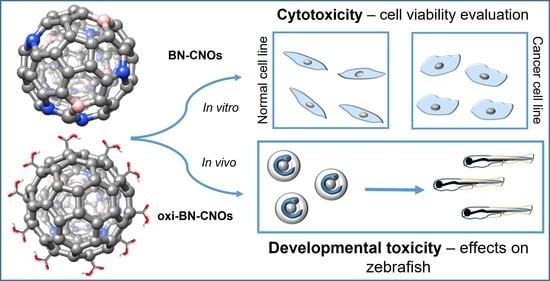
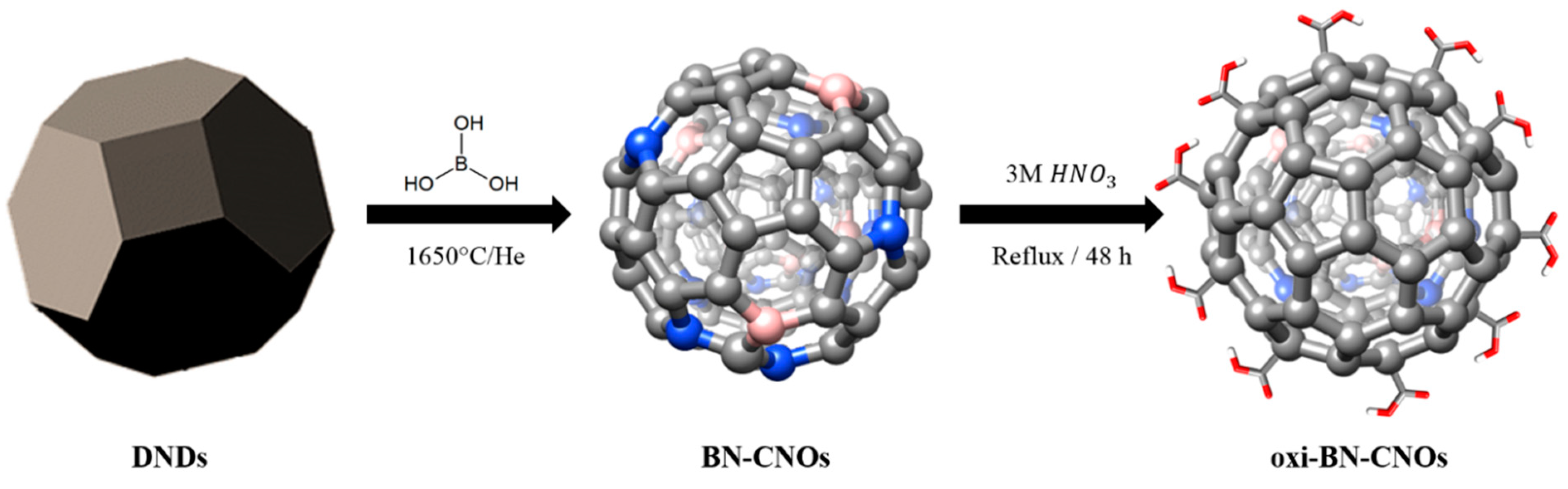
In Vitro and In Vivo Biocompatibility of Boron/Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Material Synthesis and Characterization
2.3. In Vitro Biological Methods
Cell Culture
2.4. In Vivo Biological Methods
Husbandry and Toxicity Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
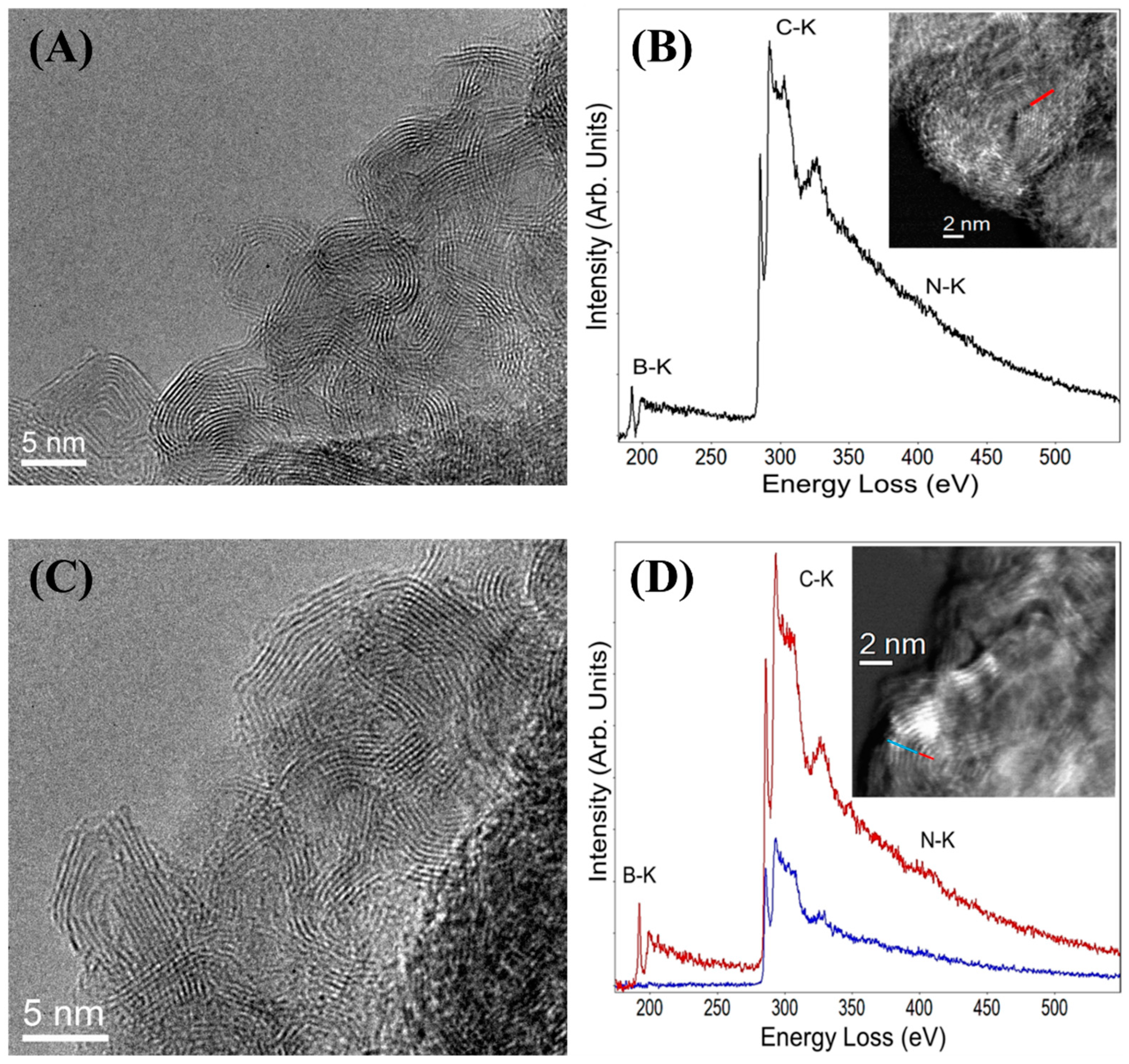
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the CNO Materials
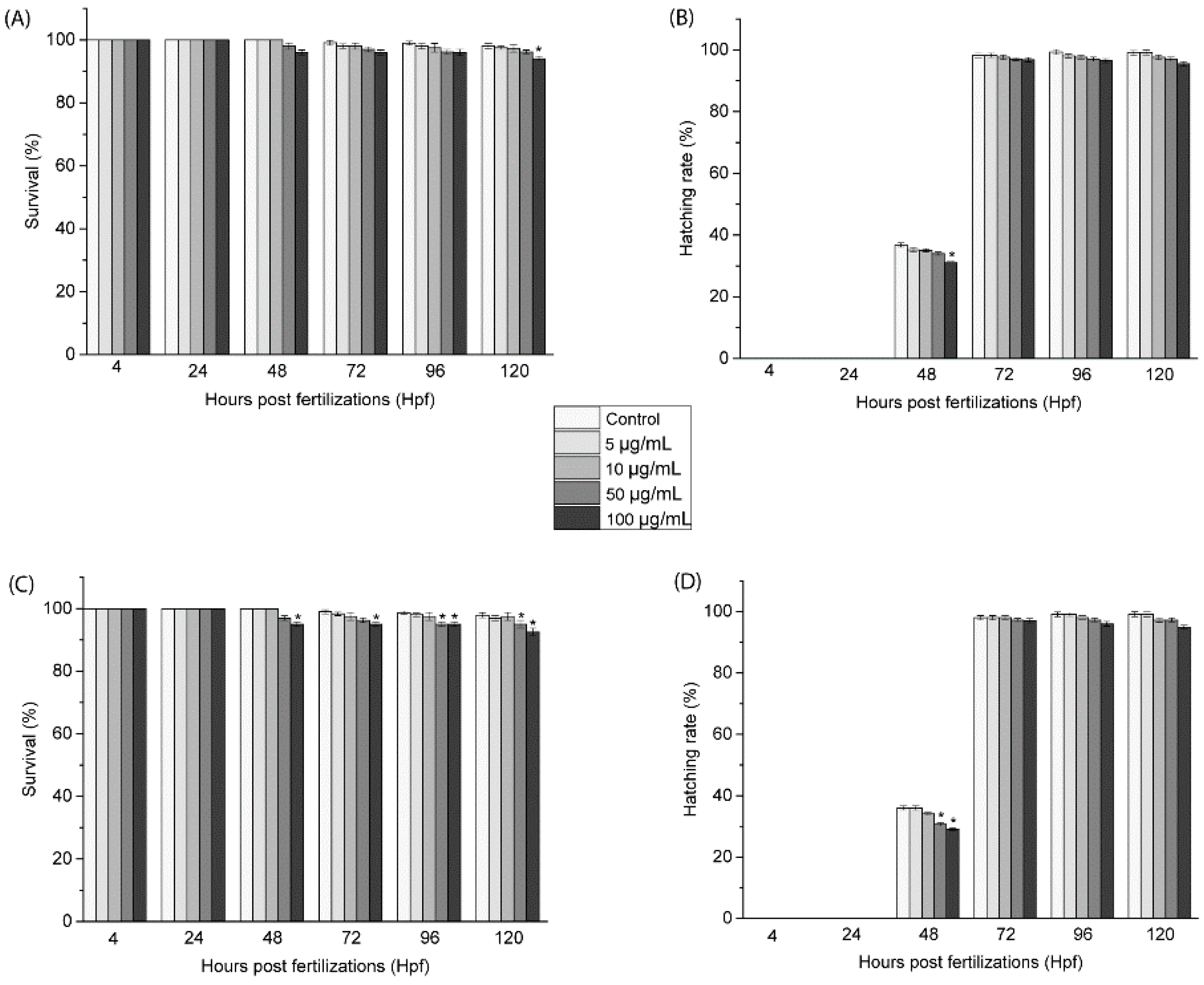
3.2. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ugarte, D. Curling and closure of graphitic networks under electron-beam irradiation. Nature 1992, 359, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camisasca, A.; Giordani, S. Carbon nano-onions in biomedical applications: Promising theranostic agents. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 468, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, S.; Camisasca, A.; d’Amora, M.; Diaspro, A.; Uchida, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Yanagisawa, K.; Maekawa, T.; Giordani, S. Far-red fluorescent carbon nano-onions as a biocompatible platform for cellular imaging. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 45676–45681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- d’Amora, M.; Maffeis, V.; Brescia, R.; Barnes, D.; Scanlan, E.; Giordani, S. Carbon Nano-Onions as Non-Cytotoxic Carriers for Cellular Uptake of Glycopeptides and Proteins. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- d’Amora, M.; Camisasca, A.; Lettieri, S.; Giordani, S. Toxicity Assessment of Carbon Nanomaterials in Zebrafish during Development. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frasconi, M.; Marotta, R.; Markey, L.; Flavin, K.; Spampinato, V.; Ceccone, G.; Echegoyen, L.; Scanlan, E.M.; Giordani, S. Multi-Functionalized Carbon Nano-onions as Imaging Probes for Cancer Cells. Chemistry 2015, 21, 19071–19080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordani, S.; Camisasca, A.; Maffeis, V. Carbon Nano-onions: A Valuable Class of Carbon Nanomaterials in Biomedicine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6915–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camisasca, A.; Giordani, S. Carbon Nano-onions for Bioimaging and Cancer Therapy Applications. In Nanooncology: Engineering Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis; Gonçalves, G., Tobias, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 417–455. [Google Scholar]
- Bartkowski, M.; Giordani, S. Carbon nano-onions as potential nanocarriers for drug delivery. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breczko, J.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Echegoyen, L. Electrochemical oxidation and determination of dopamine in the presence of uric and ascorbic acids using a carbon nano-onion and poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) composite. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 72, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolome, J.P.; Echegoyen, L.; Fragoso, A. Reactive Carbon Nano-Onion Modified Glassy Carbon Surfaces as DNA Sensors for Human Papillomavirus Oncogene Detection with Enhanced Sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6744–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, J.; Ananthoju, B.; Nair, V.; Mitra, A.; Bahadur, D.; Medhekar, N.V.; Aslam, M. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on carbon nano-onions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 442, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumba, L.R.; Camisasca, A.; Giordani, S.; Forster, R.J. Electrochemical Properties of Screen-Printed Carbon Nano-Onion Electrodes. Molecules 2020, 25, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camisasca, A.; Sacco, A.; Brescia, R.; Giordani, S. Boron/Nitrogen-Codoped Carbon Nano-Onion Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 5763–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Cellular Toxicity and Immunological Effects of Carbon-based Nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriga, R.; Herrero-Continente, T.; Palos, M.; Cebolla, V.L.; Osada, J.; Muñoz, E.; Rodríguez-Yoldi, M.J. Toxicity of Carbon Nanomaterials and Their Potential Application as Drug Delivery Systems: In Vitro Studies in Caco-2 and MCF-7 Cell Lines. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jović, D.; Jaćević, V.; Kuča, K.; Borišev, I.; Mrdjanovic, J.; Petrovic, D.; Seke, M.; Djordjevic, A. The Puzzling Potential of Carbon Nanomaterials: General Properties, Application, and Toxicity. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, R.T.; MacRae, C.A. Systematic Approaches to Toxicology in the Zebrafish. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as tools for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCollum, C.W.; Ducharme, N.A.; Bondesson, M.; Gustafsson, J.-A. Developmental toxicity screening in zebrafish. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2011, 93, 67–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blechinger Scott, R.; Warren James, T.; Kuwada John, Y.; Krone Patrick, H. Developmental toxicology of cadmium in living embryos of a stable transgenic zebrafish line. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Truong, L.; Harper, S.L.; Tanguay, R.L. Evaluation of Embryotoxicity Using the Zebrafish Model. In Drug Safety Evaluation: Methods and Protocols; Gautier, J.-C., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- d’Amora, M.; Giordani, S. Zebrafish Models of Nanotoxicity: A Comprehensive Account. In Nanomaterial Biointeractions at the Cellular, Organismal and System Levels; Sharma, N., Sahi, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 53–72. [Google Scholar]
- d’Amora, M.; Lamberti, A.; Fontana, M.; Giordani, S. Toxicity assessment of laser-induced graphene by zebrafish during development. J. Phys. Mater. 2020, 3, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenal, R.; de la Peña, F.; Stéphan, O.; Walls, M.; Tencé, M.; Loiseau, A.; Colliex, C. Extending the analysis of EELS spectrum-imaging data, from elemental to bond mapping in complex nanostructures. Ultramicroscopy 2008, 109, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenal, R.; Lopez-Bezanilla, A. In Situ Formation of Carbon Nanotubes Encapsulated within Boron Nitride Nanotubes via Electron Irradiation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 8419–8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenal, R.; March, K.; Ewels, C.P.; Rocquefelte, X.; Kociak, M.; Loiseau, A.; Stéphan, O. Atomic Configuration of Nitrogen-Doped Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 5509–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arenal, R.; Blase, X.; Loiseau, A. Boron-nitride and boron-carbonitride nanotubes: Synthesis, characterization and theory. Adv. Phys. 2010, 59, 101–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenal, R.; Stephan, O.; Cochon, J.-L.; Loiseau, A. Root-Growth Mechanism for Single-Walled Boron Nitride Nanotubes in Laser Vaporization Technique. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 16183–16189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Silva, R.; Morelos-Gómez, A.; Vega-Díaz, S.; Tristán-López, F.; Elias, A.L.; Perea-López, N.; Muramatsu, H.; Hayashi, T.; Fujisawa, K.; Kim, Y.A.; et al. Formation of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Nanoribbons via Chemical Unzipping. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2192–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhipova, E.A.; Ivanov, A.S.; Strokova, N.E.; Chernyak, S.A.; Shumyantsev, A.V.; Maslakov, K.I.; Savilov, S.V.; Lunin, V.V. Structural evolution of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes: From synthesis and oxidation to thermal defunctionalization. Carbon 2017, 125, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, S.; Shi, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Kim, Y.A.; Endo, M.; Su, D.S. Efficient and highly selective boron-doped carbon materials-catalyzed reduction of nitroarenes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 13086–13089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, E.Y.; Kim, C.K. Fabrication of nitrogen-doped nano-onions and their electrocatalytic activity toward the oxygen reduction reaction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ratso, S.; Kruusenberg, I.; Vikkisk, M.; Joost, U.; Shulga, E.; Kink, I.; Kallio, T.; Tammeveski, K. Highly active nitrogen-doped few-layer graphene/carbon nanotube composite electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media. Carbon 2014, 73, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, Z.R.; Shalagina, A.E.; Podyacheva, O.Y.; Ischenko, A.V.; Kibis, L.S.; Boronin, A.I.; Chesalov, Y.A.; Kochubey, D.I.; Romanenko, A.I.; Anikeeva, O.B.; et al. Structure and electrical conductivity of nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2009, 47, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.; Choi, H.C.; Ahn, J.P.; Hou, J.Q.; Kang, H.S. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and First Principles Calculation of BCN Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soci. 2007, 129, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Pan, F.; Jiang, L.; Fu, X.; Liang, A.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, G. Catalyst-Free Synthesis of Crumpled Boron and Nitrogen Co-Doped Graphite Layers with Tunable Bond Structure for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3313–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.; Lee, J.W. Effect of boron–nitrogen bonding on oxygen reduction reaction activity of BN Co-doped activated porous carbons. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24661–24669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achour, A.; Vizireanu, S.; Dinescu, G.; Le Brizoual, L.; Djouadi, M.A.; Boujtita, M. Electrochemical anodic oxidation of nitrogen doped carbon nanowall films: X-ray photoelectron and Micro-Raman spectroscopy study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuge, R.; Bandow, S.; Yudasaka, M.; Toyama, K.; Iijima, S.; Manako, T. Boron- and nitrogen-doped single-walled carbon nanohorns with graphite-like thin sheets prepared by CO2 laser ablation method. Carbon 2017, 111, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
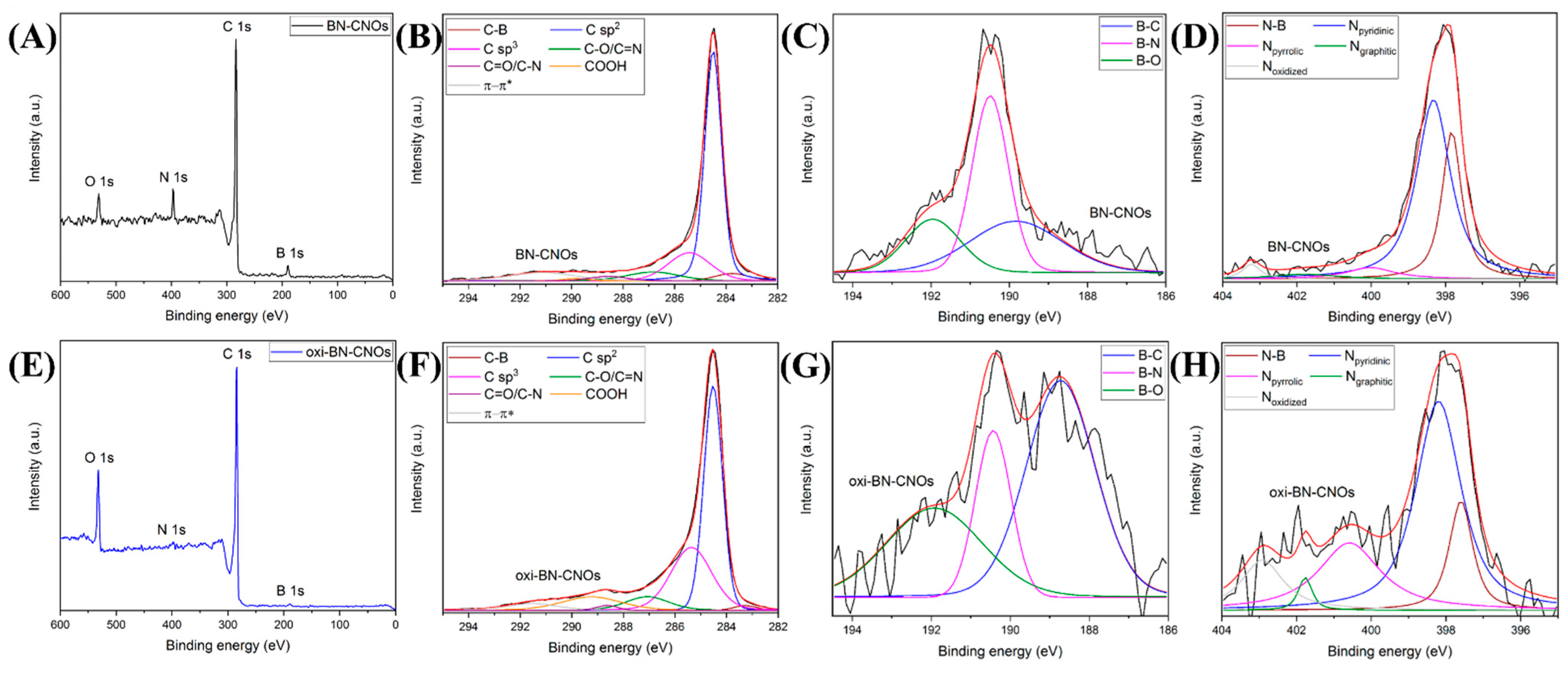

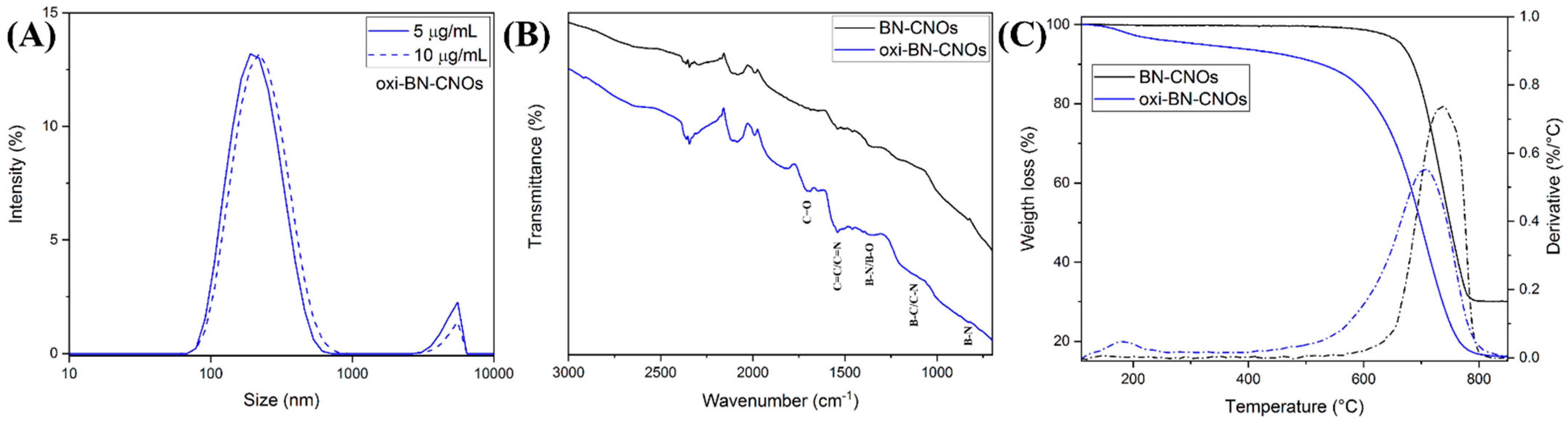


| Sample | C (at. %) | O (at. %) | B (at. %) | N (at. %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BN-CNOs | 82.0 | 4.6 | 8.0 | 5.4 |
| oxi-BN-CNOs | 86.2 | 12.0 | 1.4 | 0.3 |
| Sample | C-B | C sp2 | C sp3 | C–O/C=N | C=O/C–N | COOH | π−π* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BN-CNOs | 283.7 | 284.5 | 285.4 | 286.8 | 288.6 | 289.8 | 291.1 |
| (3.4%) | (59.6%) | (17.4%) | (7.1%) | (2.5%) | (0.9%) | (9.1%) | |
| oxi-BN-CNOs | 283.3 | 284.5 | 285.4 | 287.0 | 288.6 | 289.3 | 291.5 |
| (1.2%) | (46.5%) | (29.6%) | (7.2%) | (1.2%) | (9.8%) | (4.5%) |
| Sample | B–C | B–N | B–O | N–B | Npyridinic | Npyrrolic | Ngraphitic | Noxidized |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BN-CNOs | 189.8 | 190.5 | 191.9 | 397.8 | 398.3 | 400.0 | 401.8 | 403.2 |
| (33.8%) | (45.3%) | (20.9%) | (28.4%) | (59.5%) | (5.9%) | (3.4%) | (2.8%) | |
| oxi-BN-CNOs | 188.7 | 190.4 | 191.9 | 397.6 | 398.2 | 400.6 | 401.8 | 402.9 |
| (51.2%) | (19.45%) | (29.4%) | (13.4%) | (49.1%) | (23.3%) | (2.4%) | (11.8%) |
| Sample | Size @ 5 µg/mL | Size @ 10 µg/mL | w.l. @ 450 °C | TD | Residue @ 850 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BN-CNOs | - | - | 0.3% | 736.0 °C | 30.1% |
| oxi-BN-CNOs | 216.2 ± 12 nm | 223.3 ± 8 nm | 7.3% | 706.0 °C | 16.1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
d’Amora, M.; Camisasca, A.; Arenal, R.; Giordani, S. In Vitro and In Vivo Biocompatibility of Boron/Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113017
d’Amora M, Camisasca A, Arenal R, Giordani S. In Vitro and In Vivo Biocompatibility of Boron/Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113017
Chicago/Turabian Styled’Amora, Marta, Adalberto Camisasca, Raul Arenal, and Silvia Giordani. 2021. "In Vitro and In Vivo Biocompatibility of Boron/Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113017
APA Styled’Amora, M., Camisasca, A., Arenal, R., & Giordani, S. (2021). In Vitro and In Vivo Biocompatibility of Boron/Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113017