Swelling Effects on the Conductivity of Graphene/PSS/PAH Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PSS-Stabilized Graphene Sheets (rGO-PSS)
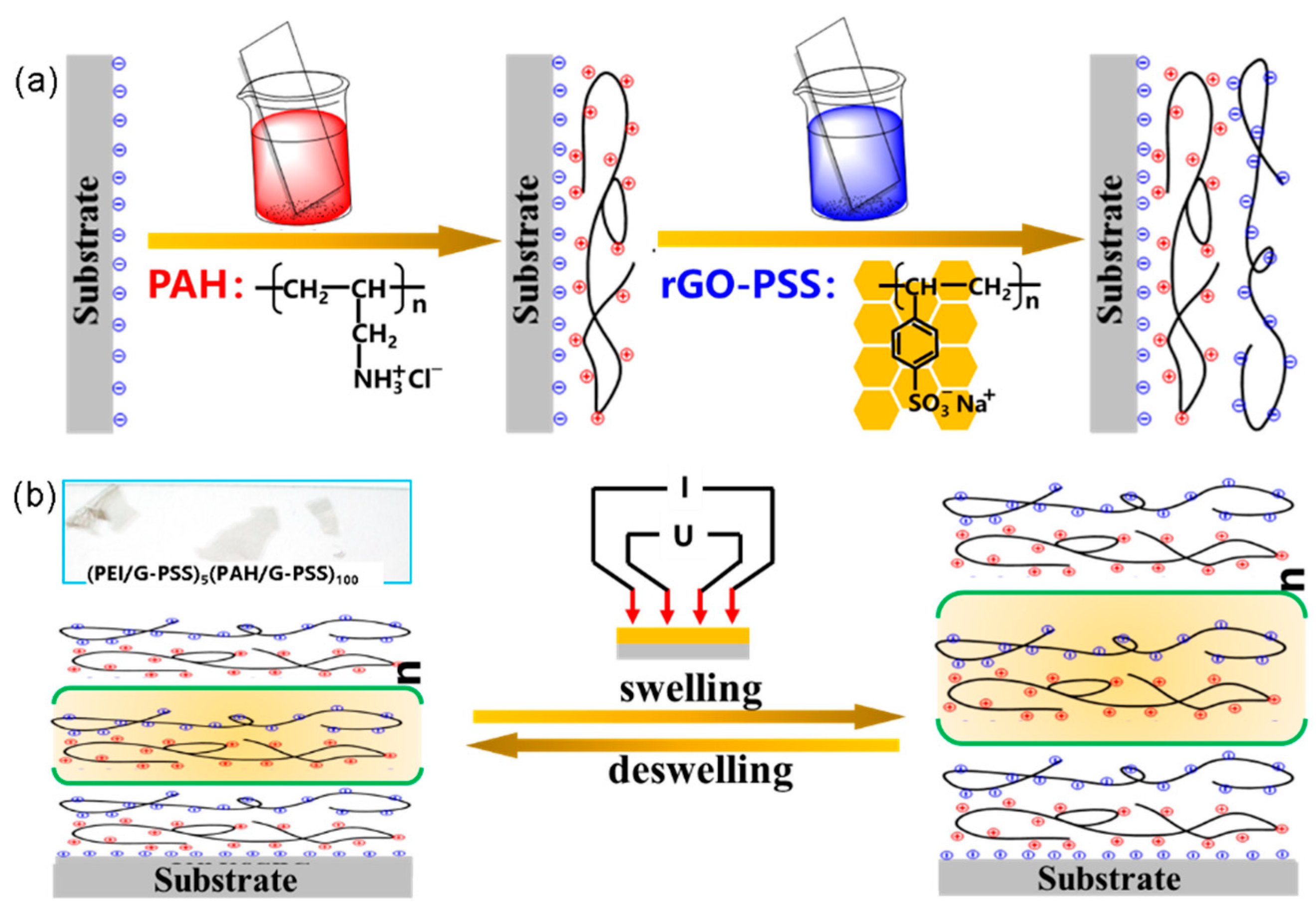
2.3. Preparing (rGO-PSS/PAH)n Multilayer Films (n: Number of Deposition Cycles)
2.4. Swelling and Sheet Resistance Tests
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.6. Characterizations
2.6.1. Spectrum Analysis
2.6.2. Morphology Characterizations
2.6.3. Mechanical Tests
2.6.4. Sheet Resistance Evaluations
3. Results and Discussion
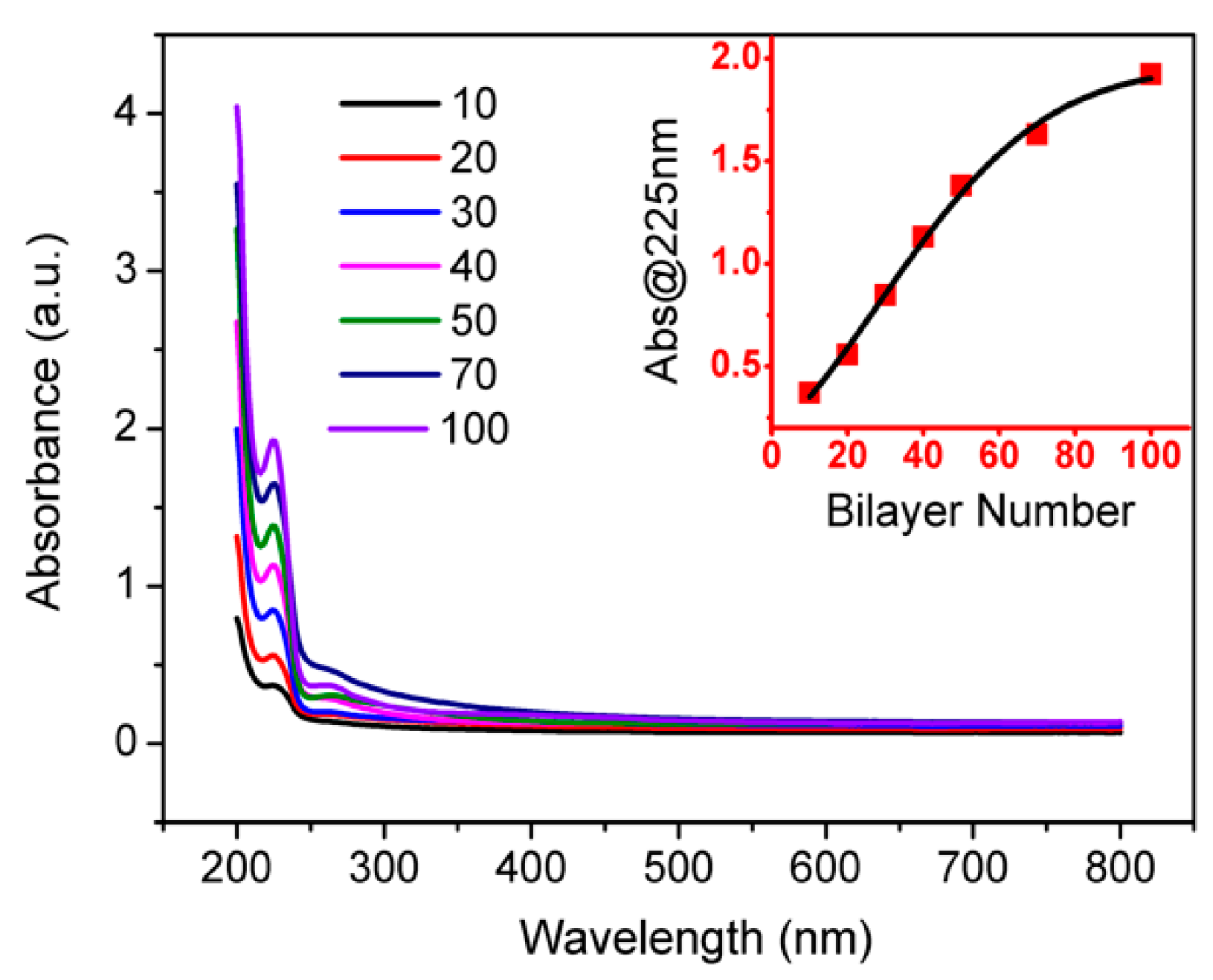
3.1. Characterizations of PSS-Stabilized Graphene Sheets (rGO-PSSs)
3.2. Fabrication of Polyelectrolyte/rGO-PSS Composite via the Layer-by-Layer Assembly Method
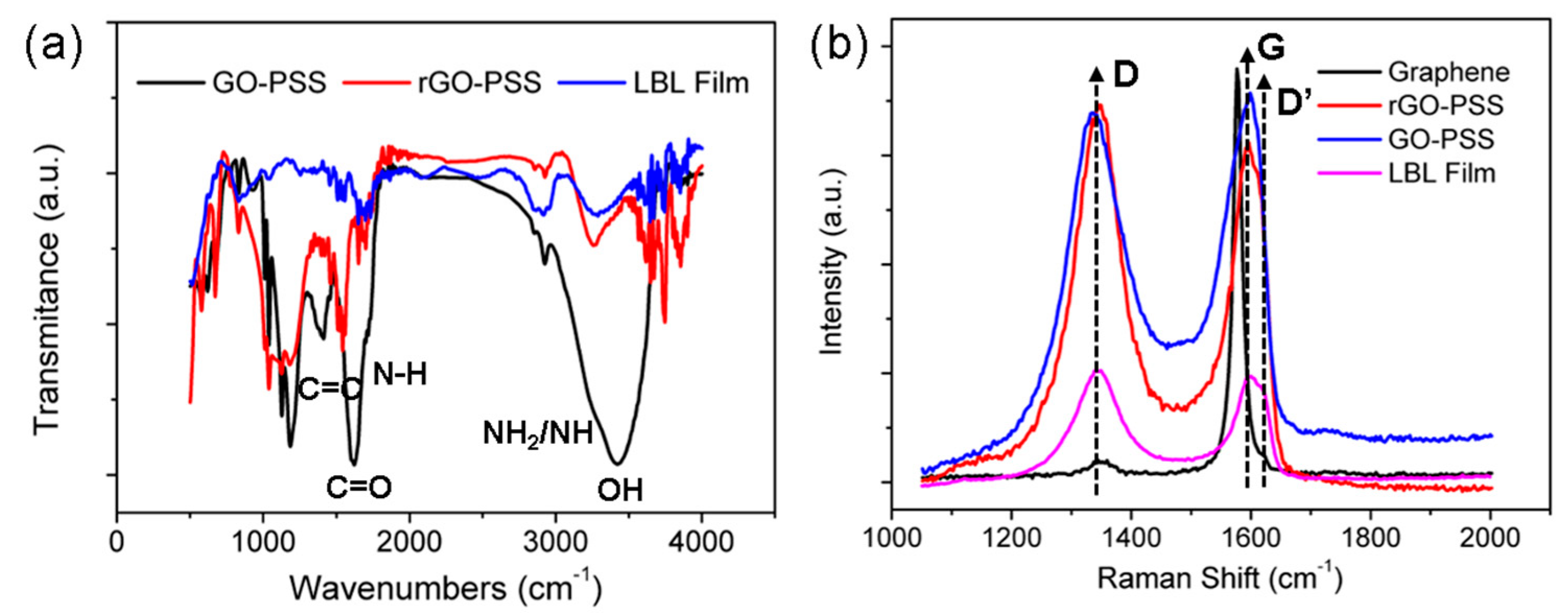
3.3. Raman and FT-IR Spectrum Analysis
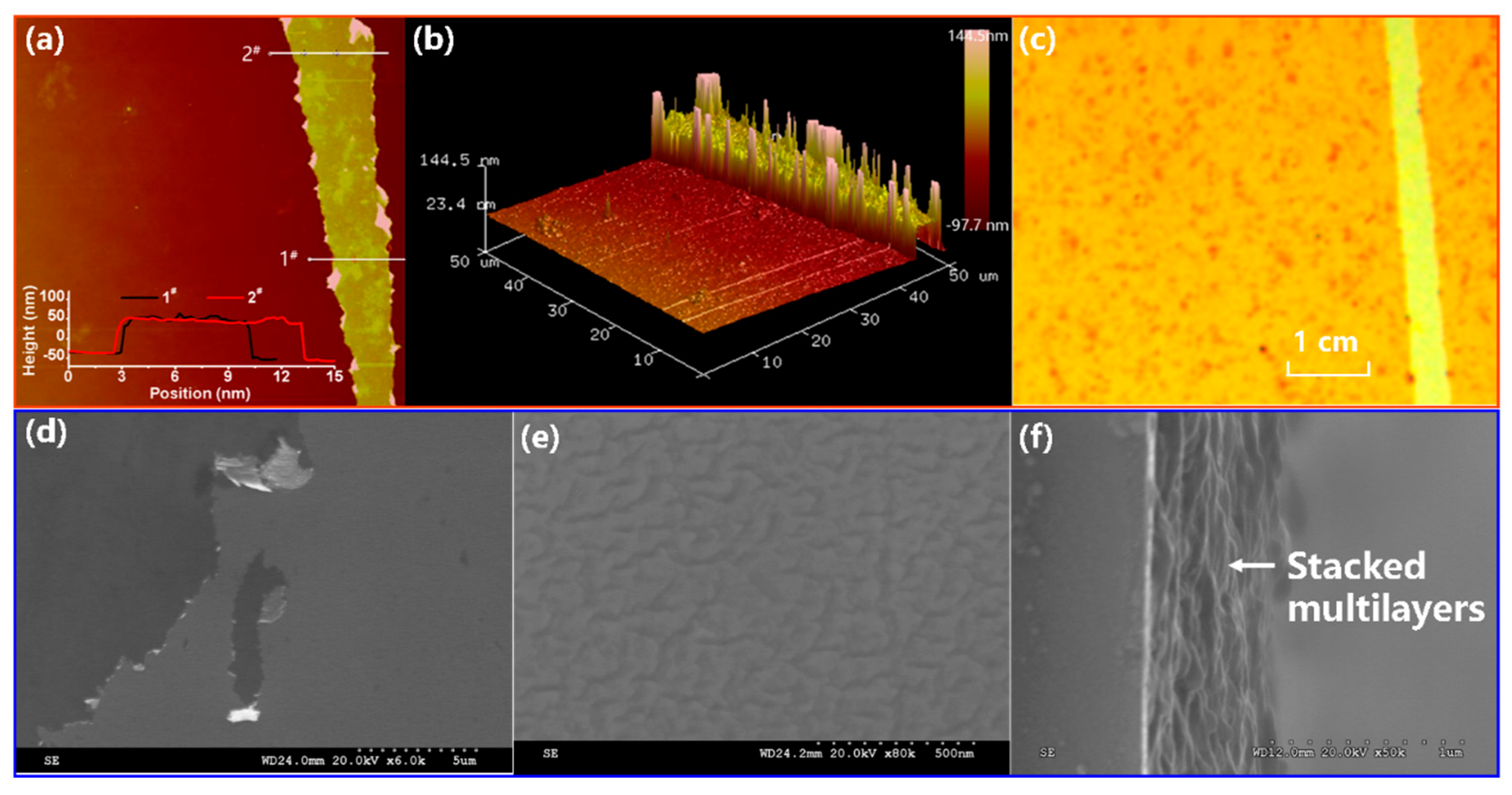
3.4. Morphology Characterizations
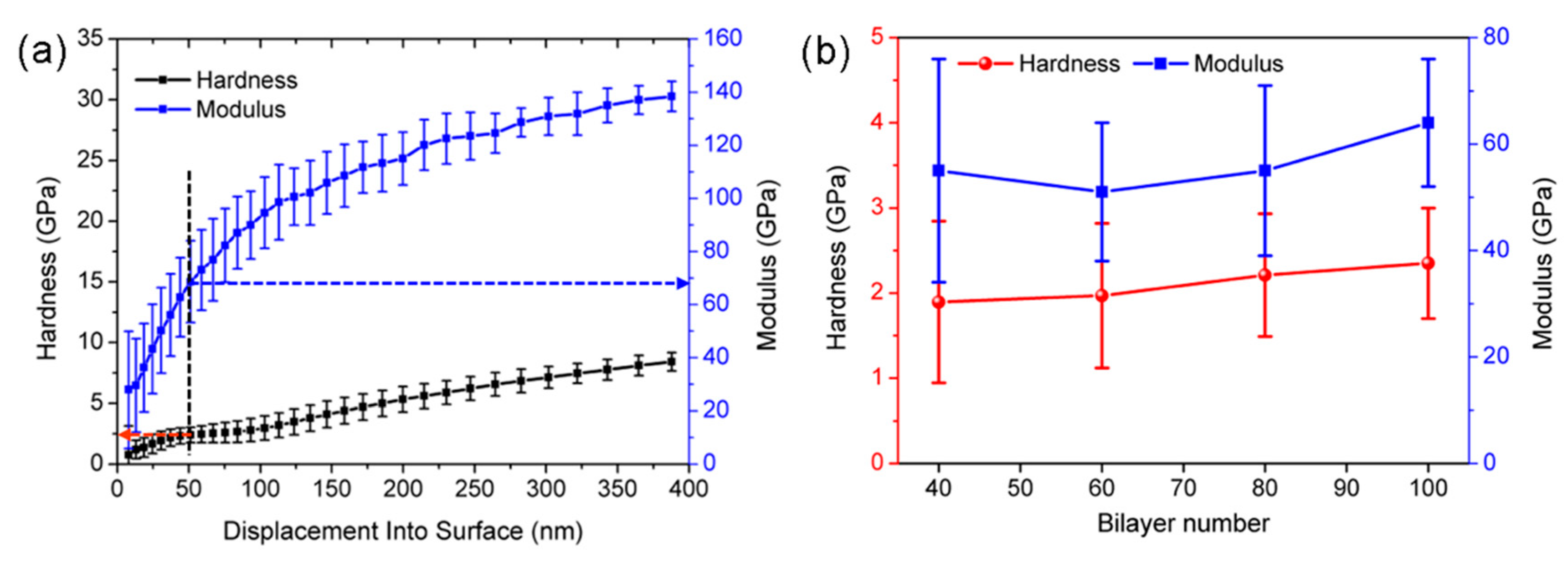
3.5. Modulus and Hardness
3.6. Sheet Resistances and Theoretical Calculations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Stedronsky, E.; Regen, S.L. Defects in a polyelectrolyte multilayer: The inside story. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16510–16511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Polyelectrolyte-based platforms for the delivery of peptides and proteins. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4937–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tang, C.; Ahmad, M.; Yaroshchuk, A.; Bruening, M.L. High selectivities among monovalent cations in dialysis through cation-exchange membranes coated with polyelectrolyte multilayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2018, 10, 44134–44143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shan, C.; Li, F.; Han, D.; Niu, L. Stable, Conductive supramolecular composite of graphene sheets with conjugated polyelectrolyte. Langmuir 2010, 26, 6708–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Haitami, A.E.; Martel, D.; Ball, V.; Nguyen, H.C.; Gonthier, E.; Labbé, P.; Voegel, J.C.; Schaaf, P.; Senger, B.; Boulmedais, F. Effect of the supporting electrolyte anion on the thickness of PSS/PAH multilayer films and on their permeability to an electroactive probe. Langmuir 2009, 25, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Feldötö, Z.; Varga, I.; Blomberg, E. Influence of salt and rinsing protocol on the structure of PAH/PSS polyelectrolyte multilayers. Langmuir 2010, 26, 17048–17057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.N.; Mccormick, M.; Barrett, C.J.; Reven, L.; Spiess, H.W. NMR studies of PAH/PSS polyelectrolyte multilayers adsorbed onto silica. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4830–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, J.A.; Schlenoff, J.B. Counterions and water in polyelectrolyte multilayers: A tale of two polycations. Langmuir 2007, 23, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbarazadeh, A. The origins of enhanced and retardedcrystallization in nanocomposite polymers. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarzadeh, A.; Halfina, B. Unravelling the effects of size, volume fraction and shape of nanoparticle additives on crystallization of nanocomposite polymers. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4702–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Ganesan, V.; Riggleman, R.A. Perspective: Outstanding theoretical questions in polymer-nanoparticle hybrids. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 020901–020918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papananou, H.; Perivolari, E.; Chrissopoulou, K.; Anastasiadis, S.H. Tuning polymer crystallinity via the appropriate selection of inorganic nanoadditives. Polymer 2018, 157, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Feng, L.; Shen, X. Conjugated polyelectrolyte/graphene multilayer films for simultaneous electrochemical sensing of three monohydroxylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 7785–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.C.; Kim, Y.; Yao, M.; Tijing, L.D.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K. Hierarchical composite membranes with robust omniphobic surface using layer-by-layer assembly technique. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2186–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.W.; Lai, C.W.; Abd Hamid, S.B.; Low, F.W.; Liu, W.W. Simple preparation of exfoliated graphene oxide sheets via simplified Hummer’s method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1109, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaram, K.; Kalyanikar, M.; Patel, M.; Brukh, R.; Flach, C.R.; Huang, R.; Khoshi, M.R.; Mendelsohn, R.; Wang, A.; Garfunkel, E.; et al. Synergy of oxygen and Piranha solution for eco-friendly production of highly conductive graphene dispersions. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhishvili, S.A.; Kharlampieva, E.; Izumrudov, V. Where polyelectrolyte multilayers and polyelectrolyte complexes meet. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 8873–8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegler, H.; Essler, F. Polyelectrolytes. 2. intrinsic or extrinsic charge compensation? Quantitative charge analysis of PAH/PSS multilayers. Langmuir 2002, 18, 6694–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, C.; Virga, A.; Benfatto, L.; Martinati, M.; De Fazio, D.; Sassi, U.; Fasolato, C.; Ott, A.K.; Postorino, P.; Yoon, D.; et al. Raman spectroscopy of graphene under ultrafast laser excitation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.B.; Lin, M.L.; Cong, X.; Liu, H.N.; Tan, P.H. Raman spectroscopy of graphene-based materials and its applications in related devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1822–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Li, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Li, N.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, R.; Bao, L. Layer-by-layer assembled architecture of polyelectrolyte multilayers and graphene sheets on hollow carbon spheres/sulfur composite for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5488–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenoff, J.B.; Yang, M.; Digby, Z.A.; Wang, Q. Ion content of polyelectrolyte complex coacervates and the donnan equilibrium. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 9149–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


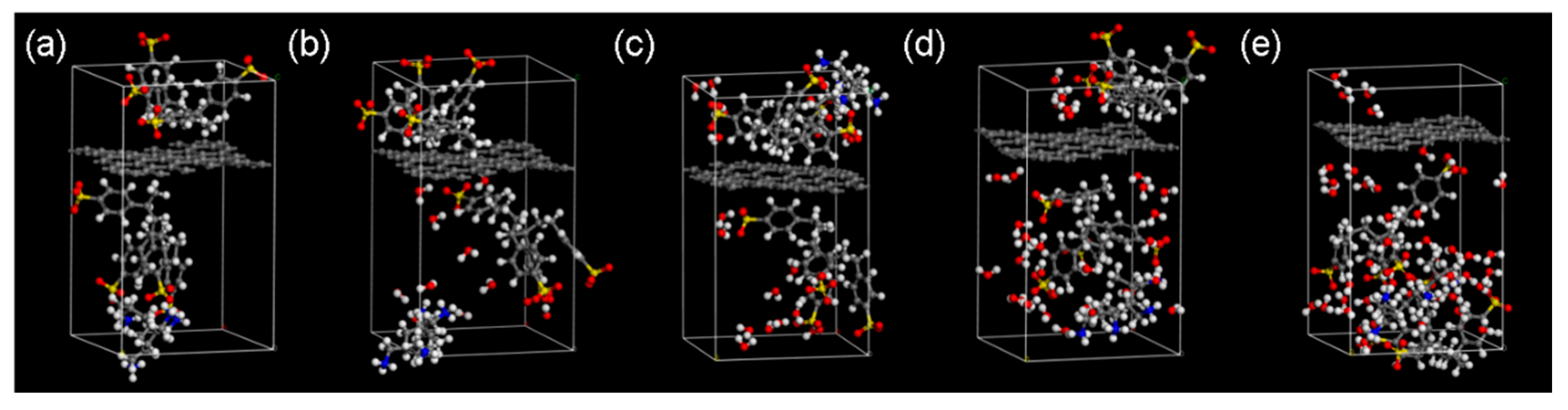

| Percentage of H2O /% | C | H | O | N | S | H2O | Density/g·cm−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 212 | 94 | 24 | 4 | 8 | 0 | 0.783 |
| 5 | 212 | 103 | 33 | 4 | 8 | 9 | 0.838 |
| 10 | 212 | 132 | 43 | 4 | 8 | 19 | 0.888 |
| 15 | 212 | 156 | 55 | 4 | 8 | 31 | 0.53 |
| 20 | 212 | 178 | 68 | 4 | 8 | 44 | 1.025 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, T.; Yang, R.; Yang, Z. Swelling Effects on the Conductivity of Graphene/PSS/PAH Composites. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123280
Zhao T, Yang R, Yang Z. Swelling Effects on the Conductivity of Graphene/PSS/PAH Composites. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(12):3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123280
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Tianbao, Ruyi Yang, and Zhi Yang. 2021. "Swelling Effects on the Conductivity of Graphene/PSS/PAH Composites" Nanomaterials 11, no. 12: 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123280
APA StyleZhao, T., Yang, R., & Yang, Z. (2021). Swelling Effects on the Conductivity of Graphene/PSS/PAH Composites. Nanomaterials, 11(12), 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123280





