Layered LiCoO2–LiFeO2 Heterostructure Composite for Semiconductor-Based Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation and Characterization
2.2. Fuel Cell Fabrication and Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
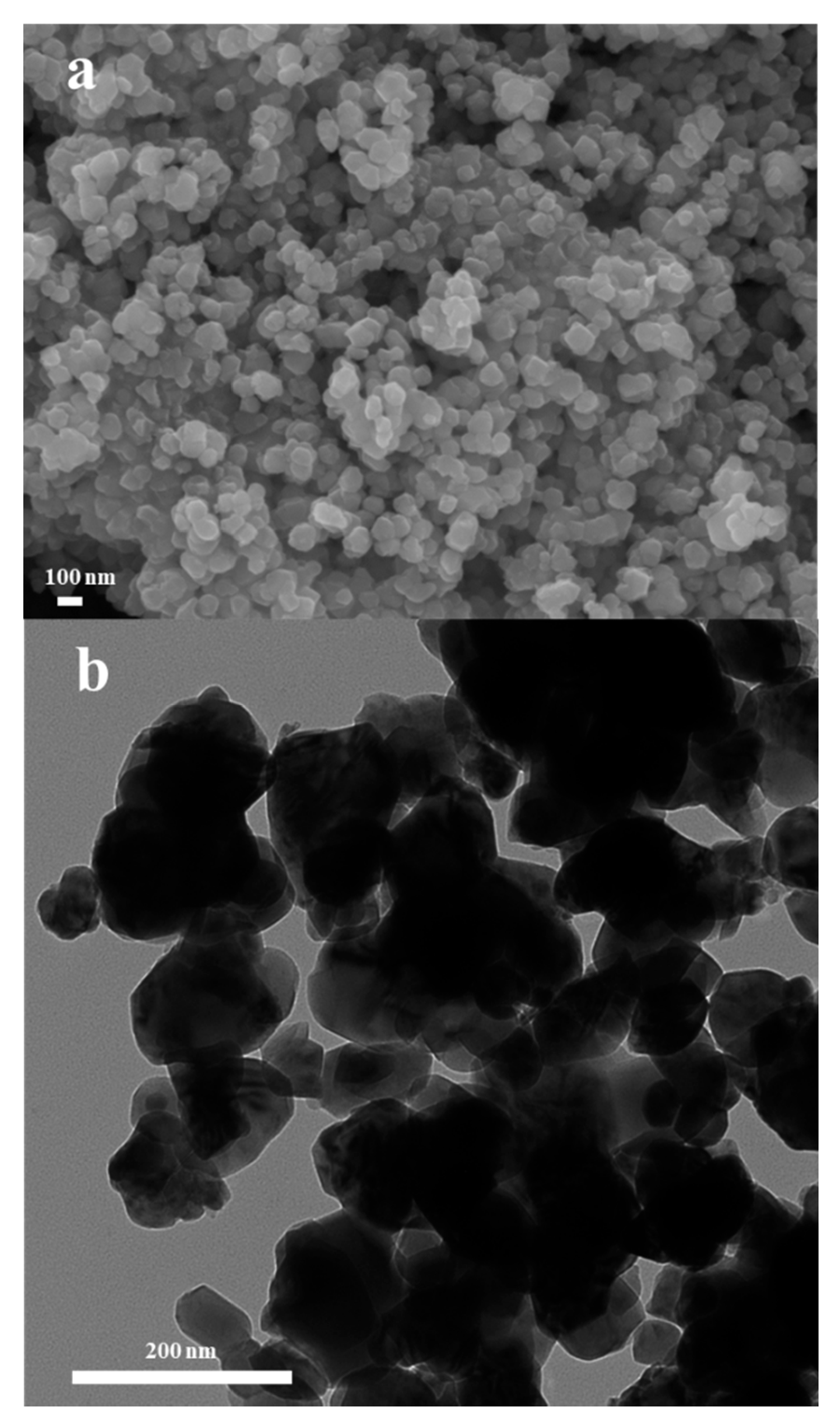
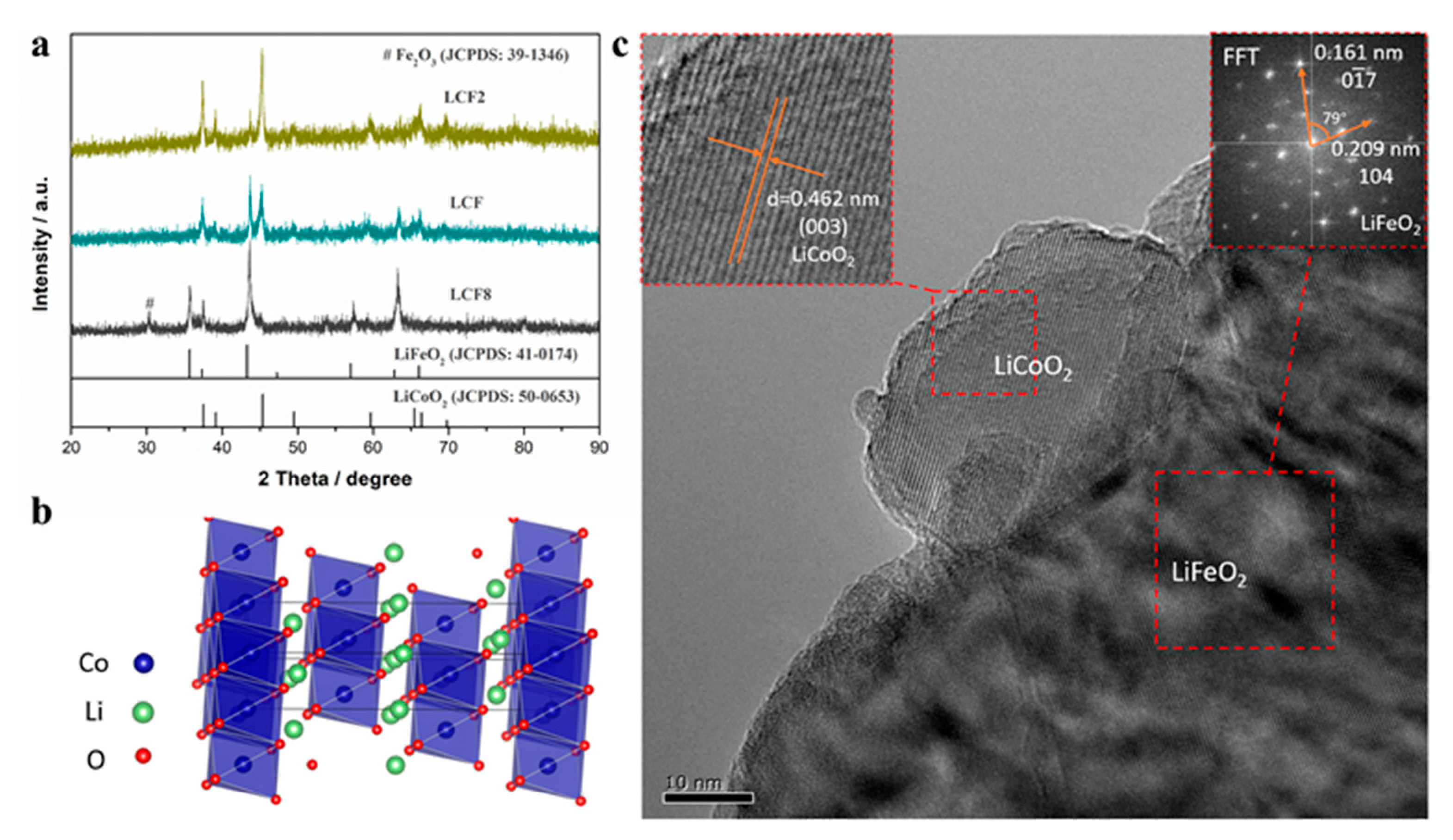
3.1. Material Characterizations
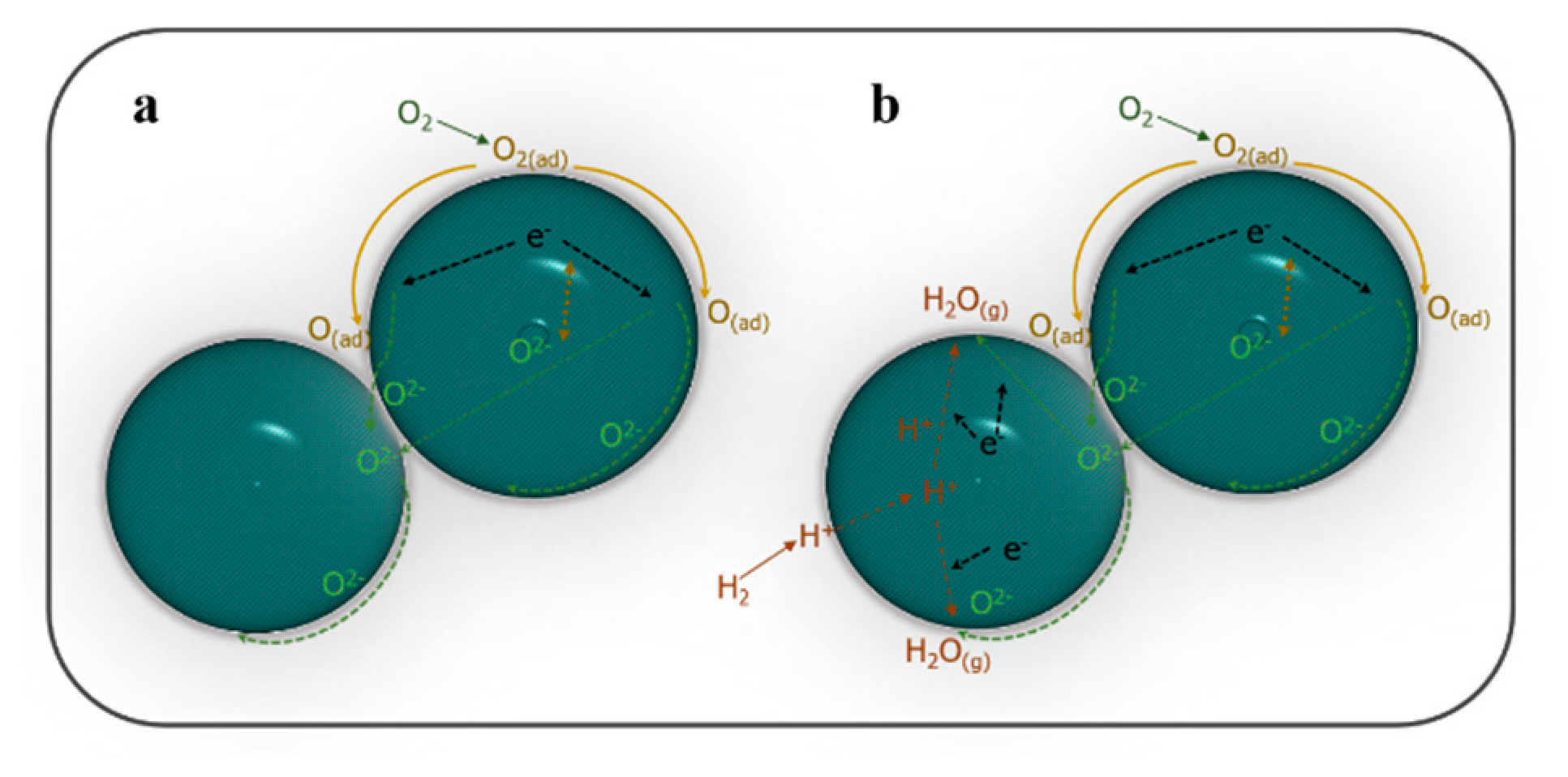
3.2. Electrical Properties
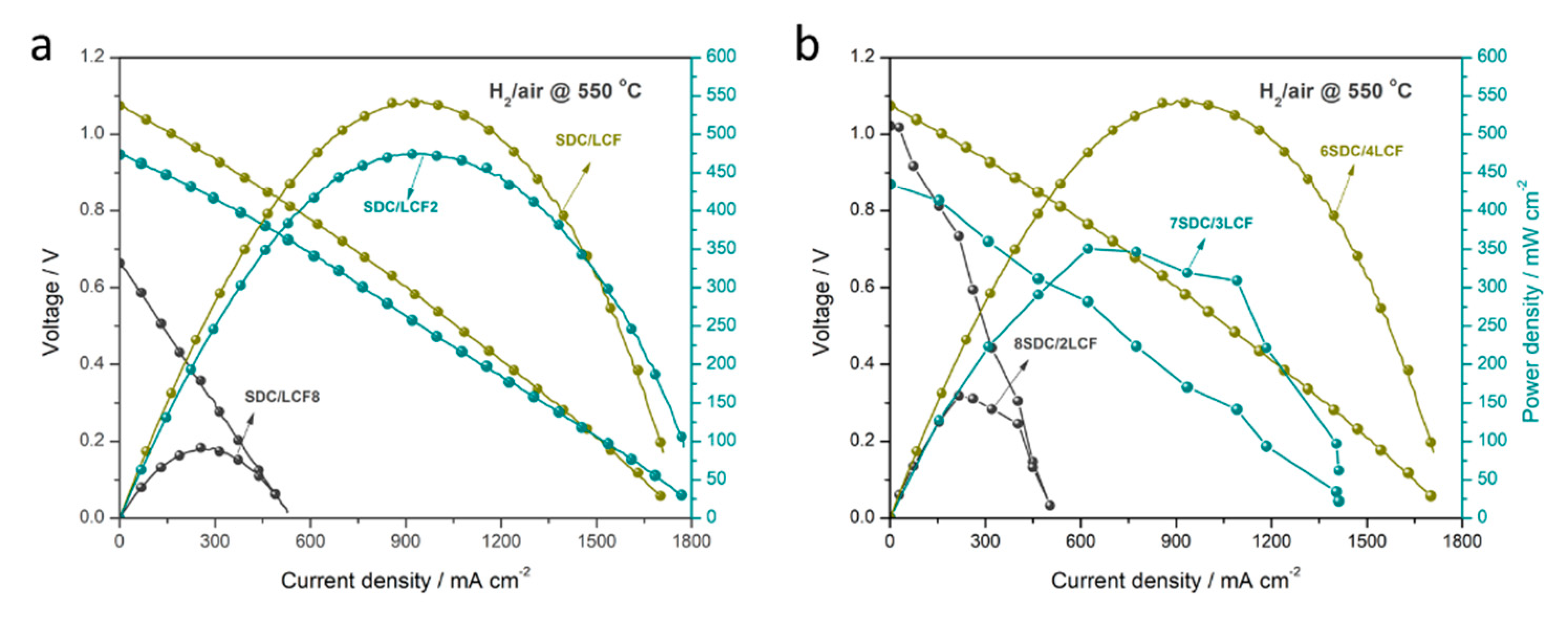
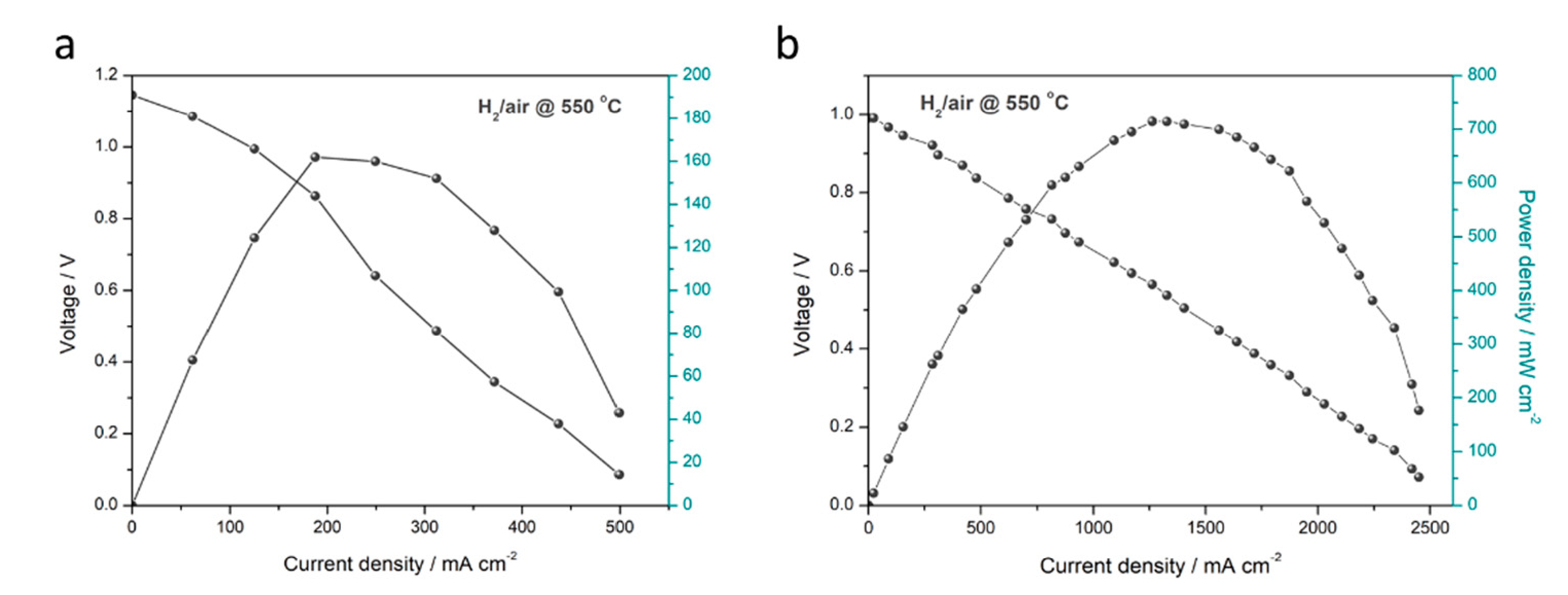
3.3. Electrochemical Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, M. Modeling of a novel SOFC-PEMFC hybrid system coupled with thermal swing adsorption for H2 purification: Parametric and exergy analyses. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 174, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Morales, J.C.; Tarancón, A.; Canales-Vázquez, J.; Méndez-Ramos, J.; Hernández-Afonso, L.; Acosta-Mora, P.; Rueda, J.R.M.; Fernández-González, R. Three dimensional printing of components and functional devices for energy and environmental applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Irvine, J.T.S. A redox-stable efficient anode for solid-oxide fuel cells. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Shao, Z. Fuel cells: Hydrogen induced insulation. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, N.; Banerjee, A.; Gupta, A.; Omar, S.; Balani, K. Progress in material selection for solid oxide fuel cell technology: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 141–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmpd, T. Reports 185. Science 2008, 676–681. [Google Scholar]
- Hibino, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Inoue, T.; Tokuno, J.; Yoshida, S.; Sano, M.A. Low-Operating-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell in Hydrocarbon-Air Mixtures. Science 2000, 288, 2031–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodenough, J.B. Ceramic technology: Oxide-ion conductors by design. Nature 2000, 404, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Lund, P.D.; Raza, R.; Ma, Y.; Fan, L.; Afzal, M.; Patakangas, J.; He, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, W.; et al. Schottky junction effect on high performance fuel cells based on nanocomposite materials. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Jiang, Z.; Fan, L.; Singh, M.; Wang, F.; Raza, R.; Sajid, M.; Wang, J.; Kim, J.; Zhu, B. Junction and energy band on novel semiconductor-based fuel cells. iScience 2021, 24, 102191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Raza, R.; Abbas, G.; Singh, M. An electrolyte-free fuel cell constructed from one homogenous layer with mixed conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2465–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Fan, L.; Lund, P. Breakthrough fuel cell technology using ceria-based multi-functional nanocomposites. Appl. Energy 2013, 106, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Raza, R.; Qin, H.; Liu, Q.; Fan, L. Fuel cells based on electrolyte and non-electrolyte separators. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Lund, P.; Raza, R.; Patakangas, J.; Huang, Q.A.; Fan, L.; Singh, M. A new energy conversion technology based on nano-redox and nano-device processes. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Bao, Z.Y.; Li, J.J.; Zhu, B. Natural Hematite for Next-Generation Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, P.D.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Yun, S.; Nasibulin, A.G.; Raza, R.; Leskelä, M.; Ni, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G.; et al. Standardized Procedures Important for Improving Single-Component Ceramic Fuel Cell Technology. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 2752–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Huang, Y.; Fan, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, B.; Xia, C.; Afzal, M.; Zhang, B.; Dong, W.; Wang, H.; et al. Novel fuel cell with nanocomposite functional layer designed by perovskite solar cell principle. Nano Energy 2016, 19, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, B.; Liu, X. Fabrication of electrolyte-free fuel cell with Mg0.4Zn0.6O/Ce0.8Sm0.2O2-δ-Li0.3Ni0.6Cu0.07Sr0.03O2-δ layer. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Zhu, B. Recent development of ceria-based nano, composite materials for low temperature ceramic fuel cells and electrolyte-free fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 234, 154–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Tao, S. Novel proton conductors in the layered oxide material LixAl0.5Co0.5O2. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Tao, S. High Ionic Conductivity in a LiFeO2 -LiAlO2 Composite Under H2 /Air Fuel Cell Conditions. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Zhu, B. Superionic Conductivity of Sm3+, Pr3+, and Nd3+ Triple-Doped Ceria through Bulk and Surface Two-Step Doping Approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 23614–23623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wu, X.; Cai, Y.; Ji, Y.; Yaqub, A.; Zhu, B. Design, fabrication, and characterization of a double layer solid oxide fuel cell DLFC. J. Power Sources 2016, 332, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergolesi, D.; Gilardi, E.; Fabbri, E.; Roddatis, V.; Harrington, G.F.; Lippert, T.; Kilner, J.A.; Traversa, E. Interface Effects on the Ionic Conductivity of Doped Ceria-Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Heterostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14160–14169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.B. Factors governing oxygen reduction in solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4791–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Bishop, S.R.; Chen, D.; Tuller, H.L. Defect Chemistry of Pr Doped Ceria Thin Films Investigated by in Situ Optical and Impedance Measurements. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zhu, B.; Su, P.C.; He, C. Nanomaterials and technologies for low temperature solid oxide fuel cells: Recent advances, challenges and opportunities. Nano Energy 2018, 45, 148–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Ghosh, S.; Aich, S.; Roy, B. Low temperature solid oxide electrolytes LT-SOE: A review. J. Power Sources 2017, 339, 103–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Fang, S.; Su, D.; Brinkman, K.S.; Chen, F. Enhancing grain boundary ionic conductivity in mixed ionic-electronic conductors. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, D.A.; Lyagaeva, J.G.; Gorbova, E.V.; Demin, A.K.; Tsiakaras, P. Advanced materials for SOFC application: Strategies for the development of highly conductive and stable solid oxide proton electrolytes. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 75, 38–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, M.T.; Chai, L.; Helander, M.G.; Tang, W.M.; Lu, Z.H. Transition metal oxide work functions: The influence of cation oxidation state and oxygen vacancies. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4557–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, M.T.; Helander, M.G.; Tang, W.M.; Wang, Z.B.; Qiu, J.; Lu, Z.H. Universal energy-level alignment of molecules on metal oxides. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lany, S.; Osorio-Guillén, J.; Zunger, A. Origins of the doping asymmetry in oxides: Hole doping in NiO versus electron doping in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B-Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2007, 75, 241203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Barriocanal, J.; Rivera-Calzada, A.; Varela, M.; Sefrioui, Z.; Iborra, E.; Leon, C.; Pennycook, S.J.; Santamaria, J. Colossal ionic conductivity at interfaces of epitaxial ZrO2:Y2O3/SrTiO3 heterostructures. Science 2008, 321, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.M.; Lee, S.; Jian, J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, P.; Jia, Q.; Wang, H.; Noh, T.W.; Kalinin, S.V.; MacManus-Driscoll, J.L. Strongly enhanced oxygen ion transport through samarium-doped CeO2 nanopillars in nanocomposite films. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Raza, R.; Tan, W.; Kim, J.S.; van Aken, P.A.; Lund, P. Charge separation and transport in La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ and ion-doping ceria heterostructure material for new generation fuel cell. Nano Energy 2017, 37, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Kashyout, A.H.; Zhu, B.; Muhammed, M. Ceria-based nanocomposite with simultaneous proton and oxygen ion conductivity for low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 2754–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Fan, L.; Deng, H.; He, Y.; Afzal, M.; Dong, W.; Yaqub, A.; Janjua, N.K. LiNiFe-based layered structure oxide and composite for advanced single layer fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 316, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Su, P.C. Layer-structured LiNi0.8Co0.2O2: A new triple H+/O2-/e-, conducting cathode for low temperature proton conducting solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 306, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lin, Q.; Muhammad, A.; Zhu, B. Electrochemical study of lithiated transition metal oxide composite for single layer fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2015, 286, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Xia, C.; Wang, B.; Tang, Y. Layered LiCoO2–LiFeO2 Heterostructure Composite for Semiconductor-Based Fuel Cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051224
Liu Y, Xia C, Wang B, Tang Y. Layered LiCoO2–LiFeO2 Heterostructure Composite for Semiconductor-Based Fuel Cells. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(5):1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051224
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanyan, Chen Xia, Baoyuan Wang, and Yongfu Tang. 2021. "Layered LiCoO2–LiFeO2 Heterostructure Composite for Semiconductor-Based Fuel Cells" Nanomaterials 11, no. 5: 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051224
APA StyleLiu, Y., Xia, C., Wang, B., & Tang, Y. (2021). Layered LiCoO2–LiFeO2 Heterostructure Composite for Semiconductor-Based Fuel Cells. Nanomaterials, 11(5), 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051224




