Anisotropic Photonics Topological Transition in Hyperbolic Metamaterials Based on Black Phosphorus
Abstract
1. Introduction
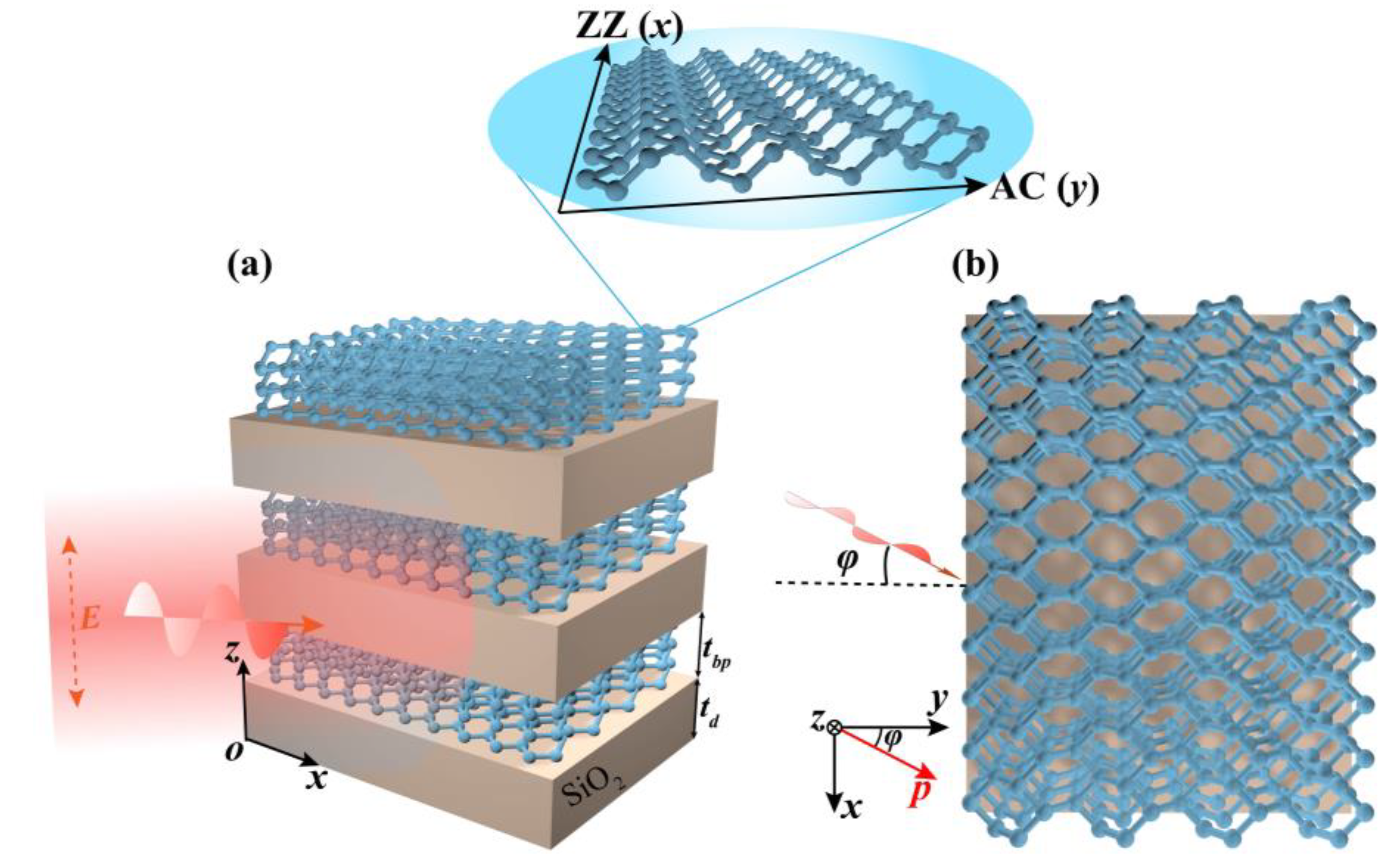
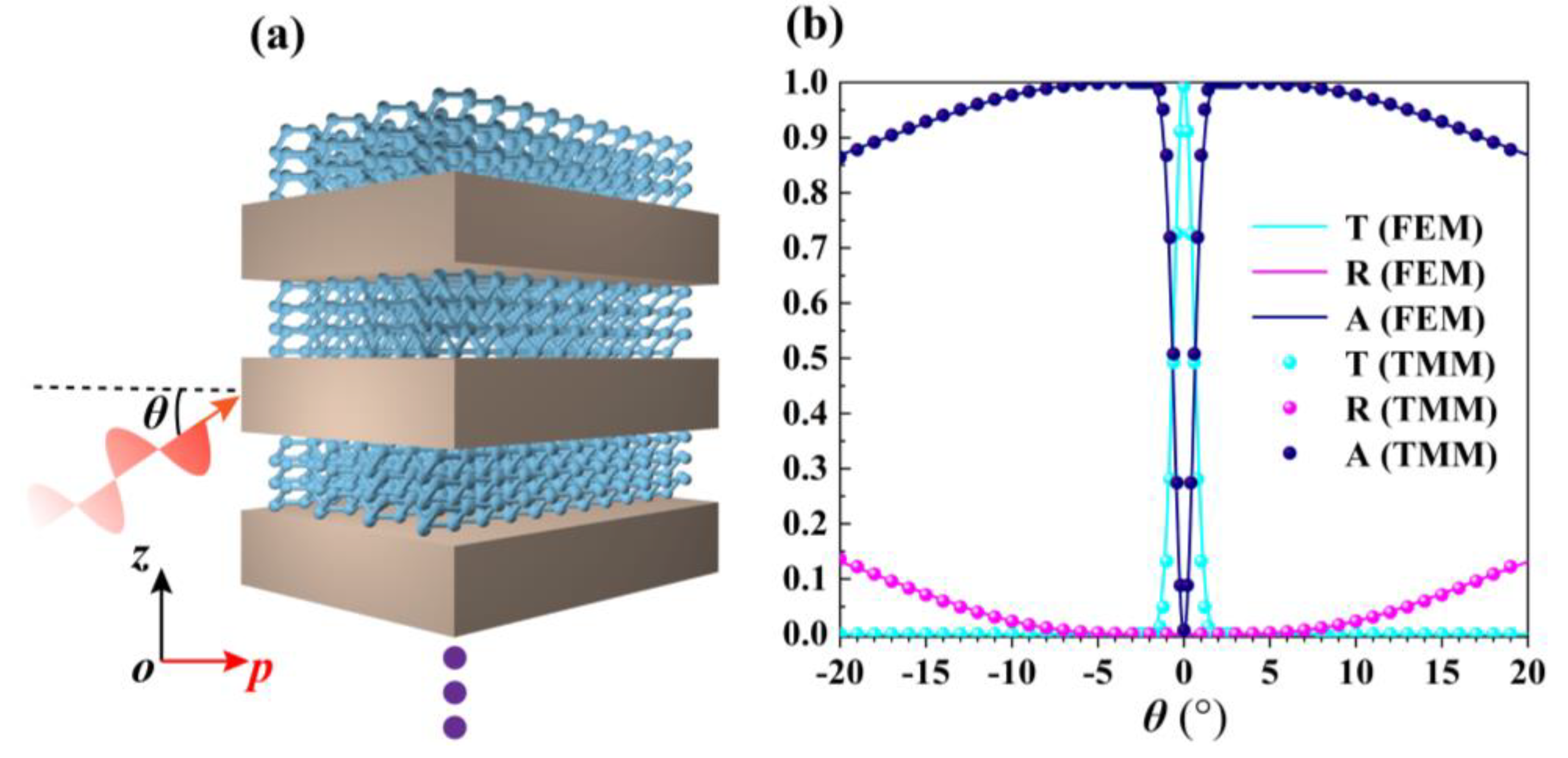
2. Design and Theories
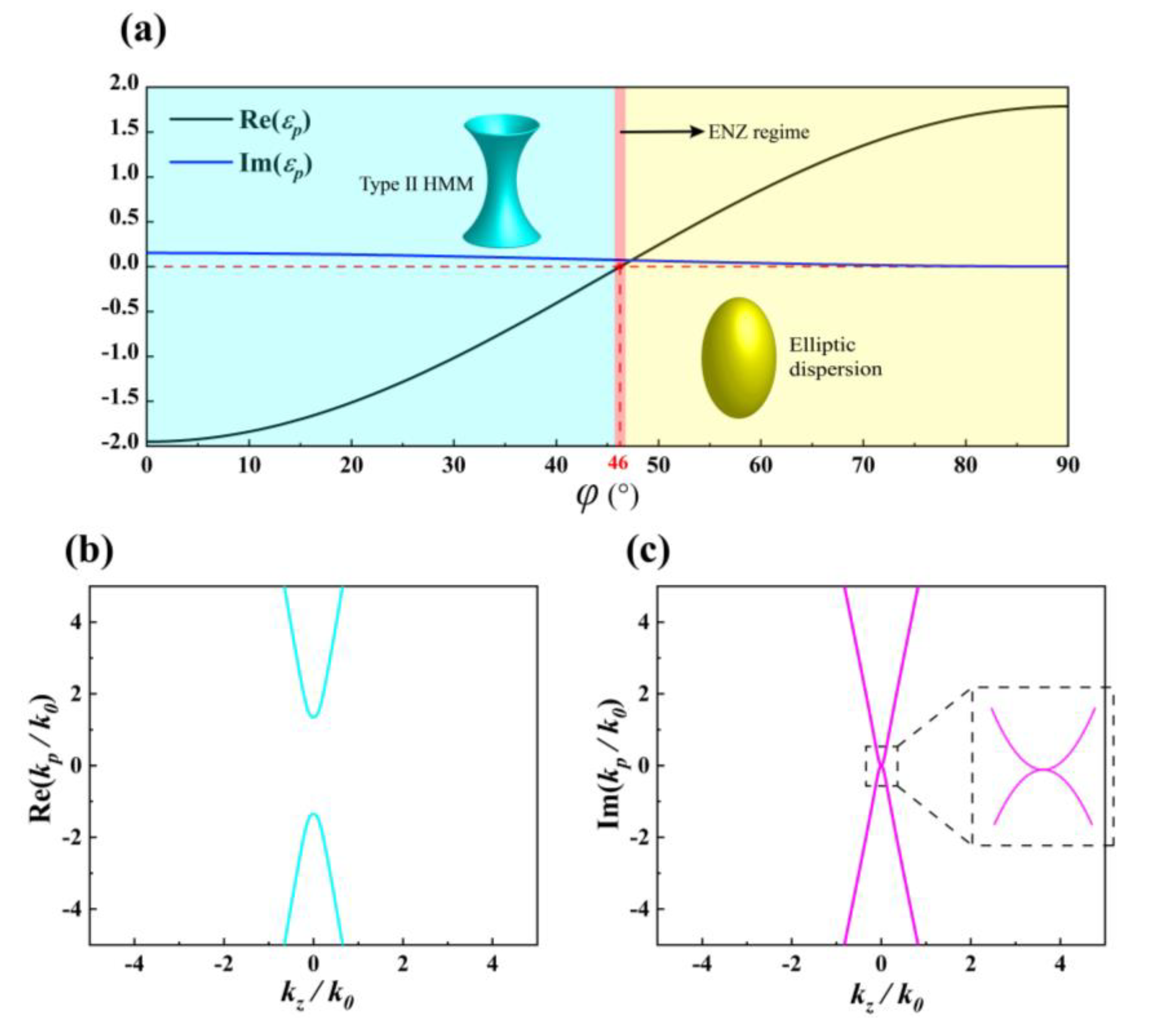
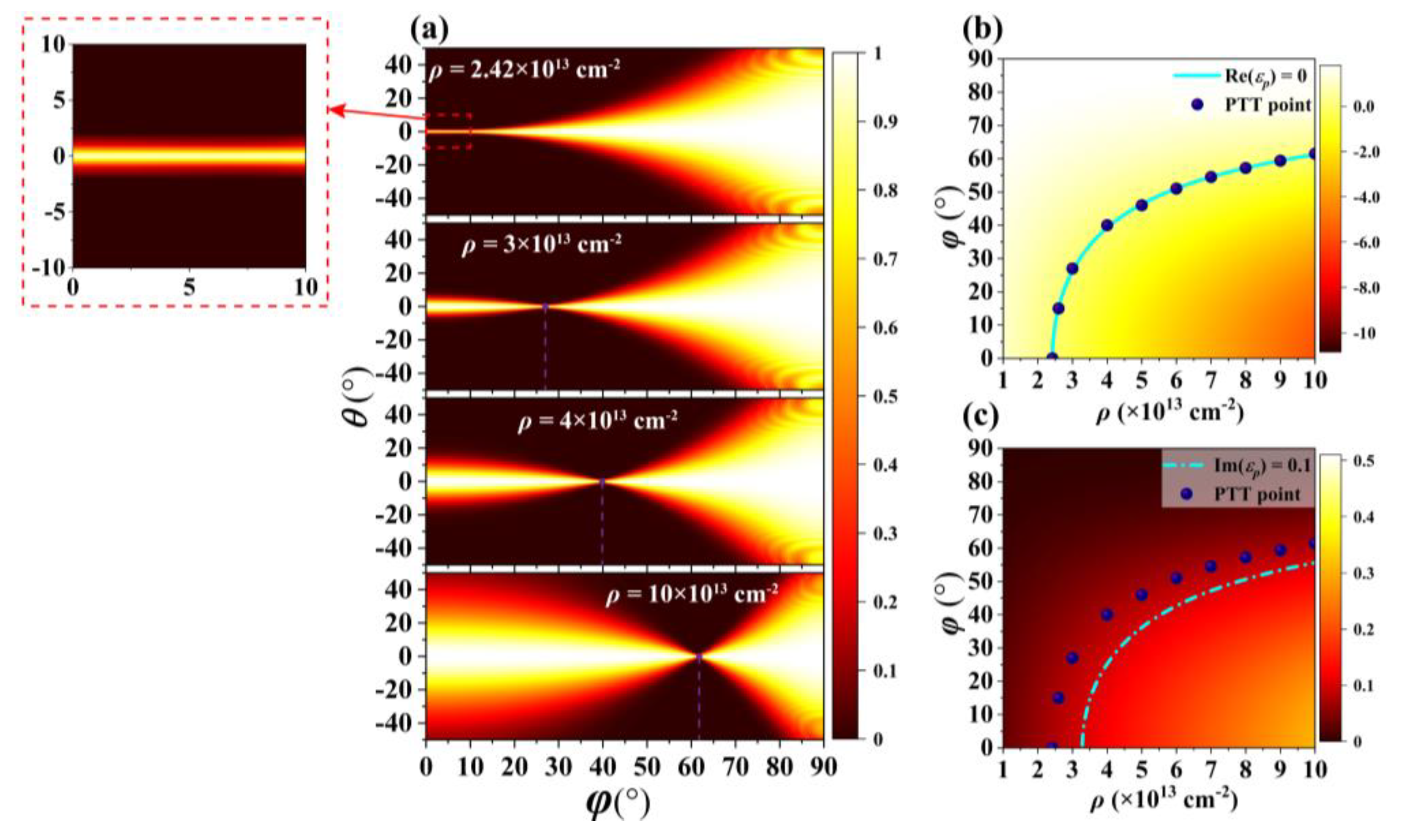
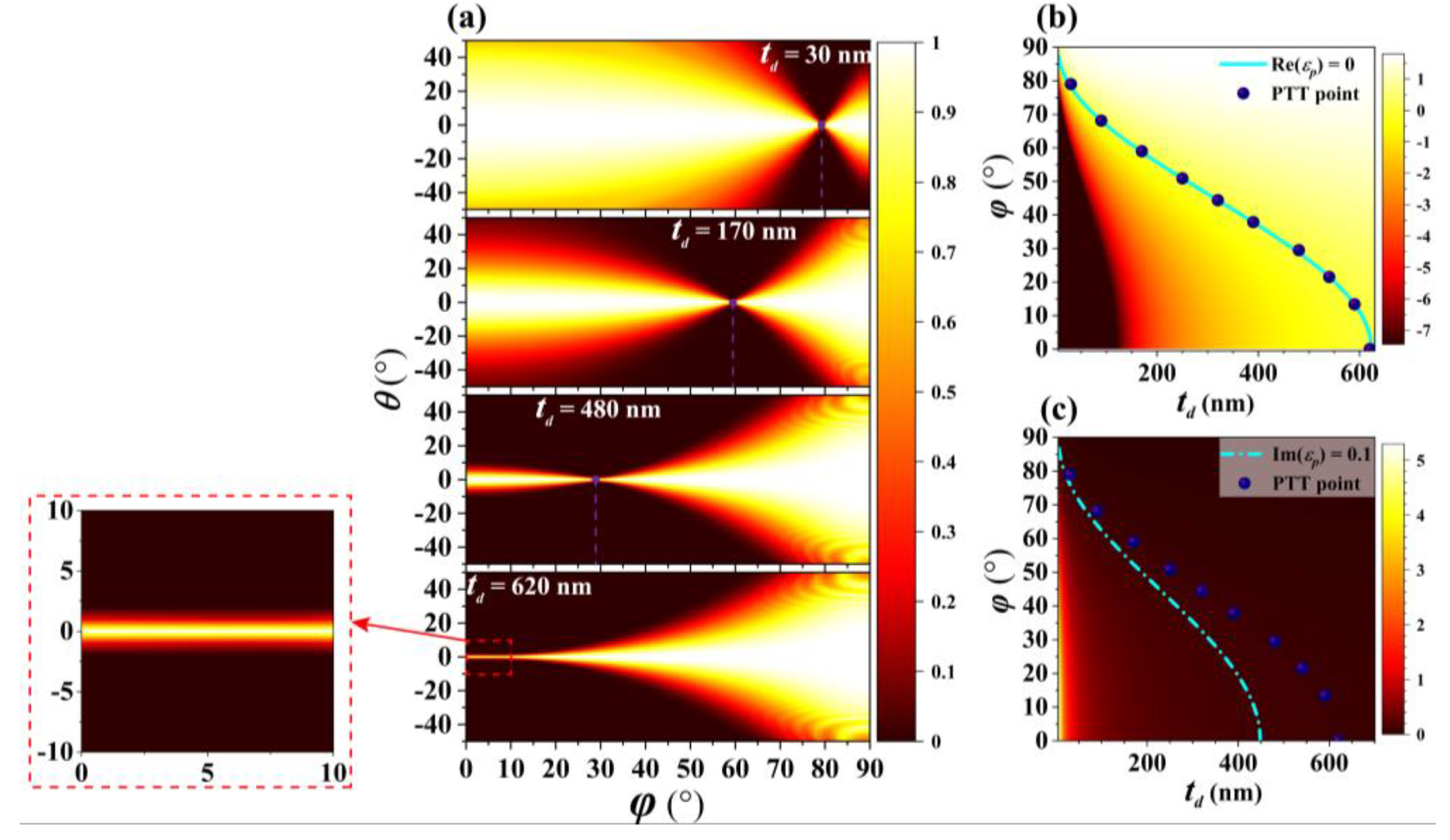
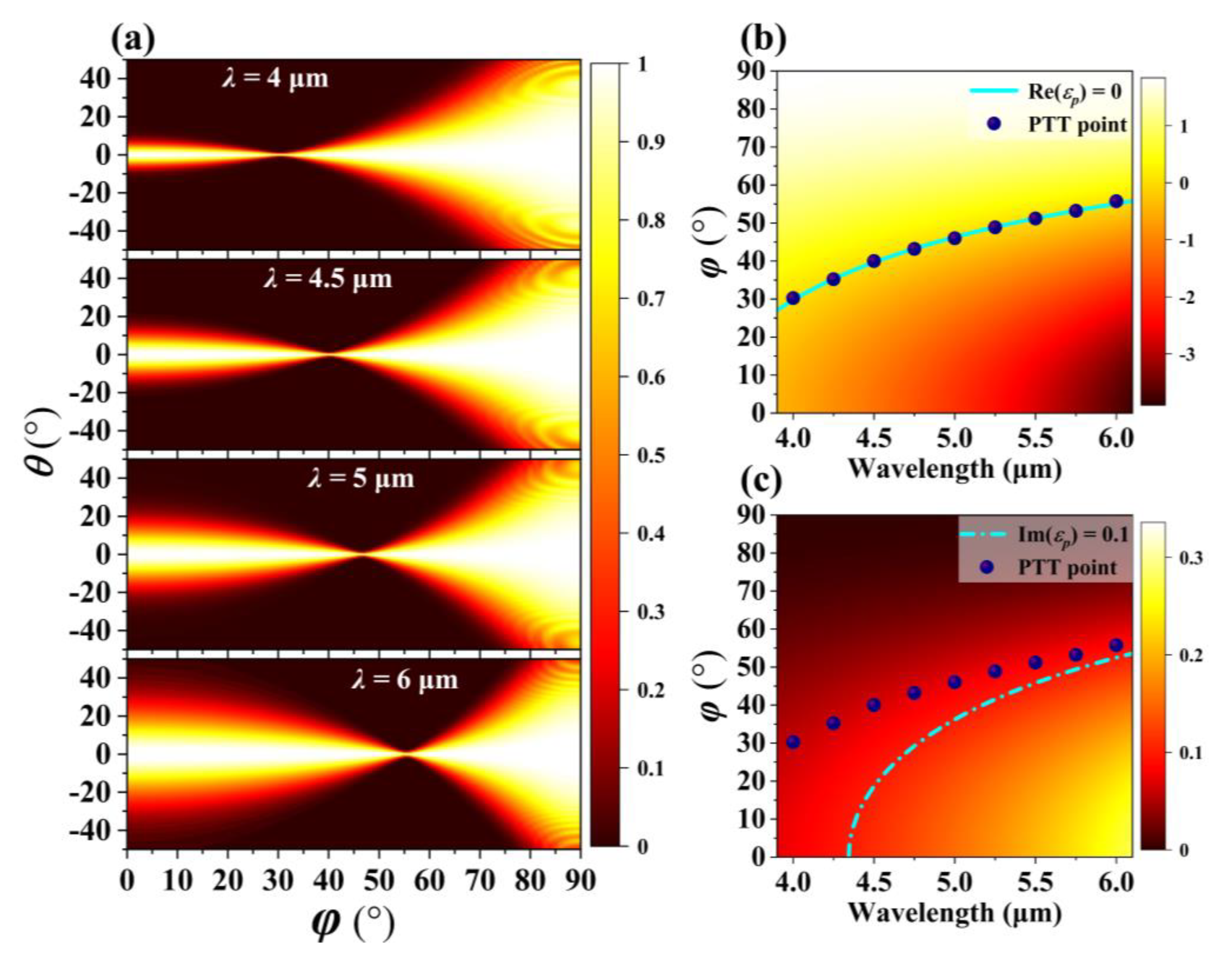
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Metamaterials: A new frontier of science and technology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2494–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendry, J.B. Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 3966–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R.; Pendry, J.B.; Wiltshire, M.C. Metamaterials and negative refractive index. Science 2004, 305, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, N.; Lee, H.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X. Sub-diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver superlens. Science 2005, 308, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lee, H.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X. Far-field optical hyperlens magnifying sub-diffraction-limited objects. Science 2007, 315, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, Z.; Alekseyev, L.V.; Narimanov, E. Optical Hyperlens: Far-field imaging beyond the diffraction limit. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 8247–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Lin, Q.; Xue, X.; Lian, J.; Liu, G.; Xu, W.; Zhai, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, H. Ultrathin multi-band coherent perfect absorber in graphene with high-contrast gratings. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 24285–24297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Liang, Y.; Liang, R.; Zhao, L.; Xu, N.; Guo, J.; Wang, F.; Meng, H.; Liu, H.; Wei, Z. Dynamically Temperature-Voltage Controlled Multifunctional Device Based on VO2 and Graphene Hybrid Metamaterials: Perfect Absorber and Highly Efficient Polarization Converter. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Bing, J.; Deng, Y.; Duan, D.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Guan, C.; Shi, J. Polarization-controlled multifrequency coherent perfect absorption in stereometamaterials. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 17236–17244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Castaño, M.; Zheng, H.; García-Pomar, J.L.; Vallée, R.; Mihi, A.; Ravaine, S. Tunable index metamaterials made by bottom-up approaches. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashin, A.V.; Evans, P.; Pastkovsky, S.; Hendren, W.; Wurtz, G.A.; Atkinson, R.; Pollard, R.; Podolskiy, V.A.; Zayats, A.V. Plasmonic nanorod metamaterials for biosensing. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, H.; Lu, F.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Y.S. Terahertz Metamaterial with Multiple Resonances for Biosensing Application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddubny, A.; Iorsh, I.; Belov, P.; Kivshar, Y. Hyperbolic metamaterials. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Simpson, R.E.; Valiyaveedu, S.K. Active hyperbolic metamaterials: Progress, materials and design. J. Opt. 2018, 20, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovsky, S.V.; Andryieuski, A.; Sipe, J.E.; Lavrinenko, A.V. From surface to volume plasmons in hyperbolic metamaterials: General existence conditions for bulk high-k waves in metal-dielectric and graphene-dielectric multilayers. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 155429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, D.J.; Krasavin, A.V.; Wade, A.; Dickson, W.; Murphy, A.; Kéna-Cohen, S.; Pollard, R.; Wurtz, G.A.; Richards, D.; Maier, S.A. Spontaneous emission inside a hyperbolic metamaterial waveguide. ACS Photonics 2017, 4, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoli, S.K.; ElKabbash, M.; Zhang, J.; Guo, C. Dynamic control of spontaneous emission rate using tunable hyperbolic metamaterials. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 1671–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, J.; Song, G.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Y.; Agarwal, G.S. Enhanced displacements in reflected beams at hyperbolic metamaterials. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 21767–21776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekanth, K.V.; Mahalakshmi, P.; Han, S.; Mani Rajan, M.S.; Choudhury, P.K.; Singh, R. Brewster Mode-Enhanced Sensing with Hyperbolic Metamaterial. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1900680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, T.; Cheng, L.; Zhong, Q.; Yan, R.; Huang, X. Tunable optical angular selectivity in hyperbolic metamaterial via photonic topological transitions. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 18970–18979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhong, Q.; Yan, R.; Huang, X. Ultrabroadband light absorption based on photonic topological transitions in hyperbolic metamaterials. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, H.N.; Jacob, Z.; Narimanov, E.; Kretzschmar, I.; Menon, V.M. Topological transitions in metamaterials. Science 2012, 336, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, P.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Y.; Xu, T. Angular optical transparency induced by photonic topological transitions in metamaterials. Laser Photonics Rev. 2018, 12, 1700309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, W.; Li, Z.Y. Super-sensitive tunable planar lens based on graphene hyperbolic metamaterials. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 24738–24746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shi, H. Dynamically tunable directional subwavelength beam propagation based on photonic spin Hall effect in graphene-based hyperbolic metamaterials. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 11309–11318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, S.; Rui, G.; Zhan, Q. Magnified photonic spin-Hall effect with curved hyperbolic metamaterials. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 233104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Zeng, R.; Al-Amri, M.; Xu, J.; Zhu, C.; He, P.; Yang, Y. Repulsive Casimir force between hyperbolic metamaterials. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 34461–34473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Xu, J.; Zhu, C.; He, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, S.-Y. Casimir force between hyperbolic metamaterials. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 023814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Wang, H.; Xiao, D.; Dubey, M.; Ramasubramaniam, A. Two-dimensional material nanophotonics. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Liu, C.H.; Liu, C.H.; Zhang, S.; Marder, S.R.; Narimanov, E.E.; Zhong, Z.; Norris, T.B. Realization of mid-infrared graphene hyperbolic metamaterials. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.M.; Wang, T.B.; Zhang, D.J.; Liu, W.X.; Yu, T.B.; Liao, Q.H.; Liu, N.H. Contribution of terahertz waves to near-field radiative heat transfer between graphene-based hyperbolic metamaterials. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 094401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, K.; De Luca, A.; Strangi, G. Negative refraction in graphene-based hyperbolic metamaterials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 023107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyszka-Zawadzka, A.; Janaszek, B.; Szczepanski, P. Tunable slow light in graphene-based hyperbolic metamaterial waveguide operating in SCLU telecom bands. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 7263–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nefedov, I.S.; Valagiannopoulos, C.A.; Melnikov, L.A. Perfect absorption in graphene multilayers. J. Opt. 2013, 15, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.H.; Martin-Moreno, L.; Mohr, D.A.; Khaliji, K.; Low, T.; Oh, S.H. Anisotropic acoustic plasmons in black phosphorus. ACS Photonics 2018, 5, 2208–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; van den Akker, A.; Feng, P.X.-L. Polarization sensitive black phosphorus nanomechanical resonators. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chen, B.; Yang, S.; Zhu, W.; Yu, J.; Guan, H.; Lu, H.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Z. Photonic spin Hall effect of monolayer black phosphorus in the Terahertz region. Nanophotonics 2018, 7, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Qin, S. Optical activity in monolayer black phosphorus due to extrinsic chirality. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 1774–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Liu, T.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, C. Tunable Anisotropic Absorption in Hyperbolic Metamaterials Based on Black Phosphorous/Dielectric Multilayer Structures. J. Lightwave Technol. 2019, 37, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Aydin, K. Biaxial hyperbolic metamaterials using anisotropic few-layer black phosphorus. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 5469–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, T.; Rodin, A.; Carvalho, A.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xia, F.; Neto, A.C. Tunable optical properties of multilayer black phosphorus thin films. Phys. Rev. B. 2014, 90, 075434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodin, A.S.; Carvalho, A.; Castro Neto, A.H. Strain-induced gap modification in black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 176801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.; Soklaski, R.; Liang, Y.; Yang, L. Layer-controlled band gap and anisotropic excitons in few-layer black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 235319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Aydin, K. Localized surface plasmons in nanostructured monolayer black phosphorus. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3457–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Guo, X.; Pan, J.; Yu, J.; Zheng, H.; Guan, H.; Lu, H.; Zhong, Y. Tunable asymmetric spin splitting by black phosphorus sandwiched epsilon-near-zero-metamaterial in the terahertz region. Opt. Express. 2019, 27, 15868–15879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Khurgin, J.B. Hyperbolic metamaterials: Beyond the effective medium theory. Optica 2016, 3, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-Q.; Ren, W.; Cao, Q. Large tunable negative lateral shift from graphene-based hyperbolic metamaterials backed by a dielectric. Superlattice. Microstruct. 2018, 120, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Z.; Wang, Y. Anisotropic Photonics Topological Transition in Hyperbolic Metamaterials Based on Black Phosphorus. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091694
Su Z, Wang Y. Anisotropic Photonics Topological Transition in Hyperbolic Metamaterials Based on Black Phosphorus. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(9):1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091694
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Zengping, and Yueke Wang. 2020. "Anisotropic Photonics Topological Transition in Hyperbolic Metamaterials Based on Black Phosphorus" Nanomaterials 10, no. 9: 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091694
APA StyleSu, Z., & Wang, Y. (2020). Anisotropic Photonics Topological Transition in Hyperbolic Metamaterials Based on Black Phosphorus. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091694



