Abstract
The overuse of chromium (Cr) has significantly negatively impacted human life and environmental sustainability. Recently, the employment of nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) for Cr(VI) removal is becoming an emerging approach. In this study, carbonized melamine foam-supported nZVI composites, prepared by a simple impregnation–carbonization–reduction method, were assessed for efficient Cr(VI) removal. The prepared composites were characterized by XPS, SEM, TEM, BET and XRD. Batch experiments at different conditions revealed that the amount of iron added, the temperature of carbonization and the initial Cr(VI) concentration were critical factors. Fe@MF-12.5-800 exhibited the highest removal efficiency of 99% Cr(VI) (10 mg/L) at neutral pH among the carbonized melamine foam-supported nZVI composites. Its iron particles were effectively soldered onto the carbonaceous surfaces within the pore networks. Moreover, Fe@MF-12.5-800 demonstrated remarkable stability (60%, 7 days) in an open environment compared with nZVI particles.
1. Introduction
The quest for rapid economic development has increased chromium (Cr) discharge into the environment due to the expansion of notably textile, leather tanning and metal-based industries [1,2]. These discharged Cr heavy metals exist dominantly in trivalent (Cr(III)) and hexavalent (Cr(VI)) forms, with the latter being more hazardous due to their strong toxicity and mobility [3], causing severe health problems such as multiorgan failure, renal necrosis and pulmonary fibrosis [4]. Hence, Cr(VI) standards for industrial effluents (0.1–0.5 mg/L) and drinking water (<50 µg/L) have been stipulated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) to curb water contamination [5]. Till date, broad categories of techniques were developed for Cr(VI) removal, including electrocoagulation [6], adsorption [7], bioremediation [8] and chemical reduction [9], of which adsorption (and/or subsequent reduction) is much preferred as it is easily designed, effective, tractable, economically feasible and no secondary contamination [10].
In comparison to conventional adsorbents (e.g., titanium dioxide, goethite, zeolites), nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) has the advantages of higher reactivity and surface energy, more active surface sites, and higher reaction rate [11,12]. However, the aggregation of nZVI limits its mobility, dispersity, durability and, mechanical strength, and the oxidization of nZVI can significantly decrease its reactivity [13,14]. Additionally, nZVI and its end products are toxic and can cause pollution if not well managed. Its interaction with biological species and promotion of disruptive oxidant generation heightens ecotoxicity [4,15,16]. To overcome these disadvantages, nZVI is often loaded onto supporting materials, including sepiolite, mesoporous silica, resin, and biochar [17,18,19,20]. Considering high stability, large specific surface area and, excellent adsorption performance, carbon-containing materials such as activated carbon, graphene and, carbon nanotubes are primarily utilized to support nZVI [21,22,23,24,25,26]. Nonetheless, these commonly used carbon-based materials have the disadvantages of high cost and complex preparation procedures.
Cheap commercial melamine foams consist of three-dimensional (3D) interlinked dendritic fibers with high elasticity, large geometric area, and apertures of about 4 microns [27]. There have also been reports showing potential applications of melamine foams. Wu et al. reported a microporous metalloporphyrin-containing framework-wrapped melamine foam for process-intensified acyl transfer [28]. Additionally, Li et al. developed superelastic and arbitrary-shaped graphene aerogels with a sacrificial skeleton of melamine foam [29]. Furthermore, Rodon Fores et al. prepared a catalytically active supramolecular hydrogel, using commercial melamine foam, that was used in a continuous flow reactor with good recyclability [30]. Melamine foam can also be carbonized to form a honeycomb-type microporous structure with high nitrogen and oxygen co-doping by a simple high-temperature carbonization process [31]. This type of material exhibits excellent adsorption capacity (>100 times their weight), high porosity (>99%), and low density (~7 mg/cm3) [32]. In addition, it displays good chemical stability and electrical conductivity, which can effectively facilitate electron transfer [33]. Although carbonized melamine foam possesses the above advantages, there is still no research on carbonized melamine foam loaded with nZVI for Cr(VI) removal.
In this work, carbonized melamine foam loaded with nZVI (denoted as Fe@MF) was prepared and optimized using a simple one-stage carbon thermal reduction method. The morphology and characteristics of Fe@MF were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), specific surface area (BET), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Additionally, the application of this material in Cr-containing sewage treatment was studied.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7), iron (III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O) (99%), sodium borohydride solution (NaBH4), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Deionized (DI) water was used in all tests. The Cr(VI) stock solution (100 mg/L) was prepared by dissolving K2Cr2O7 in DI water. Different concentrations of Cr(VI) solution (10–60 mg/L) were obtained by diluting the stock with DI water.
2.2. Fe@MF Composite Preparation
The nZVI-loaded carbonized melamine foam composite was prepared following the procedure of impregnation–carbonization–reduction described earlier [23] (Figure S1a). Firstly, 20 mL of FeCl3·6H2O solution with concentration ranging from 7.5 to 50 mmol/L was added to melamine foam (SINOYQX) blocks (5 × 3 × 2 cm3). The porous melamine foam soaked with 0, 7.5, 10, 12.5, 25, 37.5, and 50 mmol/L FeCl3·6H2O solutions were named Fe@MF-0, Fe@MF-7.5, Fe@MF-10, Fe@MF-12.5, Fe@MF-25, Fe@MF-37.5 and, Fe@MF-50, respectively. Secondly, the wet melamine foam blocks were dried at 50 °C for 48 h, followed by calcination in a tube furnace at 800 °C (10 °C/min heating rate) under N2 atmosphere for 1 h. The obtained composites were labeled Fe@MF-0-800, Fe@MF-7.5-800, Fe@MF-10-800, Fe@MF-12.5-800, Fe@MF-25-800, Fe@MF-37.5-800, and Fe@MF-50-800, respectively. For Fe@MF-12.5, different carbonization temperatures of 600 °C, 800 °C, and 1000 °C were applied and subsequently labeled Fe@MF-12.5-600, Fe@MF-12.5-800, and Fe@MF-12.5-1000.
After carbonization, the carbonized melamine foam showed a perforated network structure similar to a tetrapod architecture [34]. Although, after carbonization, the volume of the samples decreased by about two times, the 3D porous structure was still maintained (Figure S1b–d).
2.3. Analysis
According to the methods described by Milacic et al., Cr(VI) concentration was assessed with 1,5-diphenylcarbazide utilizing a spectrophotometer (UV-3101PC, Sakaemachi, Japan) at 540 nm [35]. Morphologies of the synthesized composites were analyzed using SEM equipment (Hitachi SU8020, Tokyo, Japan). The sample elemental compositions were examined with an EDS (energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy) detector (Horiba Emax 7593-H, Tokyo, Japan) attached to the SEM. Additionally, TEM images were obtained with a JEOL JEM-2100F TEM equipment (200 kV accelerating voltage: 0.23 nm point-to-point resolution). The oxidation states of elements on Fe@MF-12.5-800 surface before and after Cr(VI) removal were obtained by an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (Shimadzu, Axis, Sakaemachi, Japan). The C 1s charge correction has been set to 284.8 eV (from 285.0 eV). The background was fitted using Avantage V5.52. The line shape was also fitted by Avantage V5.52 and the %Lorentzian–Gaussian was 20%. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns for phase and crystallite analysis were collected (5–90°, 2°/min) on a Bruker D8 Advance (Karlsruhe, Germany) at room temperature. Nitrogen adsorption–desorption of Fe@MF-12.5-800 was determined on an Autosorb iQ-MP Quantachrome instrument (Boynton Beach, FA, USA). Fe content was analyzed using an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (Agilent technologies 700 Series ICP OES, Palo Alto, CA, USA).
2.4. Batch Experiments
The performance of Fe@MF composites under various conditions, including Fe3+ concentration (7.5 to 50 mmol/L) and the temperature of carbonization (600 °C, 800 °C, and 1000 °C), were conducted via batch experiments. The stability of the produced composites was investigated by measuring Cr(VI) removal efficiency after the Fe@MF composites were kept in an open environment for a desired period (0 to 7 days). Unless specified elsewhere, all the experiments were conducted in stirring flasks containing 10 mg/L Cr(VI) solution at pH 7. Additionally, all experiments stated above were conducted at room temperature.
2.5. Column Trial
Fe@MF-12.5-800 was used as the filling material in a column reactor for flow-through wastewater treatment. In this test, 10 mg/L Cr(VI) solution was taken as feedwater. The flow rates were set at 1 and 2 mL/min. For each treatment cycle (360 mL/cycle), the effluent was collected and measured for its Cr(VI) concentration. The removal efficiency was calculated according to the initial (influent) and final (effluent) Cr(VI) concentrations shown in the following Equation (1):
where C0 and Ce denote the initial and final Cr(VI) concentrations (mg/L) per cycle and V represents the Cr(VI) solution volume (L) per cycle [4].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Fe@MF Synthesis
From Figure 1a, Cr(VI) elimination was significantly affected by the Fe3+ concentration present in the melamine foam. Overall, its removal rate upsurged with increasing Fe3+ amounts. At Fe3+ concentration higher than 12.5 mmol/L, a rapid Cr(VI) adsorption of >99% occurred within 90 min. The removal efficiency significantly decreased from 99.75% to ≤39.13% when a smaller amount of Fe3+ (<12.5 mmol/L) was used. The control sample of carbonized melamine foam could remove about 10% Cr(VI) probably due to the porous structure formed during the carbonization, which was in line with previous findings [26]. By considering both the economic aspect and removal efficacy, the 12.5 mmol/L was selected as the optimum concentration.
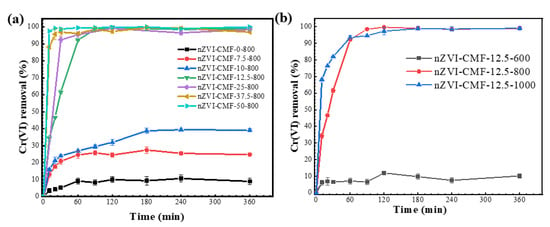
Figure 1.
Cr(VI) elimination by Fe@MF with (a) different concentrations of Fe3+ loaded and (b) different temperatures of carbonization applied.
It is well known that the carbonization temperature could remarkably affect nZVI formation [36]. The sample carbonized at 600 °C indicated a rather low Cr(VI) removal of about 12% (Figure 1b), similar to that of the control sample without Fe3+, suggesting that nZVI could not be formed at this temperature. It has been reported that Fe3+ reduction to Fe0 requires a specific temperature and sufficient carbon. Generally, Fe3O4 tends to form at relatively low temperatures (e.g., 500 °C), whereas Fe0 amounts increase gradually with temperature [37,38]. The samples produced at 800 °C and 1000 °C displayed significant Cr(VI) removal efficiency with a slightly greater initial removal rate at the higher temperature. From the perspective of energy consumption, 800 °C was selected as the optimum carbonization temperature.
3.2. Characterization of Fe@MF-12.5-800
Figure 2a shows that the morphology of Fe@MF-12.5-800 has a well-developed porous structure. Such an arrangement would be conducive to the penetration of the solution, thus increasing the contact area between the solution and the material for better pollutant removal [24]. It can be seen that nanoparticles with irregular spherical shapes were observed on the microfiber surfaces of the carbonized melamine foam (Figure 2b,c). These nanoparticles were mildly aggregated (Figure 2c,d) compared with the previously described behavior of pure nZVI particles. This suggests that the Fe@MF composite produced using the proposed method is beneficial for nZVI dispersion. EDS element mapping of the Fe@MF-12.5-800 clearly shows the presence of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and iron (Figure 2e–j). The iron was from FeCl3·6H2O, while nitrogen originated from melamine foam and N2 gas used during the carbonization [29]. The presence of nitrogen functional groups could provide active sites in the composite and improve adsorption capacity [39]. Overall, the EDS analysis revealed that the melamine foam was successfully doped with iron particles after carbonization and the Fe content measured by ICP-OES was 13.26%, similar with that in EDS and XPS (Table S1).
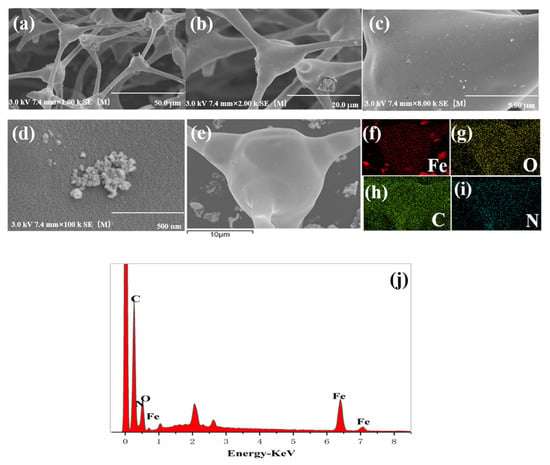
Figure 2.
Characteristics: SEM images of (a) Fe@MF-12.5-800 (×1000), (b) Fe@MF-12.5-800 (×2000), (c) Fe@MF-12.5-800 (×8000) and (d) Fe@MF-12.5-800 (×100,000). (f–i) SEM-EDS elemental distribution mapping of Fe, O, N and C obtained from (e). (j) The EDS survey of Fe@MF-12.5-800.
The N2 adsorption/desorption experiment shows that the BET surface area of Fe@MF-12.5-800 was 303.29 m2/g with a pore volume (PV) of 0.28 cm3/g. The obvious hysteresis between the durative increase in the adsorption capacity and desorption curves before P/P0 = 0.4 reveals the coexistence of mesopores on Fe@MF-12.5-800 (Figure S2a). The pore size distributions (as shown in Figure S2b) further confirmed its mesopore structure with various pore sizes mainly ranging between 2 and 10 nm. This well-developed mesoporous structure implies its potential to be a high-performance adsorbent.
The XRD spectrum of Fe@MF-12.5-800 (Figure 3a) evidenced its crystallographic structure. Those distinct peaks occurring at 44.8° and 65.1° corresponded to the Bragg plane of (110) and (200) of Fe0 (JCPDS No. 65-4899) [40]. Furthermore, peaks occurring at 26.41, 37.65, 39.82, 40.65, 42.89, 43.76, 45.88 and 49.13° corresponded to the Bragg planes of (020), (210), (002), (201), (211), (102), (112) and (221), respectively, which were in high accordance with Fe3C (JCPDS No. 65-2411) [41,42]. Hence, the main components of Fe@MF-12.5-800 were Fe3C and Fe0, which is in line with the results of Gao et al. [7]. Also, the TEM images in Figure 3b,c illustrate a significant number of particles randomly dispersed within the carbonized melamine foam. Figure 3d displays the HRTEM image with a lattice spacing of 0.199 and 0.337 nm, which corresponds to the (110) crystal plane of Fe0 and (211) crystal plane of Fe3C [41,42].
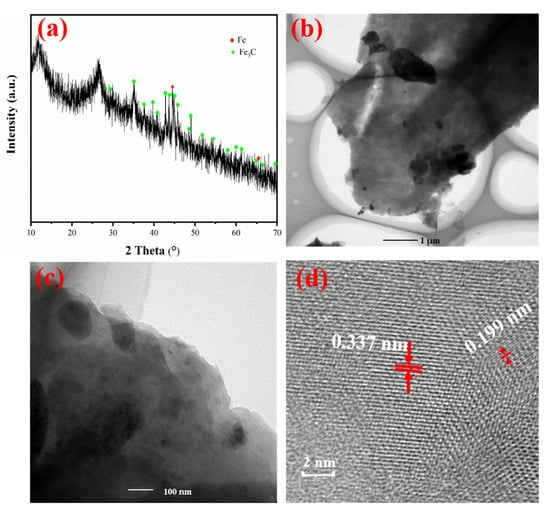
Figure 3.
(a) X-ray diffraction patterns of Fe@MF-12.5-800; (b,c) TEM images and their respective particle size distribution of Fe@MF-12.5-800; and (d) HRTEM image of Fe@MF- 12.5-800.
3.3. Batch Experiment of Cr(VI) Removal
3.3.1. Effect of 3D Porous Structure
Fe@MF-12.5-800 composite displays a 3D porous microstructure (Figure 2a,b), which could, in theory, facilitate the migration of contaminants and thus be beneficial for rapid Cr(VI) elimination. To demonstrate this, the Cr(VI) removal rate of the 3D porous Fe@MF-12.5-800 composite block was tested and compared with that of an identical sample ground into a powder form.
The rate of Cr(VI) removal by different Fe@MF-12.5-800 forms is shown in Figure 4a. For the initial 10 min of reaction, the Cr(VI) removal rate of the powdered Fe@MF-12.5-800 was about 2 times faster than that of the block form, which was due to the instant interaction between the Cr(VI) and powdered composite. However, the block and powdered Fe@MF-12.5-800 reached equilibrium at a similar time of about 90 min. This suggests that the large pores formed within the Fe@MF-12.5-800 framework minimized the mass transfer resistance, unlike the previous report [39]. The final Cr(VI) removal by the block sample was 99.75%, which was slightly higher than that of the powdered sample. This might be due to the partial nZVI oxidation during the grinding stage.
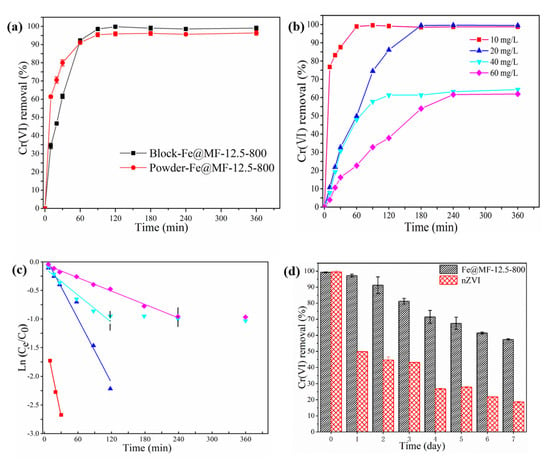
Figure 4.
The influence of different conditions on Cr(VI) using Fe@MF-12.5-800: (a) effect of block and powder form; (b) effect of initial Cr(VI) concentration; (c) kinetic modeling fitted by pseudo-first-order reaction; and (d) the effect of aging time.
3.3.2. Effect of Initial Cr(VI) Concentration
The influence of different Cr(VI) concentrations (10–60 mg/L) on their removal rate is presented in Figure 4b. When the concentrations were 10 and 20 mg/L, the added Fe@MF-12.5-800 could completely remove Cr(VI) present. Upon increasing the concentration to 40 and 60 mg/L, the removal rate was reduced to 64% and 62%, respectively. The fixed number of active sites in the Fe@MF-12.5-800 composite led to lower removal efficiency at higher Cr(VI) concentrations.
Previous studies have shown that ZVI reduction suits pseudo-first-order reactions [39]. Figure 4c shows that Fe@MF-12.5-800 had a good fit with the pseudo-first-order reaction, and the correlation coefficient was in the range of 0.95 to 0.99. Additionally, an increment in the initial concentration from 10 to 60 mg/L led to a reduction in the rate constant (Kobs) from 0.047 to 0.003 min−1, respectively. As witnessed, the rise in the Cr(VI) concentration significantly lessened the reduction rate, probably due to the competitive effect [39]. The lower reactivity of Fe@MF-12.5-800 caused nZVI to rapidly oxidize into Fe(III) when additional Cr(VI) contacted the Fe@MF-12.5-800 surface. As a result, the Kobs values reduced. Furthermore, the results showed that the reaction rate was heavily influenced by the available active surface sites, which could become a constraint with increasing Cr(VI) concentration.
3.3.3. Effect of the Aging Time
A decline in nZVI reactivity is typically caused by the aggregation and surface passivation of nZVI during the aging process. The adverse effects of aging have been shown in previous studies [43]. After aging nZVI anchored on biomass-activated carbon materials for one month, Zhang et al. reported that the rate of Cr removal was 30% of the initial rate [40]. As part of this study, we investigated the removal efficiency of Cr(VI) in fresh and aged Fe@MF-12.5-800 (Figure 4d). The results showed that Fe@MF-12.5-800 could remove about 60% of the Cr(VI) after a one-week aging period. In comparison, the much lower reactivity (only 20% Cr(VI) removed) of nZVI towards the target pollutant after aging was obtained, which could be linked to the partial blockage of the redox-active centers by the oxide film formed during the aging period [44]. The higher resistance of Fe@CMF-12.5-800 to air exposure could be due to the facilitated electron transfer between nZVI and carbon fiber through their contacted interface providing reduced power for Cr(VI) removal, which reduces the negative effect of passivation products formed on the nZVI surface [45].
3.4. Mechanisms of Cr(VI) Removal by Fe@MF-12.5-800
The reduction and adsorption mechanisms of Cr(VI) by Fe@MF-12.5-800 were analyzed using XRD and XPS. After the adsorption of Cr(VI), the small peak of Cr2p (580 eV, Figure 5a) shows the uptake of chromium on Fe@MF-12.5-800 surface. Figure 5b depicted the Cr2p XPS spectra on the surface of Fe@MF-12.5-800 after Cr (VI) removal. Two peaks located at 576.01 and 585.27 eV can be ascribed to the Cr(III) and Cr(VI), demonstrating that both Cr(VI) and Cr(III) existed [4].
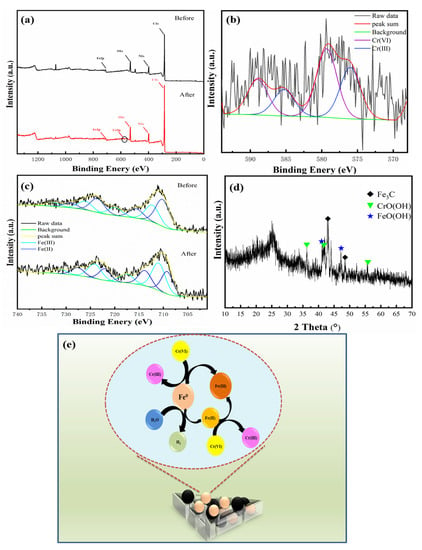
Figure 5.
(a) XPS survey spectra for Fe@MF-12.5-800 before and after Cr(VI) reactions; (b) Cr2p XPS spectra of Fe@MF-12.5-800 after reaction; (c) Fe2p of Fe@MF-12.5-800 before and after reaction; (d) XRD of Fe@MF-12.5-800 after Cr(VI) reaction; and (e) plausible mechanism for monolayer Cr(VI) adsorption onto Fe@MF-12.5-800.
Although, the XRD spectrum demonstrated the presence of Fe0 (Figure 3a), the peak at 706.7 eV ascribed to Fe0 before the Cr(VI) removal reaction was not clearly shown in the XPS spectrum (Figure 5c). Taking into account the surface sensitivity of XPS, the presence of the Fe0 peak could not be detected by XPS, which is probably due to the surface iron species being oxidized. This is also reported by Fu et al. [19]. The Fe2p peaks at 715.6 and 719.91 eV corresponded to Fe2p3/2 for Fe(II) and Fe(III), respectively, while the peaks at 729.08, and 732.71 eV were assigned to Fe2p1/2 for Fe(II) and Fe(III), respectively. Moreover, the satellite peak positions for Fe(II) were 723.58 and those for Fe(III) were 726.06 eV. The peak with binding energy located at 712.26 eV can be attributed to FeOOH.
The XRD results prove the contribution of Fe0 on the Cr(VI) removal as the disappearance of Fe0 (Figure 3a and Figure 5d) and the formation of FeO(OH) (2θ = 41.1°, 47.3°) and CrO(OH) (2θ = 36.4°, 41.7°, 55.9°) after the reaction. In this process, nZVI particles acted as reducing agents [19]. Inferring from the results, the equations governing the reactions can be represented as (Equations (2) and (3)):
Based on the above analysis, the Cr(VI) removal mechanism by Fe@MF-12.5-800 could be schematically described in Figure 5e. The production of Cr(III), Fe(II) and Fe(III) made the entire process environmentally friendly [5].
3.5. Continuous Treatment
The continuous removal of Cr(VI) through the porous Fe@MF-12.5-800 composite was tested in plastic columns. Each column was 1.6 cm in diameter and 6 cm in length, packed with 160 mg Fe@MF-12.5-800 (four pieces of identical samples). Figure 6a illustrates a schematic diagram of the reaction column set-up. In total, 360 mL of Cr(VI) heavy metal solution (10 mg/L) was continuously pumped through the reactor from the bottom at flow rates of 1 and 2 mL/min, corresponding to hydraulic retention times (HRT) of 360 and 180 min, respectively. This was followed by sampling the treated Cr(VI) solution for the remaining Cr(VI) amount. Next, the Cr(VI) solution was pumped through the reactor again to get repeated treatment.
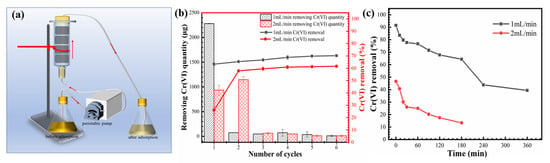
Figure 6.
(a) Schematic diagram of Fe@MF-12.5-800 column migration experiment; (b) Cr(VI) removal efficiency for the first treatment at different flow rates; (c) Cr(VI) removal by Fe@MF-12.5-800 at different flow cycles.
Figure 6b depicts the continuous flow procedure for removing Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using Fe@MF-12.5-800. When the flow rate was raised from 1 to 2 mL/min, Cr(VI) elimination decreased from 70.2% to 61.6%. Several successive cycles are shown in Figure 6c. The adsorption efficiency reduced with increasing cycles, and the Cr(VI) removed rapidly decreased at a 2 mL/min flow rate. Because of limited solute interaction time, the saturation needed for Cr(VI) removal in Fe@MF-12.5-800 reduced dramatically at higher flow rates. The chromium removal capacity of the Fe@MF-12.5-800 can be obtained by calculating the totally removed chromium and the amount of Fe@MF-12.5-800 used. Regardless of the flow rate, chromium removal capacity was about 15.67 mg/g at neutral pH (pH = 7), which is 1.96 times higher than previous published works [4].
The microstructure of the Fe@MF-12.5-800 composite after reacting with Cr(VI) is presented in Figure 7a,b. After the reaction, it was found that the Fe@MF-12.5-800 composites kept a typical carbonized MF structure and the framework of Fe@MF was maintained intact. The locally magnified SEM image showed laminated clusters formed on the surface of carbon fiber. These deposits are likely to be CrxFe1-x(OH)3, which is in line with previously reported works [45].
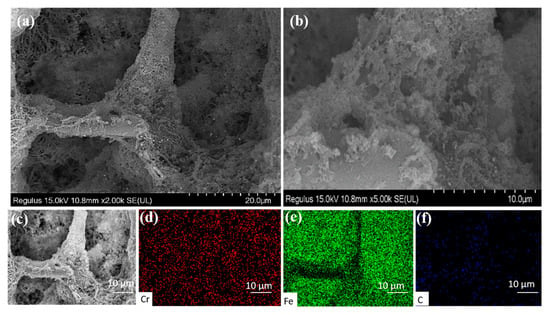
Figure 7.
(a,b) The different magnification SEM images after reaction with Cr(VI); (d–f) EDX element mapping of Cr, Fe, and C obtained from (c) after reaction with Cr(VI).
The element mapping shows evenly distributed Cr, Fe, and C elements within the framework of Fe@MF-12.5-800 (Figure 7c–f). This meant that the end products of Fe(III)/Cr(III) were finally fixed within the composite, as proven by the turbidity (OD600 = 0) of the effluent during the treatment. The fixation of end products would be beneficial to avoid secondary pollution, which normally occurred when the end products (e.g., Cr(III)/Fe(III)(oxy)hydroxides) were freely released into the environment [46].
4. Conclusions
In this study, nZVI supported by the carbonized melamine foam was examined for the effective removal of Cr(VI). Batch experiments showed that the Cr(VI) elimination efficiency increased with Fe3+ concentration and carbonization temperature. At pH = 7, more than 99% Cr(VI) removal was achieved. Additionally, the Cr(VI) elimination efficiency in block Fe@MF-12.5-800 was similar to its powder form. The block Fe@MF-12.5-800 is easy to separate from the environment, thus effectively reducing environmental pollution. Moreover, the simulation experiment showed that the material could be used as a filler in sewage treatment. The results proved that this approach enabled an effective and stable Cr(VI) removal in wastewater. Hence, this composite can be potentially used for heavy metal in situ repair.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nano12111866/s1, Figure S1: (a) The synthesis process of Fe@MF (using Fe@MF-12.5-800 as an example); (b–d) photos of Fe@MF at different stages; Table S1: The content (wt.%) of each element tested by XPS and EDS; Figure S2: (a) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distributions of Fe@MF-12.5-800.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C.; methodology, L.C.; software, Q.N.; validation, Q.N. and L.C.; formal analysis, L.C., Q.L. and M.L.; investigation, M.L., Q.L. and Q.N.; resources, L.C.; data curation, Q.N.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.L. and M.L.; writing—review and editing, L.C. and X.L., M.F.D. and X.Q.; visualization, Q.L.; supervision, L.C.; project administration, L.C.; funding acquisition, L.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the program of the Innovation/Entrepreneurship Program of Jiangsu Province, Jiangsu Province Key Project of Research and Development Plan (BE2020676), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant no. 2020M671359), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant no. BK20200914), Science and Technology Planning Social Development Project of Zhenjiang City (Grant SH2019010) and the program of the Nantong Science and technology project (Grant no. MS22021006).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data presented in this article are available at request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fang, Y.; Wen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Hu, X. Enhancing Cr(VI) reduction and immobilization by magnetic core-shell structured NZVI@MOF derivative hybrids. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wei, W.; Xu, C.; Meng, Y.; Bai, W.; Yang, W.; Lin, A. Polyethylene glycol-stabilized nano zero-valent iron supported by biochar for highly efficient removal of Cr(VI). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Lee, C.R.; Song, Y.E.; Heo, J.; Choi, S.M.; Lim, D.-H.; Cho, J.; Park, C.; Jang, M.; Kim, J.R. Hexavalent chromium as a cathodic electron acceptor in a bipolar membrane microbial fuel cell with the simultaneous treatment of electroplating wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, K.V.; Kumar, D.; Rajeshwari, A.; Madhu, G.M.; Mrudula, P.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. A comparative study with biologically and chemically synthesized nZVI: Applications in Cr (VI) removal and ecotoxicity assessment using indigenous microorganisms from chromium-contaminated site. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 2613–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarathilaka, P.; Jayaweera, V.; Wijesekara, H.; Kottegoda, I.R.M.; Rosa, S.R.D.; Vithanage, M. Insights into Starch Coated Nanozero Valent Iron-Graphene Composite for Cr(VI) Removal from Aqueous Medium. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 2813289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habibul, N.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.K.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.Q.; Sheng, G.P. Bioelectrochemical Chromium(VI) Removal in Plant-Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3882–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Nie, L.; Yang, S.; Jin, P.; Chen, R.; Ding, D.; Wang, X.C.; Wang, W.; Wu, K.; Zhang, Q. Well-defined strategy for development of adsorbent using metal organic frameworks (MOF) template for high performance removal of hexavalent chromium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamais, D.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Kavallari, I.; Nyktari, E.; Kaldis, A.; Panousi, E.; Nikitopoulos, G.; Antoniou, K.; Nasioka, M. Biological groundwater treatment for chromium removal at low hexavalent chromium concentrations. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Li, C.; Hu, J.; Hou, X. Selective determination of Cr() and non-chromatographic speciation analysis of inorganic chromium by chemical vapor generation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta 2020, 218, 121128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Sarkar, A.; Sen, S. Removal of chromium from industrial effluents using nanotechnology: A review. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2017, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. Active biochar support nano zero-valent iron for efficient removal of U (VI) from sewage water. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 852, 156993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancibia-Miranda, N.; Baltazar, S.E.; Garcia, A.; Munoz-Lira, D.; Sepulveda, P.; Rubio, M.A.; Altbir, D. Nanoscale zero valent supported by Zeolite and Montmorillonite: Template effect of the removal of lead ion from an aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jia, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, H. Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Zeng, D.; Chu, R.; Wang, T.; Liang, D.; Qiang, H. Magnetic Fe3O4 assembled on nZVI supported on activated carbon fiber for Cr(VI) and Cu(II) removal from aqueous solution through a permeable reactive column. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 5176–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Woo, Y.C.; Yao, M.; Lim, S.; Tijing, L.D.; Shon, H.K. Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) immobilization onto graphene oxide (GO)-incorporated electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofiber membrane for groundwater remediation via gravity-driven membrane filtration. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cao, Y.; Wei, E.; Gong, T.; Xian, Q. Facile synthesis of graphene nano zero-valent iron composites and their efficient removal of trichloronitromethane from drinking water. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzatahmadi, N.; Marshall, D.L.; Hou, K.; Ayoko, G.A.; Millar, G.J.; Xi, Y. Simultaneous adsorption and degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol on sepiolite-supported bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petala, E.; Dimos, K.; Douvalis, A.; Bakas, T.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R.; Karakassides, M.A. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on mesoporous silica: Characterization and reactivity for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Ma, J.; Xie, L.; Tang, B.; Han, W.; Lin, S. Chromium removal using resin supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Chen, M. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by biochars produced at different temperatures: Synthesis mechanism and effect on Cr(VI) removal. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Gong, K.; Hu, Q.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, J.; Dong, M.; Wang, N.; Ding, T.; Qiu, B.; Guo, Z. Optimizing nanocarbon shell in zero-valent iron nanoparticles for improved electron utilization in Cr(VI) reduction. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Dong, J.; Chi, Z.; Huang, H. Reduced graphene oxide-nano zero value iron (rGO-nZVI) micro-electrolysis accelerating Cr(VI) removal in aquifer. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 73, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Lv, B.; Chang, G.; Jiao, W.; Liu, Y. Removal of trace Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by porous activated carbon balls supported by nanoscale zero-valent iron composites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 7015–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Fabrication of Fe/Fe3C@porous carbon sheets from biomass and their application for simultaneous reduction and adsorption of uranium(VI) from solution. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hu, E.; Yang, S.; Gong, L.; He, F. Chromium(VI) removal by mechanochemically sulfidated zero valent iron and its effect on dechlorination of trichloroethene as a co-contaminant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Shang, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Su, A.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Han, L.; Yan, J.; Chen, M. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) by silicon rich biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.; Li, T.; Bai, R.; Sun, R.; Wong, C. Electrodeposition of Co(OH)2 Improving Carbonized Melamine Foam Performance for Compressible Supercapacitor Application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16803–16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Nie, J.; Li, H.; Xia, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, X.; Qi, R.; Wang, Z.L.; Lu, X. High-frequency supercapacitors based on carbonized melamine foam as energy storage devices for triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, A.; Le Floch, S.; Reinert, L.; Ramos, S.M.M.; Tuaillon-Combes, J.; Soneda, Y.; Chaudet, P.; Baillis, D.; Blanchard, N.; Duclaux, L.; et al. Melamine-derived carbon sponges for oil-water separation. Carbon 2016, 107, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, X.; Chu, Y.; Wang, L.; Kang, W.; Wei, D.; Li, H.; Xiong, S. Nitrogen/oxygen co-doped monolithic carbon electrodes derived from melamine foam for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17730–17739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. An Elastic Monolithic Catalyst: A Microporous Metalloporphyrin-Containing Framework-Wrapped Melamine Foam for Process-Intensified Acyl Transfer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 6013–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Jiang, D.; Liang, H.; Huo, B.; Liu, C.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Superelastic and Arbitrary-Shaped Graphene Aerogels with Sacrificial Skeleton of Melamine Foam for Varied Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodon Fores, J.; Criado-Gonzalez, M.; Chaumont, A.; Carvalho, A.; Blanck, C.; Schmutz, M.; Serra, C.A.; Boulmedais, F.; Schaaf, P.; Jierry, L. Supported Catalytically Active Supramolecular Hydrogels for Continuous Flow Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 18817–18822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaouen, L.; Renault, A.; Deverge, M. Elastic and damping characterizations of acoustical porous materials: Available experimental methods and applications to a melamine foam. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milačič, R.; Štupar, J.; Kožuh, N.; Korošin, J. Critical evaluation of three analytical techniques for the determination of chromium(VI) in soil extracts. Analyst 1992, 117, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Qiu, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, K.; Li, M.; Xu, H.; Wu, X.; Shimasaki, Y.; Oshima, Y. Short-term and persistent impacts of sublethal exposure to diazepam on behavioral traits and brain GABA levels in juvenile zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wu, M.; Chen, C.; Xu, H.; Wu, X.; Qiu, X. Impacts of chronic exposure to sublethal diazepam on behavioral traits of female and male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Kim, S.; Kang, I.J.; Hano, T.; Shimasaki, Y.; Oshima, Y. Combined toxicities of tributyltin and polychlorinated biphenyls on the development and hatching of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) embryos via in ovo nanoinjection. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Iwasaki, N.; Chen, K.; Shimasaki, Y.; Oshima, Y. Tributyltin and perfluorooctane sulfonate play a synergistic role in promoting excess fat accumulation in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) via in ovo exposure. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, B.; Smith, F.; Aracil, I.; Fullana, A. Green Synthesis of Thin Shell Carbon-Encapsulated Iron Nanoparticles via Hydrothermal Carbonization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7995–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Yao, M.; Woo, Y.C.; Tijing, L.D.; Kim, J.-H.; Shon, H.K. Recyclable nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI)-immobilized electrospun nanofiber composites with improved mechanical strength for groundwater remediation. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 171, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yang, H.; Su, C.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, Z. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted synthesis of stable reduced graphene oxide modified melamine foam with superhydrophobicity and high oil adsorption capacities. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, Y.; Cheng, K. Performance of lead ion removal by the three-dimensional carbon foam supported nanoscale zero-valent iron composite. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 125350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Su, Z.; Xie, W.; Tian, C.; Su, X.; Lin, Z. Preparation of 2D nitrogen-doped magnetic Fe3C/C by in-situ self-assembled double-template method for enhanced removal of Cr(VI). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, G.; Xu, X. Removal of chromium(VI) from wastewater by nanoscale zero-valent iron particles supported on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Peng, X.; Ai, Z.; Jia, F.; Zhang, L. Liquid Nitrogen Activation of Zero-Valent Iron and Its Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8333–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).