The Bio-Persistence of Reversible Inflammatory, Histological Changes and Metabolic Profile Alterations in Rat Livers after Silver/Gold Nanorod Administration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Gold Nanorods (AuNRs) and Gold Core/Silver Shell Nanorods (Au@Ag NRs)
2.3. Surface Coating of AuNRs and Au@Ag NRs with PDDAC
2.4. Animal Experiment and Sample Collection
2.5. Hematological Examination
2.6. Biochemical Assay of Serum
2.7. Histopathology
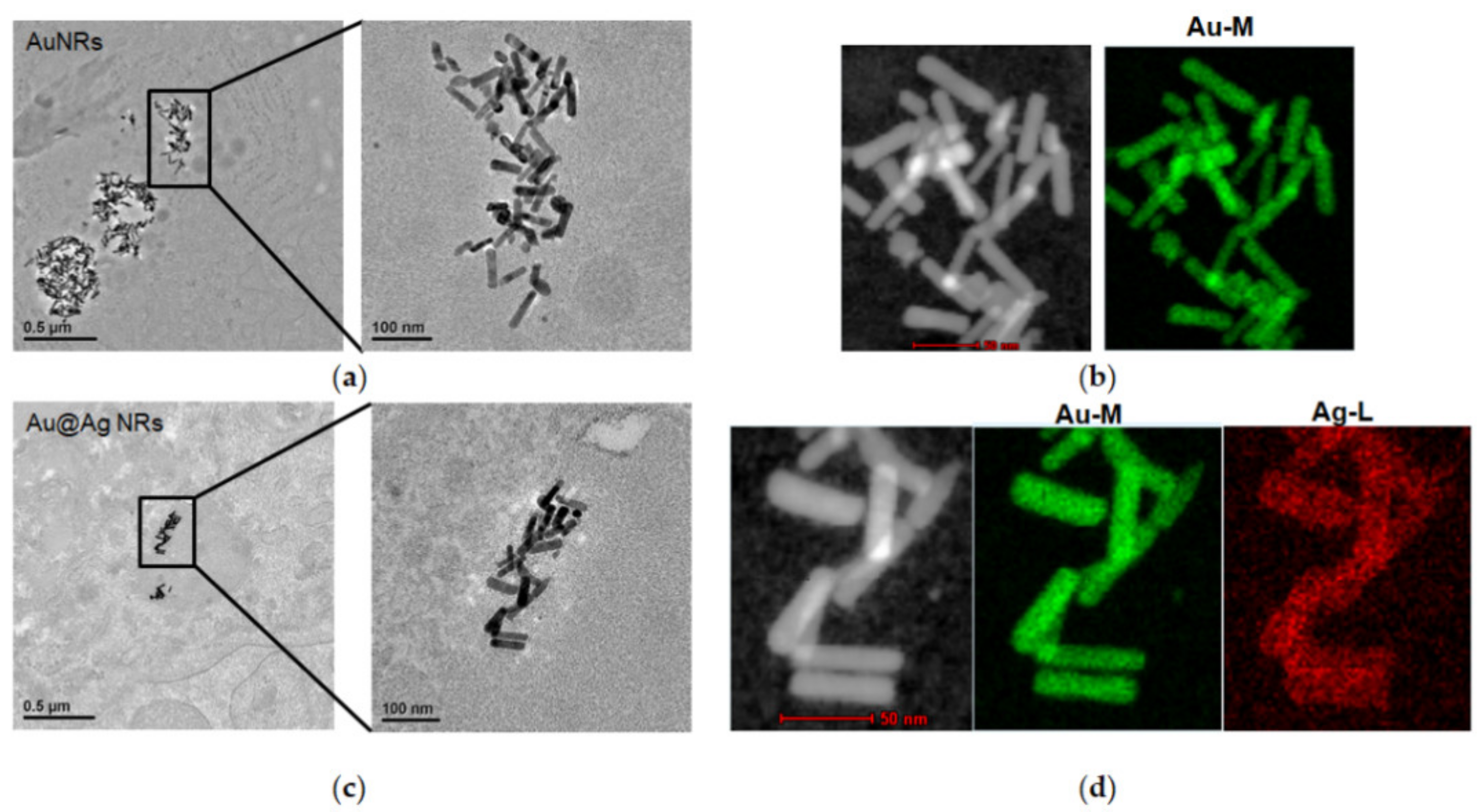
2.8. The Distribution of AuNRs or Au@AgNRs in Liver Tissues by TEM
2.9. Cytokine Detection in Serum
2.10. Metabolite Analysis in Liver Tissue Extracts
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of AuNRs and Au@Ag NRs
3.2. The Contents of Au and Ag in Blood and Organs after the Exposure of Au@Ag NRs
3.3. Hematological Changes after the Exposure of Au@Ag NRs
3.4. Effects of Au@Ag NRs on Serum Biochemical Markers
3.5. The Release of Cytokine or Grow Factor in Serum
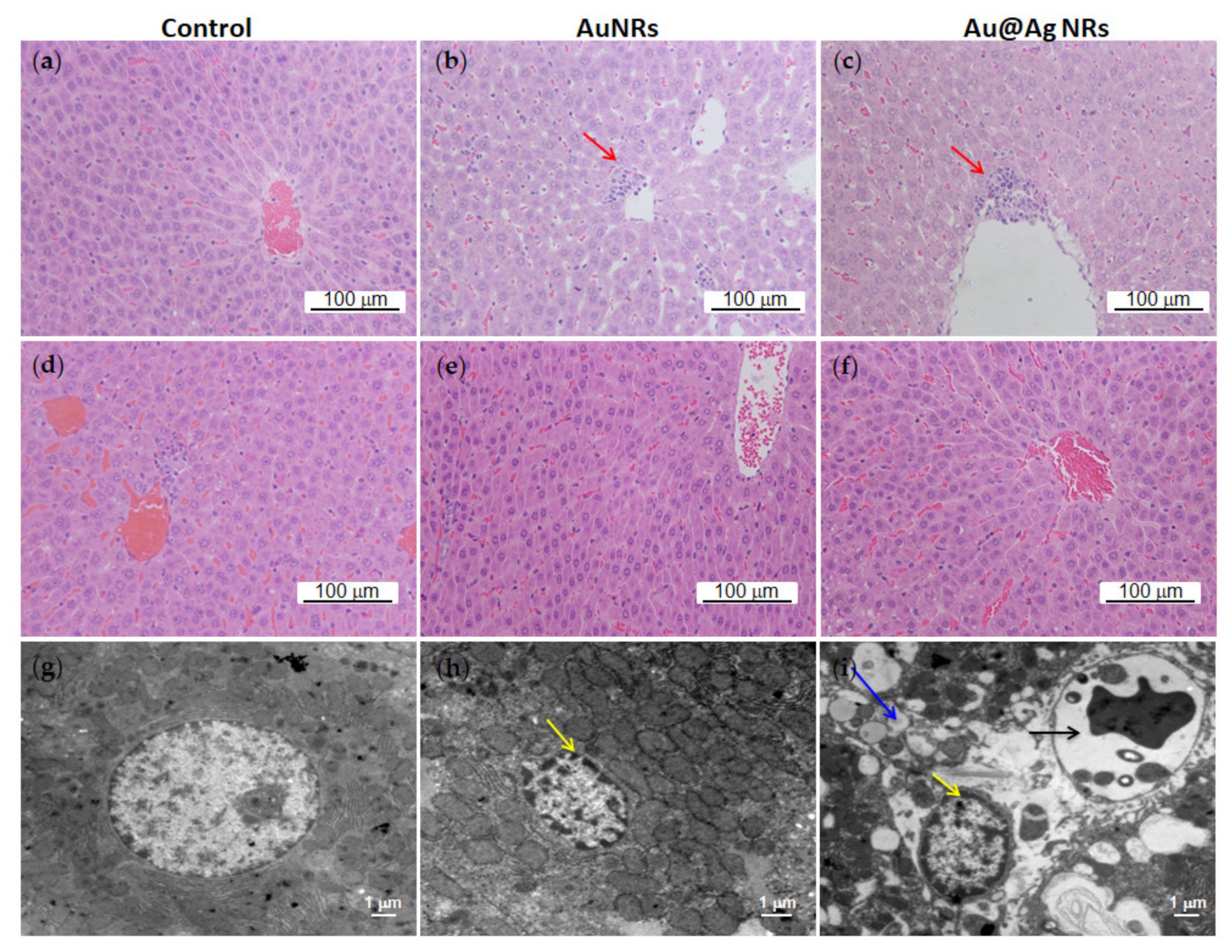
3.6. Effects of Au@Ag NRs on Histological Changes
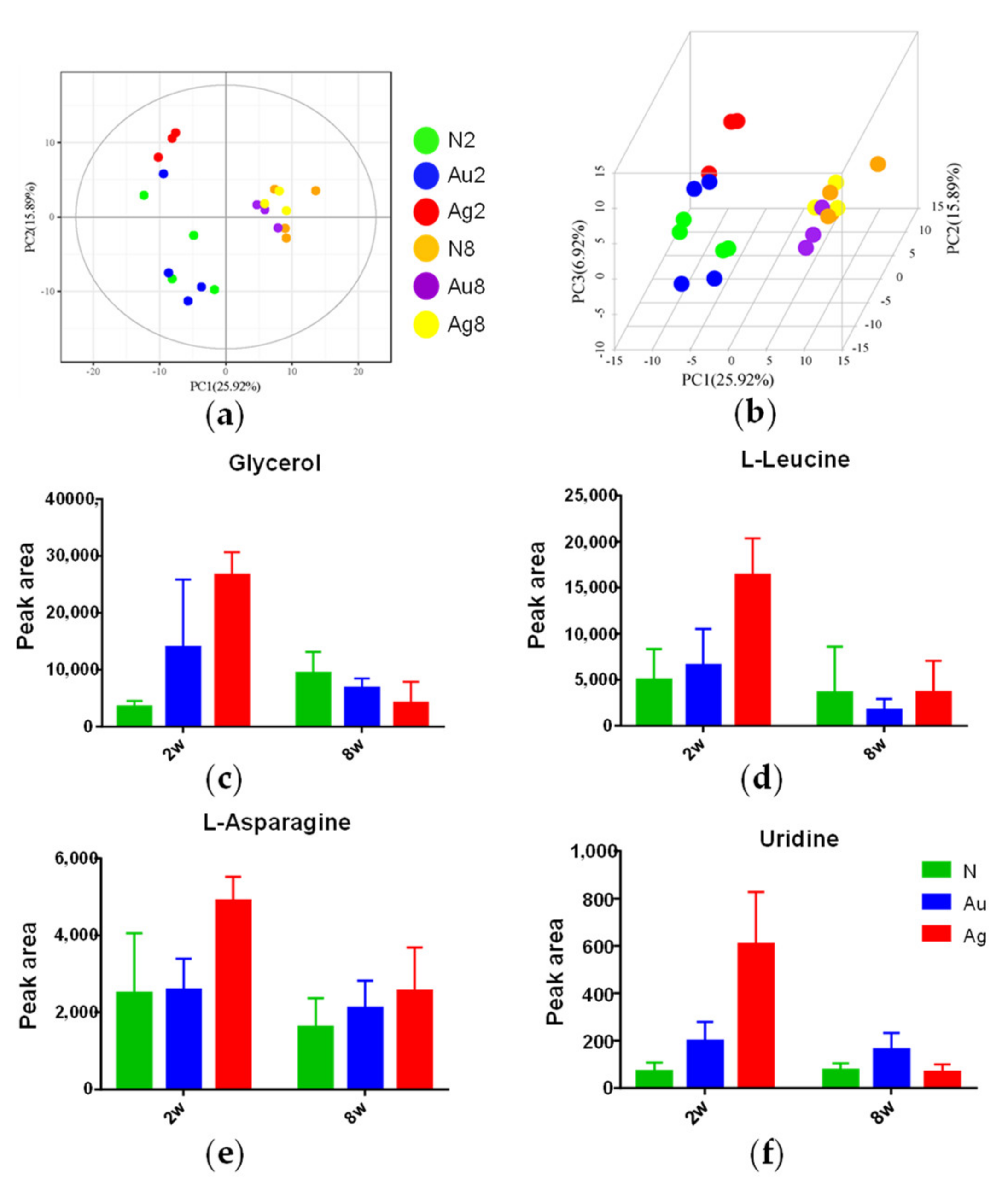
3.7. Metabolic Responses of Liver Tissues to Au@Ag NRs Treatments
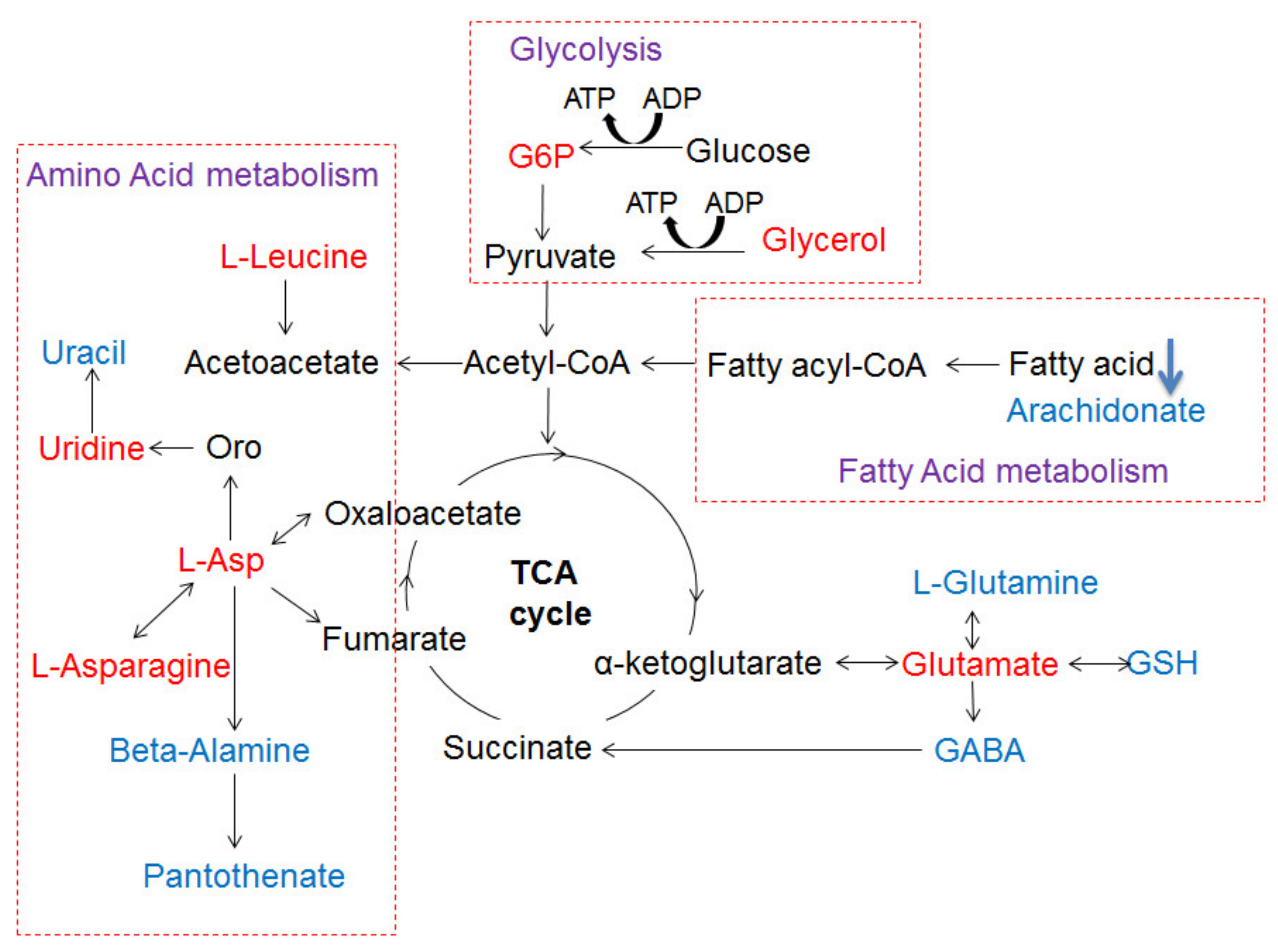
3.8. The Metabolic Networks Related to Au@Ag NRs via the Metabolite Variations in the Liver Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.K.; Goswami, K.; Sharma, R.D.; Reddy, M.V.; Dash, D. Novel microfilaricidal activity of nanosilver. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, M.; Alsalhi, M.S.; Siddiqui, M.K. Silver nanoparticle applications and human health. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2010, 411, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, J.J.; Sivalingam, P.; Chen, B. Toxicological effects of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.S.; Yin, L.; Ren, N.N.; Xian, L.; Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Gontero, B. The effect of chronic silver nanoparticles on aquatic system in microcosms. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volker, C.; Oetken, M.; Oehlmann, J. The biological effects and possible modes of action of nanosilver. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 223, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asharani, P.V.; Low Kah Mun, G.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Yi, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Park, K. Silver nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity by a Trojan-horse type mechanism. Toxicol. Vitro 2010, 24, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Song, K.S.; Sung, J.H.; Ryu, H.R.; Choi, B.G.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, J.K.; Yu, I.J. Genotoxicity, acute oral and dermal toxicity, eye and dermal irritation and corrosion and skin sensitisation evaluation of silver nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.J.; Chatterjee, N.; Lee, J.; Choi, J. Integrated mRNA and microRNA profiling reveals epigenetic mechanism of differential sensitivity of Jurkat T cells to AgNPs and Ag ions. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 229, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Dan, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Xie, L. Bio-distribution and bio-availability of silver and gold in rat tissues with silver/gold nanorod administration. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 12260–12268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teodoro, J.S.; Silva, R.; Varela, A.T.; Duarte, F.V.; Rolo, A.P.; Hussain, S.; Palmeira, C.M. Low-dose, subchronic exposure to silver nanoparticles causes mitochondrial alterations in Sprague-Dawley rats. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weldon, B.A.; Faustman, E.M.; Oberdorster, G.; Workman, T.; Griffith, W.C.; Kneuer, C.; Yu, I.J. Occupational exposure limit for silver nanoparticles: Considerations on the derivation of a general health-based value. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; You, J.R.; Kim, W.H.; Jang, J.J.; Min, S.K.; Kim, H.C.; Chung, D.H.; Jeong, J.; Kang, B.C.; et al. Comparative toxicity of silicon dioxide, silver and iron oxide nanoparticles after repeated oral administration to rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.-P.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Li, R.; Sun, B.; et al. Use of coated silver nanoparticles to understand the relationship of particle dissolution and bioavailability to cell and lung toxicological potential. Small 2014, 10, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dziendzikowska, K.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J.; Lankoff, A.; Oczkowski, M.; Krawczynska, A.; Chwastowska, J.; Sadowska-Bratek, M.; Chajduk, E.; Wojewodzka, M.; Dusinska, M.; et al. Time-dependent biodistribution and excretion of silver nanoparticles in male Wistar rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, M. Acute toxic effects and gender-related biokinetics of silver nanoparticles following an intravenous injection in mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankveld, D.P.; Oomen, A.G.; Krystek, P.; Neigh, A.; Troost-De Jong, A.; Noorlander, C.W.; Van Eijkeren, J.C.; Geertsma, R.E.; De Jong, W.H. The kinetics of the tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles of different sizes. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8350–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Park, E.J.; Chun, I.K.; Choi, K.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, J.; Lee, B.C. Bioavailability and toxicokinetics of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recordati, C.; De Maglie, M.; Bianchessi, S.; Argentiere, S.; Cella, C.; Mattiello, S.; Cubadda, F.; Aureli, F.; D’Amato, M.; Raggi, A.; et al. Tissue distribution and acute toxicity of silver after single intravenous administration in mice: Nano-specific and size-dependent effects. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Gulumian, M.; Faustman, E.M.; Workman, T.; Jeon, K.; Yu, I.J. Blood biochemical and hematological study after subacute intravenous injection of gold and silver nanoparticles and coadministered gold and silver nanoparticles of similar sizes. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8460910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, R.; Singh, R.D.; Khan, H.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Mittal, S.; Singh, V.; Arjaria, N.; Shankar, J.; Roy, S.K.; Singh, D.; et al. Oral Subchronic exposure to silver nanoparticles causes renal damage through apoptotic impairment and necrotic cell death. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, M.D.; Imam, M.S.; Paredes, A.M.; Bryant, M.S.; Cunningham, C.K.; Felton, R.P.; Jones, M.Y.; Davis, K.J.; Olson, G.R. Differential effects of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on tissue accumulation, distribution, and toxicity in the sprague dawley rat following daily oral gavage administration for 13 weeks. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 150, 131–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, D.; Garcia, T.; Blanco, J.; Sánchez, D.; Sirvent, J.; Domingo, J.; Gomez, M. Effects of oral exposure to silver nanoparticles on the sperm of rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 60, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Song, M.Y.; Park, J.D.; Song, K.S.; Ryu, H.R.; Chung, Y.H.; Chang, H.K.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, K.H.; Kelman, B.J.; et al. Subchronic oral toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.Y.; Kim, J.; Park, J.D.; Ryu, H.Y.; Yu, I.J. Histological study of gender differences in accumulation of silver nanoparticles in kidneys of Fischer 344 rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2009, 72, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Qiu, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, S. Metabolomics study on the cytotoxicity of graphene. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44712–44717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Huang, W.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, F. Metabolomics techniques for nanotoxicity investigations. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 1527–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, T.R.; Mortensen, N.; Black, S.R.; Snyder, R.W.; Levine, K.; Poitras, E.; Harrington, J.; Wingard, C.J.; Holland, N.A.; Pathmasiri, W.; et al. Disposition of intravenously or orally administered silver nanoparticles in pregnant rats and the effect on the biochemical profile in urine. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Guyot-Sionnest, P. Mechanism of silver(I)-assisted growth of gold nanorods and bipyramids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 22192–22200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Nishioka, K.; Kiya, A.; Nakashima, N.; Ishibashi, A.; Niidome, Y. Uniform and controllable preparation of Au-Ag core-shell nanorods using anisotropic silver shell formation on gold nanorods. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dan, M.; Ji, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Wen, H. Single-dosed genotoxicity study of gold nanorod core/silver shell nanostructures by pig-a, micronucleus, and comet assays. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Dan, M.; Yang, Y.; Lyu, J.; Shao, A.; Cheng, X.; Chen, L.; Xu, L. Acute toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticle in rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Suttlemyre, K.; Su, M.; Zhang, W.; Jia, W.; Du, X. ADAP-GC 2.0: Deconvolution of coeluting metabolites from GC/TOF-MS data for metabolomics studies. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6619–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Cai, G.; Zhou, B.; Li, D.; Zhao, A.; Xie, G.; Li, H.; Cai, S.; Xie, D.; Huang, C.; et al. A distinct metabolic signature of human colorectal cancer with prognostic potential. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niidome, T.; Yamagata, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kawano, T.; Katayama, Y.; Niidome, Y. PEG-modified gold nanorods with a stealth character for in vivo applications. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Ji, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Xu, H. Using gold nanorods core/silver shell nanostructures as model material to probe biodistribution and toxic effects of silver nanoparticles in mice. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, E.E.; Mwamuka, J.; Gole, A.; Murphy, C.J.; Wyatt, M.D. Gold nanoparticles are taken up by human cells but do not cause acute cytotoxicity. Small 2005, 1, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, T.; Xie, Z.; Yu, X.F.; Li, W. Surface chemistry but not aspect ratio mediates the biological toxicity of gold nanorods in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Gonzalez, C.E.; Pedziwiatr-Werbicka, E.; Shcharbin, D.; Guerrero-Beltran, C.; Abashkin, V.; Loznikova, S.; Jimenez, J.L.; Munoz-Fernandez, M.A.; Bryszewska, M.; Gomez, R.; et al. Gold nanoparticles stabilized by cationic carbosilane dendrons: Synthesis and biological properties. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 8736–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Brandão, A.; Soares, M.E.; Morais, T.; Duarte, J.A.; Pereira, L.; Soares, L.; Neves, C.; Pereira, E.; Bastos, M.D.L.; et al. Short- and long-term distribution and toxicity of gold nanoparticles in the rat after a single-dose intravenous administration. Nanomedicine 2014, 10, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Peng, J.; Wang, Z.; Gao, S. TPhP exposure disturbs carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, and the DNA damage repair system in zebrafish liver. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Zande, M.; Vandebriel, R.; Van Doren, E.; Kramer, E.; Rivera, Z.H.; Serrano-Rojero, C.S.; Gremmer, E.R.; Mast, J.; Peters, R.J.B.; Hollman, P.C.H.; et al. Distribution, elimination, and toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions in rats after 28-day oral exposure. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7427–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, W.H.; Van Der Ven, L.T.; Sleijffers, A.; Park, M.V.; Jansen, E.H.; Van Loveren, H.; Vandebriel, R.J. Systemic and immunotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in an intravenous 28 days repeated dose toxicity study in rats. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8333–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, D.K.; Jin, T.; Behari, J. Dose-dependent in-vivo toxicity assessment of silver nanoparticle in Wistar rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrastina, A.; Schnitzer, J.E. Iodine-125 radiolabeling of silver nanoparticles for in vivo SPECT imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 653–659. [Google Scholar]
- Brzoska, K.; Gradzka, I.; Kruszewski, M. Impact of silver, gold, and iron oxide nanoparticles on cellular response to tumor necrosis factor. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 356, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, E.; Dizaj, S.M.; Rahimpour, E.; Hasanzadeh, A.; Eftekhari, A.; Hosain Zadegan, H.; Halajzadeh, J.; Ahmadian, H. Effect of silver nanoparticles in the induction of apoptosis on human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarak, I.; Carrola, J.; Barros, A.S.; Gil, A.M.; Pereira, M.L.; Corvo, M.L.; Duarte, I.F. From the cover: Metabolism modulation in different organs by silver nanoparticles: An NMR metabolomics study of a mouse model. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 159, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nayak, N.C.; Sathar, S.A.; Mughal, S.; Duttagupta, S.; Mathur, M.; Chopra, P. The nature and significance of liver cell vacuolation following hepatocellular injury—An analysis based on observations on rats rendered tolerant to hepatotoxic damage. Virchows Arch. 1996, 428, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.R.; Zheng, J.; Tang, X.; Goering, P.L. Silver nanoparticle-induced autophagic-lysosomal disruption and NLRP3-inflammasome activation in HepG2 Cells is size-dependent. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 150, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzaghe, M.; Resch, T.; Schaser, E.; Kronhart, S.; Diez, C.; Niles, M.A.; Korotkova, E.; Schülke, S.; Wolfheimer, S.; Kreuz, D.; et al. Organ-specific expression of IL-1 receptor results in severe liver injury in type I interferon receptor deficient mice. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trickler, W.J.; Lantz, S.M.; Murdock, R.C.; Schrand, A.M.; Robinson, B.L.; Newport, G.D.; Schlager, J.J.; Oldenburg, S.J.; Paule, M.G.; Slikker, W.; et al. Silver nanoparticle induced blood-brain barrier inflammation and increased permeability in primary rat brain microvessel endothelial cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 118, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holland, N.A.; Thompson, L.C.; Vidanapathirana, A.K.; Urankar, R.N.; Lust, R.M.; Fennell, T.R.; Wingard, C.J. Impact of pulmonary exposure to gold core silver nanoparticles of different size and capping agents on cardiovascular injury. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of the adjuvant effect of silver nanoparticles both in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 219, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Choi, K.; Park, K. Induction of inflammatory responses and gene expression by intratracheal instillation of silver nanoparticles in mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, L.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Q.; Luo, Z.; Luo, Q.; Yu, S.; Yao, X.; Ren, Z.; Hu, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profiles of bovine mammary epithelial cells stimulated by Lipopolysaccharide. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almansour, M.; Sajti, L.; Melhim, W.; Jarrar, B.M. Ultrastructural hepatocytic alterations induced by silver nanoparticle toxicity. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2016, 40, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.; Urasaki, Y.; Pizzorno, G. Uridine prevents fenofibrate-induced fatty liver. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Bruckbauer, A.; Li, F.; Cao, Q.; Cui, X.; Wu, R.; Shi, H.; Zemel, M.B.; Xue, B. Interaction between metformin and leucine in reducing hyperlipidemia and hepatic lipid accumulation in diet-induced obese mice. Metabolism 2015, 64, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcshan, D.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Molecular toxicity mechanism of nanosilver. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madl, A.K.; Plummer, L.E.; Carosino, C.; Pinkerton, K.E. Nanoparticles, lung injury, and the role of oxidant stress. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2014, 76, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Madler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardas, S.S.; Sultana, R.; Warrier, G.; Dan, M.; Wu, P.; Grulke, E.A.; Tseng, M.T.; Unrine, J.; Graham, U.M.; Yokel, R.; et al. Rat hippocampal responses up to 90 days after a single nanoceria dose extends a hierarchical oxidative stress model for nanoparticle toxicity. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Hormesis defined. Ageing Res. Rev. 2008, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Sung, J.H.; Ryu, H.R.; Song, K.S.; Song, N.W.; Park, H.M.; Shin, B.S.; Ahn, K.; Gulumian, M.; Faustman, E.M.; et al. Tissue distribution of gold and silver after subacute intravenous injection of co-administered gold and silver nanoparticles of similar sizes. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Class | Metabolite Name | Au/N | Ag/N | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | Corr. | VIP | FC | Corr. | VIP | ||
| Alcohols | Glycerol | 7.998 ** | 0.97 | 1.8 | |||
| Amino Acid | Pyroglutamic acid | 4.443 * | 0.9 | 2.7 | / | / | / |
| L-Threonine | 1.536 ** | 0.85 | 2.6 | / | / | / | |
| L-Asparagine | / | / | / | 2.141 * | 0.73 | 1.4 | |
| L-Leucine | / | / | / | 4.409 * | 0.89 | 1.7 | |
| Gamma-Aminobutyric acid | / | / | / | 0.346 * | −0.9 | 1.7 | |
| L-Glutamine | / | / | / | 0.473 | −0.73 | 1.4 | |
| Carbohydrates | L-Arabinose | / | / | / | 3.637 ** | 0.9 | 1.7 |
| Cellobiose | / | / | / | 19.945 * | 0.91 | 1.7 | |
| Isomaltose | / | / | / | 11.056 * | 0.84 | 1.6 | |
| Kojibiose | / | / | / | 18.236 ** | 0.99 | 1.9 | |
| Alpha-Lactose | / | / | / | 1.592 * | 0.79 | 1.5 | |
| D-Maltose | / | / | / | 7.746 * | 0.89 | 1.7 | |
| Mannitol | / | / | / | 1.958 * | 0.86 | 1.6 | |
| L-Arabitol | / | / | / | 0.521 * | −0.8 | 1.5 | |
| Ribitol | / | / | / | 0.521 * | −0.8 | 1.5 | |
| Fatty Acids | Tetracosanoic acid | / | / | / | 2.87 * | 0.87 | 1.6 |
| Arachidonic acid | / | / | / | 0.496 ** | −0.9 | 1.7 | |
| Docosahexaenoic acid | / | / | / | 0.602 * | −0.79 | 1.5 | |
| Heptadecanoic acid | / | / | / | 0.605 * | −0.87 | 1.6 | |
| Myristic acid | / | / | / | 0.386 * | −0.81 | 1.5 | |
| Oleic acid | / | / | / | 0.563 * | −0.79 | 1.5 | |
| Palmitic acid | / | / | / | 0.627 * | −0.87 | 1.6 | |
| Palmitoleic acid | / | / | / | 0.720 * | −0.83 | 1.6 | |
| Lipids | MG160 | / | / | / | 0.701 ** | −0.88 | 1.6 |
| MG182 | / | / | / | 0.753* | −0.89 | 1.7 | |
| Nucleotide | Uridine | 3.213 * | 0.78 | 2.3 | 8.485 * | 0.89 | 1.7 |
| Organic Acids | Orotic acid | / | / | / | 0.064 ** | −0.91 | 1.7 |
| Petroselinic acid | / | / | / | 0.553 ** | −0.91 | 1.7 | |
| Vitamin | Pantothenic acid | / | / | / | 0.339 ** | −0.9 | 1.7 |
| Alpha-Tocopherol | / | / | / | 0.785 * | −0.83 | 1.6 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wen, H.; Wu, X.; Wu, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Huo, G.; Lyu, J.; Xie, L.; Dan, M. The Bio-Persistence of Reversible Inflammatory, Histological Changes and Metabolic Profile Alterations in Rat Livers after Silver/Gold Nanorod Administration. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102656
Liu Y, Wen H, Wu X, Wu M, Liu L, Wang J, Huo G, Lyu J, Xie L, Dan M. The Bio-Persistence of Reversible Inflammatory, Histological Changes and Metabolic Profile Alterations in Rat Livers after Silver/Gold Nanorod Administration. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102656
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ying, Hairuo Wen, Xiaochun Wu, Meiyu Wu, Lin Liu, Jiahui Wang, Guitao Huo, Jianjun Lyu, Liming Xie, and Mo Dan. 2021. "The Bio-Persistence of Reversible Inflammatory, Histological Changes and Metabolic Profile Alterations in Rat Livers after Silver/Gold Nanorod Administration" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102656
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wen, H., Wu, X., Wu, M., Liu, L., Wang, J., Huo, G., Lyu, J., Xie, L., & Dan, M. (2021). The Bio-Persistence of Reversible Inflammatory, Histological Changes and Metabolic Profile Alterations in Rat Livers after Silver/Gold Nanorod Administration. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2656. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102656








