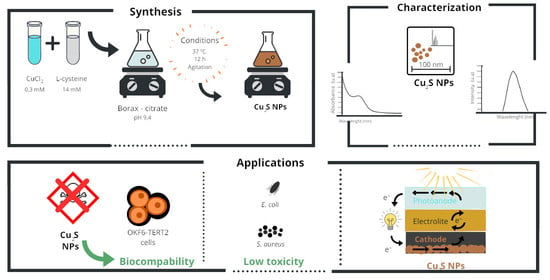
Cysteine-Mediated Green Synthesis of Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles: Biocompatibility Studies and Characterization as Counter Electrodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Cu2S Nanoparticles
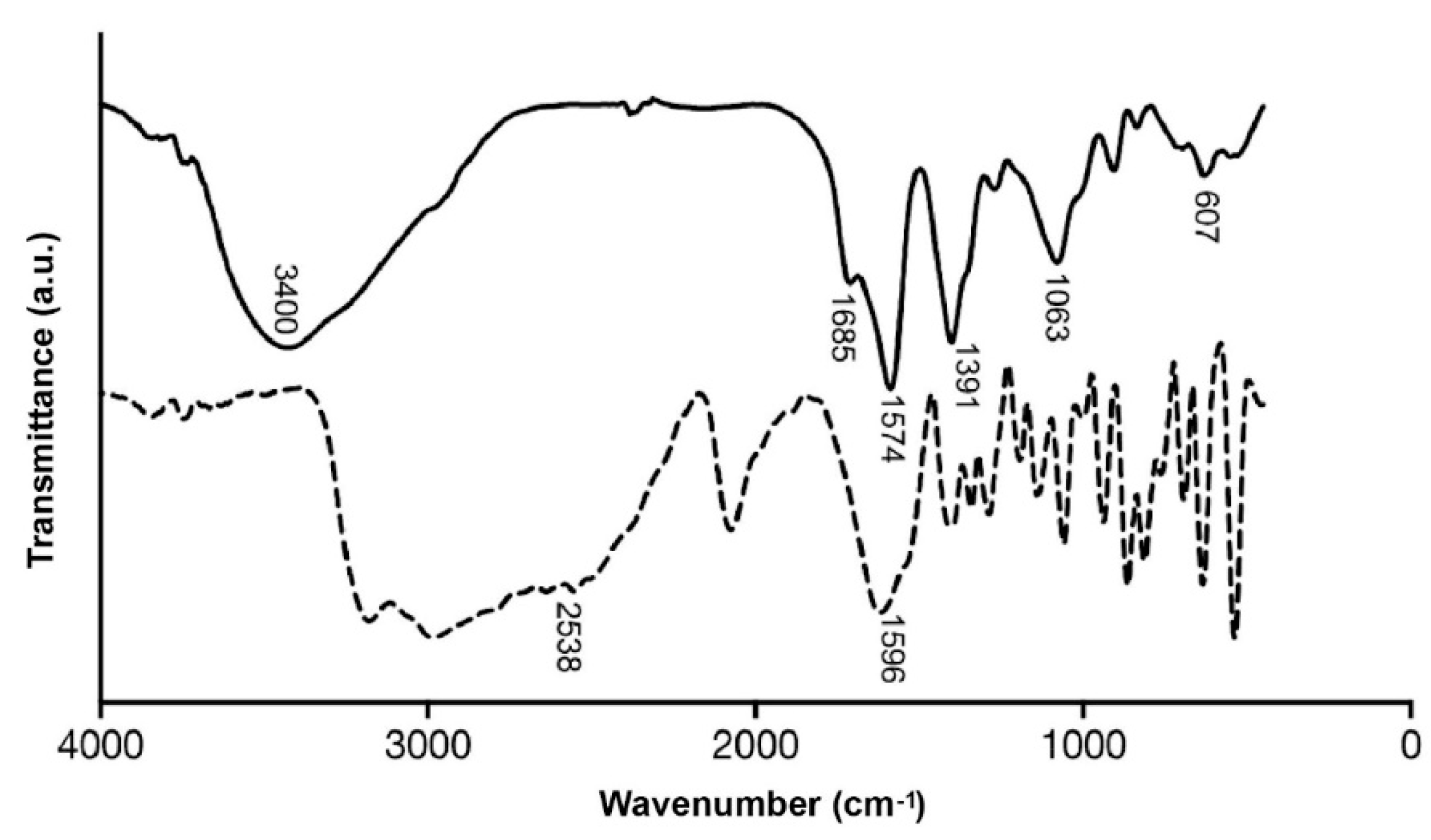
2.2. NPs Characterization
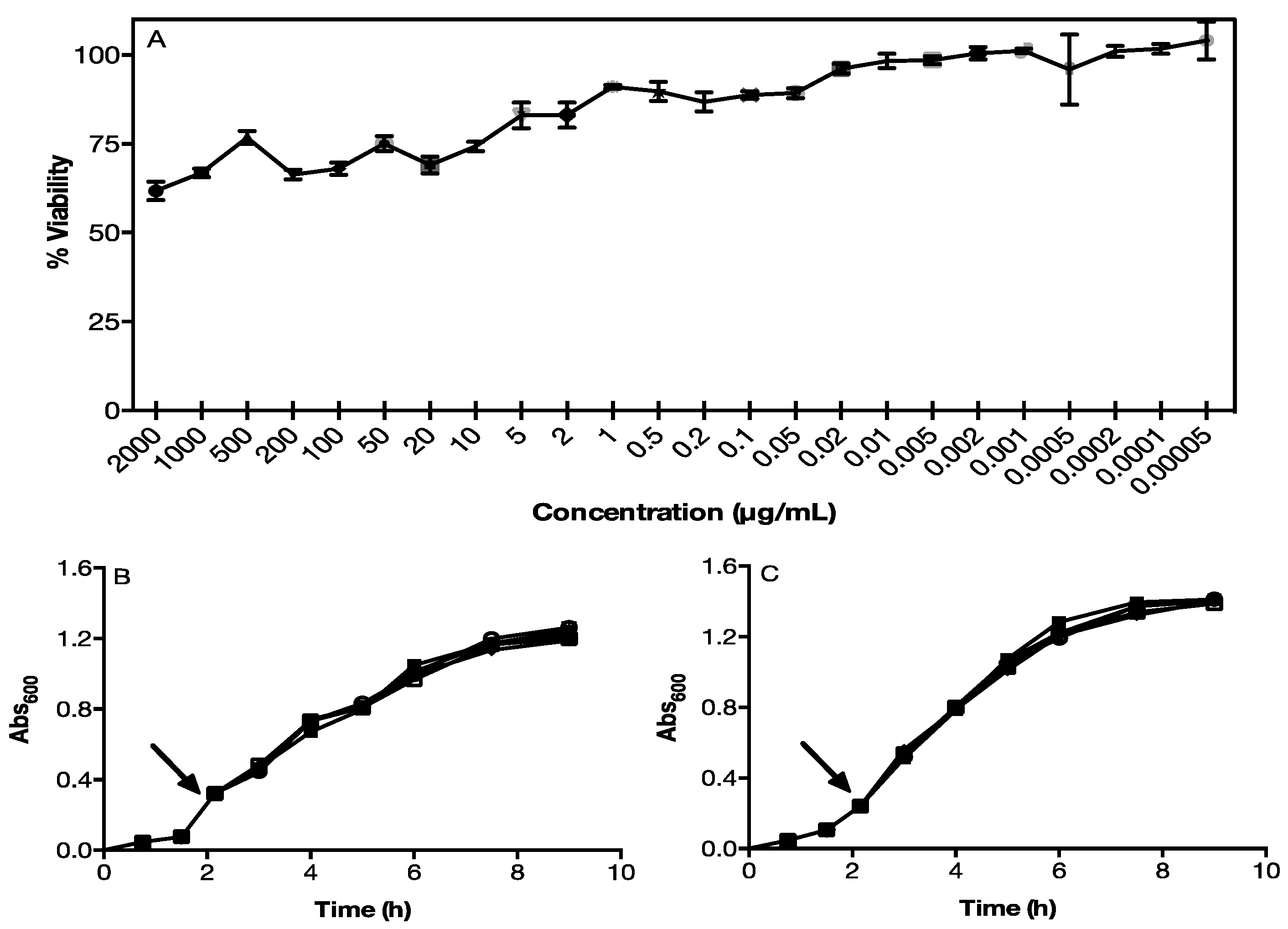
2.3. NPs Toxicity in Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
2.4. Fabrication of Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells
2.5. Electrode Impedance Spectroscopy
2.6. Characterization of Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Cu2S NPs
3.2. Cu2S NPs Characterization as Counter Electrode
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhtar, J.; Malik, M.A.; O’Brien, P.; Helliwell, M. Controlled Synthesis of PbS Nanoparticles and the Deposition of Thin Films by Aerosol-Assisted Chemical Vapour Deposition (AACVD). J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6116–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Donoso, J.M.; Monrás, J.P.; Bravo, D.; Aguirre, A.; Quest, A.F.; Osorio-Román, I.O.; Aroca, R.F.; Chasteen, T.G.; Vásquez, C.C. Biomimetic, Mild Chemical Synthesis of Cdte-GSH Quantum Dots with Improved Biocompatibility. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brelle, M.C.; McNulty, J.C.; Zhang, J.Z.; Torres-Martinez, C.L.; Mehra, R.K. Synthesis and Characterization of CuxS Nanoparticles. Nature of the Infrared Band and Charge-Carrier Dynamics. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, U.K.; Mukherjee, B. A Simple Synthesis and Characterization of CuS Nanocrystals. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2006, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haram, S.K.; Mahadeshwar, A.R.; Dixit, S.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles in Triton-X 100 Water-in-Oil Microemulsions. Undefined 1996, 100, 5868–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulandaisamy, A.J.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Significance of Nanoparticles and the Role of Amino Acids in Structuring Them—A Review. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 5222–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, G.; Wu, Q. Biomimetic and Bioinspired Synthesis of Nanomaterials/Nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2099–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunleavy, R.; Lu, L.; Kiely, C.J.; McIntosh, S.; Berger, B.W. Single-Enzyme Biomineralization of Cadmium Sulfide Nanocrystals with Controlled Optical Properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5275–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, D.; Liu, Q.; He, G. Biomimetic Synthesis and Characterisation of ZnS Nanoparticles in Aqueous Solution of Lysozyme. Micro Nano Lett. 2012, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Fu, L.; Ye, L.; Li, B.; Xu, X.; Xing, X.; He, J.; Song, Y.; Leng, C.; Guo, Y.; et al. Protein-Directed Synthesis of Highly Monodispersed, Spherical Gold Nanoparticles and Their Applications in Multidimensional Sensing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Tao, X.; Mao, C.; Zhu, J.J.; Liang, F. Aminopolycarboxyl-Modified Ag2S Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Resonance Light Scattering Sensing for Bovine Serum Albumin. Talanta 2007, 71, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.; Srivastava, S.K. Low-Temperature Synthesis of CuS Nanorods by Simple Wet Chemical Method. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pan, H.; Lou, Y.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, J.; Burda, C. Plasmonic Cu2-XS Nanocrystals: Optical and Structural Properties of Copper-Deficient Copper(I) Sulfides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4253–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raevskaya, A.E.; Stroyuk, A.L.; Kuchmii, S.Y.; Kryukov, A.I. Catalytic Activity of CuS Nanoparticles in Hydrosulfide Ions Air Oxidation. J. Mol. Catal A Chem. 2004, 212, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wu, J.; Qin, Q.; Li, Z.; Huang, X. Controllable Synthesis, Optical and Photocatalytic Properties of CuS Nanomaterials with Hierarchical Structures. Powder Technol. 2010, 198, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wadia, C.; Ma, W.; Sadtler, B.; Alivisatos, A.P. Synthesis and Photovoltaic Application of Copper(1) Sulfide Nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2345–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Órdenes-Aenishanslins, N.A.; Saona, L.A.; Durán-Toro, V.M.; Monrás, J.P.; Bravo, D.M.; Pérez-Donoso, J.M. Use of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Biosynthesized by Bacillus Mycoides in Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells. Microb. Cell Fact 2014, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emin, S.; Singh, S.P.; Han, L.; Satoh, N.; Islam, A. Colloidal Quantum Dot Solar Cells. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 1264–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Yamada, A.; Tamura, S.; Toyoda, T. CdSe Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cell Employing TiO2 Nanotube Working-Electrode and Cu2 S Counter-Electrode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Surolia, P.K.; Byrne, O.; Thampi, K.R. Efficient CdS Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells Made Using Novel Cu 2S Counter Electrode. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Choi, S.H.; Bang, J.H. New Insight into Copper Sulfide Electrocatalysts for Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells: Composition-Dependent Electrocatalytic Activity and Stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22078–22087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liao, L.; Ding, Y.; Zeng, H. Dithizone-Etched CdTe Nanoparticles-Based Fluorescence Sensor for the off–on Detection of Cadmium Ion in Aqueous Media. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10361–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, R.A.; Nafady, A.; Sirajuddin; Memon, N.; Sherazi, T.H.; Kalwar, N.H. L-Cysteine Protected Copper Nanoparticles as Colorimetric Sensor for Mercuric Ions. Talanta 2014, 130, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, V.D.; Ilić, D.P.; Nikolić, L.B.; Stanković, M.Z.; Stanojević, L.P.; Savić, I.M.; Savić, I.M. The Synthesis and Structure Characterization of Deoxyalliin and Alliin. Savrem. Tehnol./Adv. Technol. 2012, 1, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Tong, Z.; Huang, H. A Fluorescence Quenching Method for Determination of Cooper Ions with CdTe Quantum Dots. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2009, 54, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Saleem, H.; Sebastian, S.; Sundaraganesan, N. The Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman), NCA, First Order Hyperpolarizability, NBO Analysis, HOMO and LUMO Analysis of l-Cysteine by Ab Inito HF and Density Functional Method. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 78, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susi, H.; Byler, D.M.; Gerasimowicz, W.V. Vibrational Analysis of Amino Acids: Cysteine, Serine, β-Chloroalanine. J. Mol. Struct. 1983, 102, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Zeng, H.C. Highly Ordered Self-Assemblies of Submicrometer Cu2O Spheres and Their Hollow Chalcogenide Derivatives. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5963–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, D.J.; Laughlin, D.E. The Cu-S (Copper-Sulfur) System. Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 1983, 4, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Ramirez, P.V.; Arenas-Arrocena, M.C.; Santos-Cruz, J.; Vega-González, M.; Martínez-Alvarez, O.; Castaño-Meneses, V.M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; de la Fuente-Hernández, J. Growth Evolution and Phase Transition from Chalcocite to Digenite in Nanocrystalline Copper Sulfide: Morphological, Optical and Electrical Properties. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grønvold, F.; Westrum, E.F. Thermodynamics of Copper Sulfides I. Heat Capacity and Thermodynamic Properties of Copper(I) Sulfide, Cu2S, from 5 to 950 K. J. Chem. 1987, 19, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakeva, S.; Germanova, K. Electric and Photoelectric Properties of Polycrystalline Copper Sulphide. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1985, 18, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nanoparticles, T.; Saldanha, P.L.; Brescia, R.; Prato, M.; Li, H.; Povia, M.; Manna, L.; Lesnyak, V. Generalized One-Pot Synthesis of Copper Sul Fi de, Selenide-Sul Fi de, and Telluride-Sul Fi de Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, M.; Mathews, N.R.; Sanchez-Mora, E.; Pal, U.; Paraguay-Delgado, F.; Mathew, X. Synthesis of CuS Nanoparticles by a Wet Chemical Route and Their Photocatalytic Activity. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, C.; Sivamani, S.; Micha Premkumar, T.; Hariram, V. Computational Study of Leading Edge Jet Impingement Cooling with a Conical Converging Hole for Blade Cooling. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2017, 12, 6397–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Manivannan, R.; Noyel Victoria, S. Simple One-Pot Sonochemical Synthesis of Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles for Solar Cell Applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Chen, F.; Cai, W. Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles: From Sensors to Theranostics. Small 2014, 10, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, H.L.; Cronholm, P.; Gustafsson, J.; Mo, L. Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Are Highly Toxic A Comparison between Metal Oxide Nanoparticles and Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, Y.W.; An, Y.J. Microbial Toxicity of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles (CuO, NiO, ZnO, and Sb 2O 3) to Escherichia Coli, Bacillus Subtilis, and Streptococcus Aureus. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz Ahmed, K.B.; Anbazhagan, V. Synthesis of Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles and Evaluation of in Vitro Antibacterial Activity and in Vivo Therapeutic Effect in Bacteria-Infected Zebrafish. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 36644–36652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dealba-Montero, I.; Guajardo-Pacheco, J.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Araujo-Martínez, R.; Loredo-Becerra, G.M.; Martínez-Castañón, G.A.; Ruiz, F.; Jasso, M.E.C. Antimicrobial Properties of Copper Nanoparticles and Amino Acid Chelated Copper Nanoparticles Produced by Using a Soya Extract. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2017, 2017, 1064918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Hu, D.; Cheng, E.W.C.; Vargas-Reus, M.A.; Reip, P.; Allaker, R.P. Characterisation of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Huang, Q.; Li, C.; Chen, W. Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles for Photothermal Ablation of Tumor Cells. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quy, V.H.V.; Vijayakumar, E.; Ho, P.; Park, J.H.; Rajesh, J.A.; Kwon, J.M.; Chae, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, S.H.; Ahn, K.S. Electrodeposited MoS2 as Electrocatalytic Counter Electrode for Quantum Dot- and Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 260, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.; Oh, M.; Hong, V.; Quy, V.; Kwon, J.; Kim, J. Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Electrochemical Stability of Copper (I) Sul Fi de Electrode Electrodeposited on a Ti Interlayer-Coated Fl Uorine-Doped Tin Oxide Substrate and Its Application to Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells. Thin Solid Film. 2018, 660, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Shen, W.; Li, X.; Hou, Z.; Ke, S.; Shi, G.; Xu, C.; Fan, D. Materials Science & Engineering B Cation Exchange Synthesis of CuS Nanotubes Composed of Nanoparticles as Low-Cost Counter Electrodes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 227, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Luo, Y.; Shen, Q.; Toyoda, T.; Meng, Q. Screen-Printed Cu 2 S-Based Counter Electrode for Quantum-Dot-Sensitized Solar Cell. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 1168–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodes, G. Electrocatalytic Electrodes for the Polysulfide Redox System. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 127, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Chang, H. Quantum Dot–Sensitized Solar Cells Featuring CuS/CoS Electrodes Provide 4.1% Effi Ciency. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


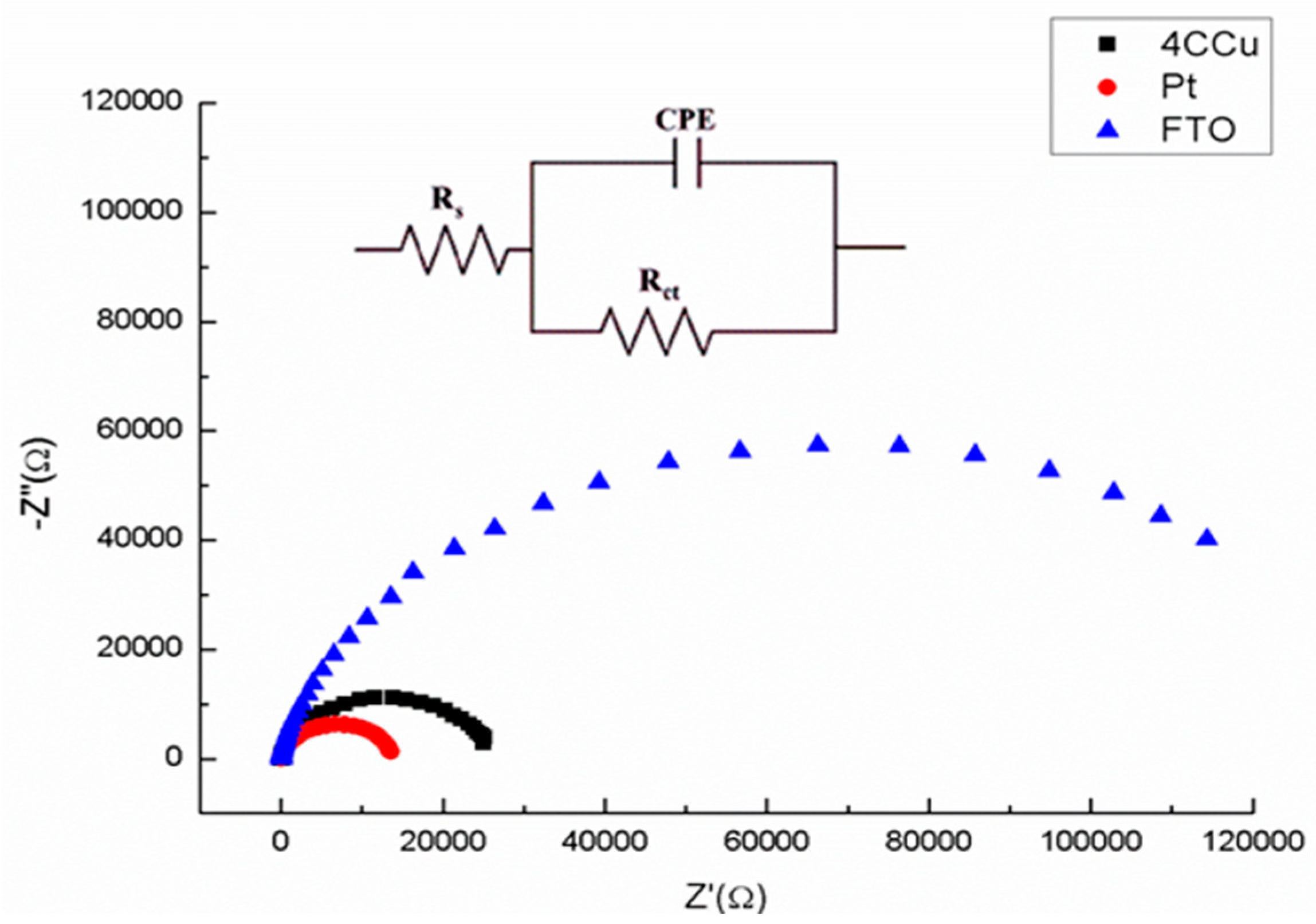
| EIS Characterization | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Counter Electrode | RS/Ω | CPET/µF | CPEP | RCT/kΩ | |||
| FTO | 18.15 | 2.82 | 0.94 | 112.7 | |||
| Pt | 16.81 | 7.83 | 0.93 | 13.8 | |||
| Cu2S (4 layers) | 26.15 | 5.54 | 0.92 | 25.3 | |||
| QDSSCs Characterization | |||||||
| Sensitizer | Electrolyte | Counter Electrode | Short Current Density | Open Circuit Voltage | Maximum Power | Fill Factor | Efficiency |
| Jsc [A/cm2] | Voc [V] | Pmax [W] | ƞ [%] | ||||
| Ruthenium | I−/I3− | Cu2S | 1.50 × 10−4 ± 4.89 × 10−11 | 0.490 ± 4.73 × 10−4 | 1.70 × 10−5 ± 2.21 × 10−12 | 0.231 ± 6.67 × 10−7 | 1.70 × 10−2 ± 2.25 × 10−6 |
| Pt | 5.20 × 10−4 ± 1.04 × 10−10 | 0.583 ± 3.02 × 10−4 | 1.92 × 10−4 ± 6.75 × 10−11 | 0.632 ± 4.47 × 10−5 | 1.92 × 10−1 ± 6.78 × 10−5 | ||
| CdTe QDs | Sn2−/S2 | Cu2S | 5.02 × 10−5 ± 1.21 × 10−10 | 0.300 ± 5.15 × 10−4 | 5.40 × 10−6 ± 2.09 × 10−12 | 0.358 ± 5.29 × 10−4 | 5.40 × 10−3 ± 2.09 × 10−6 |
| Pt | 4.49 × 10−5 ± 1.07 × 10−10 | 0.207 ± 6.47 × 10−5 | 4.04 × 10−6 ± 8.00 × 10−13 | 0.436 ± 4.85 × 10−4 | 4.04 × 10−3 ± 7.84 × 10−7 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saona, L.A.; Campo-Giraldo, J.L.; Anziani-Ostuni, G.; Órdenes-Aenishanslins, N.; Venegas, F.A.; Giordana, M.F.; Díaz, C.; Isaacs, M.; Bravo, D.; Pérez-Donoso, J.M. Cysteine-Mediated Green Synthesis of Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles: Biocompatibility Studies and Characterization as Counter Electrodes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183194
Saona LA, Campo-Giraldo JL, Anziani-Ostuni G, Órdenes-Aenishanslins N, Venegas FA, Giordana MF, Díaz C, Isaacs M, Bravo D, Pérez-Donoso JM. Cysteine-Mediated Green Synthesis of Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles: Biocompatibility Studies and Characterization as Counter Electrodes. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(18):3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183194
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaona, Luis A., Jessica L. Campo-Giraldo, Giovanna Anziani-Ostuni, Nicolás Órdenes-Aenishanslins, Felipe A. Venegas, María F. Giordana, Carlos Díaz, Mauricio Isaacs, Denisse Bravo, and José M. Pérez-Donoso. 2022. "Cysteine-Mediated Green Synthesis of Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles: Biocompatibility Studies and Characterization as Counter Electrodes" Nanomaterials 12, no. 18: 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183194
APA StyleSaona, L. A., Campo-Giraldo, J. L., Anziani-Ostuni, G., Órdenes-Aenishanslins, N., Venegas, F. A., Giordana, M. F., Díaz, C., Isaacs, M., Bravo, D., & Pérez-Donoso, J. M. (2022). Cysteine-Mediated Green Synthesis of Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles: Biocompatibility Studies and Characterization as Counter Electrodes. Nanomaterials, 12(18), 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183194