Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy: Effective Heating versus Possible Toxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles
2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
2.4. Mössbauer Spectroscopy
2.5. Vibrating Sample Magnetometry
2.6. Cell Lines
2.7. Nanoparticle Stability Assay after Incubation with Cells
2.8. Toxicity Studies of Nanoparticles
2.9. Animals and Tumor Model
2.10. Controlled MNPs Hyperthermia
2.11. MNPs Magnetic Properties Study after Intratumoral Injection and Magnetic Hyperthermia
2.12. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cobalt Ferrite MNPs Characteristic
3.2. MNPs Toxicity Study
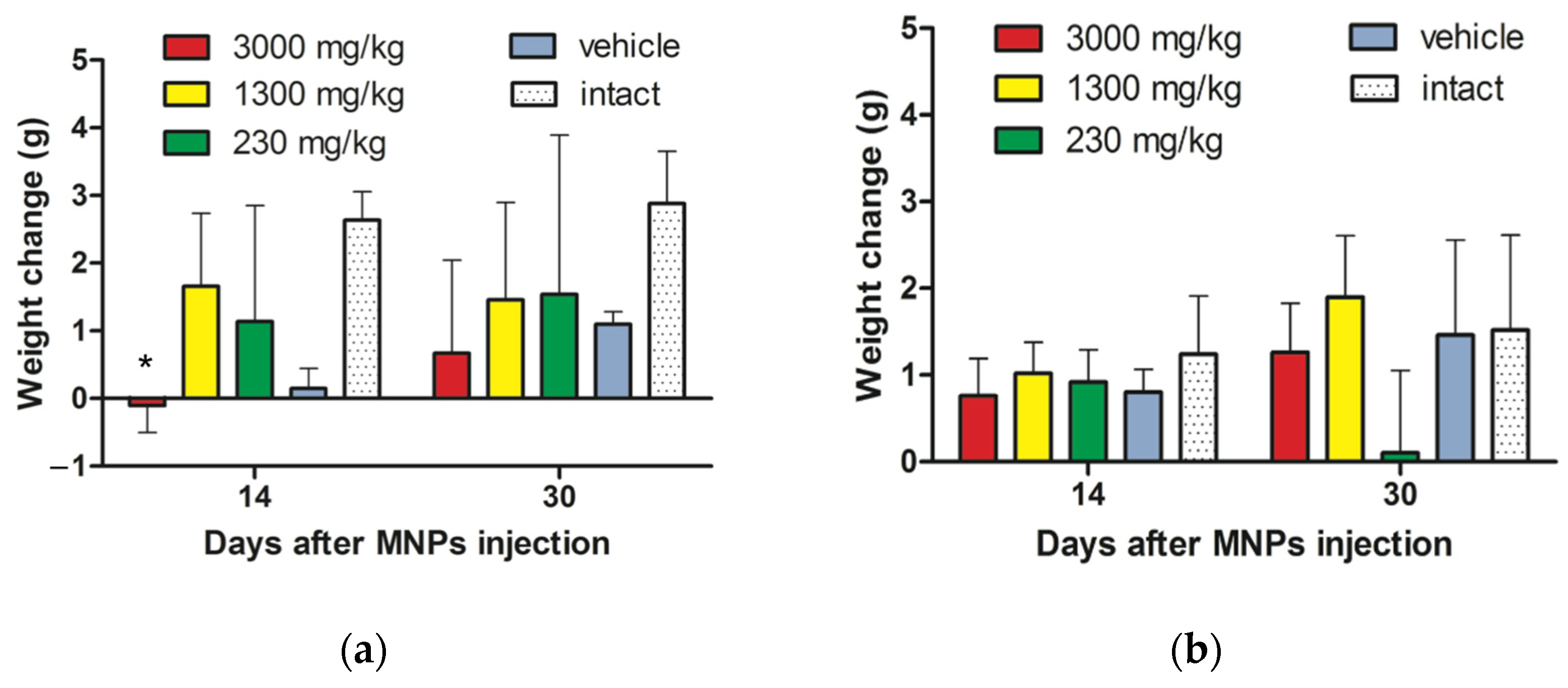
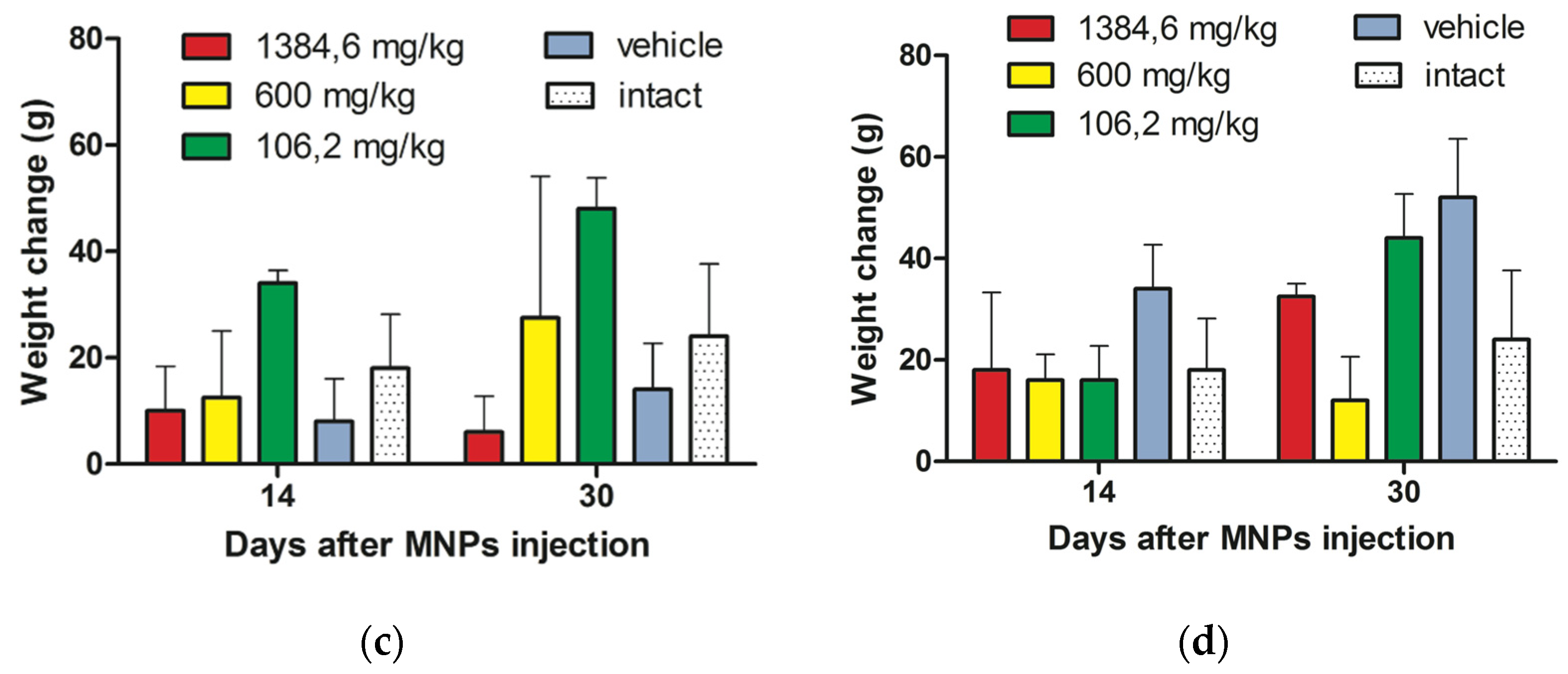
3.2.1. Animals Weight Change after MNPs Injection
3.2.2. Animals’ Behavior Changes after MNPs Injection
3.2.3. MNPs Effect on Blood Cells
3.2.4. Blood Biochemical Parameters of Laboratory Animals in the Study of MNPs Acute Toxicity
3.2.5. Histological Studies in Acute Toxicity
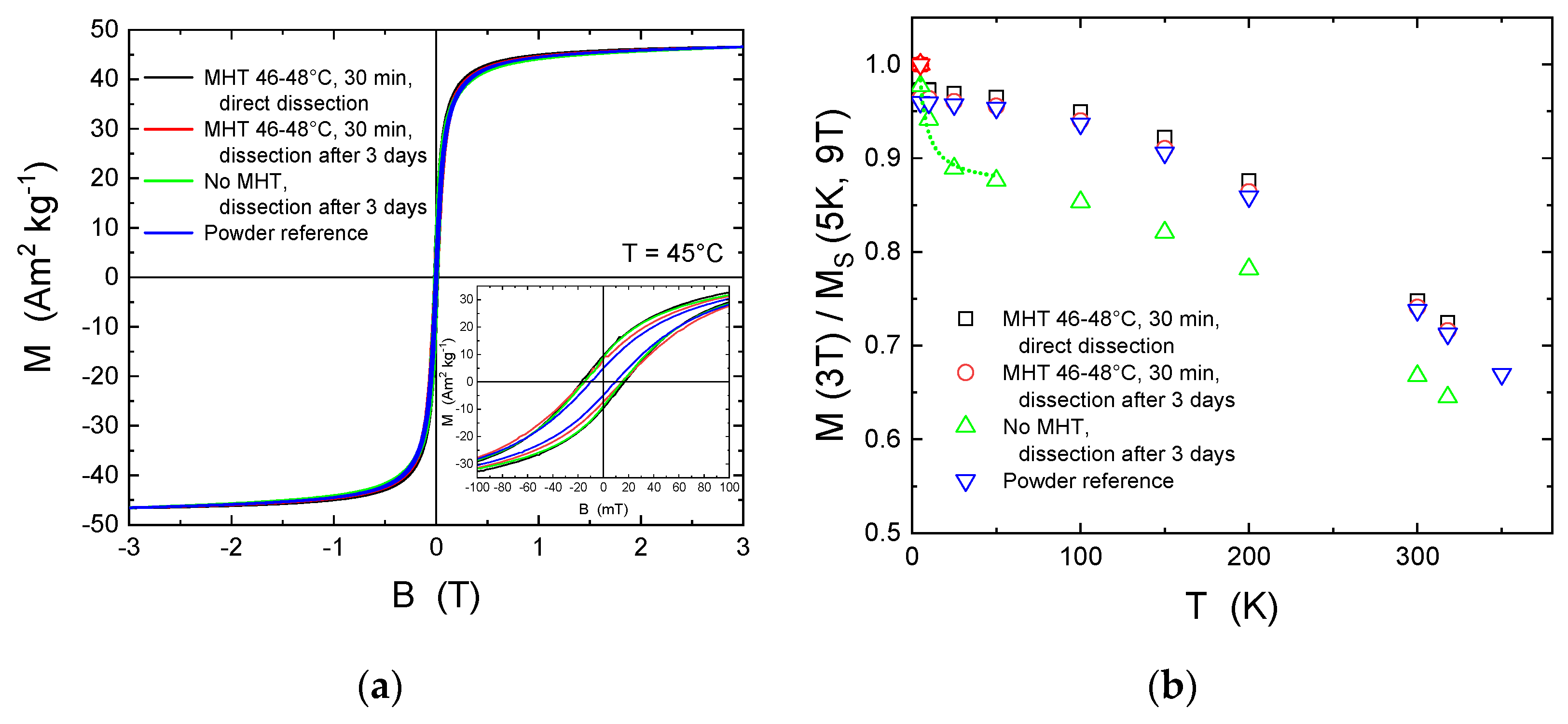
3.3. Magnetic Properties of MNPs after Intratumoral Administration
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albarqi, H.A.; Wong, L.H.; Schumann, C.; Sabei, F.Y.; Korzun, T.; Li, X.; Hansen, M.N.; Dhagat, P.; Moses, A.S.; Taratula, O.; et al. Biocompatible Nanoclusters with High Heating Efficiency for Systemically Delivered Magnetic Hyperthermia. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6383–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenojar, E.C.; Wickramasinghe, S.; Bas-Concepcion, J.; Samia, A.C.S. Structural effects on the magnetic hyperthermia properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2016, 26, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemati, Z.; Alonso, J.; Martinez, L.M.; Khurshid, H.; Garaio, E.; Garcia, J.A.; Phan, M.H.; Srikanth, H. Enhanced Magnetic Hyperthermia in Iron Oxide Nano-Octopods: Size and Anisotropy Effects. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 8370–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Quinto, C.A.; Zhang, L.; Mohindra, P.; Bao, G. Size-Dependent Heating of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6808–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Corato, R.D.; Lartigue, L.; Marangon, I.; Guardia, P.; Silva, A.K.L.; Luciani, N.; Cle’ment, O.; Flaud, P.; Singh, J.V.; et al. Heat-Generating Iron Oxide Nanocubes: Subtle “Destructurators” of the Tumoral Microenvironment. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4268–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafrouni, L.; Savadogo, O. Recent progress on magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. Prog. Biomater. 2016, 5, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, S.Y.; Paknikar, K.M.; Bodas, D.; Gajbhiye, V. Applications of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in biomedical nanotechnology. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dönmez, Ç.E.D.; Manna, P.K.; Nickel, R.; Aktürk, S.; van Lierop, J. Comparative Heating Efficiency of Cobalt-, Manganese-, and Nickel-Ferrite Nanoparticles for a Hyperthermia Agent in Biomedicines. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6858–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liébana-Viñas, S.; Simeonidis, K.; Wiedwald, U.; Li, Z.-A.; Ma, Z.; Myrovali, E.; Makridis, A.; Sakellari, D.; Vourlias, G.; Spasova, M.; et al. Optimum nanoscale design in ferrite based nanoparticles for magnetic particle hyperthermia. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 72918–72925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liébana-Viñas, S.; Simeonidis, K.; Li, Z.-A.; Ma, Z.; Myrovali, E.; Makridis, A.; Sakellari, D.; Angelakeris, M.; Wiedwald, U.; Spasova, M.; et al. Tuning the magnetism of ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 415, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazario, E.; Menendez, N.; Herrasti, P.; Cañete, M.; Connord, V.; Carrey, J. Magnetic Hyperthermia Properties of Electrosynthesized Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11405–11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomitaka, A.; Hirukawa, A.; Yamada, T.; Morishita, S.; Takemura, Y. Biocompatibility of various ferrite nanoparticles evaluated by in vitro cytotoxicity assays using HeLa cells. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Cui, F. Biocompatibility and Toxicity of Nanoparticles and Nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhadlaq, H.A.; Akhtar, M.J.; Ahamed, M. Zinc ferrite nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress in different human cells. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Długosz, O.; Szostak, K.; Staroń, A.; Pulit-Prociak, J.; Banach, M. Methods for Reducing the Toxicity of Metal and Metal Oxide NPs as Biomedicine. Materials 2020, 13, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soetaert, F.; Korangath, P.; Serantes, D.; Fiering, S.; Ivkov, R. Cancer therapy with iron oxide nanoparticles: Agents of thermal and immune therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 163–164, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez, N.L.; Tavárez, S.; González-Sánchez, Z.I. In vitro toxicity assessment of zinc and nickel ferrite nanoparticles in human erythrocytes and peripheral blood mononuclear cell. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 57, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dippong, T.; Levei, E.A.; Cadar, O. Recent Advances in Synthesis and Applications of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn) Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakil, S.; Hasan, A.; Uddin, F.; Islam, A.; Nahar, A.; Das, H.; Khan, M.N.I.; Dey, B.P.; Rokeya, B.; Hoque, S.M. In Vivo Toxicity Studies of Chitosan-Coated Cobalt Ferrite Nanocomplex for Its Application as MRI Contrast Dye. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7952–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garanina, A.S.; Naumenko, V.A.; Nikitin, A.A.; Myrovali, E.; Petukhova, A.Y.; Klimyuk, S.V.; Nalench, Y.A.; Ilyasov, A.R.; Vodopyanov, S.S.; Erofeev, A.S.; et al. Temperature-controlled magnetic nanoparticles hyperthermia inhibits primary tumor growth and metastases dissemination. Nanomed. NBM 2020, 25, 102171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurenya, A.; Nikitin, A.; Garanina, A.; Gabbasov, R.; Polikarpov, M.; Cherepanov, V.; Chuev, M.; Majouga, A.; Panchenko, V. Synthesis and Mössbauer study of 57Fe-based nanoparticles biodegradation in living cells. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 474, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freireich, E.J.; Gehan, E.A.; Rall, D.P.; Schmidt, L.H.; Skipper, H.E. Quantitative comparison of toxicity of anticancer agents in mouse, rat, hamster, dog, monkey, and man. Cancer Chemother. Res. 1966, 50, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikitin, A.A.; Yurenya, A.Y.; Zatsepin, T.S.; Aparin, I.O.; Chekhonin, V.P.; Majouga, A.G.; Farle, M.; Wiedwald, U.; Abakumov, M.A. Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Tool for Remote DNA Manipulations at a Single-Molecule Level. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 14458–14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, M.; Lagarde, F.; Maraloiu, V.A.; Blanchin, M.G.; Gendron, F.; Wilhelm, C.; Gazeau, F. Degradability of superparamagnetic nanoparticles in a model of intracellular environment: Follow-up of magnetic, structural and chemical properties. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 395103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.I.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.S. Synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles prepared by temperature-controlled coprecipitation method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2003, 337, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikarpov, D.; Gabbasov, R.; Cherepanov, V.; Loginova, N.; Loseva, E.; Nikitin, M.; Yurenia, A.; Panchenko, V. Mössbauer study of exogenous iron redistribution between the brain and the liver after administration of 57Fe3O4 ferrofluid in the ventricle of the rat brain. JMMM 2015, 380, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.S.; Hainfeld, J.F. Intravenous Magnetic Nanoparticle Cancer Hyperthermia. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bubnovskaya, L.; Belous, A.; Solopan, S.; Kovelskaya, A.; Bovkun, L.; Podoltsev, A.; Kondtratenko, I.; Osinsky, S. Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia of Rodent Tumors Using Manganese Perovskite Nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. 2014, 2014, 278761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zeng, W.; Yang, T.; Cao, Y.; Mei, C.; Kuang, Y. Toxicity assessment of nanoparticles in various systems and organs. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2016, 6, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Gomes, J.; Loureiro, J.A.; Tanqueiro, S.R.; Mouro, F.M.; Ruivo, P.; Carvalho, T.; Sebastião, A.M.; Diógenes, M.J.; Pereira, M.C. In vivo Bio-Distribution and Toxicity Evaluation of Polymeric and Lipid-Based Nanoparticles: A Potential Approach for Chronic Diseases Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8609–8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatarchuk, T.; Bououdina, M.; Macyk, W.; Shyichuk, O.; Paliychuk, N.; Yaremiy, I.; Al-Najar, B.; Pacia, M. Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Zn-Doped CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laznev, K.; Tzerkovsky, D.; Kekalo, K.; Zhavnerko, G.; Agabekov, V. Iron-Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles—Biocompatibility and Distribution After Intravenous Administration to Rat. IEEE Trans. Magn 2013, 49, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, P.B.; Silvestri, N.; Fernandez-Cabada, T.; Marinaro, F.; Fernandes, S.; Fiorito, S.; Miscuglio, M.; Serantes, D.; Ruta, S.; Livesey, K.; et al. Exploiting Unique Alignment of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles, Mild Hyperthermia, and Controlled Intrinsic Cobalt Toxicity for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drašler, B.; Drobne, D.; Novak, S.; Valant, J.; Boljte, S.; Otrin, L.; Rappolt, M.; Sartori, B.; Iglič, A.; Kralj-Iglič, V.; et al. Effects of magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles on biological and artificial lipid membranes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1559–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hajipour, M.J.; Aghaverdi, H.; Serpooshan, V.; Vali, H.; Sheibani, S.; Mahmoudi, M. Sex as an important factor in nanomedicine. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.M.M.; Tamanna, N.; Haque, A. Biochemical and histopathological profiling of Wistar rat treated with Brassica napus as a supplementary feed. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, O.M.M.; Hussein, R.M. Effects of intraperitoneally injected silver nanoparticles on histological structures and blood parameters in the albino rat. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valentini, X.; Rugira, P.; Frau, A.; Tagliatti, V.; Conotte, R.; Laurent, S.; Colet, J.-M.; Nonclercq, D. Hepatic and Renal Toxicity Induced by TiO2 Nanoparticles in Rats: A Morphological and Metabonomic Study. J. Toxicol. 2019, 2019, 5767012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Long, W.; Shen, X.; Wu, D.; Song, S.-S.; Sun, Y.-M.; Liu, P.-X.; Fan, S.; Fan, F.; et al. Sex differences in the toxicity of polyethylene glycol-coated gold nanoparticles in mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, P.; Luo, Q.; Chen, J.; Gan, Y.; Du, J.; Ding, S.; Xi, Z.; Yang, X. Intraperitoneal injection of magnetic Fe3O4-nanoparticle induces hepatic and renal tissue injury via oxidative stress in mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4809–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezealigo, U.; Ezealigo, B.; Aisida, S.O.; Ezema, F.I. Iron oxide nanoparticles in biological systems: Antibacterial and toxicology perspective. JCIS Open 2021, 4, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, K.; Javed, Y.; Jamil, Y.; Muhammad, F. Functionalized cobalt ferrite cubes: Toxicity, interactions and mineralization into ferritin proteins. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 3659–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavilán, H.; Simeonidis, K.; Myrovali, E.; Mazarío, E.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; Chantrell, R.; Balcells, L.; Angelakeris, M.; Morales, M.P.; Serantes, D. How size, shape and assembly of magnetic nanoparticles give rise to different hyperthermia scenarios. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 15631–15646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Ju, J.E.; Kim, B.I.; Pak, P.J.; Choi, E.-K.; Lee, H.-S.; Chung, N. Rod-shaped iron oxide nanoparticles are more toxic than sphere-shaped nanoparticles to murine macrophage cells. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caizer, C. Computational Study Regarding CoxFe3−xO4 Ferrite Nanoparticles with Tunable Magnetic Properties in Superparamagnetic Hyperthermia for Effective Alternative Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 0 mg kg−1 | 230 mg kg−1 | 1300 mg kg−1 | 3000 mg kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Protein (g L−1)-Male/Female | |||
| 68.9/87.2 | 86.5 */87.5 | 85.75 */88.65 | 69.6/64.7 * |
| Venous blood plasma glucose (mM L−1)-Female | |||
| 9.21 | 6.84 | 6.01 * | 5.56 * |
| 0 mg kg−1 | 106.2 mg kg−1 | 600 mg kg−1 | 1384.6 mg kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Venous Blood Plasma Glucose (mM L−1)-Male/Female | |||
| 7.55/7.59 | 7.29/7.95 | 9.38 */8.91 | 10.43 */11.6 * |
| Total bilirubin (mM L−1)-Male/Female | |||
| 7.8/7.2 | 6.6/6.6 | 1.45 */0.8 * | 1.3 */2.45 * |
| Total cholesterol (mM L−1)-Male/Female | |||
| 1.81/1.76 | 1.89/1.59 * | 1.24 */1.37 | 1.47 */1.65 |
| ALT (U L−1)-Male/Female | |||
| 88.75/75.19 | 77.3/58.87 | 53.86 */50.71 * | 58.44 */62.13 |
| AST (U L−1)-Male/Female | |||
| 144.1/149.78 | 132.9/132.21 * | 137.22/146.73 | 95.09 */94.05 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garanina, A.S.; Nikitin, A.A.; Abakumova, T.O.; Semkina, A.S.; Prelovskaya, A.O.; Naumenko, V.A.; Erofeev, A.S.; Gorelkin, P.V.; Majouga, A.G.; Abakumov, M.A.; et al. Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy: Effective Heating versus Possible Toxicity. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010038
Garanina AS, Nikitin AA, Abakumova TO, Semkina AS, Prelovskaya AO, Naumenko VA, Erofeev AS, Gorelkin PV, Majouga AG, Abakumov MA, et al. Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy: Effective Heating versus Possible Toxicity. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaranina, Anastasiia S., Alexey A. Nikitin, Tatiana O. Abakumova, Alevtina S. Semkina, Alexandra O. Prelovskaya, Victor A. Naumenko, Alexander S. Erofeev, Peter V. Gorelkin, Alexander G. Majouga, Maxim A. Abakumov, and et al. 2022. "Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy: Effective Heating versus Possible Toxicity" Nanomaterials 12, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010038
APA StyleGaranina, A. S., Nikitin, A. A., Abakumova, T. O., Semkina, A. S., Prelovskaya, A. O., Naumenko, V. A., Erofeev, A. S., Gorelkin, P. V., Majouga, A. G., Abakumov, M. A., & Wiedwald, U. (2022). Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy: Effective Heating versus Possible Toxicity. Nanomaterials, 12(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010038