Magnetically Recyclable Wool Keratin Modified Magnetite Powders for Efficient Removal of Cu2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Reagents
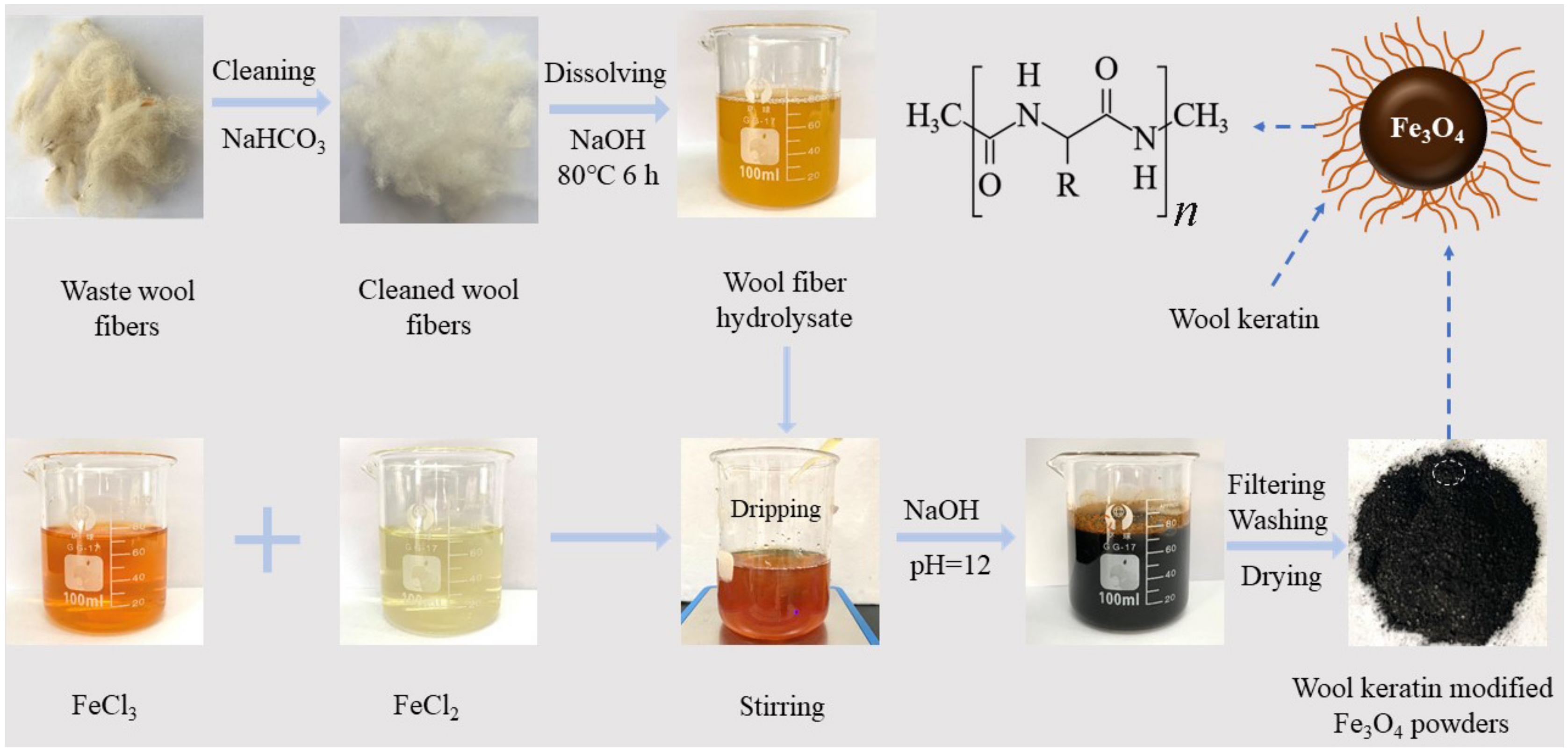
2.2. Fabrication of Fe3O4 Powders Modified with Wool Keratin
2.2.1. Preparation of Wool Keratin Hydrolysate from Wool Fibers
2.2.2. Fabrication of Wool Keratin Modified Fe3O4 Powders
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Measurements of Cu2+ Ion Adsorption Capacity
3. Results and Discussion
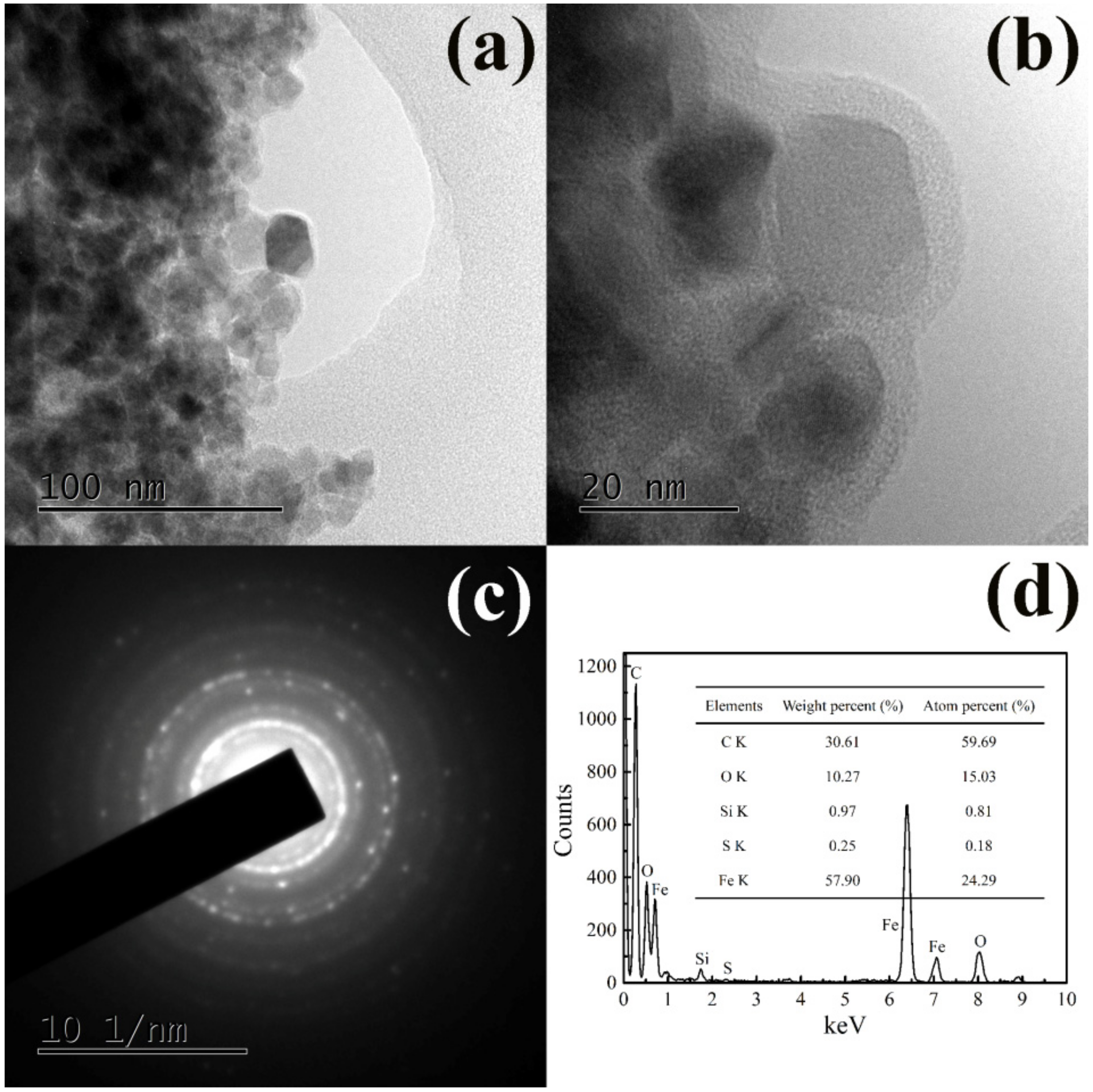
3.1. Surface Morphology Observation and Element Analysis
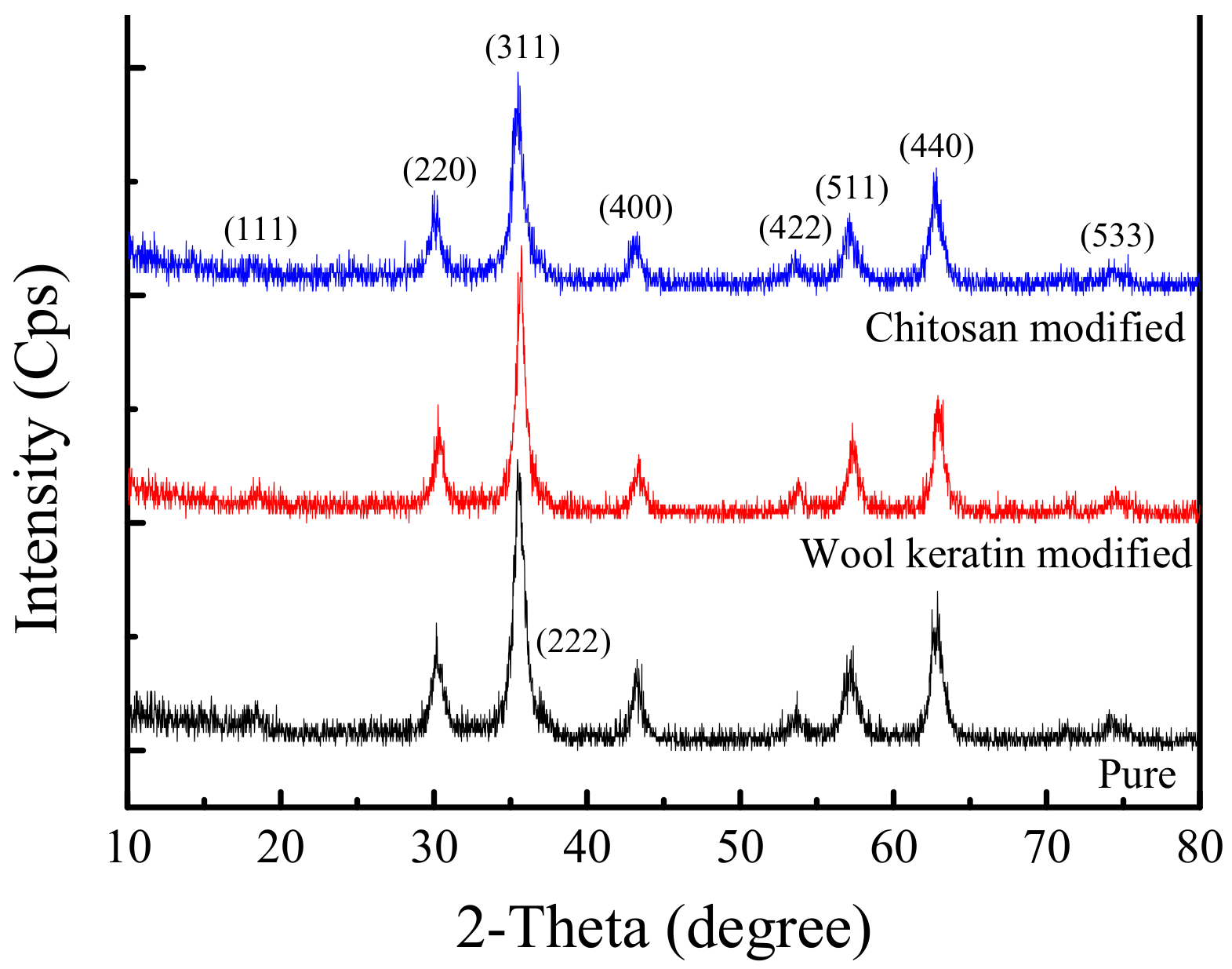
3.2. Crystal Structure Analysis
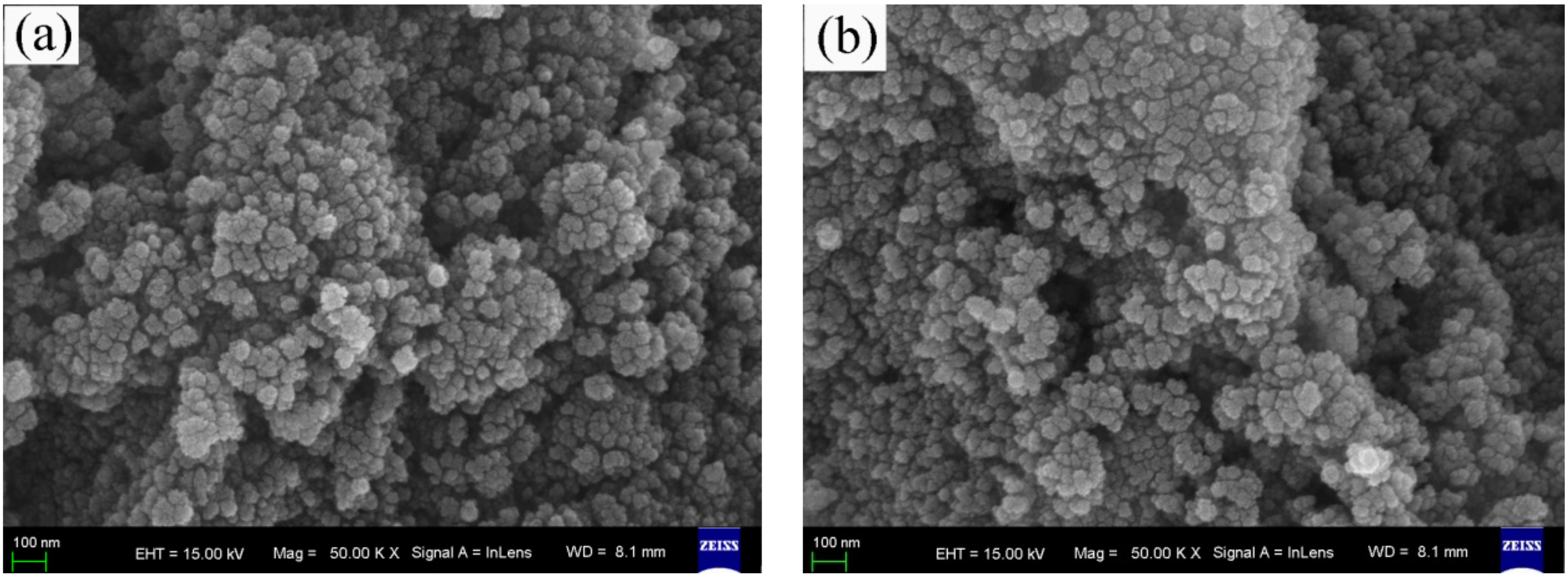
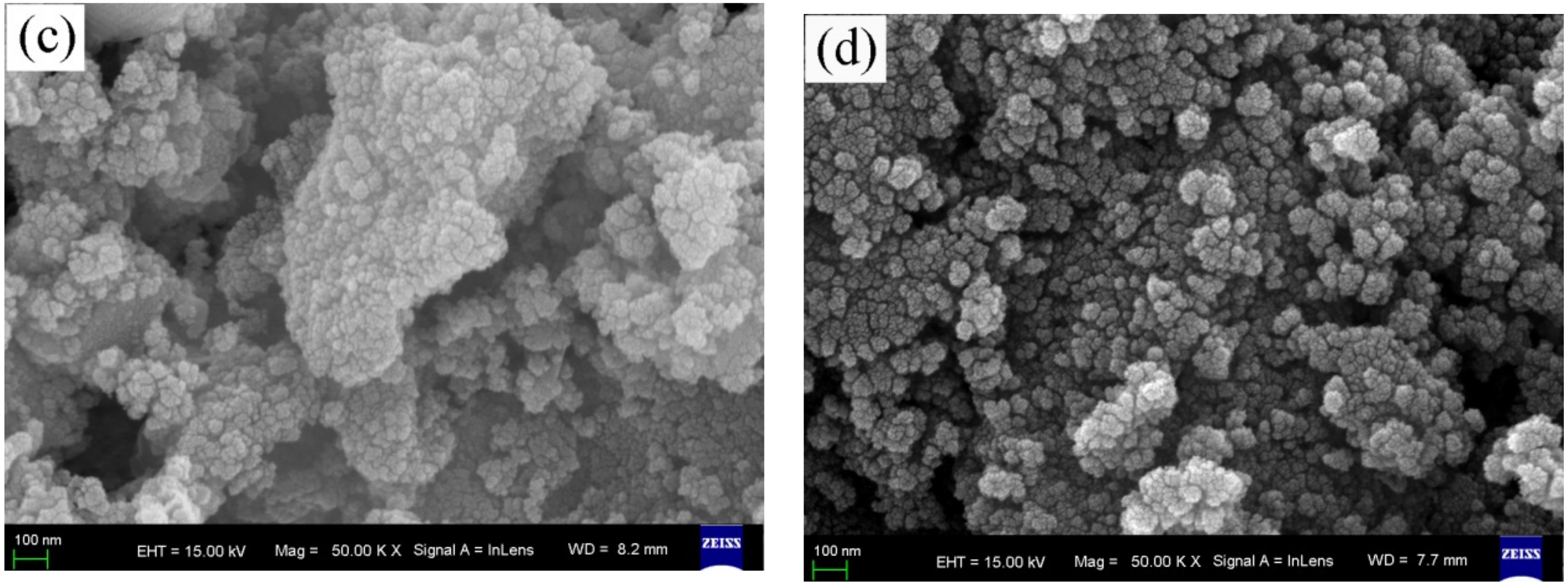
3.3. Microstructure Analysis
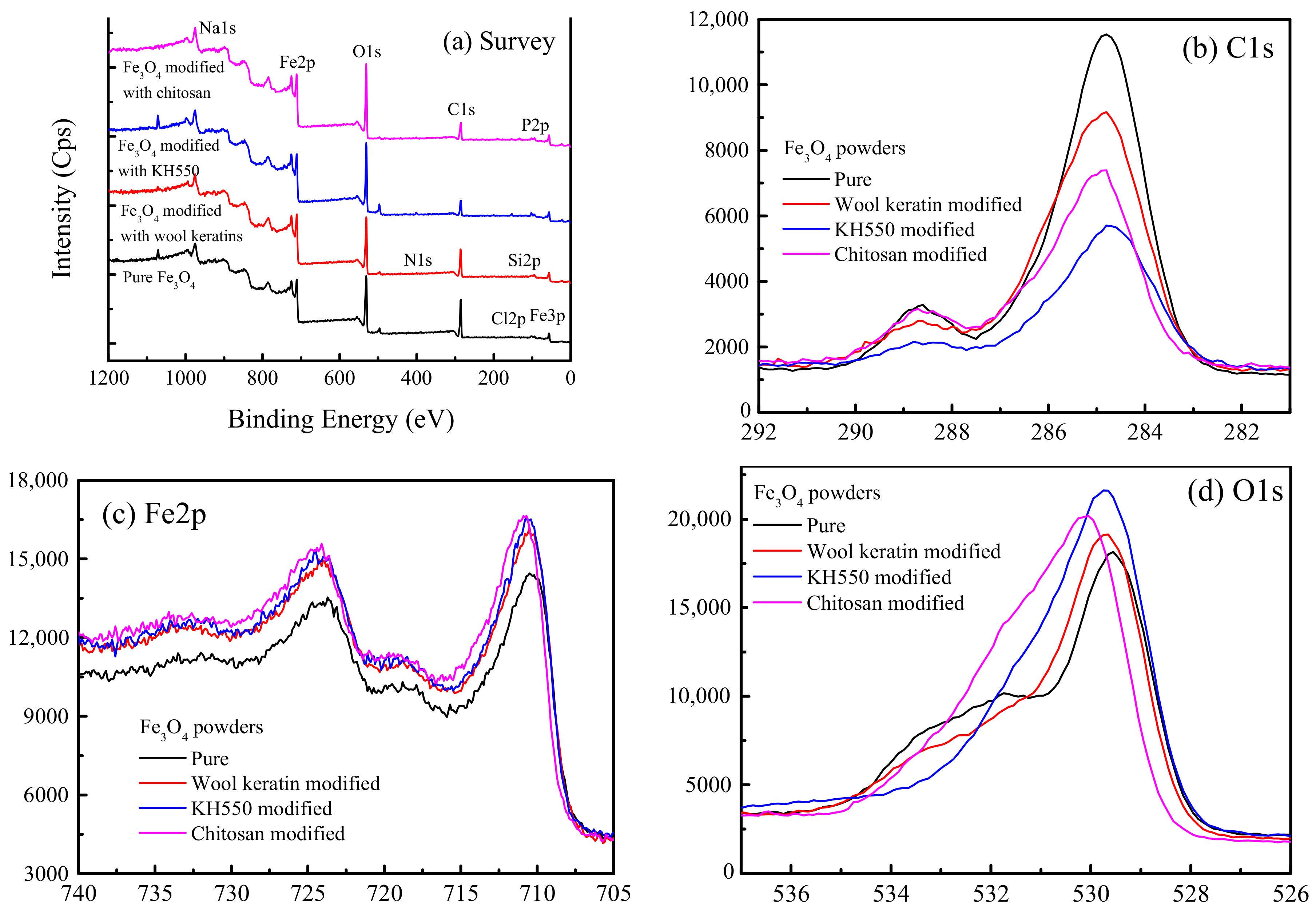
3.4. Surface Chemical Composition Analysis
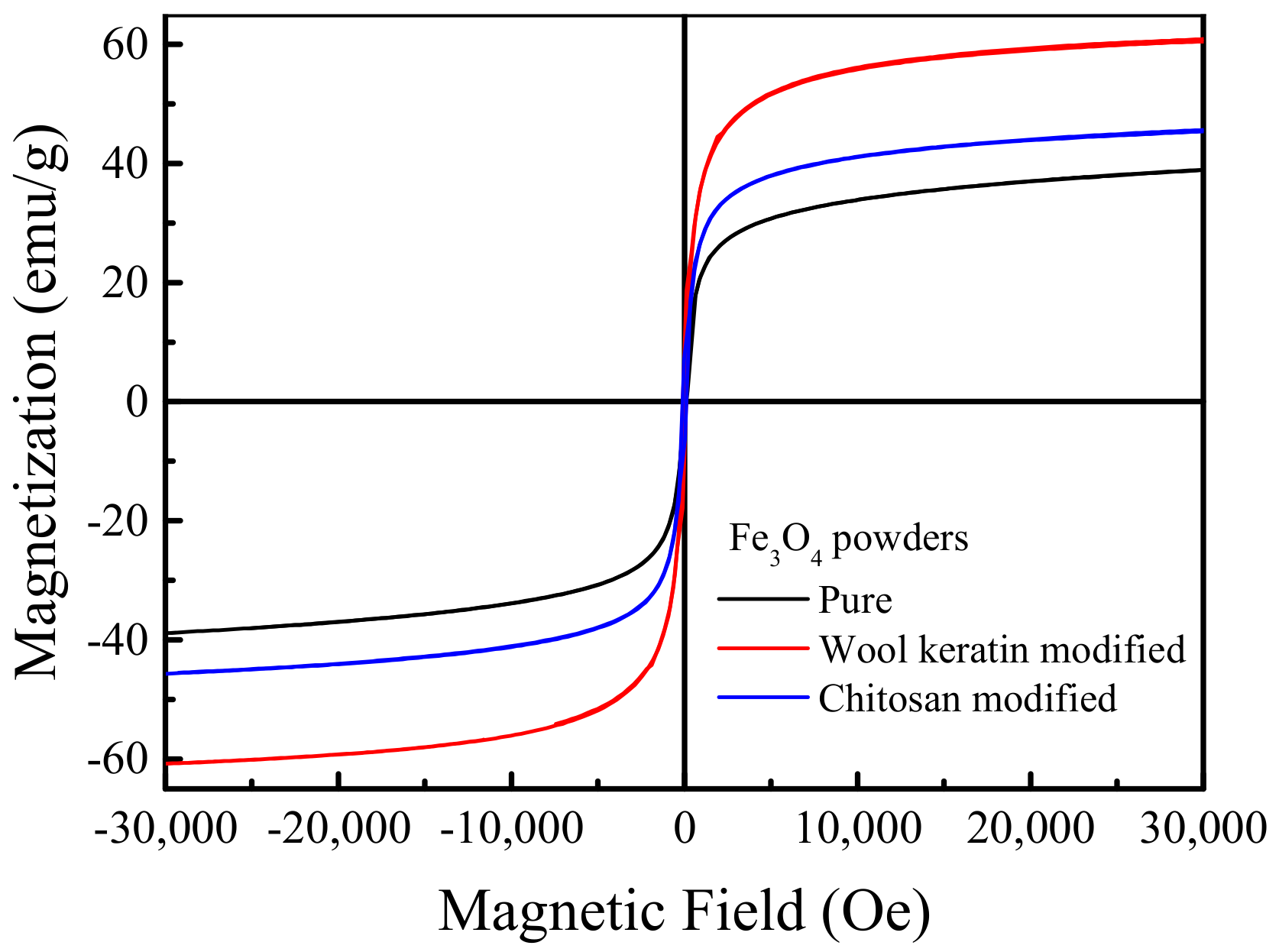
3.5. Magnetic Property Analysis
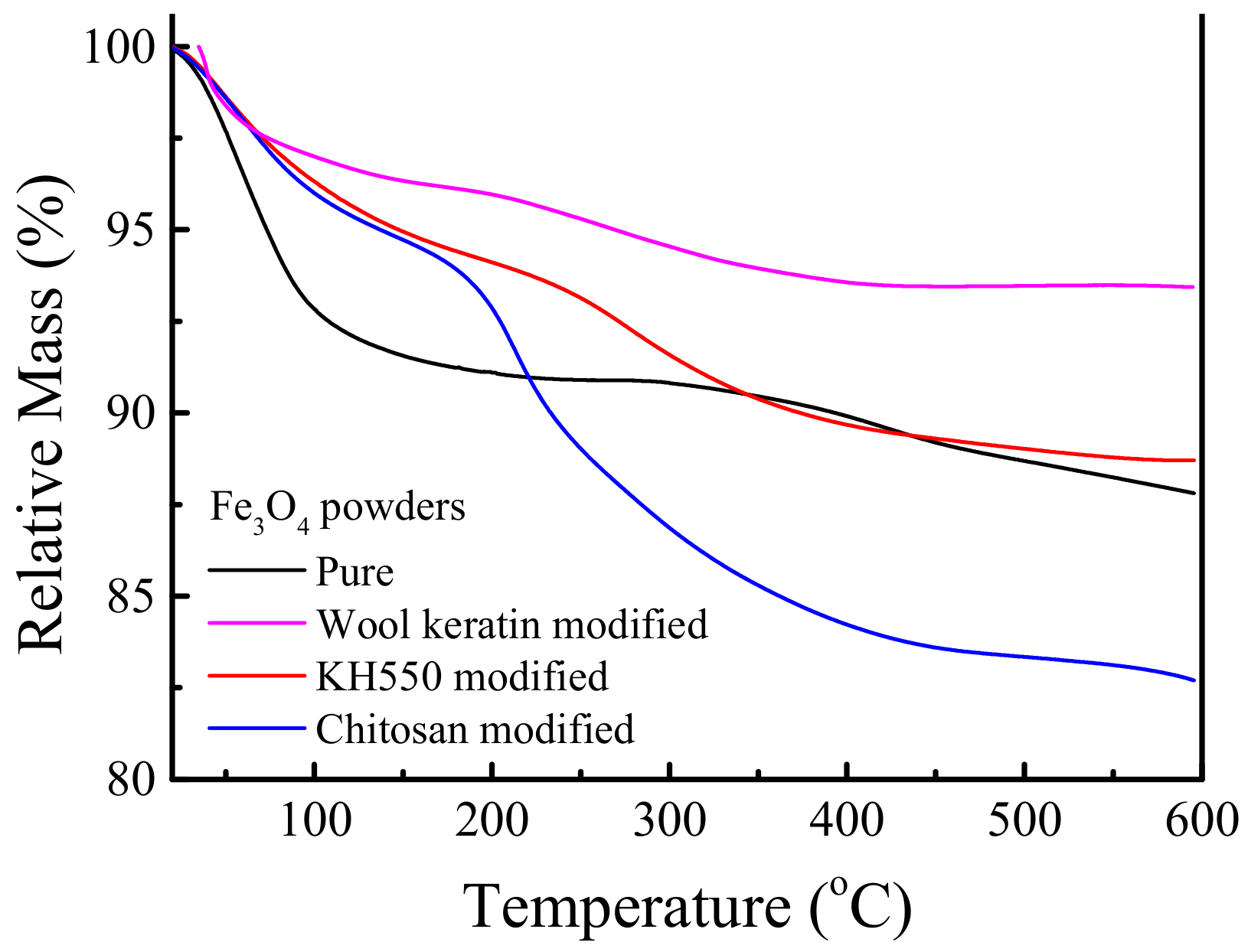
3.6. Determination of the Contents of Organic Compositions
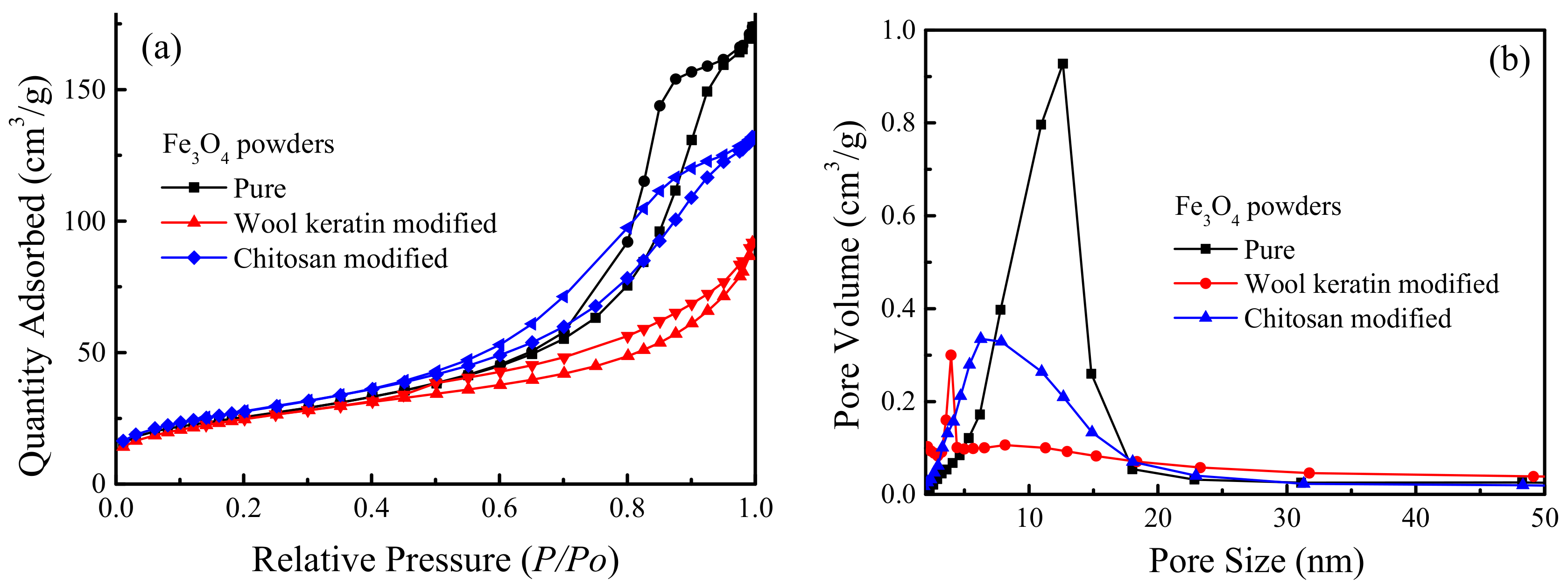
3.7. BET Specific Surface Area and Pore Size Analyses
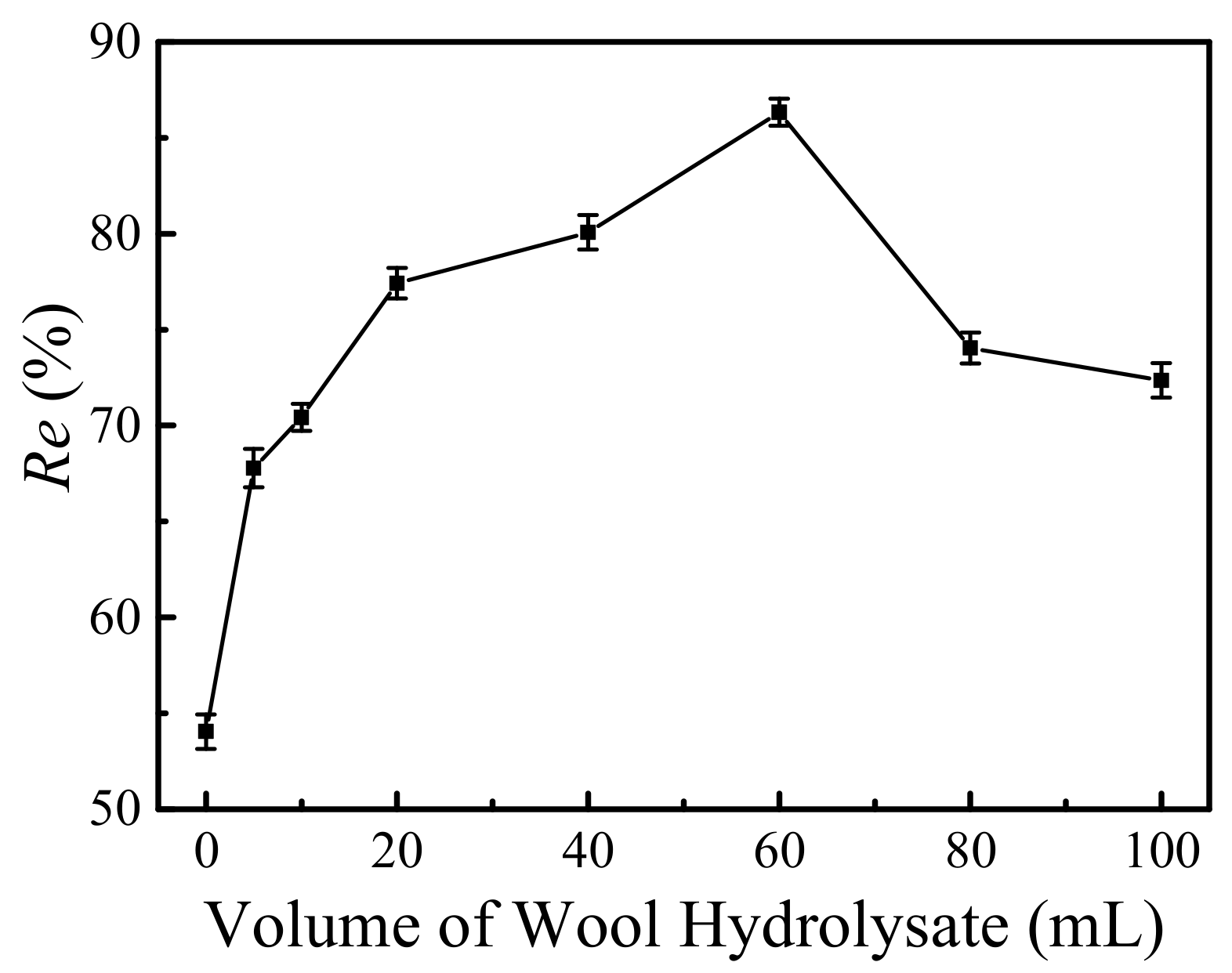
3.8. Optimization of the Amount of Wool Keratin Hydrolysate
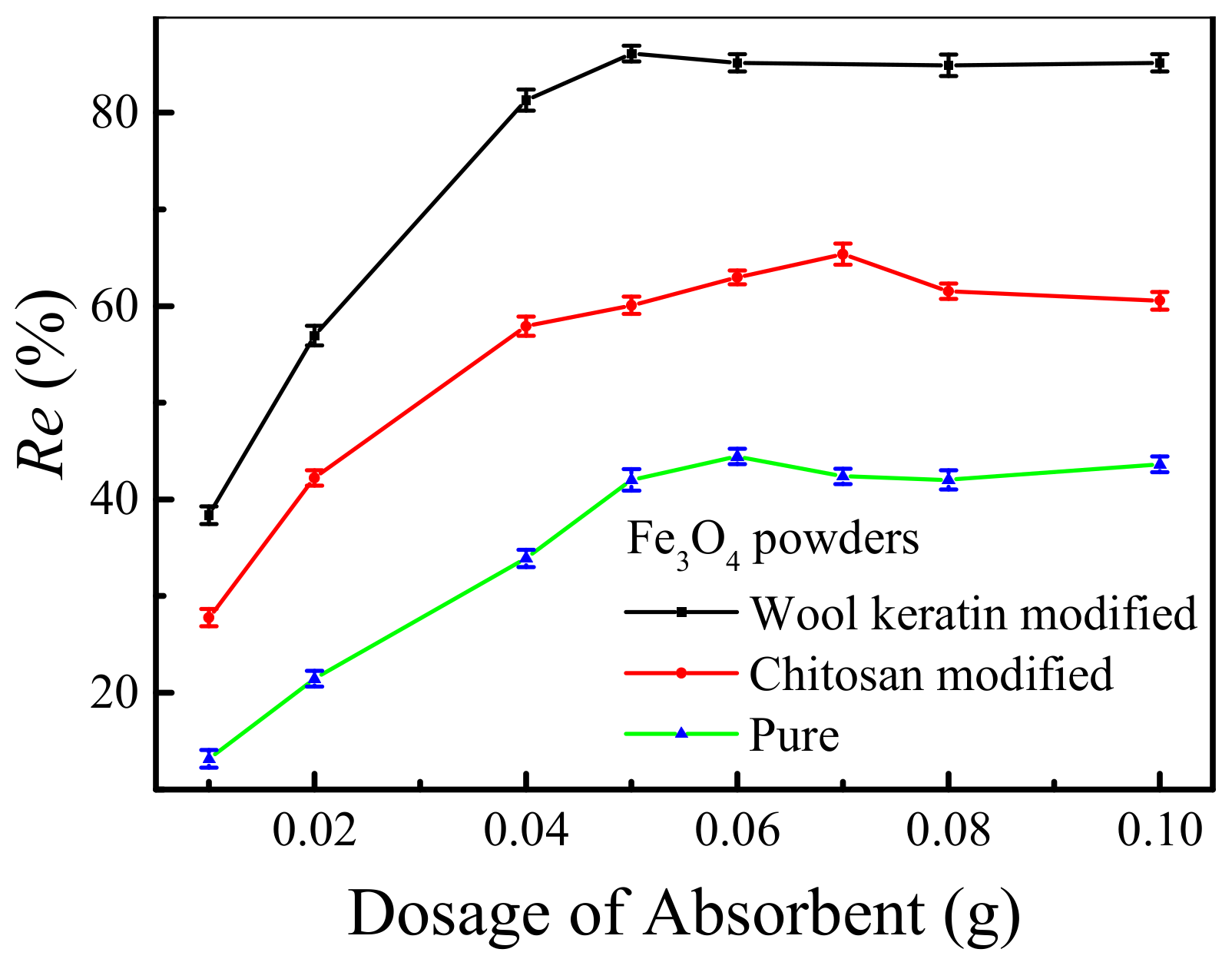
3.9. Effect of the Dosage of Powders
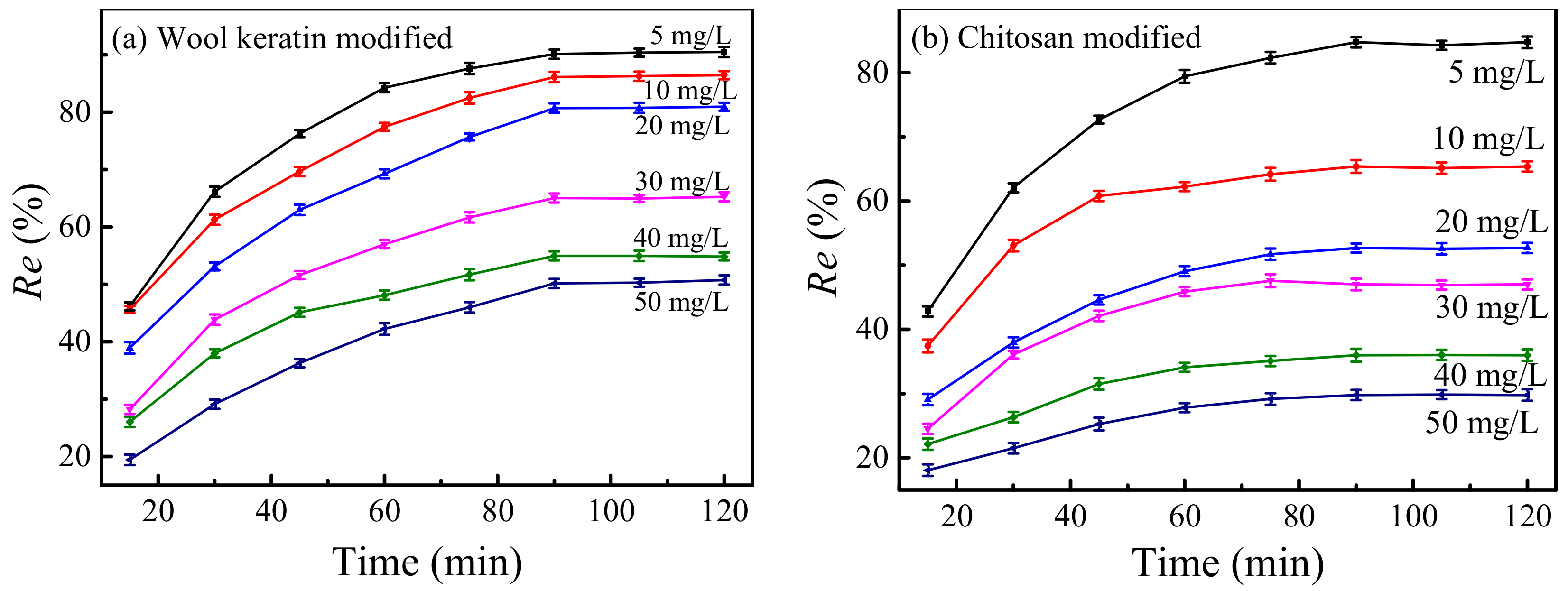
3.10. Effect of the Initial Concentration of Cu2+ Ions
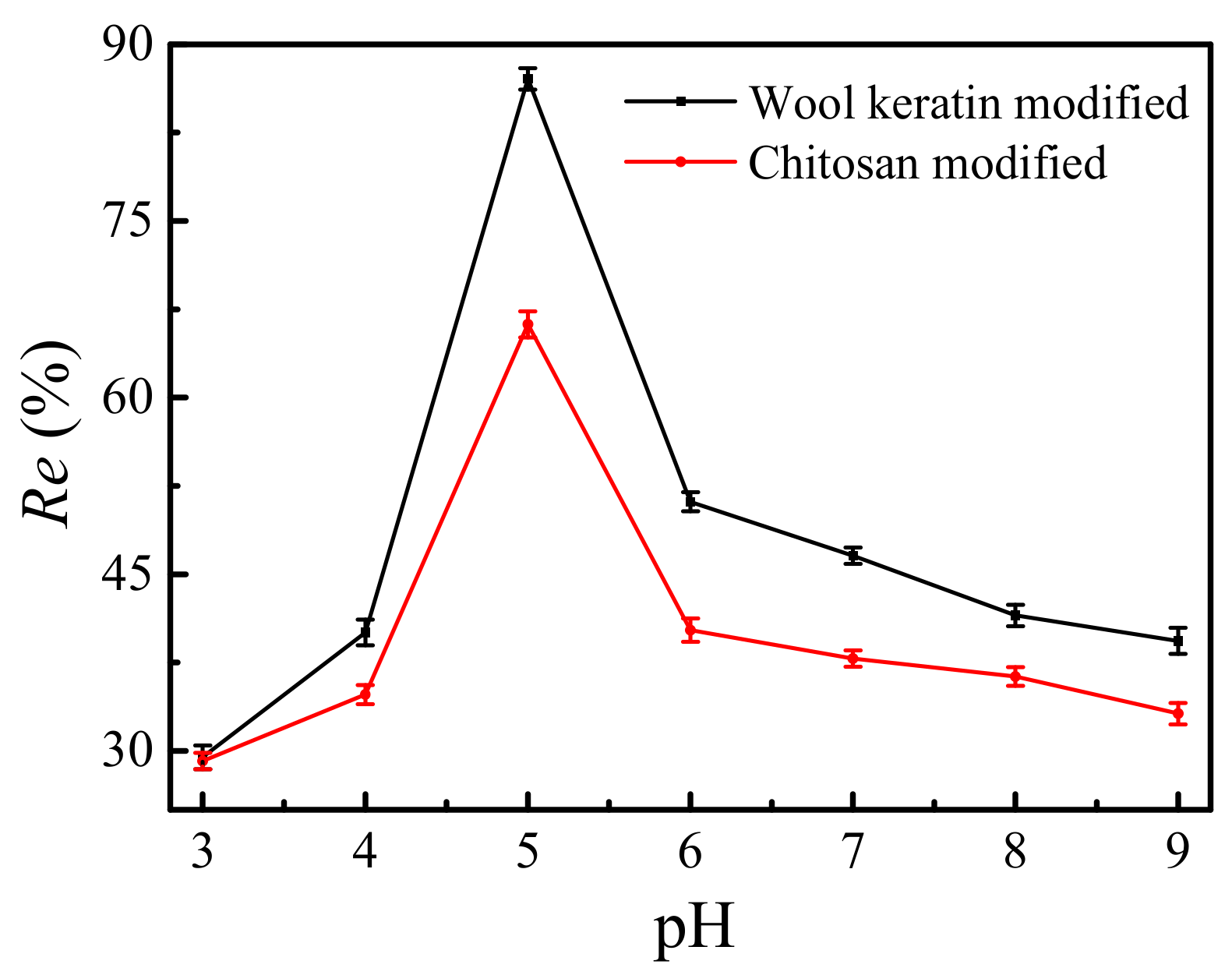
3.11. Effect of the pH Value of Solution
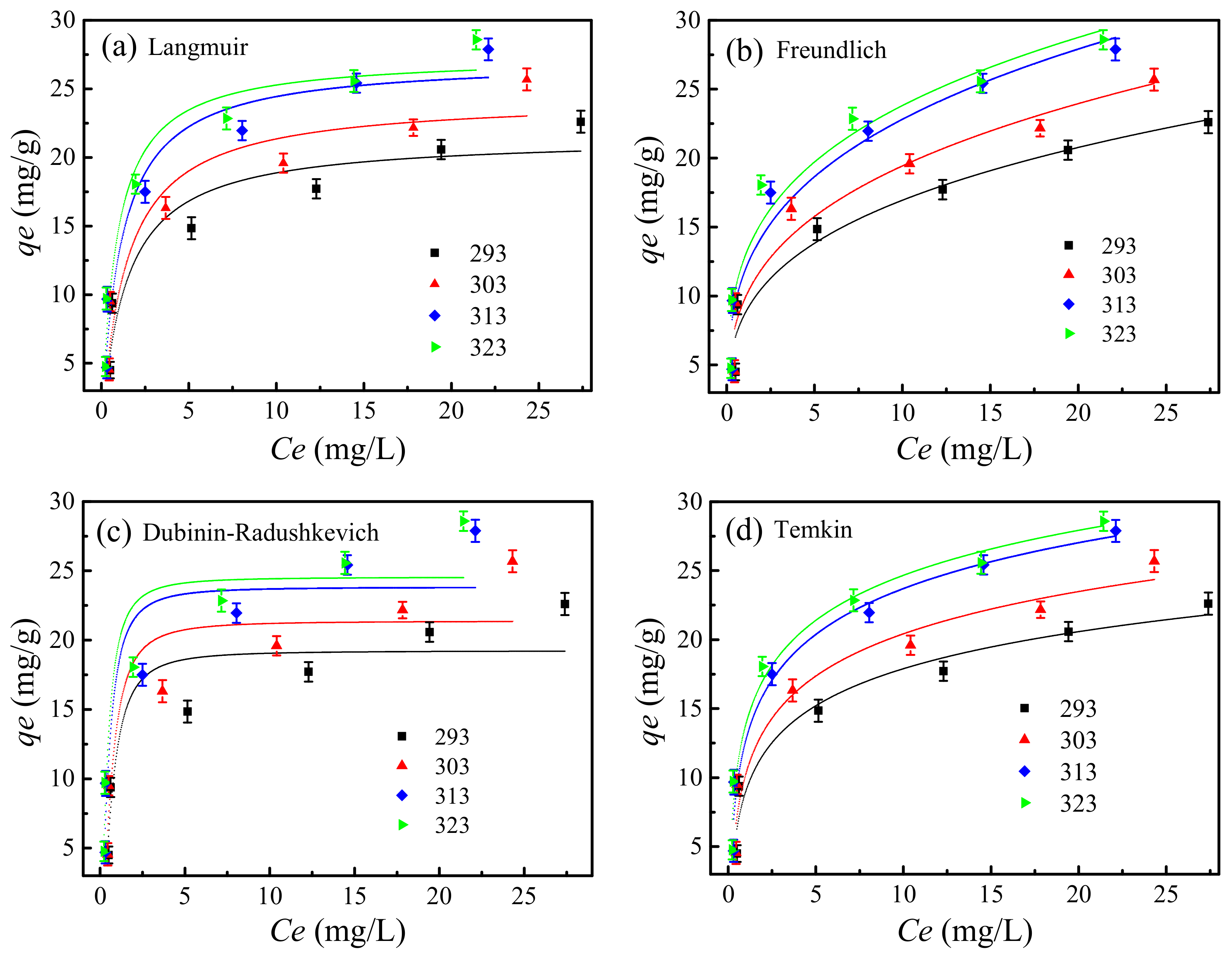
3.12. Adsorption Isotherms
3.12.1. Langmuir Isotherm
3.12.2. Freundlich Isotherm
3.12.3. Dubinin–Radushkevich (D–R) Isotherm
3.12.4. Temkin Isotherm
3.13. Adsorption Kinetics
3.13.1. Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model
3.13.2. Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model
3.13.3. Diffusion Model
3.14. Thermodynamic Studies
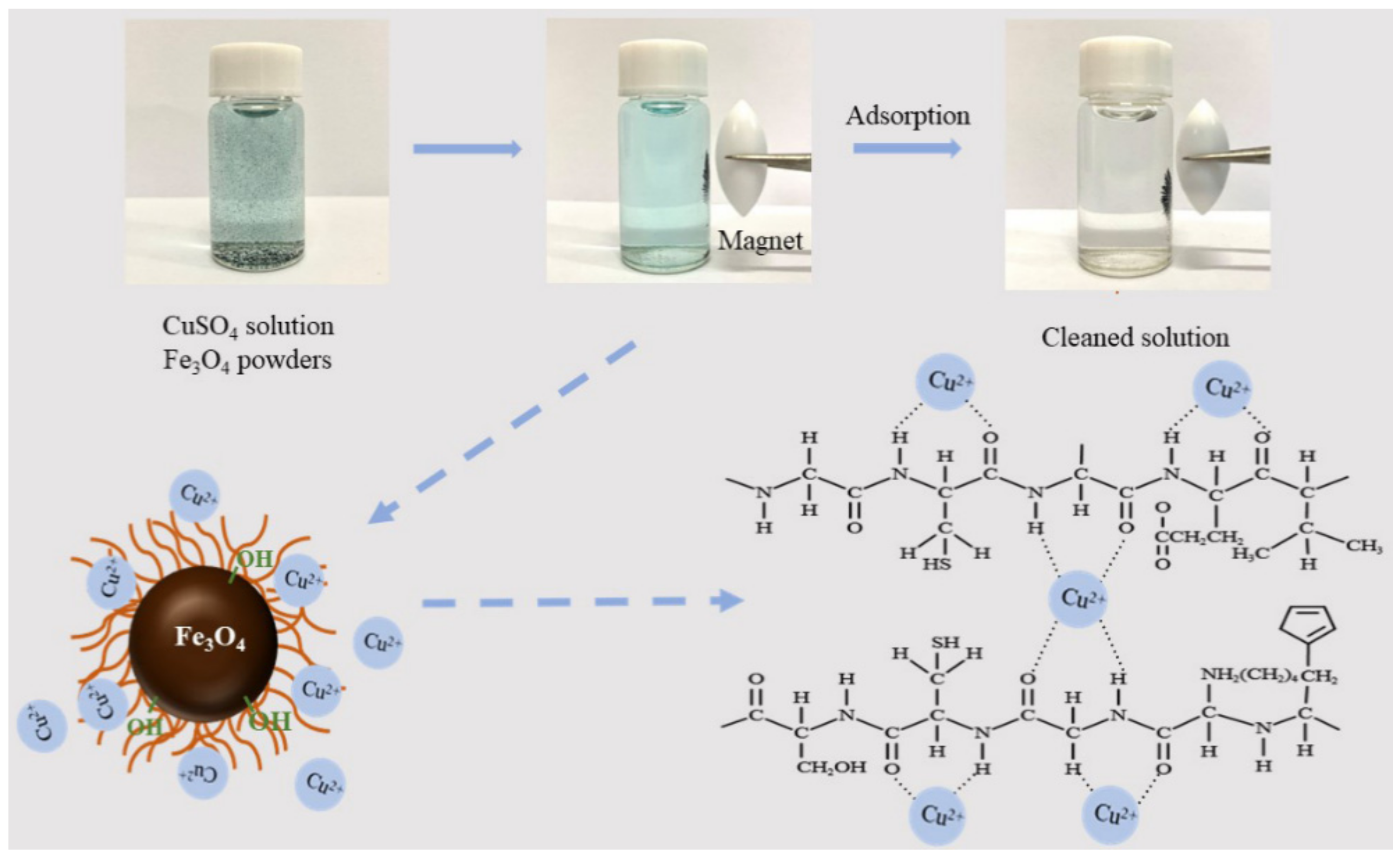
3.15. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, L.A.; Bashir, A.; Qureashi, A.; Pandith, A.H. Detection and removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1495–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.S.; Rong, H.W.; Zeng, G.M. New trends in removing heavy metals from wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6509–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstic, V.; Urosevic, T.; Pesovski, B. A review on adsorbents for treatment of water and wastewaters containing copper ions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 192, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Zubair, M.; Khosa, M.A.; Song, S.; Ullah, A. Keratin and chitosan biosorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, C.S.; Gang, E.H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Nanotibrous membrane of wool keratose/silk fibroin blend for heavy metal ion adsorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 302, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluigi, A.; Tonetti, C.; Vineis, C.; Tonin, C.; Casasola, R.; Ferrero, F. Wool keratin nanofibres for copper(II) adsorption. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2012, 6, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforova, T.; Kozlov, V.; Islyaikin, M. Sorption of d-metal cations by keratin from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowman, J.E. Diversity of trichocyte keratins and keratin associated proteins. In The Hair Fibre: Proteins, Structure and Development, 1st ed.; Plowman, J.E., Harland, D.P., Deb-Choudhury, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 1054, pp. 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shavandi, A.; Silva, T.H.; Bekhit, A.A.; Bekhit, A.E. Keratin: Dissolution, extraction and biomedical application. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 1699–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Carrillo, F.; Lopez-mesas, M.; Palet, C. Valorization of keratin biofibers for removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzlikova, Z.; Branisa, J.; Jomova, K.; Fueloep, M.; Hybler, P.; Porubska, M. Electron beam irradiated sheep wool–prospective sorbent for heavy metals in wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 193, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluigi, A.; Vineis, C.; Tonin, C.; Tonetti, C.; Varesano, A.; Mazzuchetti, G. Wool keratin-based nanofibres for active filtration of air and water. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2009, 3, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Cheng, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Li, A.M. A new porous chelating fiber: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption behavior of Pb(II). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 4072–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Abdel-Latif, D.A. Modification and characterization of PET fibers for fast removal of Hg(II), Cu(II) and Co(II) metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkhzaya, S.; Shiomori, K.; Oyuntsetseg, B. Effective adsorption of Au(III) and Cu(II) by chemically treated sheep wool and the binding mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.; Smith, S.V.; Rajkhowa, R.; Tsuzuki, T.; Wang, X.G. Milled cashmere guard hair powders: Absorption properties to heavy metal ions. Powder Technol. 2012, 218, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluigi, A.; Corbellini, A.; Rombaldoni, F.; Mazzuchetti, G. Wool-derived keratin nanofiber membranes for dynamic adsorption of heavy-metal ions from aqueous solutions. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.F.; Fernandes, T.; Trindade, T.; Daniel-da-Silva, A.L. Recent advances on magnetic biosorbents and their applications for water treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.W.; Jeon, B.H.; Chon, C.M.; Kim, Y.; Schwartz, F.W.; Lee, E.S.; Song, H. A novel chitosan/clay/magnetite composite for adsorption of Cu(II) and As(V). Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.F.; Yang, M.X.; Mo, L.D.; Xu, W.K.; Wang, S.; He, J.R.; Gu, J.J.; Ou, M.R.; Xu, X.R. Modification of chitosan/calcium alginate/Fe3O4 hydrogel microsphere for enhancement of Cu(II) adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2018, 25, 3922–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarnejad, M.; Asli, M.D.; Taromi, F.A.; Manoochehri, M. Synthesis of multi-functionalized Fe3O4-NH2-SH nanofiber based on chitosan for single and simultaneous adsorption of Pb(II) and Ni(II) from aqueous system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Kang, H.L.; Che, N.; Liu, Z.J.; Li, P.P.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.W.; Liu, R.G.; Huang, Y. Wool graft polyacrylamidoxime as the adsorbent for both cationic and anionic toxic ions from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 60609–60616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIingh, D.; Singh, S.K.; Atar, N.; Krishna, V. Amino acid functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for removal of Ni(II) from aqueous solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2016, 67, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.T.; Yang, L.R.; Dong, T.T.; Liu, Z.N.; Liu, H.Z. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using amino-modified Fe3O4-SiO2-chitosan magnetic microspheres with high acid resistance and adsorption capacity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Ramin, S. Effective removal of copper from aqueous solutions by modified magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.H.; Lv, S.; Si, C.D.; Liu, G.J.; Gao, H.T. The efficient adsorption removal of Cu(II) by using Fe3O4/TiO2/graphene ternary nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 5400–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenlaka, Y.A.B.; Lawa, Y.; Naat, J.N.; Riwu, A.A.P.; Iqbal, M.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Kusuma, H.S. The adsorption of Cr(VI) from water samples using graphene oxide-magnetic (GO-Fe3O4) synthesized from natural cellulose-based graphite (kusambi wood or Schleichera oleosa): Study of kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 6544–6556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.X.; Zhu, X.S. Nanoparticles of type Fe3O4-SiO2-graphene oxide and coated with an amino acid-derived ionic liquid for extraction of Al(III), Cr(III), Cu(II), Pb(II) prior to their determination by ICP-OES. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4279–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, L.A.; Bashir, A.; Ahmad, N.; Qureashi, A.; Pandith, A.H. Exploring metal ion adsorption and antifungal properties of carbon-coated magnetite composite. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 3208–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.K.; Li, D.Y.; Yang, H.; Guo, X.Z. Fabrication of Fe3O4@polydopamine@polyamidoamine core-shell nanocomposites and their application for Cu(ii) adsorption. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 12212–12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Panda, A.; Kim, E.; Yoom, M. Biopolymer-coated magnetite nanoparticles and metal-organic framework ternary composites for cooperative Pb(II) adsorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 4198–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, J.K.; Bi, J.T.; Xie, C.; Hao, H.X. Design and synthesis of core-shell Fe3O4@PTMT composite magnetic microspheres for adsorption of heavy metals from high salinity wastewater. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinia, A.; Mirzaeipour, R.; Jabbari, A. Nanosized Fe3O4-curcumin conjugates for adsorption of heavy metals from seawater samples. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-shamy, O.A.A.; El-azabawy, A.R.E.; El-azabawy, O.E. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite-alginate nanoparticles for enhancement of nickel and cobalt ion adsorption from wastewater. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 6326012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MirjavadiI, E.S.; Tehrani, R.M.A.; Khadir, A. Effective adsorption of zinc on magnetic nanocomposite of Fe3O4/zeolite/cellulose nanofibers: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2019, 26, 33478–33493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EsrafiliI, A.; Bagheri, S.; Kermani, M.; Gholami, M.; Moslemzadeh, M. Simultaneous adsorption of heavy metal ions (Cu2+ and Cd2+) from aqueous solutions by magnetic silica nanoparticles (Fe3O4@SiO2) modified using EDTA. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 158, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Xie, F.C. Selective adsorption of Copper (II) ions in mixed solution by Fe3O4-MnO2-EDTA magnetic nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 507, 145090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinia, A.; Heydari, S.; Jabbari, A. Synthesis and characterization of reduced graphene oxide-Fe3O4@polydopamine and application for adsorption of lead ions: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 121964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Tang, Y.B. Preparation of multifunctional nanocomposites Fe3O4@SiO2-EDTA and its adsorption of heavy metal ions in water solution. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.L.; Li, L.; Zhou, S.F.; Liu, Y.Z. Continuous preparation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles combined with surface modification by L-cysteine and their application in heavy metal adsorption. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 4228–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Wang, H.; Chai, L.Y.; Li, M.F. Effects of single- and multi-organic acid ligands on adsorption of copper by Fe3O4/graphene oxide-supported DCTA. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 478, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Zhu, L.; Lu, H.J. Surface chemical properties and adsorption of Cu (II) on nanoscale magnetite in aqueous solutions. Desalination 2011, 276, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.Y.; Liu, C.W.; Zhou, H.R.; Yu, W.M.; Wang, D.Z.; Wang, D.X. One-step synthesis of PI@Fe3O4 composite microspheres and practical applications in Cu(II) ion adsorption. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 88943–88949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.L.; Chen, B.H.; Chen, M.; Hu, S.; Cheng, H.M. Recovery of chromium(III) ions from aqueous solution by carboxylate functionalized wool fibres. J. Soc. Leather Techol. Chem. 2015, 99, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Deng, Z.J.; Han, S.X. Preparation of Fe3O4/poly(L-glutamic acid) microspheres and their adsorption of Cu(II) ions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagbi, Y.; Sarswat, A.; Mohan, D.; Pandey, A.; Solanki, P.R. Lead and chromium adsorption from water using L-cysteine functionalized magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lian, C.; Lin, K.F. Comparison of the adsorption preference using superparamagnetic Fe3O4-SH nanoparticles to remove aqueous heavy metal contaminants. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 125, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.S.; Hong, G.B.; Chen, H.W. Adsorption behavior of recyclable magnetites with N-components for adsorption of copper ion. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheikh, A.H.; Fasfous, I.I.; Al-Salamin, R.M.; Newman, A.P. Immobilization of citric acid and magnetite on sawdust for competitive adsorption and extraction of metal ions from environmental waters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5186–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Yu, Y.Y.; He, L.; Zhang, D.K.; Ye, M.M. Design of magnetic nanoparticles with high magnetic separation efficiencies and durability for Cu2+ adsorption. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 085710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonesio, M.D.; Pissetti, F.L. Magnetite particles covered by amino-functionalized poly(dimethylsiloxane) network for copper(II) adsorption from aqueous solution. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 94, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuhybani, M.; Alshahrani, A.; Algamdi, M.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Alqadami, A.A. Highly efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous systems using a new nanocomposite: Adsorption, isotherm, kinetic and mechanism studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.L.; Zhou, S.F.; Jiao, W.Z.; Qi, G.S.; Liu, Y.Z. Removal of heavy metal ions by magnetic chitosan nanoparticles prepared continuously via high-gravity reactive precipitation method. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 174, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, S.; Lee, G.R. The reaction of wool keratin with alkali. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1956, 19, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.F.; Wei, Y.Z.; Mira, H.I.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A.H.; Guibal, E. Synthesis and adsorption characteristics of grafted hydrazinyl amine magnetite-chitosan for Ni(II) and Pb(II) recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iron Ores-Determination of Copper Content Oxalicacid Bis-Cyclohexylidene Hydragide (Cuprizone) Spectrophotometric Method; National Standards of The People’s Republic of China GB/T 6730.35–2016; China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Wan, X.Y.; Zhan, Y.Q.; Long, Z.H.; Zeng, G.Y.; Ren, Y.; He, Y. High-performance magnetic poly (arylene ether nitrile) nanocomposites: Co-modification of Fe3O4 via mussel inspired poly(dopamine) and amino functionalized silane KH550. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 425, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi, M.; Saravani, A.Z.; Aroon, M.A.; Pirbazari, A.E. Photodegradation of methylene blue by a ternary magnetic TiO2/Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposite under visible light. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 225, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipsawat, P.; Wongpratat, U.; Phumying, S.; Chanlek, N.; Chokprasombat, K.; Maensiri, S. Magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 446, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.F.; Wu, P.; Li, G.Y.; Li, L.; Yi, J.C.; Wang, S.L.; Lu, S.Y.; Ding, P.; Chen, C.M.; Pan, H.Z. Optimization on preparation of Fe3O4/chitosan as potential matrix material for the removal of microcystin-LR and its evaluation of adsorption properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Guan, Y.P.; Liu, H.Z. Synthesis and characterization of micron-sized monodisperse superparamagnetic polymer particles with amino groups. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 3433–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.H.; Xiao, L.; Chen, C.H.; Shi, X.W.; Cao, Q.H.; Gao, L. In situ preparation of magnetic Fe3O4/chitosan nanoparticles via a novel reduction-precipitation method and their application in adsorption of reactive azo dye. Powder Technol. 2014, 26, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chen, D.H. Preparation and adsorption properties of monodisperse chitosan-bound Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for removal of Cu(II) ions. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2005, 283, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, X.L.; Ma, L.; Guo, M.Y.; Su, Y.Y.; Dharmarajan, R.; Chen, Z.L. Removal of doxorubicin hydrochloride using Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by euphorbia cochinchinensis extract. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.T.; Lei, X.F.; Ma, Y.; Tian, L.D.; He, X.W.; Su, K.H.; Zhang, Q.Y. Application of yolk–shell Fe3O4@N-doped carbon nanochains as highly effective microwave-absorption material. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1500–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.D.; He, X.W.; Lei, X.F.; Qiao, M.T.; Gu, J.W.; Zhang, Q.Y. Efficient and green fabrication of porous magnetic chitosan particles based on a high-adhesive superhydrophobic polyimide fiber mat. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12914–12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Han, M.L.; Su, Q.; Xia, L.Q.; Hui, Z.C. Adsorption properties of magnetic magnetite nanoparticle for coexistent Cr(VI) and Cu(II) in mixed solution. Water 2020, 12, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wang, Z.K.; Lv, Q.; Li, C.L.; Sun, S.Q.; Hu, S.Q. Preparation of amino-functionalized Fe3O4@mSiO2 core-shell magnetic nanoparticles and their application for aqueous Fe3+ removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlstrom, N.; Steinhagen, S.; Toth, G.; Pavia, H.; Edlund, U. Ulvan dialdehyde-gelatin hydrogels for removal of heavy metals and methylene blue from aqueous solution. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 249, 116841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.T.; Guimaraes, C.H.; Silva, P.M.; Oliveira, R.L.; Prediger, P. Enhanced removal of basic dye using carbon nitride/graphene oxide nanocomposites as adsorbents: High performance, recycling, and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2020, 28, 3386–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.M.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, Z.R. Adsorption of platinum (IV) and palladium (II) from aqueous solution by thiourea-modified chitosan microspheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Mudhoo, A.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Kinetic, equilibrium, thermodynamic studies and spectroscopic analysis of Alizarin Red S removal by mustard husk. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Lee, J.; Park, S.M.; Alessi, D.S.; Baek, K. Adsorption characteristics of cesium onto calcium-silicate-hydrate in concrete powder and block. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.B.; Yang, Y.R.; Lin, Z.K.; Zhao, B.C.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Zhang, A.P. Preparation of a novel bio-adsorbent of sodium alginate grafted polyacrylamide/graphene oxide hydrogel for the adsorption of heavy metal ion. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.L.; Li, B.; Fan, S.S. Biochar from rice straw for Cu2+ removal from aqueous solutions: Mechanism and contribution made by acid-soluble minerals. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.M.; Cui, W.W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.L.; Zhang, Y. Sustainable disposal of Cr(VI): Adsorption-reduction strategy for treating textile wastewaters with amino-functionalized boehmite hazardous solid wastes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6811–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.Q.; Yu, X.C.; Xue, B.N.; Liao, J.Q.; Zhu, W.T.; Tian, S.Y. Adsorption of chlortetracycline from aquaculture wastewater using modified zeolites. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2020, 55, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Huang, Z.Q. Magnetic dithiocarbamate functionalized reduced graphene oxide for the removal of Cu(II), Cd(II), Pb(II), and Hg(II) ions from aqueous solution: Synthesis, adsorption, and regeneration. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipiska, M.; Zarodnanska, S.; Hornik, M.; Duriska, L.; Holub, M.; Safarik, I. Magnetically functionalized moss biomass as biosorbent for efficient Co2+ ions and thioflavin T removal. Materials 2020, 13, 3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Mao, N.; Zhang, H. Magnetically Recyclable Wool Keratin Modified Magnetite Powders for Efficient Removal of Cu2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051068
Zhang X, Guo Y, Li W, Zhang J, Wu H, Mao N, Zhang H. Magnetically Recyclable Wool Keratin Modified Magnetite Powders for Efficient Removal of Cu2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(5):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051068
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinyue, Yani Guo, Wenjun Li, Jinyuan Zhang, Hailiang Wu, Ningtao Mao, and Hui Zhang. 2021. "Magnetically Recyclable Wool Keratin Modified Magnetite Powders for Efficient Removal of Cu2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions" Nanomaterials 11, no. 5: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051068
APA StyleZhang, X., Guo, Y., Li, W., Zhang, J., Wu, H., Mao, N., & Zhang, H. (2021). Magnetically Recyclable Wool Keratin Modified Magnetite Powders for Efficient Removal of Cu2+ Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials, 11(5), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051068






