Temperature Detectable Surface Coating with Carbon Nanotube/Epoxy Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
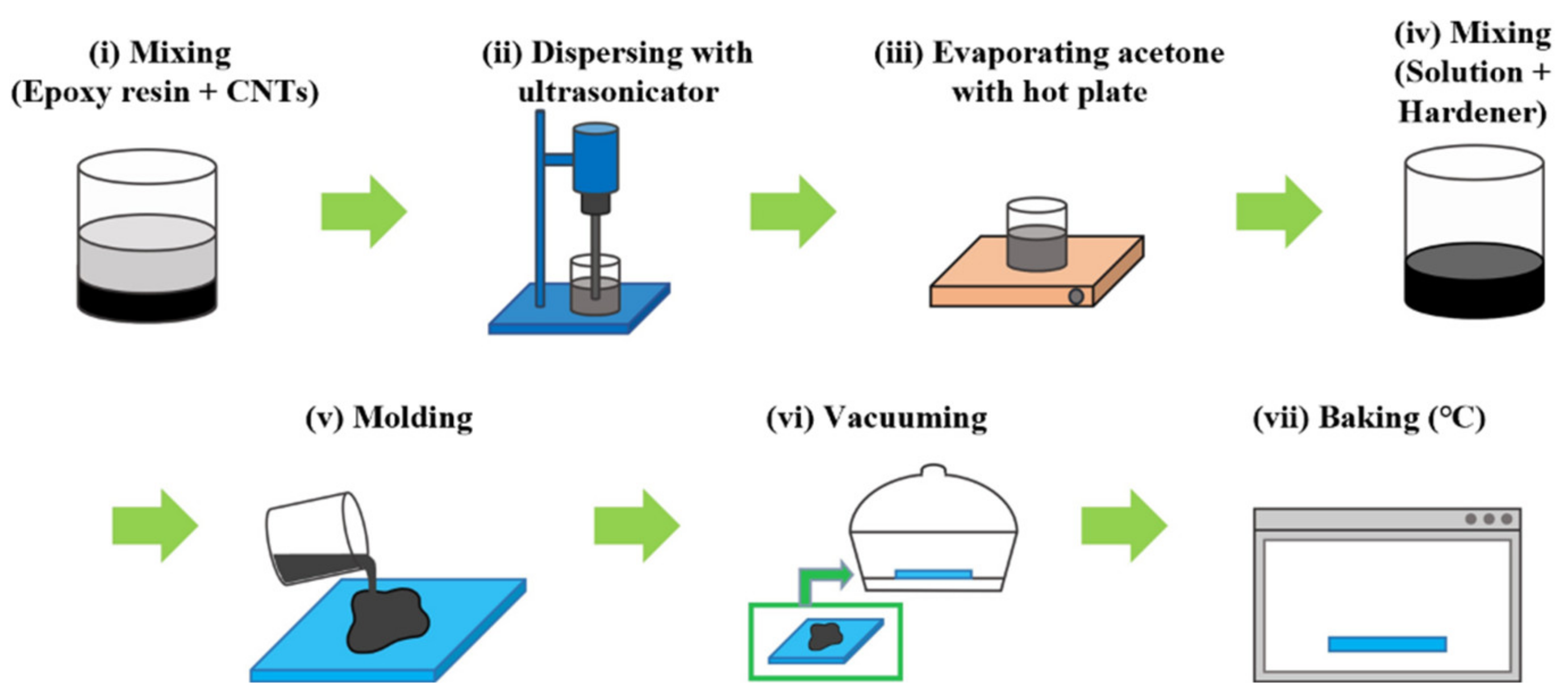
2.2. Fabrication Procedure
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrical Conductivity of CNT/EP Coating
3.2. Sensing Performance of CNT/EP Coating for Static and Cyclic Temperature
3.3. Application of Temperature Sensing System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webb, C. Infrared: Faster; smaller; cheaper. Control Instrum. 1997, 29, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Chen, W. Carbon nanotube and graphene-based bioinspired electrochemical actuators. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadagno, L.; De Vivo, B.; Di Bartolomeo, A.; Lamberti, P.D.; Sorrentino, A.; Tucci, V.; Vertuccio, L.; Vittoria, V. Effect of functionalization on the thermo-mechanical and electrical behavior of multi-wall carbon nanotube/epoxy composites. Carbon 2011, 49, 1919–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauhofer, W.; Kovacs, J.Z. A review and analysis of electrical percolation in carbon nanotube polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Vertuccio, L.; Naddeo, C.; Calabrese, E.; Barra, G.; Raimondo, M.; Sorrentino, A.; Binder, W.H.; Michael, P.; Rana, S. Reversible self-healing carbon-based nanocomposites for structural applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Assami, Y.; Habti, M.D.; Raman, V. Stiffening offshore composite wind-blades bonding joints by carbon nanotubes reinforced resin–a new concept. J. Struct. Integr. Maint. 2020, 5, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, H.G.; Schulte, K. Functionalisation effect on the thermo-mechanical behaviour of multi-wall carbon nanotube/epoxy-composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 2303–2308. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.; Yin, H. Characterization and modeling of the effective electrical conductivity of a carbon nanotube/polymer composite containing chain-structured ferromagnetic particles. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 51, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Yin, H. Effect of aligned ferromagnetic particles on strain sensitivity of multi-walled carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 141903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, S.; Park, Y. Carbon nanotube-reinforced smart composites for sensing freezing temperature and deicing by self-heating. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2018, 8, 1847980418776473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yum, S.; Yin, H.; Jang, S. Toward multi-functional road surface design with the nanocomposite coating of carbon nanotube modified polyurethane: Lab-scale experiments. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Kim, D.; Park, Y. Accelerated curing and enhanced material properties of conductive polymer nanocomposites by joule heating. Materials 2018, 11, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-K.; May, Y.-W. Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Vertuccioa, L.; Guadagnoa, L.; Spinellib, G.; Lambertib, P.; Zarrellic, M.; Russod, S.; Iannuzzod, G. Smart coatings of epoxy based CNTs designed to meet practical expectations in aeronautics. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 147, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesha, K.; Rafique, I.; Muhammad, B. Aerospace application of polymer nanocomposite with carbon nanotube, graphite, graphene oxide, and nanoclay. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 1438–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F.; Li, X.; Park, S. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, N.; Wu, L.; Yuan, W.; Peng, X.; Gu, B.; Chang, C.; Liu, Y.; Ning, H.; Li, J.; et al. Temperature-dependent piezoresistivity in an MWCNT/epoxy nanocomposite temperature sensor with ultrahigh performance. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 455501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Yue, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, C.; Wu, W.; Zhu, H. Raman spectroscopy and resistance-temperature studies of functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes/epoxy resin composite film. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 214, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidenko, N.A.; Kuksin, A.V.; Molodykh, V.V.; Pyankov, E.S.; Ichkitidze, L.P.; Zaborova, V.A.; Tsymbal, A.A.; Tkachenko, S.A.; Shafaei, H.; Diachkova, E.; et al. Flexible Strain-Sensitive Silicone-CNT Sensor for Human Motion Detection. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Yin, H. Effective electrical conductivity of carbon nanotube-polymer composites: A simplified model and its validation. Mater. Res. Express 2015, 2, 045602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, B.; Potschke, P.; Ilin, E.; Predtechenskiy, M. Melt mixed SWCNT-polypropylene composites with very low electrical percolation. Polymer 2016, 98, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, H.; Hecht, D.S.; Grüner, G. Percolation in transparent and conducting carbon nanotube networks. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2513–2517. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.; Li, L. Self-sensing carbon nanotube composites exposed to glass transition temperature. Materials 2020, 13, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Lei, R.S.; Zhu, Z.H. Effect of temperature on the electrical property of epoxy composites with carbon nanotube. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 149, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimenko, A.Y.; Kuksin, A.V.; Shaman, Y.P.; Kitsyuk, E.P.; Fedorova, Y.O.; Sysa, A.V.; Pavlov, A.A.; Glukhova, O.E. Electrically conductive networks from hybrids of carbon nanotubes and graphene created by laser radiation. Nanomaterials 2022, 11, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanli, A.; Benchirouf, A.; Müller, C.; Kanoun, O. Piezoresistive performance characterization of strain sensitive multi-walled carbon nanotube-epoxy nanocomposites. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2017, 254, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, M.; van Hoa, S. Electrical resistance of CNT-PEEK composites under compression at different temperatures. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Xue, Q.Z.; Gao, X.L.; Zheng, Q.B. Temperature dependence of the electrical properties of the carbon nanotube/polymer composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2009, 3, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Luo, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q. Carbon based polyimide nanocomposites thin film strain sensors fabricated by ink-jet printing method. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 300, 111664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itkis, M.E.; Borondics, F.; Yu, A.P.; Haddon, R.C. Bolometric infrared photoresponse of suspended single−walled carbon nanotube films. Science 2006, 312, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.T.; Li, Z.Z.; Xu, G.W.; Wu, J.Z. Suspending single−wall carbon nanotube thin film infrared bolometers on microchannels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 163110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, A.E. Bolometric detector on the basis of single-wall carbon nanotube/polymer composite. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2008, 51, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Sivasankar, V.S.; Dasgupta, A.; Das, S. Ultrathin and ultrasensitive printed carbon nanotube-based temperature sensors capable of repeated uses on surfaces of widely varying curvatures and wettabilities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 10257–10270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Qian, J.; Peng, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, Z.; Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G.; Ye, S. Screen-Printed Flexible Temperature Sensor Based on FG/CNT/PDMS Composite with Constant TCR. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 9593–9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, K.S.; Chani, M.T.S.; Khalid, F.A. Carbon nanotubes film based temperature sensors. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2011, 43, 1701–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.; Phan, H.; Nguyen, T.; Qamar, A.; Foisal, A.R.M.; Viet, T.N.; Tran, C.; Zhu, Y.; Nguyen, N.; Dao, D.V. Environment-friendly carbon nanotube based flexible electronics for noninvasive and wearable healthcare. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 10061–10068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagatay, E.; Falco, A.; Abdellah, A.; Lugli, P. Carbon nanotube based temperature sensors fabricated by large-scale spray deposition. In Proceedings of the 2014 10th Conference on Ph. D. Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PRIME), IEEE, Grenoble, France, 1–4 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, F.; Ng, C.; Liu, P.; Dong, L.; Imaizumi, Y.; Maeda, K.; Maruyama, H.; Ichikawa, A.; Fukuda, T. Ultra-small site temperature sensing by carbon nanotube thermal probes. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology, IEEE, Munich, Germany, 16–19 August 2004; pp. 146–148. [Google Scholar]
- Blasdel, N.J.; Wujcik, E.K.; Carletta, J.E.; Lee, K.S.; Monty, C.N. Fabric nanocomposite resistance temperature detector. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Volder, M.; Reynaerts, D.; Van Ho, C.; Tawfick, S.; Hart, A.J. A Temperature Sensor from a Self-Assembled Carbon Nanotube Microbridge. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE Conference on Sensors 2010, Kona, HI, USA, 1–4 November 2010; pp. 2369–2372. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, C.K.M.; Wong, V.T.S.; Chan, R.H.M.; Li, W.J. Dielectrophoretic Batch Fabrication of Bundled Carbon Nanotube Thermal Sensors. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2004, 3, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Reference | Material | |TCR| (10−3/°C) | Measured Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| In this paper (Maximum) | CNT/epoxy | 0.7 | −20 to 60 |
| [33] | CNT-GO | ~60 | 5–50, 25–70 |
| [34] | CNT/PDMS; CNT/FG/PDMS; | 1.5–2.8 ~28 | 40–80 |
| [35] | MWCNT | 2.4–2.7 | 20–75 |
| [36] | CNT yarn (without solvent) | ~0.75 | 25–80 |
| [37] | SWNT-CMC | ~3 | 0–100 |
| [38] | CNT deposited on ITO electrodes | ~0.4 | 25–90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-J.; Jung, Y.-J.; Park, J.; Jang, S.-H. Temperature Detectable Surface Coating with Carbon Nanotube/Epoxy Composites. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142369
Lee S-J, Jung Y-J, Park J, Jang S-H. Temperature Detectable Surface Coating with Carbon Nanotube/Epoxy Composites. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(14):2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142369
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seung-Jun, Yu-Jin Jung, JeeWoong Park, and Sung-Hwan Jang. 2022. "Temperature Detectable Surface Coating with Carbon Nanotube/Epoxy Composites" Nanomaterials 12, no. 14: 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142369
APA StyleLee, S.-J., Jung, Y.-J., Park, J., & Jang, S.-H. (2022). Temperature Detectable Surface Coating with Carbon Nanotube/Epoxy Composites. Nanomaterials, 12(14), 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142369








