Towards Red Emissive Systems Based on Carbon Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Discussion
2.1. Strategies to Generate Red-Shifted C-Dots
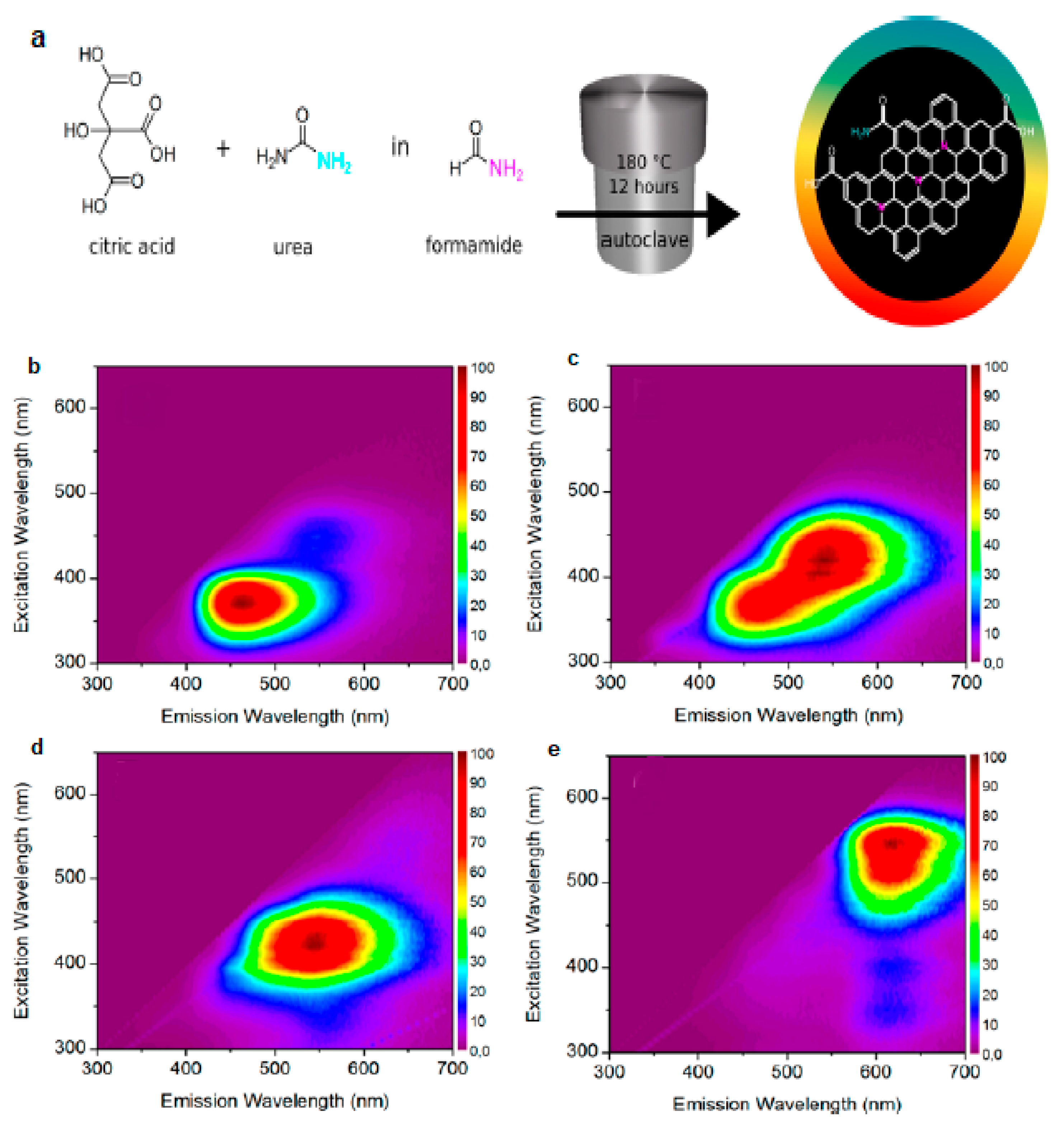
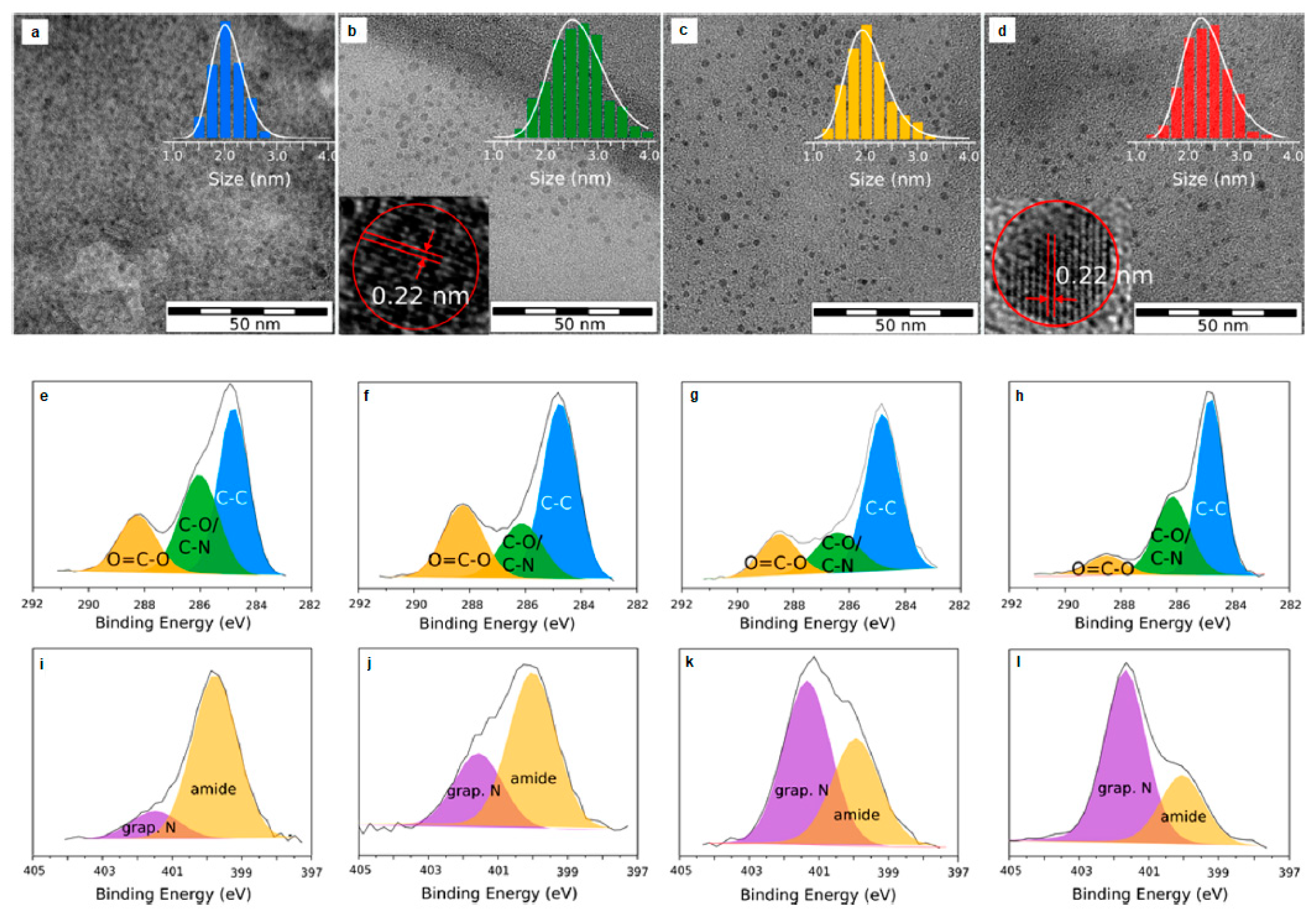
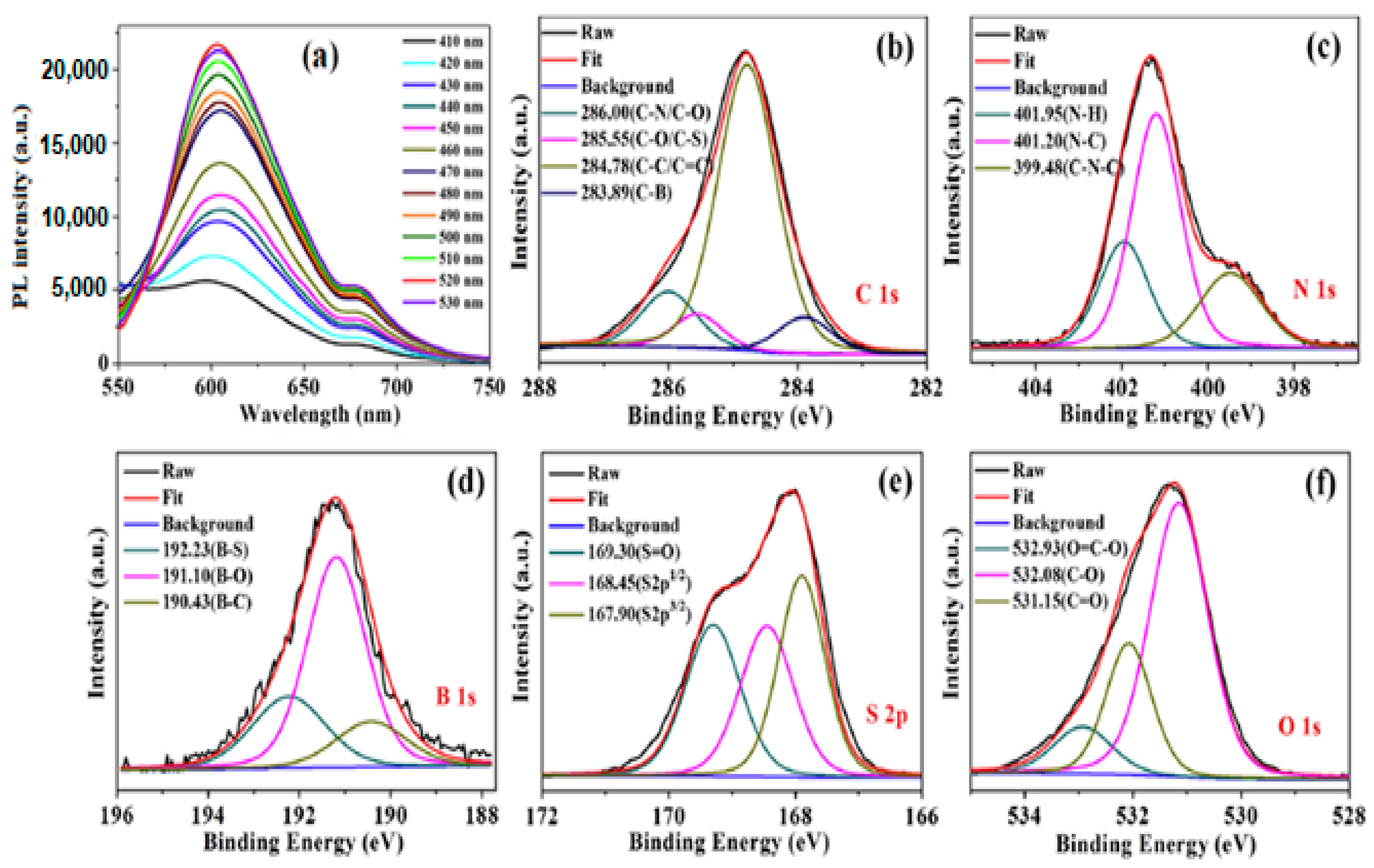
2.1.1. Heteroatom Doping
2.1.2. Extensive Conjugation Length
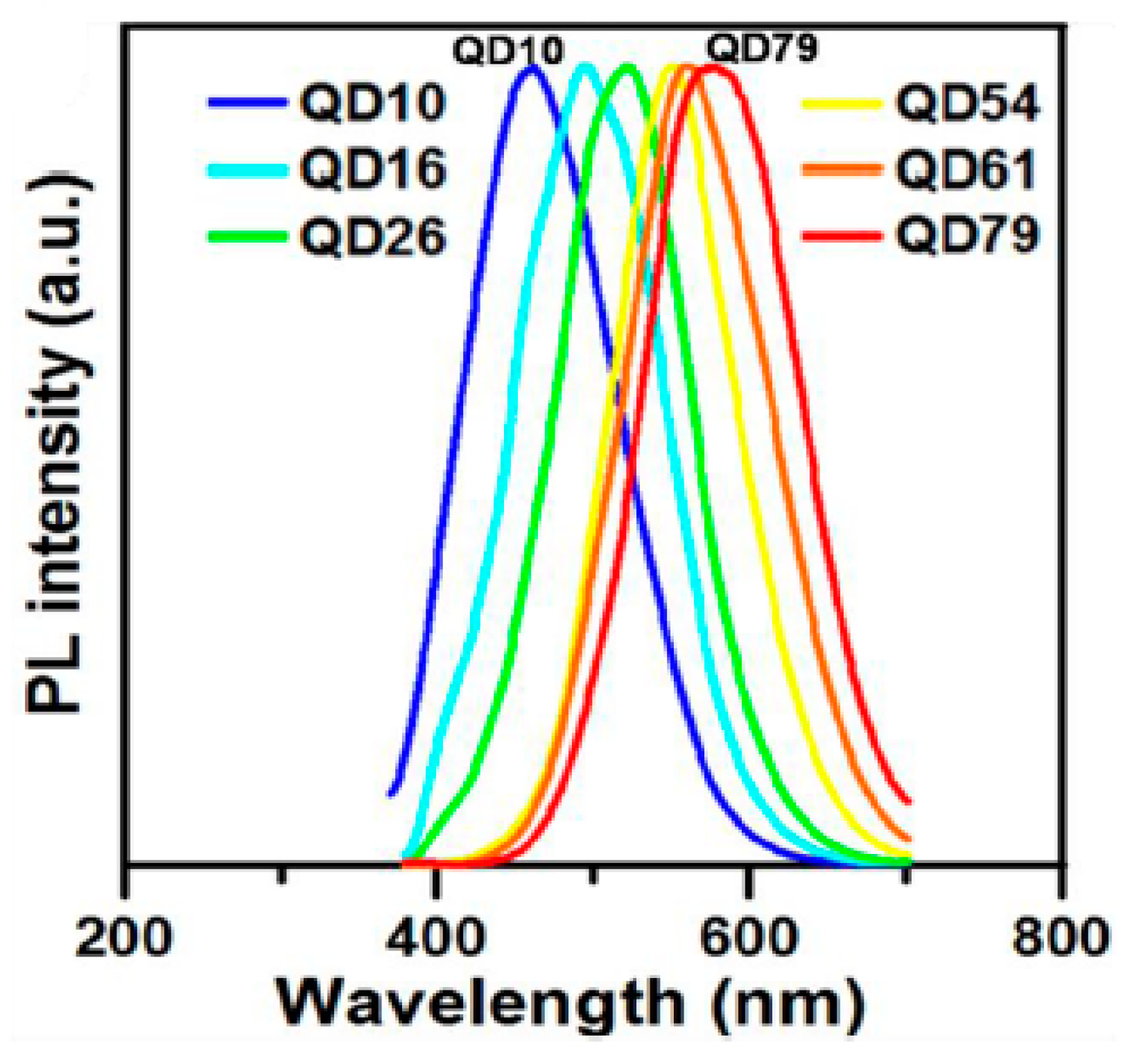
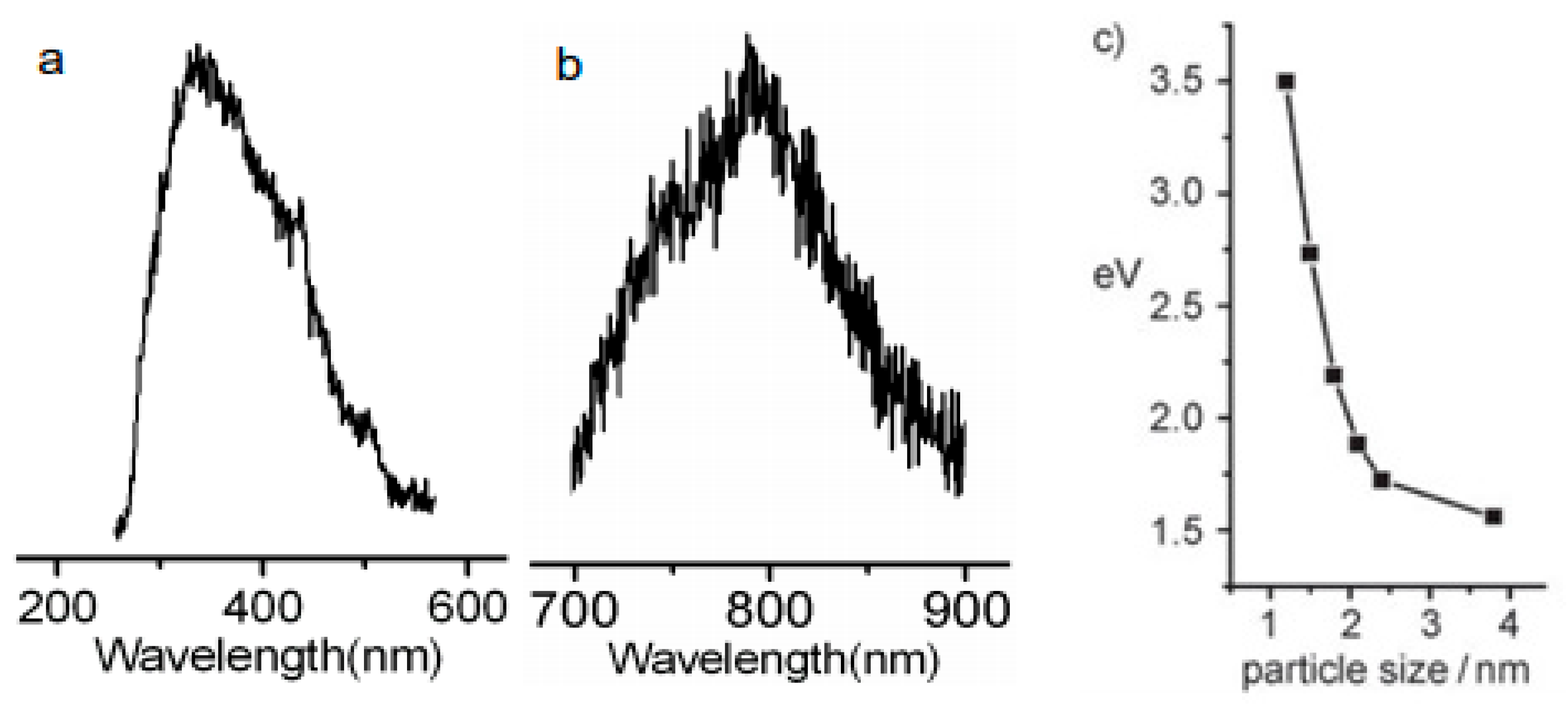
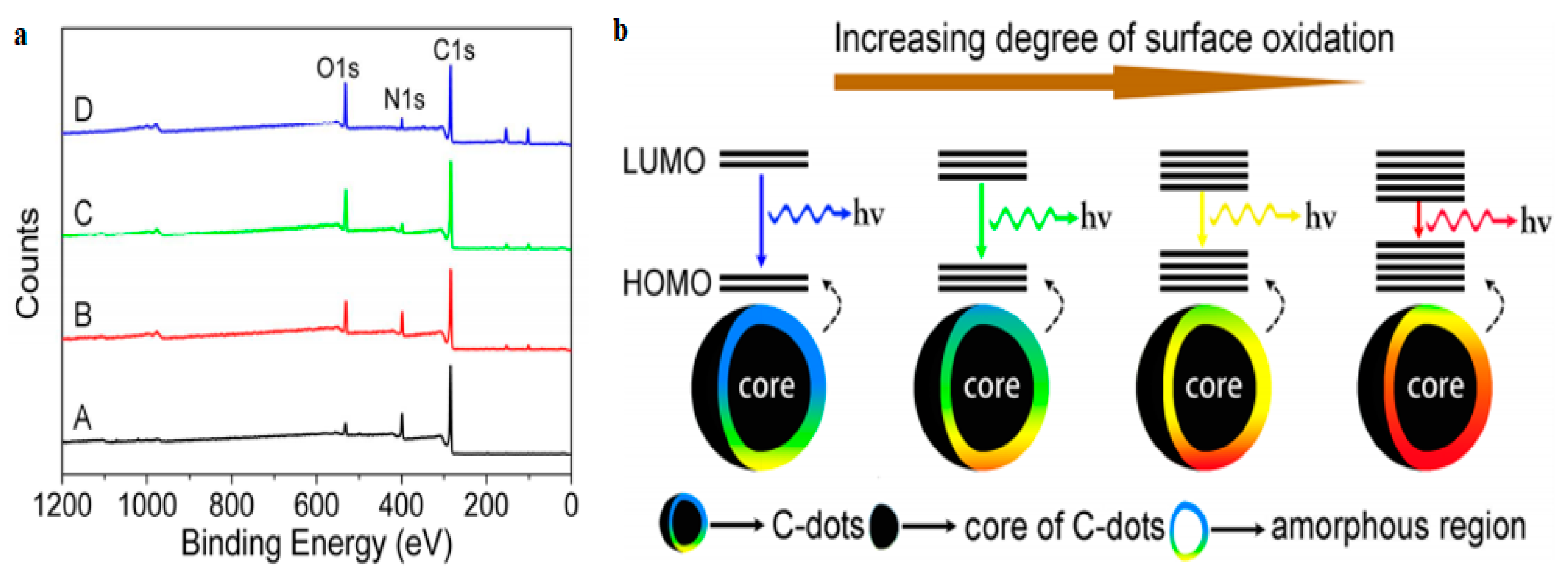
2.1.3. Surface Functionalization and Passivation
2.1.4. Solvatochromism
2.2. Applications of Aqueous Dispersions of Red C-Dots
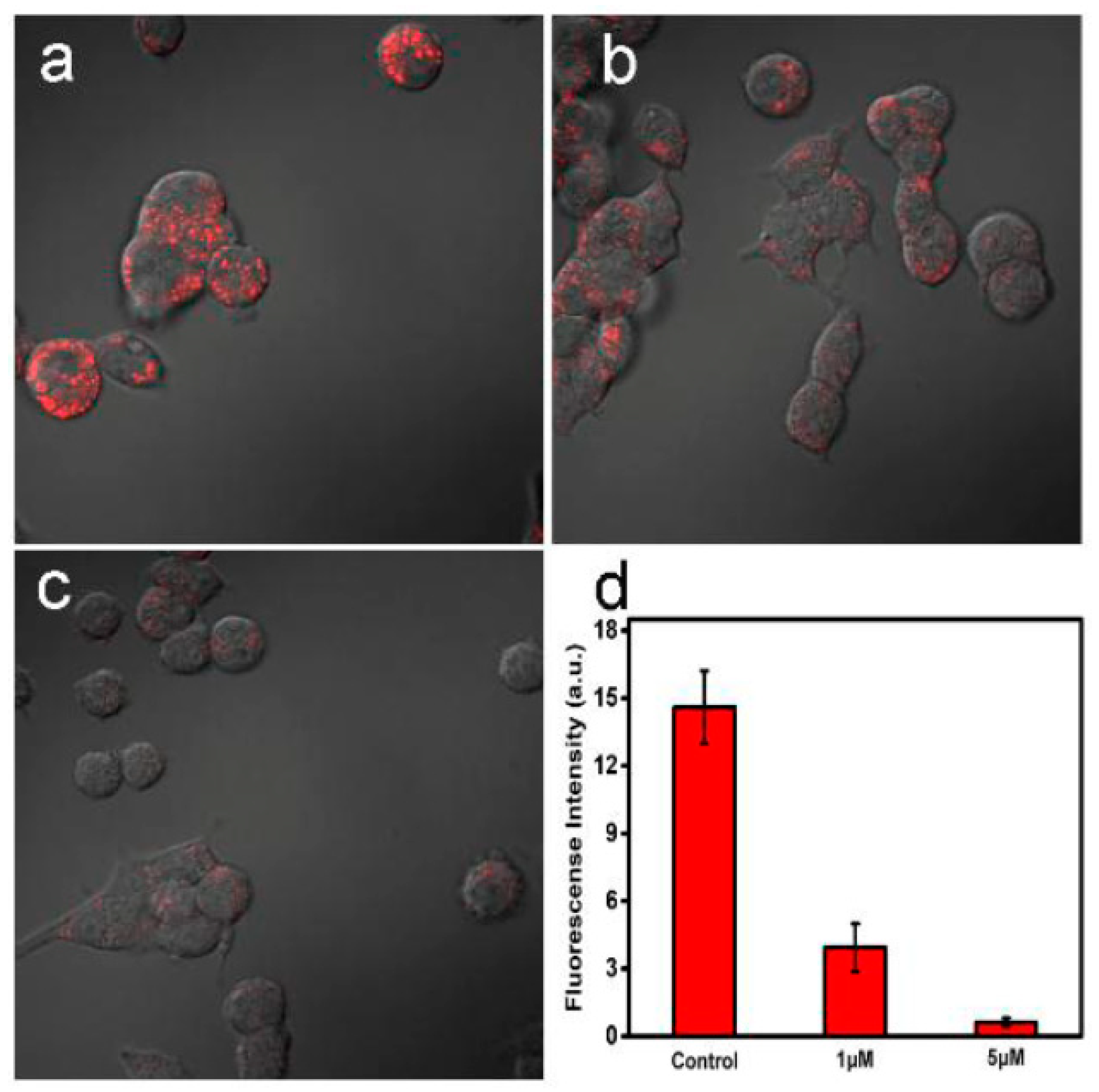
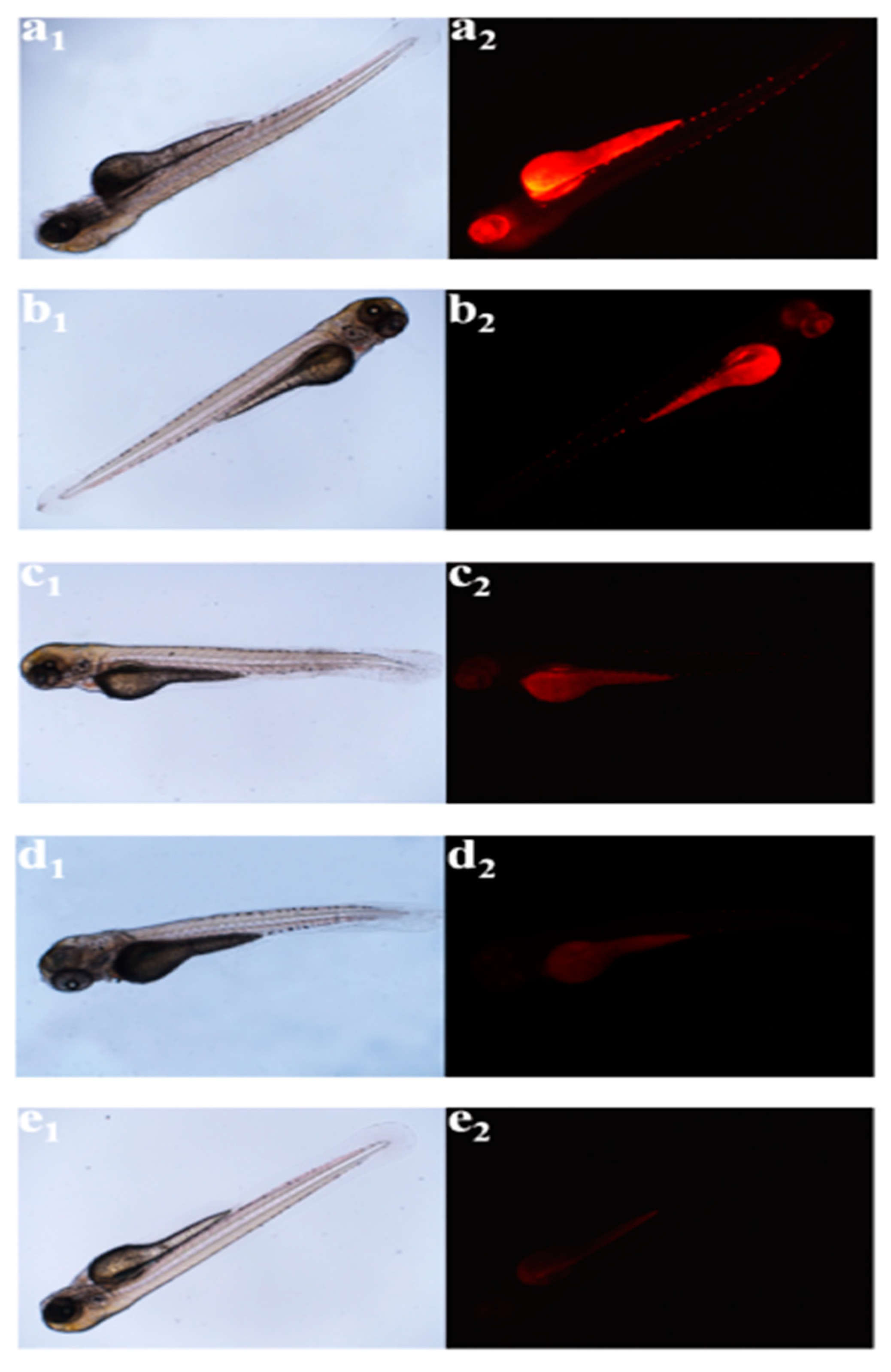
2.2.1. Bioimaging
2.2.2. Sensing/Biosensing
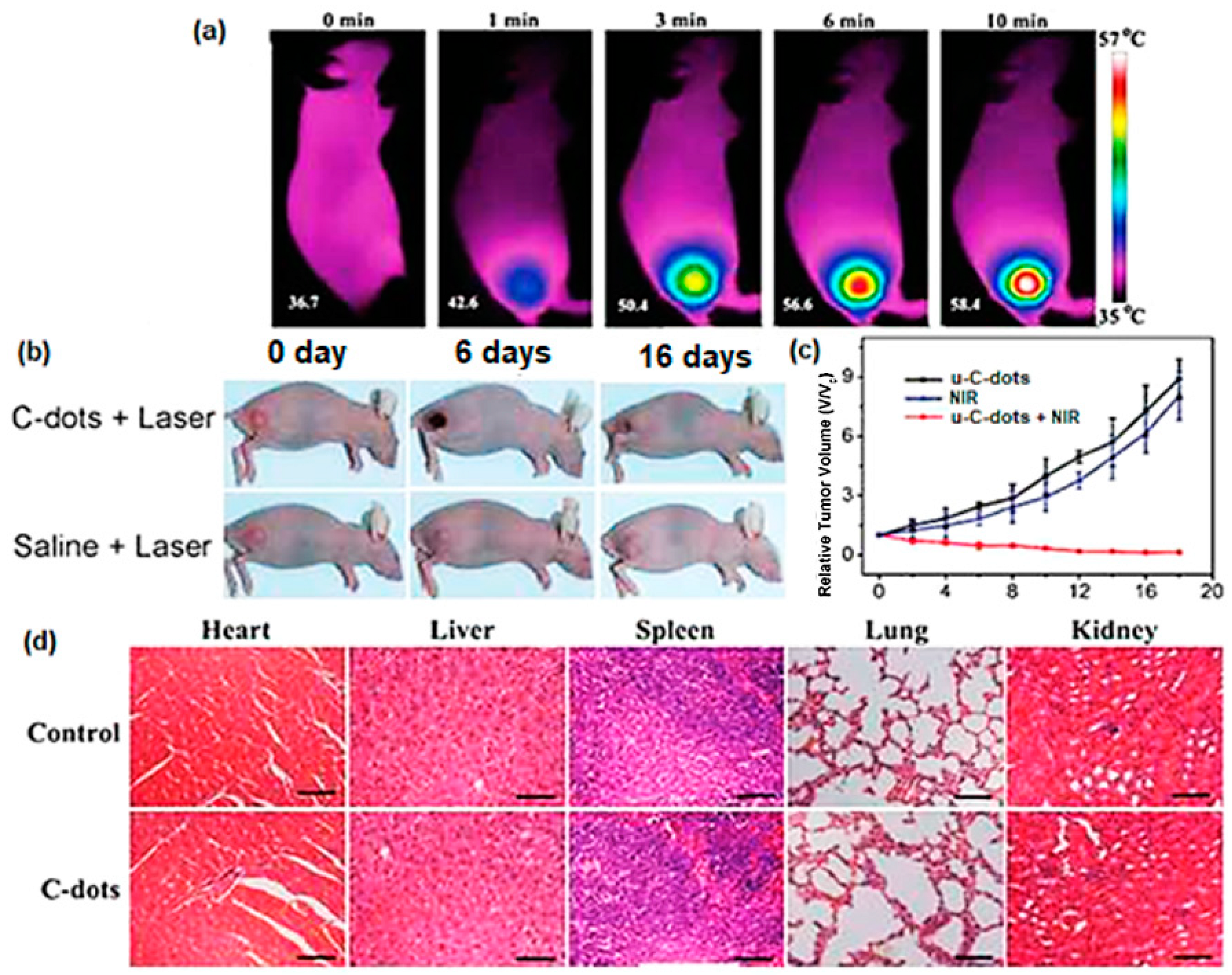
2.2.3. Photothermal Therapy (PTT)
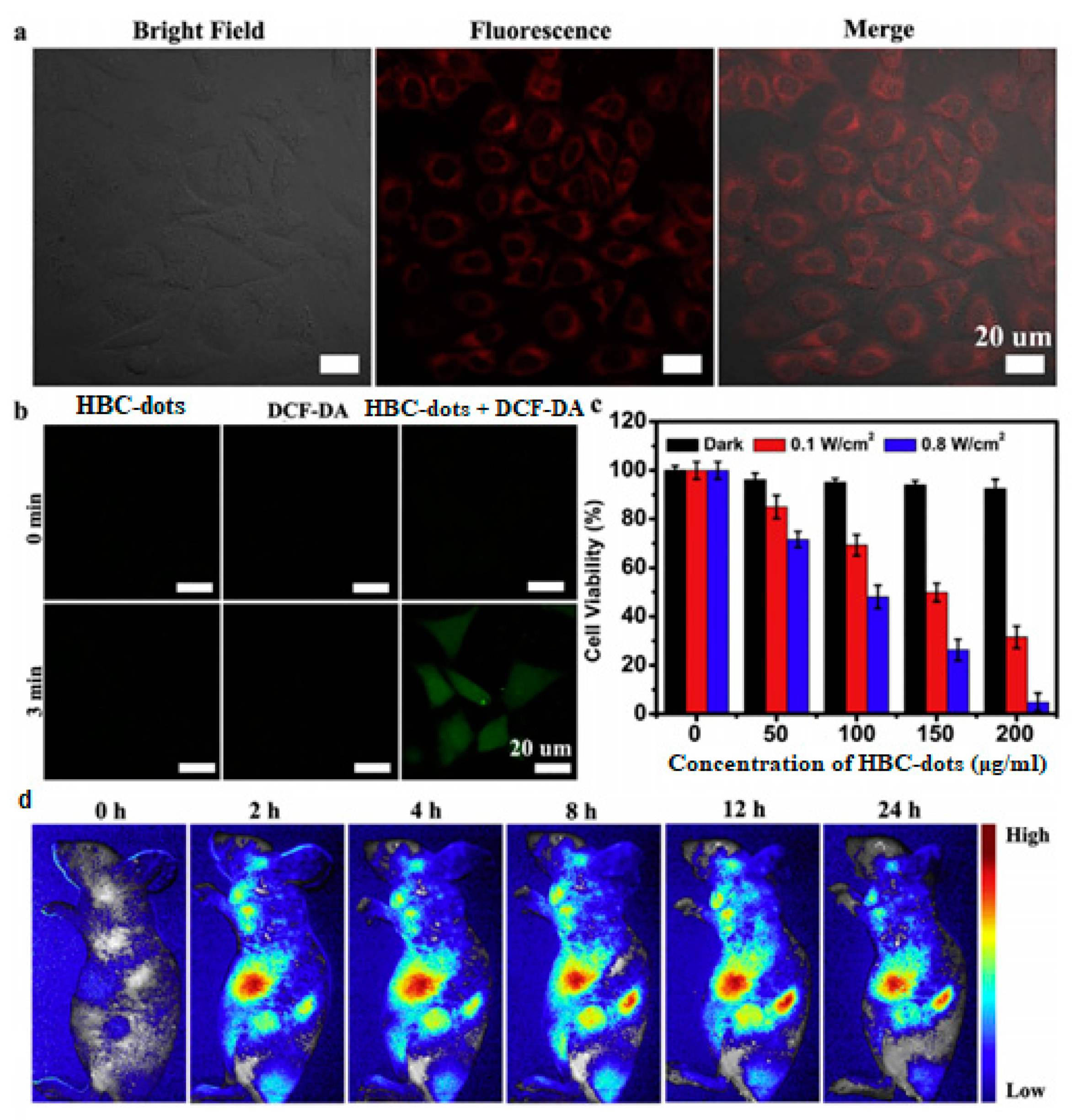
2.2.4. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
2.3. Solid-State Red C-Dots and Their Applications
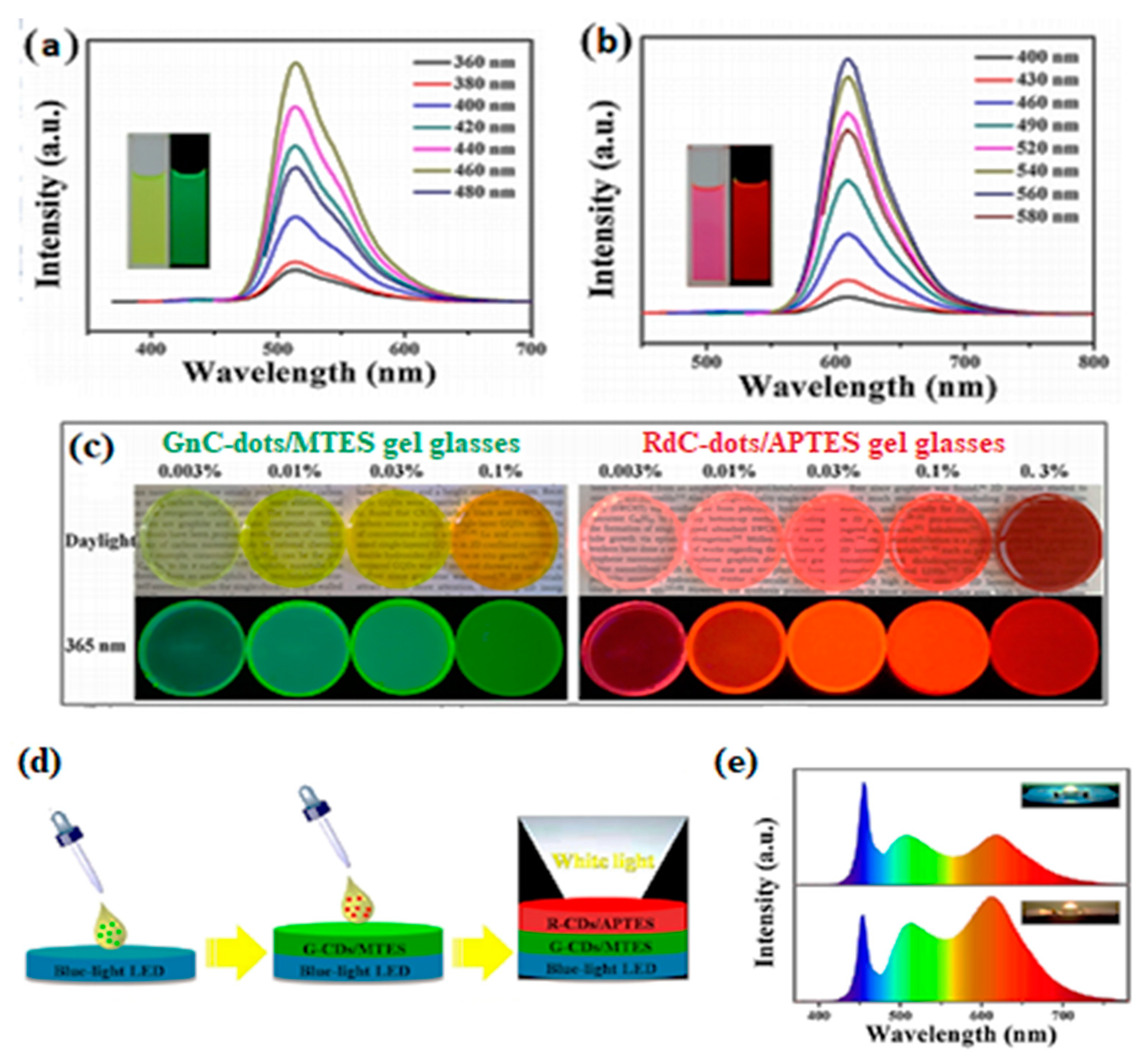
2.3.1. WLEDs (White Light-Emitting Diodes)
2.3.2. Pollutant Sensing
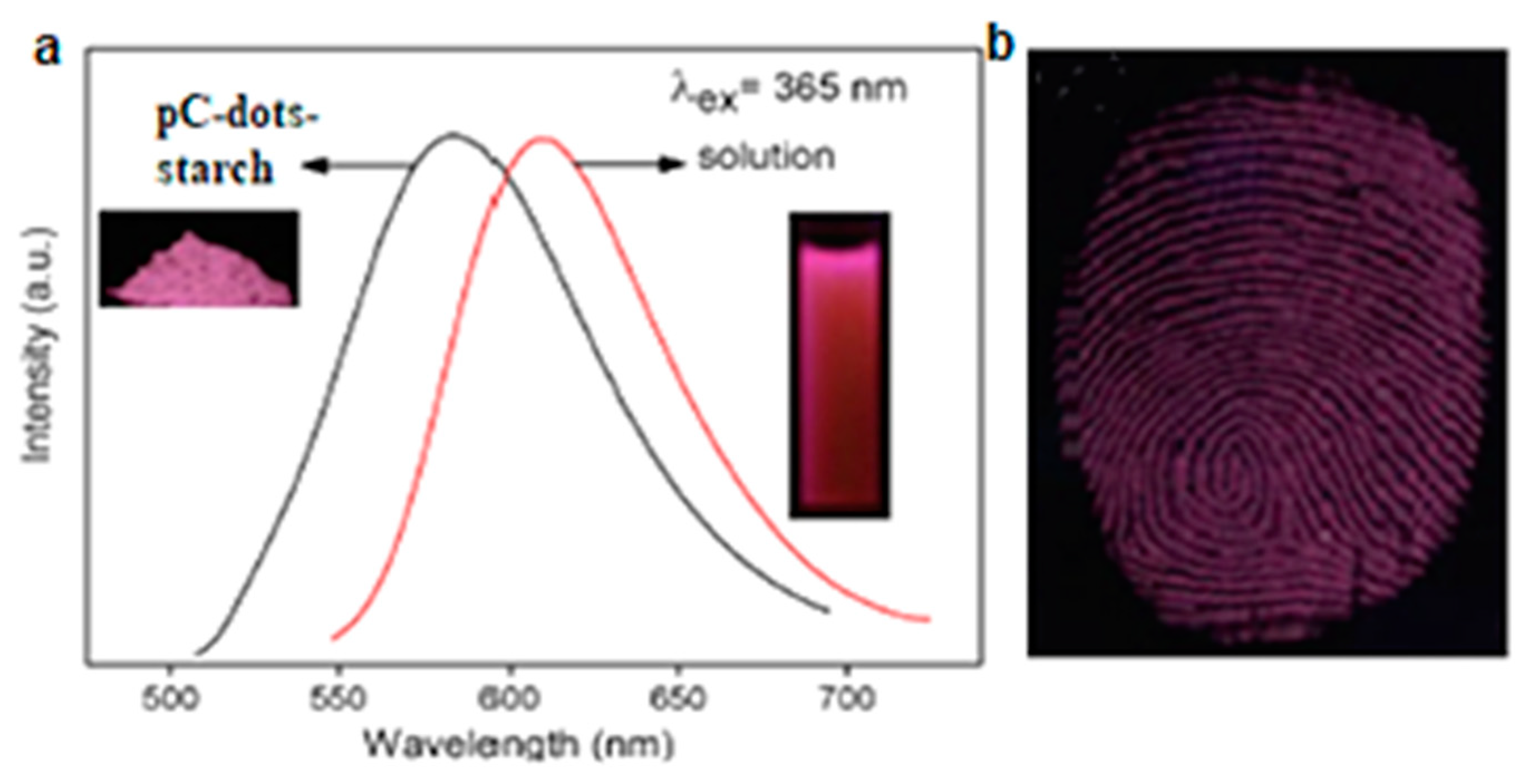
2.3.3. Nanoforensics
3. Conclusions
4. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.-T. Carbon nanodots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24230–24253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Li, S.; Fan, Z.; Meng, X.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Shining carbon dots: Synthesis and biomedical and optoelectronic applications. Nano Today 2016, 11, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, A.; Cannizzo, A.; Messina, F. Carbon nanodots: A review—From the current understanding of the fundamental photophysics to the full control of the optical response. C 2018, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelarakis, A. From highly graphitic to amorphous carbon dots: A critical review. MRS Energy Sustain. 2014, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelarakis, A. Graphene quantum dots: In the crossroad of graphene, quantum dots and carbogenic nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 20, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X. Direct synthesis of graphene quantum dots on hexagonal boron nitride substrate. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3717–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cui, X.; Li, B.; Li, L.-S. Large, solution-processable graphene quantum dots as light absorbers for photovoltaics. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yeo, P.S.E.; Gan, C.K.; Wu, P.; Loh, K. Transforming C60 molecules into graphene quantum dots. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Xiang, C.; Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Huang, K.; Yan, Z.; Cook, N.P.; Samuel, E.; Hwang, C.-C.; Ruan, G.; et al. Coal as an abundant source of graphene quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, X.T.; Gao, L.; Cui, Z.; Yang, H.; Guo, C.; Chi, Y.; Li, C.M. One-step and high yield simultaneous preparation of single- and multi-layer graphene quantum dots from CX-72 carbon black. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 8764–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Booker, C.; Li, R.; Zhou, X.; Sham, T.-K.; Sun, X.; Ding, Z. An electrochemical avenue to blue luminescent nanocrystals from multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 744–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A.; Giannelis, E.P. Photoluminescent carbogenic nanoparticles directly derived from crude biomass. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 3141–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, C.; Niu, N.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Li, S. Seeking value from biomass materials: Preparation of coffee bean shell-derived fluorescent carbon dots via molecular aggregation for antioxidation and bioimaging applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lv, J.-J.; Zhou, D.-L.; Bao, N.; Xu, Y.; Wang, A.-J.; Feng, J.-J. One-pot green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles as fluorescent probes for mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21691–21696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A.; Dallas, P.; Giannelis, E.P. Formation mechanism of carbogenic nanoparticles with dual photoluminescence emission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 134, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrat, F.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Schneider, J.; Löf, A.; Wyrwich, R.; Rogach, A.L.; Stolarczyk, J.K.; Urban, A.S.; Feldmann, J. Tracking the source of carbon dot photoluminescence: Aromatic domains versus molecular fluorophores. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7710–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, W.P.; Świergosz, T.; Bednarz, S.; Walas, K.; Bashmakova, N.V.; Bogdał, D. Luminescence phenomena of carbon dots derived from citric acid and urea—A molecular insight. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13889–13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-F.; Wu, H.-C.; Kuan, C.-H.; Lin, C.-J.; Wang, L.-W.; Chang, C.-W.; Wang, T.-W. Multi-functionalized carbon dots as theranostic nanoagent for gene delivery in lung cancer therapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Du, F.; Liu, P.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J. DNA–Carbon dots function as fluorescent vehicles for drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6889–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Lu, F.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. Degradable carbon dots from cigarette smoking with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activities against drug-resistant bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, X.; Kong, D.; Jin, R.; Sun, C.; Du, D.; Lin, Y.; Lu, G. Recent advances in carbon dots for bioimaging applications. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 5, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, W.; Han, P.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, J.; Wen, H.; Xue, W. Carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, properties, and sensing applications as a potential clinical analytical method. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 2240–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.; Heslop, K.; Kelarakis, A.; Krysmann, M.; Estevez, L. In situ generation of carbon dots within a polymer matrix. Polymer 2020, 188, 122159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.K.; Nandi, S.; Shikler, R.; Jelinek, R. Tuneable light-emitting carbon-dot/polymer flexible films prepared through one-pot synthesis. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3400–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.; Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A. Carbon dot based nanopowders and their application for fingerprint recovery. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4902–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, A.; Kelarakis, A. Carbon dots for forensic applications: A critical review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Shi, Y.; Meng, T.; Yuan, T.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Recent advances in white light-emitting diodes of carbon quantum dots. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 4826–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosso, C.; Filippini, G.; Prato, M. Carbon dots as nano-organocatalysts for synthetic applications. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8090–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havrdova, M.; Hola, K.; Skopalik, J.; Tománková, K.B.; Petr, M.; Cepe, K.; Polakova, K.; Tucek, J.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Zboril, R. Toxicity of carbon dots—Effect of surface functionalization on the cell viability, reactive oxygen species generation and cell cycle. Carbon 2016, 99, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasbender, S.; Zimmermann, L.; Cadeddu, R.-P.; Luysberg, M.; Moll, B.; Janiak, C.; Heinzel, T.; Haas, R. The low toxicity of graphene quantum dots is reflected by marginal gene expression changes of primary human hematopoietic stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, X.-X.; Wei, J.-S.; Li, X.-B.; Qin, B.-T.; Chen, X.-B.; Xiong, H.-M. Carbon dots with red/near-infrared emissions and their intrinsic merits for biomedical applications. Carbon 2020, 167, 322–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, P.; Mao, S.; Zhu, C.; Du, D.; Belfiore, L.A.; Tang, J.; Lin, Y. Red carbon dots: Optical property regulations and applications. Mater. Today 2019, 30, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Ge, L.; Yang, L.; Patel, A.K.; Morgan, S.O.; Sun, Y.-P. On the myth of “red/near-IR carbon quantum dots” from thermal processing of specific colorless organic precursors. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 4186–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Liang, K.; Zhu, J.; Yang, B.; Zhao, D.; Kong, B. Hetero-atom-doped carbon dots: Doping strategies, properties and applications. Nano Today 2020, 33, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hola, K.; Sudolská, M.; Kalytchuk, S.; Nachtigallová, D.; Rogach, A.L.; Otyepka, M.; Zbořil, R. Graphitic nitrogen triggers red fluorescence in carbon dots. ACS Nano 2016, 11, 12402–12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Ji, Y.; Wei, J.-S.; Gao, Q.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Xiong, H.-M. Facile synthesis of red-emitting carbon dots from pulp-free lemon juice for bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5272–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Niu, G.; Jia, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, P. Tunable multicolor carbon dots prepared from well-defined polythiophene derivatives and their emission mechanism. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C.; Huang, Q.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Truly fluorescent excitation-dependent carbon dots and their applications in multicolor cellular imaging and multidimensional sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7782–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Lin, H. Near-infrared emissive carbon dots for two-photon fluorescence bioimaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17350–17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Yang, E.; Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Q. Red emission nitrogen, boron, sulfur co-doped carbon dots for “on-off-on” fluorescent mode detection of Ag+ ions and l-cysteine in complex biological fluids and living cells. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1035, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, W. Preparation and application of solvent-modulated self-doped N-S multicolour fluorescence carbon quantum dots. Luminescence 2019, 35, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Yan, X.; Qu, D.; Li, D.; Tao, F.F.; Sun, Z. Red emissive sulfur, nitrogen codoped carbon dots and their application in ion detection and theraonostics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18549–18556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Jia, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Liu, Q.; Lan, M.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X.; Wang, P. Red-emissive carbon dots for fluorescent, photoacoustic, and thermal theranostics in living mice. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4169–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Cui, F.; Ren, R.; Sun, J.; Ji, J.; Pi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Red-emissive carbon dots for “switch-on” dual function sensing platform rapid detection of ferric ions and l-cysteine in living cells. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12575–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, S.; Shamsipur, M.; Taherpour, A.A.; Jamshidi, M.; Barati, A. In situ chromophore doping: A new mechanism for the long-wavelength emission of carbon dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 10638–10646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Bertran, E.; Lee, S.-T. Size dependence of energy gaps in small carbon clusters: The origin of broadband luminescence. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1998, 7, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Kang, Z.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lian, S.; Tsang, A.C.H.; Yang, X.; Lee, S.-T. Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4430–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Huang, L.; Lim, K.H.; Chen, P. Revealing the tunable photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6954–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, X.; Feng, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.-H. Tuning the optical properties of graphene quantum dots for biosensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3219–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Huang, W.-L.; Chung, C.-J.; Chiang, I.-T.; Chen, L.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Su, W.-C.; Cheng, C.; Chen, S.-J.; Teng, H. elucidating quantum confinement in graphene oxide dots based on excitation-wavelength-independent photoluminescence. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Tan, Z.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Bright multicolor bandgap fluorescent carbon quantum dots for electroluminescent light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 2016, 29, 1604436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Zhou, D.; Jing, P.; Shen, D.; Qu, S.; Zboril, R.; Rogach, A.L. Full-color inorganic carbon dot phosphors for white-light-emitting diodes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Qiao, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; et al. Surface chemistry routes to modulate the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots: From fluorescence mechanism to up-conversion bioimaging applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jun, G.H.; Hong, S.H.; Jeon, S. Tuning the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots through the charge transfer effect of functional groups. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cole, I.; Zhao, D.; Li, Q. The dual roles of functional groups in the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2015, 8, 7449–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 2015, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Wojtowicz, A.; Estevez, L.; Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A. Dramatic photoluminescence quenching in carbon dots induced by cyclic voltammetry. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 9067–9070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, B.; Deng, Z.; Jin, Y.; Kang, Y.; Chen, J. Orange, yellow and blue luminescent carbon dots controlled by surface state for multicolor cellular imaging, light emission and illumination. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Yi, C. Tuning photoluminescence and surface properties of carbon nanodots for chemical sensing. Nanoscale 2015, 8, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Pang, D.-W. Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: Surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, A.; Marino, E.; Van Dam, B.; Schall, P.; Cannas, M.; Messina, F. Solvatochromism unravels the emission mechanism of carbon nanodots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 3419–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z. Solvatochromic fluorescent carbon dots as optic noses for sensing volatile organic compounds. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 83501–83504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckmeier, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Zboril, R.; Rogach, A.L. Influence of doping and temperature on solvatochromic shifts in optical spectra of carbon dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 10591–10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Haydel, P.; Sui, N.; Wang, L.; Liang, Y.; Yu, W.W. Wide emission shifts and high quantum yields of solvatochromic carbon dots with rich pyrrolic nitrogen. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 2492–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Colvin, V.L.; Rice, Q.; Seo, J.; Feng, S.; Wang, S.; Yu, W.W. Excitation wavelength independent visible color emission of carbon dots. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Jing, P.; Sun, L.; An, Y.; Shan, X.; Lu, X.; Zhou, D.; Han, D.; Shen, D.; Zhai, Y.; et al. Near-infrared excitation/emission and multiphoton-induced fluorescence of carbon dots. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1705913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, C.; Sun, J.; He, P.; Yuan, N.; Ding, J.; Ding, G.; Xie, X. Triphenylphosphine modified graphene quantum dots: Spectral modulation for full spectrum of visible light with high quantum yield. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 33347–33350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, K.; Yang, M.; Sun, H.; Yang, B. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped conjugated carbonized polymer dots with 31% efficient red emission for in vivo imaging. Small 2018, 14, e1703919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Electrochemical synthesis of small-sized red fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a bioimaging platform. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2544–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Kang, X.; Du, L.; Liu, Y. Red fluorescent carbon dots with phenylboronic acid tags for quick detection of Fe(III) in PC12 cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 526, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Song, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Pang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, B.; Peng, X. Carbon dots with red emission for sensing of Pt2+, Au3+, and Pd2+ and their bioapplications in vitro and in vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 10, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Zheng, X.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Ren, H.; Chen, S.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, P. Synthesis of carbon dots from Hypocrella bambusae for bimodel fluorescence/photoacoustic imaging-guided synergistic photodynamic/photothermal therapy of cancer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 526, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Lan, M.; Zhou, B.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.; Niu, G.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, B.; Guan, S.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Zeng, H.; Xie, Z.; Chen, P.; Zhou, S. Highly efficient carbon dots with reversibly switchable green–red emissions for trichromatic white light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16005–16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wei, K.; He, L.; Han, X.; Qiao, H.; Asiri, A.M.; et al. Orange-red, green, and blue fluorescence carbon dots for white light emitting diodes. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, J.; Li, H. Multiple color emission of solid-state hybrid material containing carbon dots and Europium(III) complexes. J. Lumin. 2019, 220, 116959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Liu, J.; Xiang, W.; Liang, X. Red-emitting carbon dots phosphors: A promising red color convertor toward warm white light emitting diodes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 10453–10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zhou, B.; Shen, X.; Yu, Y.; Ji, S.; Wen, C.; Liang, H. Selective probing of gaseous ammonia using red-emitting carbon dots based on an interfacial response mechanism. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 18993–18999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Xu, S.; Liu, J. One pot generation of blue and red carbon dots in one binary solvent system for dual channel detection of Cr3+ and Pb2+ based on ion imprinted fluorescence polymers. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Luo, J. Fluorescence detection of malachite green in fish tissue using red emissive Se, N, Cl-doped carbon dots. Food Chem. 2020, 335, 127677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, G. One-step solvothermal synthesis of red emissive carbonized polymer dots for latent fingerprint imaging. Opt. Mater. 2018, 86, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Qin, R.; Cheng, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Yu, X.; Lu, Z.; Liu, H. Great enhancement of red emitting carbon dots with B/Al/Ga doping for dual mode anti-counterfeiting. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowska, J.D.; Murphy, A.; Mellor, C.; Fernandes, D.; Gibbons, E.N.; Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A.; Burgaz, E.; Moore, J.; Yeates, S.G. A rich gallery of carbon dots based photoluminescent suspensions and powders derived by citric acid/urea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Gong, X.; Peng, C.; Wei, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Incorporation of well-dispersed sub-5-nm graphitic pencil nanodots into ordered mesoporous frameworks. Nat. Chem. 2015, 8, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Liang, K.; Kong, B. Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) paired carbon dot-based complex nanoprobes: Versatile platforms for sensing and imaging applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 4, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundelev, E.V.; Tepliakov, N.V.; Leonov, M.Y.; Maslov, V.G.; Baranov, A.; Fedorov, A.; Rukhlenko, I.; Rogach, A.L. Towards bright red-emissive carbon dots through controlling interaction among surface emission centers. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 8121–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Qiao, L.; Su, Y.; Gao, P.; Xie, Z. A postmodification strategy to modulate the photoluminescence of carbon dots from blue to green and red: Synthesis and applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3840–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Lei, B. Far-red carbon dots as efficient light-harvesting agents for enhanced photosynthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21009–21019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Wei, J.S.; Zhong, N.; Gao, Q.Y.; Xiong, H.M. Highly efficient red-emitting carbon dots with gram-scale yield for bioimaging. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12635–12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gou, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Xi, K.; Jia, X. Rational synthesis of highly efficient ultra-narrow red-emitting carbon quantum dots for NIR-II two-photon bioimaging. Nanoscale 2019, 12, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhati, A.; Anand, S.R.; Gunture; Garg, A.K.; Khare, P.; Sonkar, S.K. Sunlight-induced photocatalytic degradation of pollutant dye by highly fluorescent red-emitting mg-n-embedded carbon dots. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9246–9256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Lu, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Qu, B.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. In situ synthesis of NIR-light emitting carbon dots derived from spinach for bio-imaging applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7328–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavalas, S.; Kelarakis, A. Towards Red Emissive Systems Based on Carbon Dots. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082089
Gavalas S, Kelarakis A. Towards Red Emissive Systems Based on Carbon Dots. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(8):2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082089
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavalas, Spyridon, and Antonios Kelarakis. 2021. "Towards Red Emissive Systems Based on Carbon Dots" Nanomaterials 11, no. 8: 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082089
APA StyleGavalas, S., & Kelarakis, A. (2021). Towards Red Emissive Systems Based on Carbon Dots. Nanomaterials, 11(8), 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082089






