Solution Blow Spun Silica Nanofibers: Influence of Polymeric Additives on the Physical Properties and Dye Adsorption Capacity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Production of Nanofibers
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Evaluation
2.4.1. Adsorption Isotherm Studies
2.4.2. Thermodynamic Studies
2.4.3. Kinetic Studies
2.4.4. Statistical Parameters
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noh, W.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, K.-W.; Lee, T.S. Selective adsorption of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate from a Cs ion mixture by electrospun mesoporous silica nanofibers. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Maneuvering the ordered mesoporosity of electrospun silica nanofibers for water harvesting. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 281, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagboya, P.N.; Dikio, E.D. Silica-based mesoporous materials. emerging designer adsorbents for aqueous pollutants removal and water treatment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 266, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, J.; Arsuaga, J.M.; Arencibia, A.; Lindo, M.; Gascón, V. Aqueous heavy metals removal by adsorption on amine-functionalized mesoporous silica. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Dong, B.; Wang, C. Adsorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solution by anatase mesoporous TiO2 nanofibers prepared via electrospinning. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Tian, N.; Tian, X.; Ma, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on amine-functionalized ordered mesoporous alumina. J. Porous Mater. 2015, 22, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.-N.; Zhang, B.; Li, F. Dendrimer-based preparation of mesoporous alumina nanofibers by electrospinning and their application in dye adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jia, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, R. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous carbon nanofibers and its adsorption for dye in wastewater. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, C.; Yuan, K.; Gan, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Template-free synthesis of MgO mesoporous nanofibers with superior adsorption for fluoride and Congo red. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 9454–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Ozisik, R.; Kotha, S.P. Rapid and efficient fabrication of multilevel structured silica micro-/nanofibers by centrifugal jet spinning. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 425, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, R.M.D.C.; Severo, L.L.; da Costa, D.L.; de Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Santata, L.N.D.L.; Neves, G.D.A.; Kiminami, R.H.G.A.; Menezes, R.R. Solution blow spun spinel ferrite and highly porous silica nanofibers. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 10984–10989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, R.M.D.C.; Mota, M.F.; Severo, L.L.; de Medeiros, E.S.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Avena-Bustillos, R.D.J.; Santana, L.N.D.L.; Neves, G.A.; Glenn, G.M.; Menezes, R. Green Synthesis of Porous N-Carbon/Silica Nanofibers by Solution Blow Spinning and Evaluation of Their Efficiency in Dye Adsorption. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3038–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Orts, W.J.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution blow spinning: A new method to produce micro- and nanofibers from polymer solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daristotle, J.L.; Behrens, A.M.; Sandler, A.; Kofinas, P. Review of the Fundamental Principles and Applications of Solution Blow Spinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34951–34963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.T. Nanofiber technology: Current status and emerging developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J.; Galán, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Walker, G. Dye adsorption onto mesoporous materials: pH influence. kinetics and equilibrium in buffered and saline media. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.-T.; Chen, X.; He, X.-M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y.-Q. Electrospun Highly Ordered Mesoporous Silica–Carbon Composite Nanofibers for Rapid Extraction and Prefractionation of Endogenous Peptides. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 4450–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherifi, Z.; Boukoussa, B.; Mokhtar, A.; Hachemaoui, M.; Zeggai, F.Z.; Zaoui, A.; Bachari, K.; Meghabar, R. Preparation of new nanocomposite poly(GDMA)/mesoporous silica and its adsorption behavior towards cationic dye. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 153, 104611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisir, M.; Kilic, A. A comparative study on SiO2 Nanofiber Production via Two Novel Non-Electrospinning Methods: Centrifugal Spinning vs Solution Blowing. Mater. Lett. 2020, 258, 126751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahhosseininia, M.; Bazgir, S.; Joupari, M.D. Fabrication and investigation of silica nanofibers via electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udayabhaskar, R.; Mangalaraja, R.; Manikandan, D.; Arjunan, V.; Karthikeyan, B. Room temperature synthesis and optical studies on Ag and Au mixed nanocomposite polyvinylpyrrolidone polymer films. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 99, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, R.; Huang, Y.; Liang, Q.; Huang, Z. A Non-Woven Network of Porous Nitrogen-doping Carbon Nanofibers as a Binder-free Electrode for Supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 230, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Moraes, E.A.; Costa, R.G.F.; Afonso, A.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Orts, W.J.; Medeiros, E.S. Nano and submicrometric fibers of poly(D.L-Lactide) obtained by solution blow spinning: Process and solution variables. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 5, 3396–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotta, M.; Zadorosny, L.; Carvalho, C.; Malmonge, J.; Malmonge, L.F. YBCO ceramic nanofibers obtained by the new technique of solution blow spinning. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 16230–16234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harkins, W.D.; Jura, G. Surfaces of solids: XIII. A vapor adsorption method for the determination of the area of a solid without the assumption of a molecular area. and the areas occupied by nitrogen and other molecules on the surface of a solid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Kyzas, G.Z. Are the thermodynamic parameters correctly estimated in liquid-phase adsorption phenomena? J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 218, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Lu, W.; Jiang, L. The fabrication of photosensitive self-assembly Au nanoparticles embedded in silica nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 340, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogatyrev, V.M.; Borisenko, N.V.; Pokrovskii, V.A. Thermal Degradation of Polyvinylpyrrolidone on the Surface of Pyrogenic Silica. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2001, 74, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Soldi, M.; Pinheiro, E.; Pires, A.; Gehlen, M.; Soldi, V. Thermal stability of poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone-co-methacrylic acid) copolymers in inert atmosphere. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 80, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, A.E.; Lang, A.J.; Vyazovkin, S. Isoconversional kinetics of degradation of polyvinylpyrrolidone used as a matrix for ammonium nitrate stabilization. Thermochim. Acta 2008, 474, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. Fabrication of refining mesoporous silica nanofibers via electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kang, S.-H.; Manuel, J.; Zhao, X.; Cho, K.K.; Ahn, J.H. Investigation into the role of silica in lithium polysulfide adsorption for lithium sulfur battery. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 69, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, F.; Turkyilmaz, M.; Küçükçongar, S. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by silica gel supported calix [4] arene cage: Investigation of adsorption properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 125, 109540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, C.; He, X. Fabrication of mesoporous dendritic silica nanofibers by using dendritic polyaniline templates. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, F.; Wang, H.; Fu, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, G. Effects of poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) content on preparation of novel thiol-functionalized mesoporous PVA/SiO2 composite nanofiber membranes and their application for adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Polymer 2010, 51, 6203–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Feng, S.; Li, S.; Jing, Y.; Shao, C. Bromopropyl functionalized silica nanofibers for effective removal of trace level dieldrin from water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 406, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Elma, M.; Wang, D.; Motuzas, J.; da Costa, J.C.D. Interlayer-free hybrid carbon-silica membranes for processing brackish to brine salt solutions by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowell, S.; Shields, J.E.; Thomas, M.A.; Thommes, M. Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area. Pore Size and Density; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alothman, Z.A. A Review: Fundamental Aspects of Silicate Mesoporous Materials. Materials 2012, 12, 2874–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghimire, P.; Gunathilake, C.; Wickramaratne, N.P.; Jaroniec, M. Tetraethyl orthosilicate-assisted synthesis of nitrogen-containing porous carbon spheres. Carbon 2017, 121, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araghi, S.H.; Entezari, M.H. Amino-functionalized silica magnetite nanoparticles for the simultaneous removal of pollutants from aqueous. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 333, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Xu, F.; Wei, W.; Gao, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P. Efficient and fast adsorption of methylene blue dye onto a nanosheet MFI zeolite. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 295, 121917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, O.V.; Evtukhova, A.V.; Kondratenko, T.; Smirnov, M.; Khokhlov, V.Y.; Erina, O.V. Manifestation of intermolecular interactions in FTIR spectra of methylene blue molecules. Vib. Spectrosc. 2016, 86, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, E.; Metin, A.; Brouers, F. Methylene blue adsorption on magnetic alginate/rice husk biocomposit. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Cai, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, R. Electrospun metal-organic frameworks with polyacrylonitrile as precursors to hierarchical porous carbon and composite nanofibers for adsorption and catalysis. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Sun, J.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.; et al. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by graphene. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Wang, F.; Liang, L.; Liu, M.; Sun, J. Magnetically separable nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon with high adsorption capacity. J. Mat. Sci. 2016, 51, 3868–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germi, T.A.; Nematollahzadeh, A. Bimodal porous silica microspheres decorated with polydopamine nano-particles for the adsorption of methylene blue in fixed-bed columns. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 470, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, M. Removal of methylene blue and mechanism on magnetic γ-Fe2O3/SiO2 nanocomposite from aqueous solution. Water Resour. Ind. 2016, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
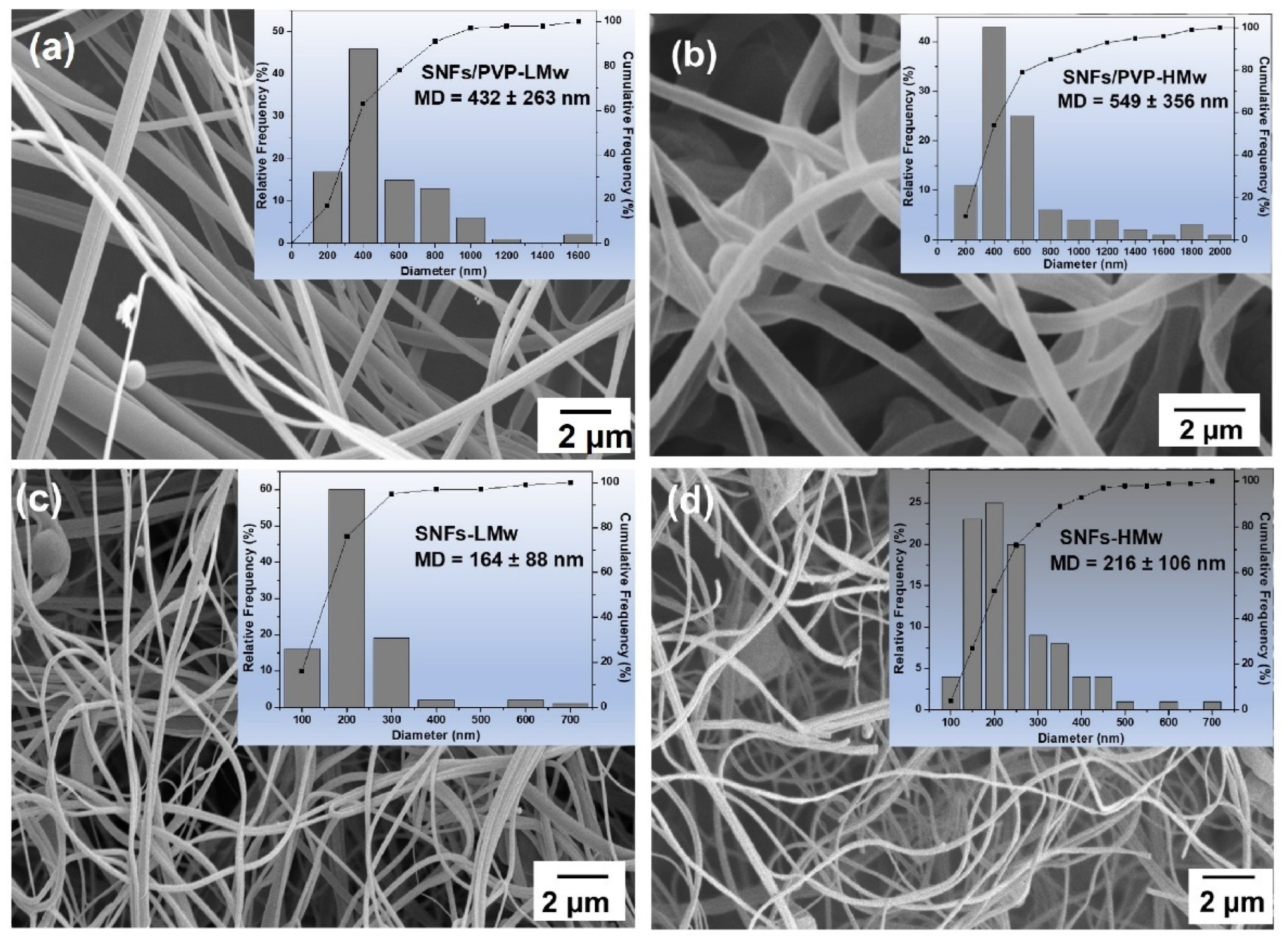

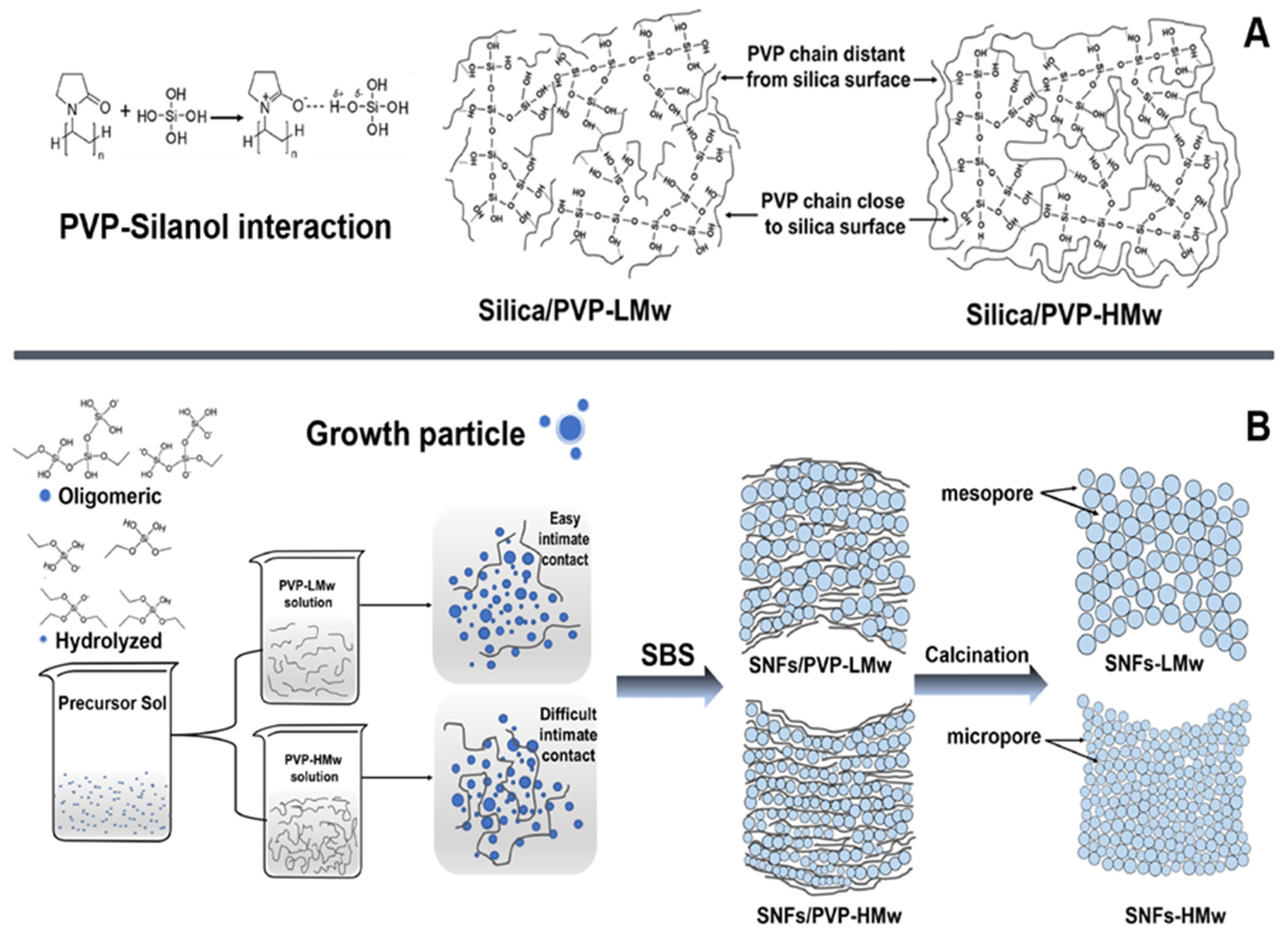
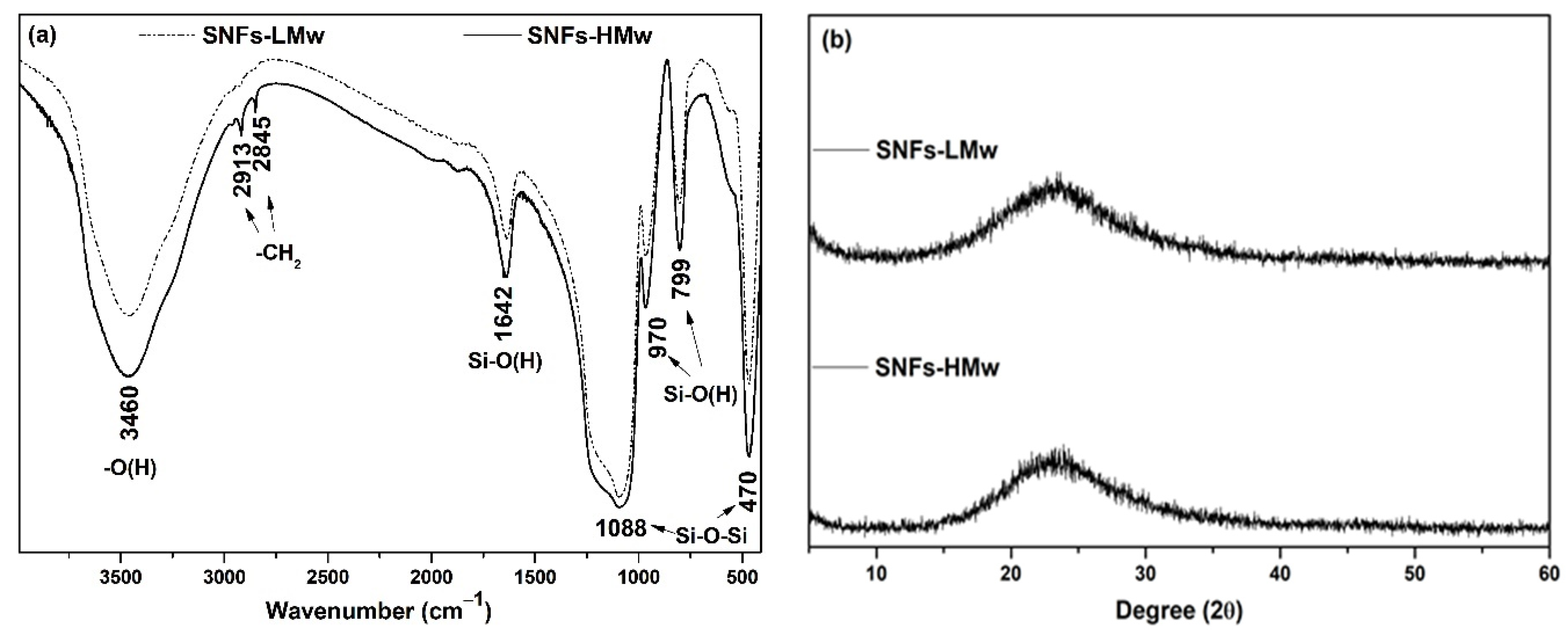
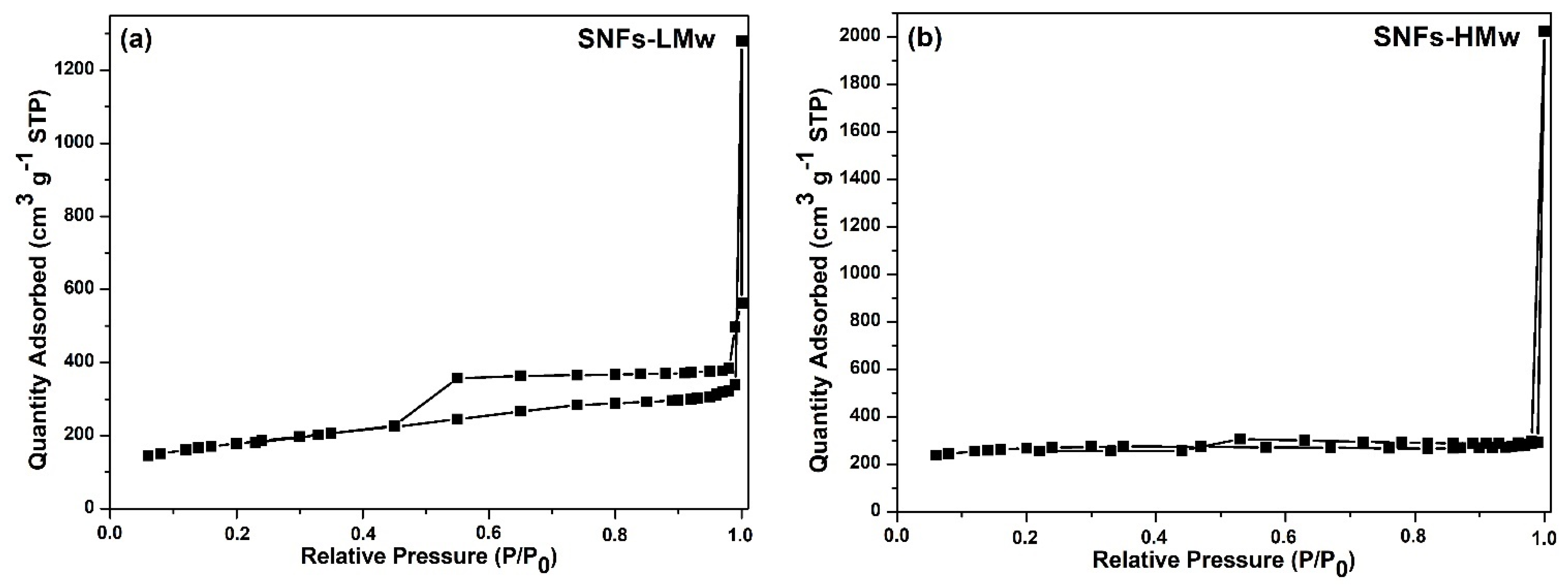


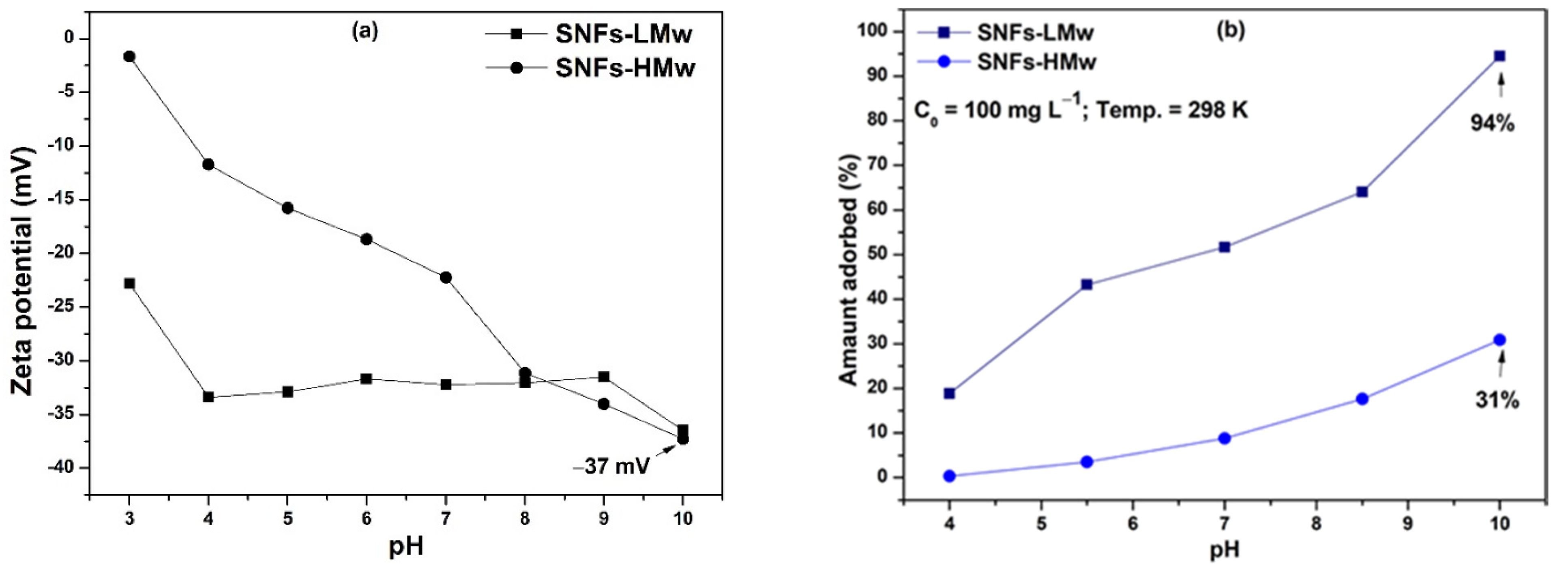
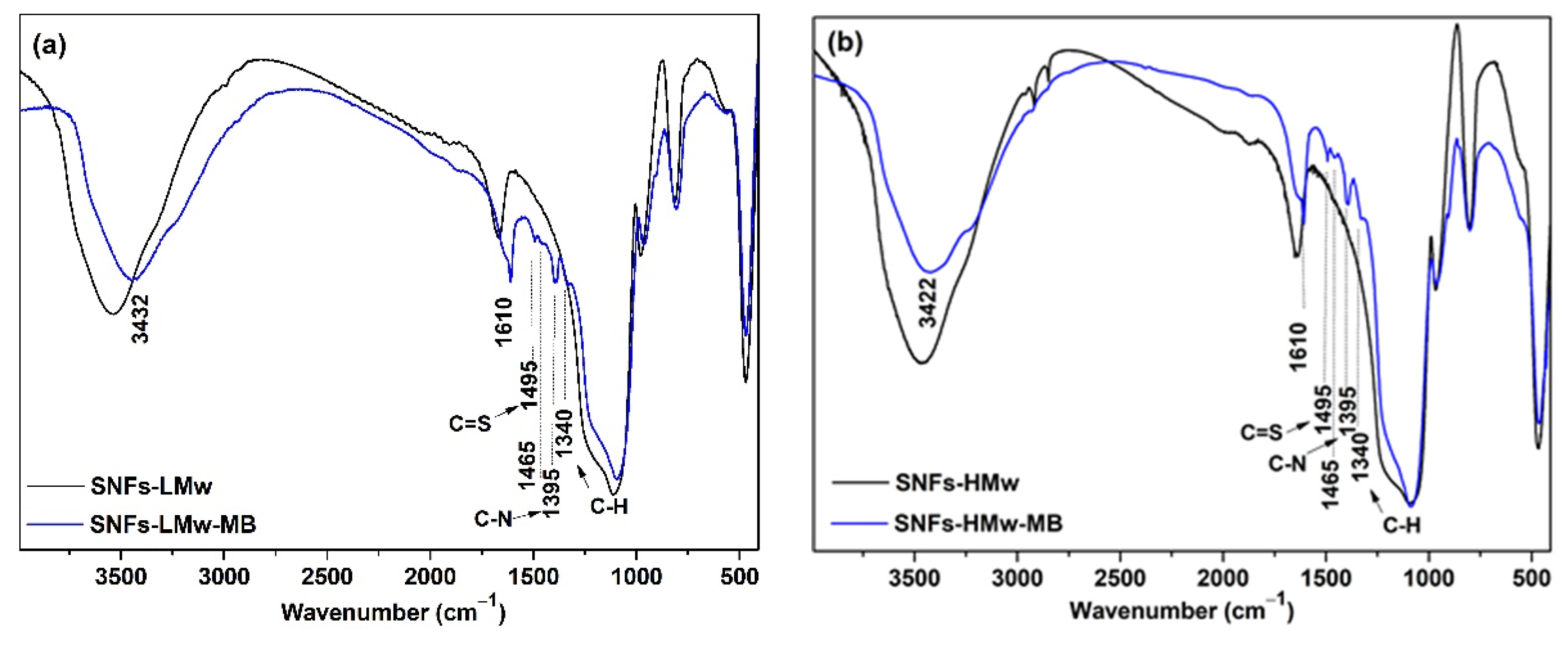
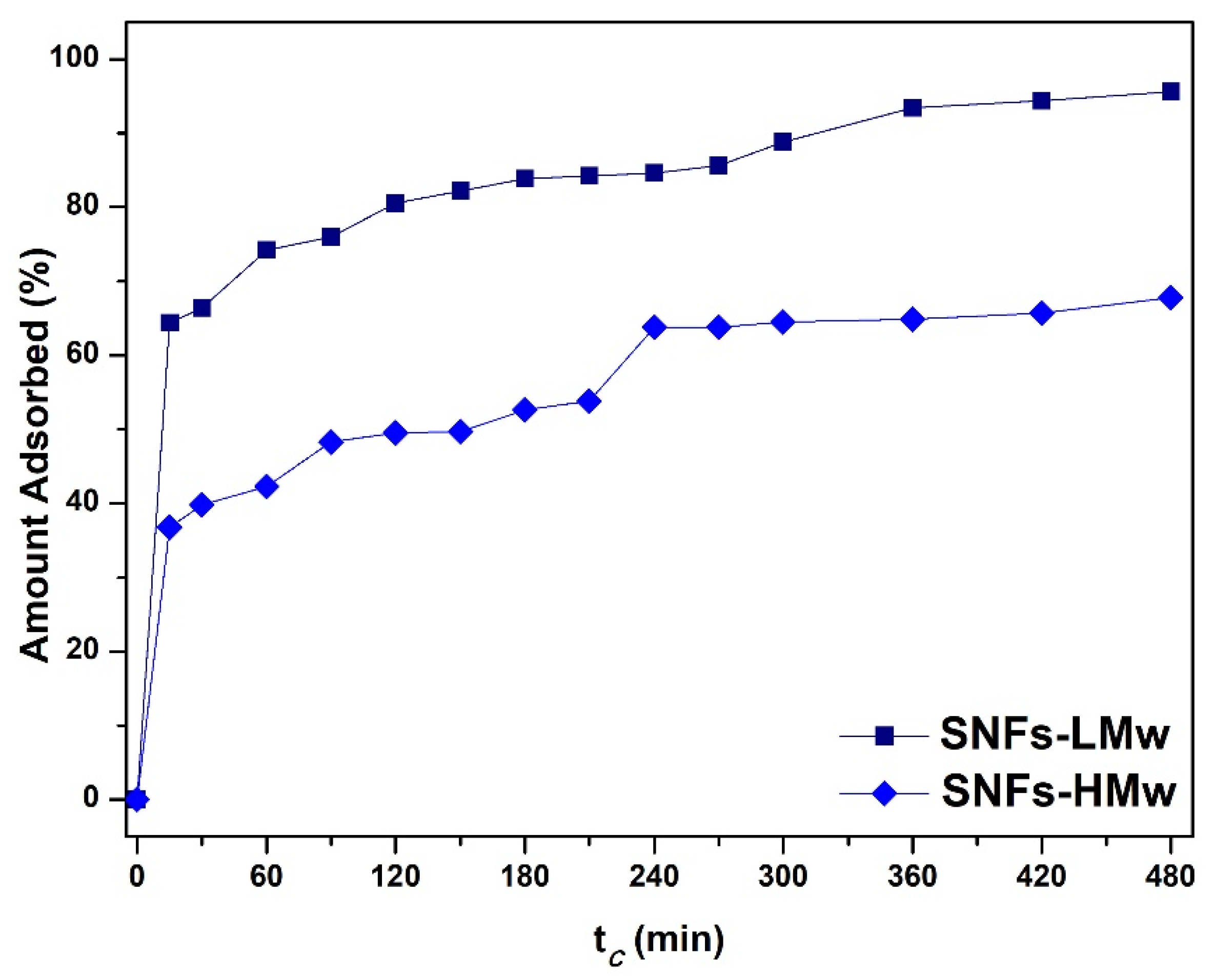
| Sample | C[%] | H[%] | N[%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNFs-LMw | 0.65 | 1.71 | 0.54 |
| SNFs-HMw | 1.86 | 1.29 | 0.56 |
| Sample | BET [m2 g−1] | BJH Desorption (a) [cm3 g−1] | Pore Diameter (b) [nm] | Micropore Volume (c) [cm3 g−1] | Micropore Area (d) [m2 g−1] | External Surface Area (e) [m2 g−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNFs-LMw | 635.6 | 0.747 | 3.67 | 0.05 | 118.9 | 516.7 |
| SNFs-HMw | 921.7 | 0.122 | 1.99 | 0.23 | 510.3 | 411.3 |
| Sample | Temperature [K] | Langmuir | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe [mg g−1] | Qmax (cal) [mg g−1] | KL [L mg−1] | R2 | SD [%] | RMSE | ||
| SNFs-LMw | 298 308 318 | 278.8 250.0 243.2 | 275.5 247.6 238.1 | 0.29 0.29 0.19 | 0.996 0.999 0.994 | 0.41 0.22 0.32 | 1.17 0.30 5.10 |
| SNFs-HMw | 298 308 318 | 123.3 72.9 69.9 | 121.9 72.8 69.7 | 0.05 0.11 0.09 | 0.987 0.997 0.997 | 0.18 0.01 0.03 | 0.49 0.01 0.03 |
| Freundlich | |||||||
| 1/n | KF [mg g−1] [L mg−1] | R2 | SD [%] | RMSE | |||
| SNFs-LMw | 298 308 318 | 0.14 0.10 0.14 | 122.4 126.7 141.2 | 0.883 0.867 0.897 | 39.12 30.82 25.50 | 78.2 24.7 20.4 | |
| SNFs-HMw | 298 308 318 | 0.13 0.17 0.31 | 31.6 25.1 16.5 | 0.808 0.812 0.852 | 15.34 9.56 8.90 | 37.4 7.9 7.6 | |
| Pseudo-First-Order Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Qe(exp) [mg g−1] | Qe(calc) [mg g−1] | K1 [10−3 min−1] | R2 | SD | RMSE |
| SNFs-LMw | 191.20 | 80.40 | 7.12 | 0.881 | 30.73 | 29.61 |
| SNFs-HMw | 135.67 | 80.22 | 7.34 | 0.913 | 15.38 | 14.82 |
| Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||||||
| Qe(calc) [mg g−1] | K2 [10−4 g mg−1 min−1] | R2 | SD | RMSE | ||
| SNFs-LMw | 191.20 | 181.82 | 4.42 | 0.998 | 2.51 | 2.42 |
| SNFs-HMw | 135.6 | 140.80 | 2.09 | 0.983 | 1.39 | 1.34 |
| Intra-Particle Diffusion | ||||||
| C [mg g−1] | Kdif [mg g−1 min−1/2] | R2 | SD | RMSE | ||
| SNFs-LMw | 191.20 | 118.64 | 11.83 | 0.971 | 20.12 | 19.39 |
| SNFs-HMw | 135.6 | 58.65 | 14.04 | 0.938 | 21.34 | 20.56 |
| SNFs-LMw | SNFs-HMw | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (K) | 298 | 308 | 318 | 298 | 308 | 318 |
| lnK | 15.44 | 15.45 | 15.03 | 13.70 | 14.45 | 14.26 |
| ΔG⁰ (kJ mol−1) | −38.25 | −39.56 | −39.74 | −33.94 | −35.98 | −37.70 |
| ΔH⁰ (kJ mol−1) | −15.49 | 21.16 | ||||
| ΔS⁰ (J mol−1 K−1) | 76.90 | 186.30 | ||||
| Adsorbent | BET [m2 g−1] | BJH Desorption [cm3 g−1] | Pore Diameter [nm] | Qe (mg g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesoporous carbon nanofibers | 392.3 | - | 3–5 | 58.992 | [8] |
| SBA15 Silica gel Mesoporous carbon MCSG60 | 780 440 650 | - | 7 6 8 | ~20 ~20 ~200 | [16] |
| Porous carbon nanofibers | 885.551 | 0.967 | 3.928 | 123.64 | [45] |
| Graphene | 295.56 | - | 3.49 | 153.85 | [46] |
| N-doped mesoporous carbon- | 166.9 | - | 3.2 and 6.0 | 163 | [47] |
| meso/macro-porous silica microspheres coated with polydopamine MSM@PDA | 612.3 | 0.91 | 6 and 100 | 83.30 | [48] |
| γ-Fe2O3/SiO2 | 74.35 | - | - | 116.09 | [49] |
| SNFs-LMw | 635.6 | 0.747 | 3.67 | 278.8 | This work |
| SNFs-HMw | 921.7 | 0.122 | 1.99 | 123.3 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farias, R.M.d.C.; Severo, L.L.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Medeiros, E.S.d.; Santana, L.N.d.L.; Neves, G.d.A.; Glenn, G.M.; Menezes, R.R. Solution Blow Spun Silica Nanofibers: Influence of Polymeric Additives on the Physical Properties and Dye Adsorption Capacity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113135
Farias RMdC, Severo LL, Klamczynski AP, Medeiros ESd, Santana LNdL, Neves GdA, Glenn GM, Menezes RR. Solution Blow Spun Silica Nanofibers: Influence of Polymeric Additives on the Physical Properties and Dye Adsorption Capacity. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113135
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarias, Rosiane Maria da Costa, Lucas Leite Severo, Artur P. Klamczynski, Eliton Souto de Medeiros, Lisiane Navarro de Lima Santana, Gelmires de Araújo Neves, Gregory Melvin Glenn, and Romualdo Rodrigues Menezes. 2021. "Solution Blow Spun Silica Nanofibers: Influence of Polymeric Additives on the Physical Properties and Dye Adsorption Capacity" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113135
APA StyleFarias, R. M. d. C., Severo, L. L., Klamczynski, A. P., Medeiros, E. S. d., Santana, L. N. d. L., Neves, G. d. A., Glenn, G. M., & Menezes, R. R. (2021). Solution Blow Spun Silica Nanofibers: Influence of Polymeric Additives on the Physical Properties and Dye Adsorption Capacity. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113135








