NIR-to-NIR Imaging: Extended Excitation Up to 2.2 μm Using Harmonic Nanoparticles with a Tunable hIGh EneRgy (TIGER) Widefield Microscope
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Prepearation
2.2. Nonlinear Diffuse Femtosecond-Pulse Reflectometry
2.3. Tunable High-Energy (TIGER) Widefield Microscopy
3. Results
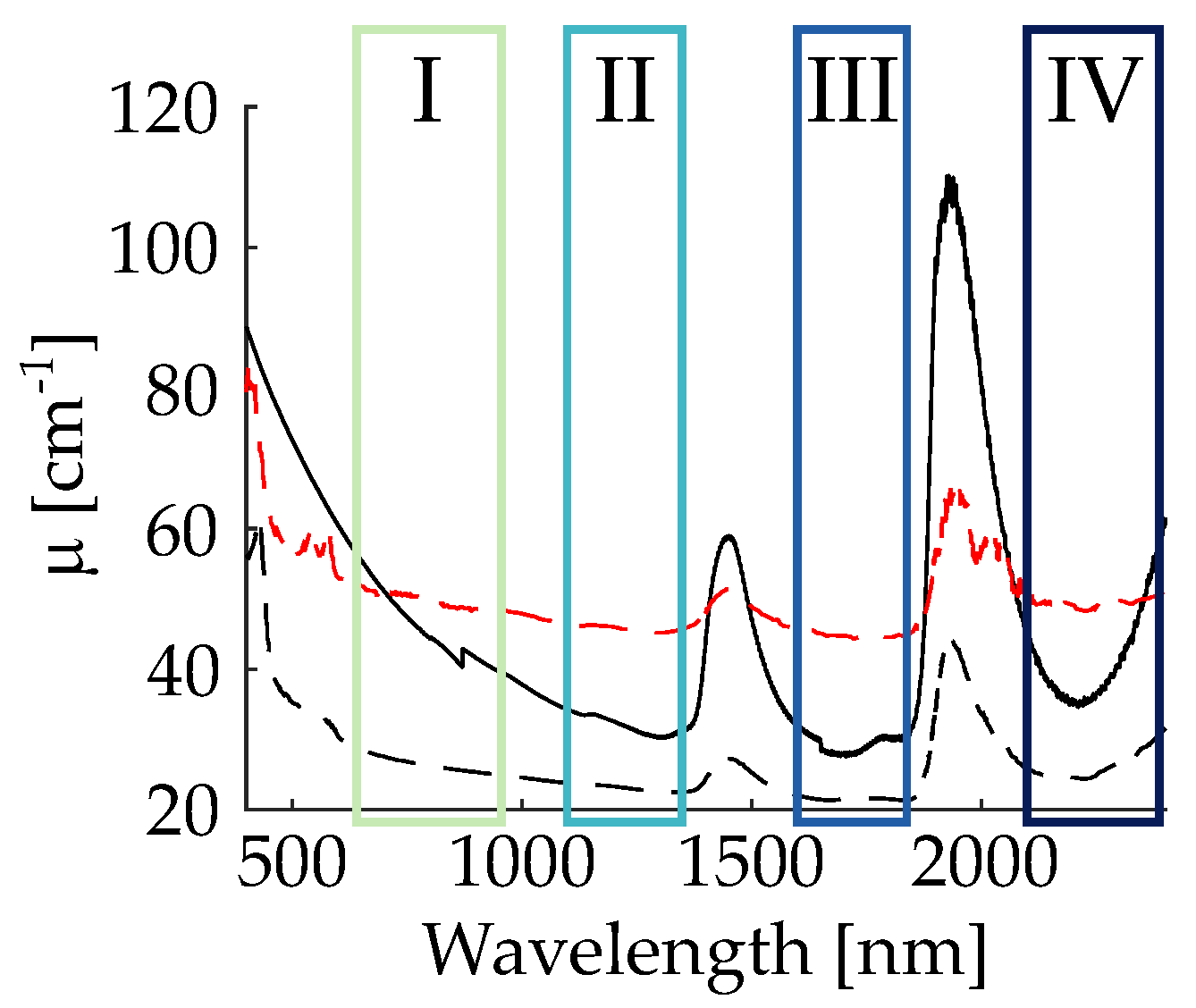
3.1. Nonlinear Diffuse Femtosecond-Pulse Reflectometry
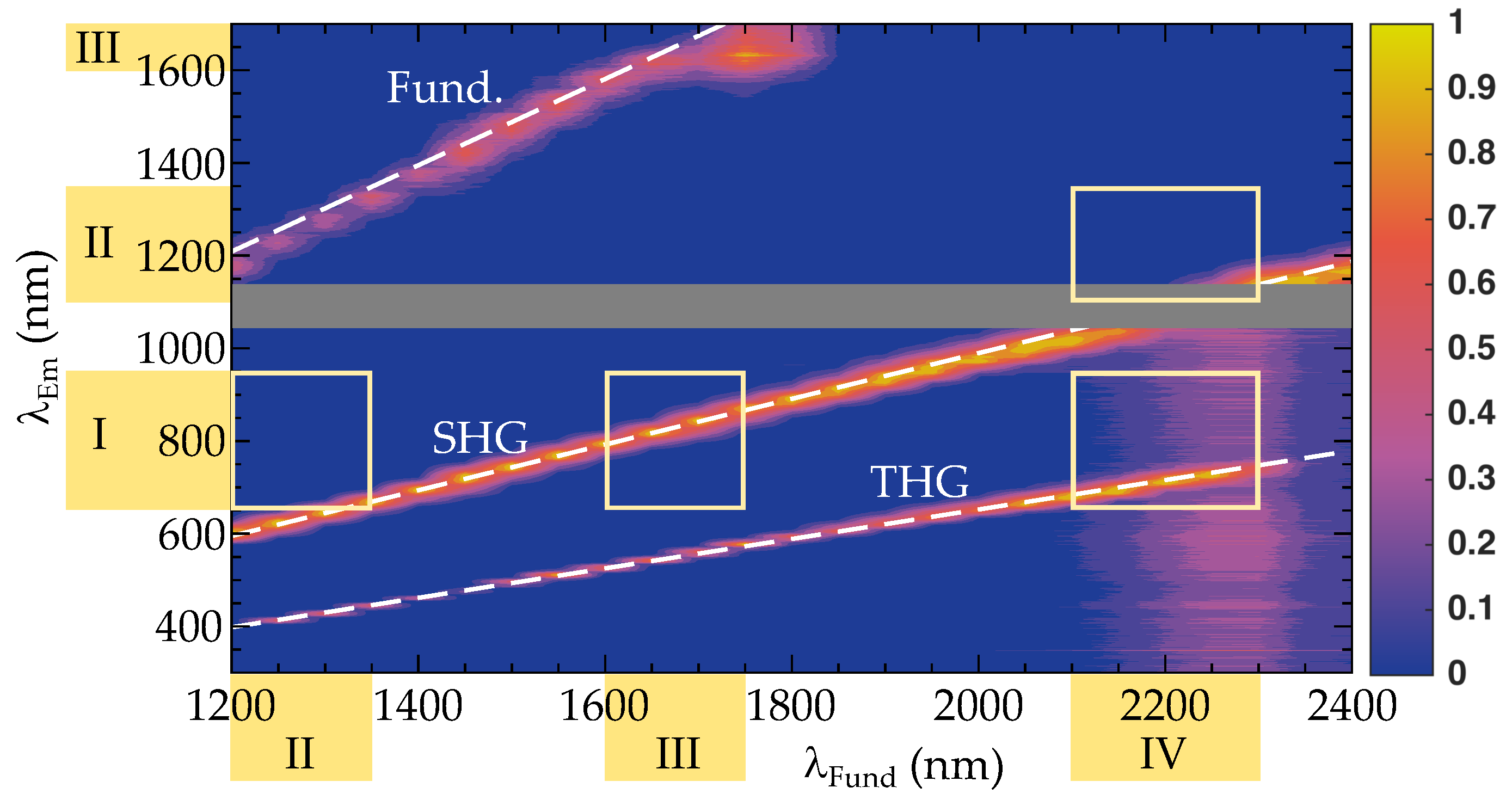
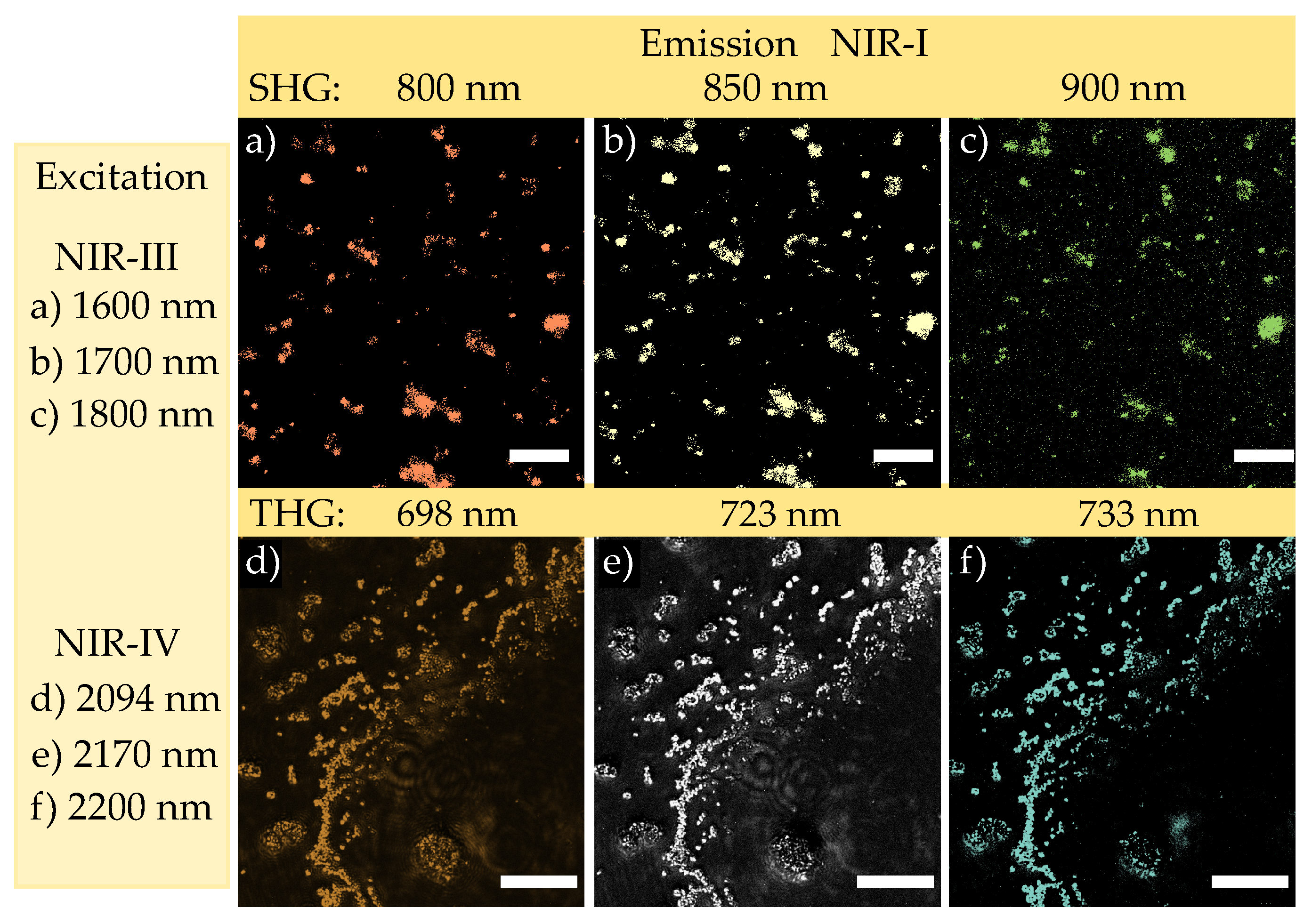
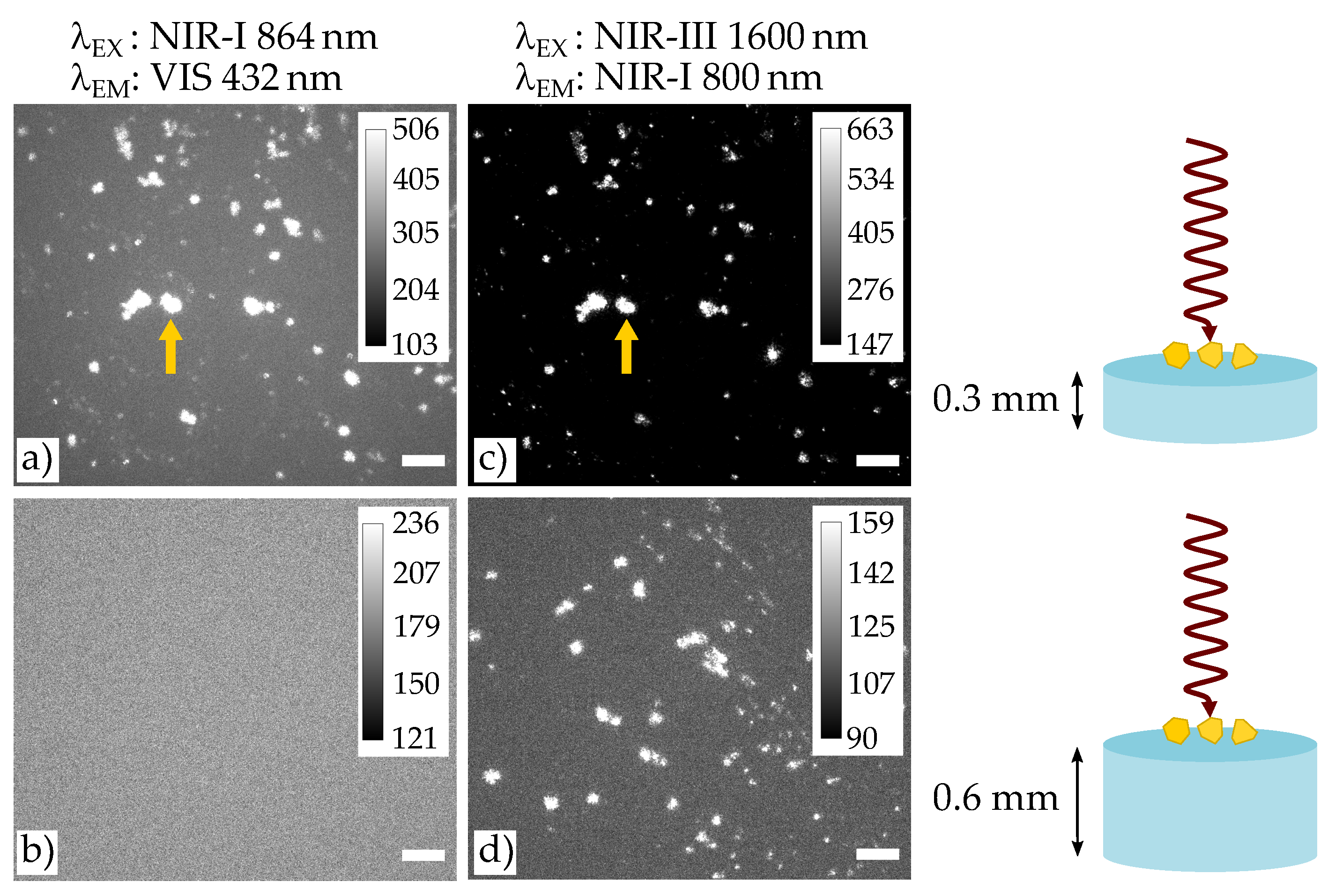
3.2. Tunable High-Energy (TIGER) Widefield Microscopy
4. Discussion
4.1. Nonlinear Diffuse fs-Pulse Reflectometry
4.2. NIR-III to NIR-I and NIR-IV to NIR-I Imaging Based on the TIGER Microscope
4.3. Perspective of Our Findings for NIR-Microscopy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NIR | Near-Infrared |
| HNP | Harmonic Nanoparticles |
| SHG | Second Harmonic Generation |
| THG | Third Harmonic Generation |
| SNR | Signal to Noise Ratio |
| OPA | Optical Parametric amplifier |
| SFG | Sum Frequency Generation |
| DFG | Difference Frequency Generation |
References
- Soga, K.; Umezawa, M.; Okubo, K. (Eds.) Transparency in Biology; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsher, K.; Sherlock, S.P.; Dai, H. Deep-tissue anatomical imaging of mice using carbon nanotube fluorophores in the second near-infrared window. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8943–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sordillo, L.A.; Pu, Y.; Pratavieira, S.; Budansky, Y.; Alfano, R.R. Deep optical imaging of tissue using the second and third near-infrared spectral windows. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 056004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmer, E.; Benayas, A.; Légaré, F.; Vetrone, F. Exploiting the biological windows: Current perspectives on fluorescent bioprobes emitting above 1000 nm. Nanoscale Horizons 2016, 1, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.M.; Conde, J.; Lipiński, T.; Bednarkiewicz, A.; Huang, C.C. Revisiting the classification of NIR-absorbing/emitting nanomaterials for in vivo bioapplications. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhu, B.; Zheng, K.; He, S.; Meng, L.; Song, J.; Yang, H. Recent Progress in NIR-II Contrast Agent for Biological Imaging. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Song, J.; Qu, J.; Cheng, Z. Crucial breakthrough of second near-infrared biological window fluorophores: Design and synthesis toward multimodal imaging and theranostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4258–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Sordillo, L.A.; Rodríguez-Contreras, A.; Alfano, R. Transmission in near-infrared optical windows for deep brain imaging. J. Biophotonics 2015, 9, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmer, E.; Venkatachalam, N.; Hyodo, H.; Hattori, A.; Ebina, Y.; Kishimoto, H.; Soga, K. Upconverting and NIR emitting rare earth based nanostructures for NIR-bioimaging. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordillo, D.C.; Sordillo, L.A.; Sordillo, P.P.; Shi, L.; Alfano, R.R. Short wavelength infrared optical windows for evaluation of benign and malignant tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovynskyi, S.; Golovynska, I.; Stepanova, L.I.; Datsenko, O.I.; Liu, L.; Qu, J.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y. Optical windows for head tissues in near-infrared and short-wave infrared regions: Approaching transcranial light applications. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201800141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Mancini, M.C.; Nie, S. Second window for in vivo imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vittadello, L.; Kijatkin, C.; Klenen, J.; Dzikonski, D.; Kömpe, K.; Meyer, C.; Paululat, A.; Imlau, M. In-vivo tracking of harmonic nanoparticles: A study based on a TIGER widefield microscope [Invited]. Opt. Mater. Express 2021, 11, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delehanty, J.B.; Boeneman, K.; Bradburne, C.E.; Robertson, K.; Medintz, I.L. Quantum dots: A powerful tool for understanding the intricacies of nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 1091–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Meenu, M.; Pandey, J.K.; Kumar, P.; Patel, R. Recent development in upconversion nanoparticles and their application in optogenetics: A review. J. Rare Earths 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuilleumier, J.; Gaulier, G.; Matos, R.D.; Mugnier, Y.; Campargue, G.; Wolf, J.P.; Bonacina, L.; Gerber-Lemaire, S. Photocontrolled Release of the Anticancer Drug Chlorambucil with Caged Harmonic Nanoparticles. Helv. Chim. Acta 2020, 103, e1900251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreil, L.; Leroux, I.; Ledevin, M.; Schleder, C.; Lagalice, L.; Lovo, C.; Fleurisson, R.; Passemard, S.; Kilin, V.; Gerber-Lemaire, S.; et al. Multi-harmonic Imaging in the Second Near-Infrared Window of Nanoparticle-Labeled Stem Cells as a Monitoring Tool in Tissue Depth. ASC Nano 2017, 11, 6672–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.W. Nonlinear Optics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 640. [Google Scholar]
- Kocsor, L.; Péter, L.; Corradi, G.; Kis, Z.; Gubicza, J.; Kovács, L. Mechanochemical Reactions of Lithium Niobate Induced by High-Energy Ball-Milling. Crystals 2019, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bock, S.; Kijatkin, C.; Berben, D.; Imlau, M. Absorption and Remission Characterization of Pure, Dielectric (Nano-)Powders Using Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy: An End-To-End Instruction. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pogue, B.W.; Patterson, M.S. Review of tissue simulating phantoms for optical spectroscopy, imaging and dosimetry. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 041102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijatkin, C.; Eggert, J.; Bock, S.; Berben, D.; Oláh, L.; Szaller, Z.; Kis, Z.; Imlau, M. Nonlinear Diffuse fs-Pulse Reflectometry of Harmonic Upconversion Nanoparticles. Photonics 2017, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.M.; Kumar, K.U.; Speghini, A.; Piccinelli, F.; Nodari, L.; Cannas, C.; Bettinelli, M.; Jaque, D.; Solé, J.G. Non-linear niobate nanocrystals for two-photon imaging. Opt. Mater. 2011, 33, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Steinbrück, A.; Buscaglia, M.T.; Buscaglia, V.; Pertsch, T.; Grange, R. Second-Harmonic Generation of Single BaTiO3 Nanoparticles down to 22 nm Diameter. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5343–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogov, A.; Irondelle, M.; Gomes, F.R.; Bode, J.; Staedler, D.; Passemard, S.; Courvoisier, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Waharte, F.; Ciepielewski, D.; et al. Simultaneous Multiharmonic Imaging of Nanoparticles in Tissues for Increased Selectivity. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joulaud, C.; Mugnier, Y.; Djanta, G.; Dubled, M.; Marty, J.C.; Galez, C.; Wolf, J.P.; Bonacina, L.; Dantec, R.L. Characterization of the nonlinear optical properties of nanocrystals by Hyper Rayleigh Scattering. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 11, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Grange, R.; Pu, Y.; Psaltis, D. Three-dimensional harmonic holographic microcopy using nanoparticles as probes for cell imaging. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 2880–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riporto, J.; Demierre, A.; Kilin, V.; Balciunas, T.; Schmidt, C.; Campargue, G.; Urbain, M.; Baltuska, A.; Dantec, R.L.; Wolf, J.P.; et al. Bismuth ferrite dielectric nanoparticles excited at telecom wavelengths as multicolor sources by second, third, and fourth harmonic generation. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 8146–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Pu, Y.; Grange, R.; Psaltis, D. Second harmonic generation from nanocrystals under linearly and circularly polarized excitations. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 11917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, C.; Riporto, J.; Uldry, A.; Rogov, A.; Mugnier, Y.; Dantec, R.L.; Wolf, J.P.; Bonacina, L. Multi-Order Investigation of the Nonlinear Susceptibility Tensors of Individual Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.R. Principles of Nonlinear Optics; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R.C. Optical second harmonic generation in piezoelectric crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1964, 5, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemla, D.S. Non-linear optical properties of condensed matter. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1980, 43, 1191–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riporto, J.; Urbain, M.; Mugnier, Y.; Multian, V.; Riporto, F.; Bredillet, K.; Beauquis, S.; Galez, C.; Monnier, V.; Chevolot, Y.; et al. Second harmonic spectroscopy of ZnO, BiFeO3 and LiNbO3 nanocrystals. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thierfelder, C.M.; Sanna, S.; Schindlmayr, A.; Schmidt, W.G. Do we know the band gap of lithium niobate. Phys. Status Solidi 2010, 7, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlau, M.; Badorreck, H.; Merschjann, C. Optical nonlinearities of small polarons in lithium niobate. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 040606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freytag, F.; Booker, P.; Corradi, G.; Messerschmidt, S.; Krampf, A.; Imlau, M. Picosecond near-to-mid-infrared absorption of pulse-injected small polarons in magnesium doped lithium niobate. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conradi, D.; Merschjann, C.; Schoke, B.; Imlau, M.; Corradi, G.; Polgár, K. Influence of Mg doping on the behaviour of polaronic light-induced absorption in LiNbO3. Phys. Status Solidi RRL -Rapid Res. Lett. 2008, 2, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extermann, J.; Bonacina, L.; Cuña, E.; Kasparian, C.; Mugnier, Y.; Feurer, T.; Wolf, J.P. Nanodoublers as deep imaging markers for multi-photon microscopy. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 15342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Dena, O.; García-Ramírez, E.V.; Fierro-Ruiz, C.D.; Vigueras-Santiago, E.; Farías, R.; Reyes-Esqueda, J.A. Effect of size and composition on the second harmonic generation from lithium niobate powders at different excitation wavelengths. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 035022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.M.; Speghini, A.; Piccinelli, F.; Nodari, L.; Bettinelli, M.; Jaque, D.; Solé, J.G. Multicolour second harmonic generation by strontium barium niobate nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Yuan, M.H.; Zeng, J.H.; Dai, Q.F.; Lan, S.; Xiao, C.; Tie, S.L. Controllable color display induced by excitation-intensity-dependent competition between second and third harmonic generation in ZnO nanorods. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsche Gesetzliche Unfallversicherung. Unfallverhütungsvorschrift Laserstrahlung; DGUV e.V: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kijatkin, C.; Bourdon, B.; Klenen, J.; Kocsor, L.; Szaller, Z.; Imlau, M. Time-Resolved Nonlinear Diffuse Femtosecond-Pulse Reflectometry Using Lithium Niobate Nanoparticles with Two Pulses of Different Colors. Adv. Photonics Res. 2021, 2, 2000019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campargue, G.; Volpe, L.L.; Giardina, G.; Gaulier, G.; Lucarini, F.; Gautschi, I.; Dantec, R.L.; Staedler, D.; Diviani, D.; Mugnier, Y.; et al. Multiorder Nonlinear Mixing in Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 8725–8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vittadello, L.; Klenen, J.; Koempe, K.; Kocsor, L.; Szaller, Z.; Imlau, M. NIR-to-NIR Imaging: Extended Excitation Up to 2.2 μm Using Harmonic Nanoparticles with a Tunable hIGh EneRgy (TIGER) Widefield Microscope. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123193
Vittadello L, Klenen J, Koempe K, Kocsor L, Szaller Z, Imlau M. NIR-to-NIR Imaging: Extended Excitation Up to 2.2 μm Using Harmonic Nanoparticles with a Tunable hIGh EneRgy (TIGER) Widefield Microscope. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(12):3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123193
Chicago/Turabian StyleVittadello, Laura, Jan Klenen, Karsten Koempe, Laura Kocsor, Zsuzsanna Szaller, and Mirco Imlau. 2021. "NIR-to-NIR Imaging: Extended Excitation Up to 2.2 μm Using Harmonic Nanoparticles with a Tunable hIGh EneRgy (TIGER) Widefield Microscope" Nanomaterials 11, no. 12: 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123193
APA StyleVittadello, L., Klenen, J., Koempe, K., Kocsor, L., Szaller, Z., & Imlau, M. (2021). NIR-to-NIR Imaging: Extended Excitation Up to 2.2 μm Using Harmonic Nanoparticles with a Tunable hIGh EneRgy (TIGER) Widefield Microscope. Nanomaterials, 11(12), 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123193






