Antimicrobial Properties of Silver-Modified Denture Base Resins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
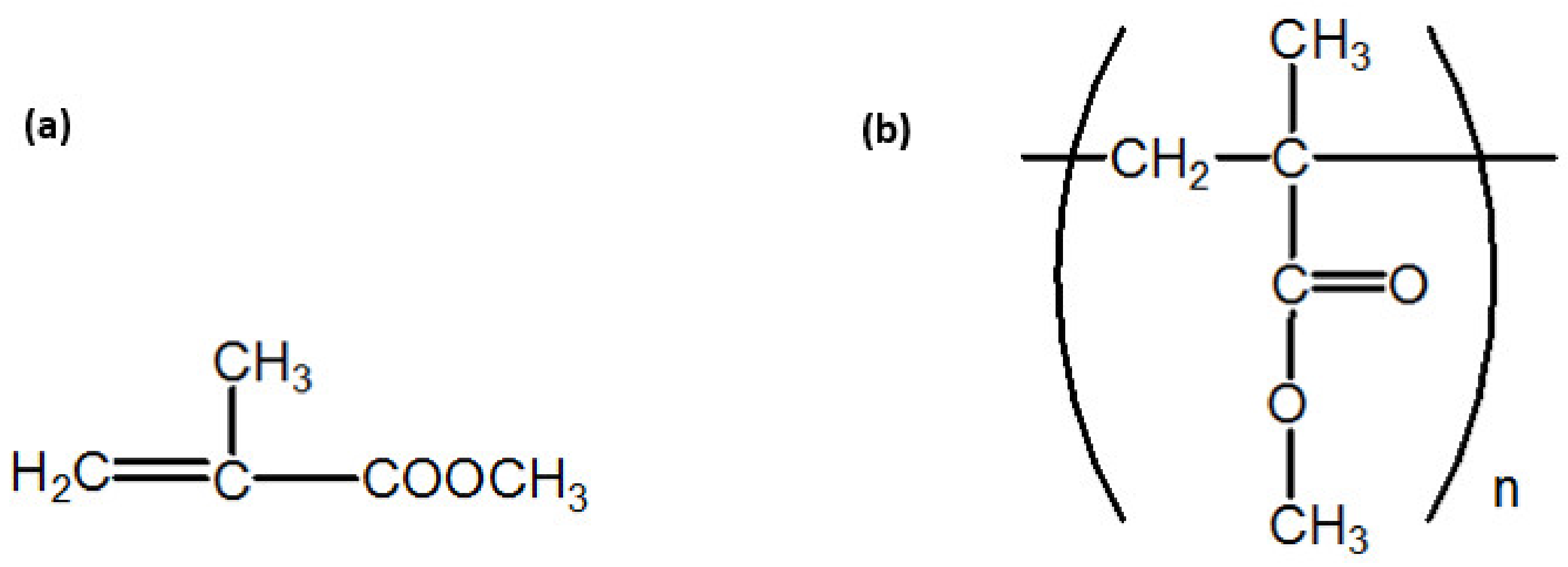
2.2. Material Modification and Sample Production
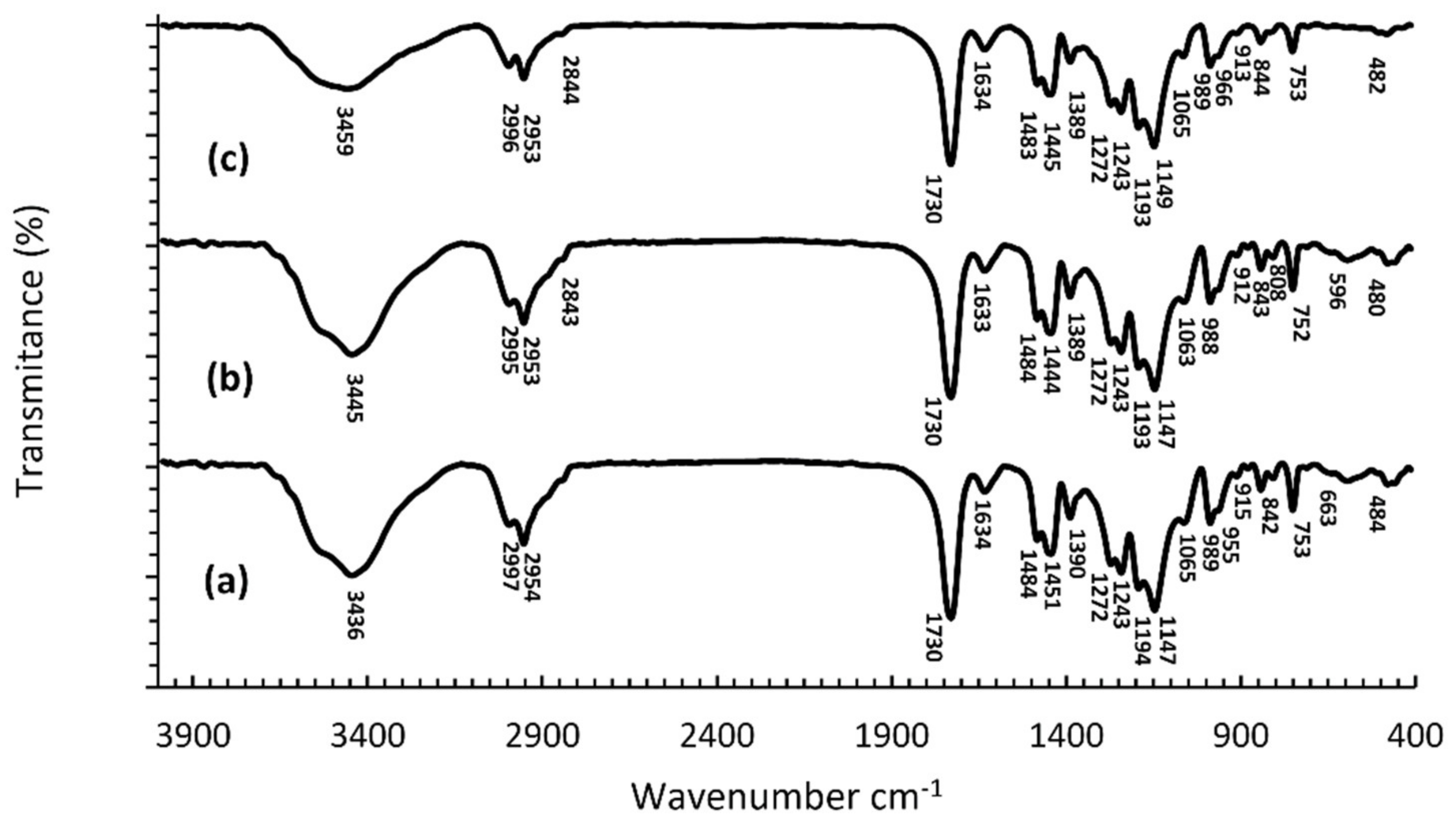
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
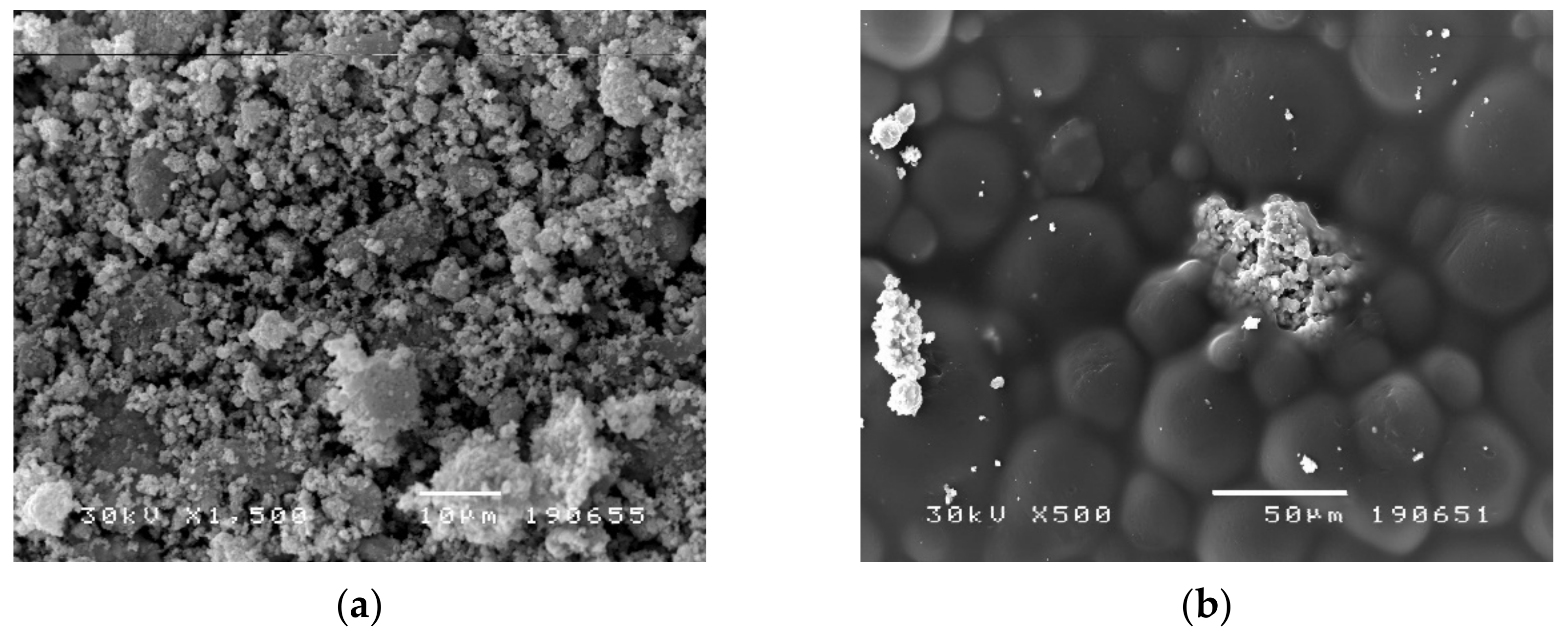
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.5. Test Organisms—Microbial Strains
2.6. Disc Diffusion Antibiotic Sensitivity Method
2.7. Microdilution Method
2.8. Modified Microdilution Method (a Broth Disk-Diffusion Method with Viable Counting)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlsson, G.E.; Omar, R. The future of complete dentures in oral rehabilitation: A critical review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2010, 37, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.W.; Chamary, N.; Lewis, M.A.O.; Milward, P.J.; McAndrew, R. Microbial Contamination of Removable Prosthodontic Appliances From Laboratories and Impact of Clinical Storage. Br. Dent. J. 2011, 211, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Compagnoni, M.A.; Pero, A.C.; Ramos, S.M.M.; Marra, J.; Paleari, A.G.; Rodriguez, L.S. Antimicrobial activity and surface properties of an acrylic resin containing a biocide polymer. Gerodontology 2014, 31, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Xie, X.; Wang, B.; Weir, M.D.; Thomas, W.; Oates, T.W.; Xu, H.H.K.; Zhang, N.; Bai, Y. Protein-repellent and Antibacterial Effects of a Novel Polymethyl Methacrylate Resin. J. Dent. 2018, 79, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendreau, L.; Loewy, Z.G. Epidemiology and Etiology of Denture Stomatitis. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 20, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contaldo, M.; Romano, A.; Mascitti, M.; Fiori, F.; Della Vella, F.; Serpico, R.; Santarelli, A. Association Between Denture Stomatitis, Candida Species and Diabetic Status. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mirizadeh, A.; Atai, M.; Ebrahimi, S. Fabrication of Denture Base Materials With Antimicrobial Properties. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saafan, A.; Zaazou, M.H. Assessmentof Photodynamic Therapy and Nanoparticles Effects on Caries Models. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, Y. Development of a novel resin-based dental material with dual biocidal modes and sustained release of Ag+ ions based on photocurable core-shell AgBr/cationic polymer nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, J.; Kuhn, D.M.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Hoyer, L.L.; McCormick, T.; Ghannoum, M.A. Biofilm formation by the fingal pathogen Candida albicans develop ment, architecture, and drug resistance. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5385–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesow, A.; Sarembe, S.; Pizzey, R.L.; Axe, A.S.; Bradshaw, D.J. Material compatibility and antimicrobial activity of consumer products commonly used to clean dentures. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, I.A.A.; Hamzah, M.I. Nanoparticles technology in medicine, as a diagnostic tool, and therapeutic applications for many chronic and genetic diseases: A review. IMJ 2019, 17, 238–253. [Google Scholar]
- Sanvicens, N.; Marco, M.-P. Multifunctional nanoparticles—Properties and prospects for their use in human medicine. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Hossain, M.K. Classification and Properties of Nanoparticles. In Metal Nanoparticle-Based Polymer Composites, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Huo, K.; Cui, L.; Zhang, W.; Ni, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chu, P.K. Antibacterial nano-structured titania coating incorporated with silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5706–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazer, M.; Shamei, A.; Alimohammadi, F. Stabilized nanosilver loaded nylon knitted fabric using BTCA without yellowing. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 74, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prombutara, P.; Kulwatthanasal, Y.; Supaka, N.; Sramala, I.; Chareonpornwattana, S. Production of nisin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for sustained antimicrobial activity. Food Control 2012, 24, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, K.; De Gusseme, B.; Verstraete, W. Biogenic silver nanoparticles (bio-Ag0) decrease biofouling of bio-Ag0/PES nanocomposite membranes. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.H.; Cheon, J. Synergism of nanomaterials with physical stimuli for biology and medicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, A.M.; Steinmetz, N.F. Design of virus-based nanomaterials for medicine, biotechnology, and energy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4074–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Mahendra, S.; Lyon, D.Y.; Brunet, L.; Liga, M.V.; Li, D.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: Potential applications and implications. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4591–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimbela, G.V.; Ngo, S.M.; Fraze, C.; Yang, L.; Stout, D.A. Antibacterial properties and toxicity from metallic nanomaterials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3941–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Joshi, H.C.; Srivastava, A.; Sharma, A.; Verma, N. An efficient antibacterial multi-scale web of carbon fibers with asymmetrically dispersed Ag-Cu bimetal nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2014, 443, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, P.; Gorain, B.; Low, S.Y.; Tan, S.A.; Ling, E.C.S.; Lim, Y.K.; Chin, C.M.; Lee, P.Y.; Lee, C.M.; Ooi, C.H.; et al. Nanotechnology based approaches for anti-diabetic drugs delivery. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 136, 52–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slawson, R.M.; Lee, H.; Trevors, J.T. Bacterial interactions with silver. Biometals 1990, 3, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Feng, H.L. Silver-ion release and particle distribution of denture base resin containing nanometer-sized silver-supported antimicrobial agent. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2008, 43, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Sondi, B.S. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.-N.; Ho, C.-M.; Chen, R.; He, Q.-Y.; Yu, W.-Y.; Sun, H.; Tam, P.K.-H.; Chiu, J.-F.; Che, C.-M. Silver nanoparticles: Partial oxidation and antibacterial activities. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 12, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.; Pradhan, A.; Pakstis, L.; Pochan, D.; Shah, S.I. Synthesis and Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolář, M.; Večeřová, R.; Pizúrová, N.; Sharma, V.K.; Nevěčná, T.; Zbořil, R. Silver colloid nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity. J. Phys. Chem. 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Sung, W.S.; Moon, S.-K.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.G. Antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles on dermatophytes. J. Microbial. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-J.; Sung, W.S.; Suh, B.K.; Moon, S.-K.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.G. Antifungal activity and mode of action of silver nano-particles on Candida albicans. BioMetals 2009, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, C.; Munstedt, H.; Rosch, A. The antimicrobial efficacy of polyamide 6/silver-nano- and microcomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 108, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Contreras, R.; Argueta-Figueroa, L.; Mejía-Rubalcava, C.; JiménezMartínez, R.; Cuevas-Guajardo, S.; Sánchez-Reyna, P.A.; Mendieta-Zeron, H. Perspectives for the use of silver nanoparticles in dental practice. Int. Dent. J. 2011, 61, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaee, M.Z.; Akhavan, A.; Sheikh, N.; Sodagar, A. Antibacterial effects of a new dental acrylic resin containing silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Ge, S. Application of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles in Dentistry. Molecules 2019, 24, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, C.J. Antifungal and physical characteristics of modified denture base acrylic incorporated with silver nanoparticles. Gerodontology 2012, 29, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, C.P.; Kaiser, R.I. Mechanical studies on the electron induced degradation of polymethyl methacrylate and Kapton. Phys. Chem. 2010, 12, 14902–14915. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Xie, E.; Han, L.; Xu, Z. Turning PMMA Nanofibres into Graphene Nanoribbons by In Sitn Electron Beam Irradiation. Abv. Mater. 2008, 9999, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tommasini, F.J.; da Cunha Ferreirab, L.; Pimenta Tienne, L.G.; de Oliveira Aguiarb, V.; da Silvaa, M.H.P.; da Mota Rochab, L.F.; de Fátima Vieira Marques, M. Poly (Methyl Methacrylate)-SiC Nanocomposites Prepared Through in Situ Polymerization. Mater. Res. 2018, 21, e20180086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Nikfa rjam, N.; Sanjani, N.S.; Qazvini, N.T. Effect of silver nanoparticle on the properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) nanocomposite network made by in situ photoiniferter-mediated photopolymerization. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2015, 38, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasojević, P.M.; Zrilić, Z.; Stamenković, D.S.; Veličković, S. Uticaj ubrzanog starenja na mehanička svojstva poli(metil-metakrilatnih) materijala za bazu zubnih proteza modifikovanih itakonatima. Hem. Ind. 2011, 65, 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, Y. Novel resin-based dental material with anti-biofilm activity and improved mechanical property by incorporating hydrophilic cationic copolymer functionalized nanodiamond. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marutani, E.; Yamamoto, S.; Ninjbadgar, T.; Tsujii, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Takano, M. Surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate on magnetite nanoparticles. Polymer 2004, 45, 2231–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Luthra, R. Silver nanoparticles in dentistry: An emerging trend. SRM J. Res. Dent. Sci. 2016, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niska, K.; Knap, N.; Kędzia, A.; Jaskiewicz, M.; Kamysz, W.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Capping agent-dependent toxicity and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles: An in vitro study. Concerns about potential application in dental practice. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, A.M.; Balaji, K.; Girilal, M.; Yadav, R.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Venketesan, R. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their synergistic effect with antibiotics: A study against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.M. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, P.; Su, C.H.; Venkat Kumar, G.; Adhikary, S.; Pandian, K.; Gopinath, S.C.; Chen, Y.; Anbu, P. Biopolymers regulate silver nanoparticle under microwave irradiation for effective antibacterial and antibiofilm activities. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Rong, K.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, R. Size-dependent antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles against oral anaerobic pathogenic bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Si, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Zhu, J.; Wu, L.; Tian, J.; Chen, X.; et al. A versatile chitosan nanogel capable of generating AgNPs in-situ and long-acting slow-release of Ag+ for highly efficient antibacterial. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Zhang, T.; Yang, N.; Niu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Chen, P.; Zhong, L.; Dong, X.; et al. POD Nanozyme optimized by charge separation engineering for light/pH activated bacteria catalytic/photodynamic therapy. Signal. Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, V.; Martinez, A. Antibacterial activity against Streptococcus mutans and diametrical tensiles trength of an interim cement modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles and terpenes: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 862.e1–862.e7. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, M.A.S.; Cheng, L.; Weir, M.D.; Hsia, R.C.; Rodrigues, L.K.A.; Xu, H.H.K. Novel dental adhesive containing antibacterial agents and calcium phosphate nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 101, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Garcia, F.; Tanomaru-Filho, M.; Chávez-Andrade, G.M.; Bosso-Martelo, R.; Basso-Bernardi, M.I.; Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J.M. Effect of silver nanoparticles on physicochemical and antibacterial properties of calcium silicate cements. Braz. Dent. J. 2016, 27, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.Y. Characterization and antimicrobial efficacy of Portland cement impregnated with silver nanoparticles. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2017, 9, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonaidi-Jafari, N.; Izadi, M. The effects of silver nanoparticles on antimicrobial activity of ProRoot mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and calcium enriched mixture (CEM). J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2016, 8, e22–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkai, K.R.; Mudda, J.A. Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of fungal-derived silver nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkai, K.R.; Mudda, J.A. Antibacterial efficacy of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm: An in vitro Study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkai, K.R.; Mudda, J.A. Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles derived from fungi against endo-perio pathogens Porphyromonas gingivalis, Bacillus pumilus, and Enterococcus faecalis. J. Conserv. Dent. 2017, 20, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, J.; Einsele, H.; Hebart, H.; Schumacher, U.; Hrastnik, C.; Daum, G. Phospholipid and sterol analysis of plasma membranes of azole-resistant Candida albicans strains. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 185, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Andrade, G.M.; Tanomaru-Filho, M. Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and antibacterial activity of poly(vinyl alcohol)-coated silver nanoparticles and farnesol as irrigating solutions. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 84, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Huang, X. A liquid crystalline precursor incorporating chlorhexidine acetate and silver nanoparticles for root canal disinfection. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habiboallah, G.; Mahdi, Z.; Majid, Z.; Nasroallah, S.; Taghavi, A.M.; Forouzanfar, A.; Arjmand, N. Enhancement of gingival wound healing by local application of silver nanoparticles periodontal dressing following surgery: A histological assessment in animal model. Mod. Res. Inflamm. 2014, 3, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Chandra, R.V.; Reddy, A.A.; Reddy, B.H.; Nagarajan, S.; Naveen, A. Evaluation of the antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on guided tissue regeneration membrane colonization—An in vitro study. J. Int. Acad. Periodontol. 2015, 17, 66–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, H.; Boughton, R.I. In situ fabrication of silver nanoparticle-filled hydrogen titanate nanotube layer on metallic titanium surface for bacteriostatic and biocompatible implantation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2903–2916. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Song, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, C. Titanium surface priming with phase-transited lysozyme to establish a silver nanoparticle-loaded chitosan/hyaluronic acid antibacterial multilayer via layer-by-layer self-assembly. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146957. [Google Scholar]
- Farhadian, N.; Usefi Mashoof, R. Streptococcus mutans counts in patients wearing removable retainers with silver nanoparticles vs those wearing conventional retainers: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 149, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Weir, M.D.; Xu, H.H.; Antonucci, J.M.; Lin, N.J.; Lin-Gibson, S.; Xu, S.M.; Zhou, X. Effect of amorphous calcium phosphate and silver nanocomposites on dental plaque microcosm biofilms. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Weir, M.D.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.H. Comparison of quaternary ammonium-containing with nano-silver-containing adhesive in antibacterial properties and cytotoxicity. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodnik, V.V.; Vukovic, J.V.; Nedeljkovic, J.M. Synthesis and characterization of silver—poly(methylmethacrylate) nanocomposites. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, M.M.; Taqa, A.A.; Hatim, N.A. Study of fourier transform infrared of adding metallic nanofillers on heat cure acrylic resin treated by microwave. Hamdan Med. J. 2019, 12, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Darman Singho, N.; Che Lah, N.A.; Johan, M.R.; Ahmad, R. FTIR Studies on silver-poly(methylmethacrylate) nanocomposites via in-situ polymerization technique. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 5596–5603. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.N.; Redhwi, H.H.; Vakalopoulou, E.; Tsagkalias, I.; Ioannidou, M.D.; Achilias, D.S. Synthesis, characterization and reaction kinetics of PMMA/silver nanocomposites prepared via in situ radical polymerization. Eur. Poly. J. 2015, 72, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaee, M.Z.; Mohammadkhani, M.; Akhavan, A.; Mohammadi, R. In situ formation of silver nanoparticles in PMMA via reduction of silver ions by butylated hydroxytoluene. Struct. Chem. 2011, 22, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, C.; Pascale, M.; Contaldo, M.; Esposito, V.; Busciolano, M.; Milillo, L.; Guida, A.; Petruzzi, M.; Serpico, R. Candida-associated denture stomatitis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2011, 16, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Garbacz, K.; Kwapisz, E.; Wierzbowska, M. Denture Stomatitis Associated With Small-Colony Variants of Staphylococcus Aureus: A Case Report. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, J. Effect of a denture base acrylic resin containing silver nanoparticles on Candida albicans adhesion and biofilm formation. Gerodontology 2016, 33, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Patil, A.; Thakur, S.; Kesharwani, P. Carbon dots: Emerging theranostic nanoarchitectures. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, C.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I.; Santos-Martinez, M.J.; Radomski, M.W. Pharmacological and toxicological effects of co-exposure of human gingival fibroblasts to silver nanoparticles and sodium fluoride. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, A.D.; Hugo, W.B. Antimicrobial activity and action of silver. Prog. Med. Chem. 1994, 31, 351–370. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Chu, L.; Rawls, H.R.; Norling, B.K.; Cardenas, H.L.; Whang, K. Development of an antimicrobial resin—A pilot study. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, D.M.; Oei, J. A novel antimicrobial orthodontic band cement with in situ-generated silver nanoparticles. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Han, Z. Antibacterial activity, cytotoxicity and mechanical behavior of nano-enhanced denture base resin with different kinds of inorganic antibacterial agents. Dent. Mater. J. 2017, 36, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Yeo, S.Y.; Yi, S.C. The effect of filler particle size on the antibacterial properties of compounded polymer/silver fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5407–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, S.; Ahila, S.C. Evaluation and comparison of anti-Candida effect of heat cure polymethylmethacrylate resin enforced with silver nanoparticles and conventional heat cure resins: An in vitro study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2014, 25, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, H.H.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Garza-Treviño, E.N.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C. PVP-coated silver nanoparticles block the transmission of cell-free and cell-associated HIV-1 in human cervical culture. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slenters, T.V.; Hauser-Gerspach, I.; Daniels, A.U.; Fromm, K.M. Silver coordination compounds as light-stable, nanostructured and anti-bacterial coatings for dental implant and restorative materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5359–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, C.; Munstedt, H.; Rosch, A. Long-term antimicrobial polyamide 6/silver-nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 6067–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, S.L.; Bowler, P.G.; Russell, D. Bacterial resistance to silver in wound care. J. Hosp. Infect. 2005, 60, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordögh, L.; Vörös, A.; Nagy, I.; Kondorosi, E.; Kereszt, A. Symbiotic plant peptides eliminate Candida albicans both in vitro and in an epithelial infection model and inhibit the proliferation of immortalized human cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 320796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, H.H.; Garza-Treviño, E.N.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Singh, D.K. Silver nano- particles are broad-spectrum bactericidal and virucidal compounds. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, H.H.; Romero-Urbina, D.G.; Pierce, C.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L.; Arellano-Jiménez, M.J.; Jose-Yacaman, M. Effect of silver nanoparticles on Candida albicans biofilms: An ultrastructural study. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panacek, A.; Kolar, M.; Vecerova, R.; Prucek, R.; Soukupova, J.; Krystof, V.; Hamal, P.; Zboril, R.; Kvıtek, L. Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles against Candida spp. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6333–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Park, S.; Roh, J.; Kim, S.; Choi, K.; Yi, J.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, J. Biofilm-inactivating activity of silver nanoparticles: A comparison with silver ions. J. Ind. End. Chem. 2013, 19, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, L.J. Candida biofilms and their role in infection. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, C.J.; Jin, L.; Samaranayake, L.P. Biofilm lifestyle of Candida: A mini review. Oral Dis. 2008, 14, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, D.R.; Gorup, L.F.; Takamiya, A.S.; Ruvollo-Filho, A.C.; de Camargo, E.R.; Barbosa, D.B. The growing importance of materials that prevent microbial adhesion: Antimicrobial effect of medical devices containing silver. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | S. aureus ATCC 6538 | C. albicans ATCC 24433 |
|---|---|---|
| Inhibition zone (mm) | ||
| PMMA cold-curing | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
| PMMA heat- curing | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 | 0.0000 ± 0.0000 |
| 2% AgNPs PMMA cold-curing | 0.0400 ± 0.0306 | 0.0200 ± 0.0058 |
| 2% AgNPs PMMA heat-curing | 0.0400 ± 0.0306 | 0.0200 ± 0.0058 |
| 5% AgNPs PMMA cold-curing | 0.0133 ± 0.0088 | 0.0300 ± 0.0058 |
| 5% AgNPs PMMA heat-curing | 0.0077 ± 0.0062 | 0.0200 ± 0.0058 |
| 10% AgNPs PMMA cold-curing | 9.0667 ± 0.0882 *** | 9.0300 ± 0.1234 ** |
| 10% AgNPs PMMA heat-curing | 9.0367 ± 0.0426 *** | 9.0200 ± 0.0945 *** |
| 10% AgCl PMMA cold-curing | 9.0233 ± 0.0962 *** | 9.0033 ± 0.2114 ** |
| 10% AgCl PMMA heat-curing | 9.0033 ± 0.0561 *** | 9.0667 ± 0.1348 *** |
| ANOVA (F, significance) | 9046.24; p < 0.001 | 2486.63; p < 0.001 |
| Sample | S. aureus ATCC 6538 | C. albicans ATCC 24433 |
|---|---|---|
| MIC/MMC, mg/mL | ||
| 10% AgNPs PMMA cold curing | 12.50/12.50 | 12.50/12.50 |
| 10% AgNPs PMMA hot curing | 12.50/12.50 | 12.50/12.50 |
| 10% AgCl PMMA cold curing | 3.13/6.25 | 3.13/3.13 |
| 10% AgCl PMMA hot curing | 3.13/6.25 | 3.13/3.13 |
| Sample | S. aureus ATCC 6538 | C. albicans ATCC 24433 |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Count × 106 | ||
| Growth Control | 99.667 ± 0.882 | 99.667 ± 0.882 |
| PMMA cold-curing | 100.000 ± 0.000 | 101.000 ± 1.528 |
| PMMA heat-curing | 100.000 ± 0.000 | 100.667 ± 1.764 |
| 2% AgNPs PMMA cold-curing | 100.000 ± 0.000 | 5.433 ± 0.260 a *** bc ** |
| 2% AgNPs PMMA heat-curing | 100.000 ± 0.000 | 2.000 ± 0.012 a *** bc ** |
| 5% AgNPs PMMA cold-curing | 0.133 ± 0.005 abc *** | 0.001 ± 0.000 a *** bc ** |
| 5% AgNPs PMMA heat-curing | 0.306 ± 0.005 abc *** | 0.000 ± 0.000 a *** bc ** |
| 10% AgNPs PMMA cold-curing | 0.000 ± 0.000 abc *** | 0.000 ± 0.000 a *** bc ** |
| 10% AgNPs PMMA heat-curing | 0.000 ± 0.000 abc *** | 0.000 ± 0.000 a *** bc ** |
| 10% AgCl PMMA cold-curing | 3.847 ± 0.144 abc *** | 1.700 ± 0.115 a *** bc ** |
| 10% AgCl PMMA heat-curing | 0.281 ± 0.012 abc *** | 0.000 ± 0.000 a *** bc ** |
| ANOVA (F. significance) | 36,952.25; p < 0.001 | 3759.21; p < 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gligorijević, N.; Mihajlov-Krstev, T.; Kostić, M.; Nikolić, L.; Stanković, N.; Nikolić, V.; Dinić, A.; Igić, M.; Bernstein, N. Antimicrobial Properties of Silver-Modified Denture Base Resins. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142453
Gligorijević N, Mihajlov-Krstev T, Kostić M, Nikolić L, Stanković N, Nikolić V, Dinić A, Igić M, Bernstein N. Antimicrobial Properties of Silver-Modified Denture Base Resins. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(14):2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142453
Chicago/Turabian StyleGligorijević, Nikola, Tatjana Mihajlov-Krstev, Milena Kostić, Ljubiša Nikolić, Nemanja Stanković, Vesna Nikolić, Ana Dinić, Marko Igić, and Nirit Bernstein. 2022. "Antimicrobial Properties of Silver-Modified Denture Base Resins" Nanomaterials 12, no. 14: 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142453
APA StyleGligorijević, N., Mihajlov-Krstev, T., Kostić, M., Nikolić, L., Stanković, N., Nikolić, V., Dinić, A., Igić, M., & Bernstein, N. (2022). Antimicrobial Properties of Silver-Modified Denture Base Resins. Nanomaterials, 12(14), 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142453







