Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: What We Know and What Do We Need to Know?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biosynthesis Is a Solely Green and Sustainable Technology for AgNPs Synthesis
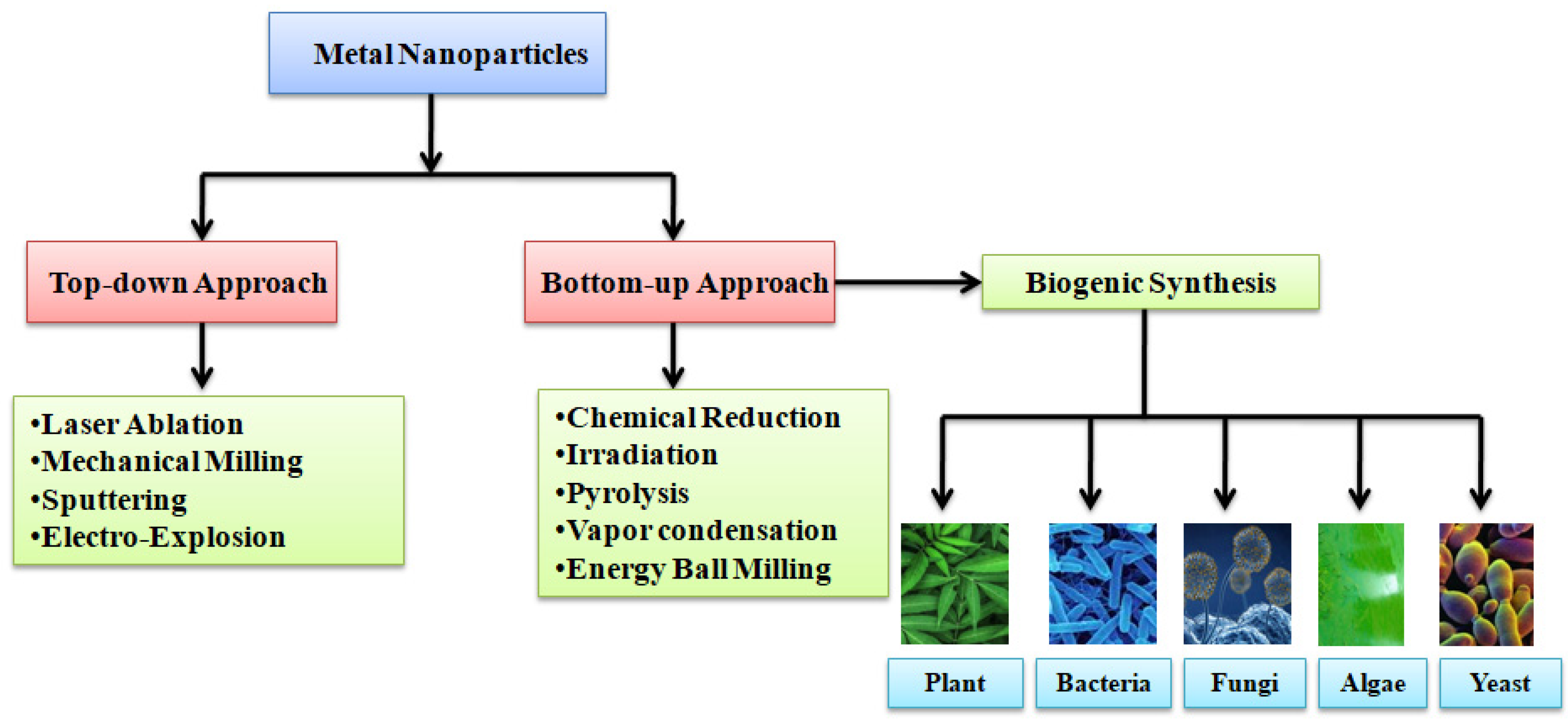
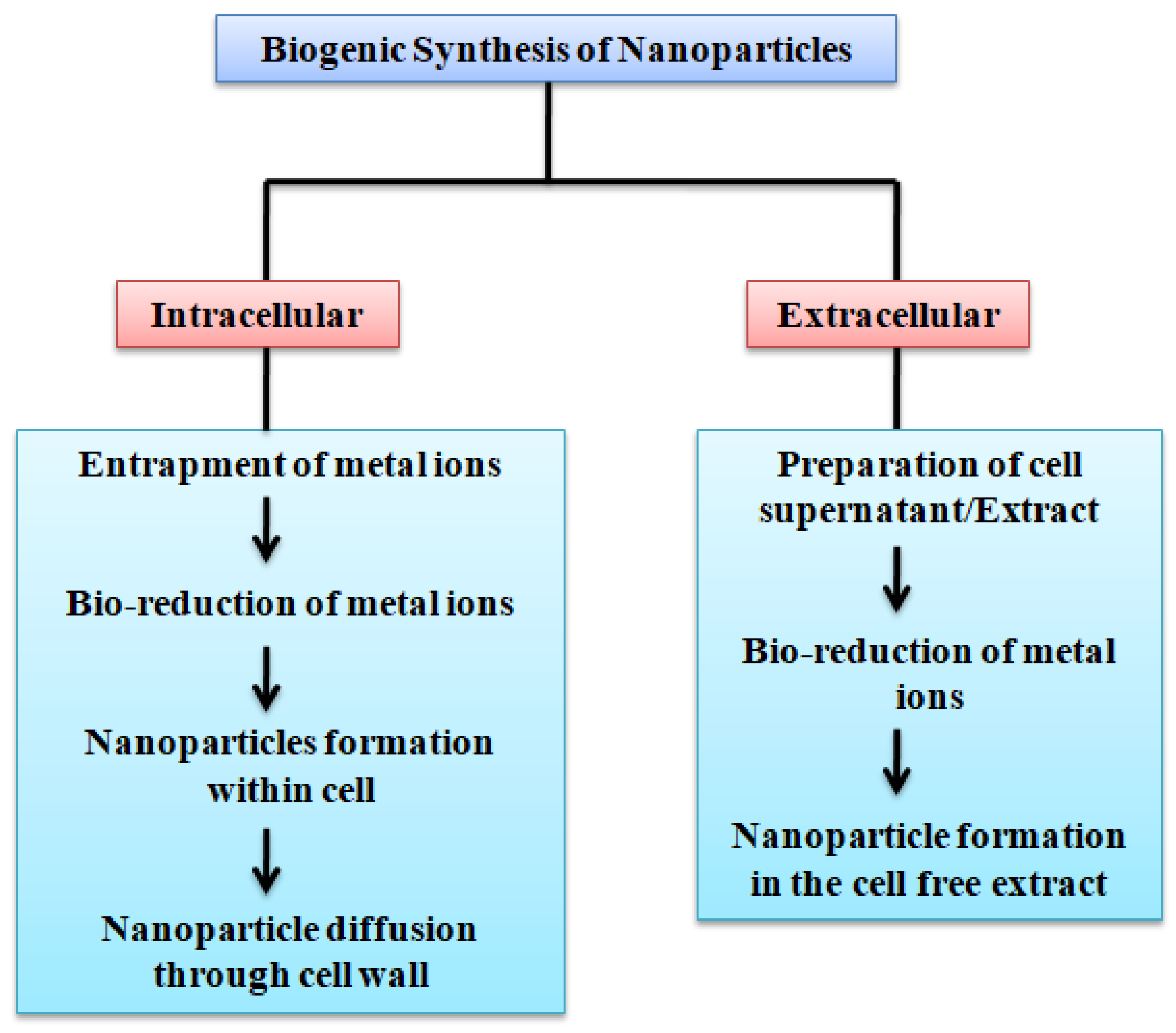
2.1. Strategies for Synthesis
2.2. Potential Biological Agents for Eco-Friendly Synthesis of AgNPs
2.3. Fungi as Promising Myconanofactories
2.4. Microfluidic Approach in Nanoparticles Biosynthesis
3. Unzipping the Mechanism Involved in Biogenic Synthesis of AgNPs
3.1. Mechanism Involved in Bacterial Synthesis of AgNPs
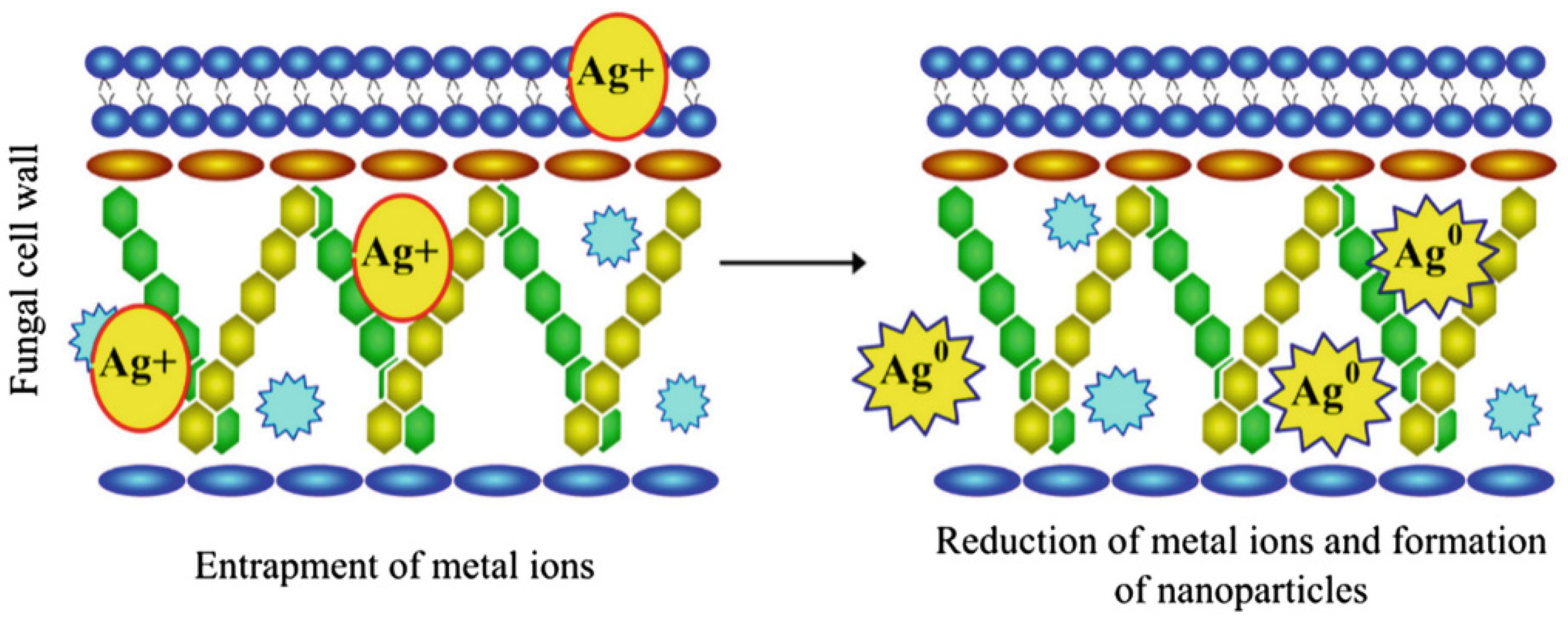
3.2. Mechanism of Mycosynthesis of AgNPs
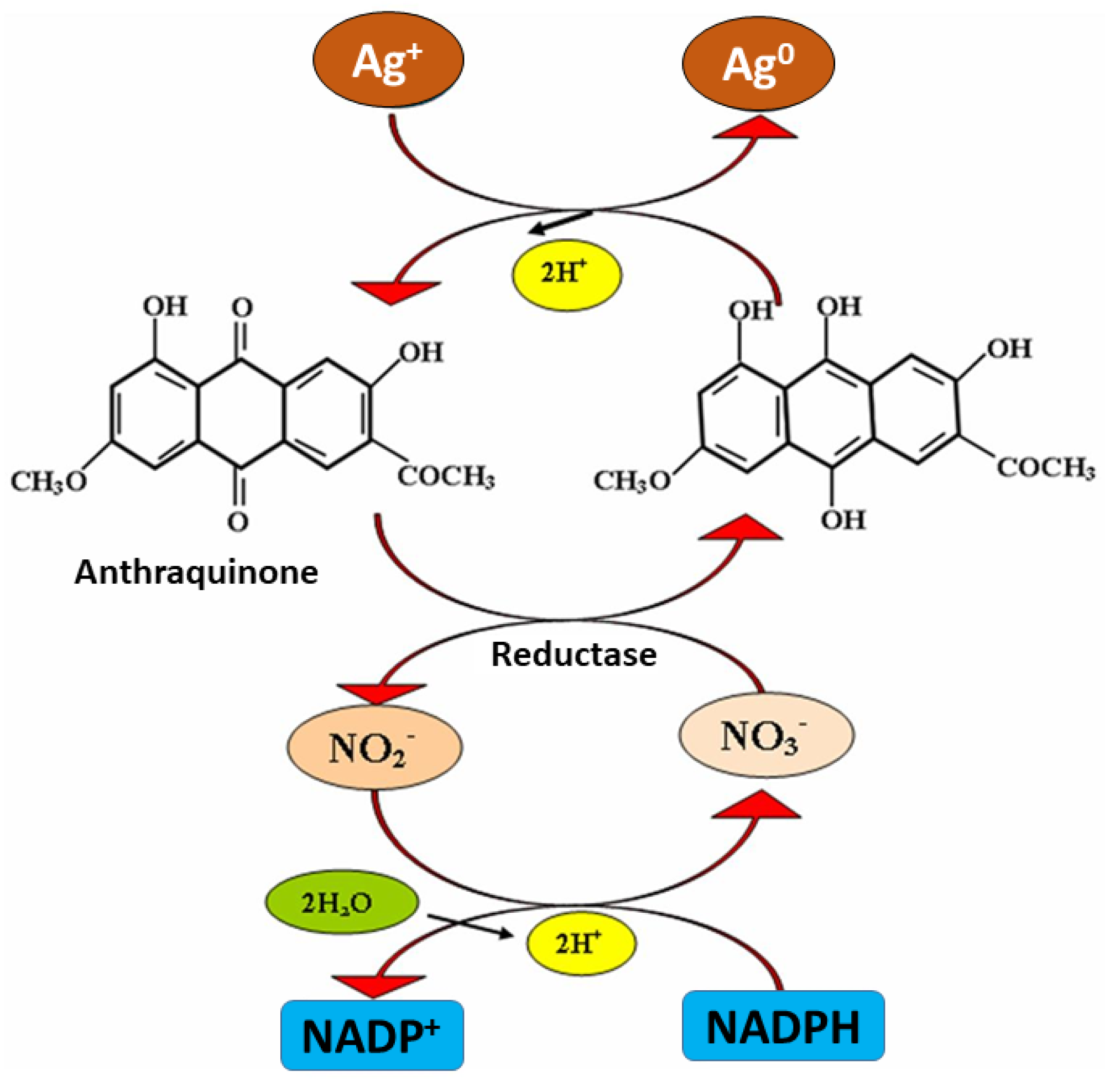
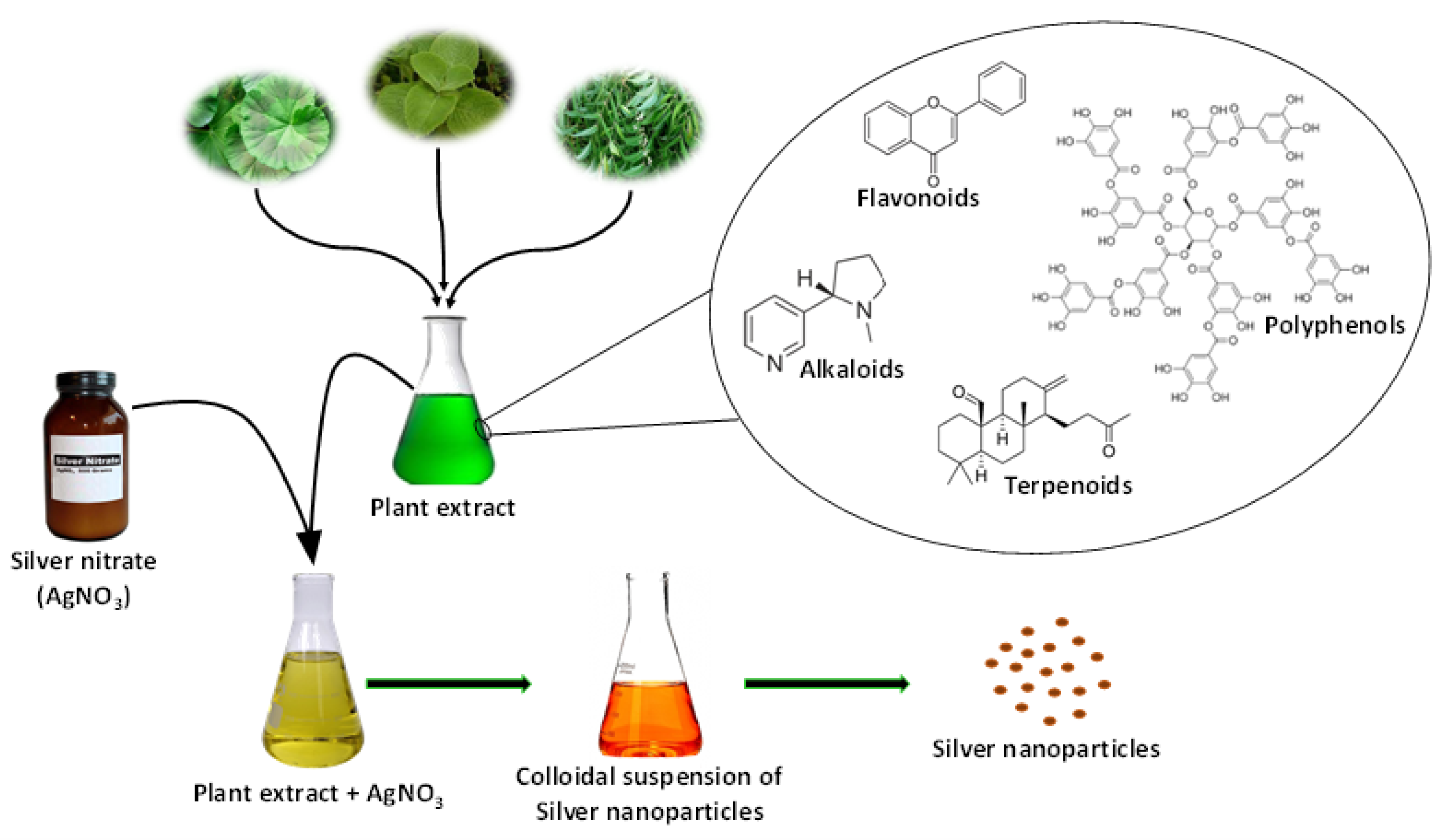
3.3. Mechanism Involved in Phytosynthesis of AgNPs
4. Purifications of Nanoparticles
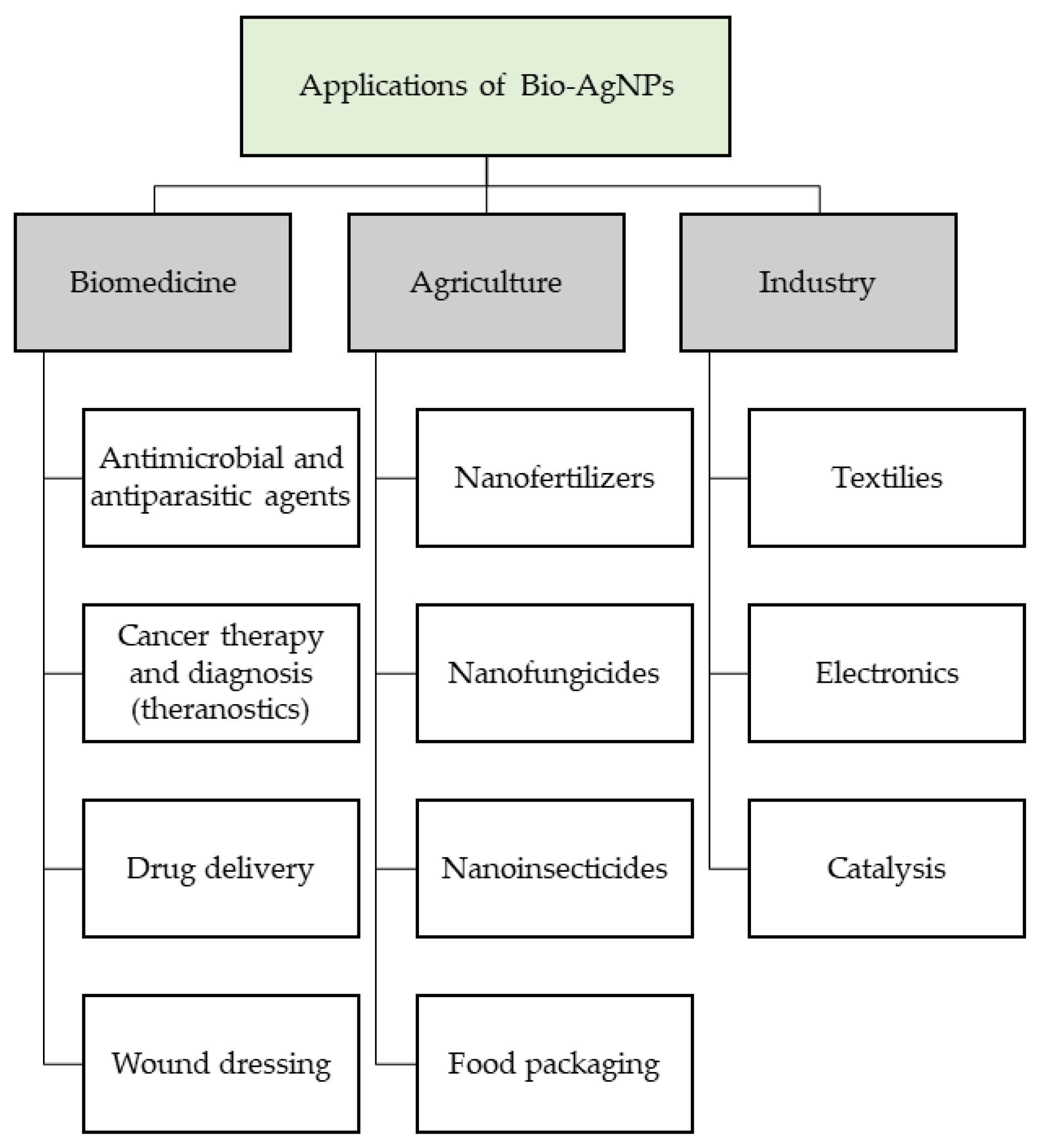
5. Multiple Applications of bio-AgNPs in Different Fields
5.1. Biomedical Applications of Biogenic AgNPs
5.1.1. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities
5.1.2. Antiviral Activity
5.1.3. Antiprotozoal Activity
5.1.4. Anticancer Activity and Theranostics
5.1.5. Antidiabetic Activity
5.2. Antioxidant Activity
5.3. Application of Biogenic AgNPs in Agriculture
5.3.1. Plant Protection
5.3.2. Plant Growth Promotion
5.4. Food Packaging
5.5. Smart Nanotextiles
5.6. Catalytic Activity
5.7. AgNPs in Sensor Development
6. Biodistribution of AgNPs
7. Toxicity of Biogenic AgNPs
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bayda, S.; Adeel, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Cordani, M.; Rizzolio, F. The History of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: From Chemical–Physical Applications to Nanomedicine. Molecules 2020, 25, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Miao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Hui, D. Mechanical properties of nanomaterials: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2020, 9, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawskar, M.; Deshmukh, S.; Bansod, S.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Comparative analysis of biosynthesised and chemosynthesised silver nanoparticles with special reference to their antibacterial activity against pathogens. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 9, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paosen, S.; Jindapol, S.; Soontarach, R.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Eucalyptus citriodora leaf extract-mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: Broad antimicrobial spectrum and mechanisms of action against hospital-acquired pathogens. APMIS 2019, 127, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, A.; Asila, V.; Boitel-Aullen, G.; Lam, M.; Salmain, M.; Boujday, S. Silver-based plasmonic nanoparticles for and their use in biosensing. Biosensors 2019, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, M.; Bonde, S.; Golinska, P.; Trzcińska-Wencel, J.; Gade, A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Shende, S.; Gaikwad, S.; Ingle, A.P. Fusarium as a novel fungus for the synthesis of nanoparticles: Mechanism and applications. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Munir, S.; Zeb, N.; Ullah, A.; Khan, B.; Ali, J.; Bilal, M.; Omer, M.; Alamzeb, M.; Salman, S.M.; et al. Green nanotechnology: A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles—An ecofriendly approach. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5087–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo-Henríquez, L.; Alfaro-Aguilar, K.; Ugalde-Álvarez, J.; Vega-Fernández, L.; Montes de Oca-Vásquez, G.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles from plant extracts and their possible applications as antimicrobial agents in the agricultural area. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypij, M.; Jędrzejewski, T.; Trzcińska-Wencel, J.; Ostrowski, M.; Rai, M.; Golińska, P. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles: Antibacterial and anticancer activities, biocompatibility, and analyses of surface-attached proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 632505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, A.; Petrovic, P.; Vunduk, J.; Pavlovic, V.; Van Griensven, L.J.L.D. The antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from medicinal mushrooms. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2020, 22, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications- an updated report. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Karishma, S.; Vo, D.N.; Jeevanantham, S.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; George, C.S. A review on biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles and its environmental applications. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Datta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. Green synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X. Silver nanoparticles: Biosynthesis and antimicrobial potentialities. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 13, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, E.; Fouad, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Yan, C.; Li, B.; Mo, J.; Chen, J. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using endophytic bacteria and their role in inhibition of rice pathogenic bacteria and plant growth promotion. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondol, A.H.; Yadav, D.; Mitra, S.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatant of Shewanella sp. ARY1 and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8295–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakhatreh, M.A.K.; Al-Rawi, O.F.; Swedan, S.F.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Khabour, O.F.; Al-Fand, M. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Citrobacter freundii as antibiofilm agents with their cytotoxic effects on human cells. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, Y.; Kaushal, S.; Sodhi, R.S. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using cynaobacterium Leptolyngbya sp. WUC 59 cell-free extract and their effects on bacterial growth and seed germination. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 3972–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, G.M.; Hussein, T.H.; Saleem, M.M. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Aspergillus flavus and their anti-oxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity properties. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2015, 38, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilger-Casagrande, M.; Germano-Costa, T.; Pasquoto-Stigliani, T.; Fraceto, L.F.; De Lima, R. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles employing Trichoderma harzianum with enzymatic stimulation for the control of Scleotinia sclerotiorum. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Kobori, T.; Ganesh, D.; Ogawa, K.; Aoyagi, H. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Mediated by Extracellular Pigment from Talaromyces purpurogenus and Their Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Serrano, C.; Guzman-Moreno, J.; Angelez-Chavez, C.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, V.; Ortega-Sigala, J.J.; Ramírez-Santoyo, R.M.; Vidales-Rodríguez, L.E. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Fusarium scirpi and its potential as an antimicrobial agent against uropathogenic Escherchia coli biofilms. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Panda, S.K.; Bastia, A.K.; Mohanta, T.K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Protium serratum and investigation of their potential impacts on food safety and control. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.; Khan, A.U.; Alam, M.J.; Park, S.; Alam, M. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and its application against phytopathogenic bacterium and fungus. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 100, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sila, M.J.; Nyambura, M.I.; Abongo, D.A.; Mwaura, F.B.; Iwuoha, E. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Eucalyptus corymbia leaf extract at optimized conditions. Nanohybrids Compos. 2019, 25, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibo, D.; Borbon-Nunez, H.A.; Diaz Le Leon, J.N.; Mendoza, E.G.; Estrada, I.; Toledano-Magaña, Y.; Tiznado, H.; Ovalle-Marroquin, M.; Soto-Ramos, A.G.; Blanco, A.; et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lysiloma acapulsensis exhibits high antimicrobial activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratošová, G.; Holišová, V.; Konvičková, Z.; Ingle, P.I.; Gaikwad, S.; Škrlová, K.; Prokop, A.; Rai, M.; Plachá, D. From biotechnology principles to functional and low-cost metallic bionanocatalysts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 154–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriya, J.; Bharathi Raja, S.; Sekar, V.; Rajasekaran, R. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity using seaweed Urospora sp. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 12192–12198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benakashani, F.; Allafchian, A.R.; Jalali, S.A.H. Biosnthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capparis spinosa L. extract and their antibacterial activity. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2016, 2, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elamawi, R.M.; Al-Harbi, R.E.; Hendi, A.A. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma longibrachiatum and their effect on phytopathogenic fungi. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2018, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, M.R.P.; Correa, R.O.; Stroppa, P.F.H.; Marques, F.C.; Andrade, G.F.S.; Correa, C.C.; Brandao, M.A.F.; Raposo, N.R.B. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Caesalpinia ferrera (Tul.) Martius extract: Physicochemical characterization, antifungal activity and cytotoxicity. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duraisamy, K.; Han, J.H.; Park, W.S.; Lee, S.M.; Wahab, R.; Lee, Y.S. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Torreya nucifera and their antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othman, A.M.; Elsayed, M.A.; Al-Balakocy, N.G.; Hassan, M.M.; Elshafei, A.M. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles induced by fungal proteins and its application in different biological activities. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sedaghat, S.; Omidi, S. Batch process biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Equisetum arvense leaf extract. Bioinspired Biomim. Nanobiomater. 2019, 8, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemlata; Meena, P.R.; Singh, A.P.; Tejavath, K.K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cucumis prophetarum aqueous leaf extract and their antibacterial and antiproliferative activity against cancer cell lines. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5520–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fathy, W.; Elsayed, K.; Essawy, E.; Tawfik, E.; Zaki, A.; Abdelhameed, M.S.; Hammouda, O. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Synechocystis sp. to be used as a flocculant agent with different microalgae strains. Curr. Nanomater. 2020, 5, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y. Fungus-mediated green synthesis of nano-silver using Aspergillus sydowii and its antifungal/antiproliferative activities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Kon, K.; Kratosova, G.; Duran, N.; Ingle, A.P.; Rai, M. Fungi as an efficient mycosystem for the synthesis of metal nanoparticles: Progress and key aspects of research. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 2099–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilger-Casagrande, M.; de Lima, R. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by Fungi: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, W.B.J. Microfluidics: History, Theory and Applications; Zimmerman, W.B.J., Ed.; CISM International Centre for Mechanical Sciences: Udine, Italy; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dallinger, D.; Kappe, C.O. Why flow means green—Evaluating the merits of continuous processing in the context of sustainability. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2017, 7, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hormes, J.; Kumar, C.S.S.R. Microfluidic synthesis of nanomaterials. Small 2008, 4, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Peng, J.; Yan, M.; Zhang, D.; Shen, A.Q. Droplet synthesis of silver nanoparticles by a microfluidic device. Chem. Eng. Process 2016, 102, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Sun, D.; Lin, L.; Lin, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Wu, W.; Li, Q. Microfluidic biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: Effect of process parameters on size distribution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Sun, D.; Odoom-Wubah, T.; Li, J.; Li, Q. Continuous-flow biosynthesis of Au–Ag bimetallic nanoparticles in a microreactor. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, R.A.; Hussein, M.H.; Abo-elmagd, R.A.; Bawazir, S.S. Synthesis and biological characterization of silver nanoparticles derived from the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria limnetica. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlalveni, C.; Lallianrawna, S.; Biswas, A.; Selvaraj, M.; Changmai, B.; Rokhum, S.L. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts and their antimicrobial activities: A review of recent literature. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 2804–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Kim, B.S. Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant leaf extracts. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Velusamy, P.; Kumar, G.V.; Jeyanthi, V.; Das, J.; Pachaiappan, R. Bio-inspired green nanoparticles: Synthesis, mechanism, and antibacterial application. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 32, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietzschold, S.; Walter, A.; Davis, C.; Taylor, A.A.; Sepunaru, L. Does nitrate reductase play a role in silver nanoparticle synthesis? Evidence for NADPH as the sole reducing agent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8070–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Sarkar, A.; Chand, P.; Bansal, P.; Gola, D.; Sharma, S.; Khantwal, S.; Mehrotra, S.A.; Chauhan, N.; Bharti, R.K. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles utilizing various biological systems: Mechanisms and applications: A review. Prog. Biomater. 2020, 9, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanism of Action and Probable Bio-Application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, N.; Daneshpajouh, S.; Seyedbagheri, S.; Atashdehghan, R.; Abdi, K.; Sarkar, S.; Minaian, S.; Shahverdi, H.R.; Shahverdi, A.R. Biological synthesis of very small silver nanoparticles by culture supernatant of Klebsiella pneumonia: The effects of visible-light irradiation and the liquid mixing process. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, K.; Selvaraj, S.; Murty, V.R. Microbial production of silver nanoparticles. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2010, 5, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Otari, S.; Patil, R.; Nadaf, N.; Ghosh, S.; Pawar, S. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from an actinobacteria Rhodococcus sp. Mater. Lett. 2012, 72, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Kumar, A.; Abraham, J. A biological approach to synthesis of silver nanoparticles with Streptomyces sp. JAR1 and its antimicrobial activity. Sci. Pharm. 2013, 81, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Wagh, P.; Wadhwani, S.; Gaidhani, S.; Kumbhar, A.; Bellare, J.; Chopade, B.A. Synthesis, optimization, and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and their enhanced antibacterial activity when combined with antibiotics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4277–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Malarkodi, C. In vitro antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles against foodborne pathogens. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2014, 4, 581890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbeshehy, E.K.; Elazzazy, A.M.; Aggelis, G. Silver nanoparticles synthesis mediated by new isolates of Bacillus spp., nanoparticle characterization and their activity against bean yellow mosaic virus and human pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y.; Sun, D.; Lin, X.; Deng, X.; He, N.; Zheng, S. Biosorption and bioreduction of diamine silver complex by Corynebacterium. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, T.; Joerger, R.; Olsson, E.; Granqvist, C.G. Silver-based crystalline nanoparticles, microbially fabricated. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13611–13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Baghdady, K.Z.; El-Shatoury, E.H.; Abdullah, O.M.; Khalil, M.M.H. Biogenic production of silver nanoparticles by Enterobacter cloacae Ism26. Turk. J. Biol. 2018, 42, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghashghaei, S.; Emtiazi, G. The methods of nanoparticle synthesis using bacteria as biological nanofactories, their mechanisms and major applications. Curr. Bionanotechnol. 2015, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, B.; Huang, P.J.; Liu, J. Rationally designed nucleobase and nucleotide coordinated nanoparticles for selective DNA adsorption and detection. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 12144–12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeevan, P.; Ramya, K.; Edith Rena, A. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by culture supernatant of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, K.; Jung, S.; Park, K.H.; Kim, Y.R. Microbial biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles in different culture media. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.R.; Stringer, S.J.; Agarwal, G.; Jones, S.E.; Stone, M.O. Biomimetic synthesis and patterning of silver nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2002, 1, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.Y.; Hahn, H.J.; Nam, K.; Choi, W.H.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, D.E.; Park, J.S. Evaluation of generations 2, 3 and 4 arginine modified PAMAM dendrimers for gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 363, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, P.; Mantion, A.; Foelske, A.; Shkilnyy, A.; Masic, A.; Thunemann, A.F.; Taubert, A. Peptide-coated silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface chemistry, and pH-triggered, reversible assembly into particle assemblies. Chemistry 2009, 15, 5831–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crookes-Goodson, W.J.; Slocik, J.M.; Naik, R.R. Bio-directed synthesis and assembly of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mukherjee, P.; Senapati, S.; Mandal, D.; Khan, M.I.; Kumar, R.; Sastry, M. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Colloids Surf. B 2003, 28, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, A.; Gade, A.; Pierrat, S.; Sonnichsen, C.; Rai, M. Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium acuminatum and its activity against some human pathogenic bacteria. Curr. Nanosci. 2008, 4, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; Alves, O.L.; DeSouza, G.H.I.; Esposito, E. Mechanistic aspects of biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by several Fusarium oxysporum strains. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2005, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.A.; Abyaneh, M.K.; Gosavi, S.W.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Pasricha, R.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, M.I. Nitrate reductase-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles from AgNO3. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, D.; Qian, Y.; Guan, B.; Gao, S.; Cui, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Wang, L. Fungus-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Aspergillus terreus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, P.; Roy, M.; Mandal, B.P.; Dey, G.K.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Ghatak, J.; Tyagi, A.K.; Kale, S.P. Green synthesis of highly stabilized nanocrystalline silver particles by a nonpathogenic and agriculturally important fungus T. asperellum. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghi, R.; Verma, P. Biomimetic synthesis and characterization of protein capped silver nanoparticles. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetchinkina, E.; Loshchinina, E.; Kupryashina, M.; Burov, A.; Pylaev, T.; Nikitina, V. Green synthesis of nanoparticles with extracellular and intracellular extracts of basidiomycetes. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Ahmad, A.; Mandal, D.; Senapati, S.; Sainkar, S.R.; Khan, M.I.; Ramani, R.; Parischa, R.; Ajayakumar, P.V.; Alam, M.; et al. Bioreduction of AuCl4− ions by the fungus Verticillium sp. and surface trapping of the gold nanoparticles formed. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 3585–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddin, T.L.; Gericke, M.; Whiteley, C.G. Analysis of the inter- and extracellular formation of platinum nanoparticles by Fusarium oxysporum f sp. lycopersici using response surface methodology. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3482–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, J.; Jain, R.; Sharma, M.M. Phytofabrication of nanoparticles through plant as nanofactories. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, H.; Sami, M.A.; Sadaf, S.; Hassan, U. Salvadora persica mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauthal, P.; Mukhopadhyay, M. Noble metal nanoparticles: Plant-mediated synthesis, mechanistic aspects of synthesis, and applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9557–9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljabali, A.A.A.; Akkam, Y.; Al Zoubi, M.S.; Al-Batayneh, K.M.; Al-Trad, B.; Abo Alrob, O.; Alkilany, A.M.; Benamara, M.; Evans, D.J. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Ziziphus zizyphus and their Antimicrobial Activity. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shankar, S.S.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Geranium leaf assisted biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Prog. 2003, 19, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.S.; Rai, A.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core-Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Sharma, S.; Alam, M.K.; Singh, V.N.; Shamsi, S.F.; Mehta, B.R.; Fatma, A. Rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dried medicinal plant of basil. Colloids Surf. B. 2010, 81, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanaja, M.; Annadurai, G. Coleus aromaticus leaf extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its bactericidal activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Parsons, J.G.; Gomez, E.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Troiani, H.E.; Santiago, P.; Jose-Yacaman, M. Formation and growth of Au nanoparticles inside live Alfalfa plants. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xia, X.; Peng, H.C. Shape-controlled synthesis of colloidal metal nanocrystals: Thermodynamic versus kinetic products. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7947–7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Rafie, M.H.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Ramadan, M.A.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Al-Dey, S.S.; Hebeish, A. Environmental synthesis of silver nanoparticles using hydroxypropyl starch and their characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Bulut, O.; Some, S.; Kumar Mandal, A.; Yilmaz, M.D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2673–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingle, A.; Rai, M.; Gade, A.; Bawaskar, M. Fusarium solani: A novel biological agent for the extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, B.; Lagzi, I.; Grzybowski, B.A. Nanoseparations: Strategies for size and/or shape-selective purification of nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, S.J.; Rastegar, M.F.; Ashrafi, M.; Yazdian, F.; Pourrahim, R.; Suresh, A.K. Influence of external factors on the production and morphology of biogenic silver nanocrystallites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qidwai, A.; Pandey, A.; Kumar, R.; Shukla, S.K.; Dikshit, A. Advances in biogenic nanoparticles and the mechanisms of antimicrobial effects. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 80, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahyaei, B.; Pourali, P. One step conjugation of some chemotherapeutic drugs to the biologically produced gold nanoparticles and assessment of their anticancer effects. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- John, M.S.; Nagoth, J.A.; Ramasamy, K.P.; Mancini, A.; Giuli, G.; Natalello, A.; Ballarini, P.; Miceli, C.; Pucciarelli, S. Synthesis of bioactive silver nanoparticles by a Pseudomonas strain associated with the Antarctic psychrophilic protozoon Euplotes focardii. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Netala, V.R.; Kotakadi, V.S.; Domdi, L.; Gaddam, S.A.; Bobbu, P.; Venkata, S.K.; Ghosh, S.B.; Tartte, V. Biogenic silver nanoparticles: Efficient and effective antifungal agents. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datkhile, K.D.; Durgawale, P.P.; Patil, M.N. Biogenic silver nanoparticles are equally cytotoxic as chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2017, 10, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kalishwaralal, K.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Venkataraman, D.; Pandian, S.R.; Muniyandi, J.; Hariharan, N.; Eom, S.H. Biosynthesis, purification and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Escherichia coli. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 74, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröfel, A.; Kratošová, G.; Šafařík, I.; Šafaříková, M.; Raška, I.; Shor, L.M. Applications of biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles—A review. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4023–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Rajakumar, G.; Chung, I.M. Nanotechnology: Current uses and future applications in the food industry. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Xie, H. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, medical applications and biosafety. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathna, T.C.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Raichur, A.M.; Mukherjee, A. Kinetic evolution studies of silver nanoparticles in a bio-based green synthesis process. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 377, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Levard, C.; Marinakos, S.M.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Michel, F.M.; Lowry, G.V. Size-controlled dissolution of organic-coated silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Jeong, J.K.; Han, J.W.; Zhang, X.F.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Multidimensional effects of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter felis, and human lung (L132) and lung carcinoma A549 cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigneshwaran, N.; Ashtaputre, N.M.; Varadarajan, P.V.; Nachane, R.P.; Paralikar, K.M.; Balasubramanian, R.H. Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus flavus. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenfen, L.Ü.; Yixian, G.A.O.; Huang, J.; Daohua, S.; Qingbiao, L.I. Roles of biomolecules in the biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: Case of Gardenia jasminoides extract. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 22, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggag, E.G.; Elshamy, A.M.; Rabeh, M.A.; Gabr, N.M.; Salem, M.; Youssif, K.A.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Antiviral potential of green synthesized silver nanoparticles of Lampranthuscoc cineus and Malephora lutea. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mujaddidi, N.; Nisa, S.; Al Ayoubi, S.; Bibi, Y.; Khan, S.; Sabir, M.; Qayyum, A. Pharmacological properties of biogenically synthesized silver nanoparticles using endophyte Bacillus cereus extract of Berberis lyceum against oxidative stress and pathogenic multidrug-resistant bacteria. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6432–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Golińska, P. Microbial Nanotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Golińska, P.; Wypij, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Gupta, I.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M. Biogenic synthesis of metal nanoparticles from actinomycetes: Biomedical applications and cytotoxicity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 8083–8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisgin, A.A.; Cetinel, S.; Zuvin, M.; Kosar, A.; Kutlu, O. Therapeutic Nanoparticles and Their Targeted Delivery Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Kim, K.; Lee, D.G. A novel mechanism for the antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Biometals 2014, 27, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.G.; Fernández-Baldo, M.A.; Berni, E.; Camí, G.; Durán, N.; Raba, J.; Sanz, M.I. Production of silver nanoparticles using yeasts and evaluation of their antifungal activity against phytopathogenic fungi. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Jafferi, H.; Habibian, S.; Lotfalian, S. Evaluation of anti biofilm and antibiotic potentiation activities of silver nanoparticles against some nosocomial pathogens. Iran. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 14, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanti, J.R.; Tomiotto-Pellissier, F.; Miranda-Sapla, M.M.; Cataneo, A.H.D.; Andrade, C.G.T.J.; Panis, C.; Rodrigues, J.H.D.S.; Wowk, P.F.; Kuczera, D.; Costa, I.N.; et al. Biogenic silver nanoparticles inducing Leishmania amazonensis promastigote and amastigote death in vitro. Acta Trop. 2018, 178, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Emam, T.M.; Elsherbiny, E.A. Bioactivity of magnesium oxide nanoparticles synthesized from cell filtrate of endobacterium Burkholderia rinojensis against Fusarium oxysporum. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypij, M.; Jędrzejewski, T.; Ostrowski, M.; Trzcińska, J.; Rai, M.; Golińska, P. Biogenic silver nanoparticles: Assessment of their cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and study of capping proteins. Molecules 2020, 25, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajaz, S.; Ahmed, T.; Shahid, M.; Noman, M.; Shah, A.A.; Mehmood, M.A.; Li, B. Bioinspired green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using a native Bacillus sp. strain AW1-2: Characterization and antifungal activity against Colletotrichum falcatum Went. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2021, 144, 109745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kalifawi, E.J.; Al-Azzawi, Y.J.; Feaza, M.A. Antibacterial, antivirulence and antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using alkhal mother shae. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1879, 022054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antibacterial Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopinath, P.M.; Narchonai, G.; Dhanasekaran, D. Mycosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of AgNPs against multidrug resistant (MDR) bacterial pathogens of female infertility cases. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crisan, C.M.; Mocan, T.; Manolea, M.; Lasca, L.I.; Tăbăran, F.A.; Mocan, L. Review on Silver Nanoparticles as a Novel Class of Antibacterial Solutions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasane, N.; Golińska, P.; Wypij, M.; Rathod, D.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M. Acidophilic actinobacteria synthesised silver nanoparticles showed remarkable activity against fungi-causing superficial mycoses in humans. Mycoses 2016, 59, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari-Sardari, A.; Mashreghi, M.; Eshghi, H.; Behnam-Rasouli, F.; Lashani, E.; Shahnavaz, B. Comparative evaluation of silver nanoparticles biosynthesis by two cold-tolerant Streptomyces strains and their biological activities. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 1985–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S. Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial effects against Escherichia fergusonii and Streptococcus mutans. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, A.; Hong, X.; Ibrahim, E.; Li, B.; Sun, G.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; An, Q. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles with Culture Supernatant of a Bacterium Pseudomonas rhodesiae and Their Antibacterial Activity against Soft Rot Pathogen Dickeya dadantii. Molecules 2019, 24, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Divya, M.; Kiran, G.; Hassan, S.; Selvin, J. Biogenic Synthesis and Effect of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) to Combat Catheter-Related Urinary Tract Infections. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, M.; Barik, S.K.; MubarakAli, D.; Prakash, P.; Pugazhendhi, A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Bacillus brevis (NCIM 2533) and their antibacterial activity against pathogenic bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawoud, T.M.; Yassin, M.A.; El-Samawaty, A.R.M.; Elgorban, A.M. Silver nanoparticles synthesized by Nigrospora oryzae showed antifungal activity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, T.; Jyoti, K.; Patnaik, A.; Singh, A.; Chauhan, R.; Chandel, S.S. Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using an endophytic fungal supernatant of Raphanus sativus. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gond, S.K.; Mishra, A.; Verma, S.K.; Sharma, V.K.; Kharwar, R.N. Synthesis and characterization of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles by an endophytic fungus isolated from Nyctanthes arbor-tristis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 90, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmath, P.; Baker, S.; Rakshith, D.; Satish, S. Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles bearing antibacterial activity. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, A.G.; RdC, R.; Selari, P.J.R.G.; de Araujo, W.L.; de Souza, A.O. Anti-biofilm action of biological silver nanoparticles produced by Aspergillus tubingensis and antimicrobial activity of fabrics carrying it. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 14764–14774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulikere, M.M.; Joshi, C. Characterization, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using marine endophytic fungus- Cladosporium cladosporioides. Process Biochem. 2019, 82, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorrami, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Khaleghi, M.; Danaei, M.; Mozafari, M.R. Selective cytotoxicity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against the MCF-7 tumor cell line and their enhanced antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Du, Z.; Ma, S.; Cheng, S.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X. Biosynthesis, antibacterial activity and anticancer effects against prostate cancer (PC-3) cells of silver nanoparticles using Dimocarpus Longan Lour. peel extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wunnoo, S.; Paosen, S.; Lethongkam, S.; Sukkurd, R.; Waen-ngoen, T.; Nuidate, T.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Biologically rapid synthesized silver nanoparticles from aqueous Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaf extract: Effects on hyphal growth, hydrolytic enzymes, and biofilm formation in Candida albicans. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 1578–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, T.; Chatterjee, B.K.; Majumdar, D.; Chakrabarti, P. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles and the modeling of bacterial growth kinetics using a modified Gompertz model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2015, 1850, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanyan, A.; Gabrielyan, L.; Schubert, R.; Trchounian, A. Silver ion bioreduction in nanoparticles using Artemisia annua L. extract: Characterization and application as antibacterial agents. AMB Express 2020, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambardzumyan, S.; Sahakyan, N.; Petrosyan, M.; Nasim, M.J.; Jacob, C.; Trchounian, A. Origanum vulgare L. extract-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles, their characterization and antibacterial activities. AMB Express 2020, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wypij, M.; Świecimska, M.; Czarnecka, J.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M.; Golinska, P. Antimicrobial and cytotoxicactivity of silvernanoparticlessynthesized from twohaloalkaliphilicactinobacterialstrainsalone and in combination with antibiotics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Sung, W.S.; Moon, S.K.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.G. Antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles on dermatophytes. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanab, A.A.; Mansourb, M.K.; Mahmoud, H.H. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles (Ag-Nps) (a model of metals) by Candida albicans and its antifungal activity on some fungal pathogens (Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Candida albicans). N. Y. Sci. J. 2013, 6, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, P.A.; Bonde, S.R.; Gaikwad, S.C.; Joshi, P.A.; Bonde, S.R.; Gaikwad, S.C.; Gade, A.K.; Abd-Elsalam, K.; Rai, M.K. Comparative studies on synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Fusarium oxysporum and Macrophomina phaseolina and its efficacy against bacteria and Malassezia furfur. J. Bionanosci. 2013, 7, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Dias, N.; Carvalho, J.; Fernandes, S.; Santos, C.; Lima, N. Synthesis, characterization and antifungal activity of chemically and fungal-produced silver nanoparticles against Trichophyton rubrum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 1601–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thanighaiarassu, R.R.; BalwinNambikkairaj, R.D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and characterization using plant leaf essential oil compound citral and their antifungal activity against human pathogenic fungi. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 902–907. [Google Scholar]
- Robles-Martínez, M.; González, J.F.C.; Pérez-Vázquez, F.J.; Montejano-Carrizales, J.M.; Pérez, E.; Patiño-Herrera, R. Antimycotic activity potentiation of Allium sativum extract and silver nanoparticles against Trichophyton rubrum. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1800525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, T.; Ghosh, N.N.; Das, M.; Adhikary, R.; Mandal, V.; Chattopadhyay, A.P. Green synthesis of antibacterial and antifungal silver nanoparticles using Citrus limetta peel extract: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, A.; Naomi, R.; Utami, N.D.; Mohammad, A.W.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mustafa, N.; Fauzi, M.B. The Potential of Silver Nanoparticles for Antiviral and Antibacterial Applications: A Mechanism of Action. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.K.; Ma, Q.H.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, D.Q.; Cong, L.; Tian, Y.L.; Yang, R.Y. The antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles on Trichosporon asahii. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Jagan, E.G.; Rajasekar, S.; Selvakumar, P.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Mohan, N. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extracts and its antibacterial activity against water borne pathogens. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 76, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Jung, J.H.; Lamsal, K.; Kim, Y.S.; Min, J.S.; Lee, Y.S. Antifungal effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) against various plant pathogenic fungi. Mycobiology 2012, 40, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lara, H.H.; Ayala-Núnez, N.V.; Turrent, L.D.C.I.; Padilla, C.R. Bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rab, S.M.G.; Halawani, E.M.; Alzahrani, S.S. Biosynthesis of silver nano-drug using Juniperus excelsa and its synergistic antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria for wound dressing applications. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.D.; Houreld, N.N.; Kroukamp, E.M.; Abrahamse, H. Cellular imaging and bactericidal mechanism of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles against human pathogenic bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 178, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escárcega-González, C.E.; Garza-Cervantes, J.A.; Vazquez-Rodríguez, A.; Montelongo-Peralta, L.Z.; Treviño-Gonzalez, M.T.; Castro, E.D.B.; Morones-Ramirez, J.R. In vivo antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles produced via a green chemistry synthesis using Acacia rigidula as a reducing and capping agent. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longhi, C.; Santos, J.P.; Morey, A.T.; Marcato, P.D.; Durán, N.; Pinge-Filho, P.; Yamauchi, L.M. Combination of fluconazole with silver nanoparticles produced by Fusarium oxysporum improves antifungal effect against planktonic cells and biofilm of drug-resistant Candida albicans. Sabouraudia 2015, 54, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galdiero, S.; Falanga, A.; Vitiello, M.; Cantisani, M.; Marra, V.; Galdiero, M. Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antiviral Agents. Molecules 2011, 16, 8894–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Kafshdooz, L.; Razban, Z.; Dastranj Tbrizi, A.; Rasoulpour, S.; Khalilov, R.; Kafshdooz, T. An overview application of silver nanoparticles in inhibition of herpes simplex virus. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortella, G.R.; Pieretti, J.C.; Rubilar, O.; Fernández-Baldo, M.; Benavides-Mendoza, A.; Diez, M.C.; Seabra, A.B. Silver, copper and copper oxide nanoparticles in the fight against human viruses: Progress and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilala, J.; Golla, N. Antibacterial and antiviral properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized by marine Actinomycetes. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019, 10, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, T.V.M.; Nagajyothi, P.C.; Muthuraman, P.; Enkhtaivan, G.; Vattikuti, S.V.P.; Tettey, C.O.; Yoo, K. Ultra-sonication-assisted silver nanoparticles using Panax ginseng root extract and their anti-cancer and antiviral activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 188, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.; Ansar, M.; Speshock, J.; Ivanciuc, T.; Qu, Y.; Casola, A.; Garofalo, R.P. Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Activity of Silver Nanoparticles in Experimental RSV Infection. Viruses 2019, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.X.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Curcumin modified silver nanoparticles for highly efficient inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3040–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Bonde, S.; Yadav, A.; Plekhanova, Y.; Reshetilov, A.; Gupta, I.; Golińska, P.; Pandit, R.; Ingle, A.P. Nanotechnology-based promising strategies for the management of COVID-19: Current development and constraints. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2020, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, L.F.; Sanfelice, R.A.; Bosqui, L.R.; Assolini, J.P.; Scandorieiro, S.; Navarro, I.T.; DepieriCataneo, A.H.; Wowk, P.F.; Nakazato, G.; Bordignon, J.; et al. Biogenic silver nanoparticles reduce adherence, infection, and proliferation of toxoplasma gondii RH strain in HeLa cells without inflammatory mediators induction. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 211, 107853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratan, Z.A.; Haidere, M.F.; Nurunnabi, M.; Shahriar, S.M.; Ahammad, A.J.S.; Shim, Y.Y.; Reaney, M.J.T.; Cho, J.Y. Green Chemistry Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Potential Anticancer Effects. Cancers 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.; Mehdi, S.J.; Irshad, M.; Ali, A.; Sardar, M.; Moshahid, M.; Rizvi, A. Effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles on human cancer cells. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2012, 4, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Park, J.H.; Han, J.W.; Kim, J.H. Comparative assessment of the apoptotic potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Bacillus tequilensis and Calocybe indica in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells: Targeting p53 for anticancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khanra, K.; Panja, S.; Choudhuri, I.; Chakraborty, A.; Bhattacharyya, N. Evaluation of antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Scopariadulcis. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2015, 7, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inbakandan, D.; Kumar, C.; Bavanilatha, M.; Ravindra, D.N.; Kirubagaran, R.; Khan, S.A. Ultrasonic-assisted green synthesis of flower like silver nanocolloids using marine sponge extract and its effect on oral biofilm bacteria and oral cancer cell lines. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathishkumar, P.; Preethi, J.; Vijayan, R.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Ameen, F.; Suresh, S.; Balagurunathan, R.; Palvannan, T. Anti-acne, anti-dandruff and anti-breast cancer efficacy of green synthesised silver nanoparticles using Coriandrum sativum leaf extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 163, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovais, M.; Khalil, T.A.; Raza, A.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, I.; Islam, N.U.; Saravanan, M.; Ubaid, M.F.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via plant extracts: Beginning a new era in cancer theranostics. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 3157–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, B.; Tafvizi, F.; ZakerBostanabad, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artemisia turcomanica leaf extract and the study of anti-cancer effect and apoptosis induction on gastric cancer cell line (AGS). Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, S.; Chowdhury, D.; Kotcherlakota, R.; Patra, S.B.V.; Bhadra, M.P.; Sreedhar, B.; Parta, C.R. Potential theranostics application of bio-synthesized silver nanoparticles (4-in-1 system). Theranostics 2014, 4, 316–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Eppakayala, V.; Jeyaraj, M.; Kim, J.-H. Cytotoxicity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 535796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurunathan, S.; Raman, J.; Malek, S.N.A.; John, P.A.; Vikineswary, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ganoderma neo-japonicum Imazeki: A potential cytotoxic agent against breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4399–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurunathan, S.; Lee, K.J.; Kalishwaralal, K.; Sheikpranbabu, S.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Eom, S.H. Antiangiogenic properties of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6341–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharara, J.; Namvar, F.; Mousavi, M.; Ramezani, T.; Mohamad, R. Anti-Angiogenesis Effect of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Saliva officinalis on Chick Chorioalantoic Membrane (CAM). Molecules 2014, 19, 13498–13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeyaraj, M.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sivanandhan, G.; MubarakAli, D.; Rajesh, M.; Arun, R. Ganapathi; A. Biogenic silver nanoparticles for cancer treatment: An experimental report. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 106, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Shandiz, S.A.S.; Ghanbar, F.; Darvish, M.R.; Ardestani, M.S.; Mirzaie, A.; Jafari, M. Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artemisia marschalliana Sprengel aerial part extract and assessment of their antioxidant, anticancer, and antibacterial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patra, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Barui, A.K.; Ganguly, A.; Sreedhar, B.; Patra, C.R. Green synthesis, characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles and their potential application for cancer therapeutics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 53, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, S.; Srivastava, B.; Bhadouria, R.; Singh, R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Holoptelea integrifolia and preliminary investigation of its antioxidant, antiinflammatory, antidiabetic and antibacterial activities. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Zahoor Ahmad, Z.; Manzoor, M.Z.; Muhammad Mujahid, M.; Faheem, Z.; Adnan, A. Optimization for biogenic microbial synthesis of silver nanoparticles through response surface methodology, characterization, their antimicrobial, antioxidant, and catalytic potential. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savary, S.; Willocquet, L.; Pethybridge, S.J.; Esker, P.; McRoberts, N.; Nelson, A. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Arya, C.; Misra, R. Mechanism of action in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbionts to control fungal diseases. In Management of Fungal Plant Pathogens; Arya, A., Perello, A.E., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2010; pp. 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Medina-Pérez, G.; Fernández-Luqueño, F.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; Sánchez-López, K.B.; Afanador-Barajas, L.N.; Prince, L. Nanotechnology in crop protection: Status and future trends. In Nano-Biopesticides Today and Future Perspectives; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamdagni, P.; Khatri, P.; Rana, J.S. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Elettaria cardamomum and their antifungal activity against phytopathogens. Adv. Mater. Proc. 2018, 3, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamawi, R.M.; Al-Harbi, R.E. Effect of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on Fusarium oxysporum fungus the cause of seed rot disease of faba bean, tomato and barley. J. Plant Prot. Pathol. 2014, 5, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, T.T.; Khan, S.; Fu, P. Fungus-(Alternaria sp.) mediated silver nanoparticles synthesis, characterization, and screening of antifungal activity against some phytopathogens. J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 2020, 8828878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, B.R.; Singh, A.; Keswani, C.; Naqvi, A.H.; Singh, H.B. Biofabricated silver nanoparticles act as a strong fungicide against Bipolarissorokiniana causing spot blotch disease in wheat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Ramachandran, R.; Mohan, K.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Optimization for rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its effect on phytopathogenic fungi. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 93, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heflish, A.A.; Hanfy, A.E.; Ansari, M.J.; Dessoky, E.S.; Attia, A.O.; Elshaer, M.M.; Behiry, S.I. Green biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Acalypha wilkesiana extract control root-knot nematode. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Otibi, F.; Perveen, K.; Al-Saif, N.A.; Alharbi, R.I.; Bokhari, N.A.; Albasher, G.; Al-Mosa, M.A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Malva parviflora and their antifungal activity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021 28, 2229–2235. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Bhatt, D.; Zaidi, M.G.H.; Saradhi, P.P.; Khanna, P.K.; Arora, S. Silver nanoparticle-mediated enhancement in growth and antioxidant status of Brassica juncea. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 2225–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Murtaza, G. Application of SNPs to improve yield of Pisum sativum L. (pea). IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, S.U.; Javed, B.; Sohail; Zehra, S.S.; Mashwani, Z.-U.-R.; Raja, N.I.; Khan, T.; ALHaithloul, H.A.S.; Alghanem, S.M.; Al-Mushhin, A.A.M.; et al. Exogenous Applications of Bio-fabricated Silver Nanoparticles to Improve Biochemical, Antioxidant, Fatty Acid and Secondary Metabolite Contents of Sunflower. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji Basheerudeen, M.A.; Mushtaq, S.A.; Soundhararajan, R.; Nachimuthu, S.K.; Srinivasan, H. Marine endophytic fungi mediated Silver nanoparticles and their application in plant growth promotion in Vigna radiata L. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Jia, X.; Huang, Y.; Ji, R.; Zhao, L. Comparation of the phytotoxicity between chemically and green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeleliere, E.; Cobbina, S.J.; Abubakari, Z.I. Review of microbial food contamination and food hygiene in selected capital cities of Ghana. Cogent. Food Agric. 2017, 3, 1395102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, R.E.; Subha, V.; Ilangovan, R. Silver nanoparticles blended PEG/PVA nanocomposites synthesis and characterization for food packaging. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6056–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsalya, E.; MosaChristas, K.; Balashanmugam, P.; Manivasagan, V.; Devasena, T.; Jaquline, C.R.I. Sustainable use of biowaste for synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its incorporation into gelatin-based nanocomposite films for antimicrobial food packaging applications. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediyilyam, S.; George, B.; Shankar, S.S.; Dennis, T.T.; Wacławek, S.; Černík, M.; Padil, V.V.T. Chitosan/Gelatin/Silver Nanoparticles Composites Films for Biodegradable Food Packaging Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhople, S.; Gaikwad, S.; Deshmukh, S.; Bonde, S.; Gade, A.; Sen, S.; Brzezinska, A.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M. Myxobacteria-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their impregnation in wrapping paper used for enhancing shelf life of apples. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 10, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shastri, J.P.; Rupani, M.G.; Jain, R.L. Antimicrobial activity of nanosilver-coated socks fabrics against foot pathogens. J. Text. Inst. 2012, 103, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.M.F.; Pervez, M.N.; Talukder, M.E.; Sultana, M.Z.; Mahmud, S.; Meraz, M.M.; Bansal, V.; Genyang, C. A Novel Coloration of Polyester Fabric through Green Silver Nanoparticles (G-AgNPs@PET). Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravindra, S.; Mohan, Y.M.; Reddy, N.N.; Raju, K.M. Fabrication of antibacterial cotton fibres loaded with silver nanoparticles via “Green Approach”. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 2010 367, 31–40. [CrossRef]
- Montes-Hernandez, G.; Di Girolamo, M.; Sarret, G.; Bureau, S.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Lelong, C.; EymardVernain, E. In Situ Formation of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) onto Textile Fibers. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shateri-Khalilabad, M.; Yazdanshenas, M.E.; Etemadifar, A. Fabricating multifunctional silver nanoparticles-coated cotton fabric. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2355–S2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabbir, M.; Mohammad, F. Multifunctional AgNPs@ Wool: Colored, UV-protective and antioxidant functional textiles. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankar, P.S.; Shukla, D. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using lemon leaves extract and its application for antimicrobial finish on fabric. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 2, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehan, M.; Elshemy, N.S.; Haggag, K.; Montaser, A.S.; Ibrahim, G.E. Phytochemicals and volatile compounds of peanut red skin extract: Simultaneous coloration and in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles for multifunctional viscose fibers. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9893–9912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuk, N.; Šala, M.; Gorjanc, M. Development of antibacterial and UV protective cotton fabrics using plant food waste and alien invasive plant extracts as reducing agents for the in-situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3215–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, G.; Kumari, R.M.; Sharma, N.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Nimesh, S. Catalytic, antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy of biosynthesised silver nanoparticles using Prosopis juliflora leaf extract along with their wound healing potential. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 190, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.; Moldovan, B. Green Synthesis of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Catalytic Removal of Harmful Organic Dyes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saha, P.; Mahiuddin, M.; Nazmul Islam, A.B.M.; Ochiai, B. Biogenic synthesis and catalyticefficacy of silver nanoparticles based on peel extracts of Citrusma croptera fruit. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 18260–18268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, I.A. Recent advances in biogenic silver nanoparticles and nano composite based plasmonic-colorimetric and electrochemical sensors. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 047003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, L.E.S.D.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R.; Camacho-López, M.A. Biogenic silver nanoparticles as sensors of Cu2+ and Pb2+ in aqueous solutions. Univ. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 5, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Khan, Z. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles, sensing and photo catalytic activities for bromothymol blue. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 3–4, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Nafady, A.; Sirajuddin; Avcı, A.; Pehlivan, E.; Nisar, J.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Balouch, A.; Shah, M.R.; Almaghrabi, O.A.; et al. Biogenic silver nanoparticles for trace colorimetric sensing of enzyme disrupter fungicide vinclozolin. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tagad, C.K.; Dugasani, S.R.; Aiyer, R.; Park, S.; Kulkarni, A.; Sabharwal, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their application for the development of optical fiber based hydrogen peroxide sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 183, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.H.; Tarek, F.K.; Nuzat, M.; Momin, M.A.; Hasan, M.R. Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Ocimum sanctum and their characterization. J. Nanosci. 2017, 2017, 1693416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Saifullah; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica aqueous leaf extract. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, T.; Rahman, M.; Ullah, A.K.M.A.; Hossain, K.F.B.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdous, Z.; Nemmar, A. Health Impact of Silver Nanoparticles: A Review of the Biodistribution and Toxicity Following Various Routes of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yan, B.; Liu, J. The biodistribution and transformation of nanoparticulate and ionic silver in rat organs in vivo. NanoImpact 2020, 20, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keat, C.L.; Aziz, A.; Eid, A.M.; Elmarzugi, N.A. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles and silver nanoparticles. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2015, 2, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, J.H.; Ji, J.H.; Yoon, J.U.; Kim, D.S.; Song, M.Y.; Jeong, J.; Han, B.S.; Han, J.H.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, J. Lung function changes in Sprague-Dawley rats after prolonged inhalation exposure to silver nanoparticles. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Kuang, H.; Zhang, W.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Wei, H.; Xu, H. Comparisons of the biodistribution and toxicological examinations after repeated intravenous administration of silver and gold nanoparticles in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziendzikowska, K.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J.; Lankoff, A.; Oczkowski, M.; Krawczyńska, A.; Chwastowska, J.; Sadowska-Bratek, M.; Chajduk, E.; Wojewódzka, M.; Dušinská, M.; et al. Time-dependent biodistribution and excretion of silver nanoparticles in male Wistar rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zande, V.M.; Vandebriel, R.J.; van Doren, E.; Kramer, E.; Herrera Rivera, Z.; Serrano-Rojero, C.S.; Gremmer, E.R.; Mast, J.; Peters, R.J.B.; Hollman, P.C.G.; et al. Distribution, Elimination, and Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions in Rats after 28-Day Oral Exposure. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7427–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, K.K.; Achary, V.M.M.; Krishnaveni, R.; Padhi, B.K.; Sarangi, S.N.; Sahu, S.N.; Panda, B.B. In vitro biosynthesis and genotoxicity bioassay of silver nanoparticles using plants. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannerselvam, B.; Thiyagarajan, D.; Pazhani, A.; Thangavelu, K.P.; Kim, H.J.; Rangarajulu, S.K. Copperpod Plant Synthesized AgNPs Enhance Cytotoxic and Apoptotic Effect in Cancer Cell Lines. Processes 2021, 9, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashajyothia, C.; Chandrakanth, R.K. A pilot toxicology study of biogenic silver nanoparticles: In vivo by intraperitoneal and intravenous infusion routes in rats. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2019, 14, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, R.; Seabra, A.B.; Durán, N. Silver nanoparticles: A brief review of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of chemically and biogenically synthesized nanoparticles. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunachalam, K.D.; Arun, L.B.; Annamalai, S.K.; Arunachalam, A.M. Potential anticancer properties of bioactive compounds of Gymnema sylvestre and its biofunctionalized silver nanoparticle. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Naggar, N.E.-A.; Hussein, M.H.; El-Sawah, A.A. Bio-fabrication of silver nanoparticles by phycocyanin, characterization, in vitro anticancer activity against breast cancer cell line and in vivo cytotoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10844–10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansar, S.; Tabassum, H.; Aladwan, N.S.M.; Ali, M.N.; Almaarik, B.; AlMahrouqi, S.; Abudawood, M.; Banu, N.; Alsubki, R. Ecofriendly silver nanoparticles synthesis by Brassica oleracea and its antibacterial, anticancer and antioxidant properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamida, R.S.; Abdelmeguid, N.E.; Ali, M.A.; Bin-Meferij, M.M.; Khalil, M.I. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using a novel cyanobacteria Desertifilum sp. extract: Their antibacterial and cytotoxicity effects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Recordati, C.; De Maglie, M.; Bianchessi, S.; Argentiere, S.; Cella, C.; Mattiello, S.; Cubadda, F.; Aureli, F.; D’Amato, M.; Raggi, A. Tissue distribution and acute toxicity of silver after single intravenous administration in mice: Nano-specific and size-dependent effects. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Netala, V.R.; Bethu, M.S.; Pushpalatha, B. Biogenesis of silver nanoparticles using endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis microspora and evaluation of their antioxidant and anticancer activities. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szerencsés, B.; Igaz, N.; Tóbiás, A.; Prucsi, Z.; Rónavári, A.; Bélteky, P.; Madarász, D.; Papp, C.; Makra, I.; Vágvölgyi, C.; et al. Size-dependent activity of silver nanoparticles on the morphological switch and biofilm formation of opportunistic pathogenic yeasts. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, V.S.; Arunkumar, J.; Marsili, E.; MubarakAlie, F.; Velusamya, P.; Vadivelu, J. Biogenic synthesis, characterization of antibacterial silver nanoparticles and its cell cytotoxicity. Arabian J. Chem. 2017, 10, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballotin, D.; Fulaz, S.; Souza, M.L.; Corio, P.; Rodrigues, A.G.; Souza, A.O. Elucidating protein involvement in the stabilization of the biogenic silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Method | Precursor | Reducing Agent | Stabilizing Agent | Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Methods | ||||
| Chemical reduction | AgNO3 | N,N′-dimethylformamide | - | <25 |
| Chemical reduction | AgNO3 | Sodium borohydrate | Surfactin (a lipopeptide biosurfactant) | 3–28 |
| Chemical reduction | AgNO3 | Trisodium citrate (initial) +SFS (secondary) | Trisodium citrate | <50 |
| Chemical reduction | AgNO3 | Trisodium citrate | Trisodium citrate | 30–60 |
| Chemical reduction | AgNO3 | Ascorbic acid | - | 200–650 |
| Chemical reduction | AgNO3 | Sodium borohydrate | Dodecanoic acid | ~7 |
| Chemical reduction | AgNO3 | Paraffin | Oleylamine | 10–14 |
| Chemical reduction (thermal) | AgNO3 | Dextrose | Polyvinyl pyrrolidone | 22 ± 4.7 |
| Chemical reduction (thermal) | AgNO3 | Hydrazine | - | 2–10 |
| Chemical reduction (oxidation of glucose) | AgNO3 | Glucose | Gluconic acid | 40–80 |
| Chemical reduction (polyol process) | AgNO3 | Ethylene glycol | Polyvinyl pyrrolidone | 5–25 |
| Chemical reduction (polyol process) | AgNO3 | Ethylene glycol | Polyvinyl pyrrolidone | 50–115 |
| Chemical reduction (microemulsion) | AgNO3 | Hydrazine hydrate | Aerosol-OT | 2–5 |
| Chemical reduction (microemulsion) | AgNO3 | Hydrazine hydrate | Aerosol-OT | <1.6 |
| Electrochemical (polyol process) | AgNO3 | Electrolysis cathode: titanium anode: Pt | Polyvinyl pyrrolidone | ~11 |
| Chemical reduction (Tollen) | AgNO3 | m-Hydroxy benzaldehyde | Sodium formaldehyde sulphoxylate | 15–260 |
| Physical Methods | ||||
| Physical synthesis | Ag wires | Electrical arc discharge, water | - | 14–27 |
| Physical synthesis | AgNO3 | Electrical arc discharge | Sodium citrate | 2–5 |
| Photochemical Methods | ||||
| Photochemical reduction (pulse radiolysis) | AgClO4 | Ethylene glycol | - | 17–70 |
| Photochemical reduction (microwave radiation) | AgNO3 | Ethylene glycol | Polyvinyl pyrrolidone | 5–10 |
| Photochemical Reduction (photoreduction) | AgNO3 | UV light | - | 4–10 |
| Photochemical reduction (X-ray radiolysis) | Ag2SO4 | X-Ray | - | ~28 |
| Photochemical reduction (X-ray radiolysis) | AgNO3 | Carboxymethylated chitosan, UV | Carboxymethylated chitosan | 2–8 |
| Biological Agent | Type | Mode of Synthesis | Size (nm) | Shape | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urospora sp. | Seaweed | Extracellular | 20–30 | Spherical | [30] |
| Aspergillus flavus | Fungus | Extracellular | 33.5 | Spherical | [21] |
| Capparis spinosa | Plant | Extracellular | 5–30 | Spherical | [31] |
| Protium serratum | Plant | Extracellular | 74.56 ± 0.46 | Spherical | [25] |
| Trichoderma longibrachiatum | Fungus | Extracellular | 10 | Spherical | [32] |
| Caesalpinia ferrera (Tul.) Maritus | Plant | Extracellular | 30–50 | Spheroidal | [33] |
| Trichoderma harzianum | Fungus | Extracellular | 50–80 | - | [22] |
| Zea mays | Plant | Extracellular | 25 | Spherical | [26] |
| Torreya nucifera | Plant | Extracellular | 10–125 | Spherical | [34] |
| Bacillus siamensis | Endophytic Bacteria | Extracellular | 25–50 | Spherical | [17] |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | Fungus | Extracellular | 84.4 | Spherical | [35] |
| Talaromyces purpurogenus | Fungus | Extracellular | 4–41 | Spherical, hexagonal, rod-shaped, and triangular- | [23] |
| Eucalyptus corymbia | Plant | Extracellular | 18–20 | Spherical | [27] |
| Equisetum arvense | Plant | Extracellular | 18–20 | - | [36] |
| Cucumis prophetarum | Plant | Extracellular | 30–50 | Irregular granulated, ellipsoidal | [37] |
| Leptolyngbya sp. WUC 59 | Cyanobacteria | Extracellular | 20–35 | Spherical | [20] |
| Lysiloma acapulsensis | Plant | Extracellular | 1.2–62 | Spherical and quasi-spherical | [28] |
| Shewanella sp. ARY1 | Bacteria | Extracellular | 38 | Spherical | [18] |
| Fusarium scirpi | Fungus | Extracellular | 2–20 | Quasi-spherical | [24] |
| Synechocystis sp. | Microalgae | Extracellular | 10–100 | - | [38] |
| Citrobacter freundii | Bacteria | Extracellular | 15–30 | Spherical | [19] |
| Aspergillus sydowii | Fungus | Extracellular | 1–24 | Spherical | [39] |
| Organism | Activity | Target | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | |||
| Pilimelia columellifera subsp. pallida (SF23, C9) | antifungal | Malassezia furfur, Trichophyton rubrum, Candida albicans, C. tropicalis | [129] |
| Streptomyces sp. OSIP1 and OSNP14 | antibacterial | Staphylococcus aureus Bacillus subtilis, Proteus mirabilis Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [130] |
| Bacillus cereus | antibacterial | Escherichia fergusonii, Streptococcus mutans | [131] |
| Pseudomonas rhodesiae | antibacterial | Dickeya dadantii | [132] |
| Alcaligenes sp. | antibacterial and antifungal | Bacillus sp., Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans | [133] |
| Bacillus brevis | antibacterial | MDR Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi | [134] |
| Fungi | |||
| Nigrospora oryzae | antifungal | Fusarium spp. | [135] |
| Alternaria sp. | antibacterial | Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Serratia marcescens | [136] |
| Phomopsis helianthi | antibacterial | Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [137] |
| Colletotrichum sp. | antibacterial | Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhimurium | [138] |
| Aspergillus tubingensis | antifungal | Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis | [139] |
| Cladosporium cladosporioides | antibacterial and antifungal | Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermis, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Candida albicans | [140] |
| Plants | |||
| Juglans regia | antibacterial | Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus | [141] |
| Dimocarpus Longan | antibacterial | Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus | [142] |
| Eucalyptus camaldulensis | antifungal | Candida albicans | [143] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Trzcińska-Wencel, J.; Wypij, M.; Bonde, S.; Yadav, A.; Kratošová, G.; Golińska, P. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: What We Know and What Do We Need to Know? Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112901
Rai M, Ingle AP, Trzcińska-Wencel J, Wypij M, Bonde S, Yadav A, Kratošová G, Golińska P. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: What We Know and What Do We Need to Know? Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112901
Chicago/Turabian StyleRai, Mahendra, Avinash P. Ingle, Joanna Trzcińska-Wencel, Magdalena Wypij, Shital Bonde, Alka Yadav, Gabriela Kratošová, and Patrycja Golińska. 2021. "Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: What We Know and What Do We Need to Know?" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112901
APA StyleRai, M., Ingle, A. P., Trzcińska-Wencel, J., Wypij, M., Bonde, S., Yadav, A., Kratošová, G., & Golińska, P. (2021). Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles: What We Know and What Do We Need to Know? Nanomaterials, 11(11), 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112901







