Hydrogenated Amorphous TiO2−x and Its High Visible Light Photoactivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation of HA-TiO2−x
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Photodegradation Performances of HA-TiO2−x
2.5. Theoretical Calculation Methods
3. Results and Discussion
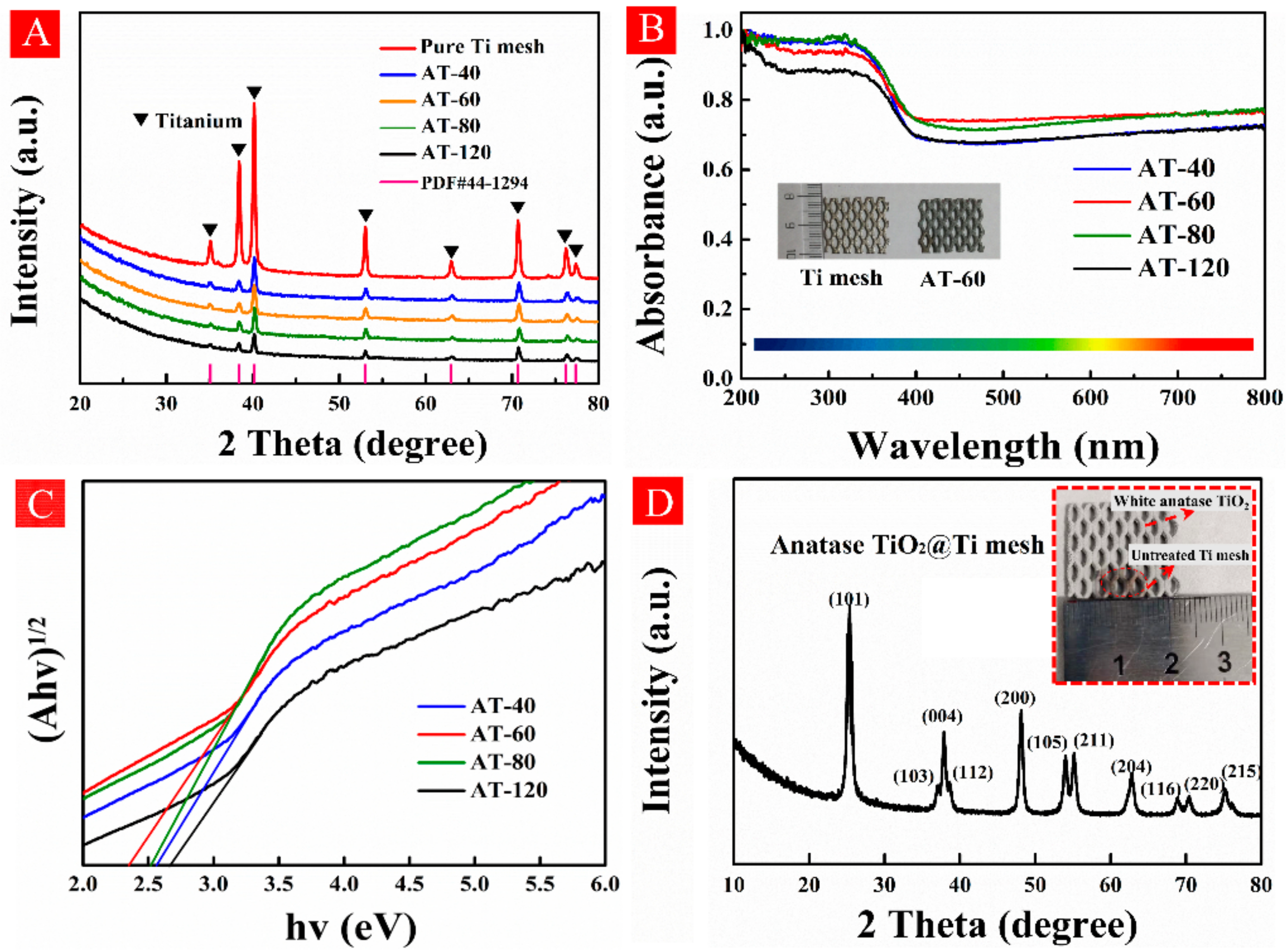
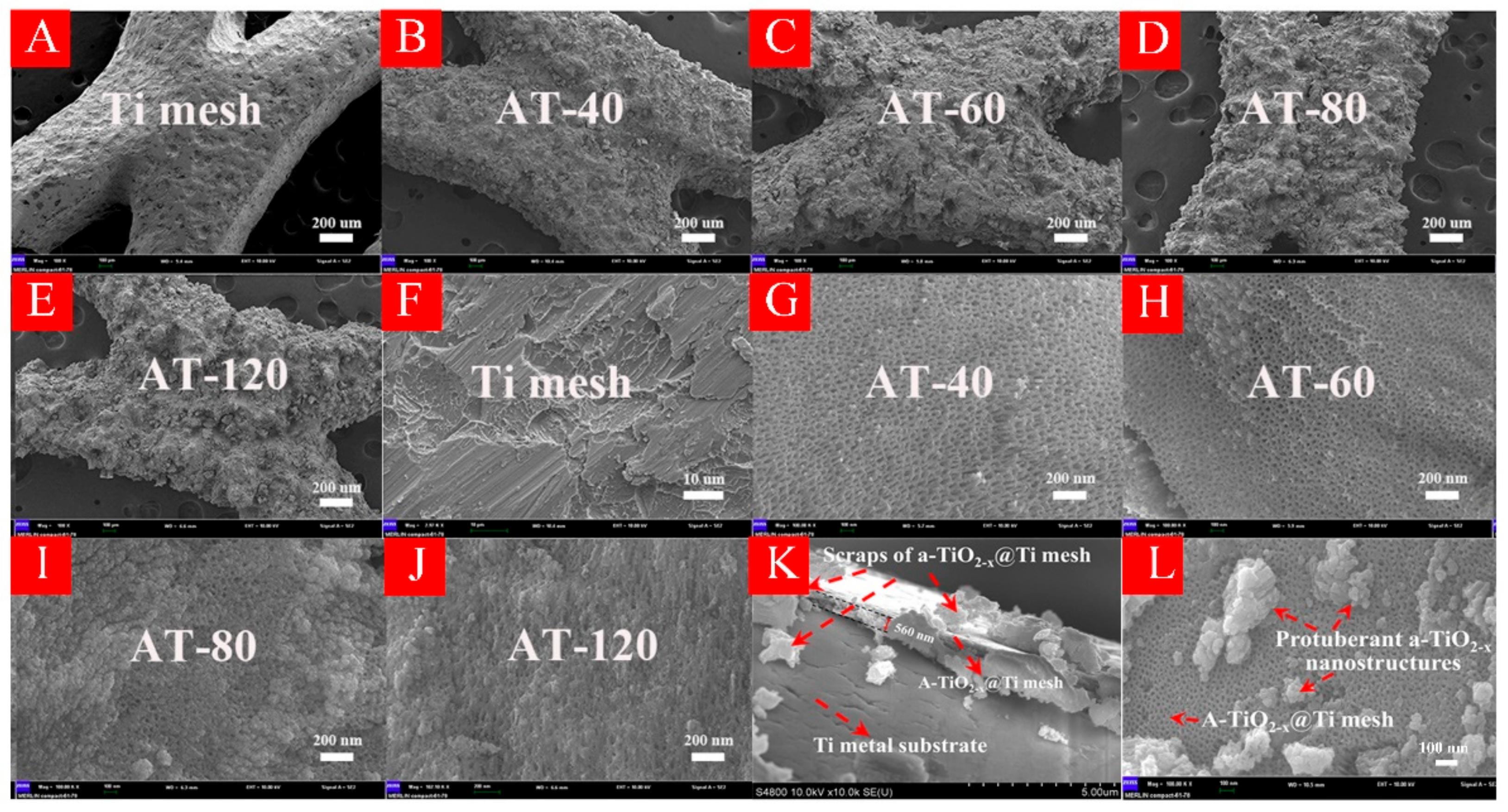
3.1. Characterizations of HA-TiO2−x
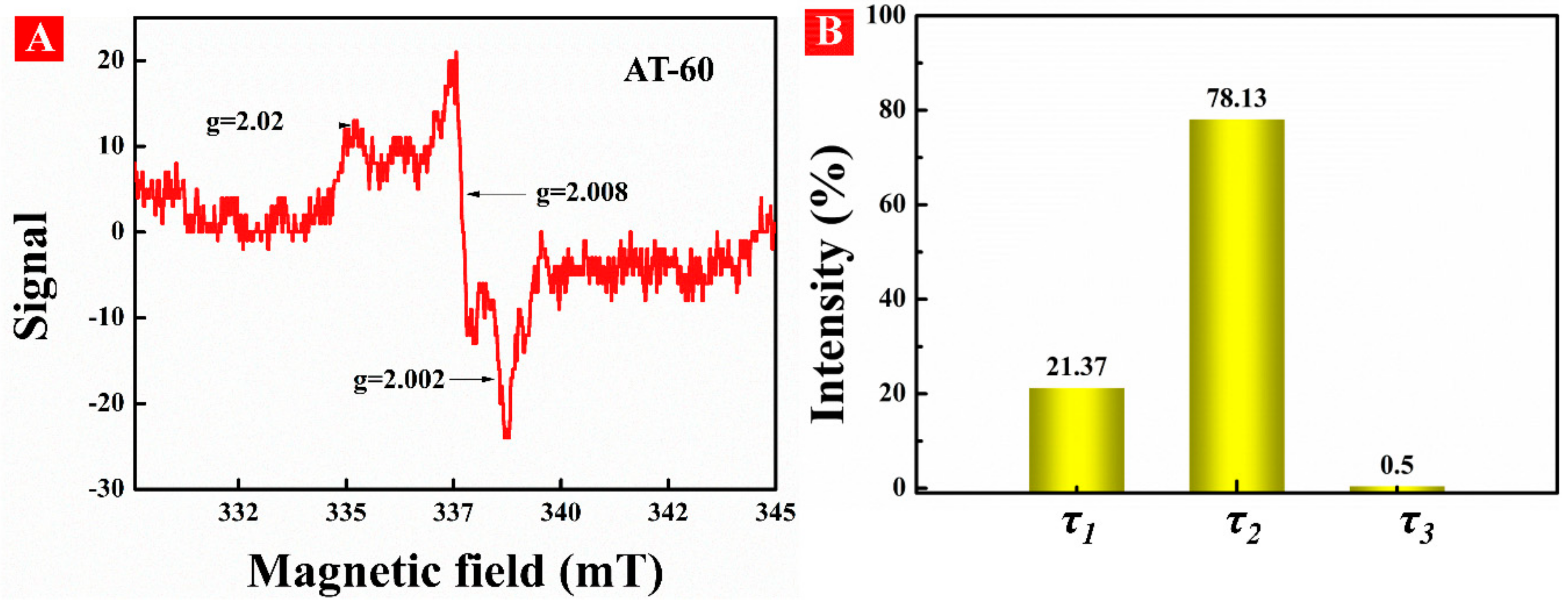
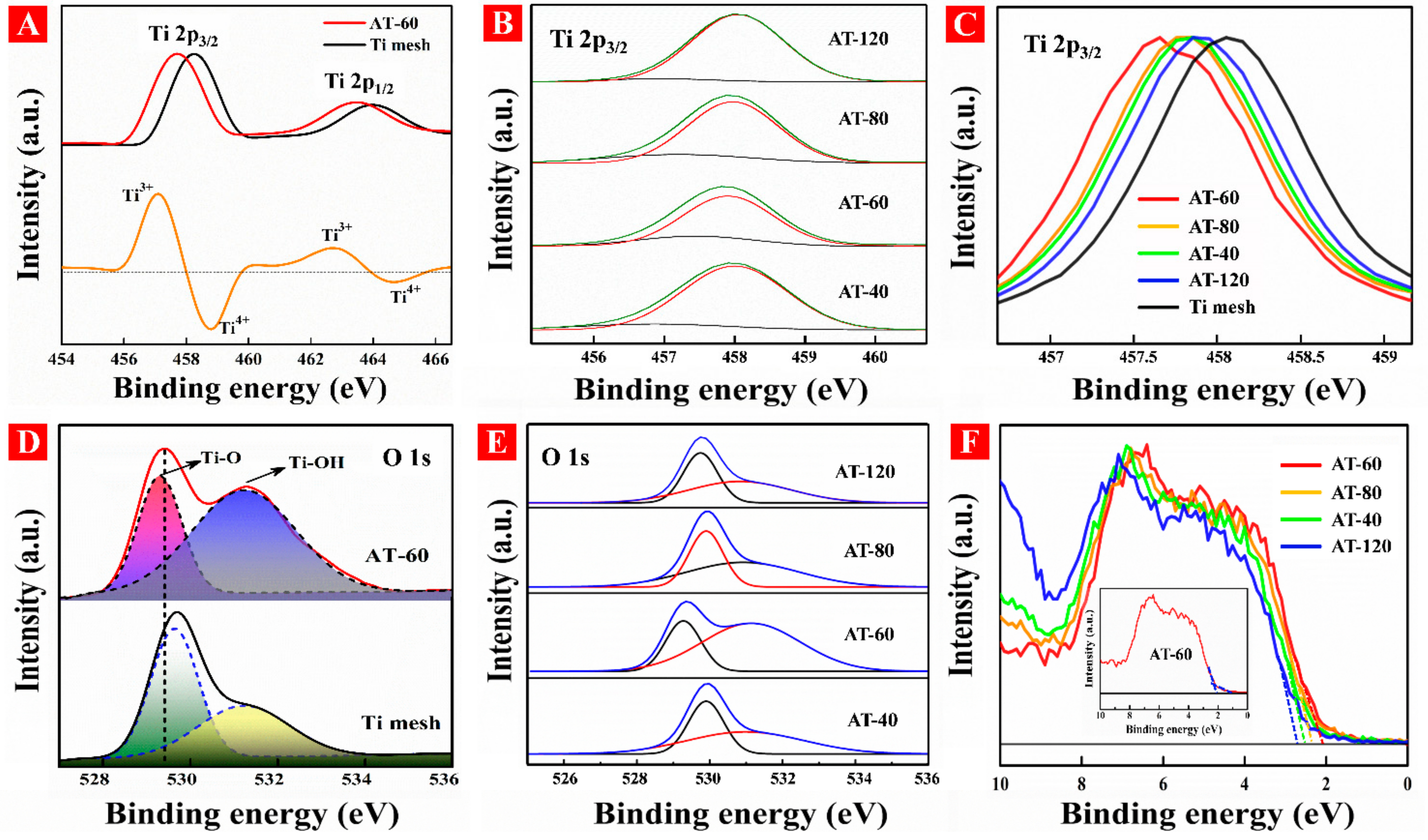
3.2. Formation of OV in HA-TiO2−x
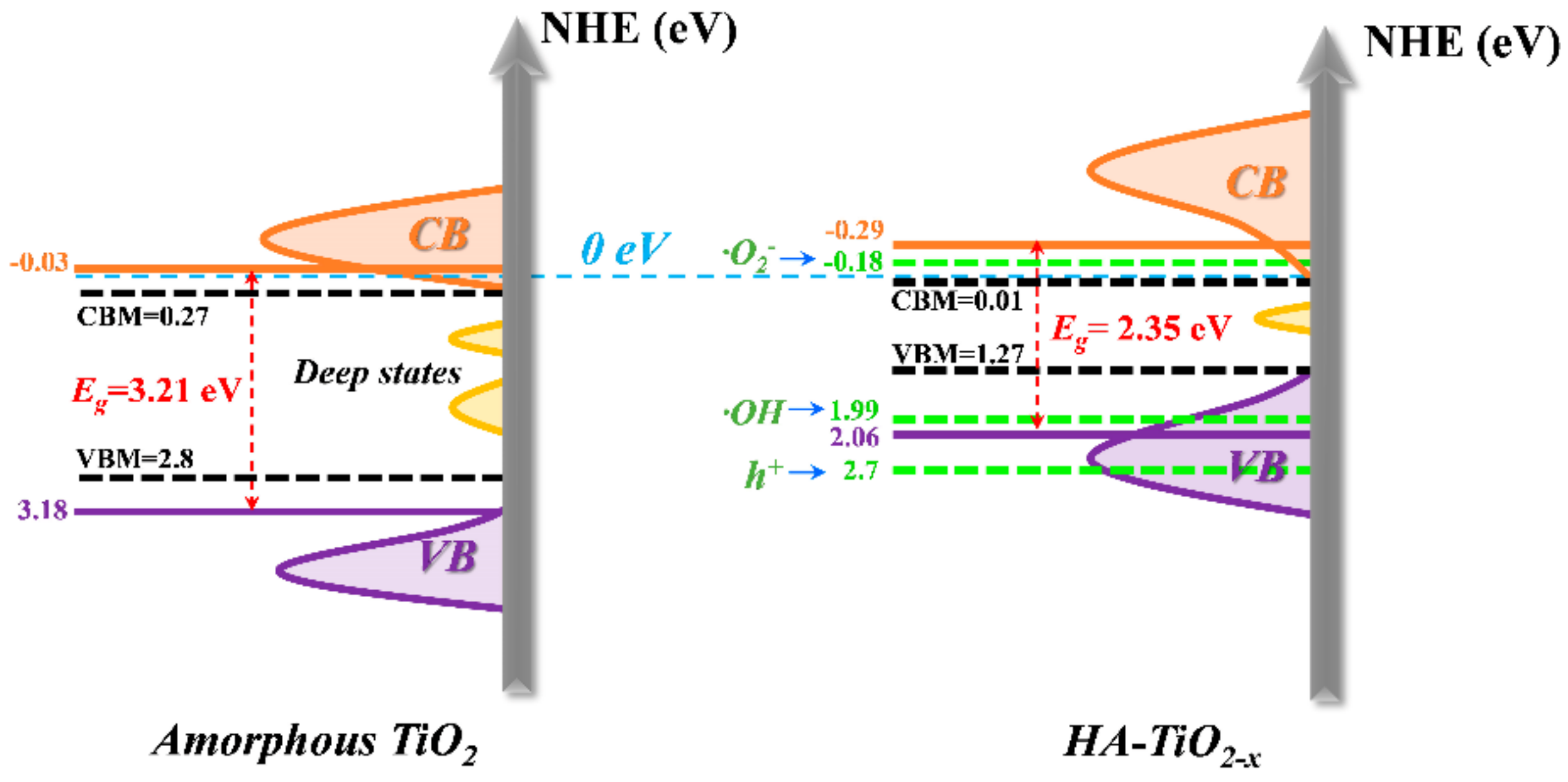
3.3. Electronic Structures of HA-TiO2−x
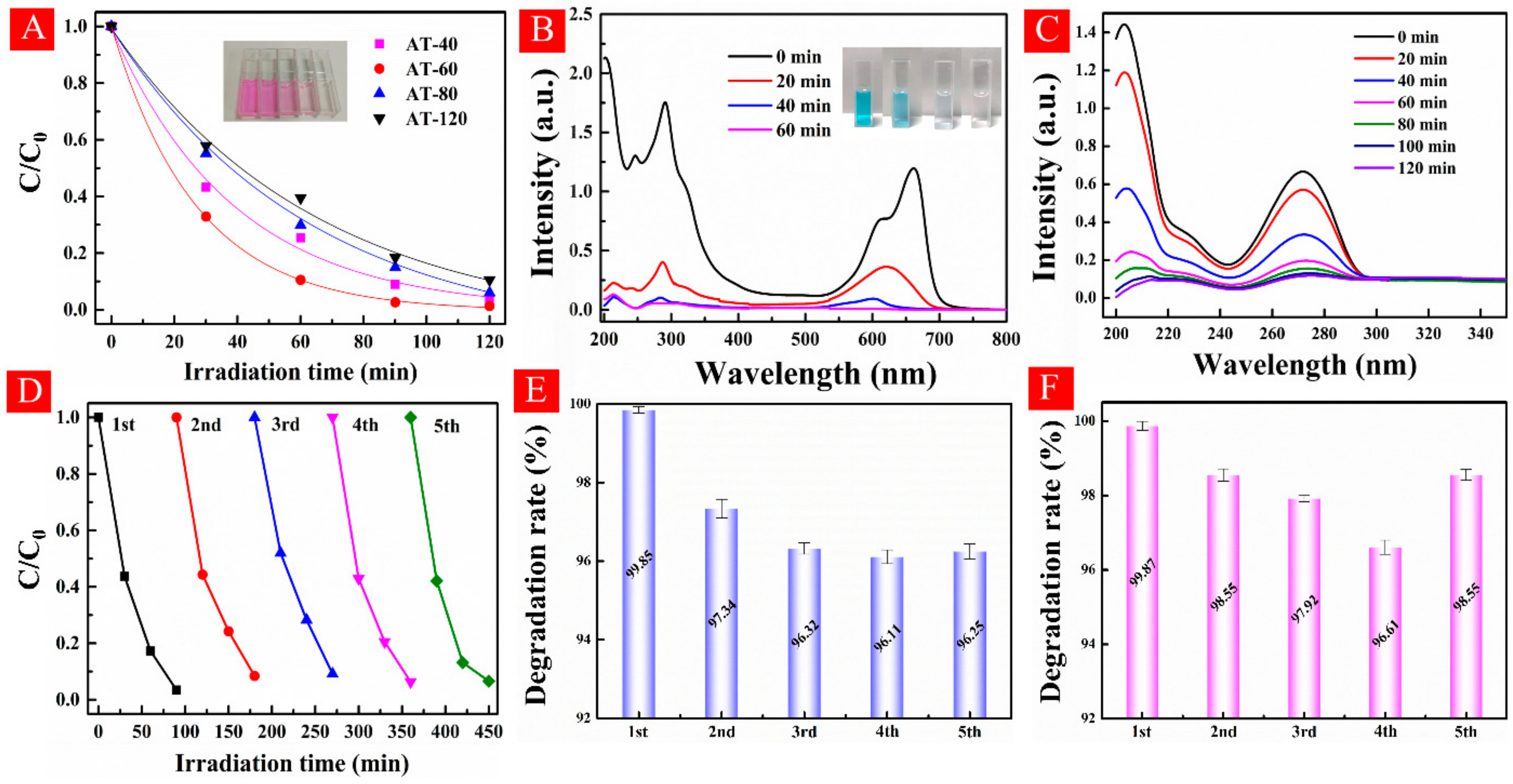
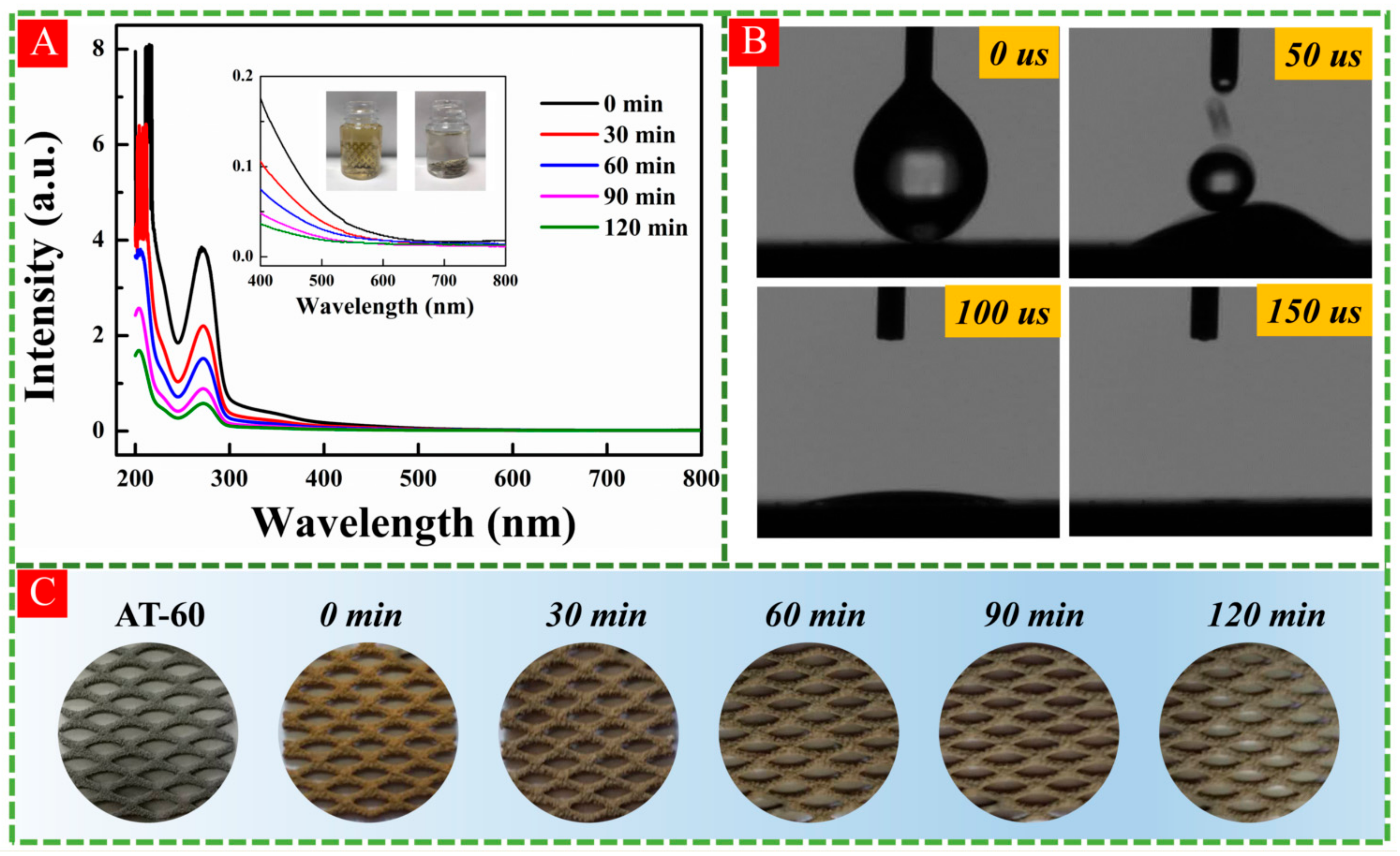
3.4. Photocatalytic Performance Examinations
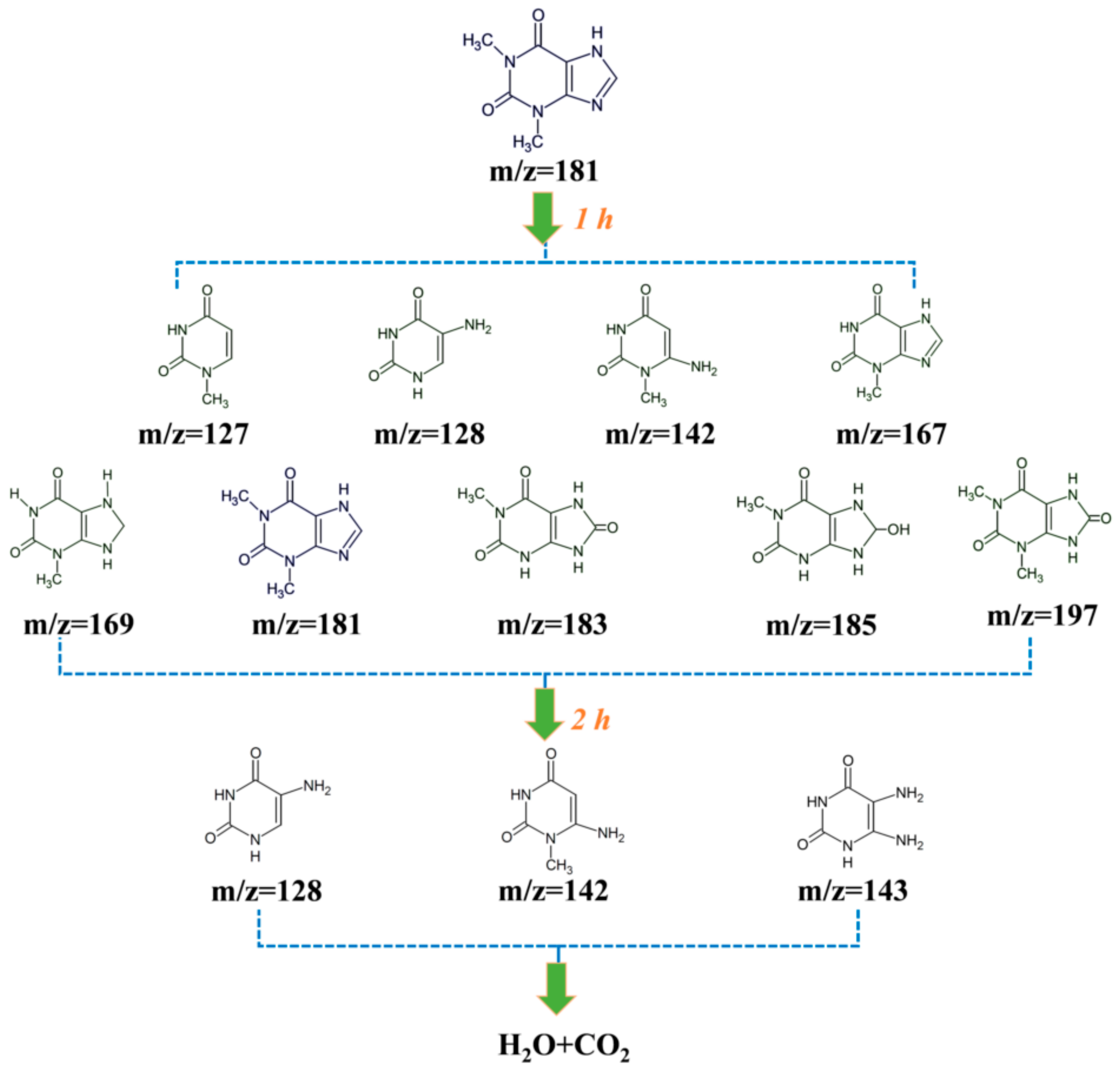
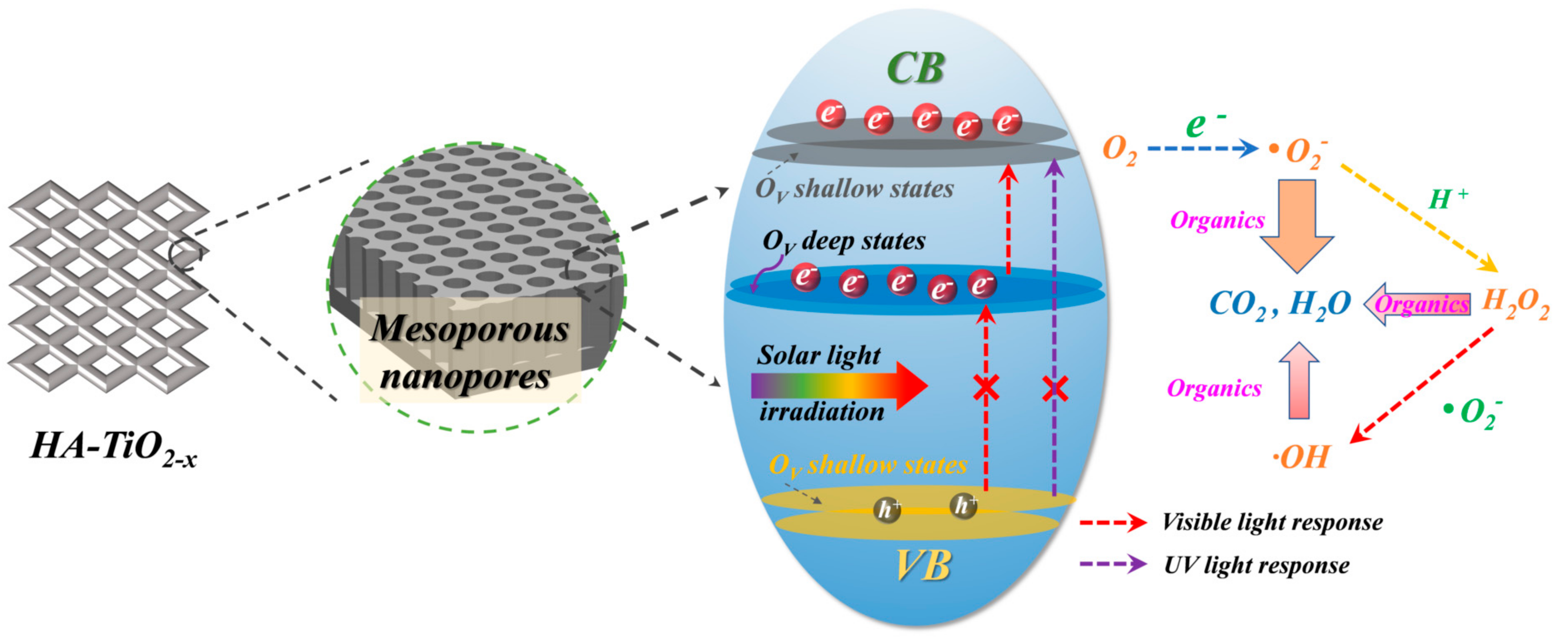
3.5. Reactive Species Tests and Photodegradation Mechanism
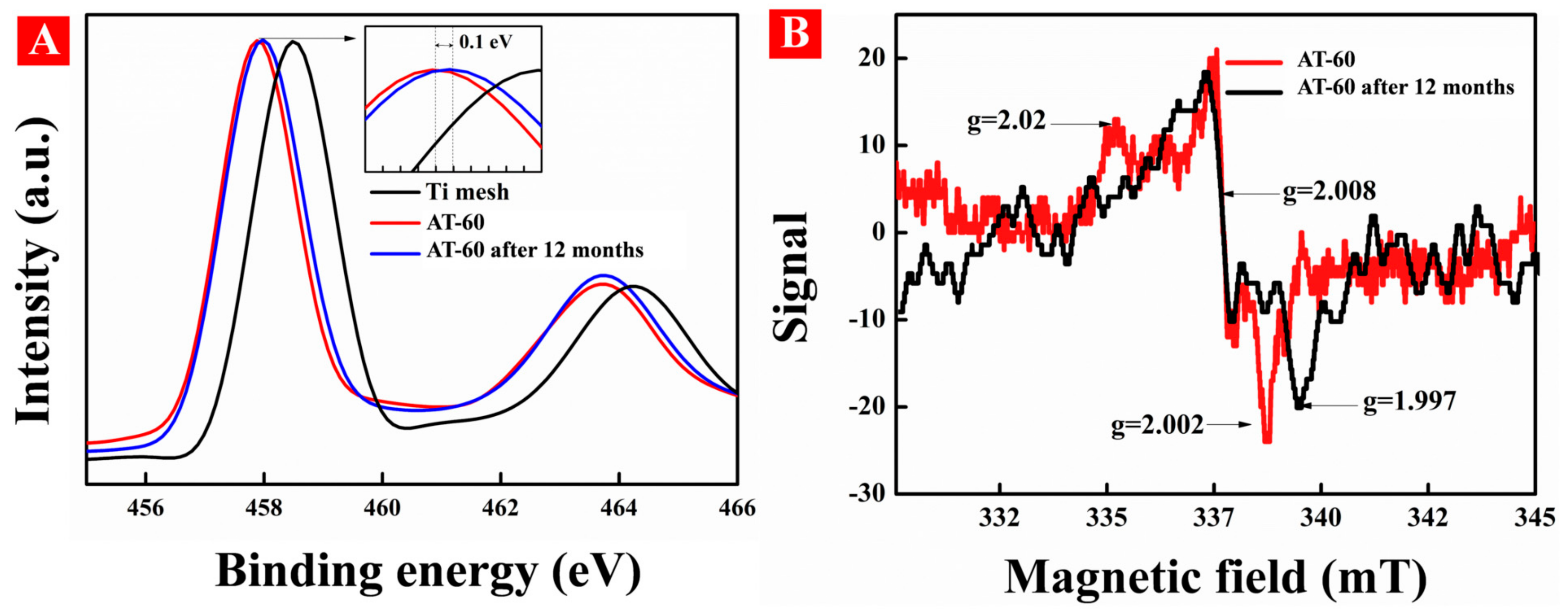
3.6. Verification of Long-Term Stability of Surface OV
3.7. The Formation Mechanism of HA-TiO2−x
4. Conclusions
- Hydrogenated amorphous TiO2−x was reported for the first time. First-principle calculations revealed the unique bandgap structure that both band tail states near valence band and conduction one were generated, leading to extraordinary visible-light absorption.
- The distinct liquid plasma hydrogenation strategy can effectively produce abundant surface OV on amorphous TiO2.
- The special photodegradation mechanism. In visible-light photodegradation, O2− and OH were accounted for polluted water decomposition, nevertheless, h+ was almost not contributed to the visible photoactivity.
- The concentration of OV heavily affected photocatalytic efficiency. The higher OV concentration the HA-TiO2−x possessed, the narrower the bandgap it received, and the higher photocatalytic efficiency it exhibited.
- The excellent visible-light photodegradation and stability. HA-TiO2−x exhibited superior visible-light photodegradations in RhB (98.7%), MB (99.85%), and theophylline (99.87). Moreover, surface OV in HA-TiO2−x was rather stable and can be preserved in an ambient atmosphere over 12 months.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naldoni, A.; Altomare, M.; Zoppellaro, G.; Liu, N.; Kment, Š.; Zbořil, R.; Schmuki, P. Photocatalysis with Reduced TiO2: From Black TiO2 to Cocatalyst-Free Hydrogen Production. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaraman, T.S.; Parikh, S.P.; Gandhi, V.G. Black TiO2: A Review of Its Properties and Conflicting Trends. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 123918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Huang, F. Black Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1861–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, Z.; Qiu, X.; Cao, X.; Zhang, P.; Teobaldi, G.; Liu, L.-M.; Guo, L. Amorphous Domains in Black Titanium Dioxide. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Biesold, G.M.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Z. Amorphous Inorganic Semiconductors for the Development of Solar Cell, Photoelectrocatalytic and Photocatalytic Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6914–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zywitzki, G.; Jing, H.; Tüysüz, H.; Chan, C.K. High Surface area, Amorphous Titania with Reactive Ti3+ Through a Photo-Assisted Synthesis Method for Photocatalytic H2 Generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 10957–10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Selective Hydrogenation Via Cascade Catalysis on Amorphous TiO2. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 6585–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Song, P.; Cui, J.; Liang, S. Amorphous TiO2 Nanostructures: Synthesis, Fundamental Properties and Photocatalytic Applications. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 4198–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanna, M.; Wongnawa, S. Mixed Amorphous and Nanocrystalline TiO2 Powders Prepared by Sol–Gel Method: Characterization and Photocatalytic Study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 110, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimny, K.; Roques-Carmes, T.; Carteret, C.; Stébé, M.J.; Blin, J.L. Synthesis and Photoactivity of Ordered Mesoporous Titania with a Semicrystalline Framework. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaker, K.; Carteret, C.; Lebeau, B.; Marichal, C.; Vidal, L.; Stébé, M.-J.; Blin, J.-L. Water-Catalyzed Low-Temperature Transformation from Amorphous to Semi-Crystalline Phase of Ordered Mesoporous Titania Framework. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Park, J.H. Surface Localization of Defects in Black TiO2: Enhancing Photoactivity or Reactivity. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushing, S.K.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J.; Ding, B.; Chen, C.K.; Chen, C.-J.; Liu, R.-S.; Bristow, A.D.; Bright, J.; Zheng, P.; et al. Effects of Defects on Photocatalytic Activity of Hydrogen-Treated Titanium Oxide Nanobelts. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldoni, A.; Allieta, M.; Santangelo, S.; Marelli, M.; Fabbri, F.; Cappelli, S.; Bianchi, C.L.; Psaro, R.; Santo, V.D. Effect of Nature and Location of Defects on Bandgap Narrowing in Black TiO2 Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7600–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Huang, X.; Chen, T.; Zhao, W.; Bi, Q.; Xu, J.; Han, Y.; Huang, F. Hydrogenated Blue Titania for Efficient Solar to Chemical Conversions: Preparation, Characterization, and Reaction Mechanism of CO2 Reduction. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, N.; Gao, C.; Xiong, Y. Defect Engineering in Photocatalytic Materials. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 296–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ravishankar, S.; Ma, M.; Veerappan, G.; Bisquert, J.; Fabregat-Santiago, F.; Park, J.H. Overcoming Charge Collection Limitation at Solid/Liquid Interface by a Controllable Crystal Deficient Overlayer. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1600923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Chen, A.; Luo, Y.; Lu, P.; Dai, Y.; Enriquez, E.; Dowden, P.; Xu, H.; Kotula, P.G.; Azad, A.K.; et al. Conducting Interface in Oxide Homojunction: Understanding of Superior Properties in Black TiO2. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5751–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Wu, B.; Khan, A.Q.; Zeng, H. In Situ Glow Discharge Plasma Electrolytic Synthesis of Reduced TiO2 for Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalysis. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 055022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Feng, G.; Hu, M.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, H. Liquid-Plasma Hydrogenated Synthesis of Gray Titania with Engineered Surface Defects and Superior Photocatalytic Activity. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kang, S.-Z.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Qin, L.; Mu, J. Multi-Layered Mesh-Like MoS2 Hierarchical Nanostructure Fabricated on Ti Foil: An Efficient Noble Metal-Free Photocatalyst for Visible-Light-Driven H2 Evolution from Water. Catal. Commun. 2016, 82, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Peng, Y.; Lin, L.; Fan, C.-M.; Gao, G.-Q.; Wang, R.-X.; Xu, A.-W. Stable Blue TiO2−x Nanoparticles for Efficient Visible Light Photocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 4429–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, V.N.; Serpone, N. Photoinduced Coloration and Photobleaching of Titanium Dioxide in TiO2/Polymer Compositions upon UV- and Visible-Light Excitation of Color Centers’ Absorption Bands: Direct Experimental Evidence Negating Band-Gap Narrowing in Anion-/Cation-Doped TiO2s. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 15277–15288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, S.; Bard, A.J. Novel Carbon-Doped TiO2 Nanotube Arrays with High Aspect Ratios for Efficient Solar Water Splitting. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Lin, J.; Qiao, B.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Miao, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Catalytically Active Rh Sub-Nanoclusters on TiO2 for CO Oxidation at Cryogenic Temperatures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2820–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Abdel-Mageed, A.M.; Li, D.; Bansmann, J.; Cisneros, S.; Biskupek, J.; Huang, W.; Behm, R.J. Morphology-Engineered Highly Active and Stable Ru/TiO2 Catalysts for Selective CO Methanation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10732–10736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makal, P.; Das, D. Self-Doped TiO2 Nanowires in TiO2-B Single Phase, TiO2-B/Anatase and TiO2-Nnatase/Rutile Heterojunctions Demonstrating Individual Superiority in Photocatalytic Activity under Visible and UV Light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, S.; Berglund, S.P.; Hahn, N.T.; Bard, A.J.; Mullins, C.B. Enhancing Visible Light Photo-Oxidation of Water with TiO2 Nanowire Arrays via Cotreatment with H2 and NH3: Synergistic Effects between Ti3+ and N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3659–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Jana, D.; Banerjee, A.; Manik, S.; Pradhan, S.K.; Sutradhar, M.; Sarkar, A. Annealing Effect on Nano-ZnO Powder Studied from Positron Lifetime and Optical Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Dulub, O.; Cheng, H.; Selloni, A.; Diebold, U. Evidence for the Predominance of Subsurface Defects on Reduced Anatase TiO2 (101). Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 106105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhao, X.; Fang, P. Formation of AgI/TiO2 Nanocomposite Leads to Excellent Thermochromic Reversibility and Photostability. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9263–9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wei, S.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xu, B.; Pan, F.; Tang, A.; Chen, X. Effect of Deposition Parameters on Properties of TiO2 Films Deposited by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 10991–10998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, J.J.; Yan, N.F.; Pan, G.L.; Li, G.R.; Gao, X.P. Aluminum Storage Behavior of Anatase TiO2 Nanotube Arrays in Aqueous Solution for Aluminum Ion Batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9743–9746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-M. Formation and Characterization of TiO2–SnOx–Sn Composite Nanowires Fabricated by Reduction/Oxidation of Sn and Ti Ions. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Ma, X.; Sun, C.; Zhao, B.; Chen, F. Surface Oxygen Vacancies Enriched Pt/TiO2 Synthesized with a Defect Migration Strategy for Superior Photocatalytic Activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 145021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, P.Y.; Chen, X.; Mao, S.S.; Shen, D.Z. Hydrogenation and Disorder in Engineered Black TiO2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 065505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, D. Chemistry and Physics of Amorphous Semiconductors. J. Chem. Educ. 1980, 57, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Khan, M.; He, J.; Lo, I.M.C. Recent Developments and Challenges in Practical Application of Visible–Light–Driven TiO2–Based Heterojunctions for PPCP Degradation: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Du, H.; Tan, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yin, F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X. Semi-Continuous Pressurized Hot Water Extraction of Black Tea. J. Food Eng. 2018, 227, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xia, X.; Chen, W.; Hu, L.; Mo, L.e.; Huang, Y.; Dai, S. Inside-Out Ostwald Ripening: A Facile Process towards Synthesizing Anatase TiO2 Microspheres for High-Efficiency Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1891–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, S.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Z.; Xue, Q. Review on Electrical Discharge Plasma Technology for Wastewater Remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 348–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, V.N.; Serpone, N. On the Origin of the Spectral Bands in the Visible Absorption Spectra of Visible-Light-Active TiO2 Specimens Analysis and Assignments. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 15110–15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Matsushita, S.; Wei, S.; Gao, W. Defective black TiO2 synthesized via anodization for visible-light photocatalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Zhang, G.; Yang, X. Preparation of Ti mesh supported WO3/TiO2 nanotubes composite and its application for photocatalytic degradation under visible light. Mater. Lett. 2015, 145, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Mi, L.; Tian, Z.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, S. Promoting Photodegradation Efficiency via a Heterojunction photocatalyst combining with oxygen direct and fast diffusion from the gas phase to active catalytic sites. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 44922–44930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Wang, M.; Ali, R.; Nie, S.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, R.; Lau, W.M.; He, L.; Tang, H.; Jian, X. Multi-layered porous hierarchical TiO2/g-C3N4 hybrid coating for enhanced visible light photocatalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 495, 143435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çırak, B.B.; Caglar, B.; Kılınç, T.; Karadeniz, S.M.; Erdoğan, Y.; Kılıç, S.; Kahveci, E.; Ekinci, A.E.; Çırak, Ç. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanorice decorated TiO2 nanotubes for enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 109, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Tan, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, G.; Pan, H. Fabrication of In2O3/TiO2 nanotube arrays hybrids with homogeneously developed nanostructure for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 106, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, T.N.Q.; Phan, T.B.; Nam, N.D.; Thu, V.T. In situ charge transfer at the Ag@ZnO photoelectrochemical interface toward the high photocatalytic performance of H2 evolution and RhB degradation. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 12195–12206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhebshi, N.; Huang, H.; Ghandour, R.; Alghamdi, N.K.; Alharbi, O.; Aljurban, S.; He, J.H.; Al-Jawhari, H. Green synthesized CuxO@Cu nanocomposites on a Cu mesh with dual catalytic functions for dye degradation and hydrogen evaluation. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 848, 156284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Chen, Q.; Lan, R.; Jiang, R.; Quan, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, F.; Jia, Y. Effect of anodization parameters on morphology and photocatalysis properties of TiO2 nanotube arrays. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Ma, Q.; Cui, Y.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, Q. Fabrication of TiO2 nanorods/nanosheets photoelectrode on Ti mesh by hydrothermal method for degradation of methylene blue:influence of calcination temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Tan, X.; Du, X.; Gao, S. Solvothermal fabrication and construction of highly photoelectrocatalytic TiO2 NTs/Bi2MoO6 heterojunction based on titanium mesh. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 556, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Bandgap (eV) | Mean ± SD (eV) | VBM (eV) | Mean ± SD (eV) | Ti3+/Ti4+ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT-40 | 2.57 | 2.57 ± 0.03 | 2.38 | 2.38 ± 0.02 | 16% |
| AT-60 | 2.35 | 2.35 ± 0.01 | 2.03 | 2.03 ± 0.03 | 26% |
| AT-80 | 2.52 | 2.52 ± 0.02 | 2.24 | 2.24 ± 0.01 | 22% |
| AT-120 | 2.66 | 2.66 ± 0.01 | 2.55 | 2.55 ± 0.02 | 13% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, G.; Hu, M.; Yuan, S.; Nan, J.; Zeng, H. Hydrogenated Amorphous TiO2−x and Its High Visible Light Photoactivity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112801
Feng G, Hu M, Yuan S, Nan J, Zeng H. Hydrogenated Amorphous TiO2−x and Its High Visible Light Photoactivity. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112801
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Guang, Mengyun Hu, Shuai Yuan, Junyi Nan, and Heping Zeng. 2021. "Hydrogenated Amorphous TiO2−x and Its High Visible Light Photoactivity" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112801
APA StyleFeng, G., Hu, M., Yuan, S., Nan, J., & Zeng, H. (2021). Hydrogenated Amorphous TiO2−x and Its High Visible Light Photoactivity. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112801









