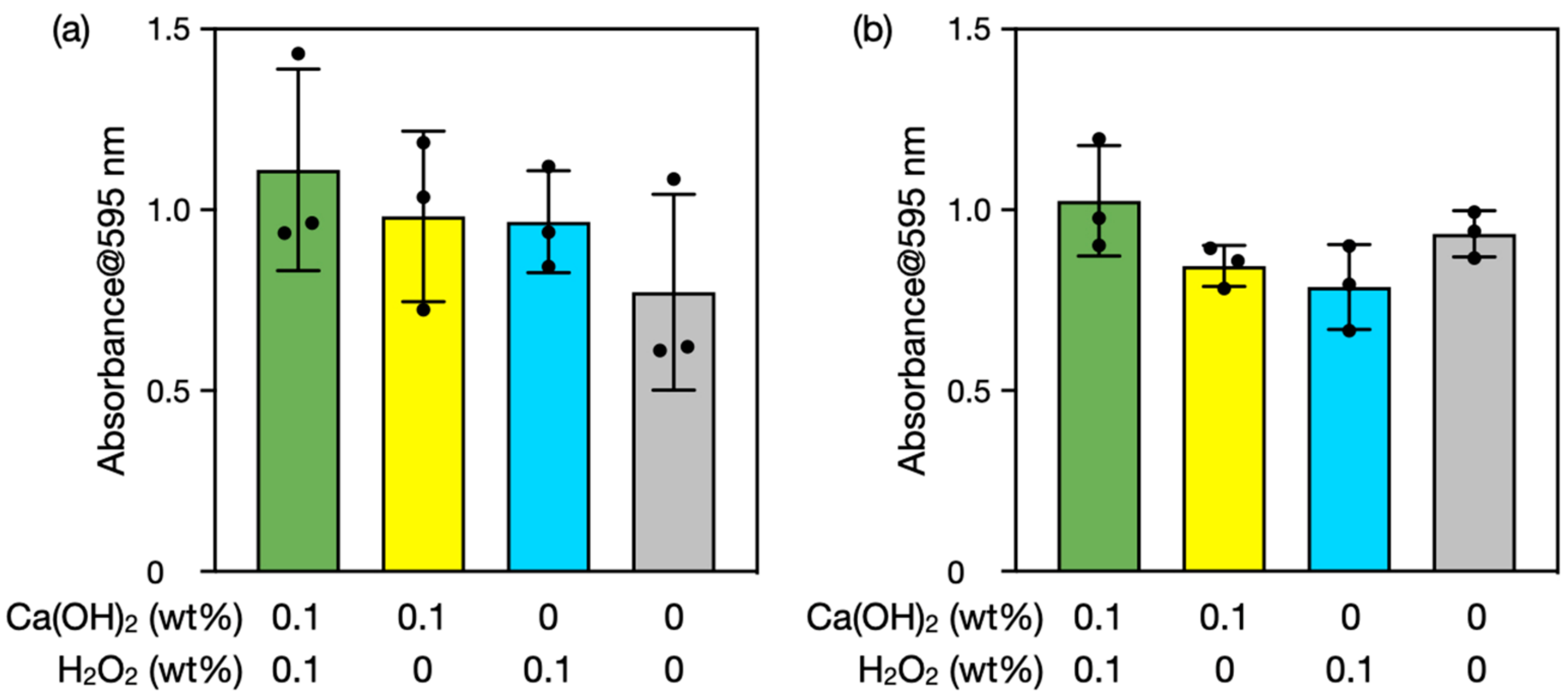
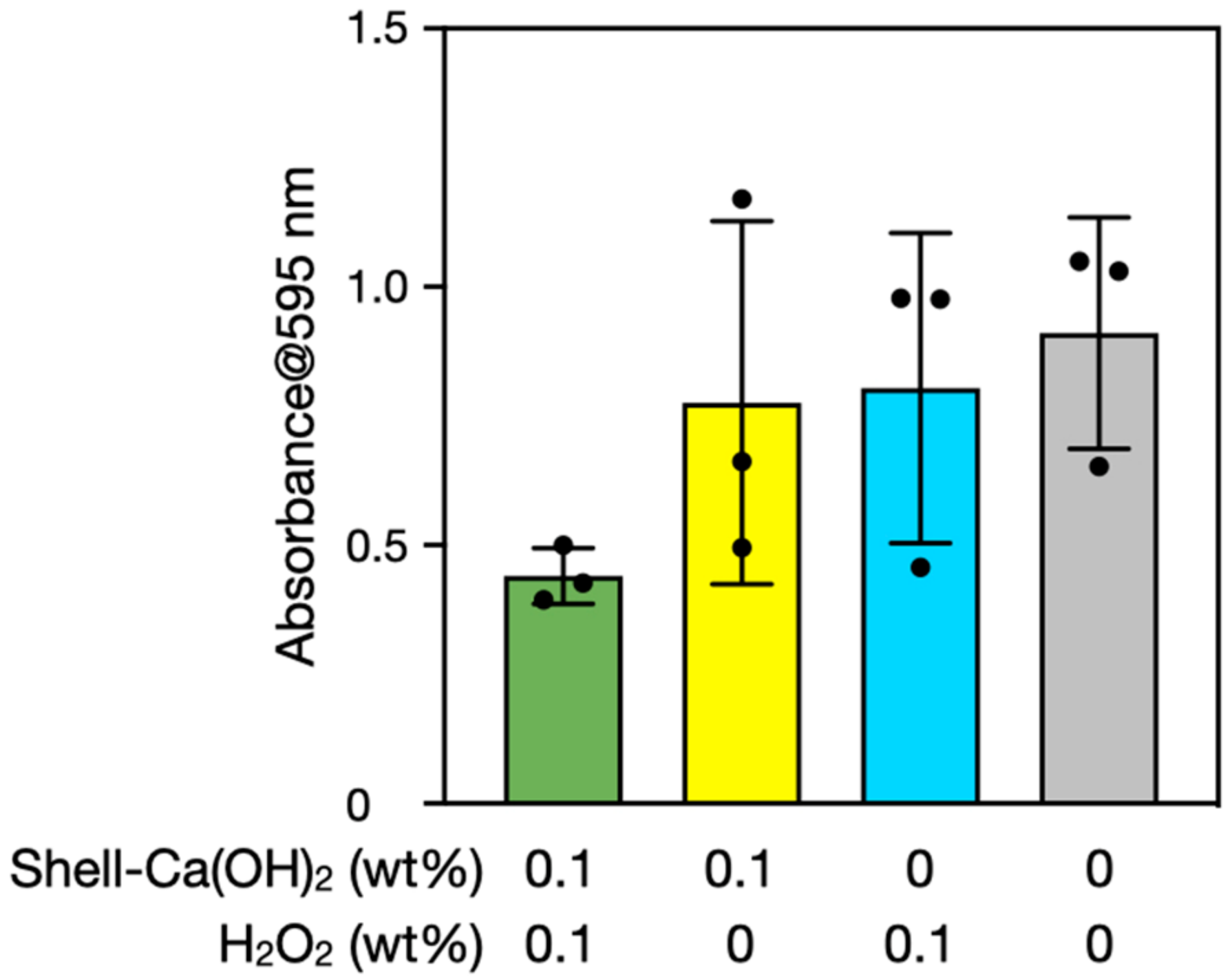
3.4. Biofilm Degradation Using Seashell-Derived Ca(OH)2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donlan, R.M. Biofilms: Microbial life on surfaces. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobley, L.; Harkins, C.; MacPhee, C.E.; Stanley-Wall, N.R. Giving structure to the biofilm matrix: An overview of individual strategies and emerging common themes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; He, J. Biofilms: The microbial “protective clothing” in extreme environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbaugh, K.P.; Sauer, K. Biofilm dispersion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayta, E.N.; Ertelt, M.J.; Kretschmer, M.; Lieleg, O. Bacterial materials: Applications of natural and modified biofilms. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2101024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R.M.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms: Survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, C.C.C.R. Biofilms: Recent developments on an old battle. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2007, 1, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srey, S.; Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.-D. Biofilm formation in food industries: A food safety concern. Food Control 2013, 31, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestby, L.K.; Grønseth, T.; Simm, R.; Nesse, L.L. Bacterial biofilm and its role in the pathogenesis of disease. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B. Approaches to prevention, removal and killing of biofilms. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2003, 51, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-López, V.M.; Marín, A.; Medina-Martínez, M.S.; Gil, M.I.; Allende, A. Generation of trihalomethanes with chlorine-based sanitizers and impact on microbial, nutritional and sensory quality of baby spinach. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 85, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J. Antimicrobial characteristics of heated scallop shell powder and its application. Biocontrol Sci. 2011, 16, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, Y.; Ishihara, M.; Hiruma, S.; Takayama, T.; Nakamura, S.; Ando, N. Recent progress in the development of disinfectants from scallop shell-derived calcium oxide for clinical and daily use. Biocontrol Sci. 2021, 26, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J.; Satoh, M.; Horikawa, M.; Shiga, H.; Kojima, H. Heated scallop-shell powder slurry treatment of shredded cabbage. J. Food Prot. 2001, 64, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodur, T.; Yaldirak, G.; Kola, O.; Çaĝri-MehmetoĜlu, A. Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7 on frankfurters using scallop-shell powder. J. Food Saf. 2010, 30, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagri-Mehmetoglu, A. Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enteritidis on chicken wings using scallop-shell powder. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2600–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Ohata, H.; Inoue, A.; Ishihara, M.; Nakamura, S.; Fukuda, K.; Takayama, T.; Murakami, K.; Hiruma, S.; Yokoe, H. Application of colloidal dispersions of bioshell calcium oxide (BiSCaO) for disinfection. Polymers 2019, 11, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Ishihara, M.; Sato, Y.; Takayama, T.; Hiruma, S.; Ando, N.; Fukuda, K.; Murakami, K.; Yokoe, H. Concentrated bioshell calcium oxide (BiSCaO) water kills pathogenic microbes: Characterization and activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, M.; Hata, Y.; Hiruma, S.; Takayama, T.; Nakamura, S.; Sato, Y.; Ando, N.; Fukuda, K.; Murakami, K.; Yokoe, H. Safety of concentrated bioshell calcium oxide water application for surface and skin disinfections against pathogenic microbes. Molecules 2020, 25, 4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, S.; Hata, Y.; Ishihara, M.; Takayama, T.; Nakamura, S.; Ando, N.; Fukuda, K.; Sato, Y.; Murakami, K.; Yokoe, H. Efficacy of bioshell calcium oxide water as disinfectants to enable face mask reuse. Biocontrol Sci. 2021, 26, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Ohshima, Y.; Irie, F.; Kikuchi, M.; Sawai, J. Disinfection treatment of heated scallop-shell powder on biofilm of Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 surrogated for E. coli O157:H7. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 4, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J.; Nagasawa, K.; Kikuchi, M. Ability of heated scallop-shell powder to disinfect Staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 19, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, H.; Akimoto, T.; Fukikoshi, N.; Wada, R.; Sawai, J. Antibiofilm effects of heated scallop shell powder on Campylobacter jejuni biofilms. Membranes 2022, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.T.; Bradshaw, D.J.; Fulford, M.R.; Marsh, P.D. Microbiological evaluation of a range of disinfectant products to control mixed-species biofilm contamination in a laboratory model of a dental unit water system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, I.; Sabri, A.N. Effect of biocides on biofilm bacteria from dental unit water lines. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 56, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, P.V.; LoVetri, K.; Yakandawala, N.; Romeo, T.; Zhanel, G.G.; Cvitkovitch, D.G.; Madhyastha, S. Antibiofilm activity of sodium bicarbonate, sodium metaperiodate and SDS combination against dental unit waterline-associated bacteria and yeast. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinbobola, A.B.; Amaeze, N.J.; Mackay, W.G.; Ramage, G.; Williams, C. ‘Secondary biofilms’ could cause failure of peracetic acid high-level disinfection of endoscopes. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 107, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.M.; Sun, R.C.; Salisbury, D.; Fowler, P.; Tomkinson, J. Comparative study of hemicelluloses from wheat straw by alkali and hydrogen peroxide extractions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1999, 66, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.E.; Moore, S.B. Alkaline hydrogen peroxide bleaching of cellulose. Cellulose 2000, 7, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linley, E.; Denyer, S.P.; McDonnell, G.; Simons, C.; Maillard, J.-Y. Use of hydrogen peroxide as a biocide: New consideration of its mechanisms of biocidal action. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.Q.; Du, Y.M.; Xiao, L. Effect of hydrogen peroxide treatment on the molecular weight and structure of chitosan. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 76, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J.; Ceri, H. High-throughput metal susceptibility testing of microbial biofilms. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukatani, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Suenaga, H.; Shiga, M.; Ikegami, T. Rapid and simple determination of minimum biofilm eradication concentration by a colorimetric microbial viability assay based on reduction of a water-soluble tetrazolium salt and combined effect of antibiotics against microbial biofilm. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2016, 6, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, J.H.; Kadouri, D.E.; O’Toole, G.A. Growing and analyzing static biofilms. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2011, 22, 1B.1.1–1B.1.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, B.M.; Anderson, G.G. Biofilm formation in the 96-well microtiter plate. In Pseudomonas Methods and Protocols; Filloux, A., Ramos, J.-L., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1149, pp. 631–641. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.; Rusconi, R.; Stocker, R. Biofilm disruption by an air bubble reveals heterogeneous age-dependent detachment patterns dictated by initial extracellular matrix distribution. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2017, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hata, Y.; Bouda, Y.; Hiruma, S.; Miyazaki, H.; Nakamura, S. Biofilm Degradation by Seashell-Derived Calcium Hydroxide and Hydrogen Peroxide. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203681
Hata Y, Bouda Y, Hiruma S, Miyazaki H, Nakamura S. Biofilm Degradation by Seashell-Derived Calcium Hydroxide and Hydrogen Peroxide. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(20):3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203681
Chicago/Turabian StyleHata, Yuuki, Yuta Bouda, Sumiyo Hiruma, Hiromi Miyazaki, and Shingo Nakamura. 2022. "Biofilm Degradation by Seashell-Derived Calcium Hydroxide and Hydrogen Peroxide" Nanomaterials 12, no. 20: 3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203681
APA StyleHata, Y., Bouda, Y., Hiruma, S., Miyazaki, H., & Nakamura, S. (2022). Biofilm Degradation by Seashell-Derived Calcium Hydroxide and Hydrogen Peroxide. Nanomaterials, 12(20), 3681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203681





