Facile Synthesis of N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots as Novel Transfection Agents for mRNA and pDNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of NGQDs
2.2. Characterization of NGQDs
2.3. Loading Capacity
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Gene Transfections Efficiency
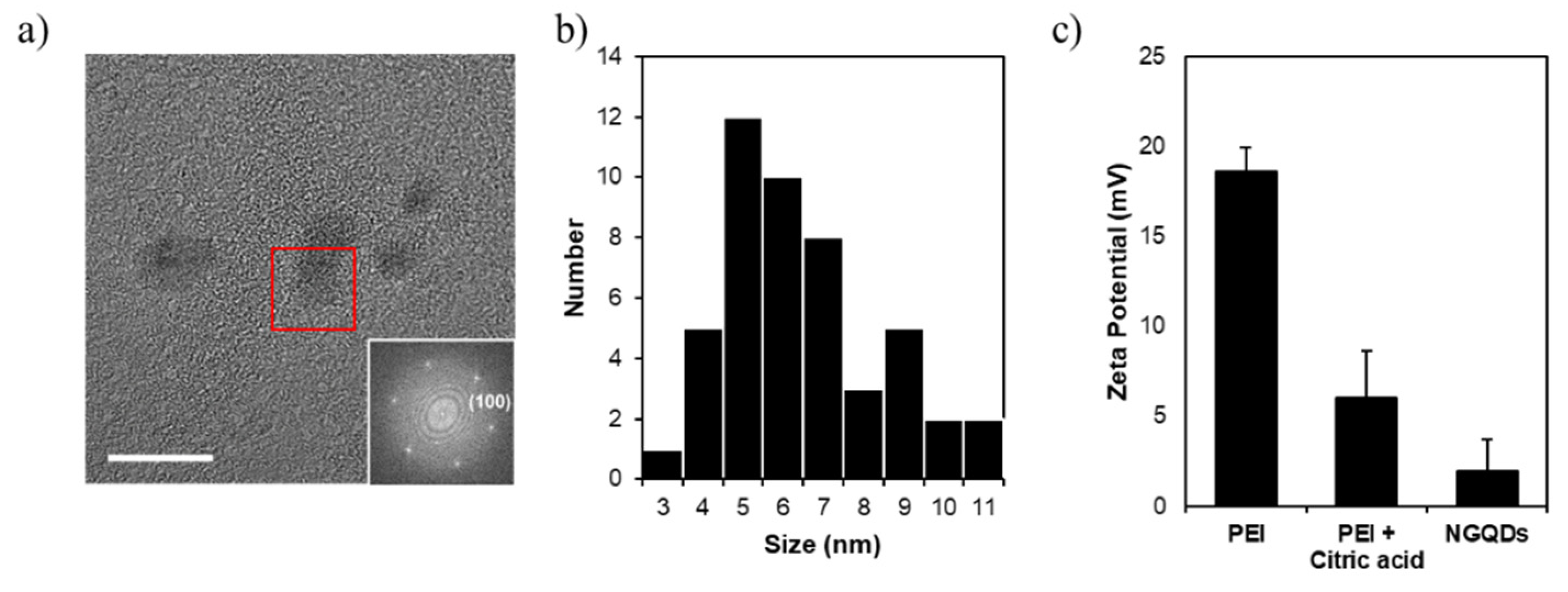
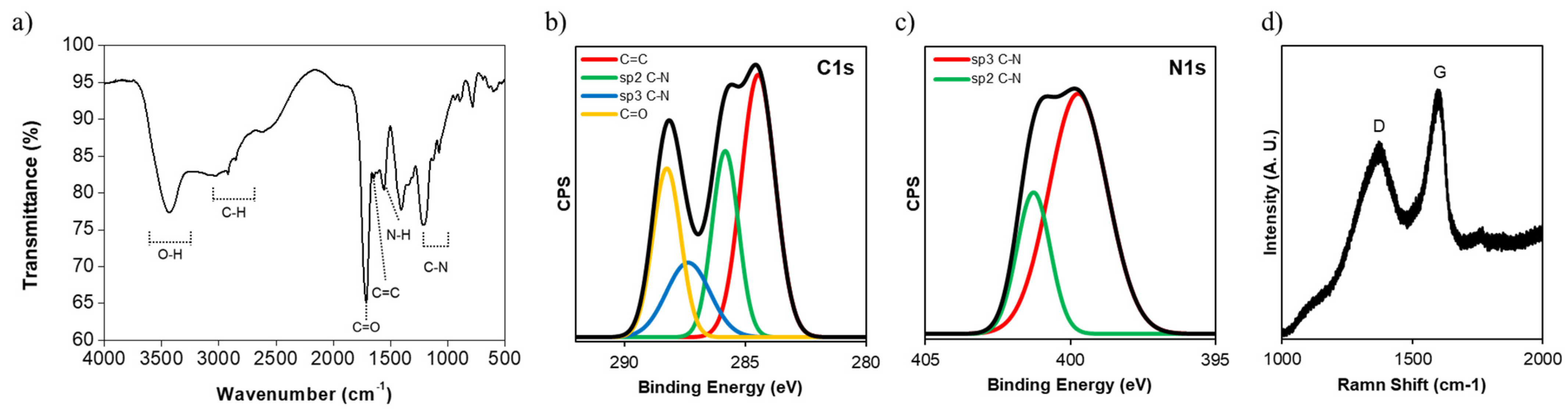
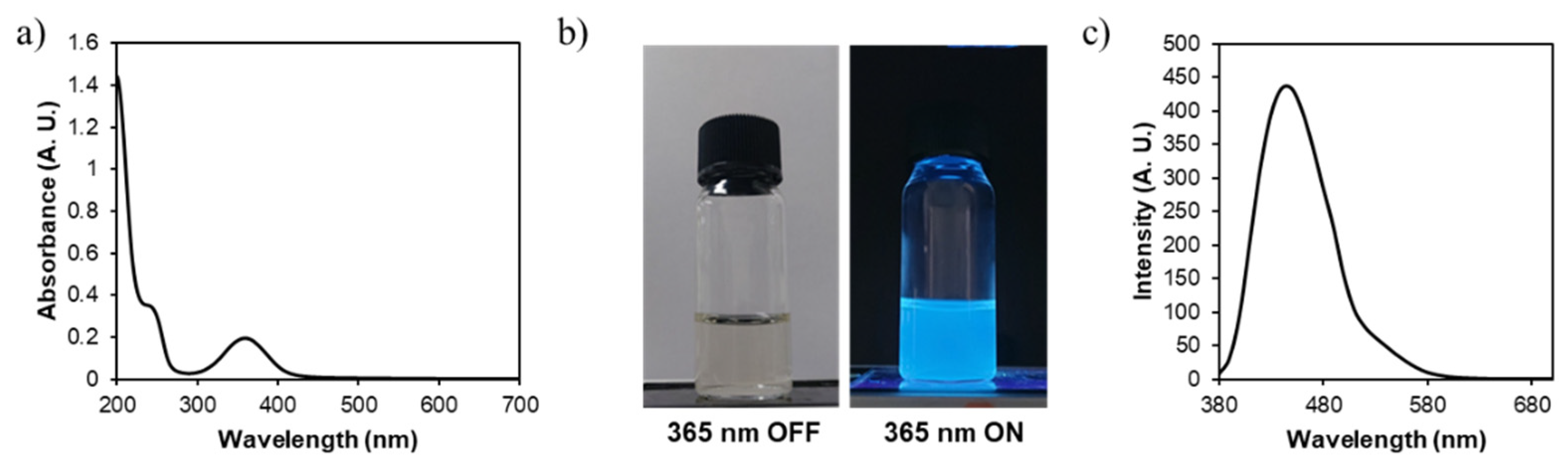
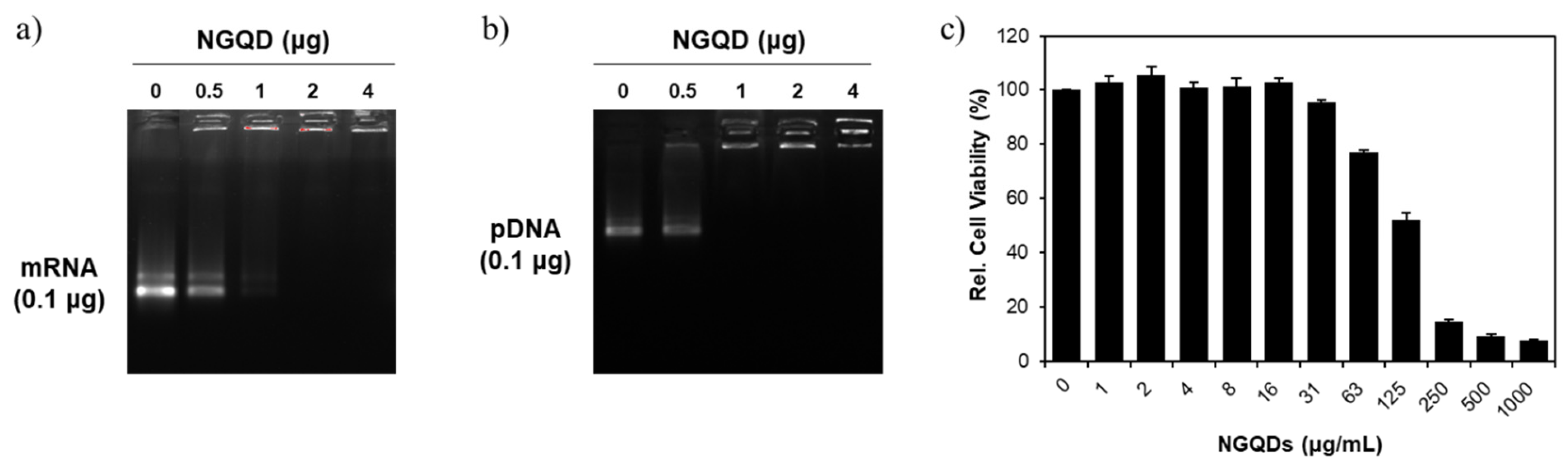
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knoll, M.D.; Wonodi, C. Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine efficacy. Lancet 2021, 397, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.S. Rapid COVID-19 vaccine development. Science 2020, 368, 945–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh Le, T.; Andreadakis, Z.; Kumar, A.; Gomez Roman, R.; Tollefsen, S.; Saville, M.; Mayhew, S. The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, L.; Mascola, J.R.; Fauci, A.S.; Collins, F.S. A strategic approach to COVID-19 vaccine R&D. Science 2020, 368, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; McGeer, A. The starting line for COVID-19 vaccine development. Lancet 2020, 395, 1815–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyanathan, M.; Afkhami, S.; Smaill, F.; Miller, M.S.; Lichty, B.D.; Xing, Z. Immunological considerations for COVID-19 vaccine strategies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Chemaitelly, H.; Butt, A.A. Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine against the B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 Variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Beiss, V.; Fiering, S.N.; Steinmetz, N.F. COVID-19 Vaccine Frontrunners and Their Nanotechnology Design. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12522–12537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellet, J.; Pepper, M.S. A COVID-19 Vaccine: Big Strides Come with Big Challenges. Vaccines 2021, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Pant, A.B. Efforts at COVID-19 Vaccine Development: Challenges and Successes. Vaccines 2020, 8, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benenson, S.; Oster, Y.; Cohen, M.J.; Nir-Paz, R. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness among Health Care Workers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.W.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine Candidates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, S.A.; Baillie, V.; Cutland, C.L.; Voysey, M.; Koen, A.L.; Fairlie, L.; Padayachee, S.D.; Dheda, K.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 COVID-19 Vaccine against the B.1.351 Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, I.F.N.; Poland, G.A. Single-dose Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine followed by a 12-week booster. Lancet 2021, 397, 854–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, T.; Parker, N.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. History of gene therapy. Gene 2013, 525, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, C.E.; High, K.A.; Joung, J.K.; Kohn, D.B.; Ozawa, K.; Sadelain, M. Gene therapy comes of age. Science 2018, 359, eaan4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weissman, D.; Karikó, K. mRNA: Fulfilling the Promise of Gene Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1416–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheridan, C. Gene therapy finds its niche. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deverman, B.E.; Ravina, B.M.; Bankiewicz, K.S.; Paul, S.M.; Sah, D.W.Y. Gene therapy for neurological disorders: Progress and prospects. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 641–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, R. The basic science of gene therapy. Science 1993, 260, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somia, N.; Verma, I.M. Gene therapy: Trials and tribulations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2000, 1, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldini, L. Gene therapy returns to centre stage. Nature 2015, 526, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pozo-Rodríguez, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A. Applications of lipid nanoparticles in gene therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 109, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barenholz, Y. Doxil®—The first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A.E.; Zhou, Q. Lipid Nanoparticles—From Liposomes to mRNA Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Research Diversity and Advancement. ACS Nano 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Marks, F.; Clemens, J.D. Looking beyond COVID-19 vaccine phase 3 trials. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, J.; Arvidson, G.; Karlsson, G.; Almgren, M. Complexes between cationic liposomes and DNA visualized by cryo-TEM. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1995, 1235, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imani, R.; Mohabatpour, F.; Mostafavi, F. Graphene-based Nano-Carrier modifications for gene delivery applications. Carbon 2018, 140, 569–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.M.; Kang, J.H.; Hong, B.H. Graphene-based nanomaterials for versatile imaging studies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4835–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Pan, Y.; Ping, Y.; Sahoo, N.G.; Wu, T.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Gan, L.H. Chitosan-Functionalized Graphene Oxide as a Nanocarrier for Drug and Gene Delivery. Small 2011, 7, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Yang, X.; Shi, X.; Tan, X.; Peng, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. Polyethylene Glycol and Polyethylenimine Dual-Functionalized Nano-Graphene Oxide for Photothermally Enhanced Gene Delivery. Small 2013, 9, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dideikin, A.T.; Vul’, A.Y. Graphene Oxide and Derivatives: The Place in Graphene Family. Front. Phys. 2019, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Hu, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Yong, K.-T.; Lu, F.; Liang, Y.; Li, Z. SiRNA Delivery with PEGylated Graphene Oxide Nanosheets for Combined Photothermal and Genetherapy for Pancreatic Cancer. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Namgung, R.; Singha, K.; Oh, I.-K.; Kim, W.J. Graphene Oxide-Polyethylenimine Nanoconstruct as a Gene Delivery Vector and Bioimaging Tool. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene Quantum Dots Derived from Carbon Fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Tang, L.; Teng, K.S.; Lau, S.P. Graphene quantum dots from chemistry to applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 10, 221–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yoo, J.M.; Hwang, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, S.P.; Park, M.J.; Lee, M.; Choi, S.; Kwon, S.H.; et al. Graphene quantum dots prevent α-synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-C.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Shin, N.; Yoo, J.M.; Kang, I.; Kim, J.-J.; Lee, S.-E.; Kim, D.; Choi, S.W.; et al. Oral administration of microbiome-friendly graphene quantum dots as therapy for colitis. 2D Mater. 2021, 8, 025036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Chen, P.; Zhu, D.; Wu, L.; Cui, Y. A graphene quantum dot-based FRET system for nuclear-targeted and real-time monitoring of drug delivery. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15477–15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannazzo, D.; Pistone, A.; Salamò, M.; Galvagno, S.; Romeo, R.; Giofré, S.V.; Branca, C.; Visalli, G.; di Pietro, A. Graphene quantum dots for cancer targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 518, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Kang, Z.; Liang, L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, J.-W. Graphene quantum dot assisted translocation of drugs into a cell membrane. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4503–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, C.; Lv, Y.; Ma, G.; Wei, W.; Tian, Z. Beyond a Carrier: Graphene Quantum Dots as a Probe for Programmatically Monitoring Anti-Cancer Drug Delivery, Release, and Response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27396–27401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.C.; Islam, M.T.; Nandy, P.K.; Hossain, M.M. Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs) for Bioimaging and Drug Delivery Applications: A Review. ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 889–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Guan, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Highly efficient cascading synergy of cancer photo-immunotherapy enabled by engineered graphene quantum dots/photosensitizer/CpG oligonucleotides hybrid nanotheranostics. Biomaterials 2019, 205, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, N.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Zhang, M.; et al. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots and their applications in drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Gao, H.; Wu, S.; Li, X. Facile synthesis the nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots for selective fluorescence detection of heavy metal ions. Mater. Lett. 2017, 193, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.-W.; Liu, Y.-T.; Xie, X.-M.; Ye, X.-Y. Aluminothermic reduction enabled synthesis of silicon hollow microspheres from commercialized silica nanoparticles for superior lithium storage. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8401–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnerero, J.M.; Jimenez-Ruiz, A.; Castillo, P.M.; Prado-Gotor, R. Covalent and Non-Covalent DNA-Gold-Nanoparticle Interactions: New Avenues of Research. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafary, S.M.; Nikkhah, M.; Hatamie, S.; Hosseinkhani, S. Simultaneous Gene Delivery and Tracking through Preparation of Photo-Luminescent Nanoparticles Based on Graphene Quantum Dots and Chimeric Peptides. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinejad, R.; Dadashzadeh, A.; Moghassemi, S.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Dehshahri, A.; Pardakhty, A.; Sassan, H.; Sohrevardi, S.-M.; Mandegary, A. Shedding light on gene therapy: Carbon dots for the minimally invasive image-guided delivery of plasmids and noncoding RNAs—A review. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 18, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, A.; Hashemi, E. A pseudohomogeneous nanocarrier based on carbon quantum dots decorated with arginine as an efficient gene delivery vehicle. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Du, P.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; et al. Photoluminescent Cationic Carbon Dots as efficient Non-Viral Delivery of Plasmid SOX9 and Chondrogenesis of Fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.; Akhter, S.; Pichon, C.; Midoux, P. Intracellular Availability of pDNA and mRNA after Transfection: A Comparative Study among Polyplexes, Lipoplexes, and Lipopolyplexes. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.; Fasbender, S.; Pilch, R.; Kurth, J.; Franken, A.; Ludescher, M.; Naskou, J.; Hallenberger, A.; Gall, C.V.; Mohr, C.J.; et al. From in vitro to ex vivo: Subcellular localization and uptake of graphene quantum dots into solid tumors. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 395101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Sabirsh, A.; Ye, L.; Wu, X.; Lu, H.; Liu, J. A Novel Graphene Quantum Dot-Based mRNA Delivery Platform. ChemistryOpen 2021, 10, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Han, T.; Zhou, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J. Insight into the Cellular Internalization and Cytotoxicity of Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Revia, R.A.; Zhang, M. Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Applications in Bioimaging, Biosensing, and Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 1904362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Fan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Han, M.; Fan, L. The uptake mechanism and biocompatibility of graphene quantum dots with human neural stem cells. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5799–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, C.; Zhou, X.; Han, T.; Xin, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S. Enhancing Cell Nucleus Accumulation and DNA Cleavage Activity of Anti-Cancer Drug via Graphene Quantum Dots. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henna, T.K.; Pramod, K. Graphene quantum dots redefine nanobiomedicine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, I.C.C.; Sério, S.; Ferreira, Q.; Jones, N.C.; Hoffmann, S.V.; Ribeiro, P.A.; Raposo, M. Graphene Oxide Layer-by-Layer Films for Sensors and Devices. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.W.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Mechanisms of Quantum Dot Nanoparticle Cellular Uptake. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 110, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanada, S.; Fujioka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kanaya, F.; Manome, Y.; Yamamoto, K. Cell-Based in Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model Can Rapidly Evaluate Nanoparticles’ Brain Permeability in Association with Particle Size and Surface Modification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1812–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perini, G.; Palmieri, V.; Ciasca, G.; de Spirito, M.; Papi, M. Unravelling the Potential of Graphene Quantum Dots in Biomedicine and Neuroscience. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perini, G.; Palmieri, V.; Ciasca, G.; D’Ascenzo, M.; Gervasoni, J.; Primiano, A.; Rinaldi, M.; Fioretti, D.; Prampolini, C.; Tiberio, F.; et al. Graphene Quantum Dots’ Surface Chemistry Modulates the Sensitivity of Glioblastoma Cells to Chemotherapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
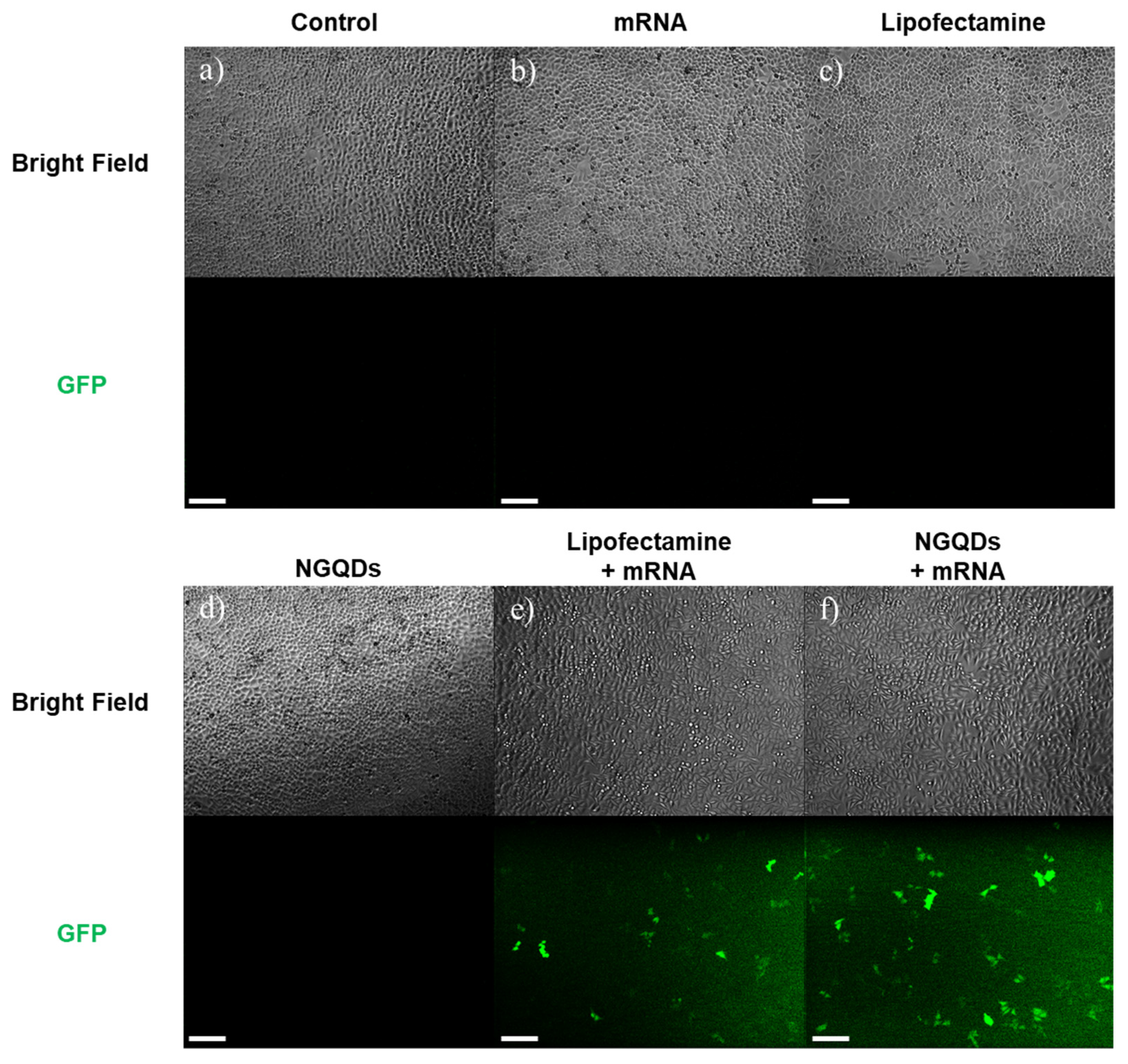
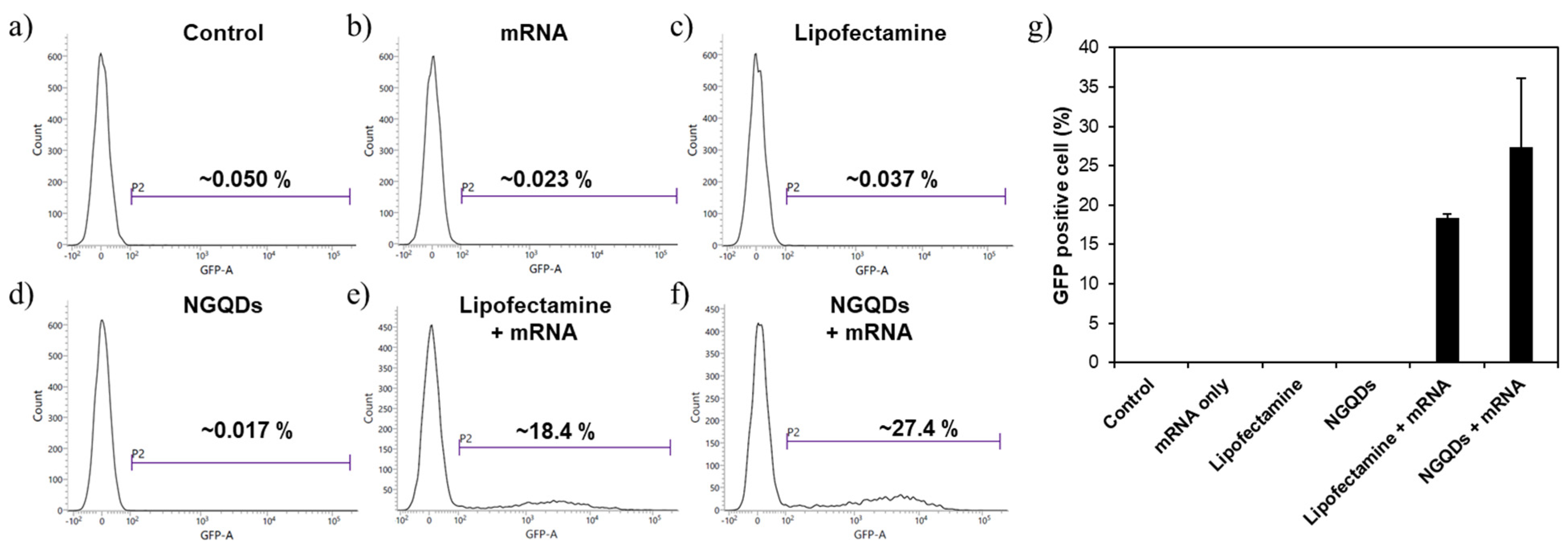
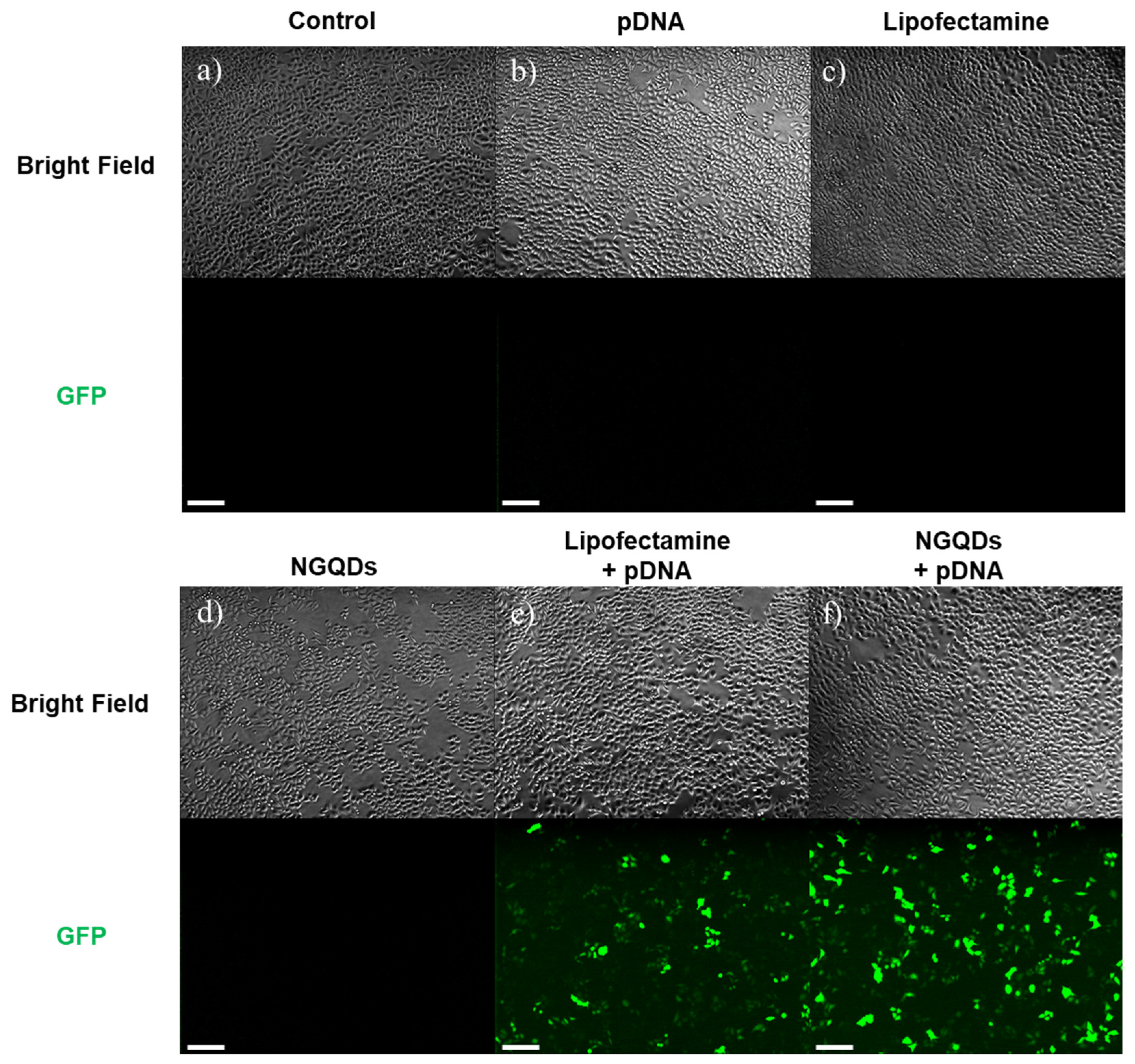
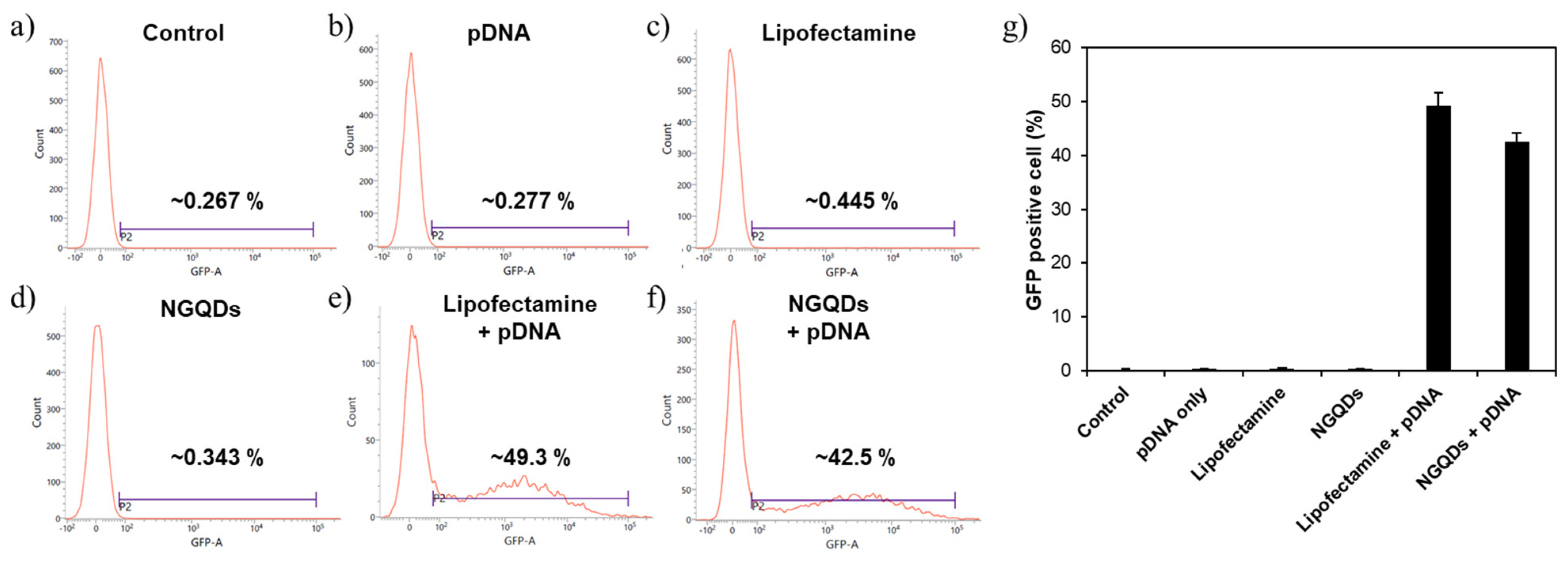
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, M.; Song, J.; Hong, B.H. Facile Synthesis of N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots as Novel Transfection Agents for mRNA and pDNA. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112816
Ahn M, Song J, Hong BH. Facile Synthesis of N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots as Novel Transfection Agents for mRNA and pDNA. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112816
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Minchul, Jaekwang Song, and Byung Hee Hong. 2021. "Facile Synthesis of N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots as Novel Transfection Agents for mRNA and pDNA" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112816
APA StyleAhn, M., Song, J., & Hong, B. H. (2021). Facile Synthesis of N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots as Novel Transfection Agents for mRNA and pDNA. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 2816. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112816





