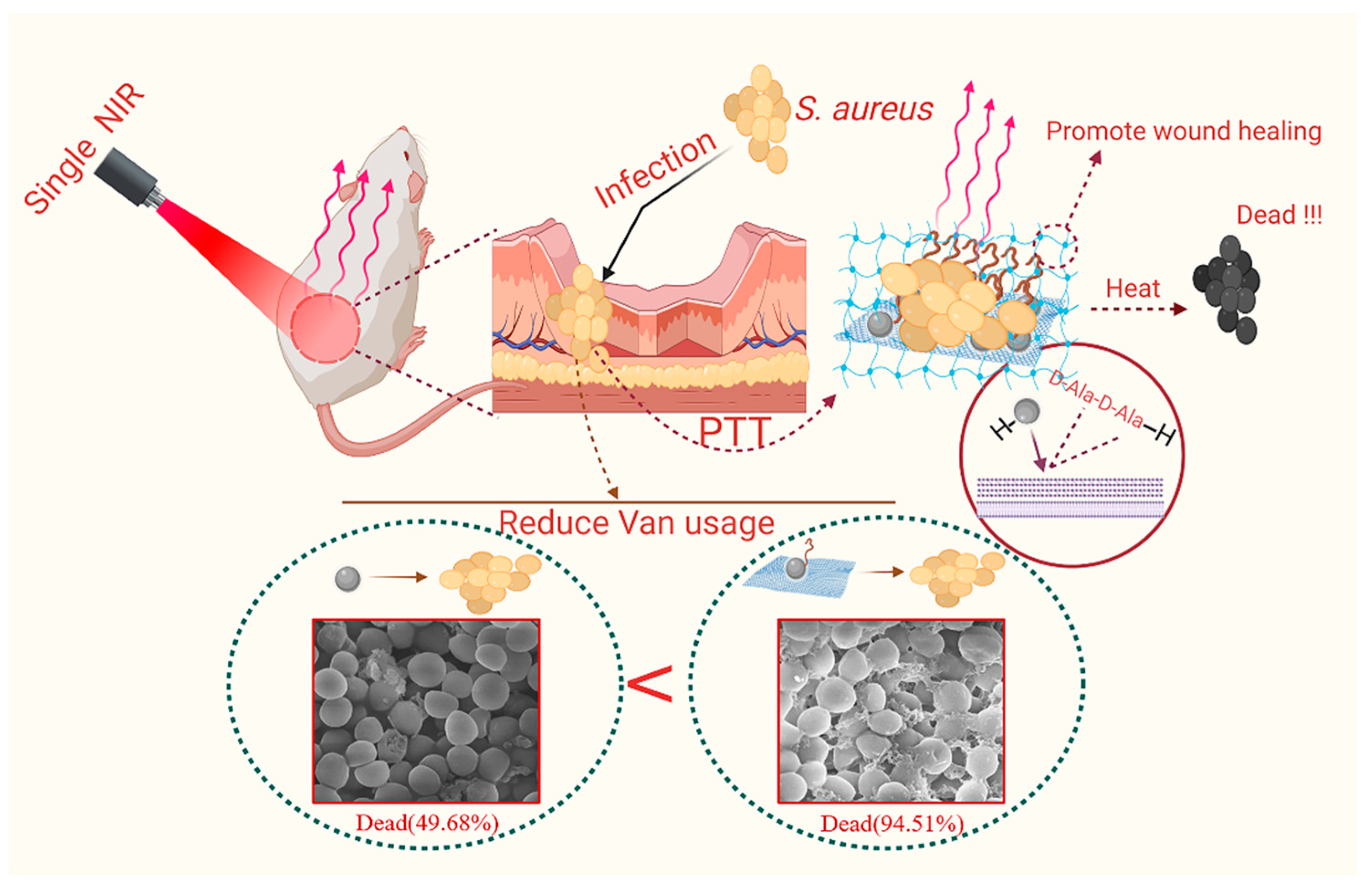
Synthesis of a Two-Dimensional Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheet and Ultrasensitive Trapping of Staphylococcus Aureus for Enhanced Photothermal and Antibacterial Wound-Healing Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MoS2 Nanosheets
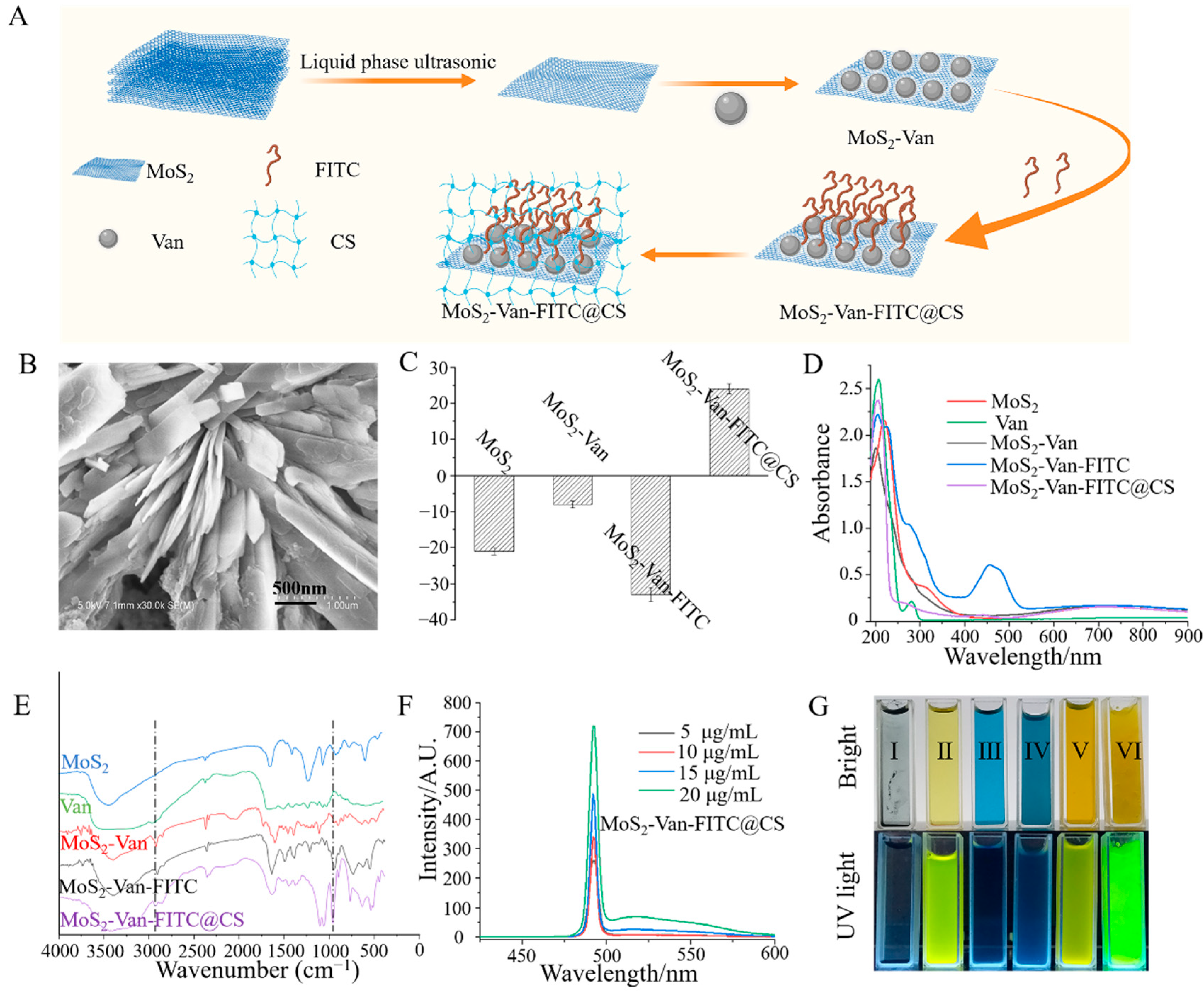
2.3. Synthesis of MoS2-Van-FITC
2.4. Synthesis of the MoS2-Van-FITC@CS Hydrogel
2.5. Characterization
2.6. In Vitro Antibacterial Assays
2.7. Cellular Uptake Assays
2.8. LIVE–DEAD Assays
2.9. Cell Integrity Assays
2.10. Establishment of the Wound Mice Model
2.11. Wound Healing Assays
2.12. Safety Evaluation of MoS2-Van-FITC@CS
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of MoS2-Van-FITC@CS
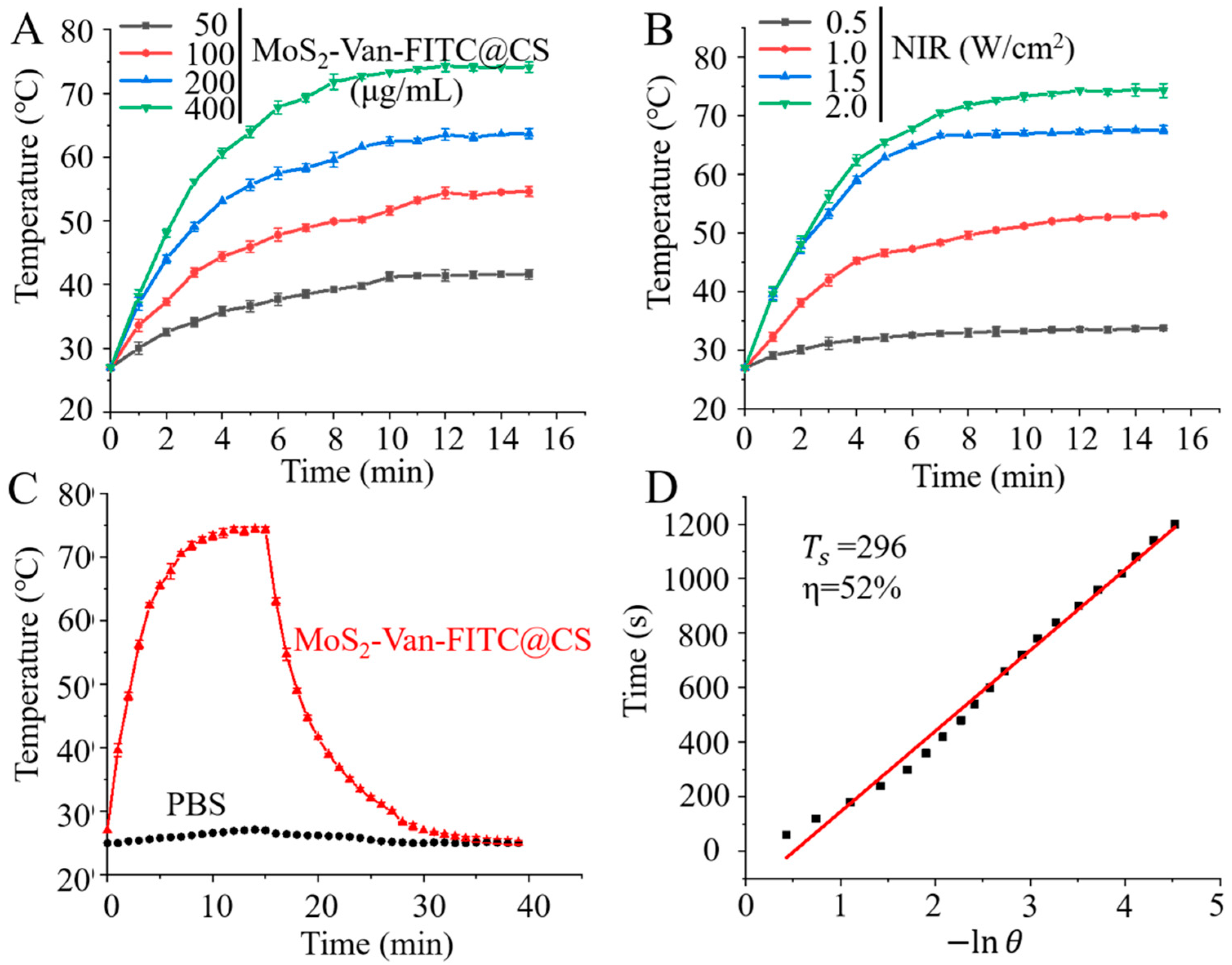
3.2. In Vitro Photothermal Efficiency
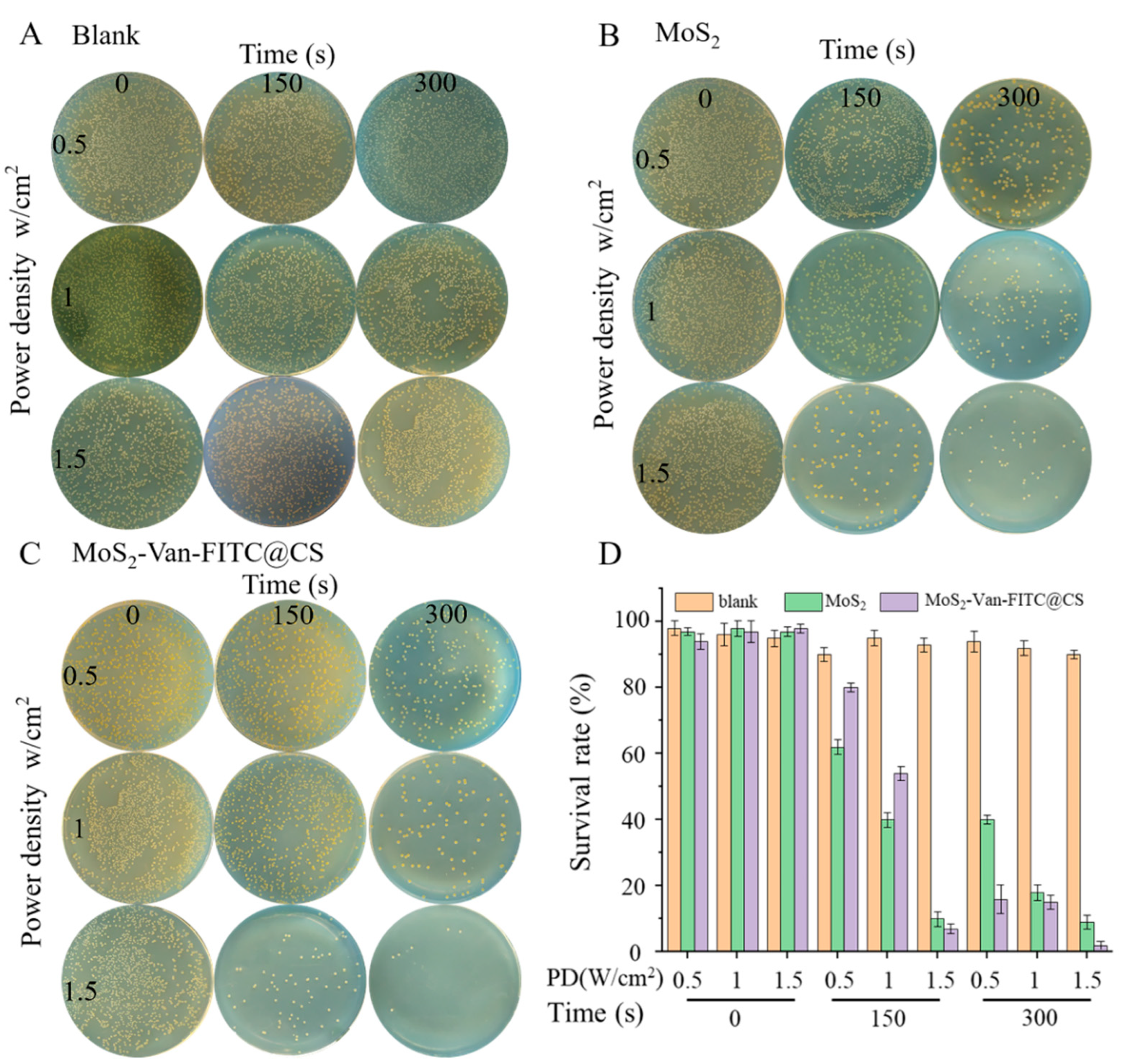
3.3. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity
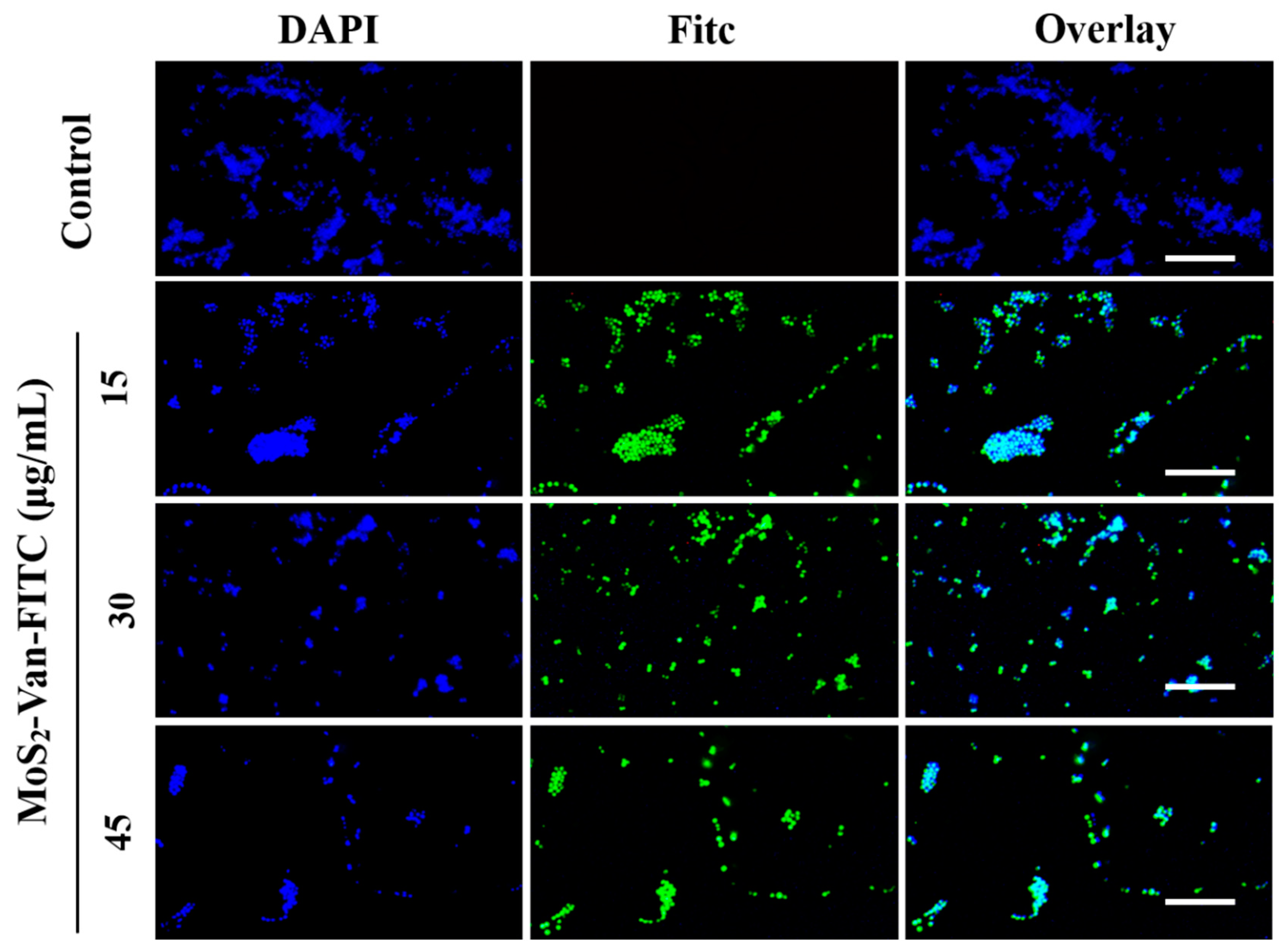
3.4. Cellular Uptake Assays
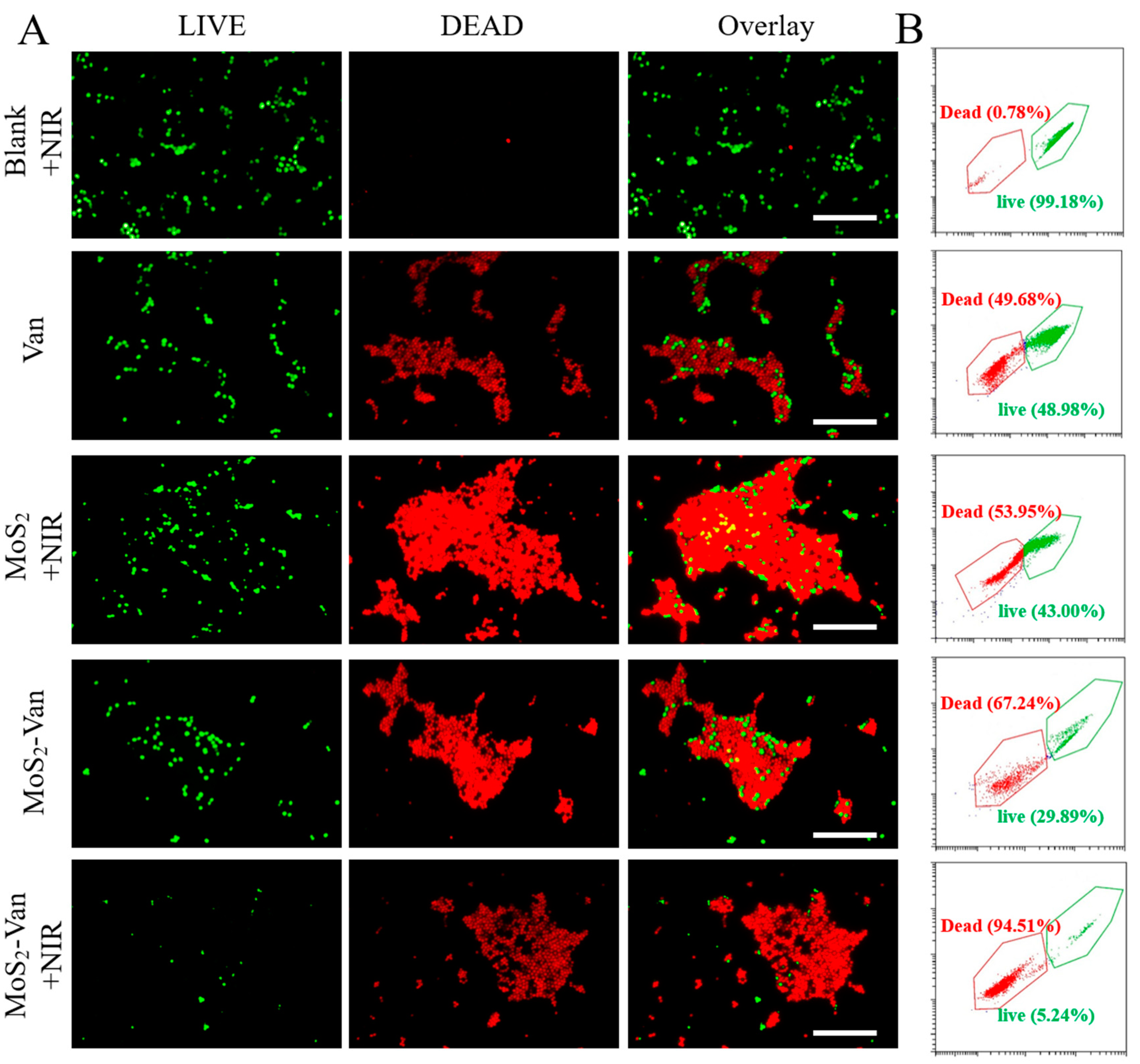
3.5. Fluorescent Staining Analysis of Antibacterial Activity
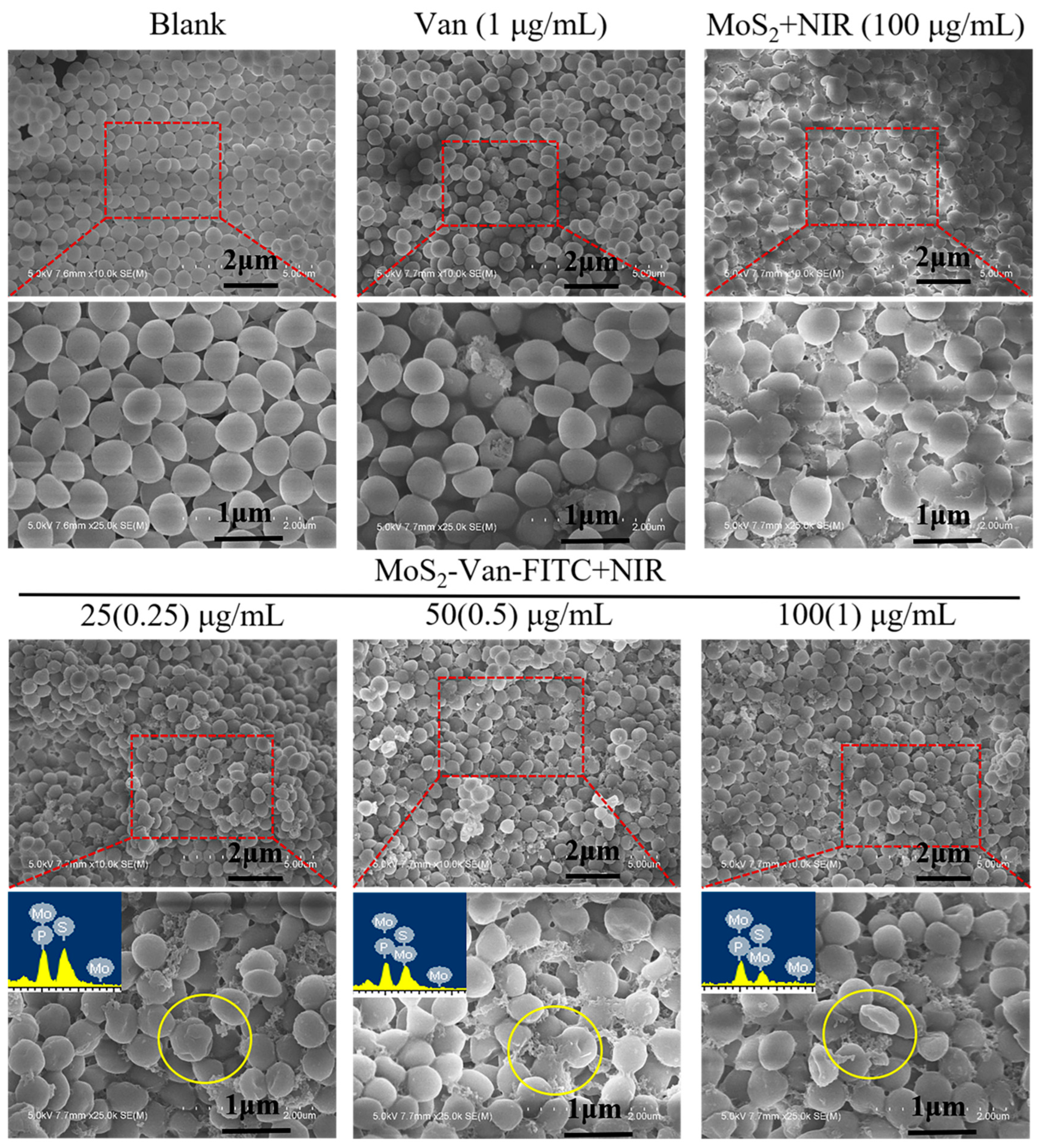
3.6. Cell Integrity Study
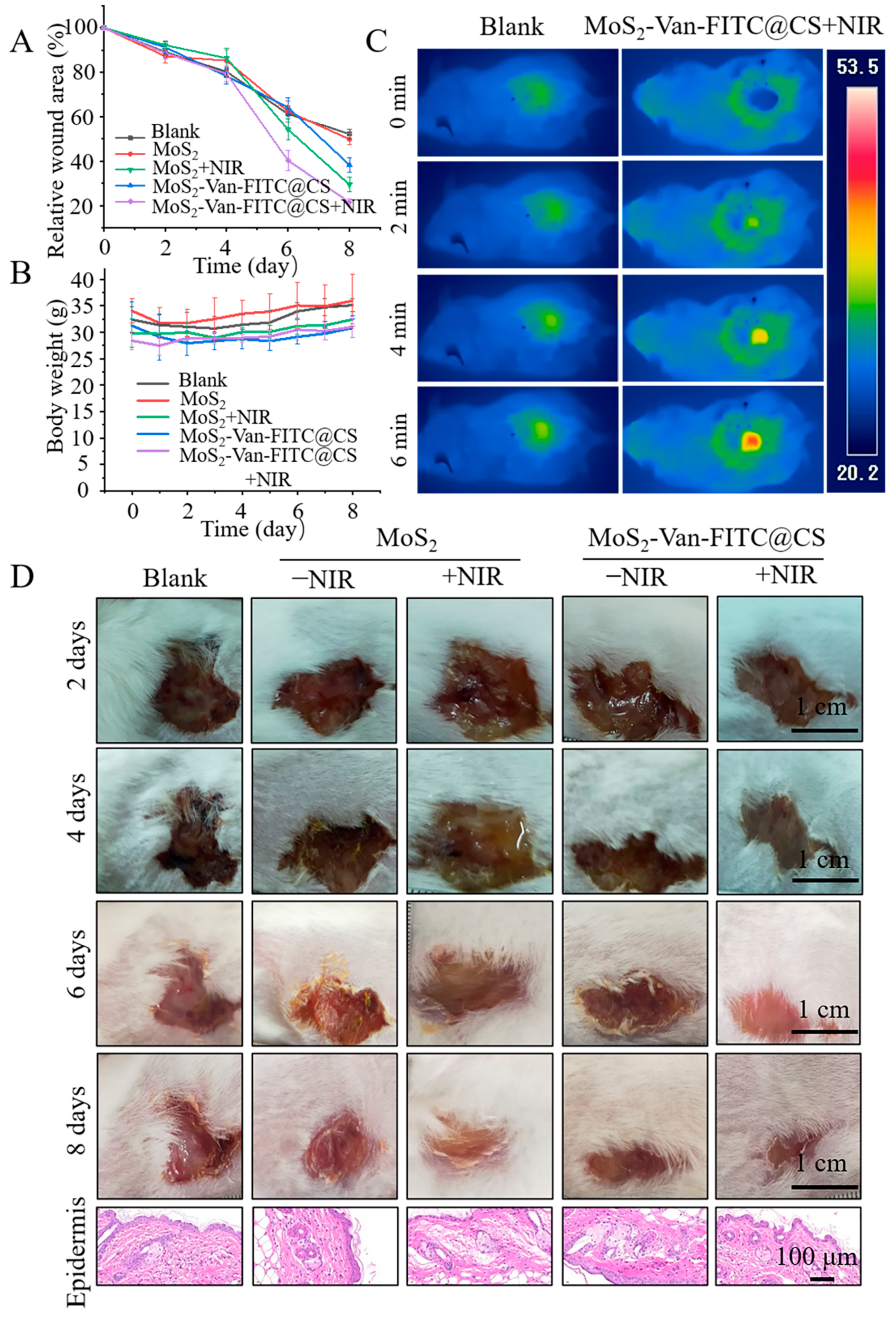
3.7. In Vivo Wound Healing Evaluation
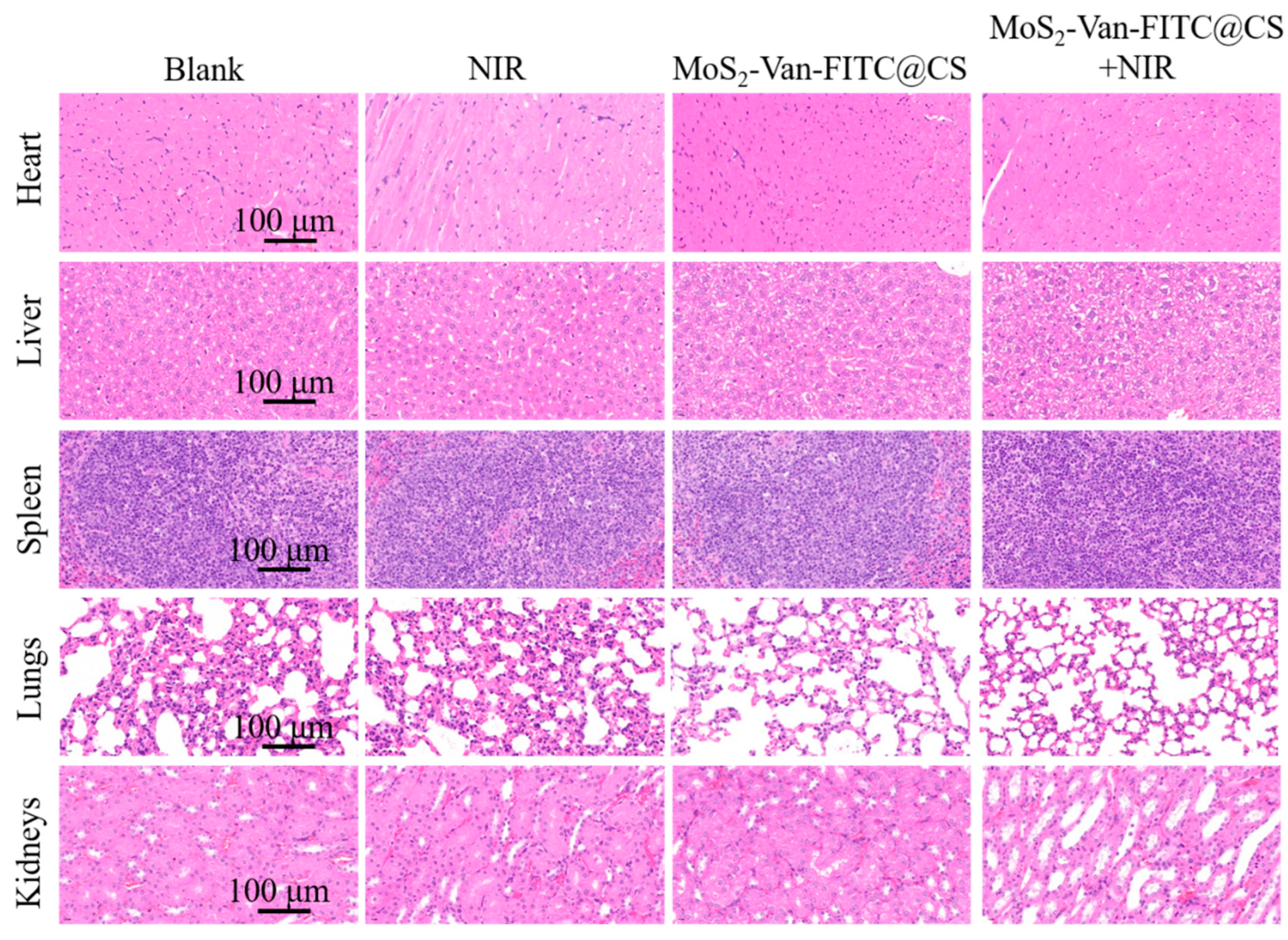
3.8. Biosafety Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vlazaki, M.; Huber, J.; Restif, O. Integrating mathematical models with experimental data to investigate the within-host dynamics of bacterial infections. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Song, P.; Xin, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ge, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, W. The Effects of Luminescent CdSe Quantum Dot-Functionalized Antimicrobial Peptides Nanoparticles on Antibacterial Activity and Molecular Mechanism. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1849–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, H. Gold Nanoclusters for Bacterial Detection and Infection Therapy. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, W.; Mou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F.; Yang, E.; Wang, W. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Silver Nanoparticle-Decorated Quercetin Antibacterial Molecular Mechanism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10047–10060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Li, N.; Mou, Z.; Sun, D.; Cai, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, Y. Quercetin loading CdSe/ZnS nanoparticles as efficient antibacterial and anticancer materials. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 167, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlie, S.; Boucher, C.E.; Bragg, R.R. Molecular basis of bacterial disinfectant resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 2020, 48, 100672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Bert, F.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.-H. The challenges of multi-drug-resistance in hepatology. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Liu, H.; Liao, K.; Hu, Q.; Guo, R.; Deng, K. Functionalized GO Nanovehicles with Nitric Oxide Release and Photothermal Activity-Based Hydrogels for Bacteria-Infected Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 28952–28964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Gao, B.; Wang, Z. Palygorskite/silver nanoparticles incorporated polyamide thin film nanocomposite membranes with enhanced water permeating, antifouling and antimicrobial performance. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Pang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Ming, J.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, C.; Lv, P.; Chu, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; et al. Ultrasound-Switchable Nanozyme Augments Sonodynamic Therapy against Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Infection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2063–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Lin, C.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, X.; Chen, M.; He, Y.; Peng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cai, K. Copper-nanoparticle-embedded hydrogel for killing bacteria and promoting wound healing with photothermal therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2534–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Yang, F.; Nie, C.; Yang, Y.; Ji, H.; He, C.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, C. Mussel-Inspired Synthesis of NIR-Responsive and Biocompatible Ag-Graphene 2D Nanoagents for Versatile Bacterial Disinfections. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Yue, L.; Wang, Z. High antibacterial activity of chitosan—Molybdenum disulfide nanocomposite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 215, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Yu, J.; Lv, F.; Yan, L.; Zheng, L.R.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Functionalized Nano-MoS2 with Peroxidase Catalytic and Near-Infrared Photothermal Activities for Safe and Synergetic Wound Antibacterial Applications. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 11000–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, F.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bu, T.; Jia, P.; Zhe, T.; Wang, L. Multifunctional Magnetic Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles as Fenton-like Reaction and Near-Infrared Photothermal Agents for Synergetic Antibacterial Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31649–31660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.; Guo, M.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, X. Synergistic antibacterial activity of streptomycin sulfate loaded PEG-MoS2/rGO nanoflakes assisted with near-infrared. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 116, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, A.R.; Lainhart, W.; Wallace, M.A.; Shupe, A.; Burnham, C.D. Evaluation of telavancin susceptibility in isolates of Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yan, R.; Yi, X.; Li, J.; Rao, J.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y.Q.; Chen, C. Bacteria-Activated Theranostic Nanoprobes against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4428–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Duan, X.; Kong, L.; Wu, H.; Cheng, W.; Min, X.; Ding, S. An enzyme-free electrochemiluminesce aptasensor for the rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus by the quenching effect of MoS2-PtNPs-vancomycin to S2O82−/O2 system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.C.; Boger, D.L. Maxamycins: Durable Antibiotics Derived by Rational Redesign of Vancomycin. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2587–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Hansford, K.A.; Gong, Y.; Butler, M.S.; Muldoon, C.; Huang, J.X.; Ramu, S.; Silva, A.B.; Cheng, M.; Kavanagh, A.M.; et al. Protein-inspired antibiotics active against vancomycin- and daptomycin-resistant bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Ren, C.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, F.; Ding, D.; Xu, B.; Liu, J. Dual Fluorescent- and Isotopic-Labelled Self-Assembling Vancomycin for in vivo Imaging of Bacterial Infections. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 2356–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yu, F.; Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Li, X.L.; Cheng, B.; Mo, X.M.; Chen, C.; Pan, J.F. Moist-Retaining, Self-Recoverable, Bioadhesive, and Transparent in Situ Forming Hydrogels To Accelerate Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuutila, K.; Eriksson, E. Moist Wound Healing with Commonly Available Dressings. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basha, S.I.; Ghosh, S.; Vinothkumar, K.; Ramesh, B.; Kumari, P.H.P.; Mohan, K.V.M.; Sukumar, E. Fumaric acid incorporated Ag/agar-agar hybrid hydrogel: A multifunctional avenue to tackle wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 111, 110743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Itzhaki, E.; Hadad, E.; Gedanken, A.; Margel, S. Microwave-Synthesized Polysaccharide-Derived Carbon Dots as Therapeutic Cargoes and Toughening Agents for Elastomeric Gels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 51940–51951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C.; Ye, C.; Huang, M.; Wang, S. Preparation of injectable temperature-sensitive chitosan-based hydrogel for combined hyperthermia and chemotherapy of colon cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Meng, X.; Wu, Z.; Qi, X. Modified chitosan thermosensitive hydrogel enables sustained and efficient anti-tumor therapy via intratumoral injection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, H.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Preparation of MoS2/WS2 nanosheets by liquid phase exfoliation with assistance of epigallocatechin gallate and study as an additive for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Mei, X.; Li, Q. A Facile Way to Fabricate High-Performance Solution-Processed n-MoS2/p-MoS2 Bilayer Photodetectors. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Li, J.; Liang, T.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Hanagata, N.; Su, H.; Xu, M. Antibacterial activity of two-dimensional MoS2 sheets. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10126–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Mou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, E.; Guo, F.; Sun, D.; Wang, W. Molybdenum disulfide nanosheets loaded with chitosan and silver nanoparticles effective antifungal activities: In vitro and in vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 97, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, H.; Kato, A.; Nakamura, T.; Tachibana, T.; Sakurai, T.; Nanami, M.; Suzuki, M. The importance of characterization of FITC-labeled antibodies used in tissue cross-reactivity studies. Acta Histochem. 2011, 113, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, J.; Shao, Z.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y. Encapsulation of mesenchymal stem cells in chitosan/beta-glycerophosphate hydrogel for seeding on a novel calcium phosphate cement scaffold. Med. Eng. Phys. 2018, 56, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Xin, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xu, T.; Cha, D.; Fan, B. Fabrication and evaluation of thermosensitive chitosan/collagen/alpha, beta-glycerophosphate hydrogels for tissue regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Guo, H.; Huang, H.; Huang, S.; Huang, S.; Xue, W.; Zhu, P.; Guo, R. Nitric oxide released injectable hydrogel combined with synergistic photothermal therapy for antibacterial and accelerated wound healing. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 20, 100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Das, T.K.; Ghosh, S.; Das, S.; Bose, M.; Mondal, M.; Das, A.K.; Das, N.C. Acoustic cavitation assisted destratified clay tactoid reinforced in situ elastomer-mimetic semi-IPN hydrogel for catalytic and bactericidal application. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 60, 104797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, W.; Li, N.; Zhao, Z.; Mou, Z.; Yang, E.; Wang, W. Silver nanoparticles-quercetin conjugation to siRNA against drug-resistant Bacillus subtilis for effective gene silencing: In vitro and in vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 63, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, R.; Vaseeharan, B.; Vijayakumar, S.; Abinaya, M.; Govindarajan, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Al-Anbr, M.N. Crustin-capped selenium nanowires against microbial pathogens and Japanese encephalitis mosquito vectors—Insights on their toxicity and internalization. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 51, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.-Y.; Zhu, G.-Y.; Yu, C.-H.; Chen, G.-Y.; Zhang, C.-L.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Q.-M.; Peng, Q. Functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets with unique three-in-one properties for efficient and tunable antibacterial applications. Nano Res. 2020, 14, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Yang, E.; Mou, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, W. Quercetin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: A highly effective antibacterial agent in vitro and anti-infection application in vivo. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhong, D.; Xie, T.; Yao, K.; Yang, S.; Zhou, M. Cupriferous Silver Peroxysulfite Superpyramids as a Universal and Long-Lasting Agent to Eradicate Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Promote Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 4, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Chen, B.; Yin, Z.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Adhesive Hemostatic Conducting Injectable Composite Hydrogels with Sustained Drug Release and Photothermal Antibacterial Activity to Promote Full-Thickness Skin Regeneration during Wound Healing. Small 2019, 15, e1900046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ding, X.; Cheng, H.; Yin, C.; Yan, J.; Mou, Z.; Wang, W.; Cui, D.; Fan, C.; Sun, D. Dual-Targeted Gold Nanoprism for Recognition of Early Apoptosis, Dual-Model Imaging and Precise Cancer Photothermal Therapy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5610–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Cui, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Wu, S. Photo-responsive chitosan/Ag/MoS2 for rapid bacteria-killing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y. Multifunctional MoS2 nanosheets with Au NPs grown in situ for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gu, B.; Liu, Q.; Pang, Y.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Combined use of vancomycin-modified Ag-coated magnetic nanoparticles and secondary enhanced nanoparticles for rapid surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of bacteria. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1159–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vimberg, V.; Gazak, R.; Szucs, Z.; Borbas, A.; Herczegh, P.; Cavanagh, J.P.; Zieglerova, L.; Zavora, J.; Adamkova, V.; Novotna, G.B. Fluorescence assay to predict activity of the glycopeptide antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Materials | Bacteria | |
|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | |
| MoS2 | >128 | >128 |
| Van | 2 | >128 |
| MoS2-Van-FITC | 64 | 64 |
| MoS2-Van-FITC@CS | 64 | 64 |
| MoS2 + NIR | 64 | 128 |
| MoS2-Van-FITC + NIR | 36 | 128 |
| MoS2-Van-FITC@CS + NIR | 36 | 128 |
| Kanamycin | 6 | 12 |
| Ampicillin | 18 | 24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Kuang, Z.; Song, P.; Li, W.; Gui, L.; Tang, C.; Tao, Y.; Ge, F.; Zhu, L. Synthesis of a Two-Dimensional Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheet and Ultrasensitive Trapping of Staphylococcus Aureus for Enhanced Photothermal and Antibacterial Wound-Healing Therapy. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12111865
Zhang W, Kuang Z, Song P, Li W, Gui L, Tang C, Tao Y, Ge F, Zhu L. Synthesis of a Two-Dimensional Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheet and Ultrasensitive Trapping of Staphylococcus Aureus for Enhanced Photothermal and Antibacterial Wound-Healing Therapy. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(11):1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12111865
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Weiwei, Zhao Kuang, Ping Song, Wanzhen Li, Lin Gui, Chuchu Tang, Yugui Tao, Fei Ge, and Longbao Zhu. 2022. "Synthesis of a Two-Dimensional Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheet and Ultrasensitive Trapping of Staphylococcus Aureus for Enhanced Photothermal and Antibacterial Wound-Healing Therapy" Nanomaterials 12, no. 11: 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12111865
APA StyleZhang, W., Kuang, Z., Song, P., Li, W., Gui, L., Tang, C., Tao, Y., Ge, F., & Zhu, L. (2022). Synthesis of a Two-Dimensional Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheet and Ultrasensitive Trapping of Staphylococcus Aureus for Enhanced Photothermal and Antibacterial Wound-Healing Therapy. Nanomaterials, 12(11), 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12111865






