Scanning Deposition Method for Large-Area Diamond Film Synthesis Using Multiple Microwave Plasma Sources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
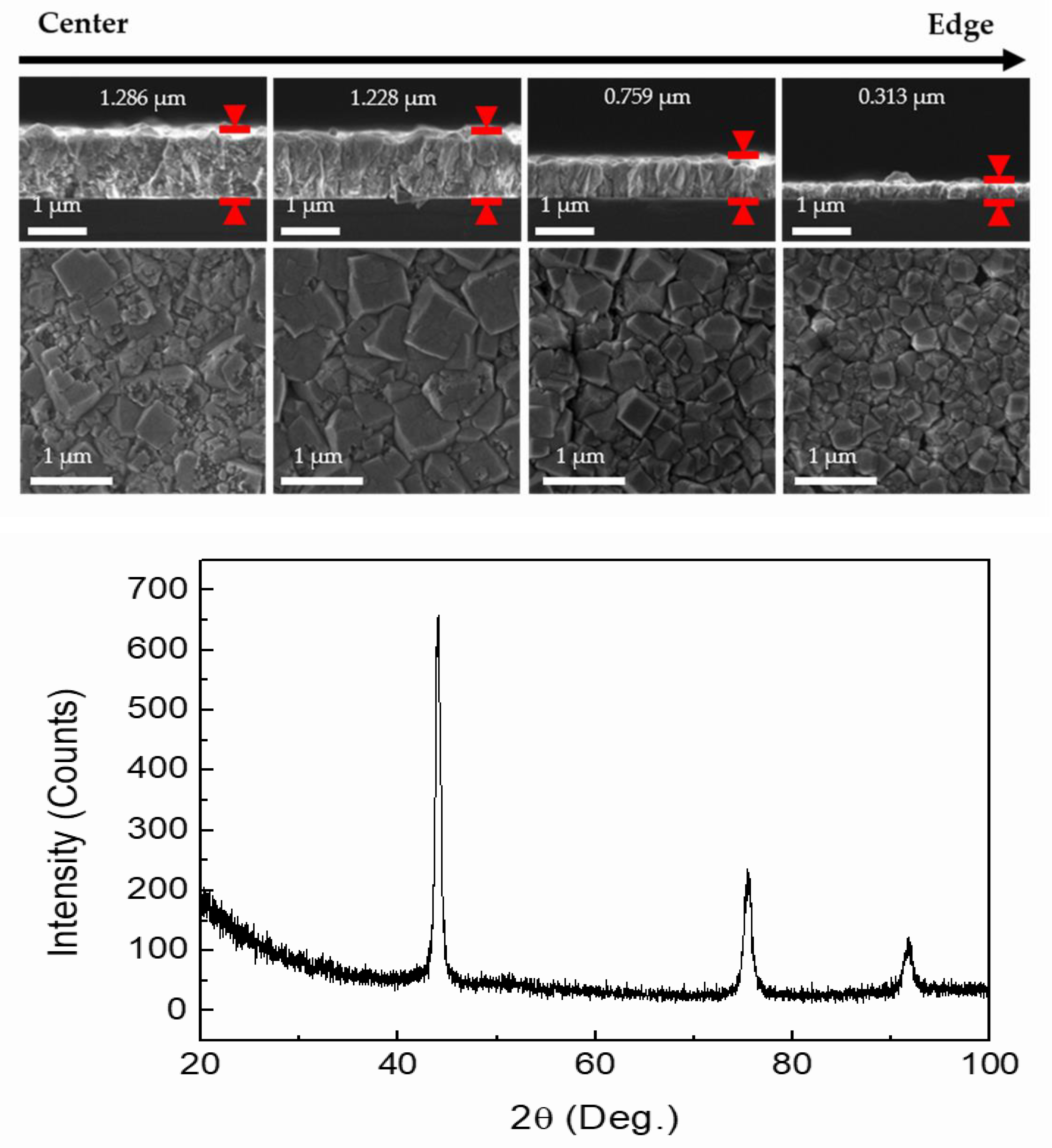
3.1. Process Improvement for Diamond Synthesis Using the Single Plasma Source
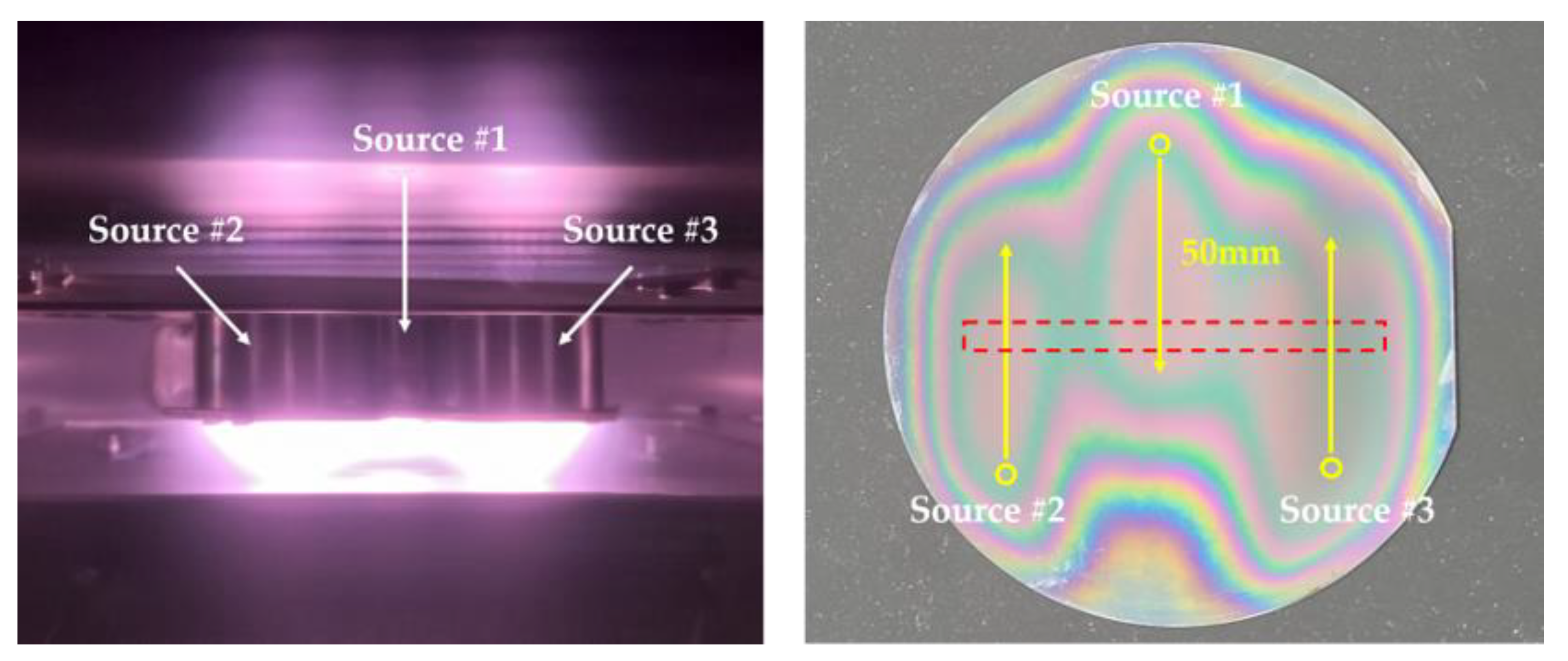
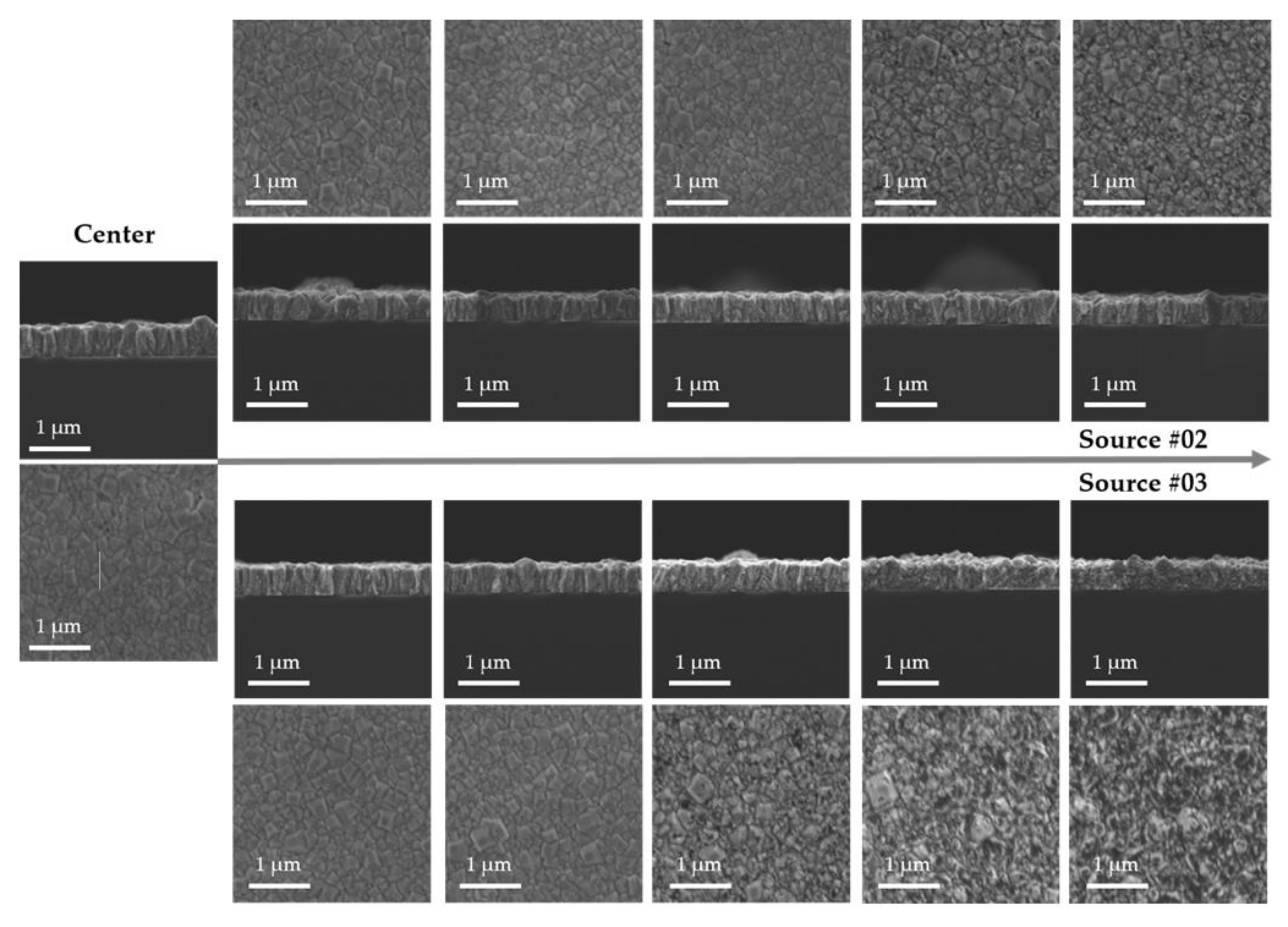
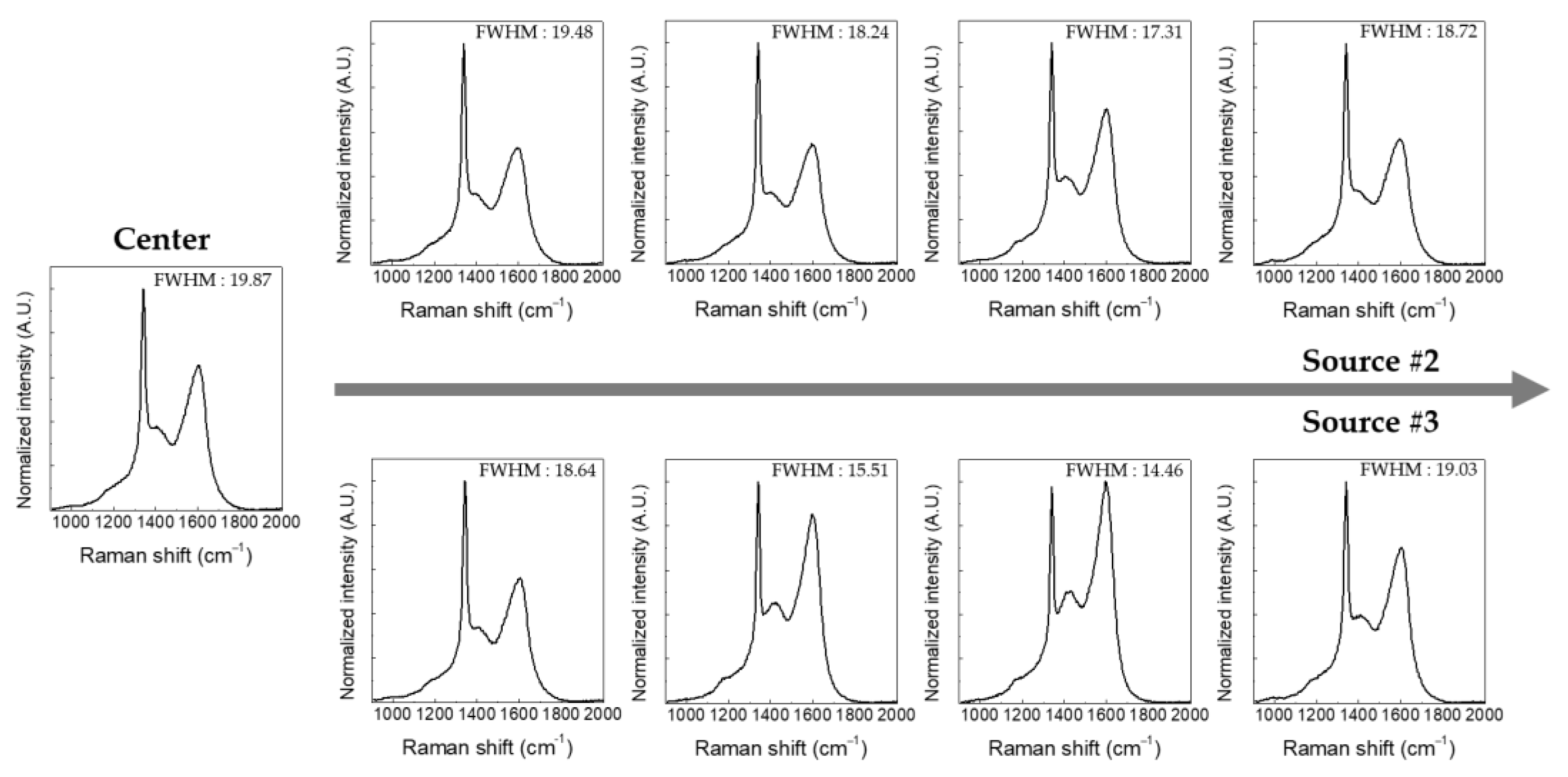
3.2. Large-Area Diamond Synthesis Using a Multi-Surface-Wave Plasma Source
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davim, J.P. Diamond tool performance in machining metal-matrix composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 128, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkihazi, E.E.; Sedov, V.S.; Sovyk, D.N.; Khomich, A.A.; Bolshakov, A.P.; Ryzhkov, S.G.; Khomich, A.V.; Vinogradov, D.V.; Ralchenko, V.G.; Konov, V.I. Plateholder design for deposition of uniform diamond coatings on WC-Co substrates by microwave plasma CVD for efficient turning application. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 75, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auciello, O.; Aslam, D.M. Review on advances in microcrystalline, nanocrystalline and ultrananocrystalline diamond films-based micro/nano-electromechanical systems technologies. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 7171–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.; Koizumi, S.; Yater, J.; Koeck, F. Diamond electron emission. MRS Bull. 2014, 39, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalin, V.E.; Krymskii, M.I.; Krymskii, K.M. Several applications of diamonds in high-power optics and electronics. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. 2018, 63, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.O.; Shen, Y.; Pang, Y.Y.; Leung, W.K.; Zhao, N.; Yang, S. Diamond quantum sensors: From physics to applications on condensed matter research. Funct. Diam. 2021, 1, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdi, S.; Kolahdouz, M.; Moeen, M.; Kovi, K.K.; Balmer, R.S.; Radamson, H.H.; Isberg, J. Single crystal diamond for infrared sensing applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 163510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, D.; Suzuki, M.; Lloret, F.; Alba, G.; Villar, P. Diamond for electronics: Materials, processing and devices. Materials 2021, 14, 7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, H.; Baines, Y.; Beam, E.; Borga, M.; Bouchet, T.; Chalker, P.R.; Charles, M.; Chen, K.J.; Chowdhury, N.; Chu, R.; et al. The 2018 GaN power electronics roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 163001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, F.P.; Hall, H.T.; Strong, H.M.; Wentorfjun, R.H. Man-made diamonds. Nature 1955, 176, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Sato, Y.; Kamo, M.; Setaka, N. Vapor deposition of diamond particles from methane. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 21, L183–L185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Sato, Y.; Tsutsumi, M.; Setaka, N. Growth of diamond particles from methane-hydrogen gas. J. Mater. Sci. 1982, 17, 3106–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawabe, A.; Inuzuka, T. Growth of diamond thin films by electron assisted chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1985, 46, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawabe, A.; Inuzuka, T. Growth of diamond thin films by electron-assisted chemical vapour deposition and their characterization. Thin Solid Film. 1986, 137, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahama, K.; Hirata, K.; Nakamatsu, H.; Kawai, S.; Fujimori, N.; Imai, T.; Yoshino, H.; Doi, A. Synthesis of diamond by laser-induced chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1986, 49, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S. Chemical vapour deposition of diamond in RF glow discharge. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1985, 4, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamo, M.; Sato, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Setaka, N. Diamond synthesis from gas phase in microwave plasma. J. Cryst. Growth. 1983, 62, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, Y.; Amanuma, S.; Komaki, K. The synthesis of high-quality diamond in combustion flames. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 68, 6401–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, K.; Sasaki, K.; Kawarada, M.; Koshino, N. High rate synthesis of diamond by dc plasma jet chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1988, 52, 437–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikharev, A.L.; Gorbachev, A.M.; Lobaev, M.A.; Radishev, D.B. Multimode cavity type MPACVD reactor for large area diamond film deposition. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 83, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehedi, H.A.; Achard, J.; Rats, D.; Brinza, O.; Tallaire, A.; Mille, V.; Silva, F.; Provent, C.; Gicquel, A. Low temperature and large area deposition of nanocrystalline diamond films with distributed antenna array microwave-plasma reactor. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2014, 47, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudrillart, B.; Nave, A.S.C.; Hamann, S.; Bénédic, F.; Lombardi, G.; van Helden, J.H.; Röpcke, J.; Achard, J. Growth processes of nanocrystalline diamond films in microwave cavity and distributed antenna array systems: A comparative study. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 71, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Tsugawa, K.; Ishihara, M.; Koga, Y.; Hasegawa, M. Large-area surface wave plasmas using microwave multi-slot antennas for nanocrystalline diamond film deposition. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2009, 19, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, M.; Remes, Z.; Babchenko, O.; Kromka, A. Optical study of defects in nano-diamond films grown in linear antenna microwave plasma CVD from H2/CH4/CO2 gas mixture. Phys. Status Solidi B 2012, 249, 2635–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.J.; Girka, O. Compact water-cooled surface wave plasma source for remote plasma cleaning. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 123307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushin, G.N.; Osswald, S.; Padalko, V.I.; Bogatyreva, G.P.; Gogotsi, Y. Effect of sintering on structure of nanodiamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, S.; Yushin, G.; Mochalin, V.; Kucheyev, S.O.; Gogotsi, Y. Control of sp2/sp3 carbon ratio and surface chemistry of nanodiamond powders by selective oxidation in air. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11635–11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawer, S.; Nugent, K.W.; Jamieson, D.N.; Orwa, J.O.; Bursill, L.A.; Peng, J.L. The Raman spectrum of nanocrystalline diamond. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 332, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawer, S.; Nemanich, R.J. Raman spectroscopy of diamond and doped diamond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 362, 2537–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, S.; Thomsen, C. Raman spectroscopy of graphite. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 362, 2271–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Raman spectroscopy of amorphous, nanostructured, diamond-like carbon, and nanodiamond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 362, 2477–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, M.; Takase, T.; Mitsuda, Y. Raman spectra of various diamonds. Mineral. J. 1993, 16, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Tzeng, Y. Mechanisms of suppressing secondary nucleation for low-power and low-temperature microwave plasma self-bias-enhanced growth of diamond films in argon diluted methane. AIP Adv. 2011, 1, 042117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, K.; Kawaki, S.; Ishihara, M.; Kim, J.; Koga, Y.; Sakakita, H.; Koguchi, H.; Hasegawa, M. Nanocrystalline diamond growth in a surface-wave plasma. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2011, 20, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennig, P.A.; Stevenson, D.A. Influence of substrate topography on the nucleation of diamond thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1991, 59, 1562–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spitsyn, B.V.; Bouilov, L.L.; Derjaguin, B.V. Vapor growth of diamond on diamond and other surfaces. J. Cryst. Growth 1981, 52, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, O.A. Nanocrystalline diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2011, 20, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Process Conditions | |
|---|---|
| Inlet gas | CH4, H2, Ar |
| Gas ratio (CH4/H2) | 0.4–1.0% |
| Pressure | 400–800 mTorr |
| Wafer temperature | 700–950 °C |
| Wafer treatment | Mechanical scratch/ultrasonic (5% nanodiamond) |
| Microwave power | 700–800 W |
| Plasma source | Single, triple |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.P.; Lee, K.-i.; You, H.J.; Jang, S.O.; Choi, Y.S. Scanning Deposition Method for Large-Area Diamond Film Synthesis Using Multiple Microwave Plasma Sources. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12121959
Hong SP, Lee K-i, You HJ, Jang SO, Choi YS. Scanning Deposition Method for Large-Area Diamond Film Synthesis Using Multiple Microwave Plasma Sources. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(12):1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12121959
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Seung Pyo, Kang-il Lee, Hyun Jong You, Soo Ouk Jang, and Young Sup Choi. 2022. "Scanning Deposition Method for Large-Area Diamond Film Synthesis Using Multiple Microwave Plasma Sources" Nanomaterials 12, no. 12: 1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12121959
APA StyleHong, S. P., Lee, K.-i., You, H. J., Jang, S. O., & Choi, Y. S. (2022). Scanning Deposition Method for Large-Area Diamond Film Synthesis Using Multiple Microwave Plasma Sources. Nanomaterials, 12(12), 1959. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12121959





