The Deactivation Mechanism of the Mo-Ce/Zr-PILC Catalyst Induced by Pb for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Catalyst Preparation
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
2.3. NH3-SCR Activity Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. NH3-SCR Activity
3.2. Crystal Phase and Textural Characteristics
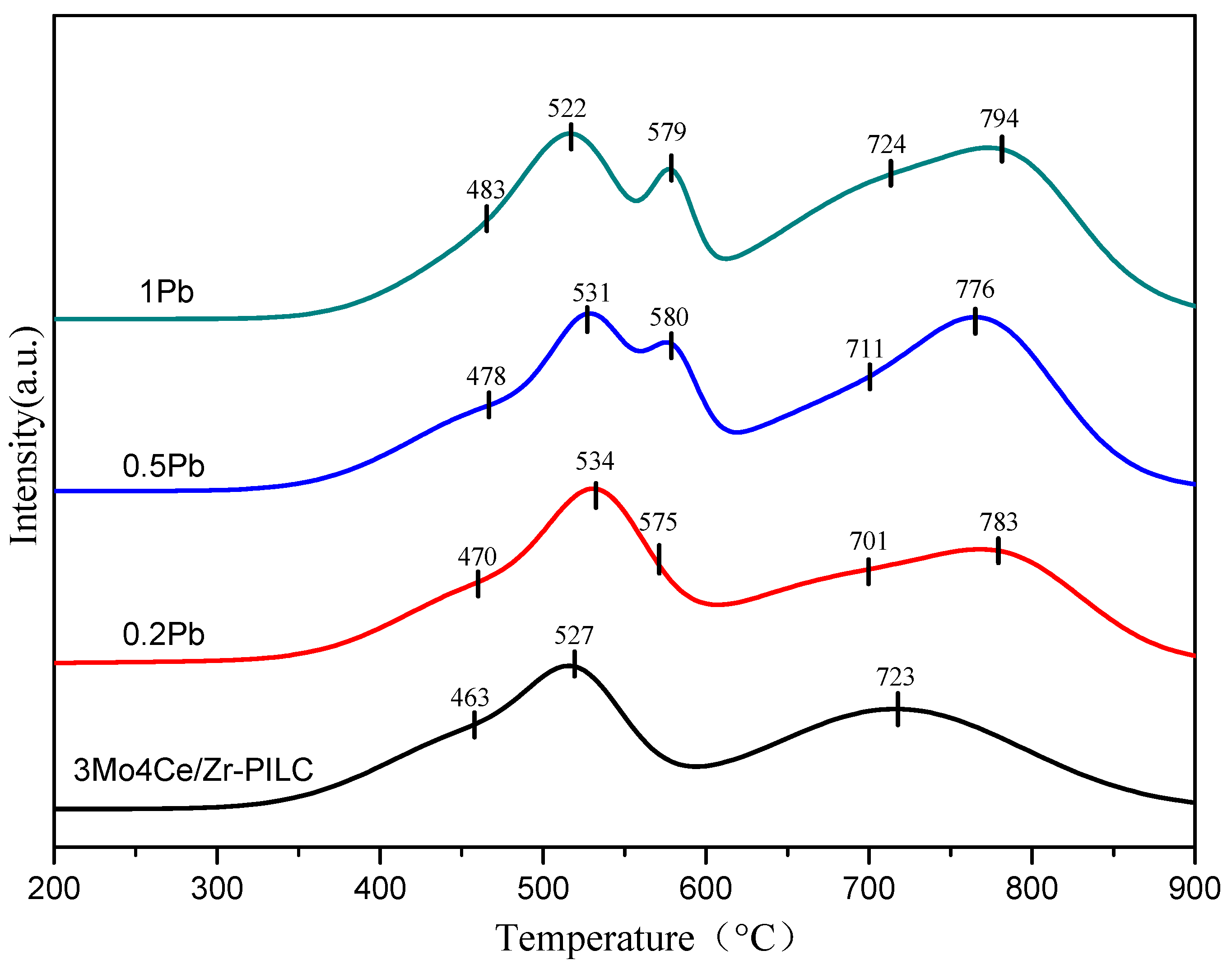
3.3. Redox Properties
3.4. Surface Property
3.5. Surface Acidity
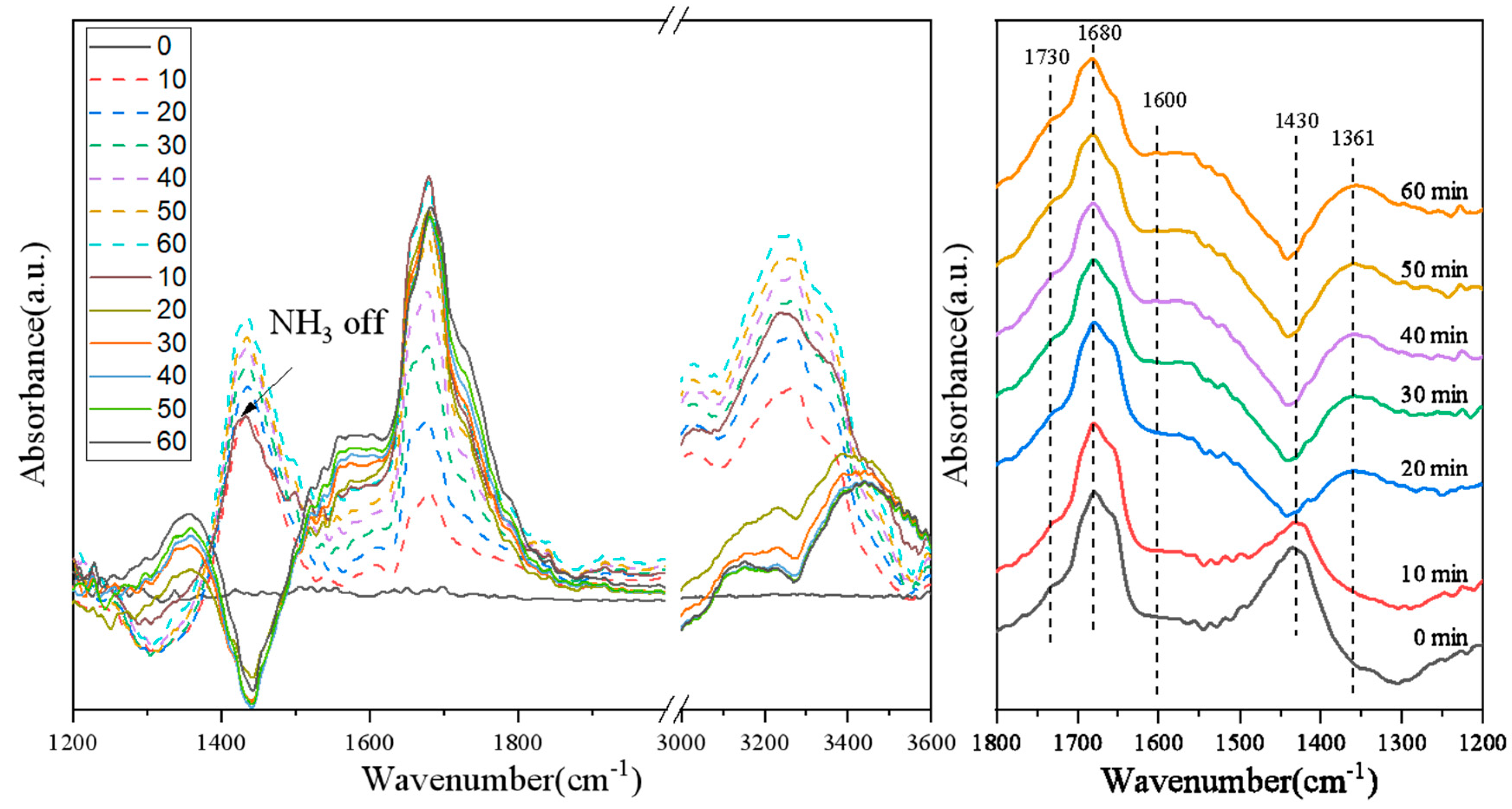
3.6. Switching Feed Gas from NO + O2 + N2 + NH3 to NO + O2 + N2 on Various Catalysts
3.7. Pb Poisoning Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shan, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, G.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; He, H. Theory and practice of metal oxide catalyst design for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Catal. Today 2021, 376, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Diao, Q.; Hu, X.; Wu, X.; Xiao, K.; Wang, J. Modification of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst by loading of MnOx for enhanced low-temperature NH3-SCR performance. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, G.; Han, Y.; Chang, Y.; Gong, P. Mn/beta and Mn/ZSM-5 for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia: Effect of manganese precursors. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; He, H.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Challenges and opportunities for manganese oxides in low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3:H2O resistance ability. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Ge, M. Promotional effect of Ce-doped V2O5-WO3/TiO2 with low vanadium loadings for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 21177–21184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, S. Improvement of NH3-SCR performance and SO2 resistance over Sn modified CeMoOx electrospun fibers at low temperature. Catal. Today 2019, 327, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Tang, C.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Gao, F.; Dong, L. Effect of metal ions doping (M = Ti4+, Sn4+) on the catalytic performance of MnOx/CeO2 catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 495, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y. Preparation of novel CeMox hollow microspheres for low-temperature SCR removal of NOx with NH3. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 59185–59194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Shi, Y.; Gao, F.; Zhao, S.; Yi, H.; Xie, Z. Promotional role of Mo on Ce0.3FeOx catalyst towards enhanced NH3-SCR catalytic performance and SO2 resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Kong, M.; Liu, Q.; Ren, S. New insights into the deactivation mechanism of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst during selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Synergies between arsenic and potassium species. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 37724–37732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Weng, X. Deactivation mechanism of Ce/TiO2 selective catalytic reduction catalysts by the loading of sodium and calcium salts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, M.; Jarars, S.; Persson, B. Poisoning of De-NOx SCR catalyst by flue gases from a waste incineration plant. In Catalyst Deactivation 1991, Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium, Studies in Surface Science & Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; Volume 68, pp. 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Ye, Q.; Li, C.; Cheng, S.; Kang, T.; Dai, H. Ceria-modified Al-Mn-pillared clay catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Fu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Xiong, S.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N.; Li, J. Competition of selective catalytic reduction and non-selective catalytic reduction over MnOx/TiO2 for NO removal: The relationship between gaseous NO concentration and N2O selectivity. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.; Zhang, G.; Qiu, W.; Song, L.; Zhang, R.; He, H. Resistance to SO2 poisoning of V2O5/TiO2-PILC catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cheng, J.; Ye, Q.; Meng, F.; Wang, X.; Dai, H. Poisoning effects of alkali and alkaline earth metal doping on selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over the Nb-Ce/Zr-PILC catalysts. Catalysts 2021, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Shi, J.-W.; Liu, C.; Gao, C.; Fan, Z.; Niu, C. Mn/CeO2 catalysts for SCR of NOx with NH3: Comparative study on the effect of supports on low-temperature catalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 411, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Liu, F.; Shi, X.; Liu, K.; Lian, Z.; Xie, L.; He, H. Significant promotion effect of Mo additive on a novel Ce-Zr mixed oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9497–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, T.; Sapi, A.; Abel, M.; Kiss, J.; Szenti, I.; Baan, K.; Gomez-Perez, J.F.; Kukovecz, A.; Konya, Z. Surface engineering of CeO2 catalysts: Differences between solid solution based and interfacially designed Ce1−xMxO2 and MO/CeO2 (M = Zn, Mn) in CO2 hydrogenation reaction. Catal. Lett. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, L.; Zeng, G.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M. The poisoning effect of PbO on Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Du, X.; Fu, Y.; Mao, J.; Luo, Z.; Ni, M.; Cen, K. Theoretical and experimental study on the deactivation of V2O5 based catalyst by lead for selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxides. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, S.; Gao, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. Niobium oxide confined by ceria nanotubes as a novel SCR catalyst with excellent resistance to potassium, phosphorus, and lead. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 231, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ning, P.; Song, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Long, K.; Zhang, Q. Mechanistic aspects of NH3-SCR reaction over CeO2/TiO2−ZrO2−SO42− catalyst: In situ DRIFTS investigation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Lu, C.; Pan, W.; Zhen, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Ding, H.; Yang, N. A comparative study of the poisoning effect of Zn and Pb on Ce/TiO2 catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Catal. Commun. 2015, 59, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Hao, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Fang, B.; Wei, K.; Qi, L.; Jin, S.; Wei, C. Study on denitration and sulfur removal performance of Mn-Ce supported fly ash catalyst. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, G.; Shin, M.; Kim, H.-D.; Cho, D.-S.; Lee, H. Electron redistribution and acid site of tungsten-doped CeTiOx with oxygen vacancies. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2021, 120, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of the calcination temperature on the performance of a CeMoOx catalyst in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia. Catal. Today 2015, 245, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, X.; Shan, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shan, W.; Yu, Y.; He, H. Hydrothermal stability of CeO2-WO3-ZrO2 mixed oxides for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11769–11777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lin, T.; Gong, M.; Chen, Y. Catalytic performance of acidic zirconium-based composite oxides monolithic catalyst on selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Guo, R.; Pan, W.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Lu, C.; Wang, S. The deactivation mechanism of Cl on Ce/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 378, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tan, W.; Wei, X.; Fan, Z.; Liu, A.; Guo, K.; Ma, K.; Yu, S.; Ge, C.; Tang, C.; et al. Mo doping as an effective strategy to boost low temperature NH3-SCR performance of CeO2/TiO2 catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2018, 114, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y. Molybdenum modified CeAlOx catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 386, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liang, G.; Liu, S.; Gao, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, R.; Zhu, X. The poisoning effect of PbO on CeO2-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Mol. Catal. 2020, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Shi, X.; Yu, Y.; He, H. Alkali resistance promotion of Ce-doped vanadium-titanic-based NH3-SCR catalysts. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 73, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Ma, L. Promoting effect of MoO3 on the NOx reduction by NH3 over CeO2/TiO2 catalyst studied with in situ DRIFTS. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


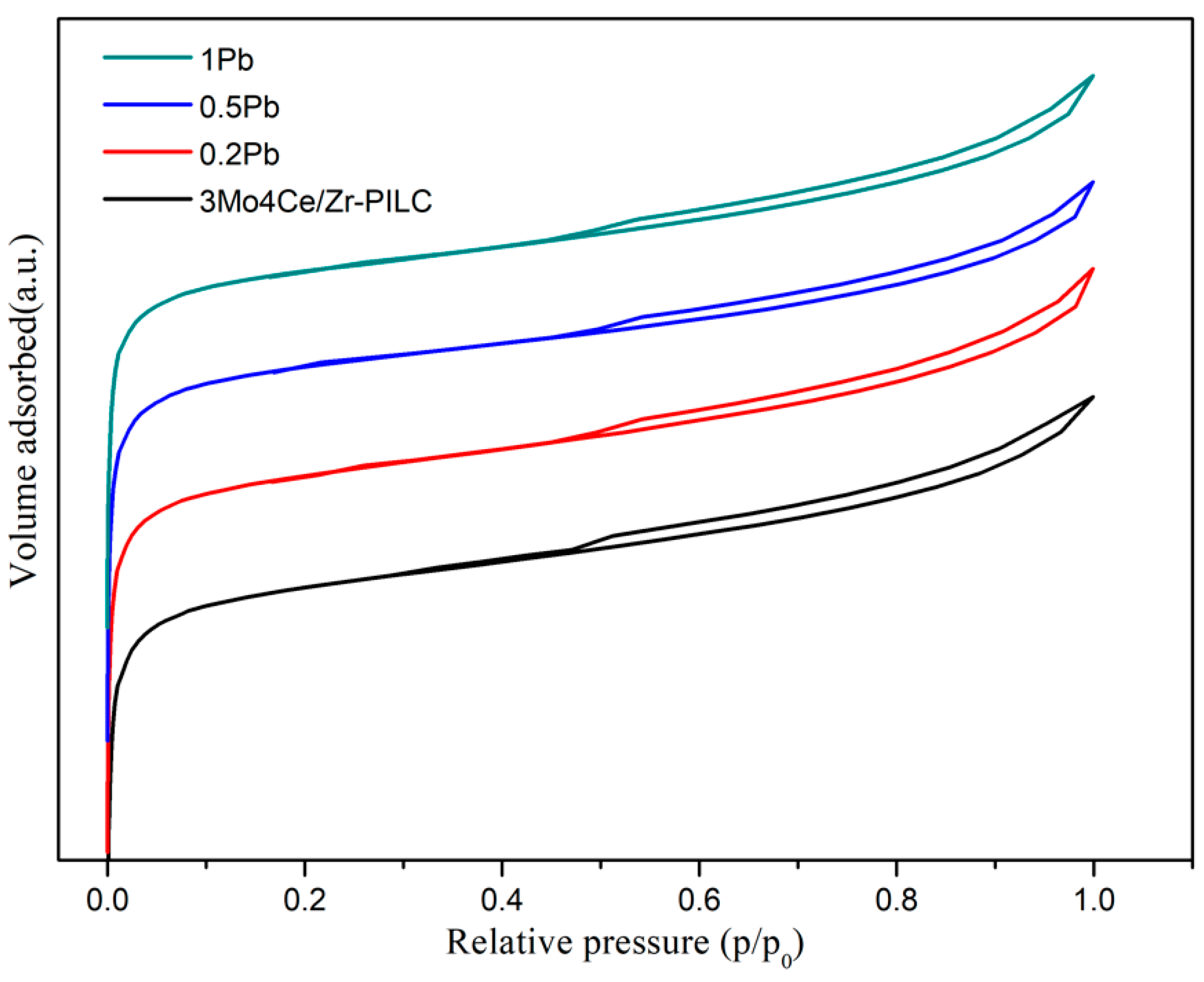





| Catalyst | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|
| 3Mo4Ce/Zr-PILC | 270 | 0.164 |
| 0.2Pb | 259 | 0.161 |
| 0.5Pb | 256 | 0.154 |
| 1Pb | 243 | 0.152 |
| Catalyst | Reduction Peak Temperature (°C) | H2 Consumption (mmol/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 | Peak 4 | Peak 5 | ||
| 3Mo4Ce/Zr-PILC | 463 | 527 | - | 723 | - | 0.79 |
| 0.2Pb | 470 | 534 | 575 | 701 | 783 | 0.90 |
| 0.5Pb | 478 | 531 | 580 | 711 | 776 | 1.01 |
| 1Pb | 483 | 522 | 579 | 724 | 794 | 1.10 |
| Catalyst | Composition of Cerium Species (at%) | Composition of Oxygen Species (mol%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce3+ | Ce4+ | Ce3+/Ce4+ Atomic Ratio | Oα | Oβ | Oγ | |
| 3Mo4Ce/Zr-PILC | 30.3 | 69.7 | 0.43 | 13.4 | 39.4 | 47.2 |
| 0.2Pb | 26.2 | 73.8 | 0.36 | 13.1 | 34.7 | 52.2 |
| 0.5Pb | 24.3 | 75.7 | 0.32 | 13.1 | 31.4 | 55.5 |
| 1Pb | 21.1 | 78.9 | 0.27 | 13.4 | 24.8 | 61.8 |
| Catalyst | Temperature (°C) | Acidity (mmolNH3/g) | Total Desorption Amount (mmolNH3/g) (mmol/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak Peak | Medium Peak | Strong Peak | Weak Peak | Medium Peak | Strong Peak | ||
| 3Mo4Ce/Zr-PILC | 171 | 220 | 311 | 0.046 | 0.131 | 0.087 | 0.264 |
| 0.2Pb | 166 | 215 | 305 | 0.043 | 0.125 | 0.079 | 0.247 |
| 0.5Pb | 173 | 223 | 310 | 0.040 | 0.103 | 0.070 | 0.213 |
| 1Pb | 163 | 214 | 301 | 0.042 | 0.096 | 0.064 | 0.202 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Cheng, J.; Ye, Q.; Meng, F.; Wang, X.; Dai, H. The Deactivation Mechanism of the Mo-Ce/Zr-PILC Catalyst Induced by Pb for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102641
Li C, Cheng J, Ye Q, Meng F, Wang X, Dai H. The Deactivation Mechanism of the Mo-Ce/Zr-PILC Catalyst Induced by Pb for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102641
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chenxi, Jin Cheng, Qing Ye, Fanwei Meng, Xinpeng Wang, and Hongxing Dai. 2021. "The Deactivation Mechanism of the Mo-Ce/Zr-PILC Catalyst Induced by Pb for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102641
APA StyleLi, C., Cheng, J., Ye, Q., Meng, F., Wang, X., & Dai, H. (2021). The Deactivation Mechanism of the Mo-Ce/Zr-PILC Catalyst Induced by Pb for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102641







