Silver Nanoparticles and Ionic Silver Separation Using a Cation-Exchange Resin. Variables Affecting Their Separation and Improvements of AgNP Characterization by SP-ICPMS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Materials, and Apparatus
2.2. Instrumentation
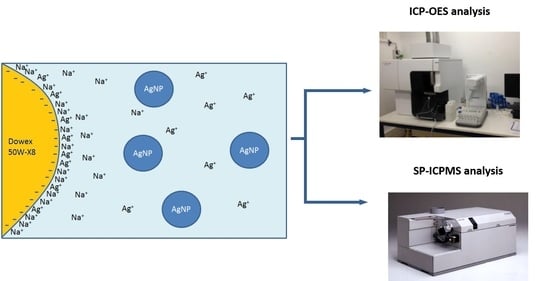
2.3. Separation Procedure
- Batch Studies
- Column Studies
3. Results and Discussion
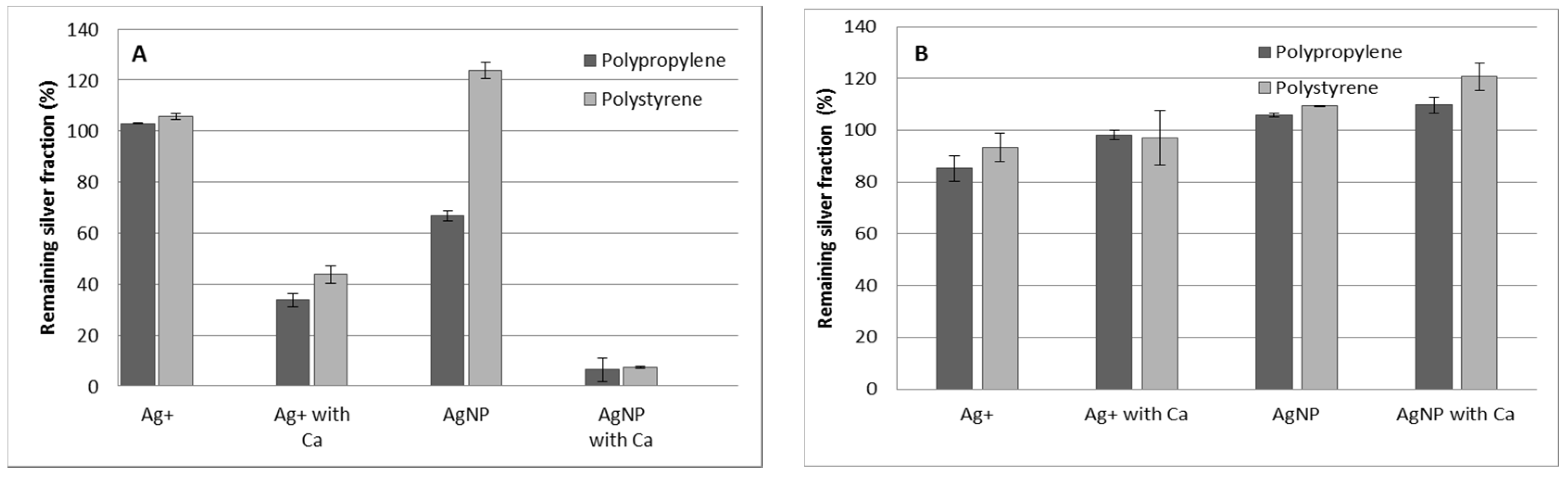
3.1. Effect of the Material Container without the Presence of Resin
3.2. Resin Conditioning and Contact Time
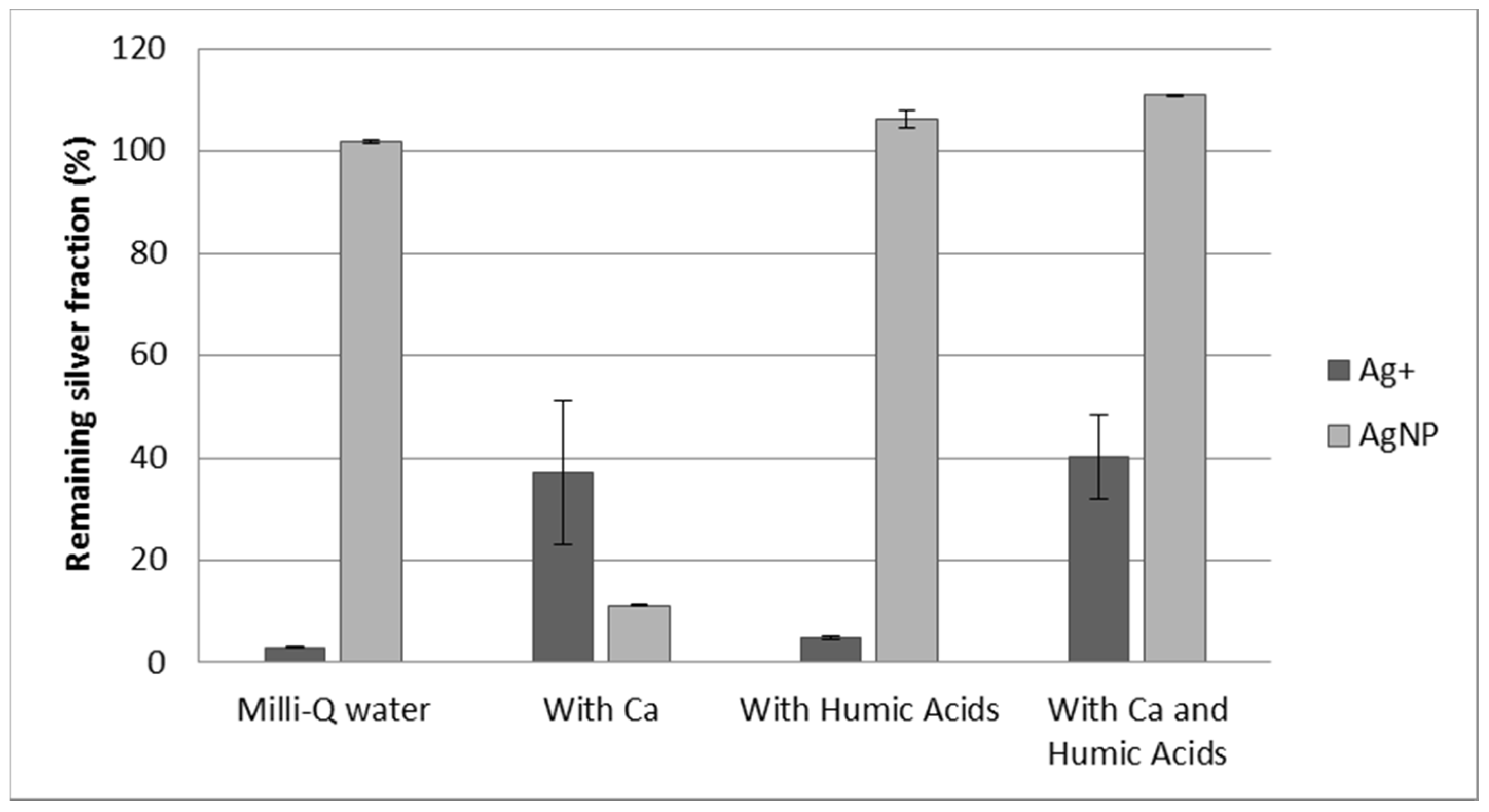
3.3. Effect of Calcium and Humic Acids in the Separation
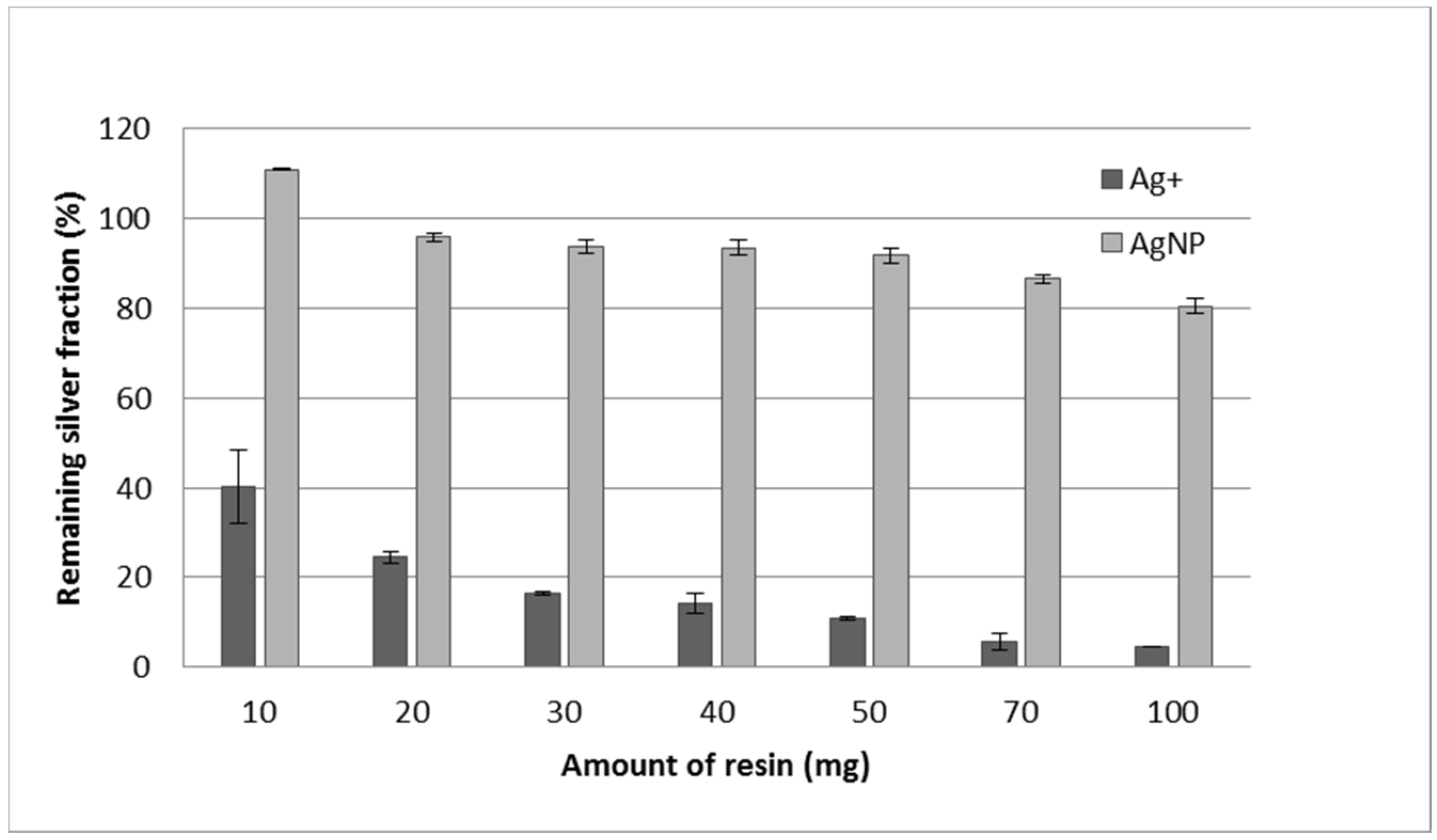
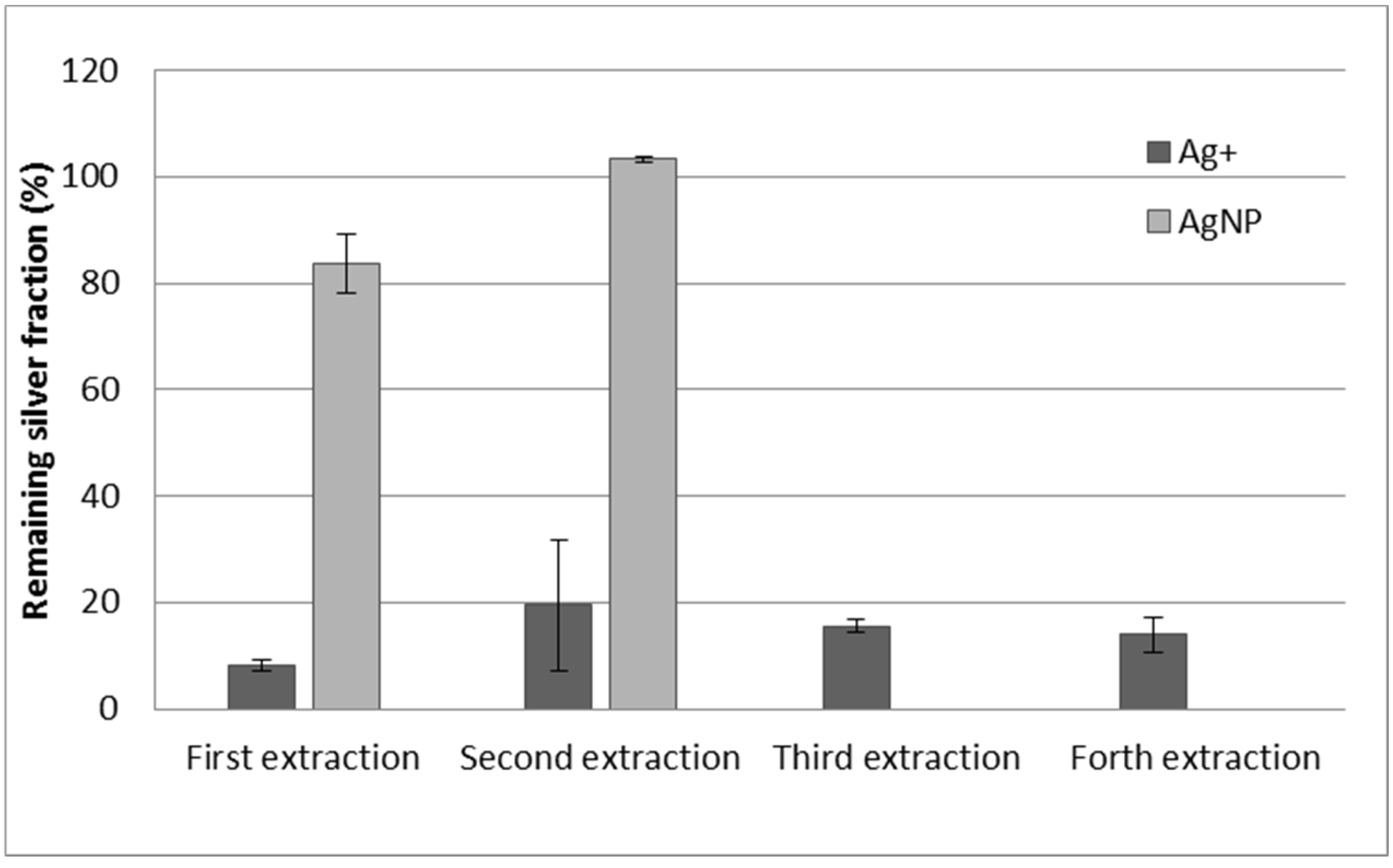
3.4. Effect of Resin Quantity, Double Extraction Procedure, and Reuse of the Resin
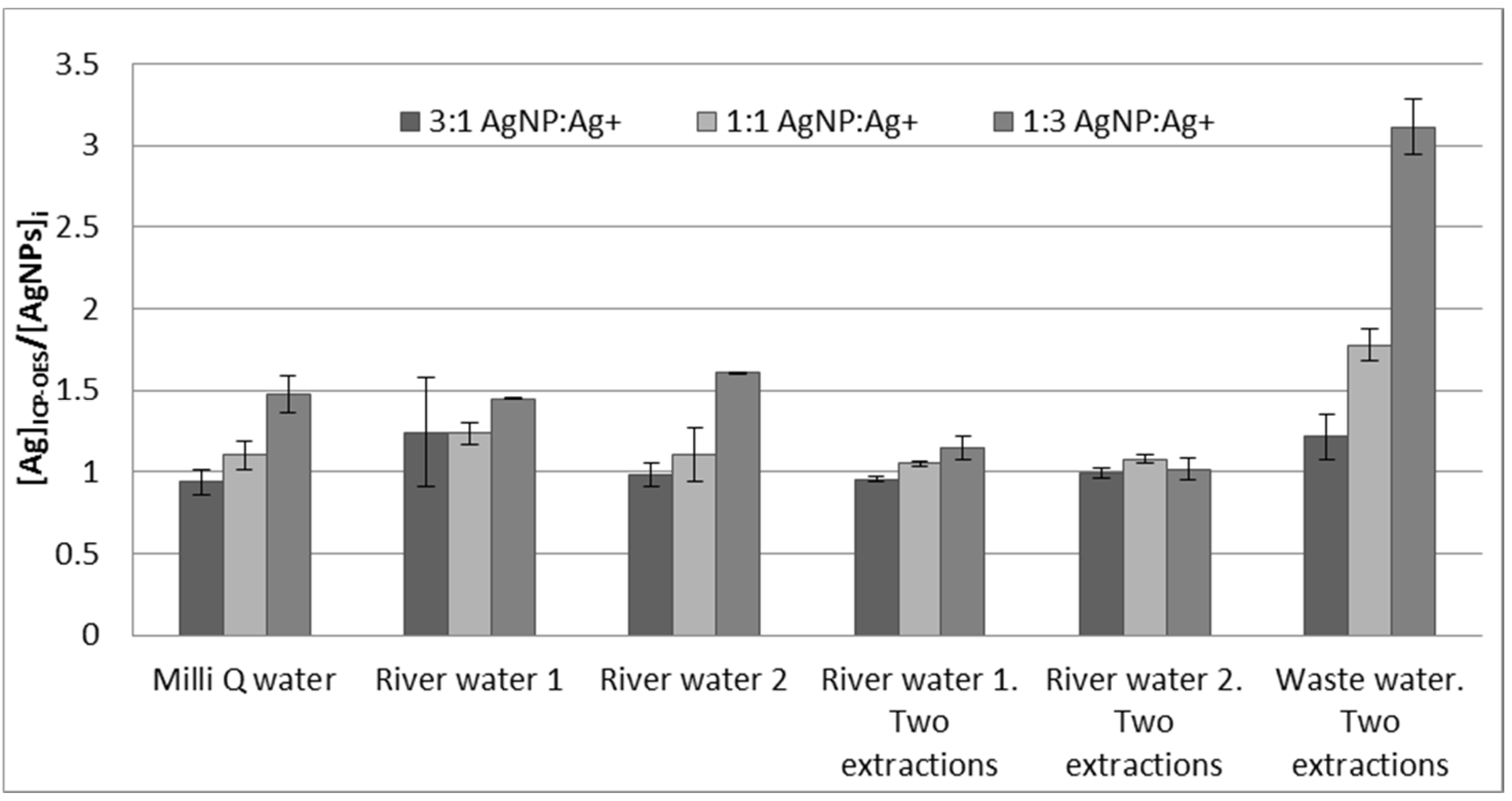
3.5. Analysis of Mixtures of Ag+/AgNPs and Application to River Water and Wastewater Samples
3.6. Separation of Ag+ and AgNPs Using Column Experiments
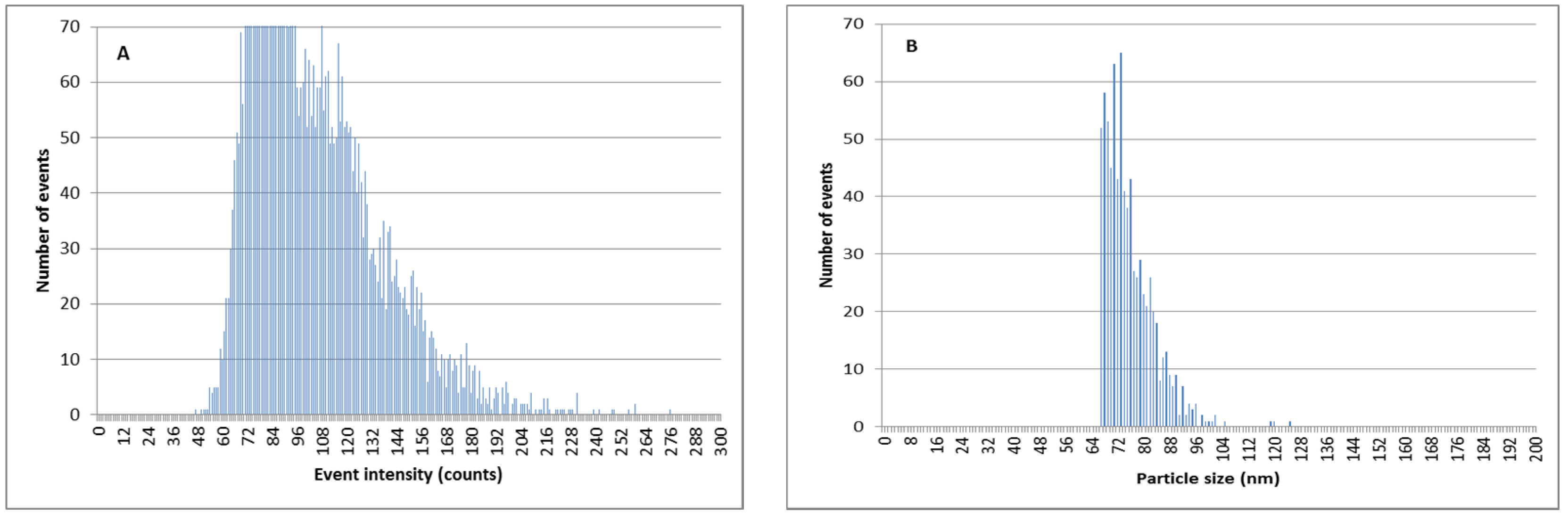
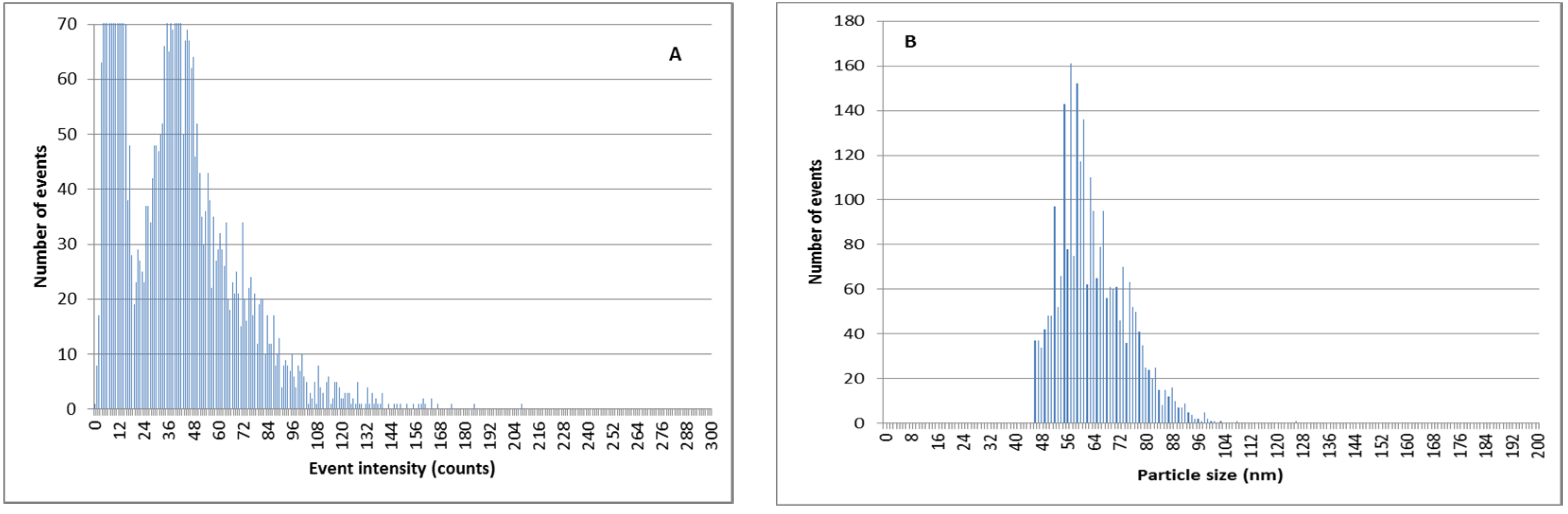
3.7. Separation of Ag+ from AgNPs Previous to SP-ICPMS Analysis for a Better Quantification and Characterization of AgNPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, R.; Xie, H. Nanoparticles in Daily Life: Applications, Toxicity and Regulations. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2018, 37, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Yousaf, B.; Ali, M.U.; Munir, M.A.M.; El-Naggar, A.; Rinklebe, J.; Naushad, M. Transformation pathways and fate of engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) in distinct interactive environmental compartments: A review. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Project on Emerging Nanotechnologies: Consumer Products Inventory. Available online: http://www.nanotechproject.org/cpi/products/ (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- The Nanodatabase. Available online: http://nanodb.dk/ (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Rezvani, E.; Rafferty, A.; McGuinness, C.; Kennedy, J. Adverse effects of nanosilver on human health and the environment. Acta Biomater. 2019, 94, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, A.; Kanel, S.R.; Ray, C.; Snow, D.D.; Nadagouda, M.N. Nanomaterials in the environment, human exposure pathway, and health effects: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, V.; Minkina, T.; Mazarji, M.; Shende, S.; Sushkova, S.; Mandzhieva, S.; Burachevskaya, M.; Chaplygin, V.; Singh, A.; Jatav, H. Accumulation of nanoparticles in the soil-plant systems and their effects on human health. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2020, 65, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Kang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, M. Behavior, remediation effect and toxicity of nanomaterials in water environments. Environ. Res. 2019, 174, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kah, M.; Hofmann, T. Nanopesticide research: Current trends and future priorities. Environ. Int. 2014, 63, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaegi, R.; Voegelin, A.; Sinnet, B.; Zuleeg, S.; Hagendorfer, H.; Burkhardt, M.; Siegrist, H. Behavior of Metallic Silver Nanoparticles in a Pilot Wastewater Treatment Plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3902–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, C.S.; Murayama, M.; Hochella, M.F. Discovery and Characterization of Silver Sulfide Nanoparticles in Final Sewage Sludge Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7509–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, B.; Fang, T. Chemical transformation of silver nanoparticles in aquatic environments: Mechanism, morphology and toxicity. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levard, C.; Hotze, E.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Gordon, E.; Brown, J. Environmental Transformations of Silver Nanoparticles: Impact on Stability and Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6900–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Hurt, R.H. Ion Release Kinetics and Particle Persistence in Aqueous Nano-Silver Colloids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzadi Tayemeh, M.; Esmailbeigi, M.; Shirdel, I.; Joo, H.S.; Johari, S.A.; Banan, A.; Nourani, H.; Mashhadi, H.; Jami, M.J.; Tabarrok, M. Perturbation of fatty acid composition, pigments, and growth indices of Chlorella vulgaris in response to silver ions and nanoparticles: A new holistic understanding of hidden ecotoxicological aspect of pollutants. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Toxicity mechanism of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Photosynthesis, oxidative stress, membrane permeability, and ultrastructure analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 15032–15042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylona, Z.; Panteris, E.; Moustakas, M.; Kevrekidis, T.; Malea, P. Physiological, structural and ultrastructural impacts of silver nanoparticles on the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalau, C.M.; Simioni, C.; Vicentini, D.S.; Ouriques, L.C.; Mohedano, R.A.; Puerari, R.C.; Matias, W.G. Toxicological effects of AgNPs on duckweed (Landoltia punctata). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, C.S.; Matias, M.V.F.; Toledo, E.K.M.; Smaniotto, S.; Ximenes-da-Silva, A.; Tonholo, J.; Santos, E.L.; Machado, S.S.; Zanta, C.L.P.S. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles on different tissues in adult Danio rerio. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehennaoui, K.; Cambier, S.; Minguez, L.; Serchi, T.; Guérold, F.; Gutleb, A.C.; Giamberini, L. Sub-chronic effects of AgNPs and AuNPs on Gammarus fossarum (Crustacea Amphipoda): From molecular to behavioural responses. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 210, 111775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, F.; Bolea, E.; Cepriá, G.; Gómez, M.T.; Jiménez, M.S.; Pérez-Arantegui, J.; Castillo, J.R. Detection, characterization and quantification of inorganic engineered nanomaterials: A review of techniques and methodological approaches for the analysis of complex samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 904, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Ranville, J.F.; Bednar, A.; Kazor, K.; Hering, A.S.; Higgins, C.P. Tracking dissolution of silver nanoparticles at environmentally relevant concentrations in laboratory, natural, and processed waters using single particle ICP-MS (spICP-MS). Environ. Sci. Nano 2014, 1, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Z.Q.; Liu, J.-F.; Guo, X.-R.; Yin, Y.-G.; Byeon, S.K.; Moon, M.H.; Jiang, G.-B. Toward Full Spectrum Speciation of Silver Nanoparticles and Ionic Silver by On-Line Coupling of Hollow Fiber Flow Field-Flow Fractionation and Minicolumn Concentration with Multiple Detectors. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8441–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, G. Elemental Mass Size Distribution for Characterization, Quantification and Identification of Trace Nanoparticles in Serum and Environmental Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3892–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.-F. Rapid Chromatographic Separation of Dissoluble Ag(I) and Silver- Containing Nanoparticles of 1−100 Nanometer in Antibacterial Products and Environmental Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14516–14524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Lamana, J.; Slaveykova, V.I. Silver nanoparticle behaviour in lake water depends on their surface coating. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, L.M.; Hoque, M.E.; Mitrano, D.M.; Ranville, J.F.; Cheever, B.; Frost, P.C.; Xenopoulos, M.A.; Hintelmann, H.; Metcalfe, C.D. The persistence and transformation of silver nanoparticles in littoral lake mesocosms monitored using various analytical techniques. Environ. Chem. 2014, 11, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, A.R.; Adams, C.D.; Ma, Y.; Stephan, C.; Eichholz, T.; Shi, H. Fate of nanoparticles during alum and ferric coagulation monitored using single particle ICP-MS. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.; Sun, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, L. Occurrence and trophic transfer of nanoparticulate Ag and Ti in the natural aquatic food web of Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 3431–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajec, M.; Kukulska-Zając, E.; Król, A. Determination of silver nanoparticles in liquid environmental samples. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 5775–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.J.B.; van Bemmel, G.; Milani, N.B.L.; den Hertog, G.C.T.; Undas, A.K.; van der Lee, M.; Bouwmeester, H. Detection of nanoparticles in Dutch surface waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, A.R.; Adams, C.D.; Ma, Y.; Stephan, C.; Eichholz, T.; Shi, H. Single particle ICP-MS characterization of titanium dioxide, silver, and gold nanoparticles during drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- António, D.; Cascio, C.; Jaksic, Z.; Jurasin, D.; Lyons, D.; Nogueira, A.; Rossi, F.; Calzolai, L. Assessing silver nanoparticles behaviour in artificial seawater by mean of AF4 and spICP-MS. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toncelli, C.; Mylona, K.; Kalantzi, I.; Tsiola, A.; Pitta, P.; Tsapakis, M.; Pergantis, S.A. Silver nanoparticles in seawater: A dynamic mass balance at part per trillion silver concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toncelli, C.; Mylona, K.; Tsapakis, M.; Pergantis, S.A. Flow injection with on-line dilution and single particle inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry for monitoring silver nanoparticles in seawater and in marine microorganisms. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théoret, T.; Wilkinson, K.J. Evaluation of enhanced darkfield microscopy and hyperspectral analysis to analyse the fate of silver nanoparticles in wastewaters. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3920–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azodi, M.; Sultan, Y.; Ghoshal, S. Dissolution behavior of silver nanoparticles and formation of secondary silver nanoparticles in municipal wastewater by single-particle ICP-MS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 13318–13327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgantzopoulou, A.; Almeida Carvalho, P.; Vogelsang, C.; Tilahun, M.; Ndungu, K.; Booth, A.M.; Thomas, K.V.; Macken, A. Ecotoxicological Effects of Transformed Silver and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in the Effluent from a Lab-Scale Wastewater Treatment System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9431–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.; Shih, Y.; Su, C.-H.; Ho, H.-C. Comparison of three analytical methods to measure the size of silver nanoparticles in real environmental water and wastewater samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meermann, B.; Nischwitz, V. ICP-MS for the analysis at the nanoscale-a tutorial review. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1432–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mai, H.; Espada-Bellido, E.; Stitou, M.; García-Vargas, M.; Galindo-Riaño, M.D. Determination of ultra-trace amounts of silver in water by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry using a new modified carbon paste electrode. Talanta 2016, 151, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, S.; Hodge, V.; Schumacher, B.; Sovocool, W. Sampling for silver nanoparticles in aqueous media using a rotating disk electrode: Evidence for selective sampling of silver nanoparticles in the presence of ionic silver. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.Z.; Pumera, M. Fate of silver nanoparticles in natural waters; Integrative use of conventional and electrochemical analytical techniques. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5006–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chao, J.; Liu, R.; Tan, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, G. Cloud Point Extraction as an Advantageous Preconcentration Approach for Analysis of Trace Silver Nanoparticles in Environmental Waters. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6496–6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, G.; Baumgartner, T.; Schuster, M. Influence of Particle Coating and Matrix Constituents on the Cloud Point Extraction Efficiency of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) and Application for Monitoring the Formation of Ag-NPs from Ag+. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urstoeger, A.; Wimmer, A.; Kaegi, R.; Reiter, S.; Schuster, M. Looking at Silver-Based Nanoparticles in Environmental Water Samples: Repetitive Cloud Point Extraction Bridges Gaps in Electron Microscopy for Naturally Occurring Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12063–12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, A.; Urstoeger, A.; Funck, N.C.; Adler, F.P.; Lenz, L.; Doeblinger, M.; Schuster, M. What happens to silver-based nanoparticles if they meet seawater? Water Res. 2020, 171, 115399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, A.; Kalinnik, A.; Schuster, M. New insights into the formation of silver-based nanoparticles under natural and semi-natural conditions. Water Res. 2018, 141, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, G.; Hutterer, C.; Schuster, M. Ultra-trace determination of silver nanoparticles in water samples using cloud point extraction and ETAAS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2013, 28, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; Feng, Y.; Tan, Z.; Liu, R.; Yin, Y. Speciation Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions in Antibacterial Products and Environmental Waters via Cloud Point Extraction-Based Separation. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6875–6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, L.; Li, H.P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.G.; Long, C.L. Separation and determination of silver nanoparticle in environmental water and the UV-induced photochemical transformations study of AgNPs by cloud point extraction combined ICP-MS. Talanta 2016, 161, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadir, Z.; Torrent, L.; Hidalgo, M.; Marguí, E. Simultaneous determination of silver and gold nanoparticles by cloud point extraction and total reflection X-ray fluorescence analysis. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2018, 149, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, I.; Vicente-Martínez, Y.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Speciation of silver nanoparticles and Ag(I) species using cloud point extraction followed by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2014, 101, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Mayan, J.J.; Cerneira-Temperan, B.; Pena-Vazquez, E.; Barciela-Alonso, M.C.; Dominguez-Gonzalez, M.R.; Bermejo-Barrera, P. Evaluation of a cloud point extraction method for the preconcentration and quantification of silver nanoparticles in water samples by ETAAS. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-H.; Tseng, W.-L. Combined cloud point extraction and Tween 20-stabilized gold nanoparticles for colorimetric assay of silver nanoparticles in environmental water. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 2915–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Ding, R.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Size characterization of silver nanoparticles after separation from silver ions in environmental water using magnetic reduced graphene oxide. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urstoeger, A.; Zacherl, L.; Muhr, M.; Selic, Y.; Wenisch, M.; Klotz, M.; Schuster, M. Magnetic solid phase extraction of silver-based nanoparticles in aqueous samples: Influence of particle composition and matrix effects on its application to environmental samples and species-selective elution and determination of silver sulphide nanoparti. Talanta 2021, 225, 122028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hartmann, G.; Döblinger, M.; Schuster, M. Quantification of Nanoscale Silver Particles Removal and Release from Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants in Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7317–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Avilés, P.; Huang, Y.; Keller, A.A. Multi-technique approach to study the stability of silver nanoparticles at predicted environmental concentrations in wastewater. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertfeger, D.; Velicogna, J.; Jesmer, A.; Mcshane, H.; Scroggins, R.; Princz, J. Ion exchange technique (IET) to characterise Ag+ exposure in soil extracts contaminated with engineered silver nanoparticles. Environ. Chem. 2017, 14, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadioui, M.; Leclerc, S.; Wilkinson, K.J. Multimethod quantification of Ag+ release from nanosilver. Talanta 2013, 105, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrent, L.; Laborda, F.; Marguí, E.; Hidalgo, M.; Iglesias, M. Combination of cloud point extraction with single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry to characterize silver nanoparticles in soil leachates. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5317–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, H.E.; Rogers, N.J.; Jarolimek, C.; Coleman, V.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Determining Transport Efficiency for the Purpose of Counting and Sizing Nanoparticles via Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9361–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, R.; Herrera-Rivera, Z.; Undas, A.; Van Der Lee, M.; Marvin, H.; Bouwmeester, H.; Weigel, S. Single particle ICP-MS combined with a data evaluation tool as a routine technique for the analysis of nanoparticles in complex matrices. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, E.; Sigg, L.; Talinli, I. A systematic evaluation of agglomeration of Ag and TiO2 nanoparticles under freshwater relevant conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy, E.; Murray, I.; Kavanagh, S.; Morrison, L.; Fogarty, A.; Cormican, M.; Dockery, P.; Prendergast, M.; Rowan, N.; Morris, D. Silver nanoparticles in the environment: Sources, detection and ecotoxicology. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worms, I.A.M.; Wilkinson, K.J. Determination of Ni2+ using an equilibrium ion exchange technique: Important chemical factors and applicability to environmental samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 616, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| River Water 1 | River Water 2 | Wastewater | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity (μS·cm−1) | 314 | 367 | 956 |
| pH | 8.3 | 8.2 | 7.2 |
| TOC (mg (C)·L−1) | 1.975 | 1.815 | - |
| Alkalinity (mg (CaCO3)·L−1) | 107.3 | 117.1 | - |
| Sodium (mg (Na+)·L−1) | 22.88 | 22.77 | 115.96 |
| Potassium (mg (K+)·L−1) | 1.74 | 1.80 | 22.22 |
| Magnesium (mg (Mg2+)·L−1) | 5.81 | 6.67 | 12.87 |
| Calcium (mg (Ca2+)·L−1) | 28.99 | 34.77 | 74.48 |
| Agilent 5100 Vertical Dual View ICP-OES | ||
|---|---|---|
| Instrumental characteristics | RF power | 1200 W |
| Pump speed | 12 rpm | |
| Nebulizer chamber | Double pass glass cyclonic | |
| Nebulizer | Concentric glass | |
| Torch inner diameter | 1.8 mm | |
| Nebulizer flow rate | 0.7 L·min−1 | |
| Argon gas flow rate | 12 L·min−1 | |
| Plasma configuration | Axial (double vision) | |
| Wavelength selector | Echelle polychromator | |
| Data acquisition parameters | Ag wavelength | 328.068 nm |
| Detector | Charge-coupled device (CCD) | |
| Reading time | 1 s | |
| Readings per replicate | 3 | |
| Agilent 7500c ICP-MS | ||
| Instrumental characteristics | RF power | 1500 W |
| Sample uptake rate | 0.3 mL·min−1 | |
| Nebulizer chamber | Double pass scott | |
| Nebulizer | Babington | |
| Torch inner diameter | 2.5 mm | |
| Nebulizer gas flow rate | 1.1 L·min−1 | |
| Sampling cone | Ni, 1 mm aperture diameter | |
| Skimmer cone | Ni, 0.4 mm aperture diameter | |
| Argon gas flow rate | 15 L·min−1 | |
| Analyzer | Quadrupole | |
| Detector | Electron multiplier | |
| Data acquisition parameters | Single particle measuring mode | |
| Isotopes monitored | 107 | |
| Dwell time | 10 ms | |
| Acquisition time | 60 s | |
| Points per spectral peak | 1 | |
| Readings per replicate | 5730 | |
| Manufacturer Value | Calculated Size before Extraction | Calculated Size after Double Extraction |
|---|---|---|
| 79 nm | 81 nm | 78 nm |
| 59 nm | 74 nm | 62 nm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iglesias, M.; Torrent, L. Silver Nanoparticles and Ionic Silver Separation Using a Cation-Exchange Resin. Variables Affecting Their Separation and Improvements of AgNP Characterization by SP-ICPMS. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102626
Iglesias M, Torrent L. Silver Nanoparticles and Ionic Silver Separation Using a Cation-Exchange Resin. Variables Affecting Their Separation and Improvements of AgNP Characterization by SP-ICPMS. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102626
Chicago/Turabian StyleIglesias, Mònica, and Laura Torrent. 2021. "Silver Nanoparticles and Ionic Silver Separation Using a Cation-Exchange Resin. Variables Affecting Their Separation and Improvements of AgNP Characterization by SP-ICPMS" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102626
APA StyleIglesias, M., & Torrent, L. (2021). Silver Nanoparticles and Ionic Silver Separation Using a Cation-Exchange Resin. Variables Affecting Their Separation and Improvements of AgNP Characterization by SP-ICPMS. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102626