Peroral Toxicological Assessment of Two-Dimensional Forms of Nickel Nanoparticles Sized between 20 and 120 nm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanomaterials
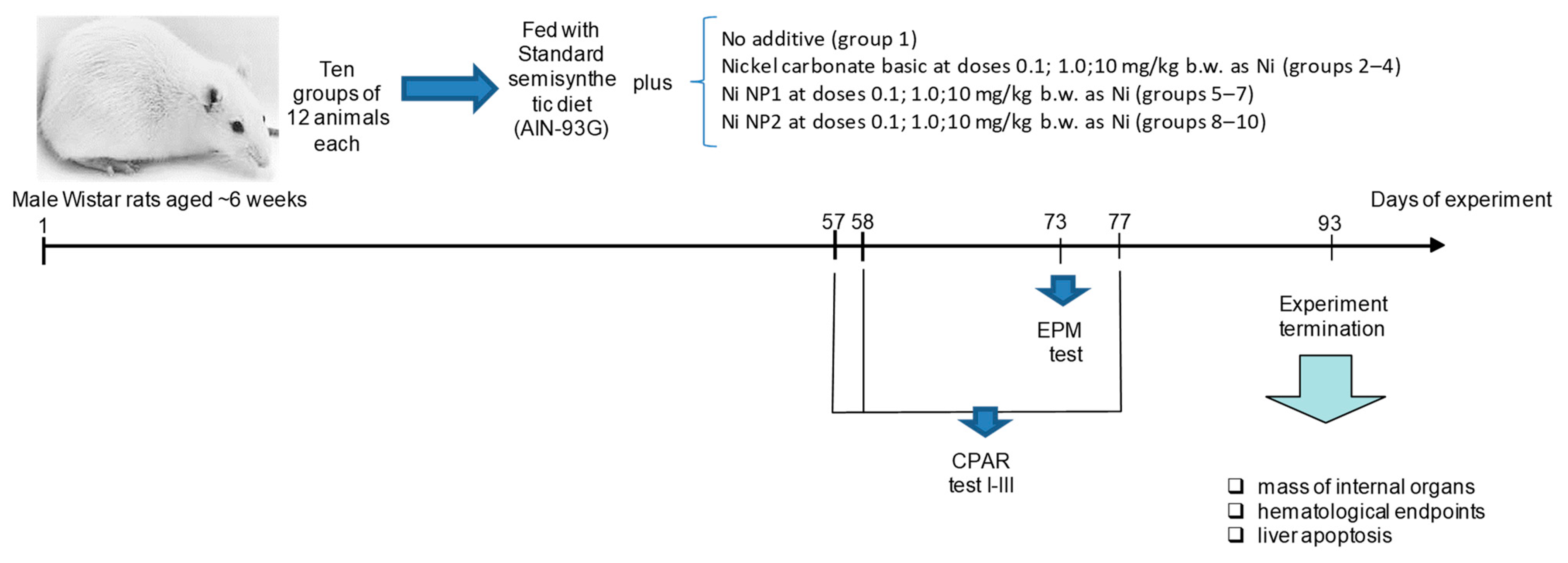
2.2. Animals and Design
2.3. Behavioral Responses
2.4. Methods of Sample Analysis
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Nanomaterials
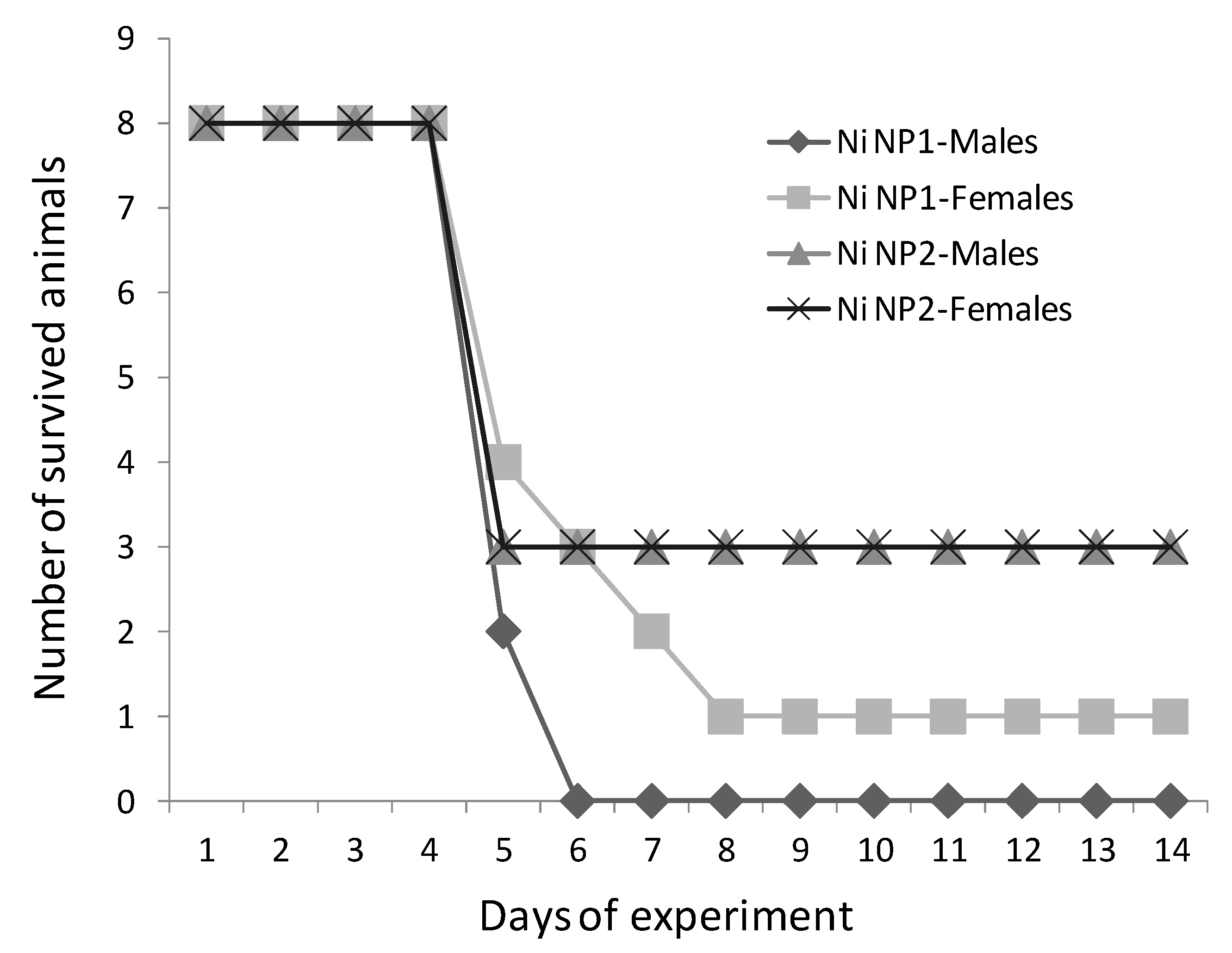
3.2. Acute Oral Toxicity
3.3. Subchronic 92-Day Oral Toxicity
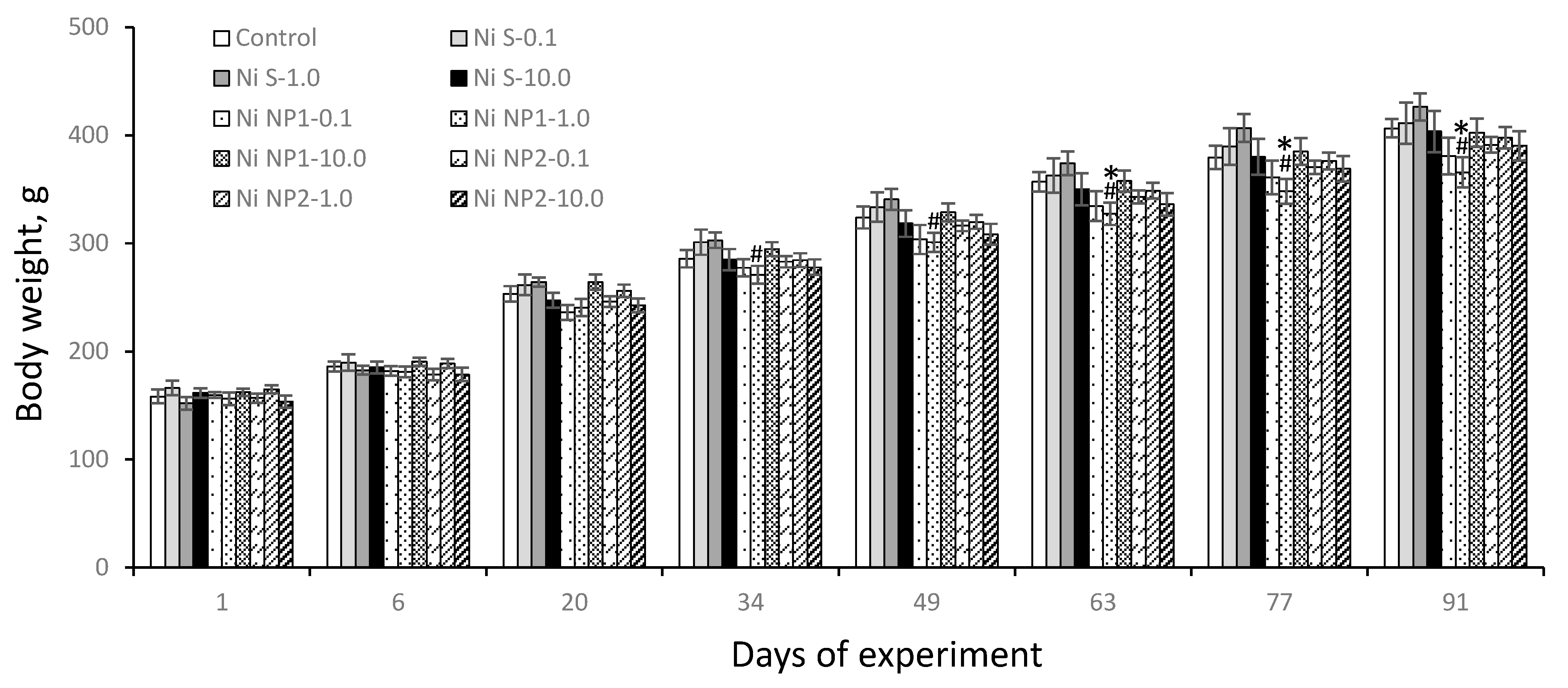
3.3.1. Integral Indicators
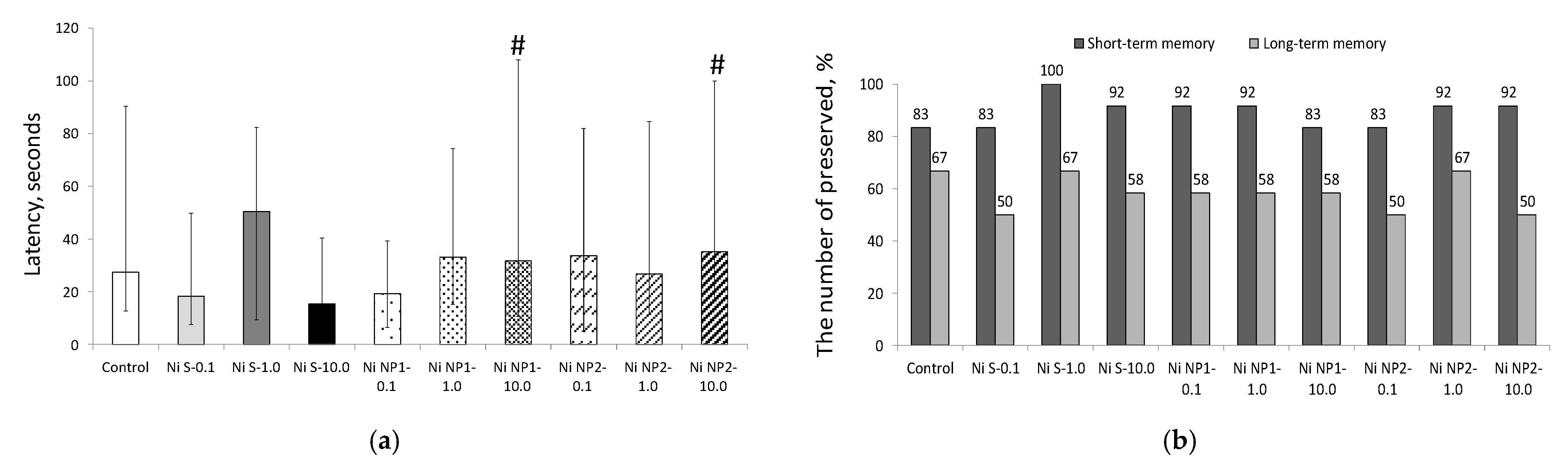
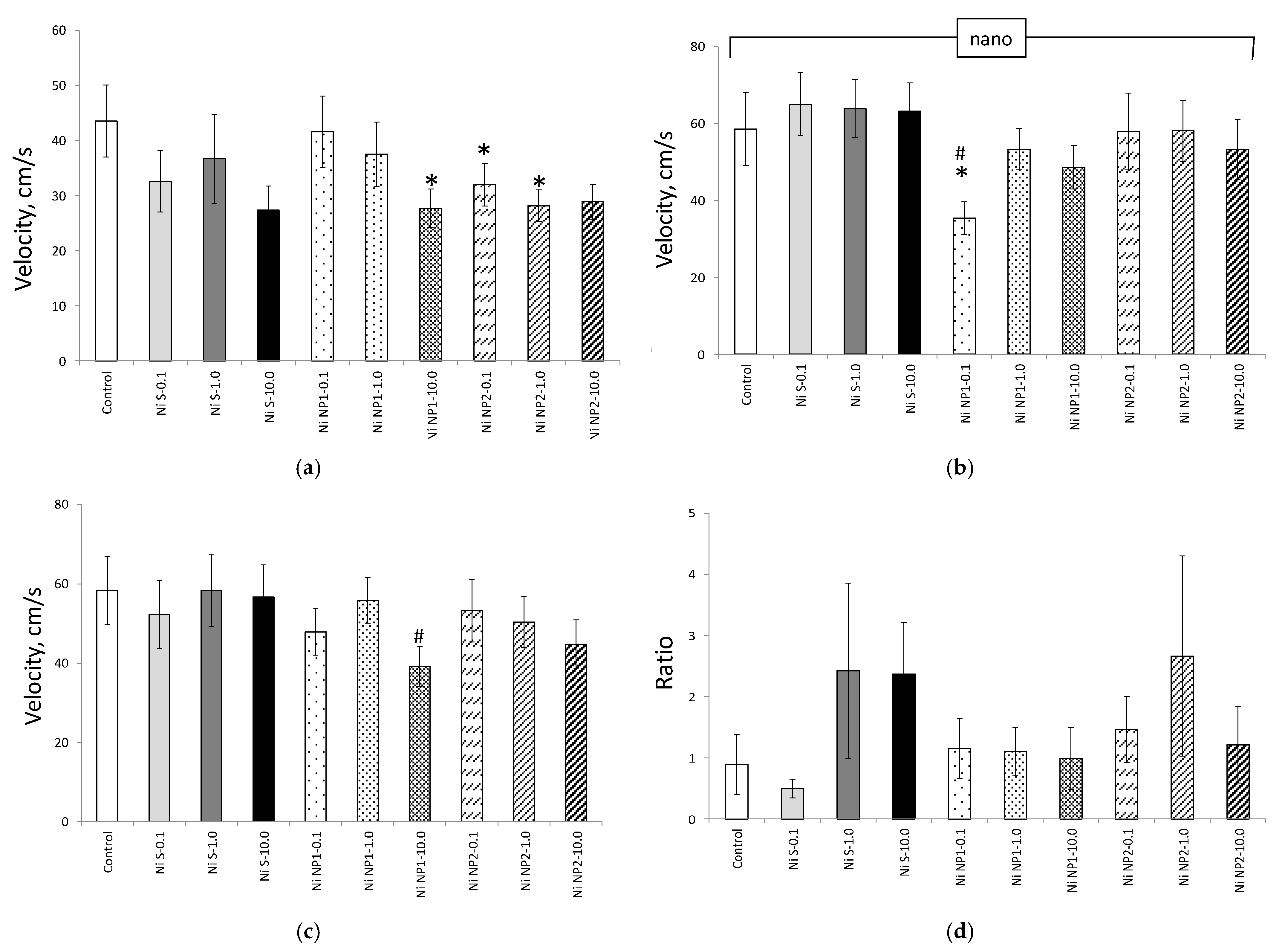
3.3.2. Behavioral Responses
3.3.3. Hematological Indicators
3.3.4. Liver Apoptosis
3.3.5. Nickel Accumulation in the Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, R.D. Fats and Oils: Formulating and Processing for Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Zhu, A.; Liu, F.; Zou, L.; Su, L.; Li, S.; Sun, Y. Role of NF-κ B activation and Th1/Th2 imbalance in pulmonary toxicity induced by nano NiO. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 32, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Schott, J.A.; Liu, X.; Mahurin, S.M.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Fulvio, P.F.; Chisholm, M.F.; et al. Solid-state synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon catalysts via a mechanochemical assembly through coordination cross-linking. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, D.; Sheet, S.K.; Khatua, S.; Biswas, K.; Joshi, S.; Myrboh, B. A reusable magnetic nickel nanoparticle based catalyst for the aqueous synthesis of diverse heterocycles and their evaluation as potential anti-bacterial agent. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5018–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, I.; Stergar, J.; Drofenik, M.; Ferk, G.; Makovec, D. Synthesis of copper–nickel nanoparticles prepared by mechanical milling for use in magnetic hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 2254–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowska, S.; Brzóska, M.M. Metals in cosmetics: Implications for human health. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 551–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, G.; Roopan, S.M.; Dhamodaran, K.I.; Elumalai, K.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V. Spectroscopic investigation of biosynthesized nickel nanoparticles and its larvicidal, pesticidal activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 162, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S.I.; Roca, C.P.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.J.; Amorim, M.J. High-throughput transcriptomics: Insights into the pathways involved in (nano) nickel toxicity in a key invertebrate test species. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 245, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsnelson, B.; Privalova, L.; Sutunkova, M.; Gurvich, V.; Loginova, N.; Minigalieva, I.; Kireyeva, E.; Shur, V.; Shishkina, E.; Beikin, Y.; et al. Some inferences from in vivo experiments with metal and metal oxide nanoparticles: The pulmonary phagocytosis response, subchronic systemic toxicity and genotoxicity, regulatory proposals, searching for bioprotectors (a self-overview). Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3013–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magaye, R.; Zhao, J. Recent progress in studies of metallic nickel and nickel-based nanoparticles’ genotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Suhail, M.; Mathew, S.; Shah, M.A.; Harakeh, S.M.; Ahmad, S.; Kazmi, Z.; Alhamdan, M.A.R.; Chaudhary, A.; Damanhouri, G.A.; et al. Nanomaterial Induced Immune Responses and Cytotoxicity. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Eastlake, A.; Topmiller, J.L.; Sparks, C.; Martinez, K.; Geraci, C.L. Nano-metal oxides: Exposure and engineering control assessment. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2017, 14, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumala, N.; Mangalampalli, B.; Chinde, S.; Kumari, S.I.; Mahoob, M.; Rahman, M.F.; Grover, P. Genotoxicity study of nickel oxide nanoparticles in female Wistar rats after acute oral exposure. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumala, N.; Mangalampalli, B.; Kamal, S.S.K.; Grover, P. Repeated oral dose toxicity study of nickel oxide nanoparticles in Wistar rats: A histological and biochemical perspective. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 1012–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaye, R.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Zhou, Q.; Mao, G.; Shi, H.; Yue, X.; Zou, B.; Xu, J.; et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the toxicities induced by metallic nickel nano and fine particles. Histochem. J. 2016, 47, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, A.; Chang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Sun, Y.; Zou, L.; Sun, Y.; Su, L. Role of nitrative stress in nano nickel ox-ide-induced lung injury in rats. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 2016, 45, 563–567. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, K.; Kadoya, C.; Ogami, A.; Oyabu, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Ueno, S.; Myojo, T. Changes over time in pulmonary inflammatory response in rat lungs after intratracheal instillation of nickel oxide nanoparticles. J. Occup. Health 2020, 62, 12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietruska, J.R.; Liu, X.; Smith, A.; McNeil, K.; Weston, P.; Zhitkovich, A.; Hurt, R.; Kane, A.B. Bioavailability, Intracellular Mobilization of Nickel, and HIF-1α Activation in Human Lung Epithelial Cells Exposed to Metallic Nickel and Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 124, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-309-15400-0.
- OECD. Test No. 420: Acute Oral Toxicity-Fixed Dose Procedure. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 2002; Section 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.G. Components of the AIN-93 Diets as Improvements in the AIN-76A Diet. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 838S–841S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzhelskaya, K.V.; Shipelin, V.A.; Shumakova, A.A.; Musaeva, A.D.; Soto, J.S.; Riger, N.A.; Trusov, N.V.; Kirbaeva, N.V.; Apryatin, S.A.; Gmoshinski, I.V. Effects of quercetin on the neuromotor function and behavioral responses of Wistar and Zucker rats fed a high-fat and high-carbohydrate diet. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 378, 112270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Meyer, N. Annexin V/7-AAD Staining in Keratinocytes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 740, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Gu, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y. Toxicity of manufactured nanomaterials. Particuology 2022, 69, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Scientific Committee; More, S.; Bampidis, V.; Benford, D.; Bragard, C.; Halldorsson, T.; Hernández-Jerez, A.; Bennekou, S.H.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Lambré, C.; et al. Guidance on risk assessment of nanomaterials to be applied in the food and feed chain: Human and animal health. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, L.; Leblanc, J.-C.; Guerin, T. Determination of several elements in duplicate meals from catering establishments using closed vessel microwave digestion with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry detection: Estimation of daily dietary intake. Food Addit. Contam. 2003, 20, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saquib, Q.; Attia, S.M.; Ansari, S.M.; Al-Salim, A.; Faisal, M.; Alatar, A.A.; Musarrat, J.; Zhang, X.; Al-Khedhairy, A. p53, MAPKAPK-2 and caspases regulate nickel oxide nanoparticles induce cell death and cytogenetic anomalies in rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Gao, X.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, K.; Tang, M. Mechanisms involved in reproductive toxicity caused by nickel nanoparticle in female rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Hu, W.; Lu, C.; Cheng, K.; Tang, M. Mechanisms underlying nickel nanoparticle induced reproductive toxicity and chemo-protective effects of vitamin C in male rats. Chemosphere 2018, 218, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, A.D.; Aitken, R.J.; Butz, T.; Colvin, V.; Donaldson, K.; Oberdörster, G.; Philbert, M.A.; Ryan, J.; Seaton, A.; Stone, V.; et al. Safe handling of nanotechnology. Nature 2006, 444, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åkerlund, E.; Cappellini, F.; Di Bucchianico, S.; Islam, S.; Skoglund, S.; Derr, R.; Wallinder, I.O.; Hendriks, G.; Karlsson, H.L. Genotoxic and mutagenic properties of Ni and NiO nanoparticles investigated by comet assay, γ-H2AX staining, Hprt mutation assay and ToxTracker reporter cell lines. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 59, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinali, S.H.; Boushehri, Z.P.; Rasti, B.; Mirpour, M.; Shahpasand, K.; Falahati, M. Biophysical, molecular dynamics and cellular studies on the interaction of nickel oxide nanoparticles with tau proteins and neuron-like cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 125, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsnelson, B.A.; Minigaliyeva, I.A.; Panov, V.; Privalova, L.; Varaksin, A.N.; Gurvich, V.B.; Sutunkova, M.; Shur, V.Y.; Shishkina, E.; Valamina, I.E.; et al. Some patterns of metallic nanoparticles’ combined subchronic toxicity as exemplified by a combination of nickel and manganese oxide nanoparticles. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2015, 86, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bucchianico, S.; Gliga, A.R.; Åkerlund, E.; Skoglund, S.; Wallinder, I.O.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H.L. Calcium-dependent cyto- and genotoxicity of nickel metal and nickel oxide nanoparticles in human lung cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, A.; Costa, M. Elucidating the mechanisms of nickel compound uptake: A review of particulate and nano-nickel endocytosis and toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 260, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minigalieva, I.; Bushueva, T.; Fröhlich, E.; Meindl, C.; Öhlinger, K.; Panov, V.; Varaksin, A.; Shur, V.; Shishkina, E.; Gurvich, V.; et al. Are in vivo and in vitro assessments of comparative and combined toxicity of the same metallic nanoparticles compatible, or contradictory, or both? A juxtaposition of data obtained in respective experiments with NiO and Mn3O4 nanoparticles. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2017, 109, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dimensions, nm | Nanomaterials | |
|---|---|---|
| Ni NP1 | Ni NP2 | |
| Mean diameter (M) | 53.7 | 70.9 |
| Standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) | 2.9 | 3.3 |
| Standard deviation (S.D.) | 29.3 | 32.0 |
| Median (Med) | 47.0 | 64.0 |
| The smallest diameter | 15.0 | 17.0 |
| The largest diameter | 180.0 | 192.0 |
| The number of particles within dimensional range: | ||
| Less than 50 nm | 55.5 | 24.0 |
| 50–100 nm | 37.8 | 57.1 |
| More than 100 nm | 6.7 | 18.9 |
| Normality distribution test (Kolmogorov–Smirnov criterion), p | 0.034 | >0.1 |
| ζ-potential, mV | +25.71 | −3.33 |
| Group | Body Weight, g | Relative Organ Weight (% of Body Weight) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | Spleen | Thymus | Brain | ||
| 1. Control | 413 ± 9 | 3.09 ± 0.06 | 0.28 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.46 ± 0.01 |
| 2. Ni S 0.1 mg/kg b.w. | 415 ± 20 | 2.86 ± 0.11 * | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.02 |
| 3. Ni S 1.0 mg/kg b.w. | 431 ± 14 | 2.92 ± 0.13 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.48 ± 0.02 |
| 4. Ni S 10 mg/kg b.w. | 407 ± 20 | 2.94 ± 0.07 | 0.21 ± 0.018 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.51 ± 0.02 |
| 5. Ni NP1 0.1 mg/kg b.w. | 384 ± 18 | 2.89 ± 0.08 | 0.21 ± 0.01 *# | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.52 ± 0.03 |
| 6. Ni NP1 1.0 mg/kg b.w. | 371 ± 14 *# | 2.91 ± 0.07 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.02 * |
| 7. Ni NP1 10 mg/kg b.w. | 407 ± 13 | 2.90 ± 0.09 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.01 *# | 0.49 ± 0.01 |
| 8. Ni NP2 0.1 mg/kg b.w. | 395 ± 7 | 2.80 ± 0.07* | 0.22 ± 0.02 # | 0.10 ± 0.01 *# | 0.51 ± 0.01 * |
| 9. Ni NP2 1.0 mg/kg b.w. | 401 ± 10 | 2.82 ± 0.05* | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.01 * | 0.50 ± 0.01 * |
| 10. Ni NP2 10 mg/kg b.w. | 393 ± 14 | 2.80 ± 0.05* | 0.21 ± 0.02 Ø | 0.11 ± 0.01 * | 0.50 ± 0.01 * |
| Factors | - | Ni × nano | - | - | - |
| Group | Indicators (M ± S.E.M), Measurement Units | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leucocytes Total, 109 × L−1 | Neutro- Philes, 109 × L−1 | Basophiles, 107 × L−1 | Lympho- Cytes, 109 × L−1 | Monocytes, 109 × L−1 | Trombo- Cytes, 109 × L−1 | Mean Volume of Trombocyte, μm3 | Trombocrit, % | |
| 1. Control | 10.4 ± 1.0 | 1.73 ± 0.18 | 5.66 ± 0.78 | 6.92 ± 0.51 | 1.49 ± 0.38 | 634 ± 22 | 6.57 ± 0.15 | 0.42 ± 0.02 |
| 2. Ni S 0.1 mg/kg b.w. | 7.5 ± 1.0 | 1.70 ± 0.39 | 4.65 ± 1.28 | 4.69 ± 0.66 * | 0.87 ± 0.25 | 618 ± 41 | 6.84 ± 0.17 | 0.42 ± 0.03 |
| 3. Ni S 1.0 mg/kg b.w. | 8.7 ± 1.5 | 1.84 ± 0.26 | 7.01 ± 1.99 | 5.46 ± 1.11 | 0.97 ± 0.22 | 622 ± 44 | 6.80 ± 0.24 | 0.42 ± 0.02 |
| 4. Ni S 10 mg/kg b.w. | 7.8 ± 1.2 | 1.40 ± 0.36 | 4.35 ± 1.22 | 5.53 ± 0.90 | 0.95 ± 0.17 | 632 ± 39 | 6.54 ± 0.07 | 0.41 ± 0.02 |
| 5. Ni NP1 0.1 mg/kg b.w. | 9.4 ± 1.5 | 1.72 ± 0.31 | 5.96 ± 1.74 | 7.06 ± 1.16 | 0.74 ± 0.11 | 648 ± 34 | 6.31 ± 0.11 # | 0.41 ± 0.02 |
| 6. Ni NP1 1.0 mg/kg b.w. | 11.5 ± 1.3 | 2.85 ± 0.72 | 7.40 ± 1.42 | 7.72 ± 0.91 | 1.03 ± 0.13 | 515 ± 41 | 6.73 ± 0.16 | 0.34 ± 0.02 *# |
| 7. Ni NP1 10 mg/kg b.w. | 13.4 ± 1.6 # | 1.87 ± 0.16 | 7.48 ± 0.98 | 9.15 ± 1.09 # | 1.57 ± 0.12 # | 591 ± 41 # | 6.56 ± 0.12 | 0.39 ± 0.02 |
| 8. Ni NP2 0.1 mg/kg b.w. | 12.0 ± 1.4 # | 2.42 ± 0.28 | 5.44 ± 0.89 | 6.98 ± 0.84 # | 1.27 ± 0.12 ∅ | 555 ± 30 ∅ | 6.54 ± 0.11 | 0.36 ± 0.02 |
| 9. Ni NP2 1.0 mg/kg b.w. | 10.5 ± 0.7 | 1.95 ± 0.21 | 9.68 ± 0.90 * | 7.14 ± 0.57 | 1.33 ± 0.17 | 544 ± 40 | 6.89 ± 0.32 | 0.37 ± 0.01 |
| 10. Ni NP2 10 mg/kg b.w. | 11.5 ± 1.2 | 2.72 ± 0.41 # | 5.81 ± 0.97 | 7.47 ± 0.92 | 1.10 ± 0.14 ∅ | 578 ± 47 ∅ | 6.09 ± 0.09 *#∅ | 0.35 ± 0.03 |
| Factors | nano | nano | Ni nano | - | Ni | nano | ||
| Group | Content, μg/g (Wet Weight) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | Kidney | Spleen | |
| 1. Control | 1.12 ± 0.15 | 0.50 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.12 |
| 2. Ni S 0.1 mg/kg b.w. | 1.35 ± 0.03 | 0.71 ± 0.25 | 0.20 ± 0.03 |
| 3. Ni S 1.0 mg/kg b.w. | 1.65 ± 0.32 | 1.57 ± 0.28 * | 0.18 ± 0.01 |
| 4. Ni S 10 mg/kg b.w. | 0.76 ±0.06 * | 3.94 ± 0.79 * | 0.36 ± 0.04 |
| 5. Ni NP1 0.1 mg/kg b.w. | 0.61 ± 0.05 *# | 0.70 ± 0.21 | 0.24 ± 0.05 |
| 6. Ni NP1 1.0 mg/kg b.w. | 0.61 ± 0.02 *# | 0.65 ± 0.11 # | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| 7. Ni NP1 10 mg/kg b.w. | 0.66 ± 0.03 * | 2.92 ± 0.46 * | 0.33 ± 0.05 |
| 8. Ni NP2 0.1 mg/kg b.w. | 0.62 ± 0.01 * | 0.38 ± 0.04 * | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| 9. Ni NP2 1.0 mg/kg b.w. | 0.58 ± 0.02 *# | 0.68 ± 0.22 # | 0.16 ± 0.02 |
| 10. Ni NP2 10 mg/kg b.w. | 0.58 ± 0.02 *#Ø | 2.36 ± 0.55 * | 0.22 ± 0.02 # |
| Factors | Ni, nano, Ni×nano | Ni, nano | Ni |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shipelin, V.A.; Shumakova, A.A.; Trushina, E.N.; Mustafina, O.K.; Masyutin, A.G.; Kolobanov, A.I.; Sokolov, I.E.; Gmoshinski, I.V.; Khotimchenko, S.A.; Nikityuk, D.B. Peroral Toxicological Assessment of Two-Dimensional Forms of Nickel Nanoparticles Sized between 20 and 120 nm. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193523
Shipelin VA, Shumakova AA, Trushina EN, Mustafina OK, Masyutin AG, Kolobanov AI, Sokolov IE, Gmoshinski IV, Khotimchenko SA, Nikityuk DB. Peroral Toxicological Assessment of Two-Dimensional Forms of Nickel Nanoparticles Sized between 20 and 120 nm. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(19):3523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193523
Chicago/Turabian StyleShipelin, Vladimir A., Antonina A. Shumakova, Eleonora N. Trushina, Oksana K. Mustafina, Alexander G. Masyutin, Alexey I. Kolobanov, Ilya E. Sokolov, Ivan V. Gmoshinski, Sergey A. Khotimchenko, and Dmitry B. Nikityuk. 2022. "Peroral Toxicological Assessment of Two-Dimensional Forms of Nickel Nanoparticles Sized between 20 and 120 nm" Nanomaterials 12, no. 19: 3523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193523
APA StyleShipelin, V. A., Shumakova, A. A., Trushina, E. N., Mustafina, O. K., Masyutin, A. G., Kolobanov, A. I., Sokolov, I. E., Gmoshinski, I. V., Khotimchenko, S. A., & Nikityuk, D. B. (2022). Peroral Toxicological Assessment of Two-Dimensional Forms of Nickel Nanoparticles Sized between 20 and 120 nm. Nanomaterials, 12(19), 3523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193523






