A Robust Superhydrophobic Polyurethane Sponge Loaded with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Efficient and Selective Oil-Water Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pretreatment of Original PU Sponge
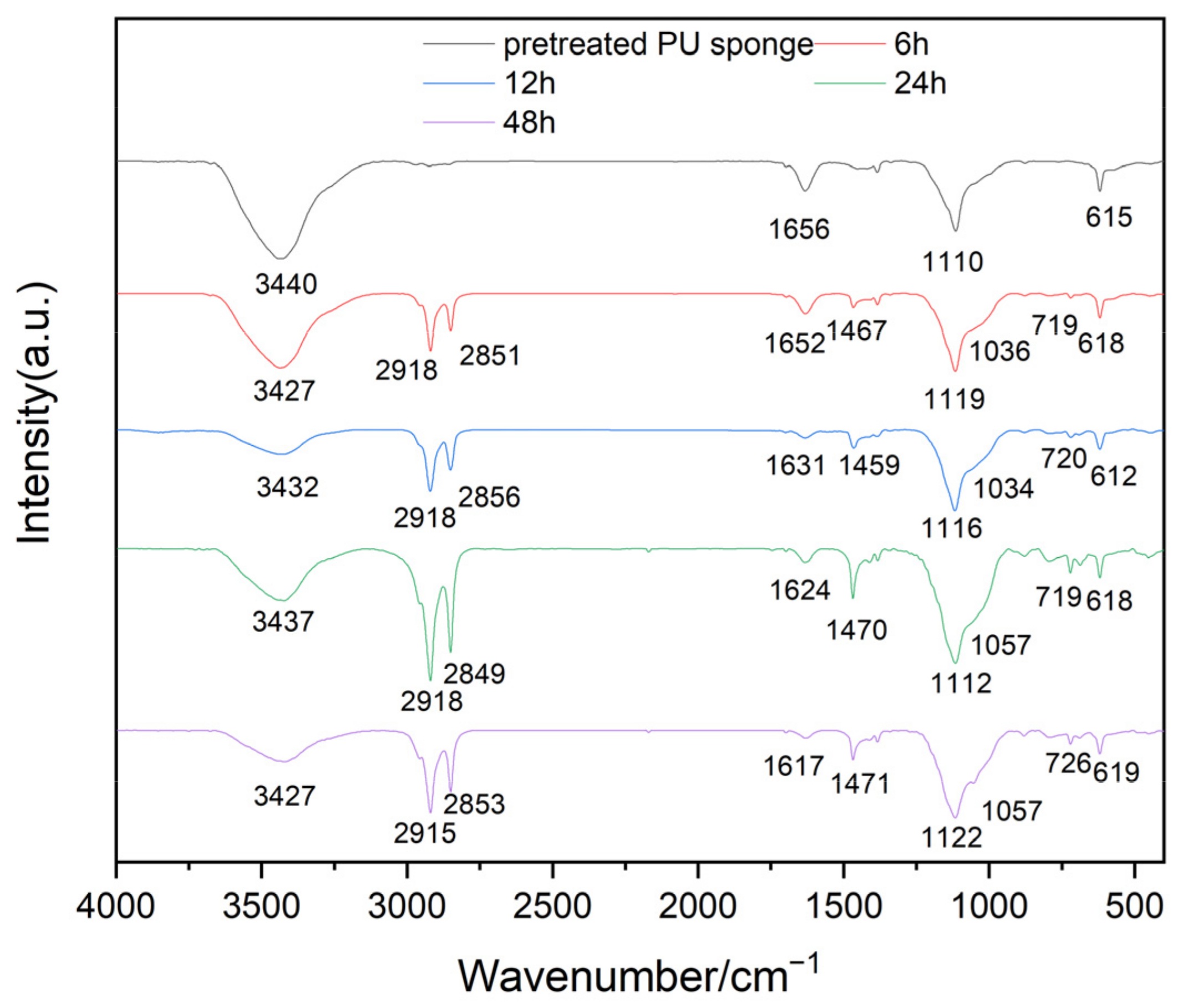
2.3. Preparation of Coupling Agent-CNTs/PU Sponges
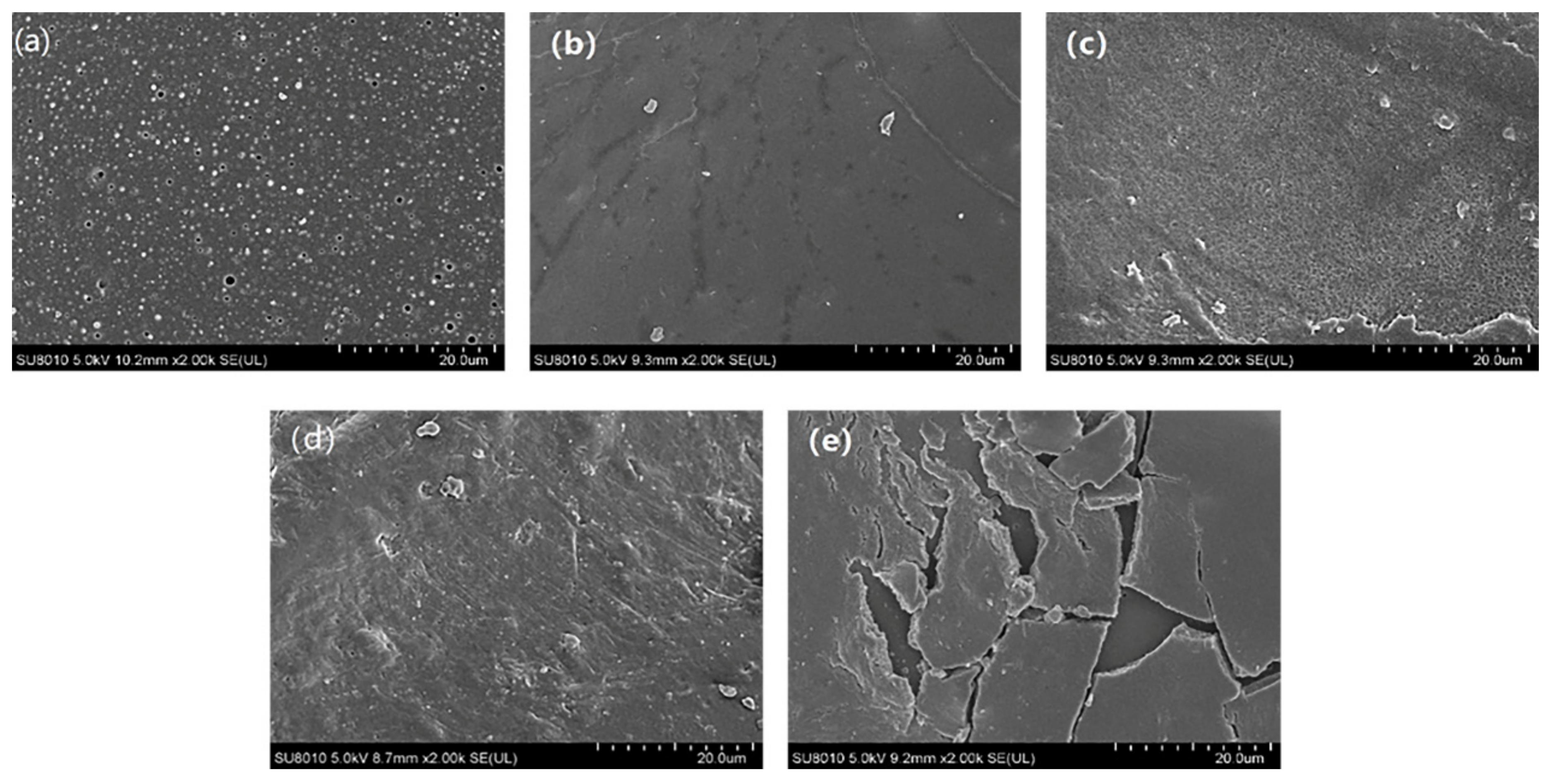
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Oil Absorption of the OTS-CNTs/PU Sponge to Different Oils
3. Result and Discussion
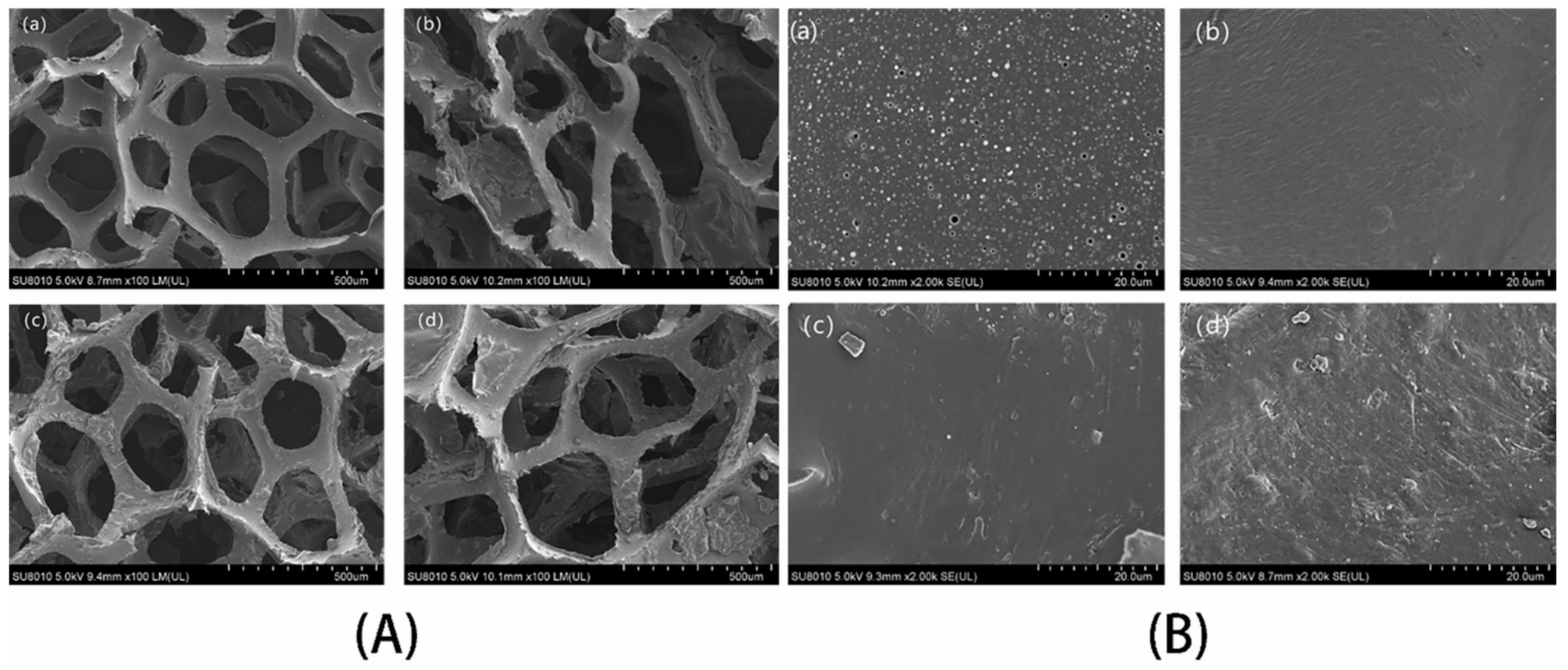
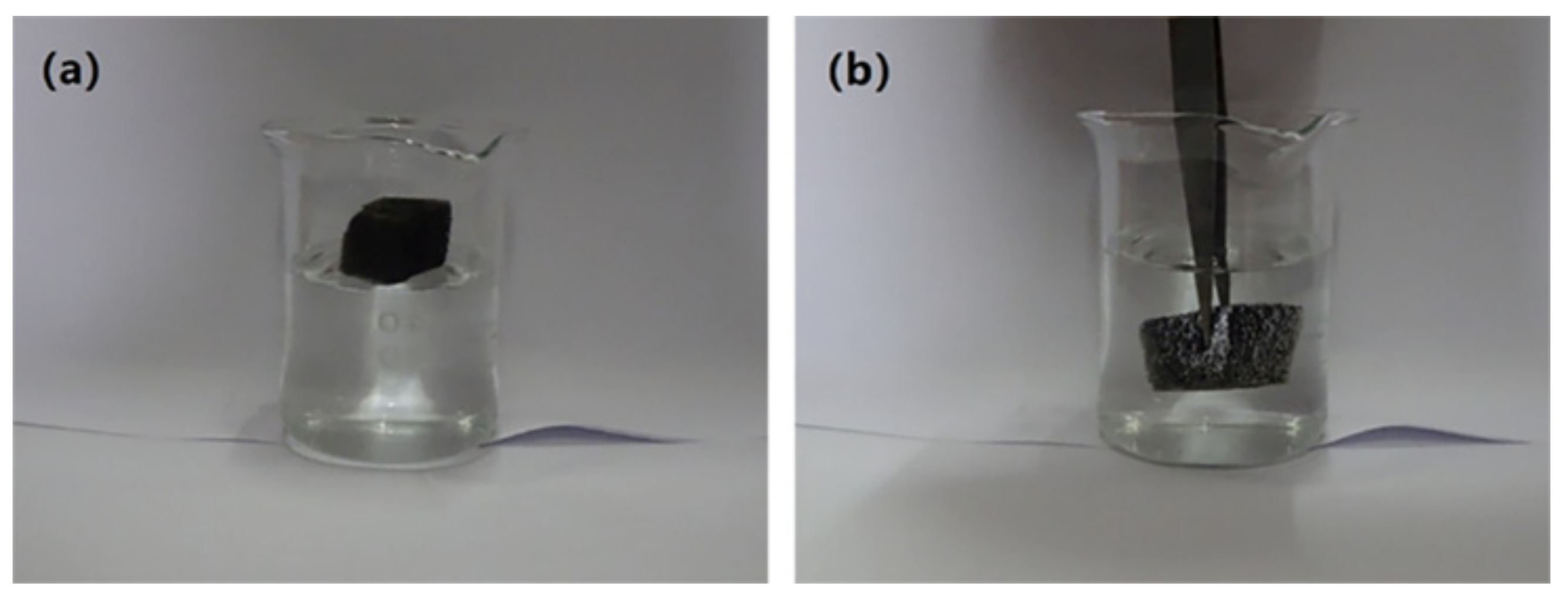
3.1. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Sponge
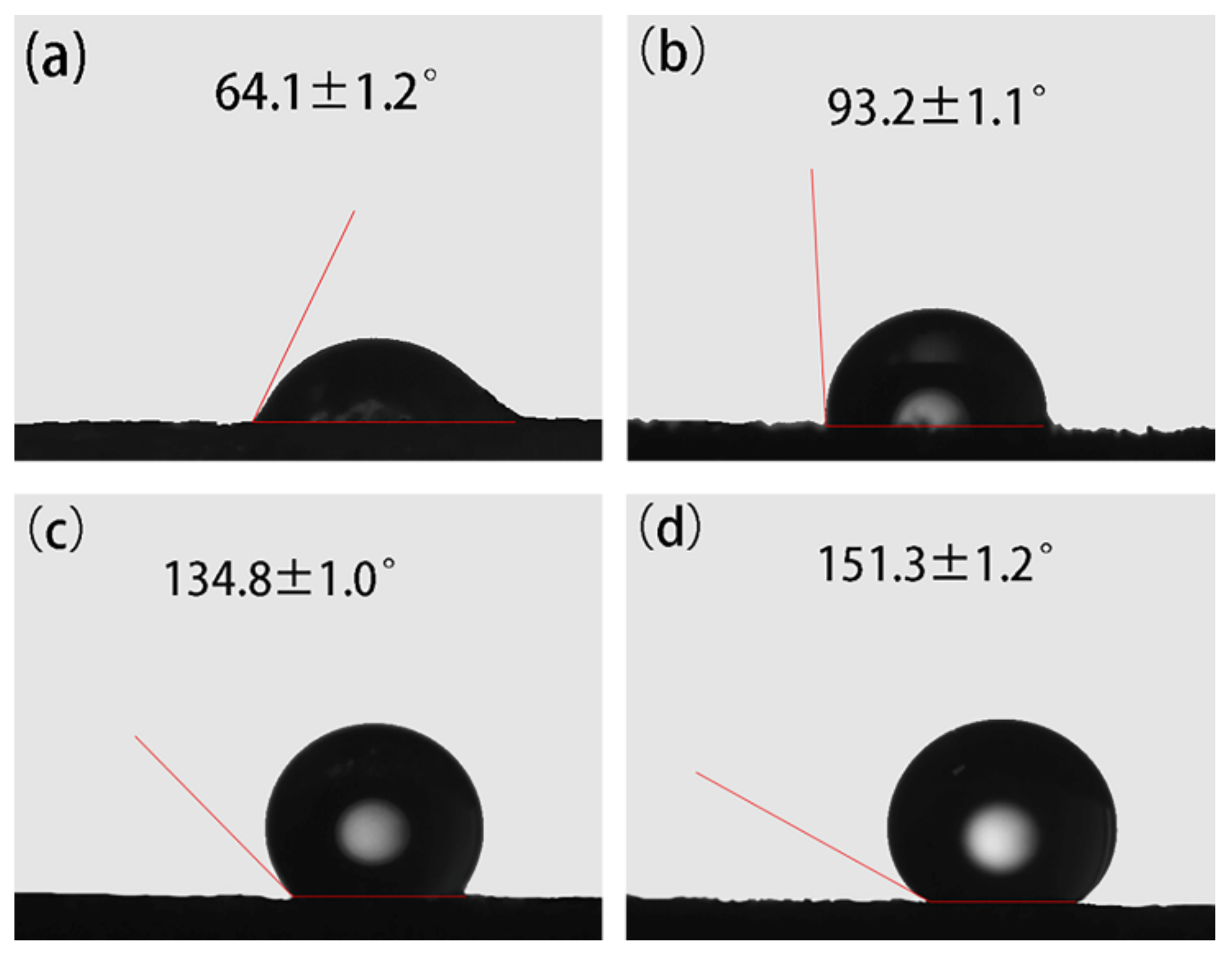
3.1.1. Selection of Coupling Agents
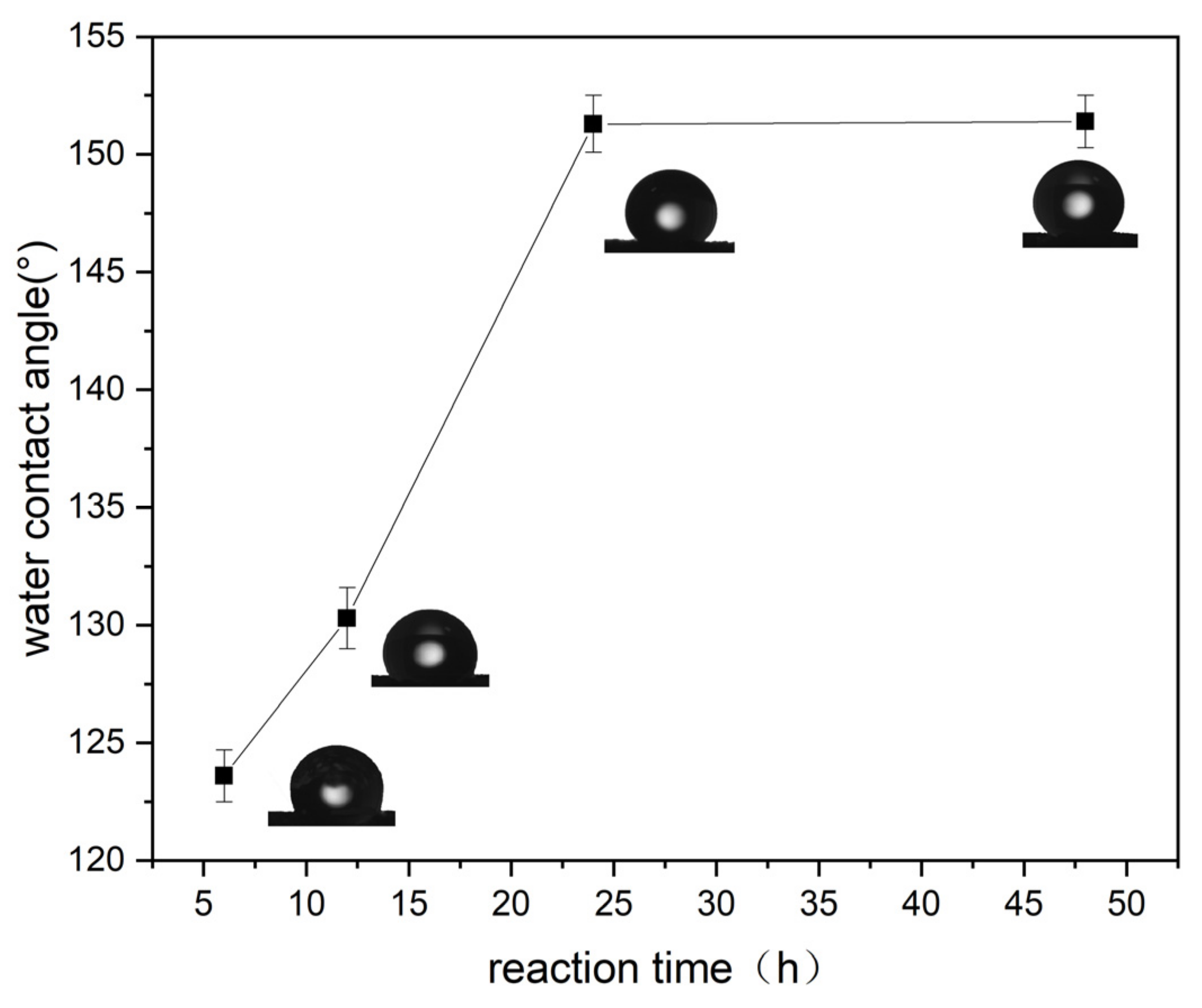
3.1.2. Selection of Coupling Time
3.2. Oil Absorption Test
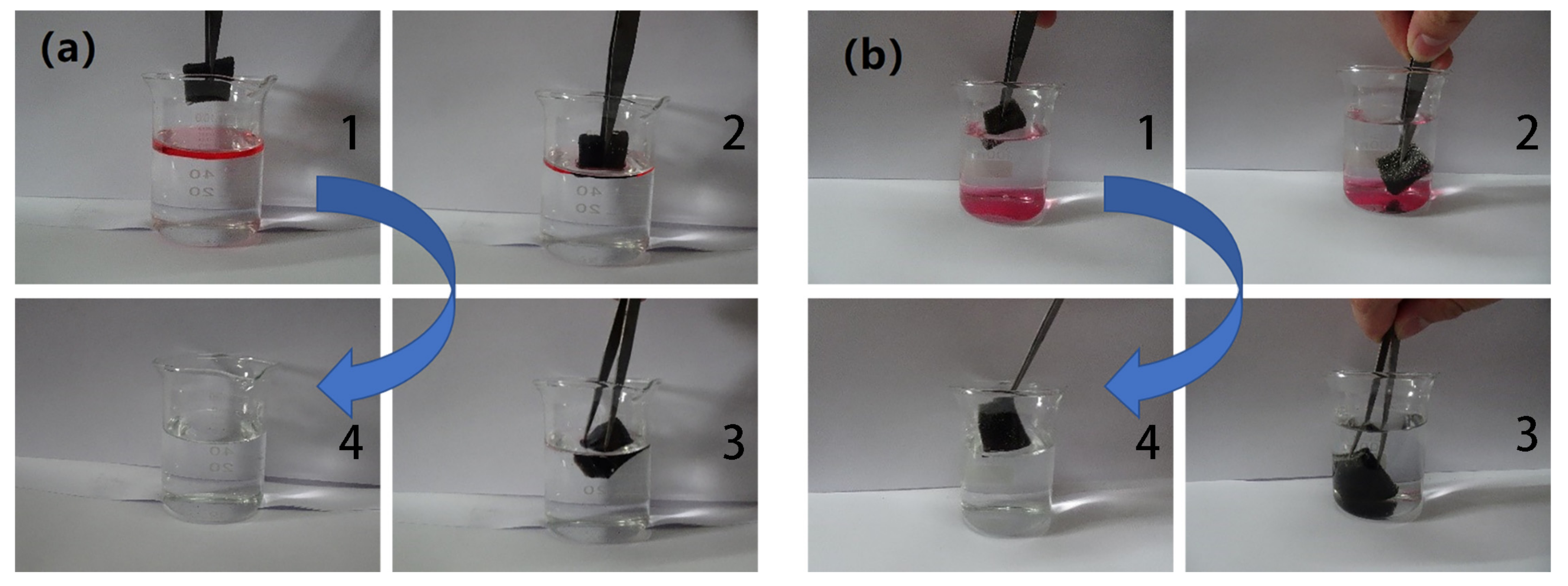
3.2.1. Oil-Water Separation Process
3.2.2. Impact of Environmental Factors on the Efficiency of Oil-Water Separation
Effect of Density and Viscosity
Effect of Temperature
Effect of Ionic Strength
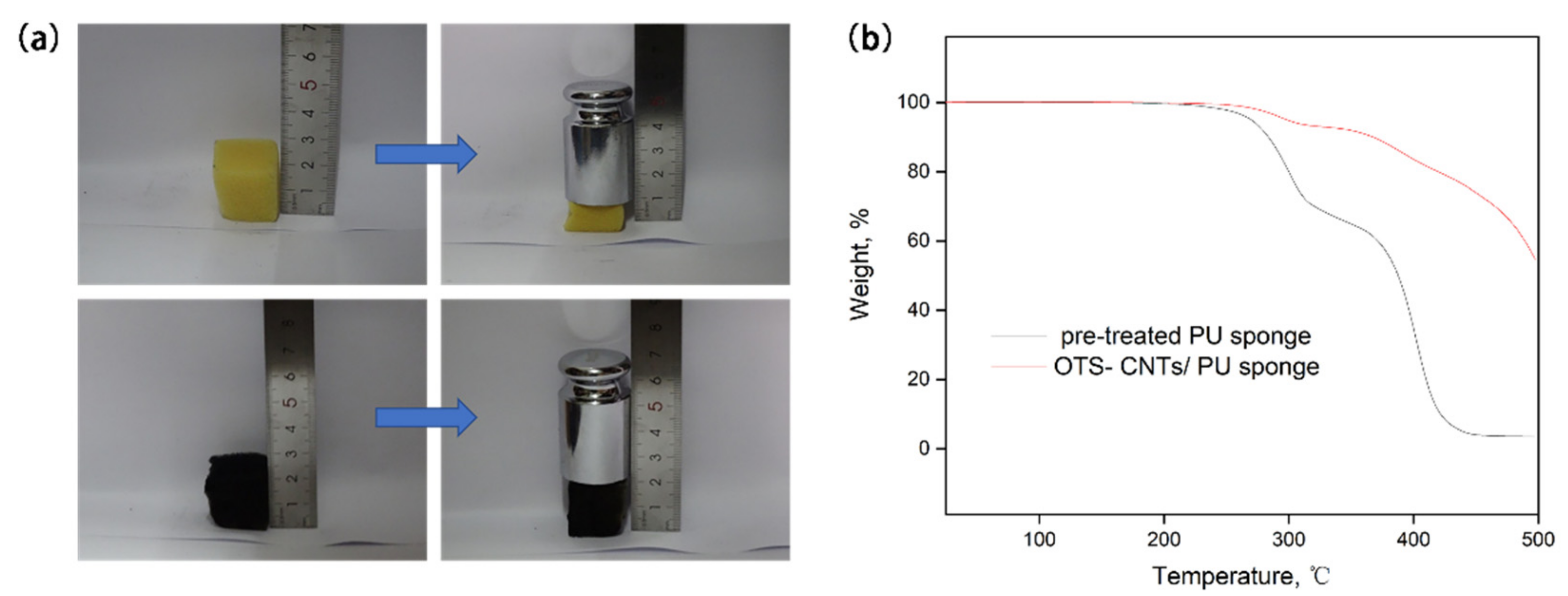
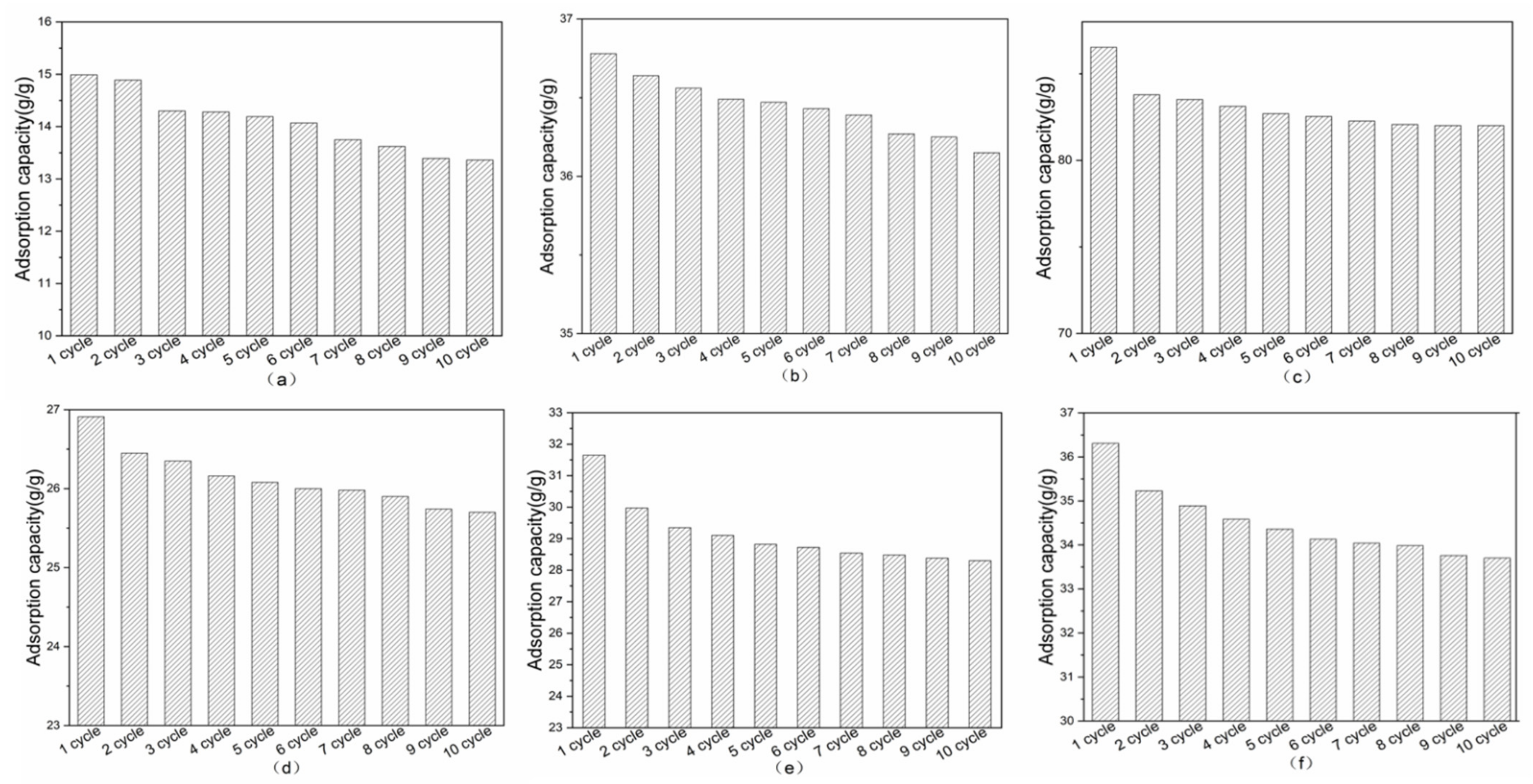
3.3. Reusability of the Superhydrophobic Sponge
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhumal, P.S.; Khose, R.V.; Wadekar, P.H.; Lokhande, K.D.; Some, S. Graphene-bentonite supported free-standing, flexible membrane with switchable wettability for selective oil–water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulal, D.K.; Khose, R.V.; Pethsangave, D.A.; Wadekar, P.H.; Some, S. Biomass-derived lignocellulosic graphene composite: Novel approach for removal of oil and organic solvent. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 4568–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A. Oil pollution in the North Sea: The impact of governance measures on oil pollution over several decades. Hydrobiologia 2019, 845, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamaly, S.; Giwa, A.; Hasan, S.W. Recent improvements in oily wastewater treatment: Progress, challenges, and future opportunities. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Majed, A.A.; Adebayo, A.R.; Hossain, M.E. A sustainable approach to controlling oil spills. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broje, V.; Keller, A.A. Improved mechanical oil spill recovery using an optimized geometry for the skimmer surface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7914–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broje, V.; Keller, A.A. Effect of operational parameters on the recovery rate of an oleophilic drum skimmer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurell, J.; Gullett, B.K. Aerostat sampling of PCDD/PCDF emissions from the gulf oil spillin situ burns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9431–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawinski, E.B.; Soule, M.C.K.; Valentine, D.L.; Boysen, A.K.; Longnecker, K.; Redmond, M.C. Fate of dispersants associated with the deepwater horizon oil spill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, U.C.; Fragouli, D.; Bayer, I.S.; Athanassiou, A. Functionalized cellulose networks for efficient oil removal from oil–water emulsions. Polymers 2016, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Geng, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Review on the aerogel-type oil sorbents derived from nanocellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Xu, Y.; Liang, L.; Wang, J.; Luo, L.X. Removal of COD from heavy oil wastewater by activated carbon. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Germany, 2012; pp. 2325–2328. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Sumathi, S.; Hameed, B.H. Residual oil and suspended solid removal using natural adsorbents chitosan, bentonite and activated carbon: A comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 108, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavandi, A.; Haddadian, Z.; Ismail, M.H.S.; Abdullah, N.; Abidin, Z.Z. Removal of residual oils from palm oil mill effluent by adsorption on natural zeolite. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4017–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Cheng, H.; Fane, A.G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H. Recent development of advanced materials with special wettability for selective oil/water separation. Small 2016, 12, 2186–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Pickett, K.; Panchal, A.; Liu, M.; Lvov, Y.M. Superhydrophobic polyurethane foam coated with polysiloxane-modified clay nanotubes for efficient and recyclable oil absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25445–25456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Men, X.; Zhu, X. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic sponge with selective absorption and collection of oil from water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 9411–9416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Liu, Z.; Gao, D.; Yuan, R.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y. A novel carbon nanotubes reinforced superhydrophobic and superoleophilic polyurethane sponge for selective oil–water separation through a chemical fabrication. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 3, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hao, M.; Wu, T.; Li, Y. Efficient treatment of crude oil-contaminated hydrodesulphurization catalyst by using surfactant/solvent mixture. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.M.; Anis, B.; Khalil, A.S. Facile surface treatment and decoration of graphene-based 3D polymeric sponges for high performance separation of heavy oil-in-water emulsions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, N.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. Special wettable materials for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Zhang, B.; Xie, L.; Wang, F. MWCNTs polyurethane sponges with enhanced super-hydrophobicity for selective oil–water separation. Surf. Eng. 2020, 36, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamsaz, A.; Goharshadi, E.K. Flame retardant, superhydrophobic, and superoleophilic reduced graphene oxide/orthoaminophenol polyurethane sponge for efficient oil/water separation. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 307, 112979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Qiu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Gao, J. Cost-effective reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge as a highly efficient and reusable oil-absorbent. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10018–10026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, T. Robust superhydrophobic sepiolite-coated polyurethane sponge for highly efficient and recyclable oil absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5560–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.-T.; He, F.-A.; Li, D.-H. Superhydrophobic modification of polyurethane sponge for the oil-water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 359, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Pan, Q. Mussel-inspired direct immobilization of nanoparticles and application for oil–water separation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, P.; Su, H.; Qian, H.; Ma, H. One-step fabrication of superhydrophobic sponge with magnetic controllable and flame-retardancy for oil removing and collecting. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, e4935344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Yang, B.; Barras, A.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Polyurethane sponge functionalized with superhydrophobic nanodiamond particles for efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Li, Y.; Fei, T.; Gong, W. Facile one-pot synthesis of superhydrophobic reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge at the presence of ethanol for oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjandra, R.; Lui, G.; Veilleux, A.; Broughton, J.; Chiu, G.; Yu, A. Introduction of an enhanced binding of reduced graphene oxide to polyurethane sponge for oil absorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3657–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Volder, M.F.L.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon nanotubes: Present and future commercial applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Miao, J.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, F.-X.; Bin Yang, H.; Liu, B.; Yang, Y. Carbon nanotube catalysts: Recent advances in synthesis, characterization and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3295–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, K.R.; Dora, D.T.K.; Pant, K.; Roy, S. An ultra-light flexible aerogel-based on methane derived CNTs as a reinforcing agent in silica-CMC matrix for efficient oil adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, K.; Burghard, M. Chemically functionalized carbon nanotubes. Small 2005, 1, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.H.; Cassity, K.; Andrews, R.; Meier, M.; Osbeck, S.; Andreu, A.; Johnston, C.; Crossley, A. Surface studies of hydroxylated multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 4835–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Hu, H.; Sui, W.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, G. Thermoresponsive polyurethane sponges with temperature-controlled superwettability for oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.-L.; Wei, Y.-Z.; Zou, L.-M.; Xu, S. Preparation and characterization of hydroxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 421, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; He, D.; Hu, H.; Yi, P.; Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Li, G. Preparation and properties of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)/Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-based amphiphilic polyurethane elastomers. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4377–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, D.; Dhiman, S.; Rattan, G.; Monga, S.; Singhal, S.; Kaushik, A. Superhydrophobic modification of cellulose sponge fabricated from discarded jute bags for oil water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Bian, C.; Yang, G.; Qiang, X. Facile fabrication of water-based and non-fluorinated superhydrophobic sponge for efficient separation of immiscible oil/water mixture and water-in-oil emulsion. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, D.; Li, Y.; Wu, T. Effective removal of emulsified oil from oily wastewater using surfactant-modified sepiolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 157, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Men, X.; Xue, Q. One-pot fabrication of nanoporous polymer decorated materials: From oil-collecting devices to high-efficiency emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5077–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zha, F.; She, H. Robust superhydrophobic attapulgite coated polyurethane sponge for efficient immiscible oil/water mixture and emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 15546–15553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Q.; Qiu, F.; Yang, D.; Ou, Z. Recyclable biomass carbon@SiO2@MnO2 aerogel with hierarchical structures for fast and selective oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, R.; Shi, L.; Jin, Y.; Qing, W.; Tang, C.; Wang, P. Solar-assisted fast cleanup of heavy oil spills using a photothermal sponge. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 9192–9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, P.; Gu, Y. Effects of asphaltene content on the heavy oil viscosity at different temperatures. Fuel 2007, 86, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomair, O.; Jumaa, M.; Alkoriem, A.; Hamed, M. Heavy oil viscosity and density prediction at normal and elevated temperatures. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2016, 6, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, J.; Shi, L.-A.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Yao, H.-B.; Zhu, Y.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.-W.; Wu, H.-A.; Yu, S.-H. Joule-heated graphene-wrapped sponge enables fast clean-up of viscous crude-oil spill. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Solvas, E.; García, D.G.; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A. Towards physical properties tailoring of carbon nanotubes-reinforced ceramic matrix composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 3001–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethsangave, D.A.; Wadekar, P.; Khose, R.V.; Some, S. Super-hydrophobic carrageenan cross-linked graphene sponge for recovery of oil and organic solvent from their water mixtures. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khose, R.V.; Wadekar, P.; Pethsangave, D.A.; Chakraborty, G.; Ray, A.K.; Some, S. Novel approach towards the synthesis of highly efficient flame retardant electrode and oil/organic solvent absorber. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, M.; Azizian, S. Synthesis of a novel highly oleophilic and highly hydrophobic sponge for rapid oil spill cleanup. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25326–25333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukawski, D.; Lisiecki, F.; Dudkowiak, A. Coating cellulosic materials with graphene for selective absorption of oils and organic solvents from water. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-López, A.J.; Muñoz-Sandoval, E.; López-Urías, F. Efficient carbon nanotube sponges production boosted by acetone in CVD-Synthesis. Carbon 2018, 135, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gu, B.; Qiu, F.; Peng, X.; Yue, X.; Yang, D. Preparation of carbon nanotubes/Polyurethane hybrids as a synergistic absorbent for efficient oil/water separation. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sandoval, E.; Cortés-López, A.J.; Flores-Gómez, B.; Fajardo-Diaz, J.L.; Sanchez-Salas, R.; López-Urías, F. Carbon sponge-type nanostructures based on coaxial nitrogen-doped multiwalled carbon nanotubes grown by CVD using benzylamine as precursor. Carbon 2017, 115, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, F. Hydrophobic modification of polyurethane foam for oil spill cleanup. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1648–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouri, M.R.; Javanbakht, V.; Ghotbabadi, D.J.; Mehravar, M. Oily wastewater treatment by a magnetic superoleophilic nanocomposite foam. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | Density (g/mL) | Viscosity (mPas) | Absorption Capacity (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean oil | 0.919 | 76.59 | 14.99 |
| Kerosene | 0.79 | 3.489 | 36.78 |
| Petroleum ether | 0.705 | 1.75 | 26.91 |
| Chloroform | 1.484 | 1.726 | 86.53 |
| Crude oil | 0.835 | 6.087 | 36.81 |
| Hexadecane | 0.773 | 7.645 | 31.65 |
| Absorption Capacity (g/g) | Soybean Oil | Kerosene | Petroleum Ether | Chloroform | Crude Oil | Hexadecane |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTS-CNTs/PU sponge | 14.99 | 36.78 | 26.91 | 86.53 | 36.81 | 31.65 |
| OTS-PU sponge | 14.81 | 36.60 | 26.82 | 86.39 | 35.66 | 31.57 |
| Pre-treated PU sponge | 14.17 | 35.66 | 26.15 | 85.37 | 32.68 | 30.89 |
| Samples | Temperature (°C) | Viscosity (mPas) | Absorption Capacity (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroform | 20 | 3.177 | 86.53 |
| 40 | 3.063 | 85.76 | |
| 60 | 2.941 | 85.62 | |
| 80 | * | * | |
| Crude oil | 20 | 11.78 | 36.81 |
| 40 | 9.276 | 37.26 | |
| 60 | 7.413 | 37.91 | |
| 80 | 6.087 | 38.68 | |
| Kerosene | 20 | 3.489 | 36.79 |
| 40 | 2.764 | 35.92 | |
| 60 | 1.697 | 35.02 | |
| 80 | 1.671 | 35.00 |
| Samples | c(NaCl) | WCA | Absorption (g/g) | c(CaCl2) | WCA | Absorption (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroform | 0 | 151.3° | 86.53 | 0 | 151.3° | 86.53 |
| 0.002 | 143.1° | 86.39 | 0.002 | 142.8° | 85.88 | |
| 0.004 | 141.6° | 86.12 | 0.004 | 140.5° | 85.59 | |
| 0.006 | 134.4° | 85.76 | 0.006 | 132.6° | 85.15 | |
| 0.008 | 125.2° | 85.12 | 0.008 | 120.9° | 85.11 | |
| Crude oil | 0 | 151.3° | 36.81 | 0 | 151.3° | 36.81 |
| 0.002 | 143.1° | 36.17 | 0.002 | 142.8° | 35.94 | |
| 0.004 | 141.6° | 36.10 | 0.004 | 140.5° | 35.74 | |
| 0.006 | 134.4° | 36.08 | 0.006 | 132.6° | 35.60 | |
| 0.008 | 125.2° | 35.77 | 0.008 | 120.9° | 35.58 | |
| Kerosene | 0 | 151.3° | 36.79 | 0 | 151.3° | 36.79 |
| 0.002 | 143.1° | 36.68 | 0.002 | 142.8° | 36.63 | |
| 0.004 | 141.6° | 36.64 | 0.004 | 140.5° | 36.4 | |
| 0.006 | 134.4° | 36.51 | 0.006 | 132.6° | 36.07 | |
| 0.008 | 125.2° | 36.27 | 0.008 | 120.9° | 36.06 |
| Adsorption Material | WCA | Sorbate | Oil Adsorption Capacity (g/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulosic materials | 148 ° | diesel oil | 33 | [55] |
| PU-PNIPAAm | 135° | 1,2-dibromoethane | 11.31 | [37] |
| N-CNS | 142° | ethylene glycol | 30 | [50,56] |
| CNTs/PUF | 131° | chloroform | 33.04 | [57] |
| PU–NDs-fPDA sponge | >150° | chloroform | 59.26 | [29] |
| CSTN | 150° | chloroform | 74.32 | [58] |
| RGO/OAP/PU | >150° | chloroform | 80.28 | [23] |
| PUf-g-LMA | * | kerosene | 20.97 | [59] |
| NCPUF | 148° | kerosene | 27.7 | [60] |
| OTS-CNTs/PU sponge | 150.2° | kerosene | 36.78 | Present work |
| OTS-CNTs/PU sponge | 150.2° | chloroform | 86.53 | Present work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Wu, T.; Li, Y. A Robust Superhydrophobic Polyurethane Sponge Loaded with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Efficient and Selective Oil-Water Separation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123344
Liu D, Wang S, Wu T, Li Y. A Robust Superhydrophobic Polyurethane Sponge Loaded with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Efficient and Selective Oil-Water Separation. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(12):3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123344
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, De, Shiying Wang, Tao Wu, and Yujiang Li. 2021. "A Robust Superhydrophobic Polyurethane Sponge Loaded with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Efficient and Selective Oil-Water Separation" Nanomaterials 11, no. 12: 3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123344
APA StyleLiu, D., Wang, S., Wu, T., & Li, Y. (2021). A Robust Superhydrophobic Polyurethane Sponge Loaded with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Efficient and Selective Oil-Water Separation. Nanomaterials, 11(12), 3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123344





