DNA Origami Nano-Sheets and Nano-Rods Alter the Orientational Order in a Lyotropic Chromonic Liquid Crystal
Abstract
1. Introduction
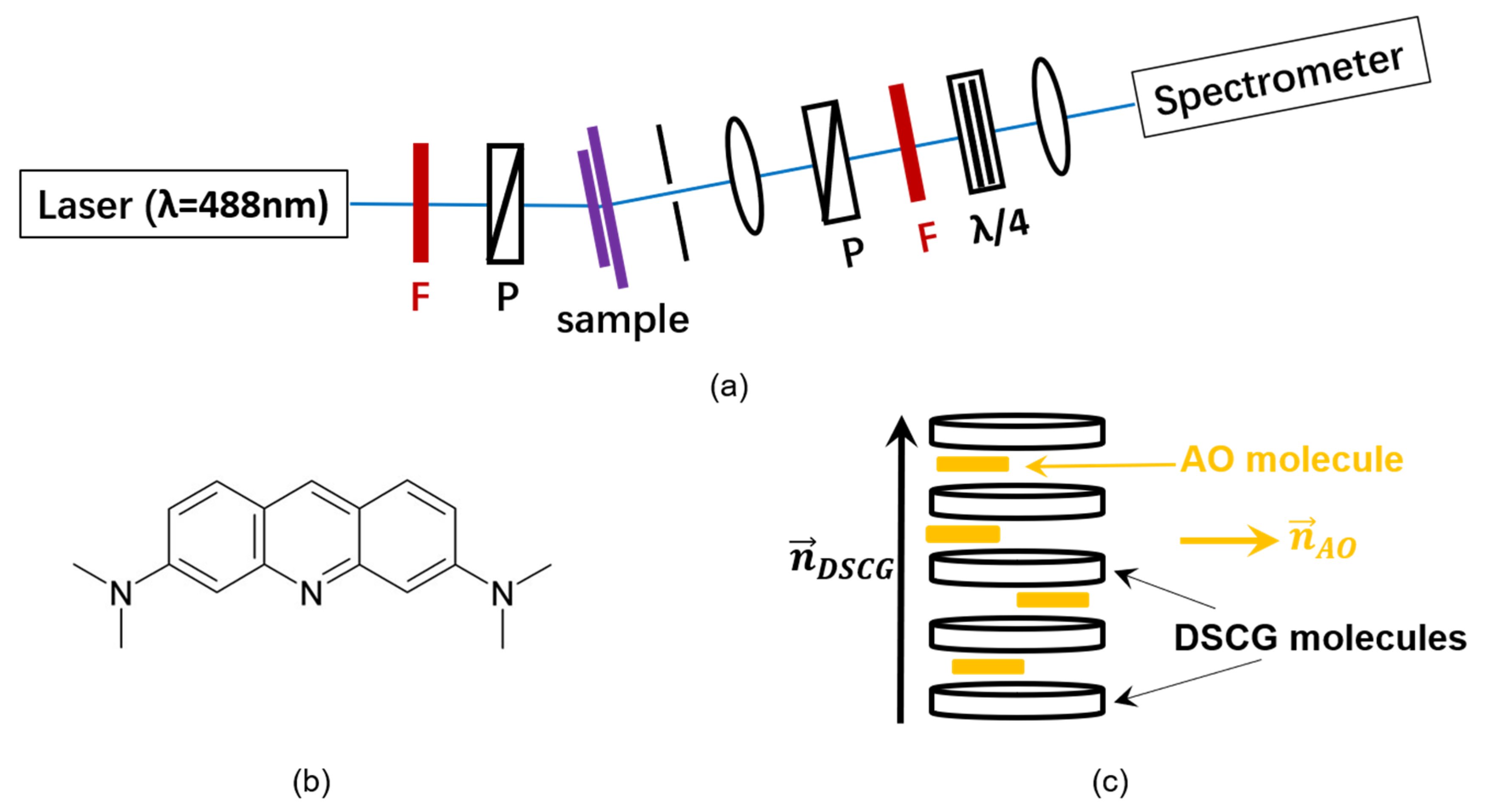
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Experimental Details
Appendix A.1. DNA Origami Synthesis
| Design | No. of Nucleotides of the Scaffold | No. of Staples | Cooling Duration of Folding (h) | Buffer | Concentration of MgCl2 (mM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1LS | 7249 | 184 | 4.8 | TE | 16 |
| 2LS | 8064 | 223 | 19.8 | TE | 16 |
| 24HB | 7560 | 210 | 25.3 | TE | 14 |
| 18HB | 7560 | 196 | 25.3 | TE | 18 |
| 14HB | 8634 | 227 | 24.6 | TE | 18 |
| 6HB | 7249 1 | 170 | 1.5 | TAE | 10 |

Appendix A.2. Preparation of Liquid Crystal Nanocomposites
| DNA Nanoparticle | Final Concentration of DNA Nanoparticle [nM] | Final Concentration of DSCG [wt.%] | Final Concentration of AO [μM] | Final Concentration of NaCl [M] | Final Concentration of Buffer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1LS | 1.81 | 10 | 50 | 0.25 | 1× |
| 2LS | 3.88 | 10 | 50 | 0.25 | 1× |
| 24HB | 8.90 | 10 | 50 | 0.25 | 1× |
| 18HB | 12.00 | 10 | 50 | 0.25 | 1× |
| 14HB | 9.63 | 10 | 50 | 0.25 | 1× |
| 6HB | 12.28 | 10 | 50 | 0.25 | 1× |
Appendix A.3. Preparation of Nanocomposite Test Cells
Appendix A.4. Characterization of the Aligned Sample
Appendix A.5. Alignment Study of the Dichroic Intercalating Fluorescent Dye
References
- De Gennes, P.G.; Prost, J. The Physics of Liquid Crystals; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Goodby, J.W.; Collings, P.J.; Kato, T.; Tschierske, C.; Gleeson, H.; Raynes, P. Handbook of Liquid Crystals; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Blinov, L.; Chigrinov, V.G. Electro-Optic Effects in Liquid Crystal Materials; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Smalyukh, I.I.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Kuzmin, A.N.; Kachynski, A.V.; Prasad, P.N. Elasticity-mediated self-organization and colloidal interactions of solid spheres with tangential anchoring in a nematic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 157801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musevic, I.; Skarabot, M.; Tkalec, U.; Ravnik, M.; Žumer, S. Two-dimensional nematic colloidal crystals self-assembled by topological defects. Science 2006, 313, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musevic, I. Interactions, topology and photonic properties of liquid crystal colloids and dispersions. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2019, 227, 2455–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schoot, P.; Popa-Nita, V.; Kralj, S. Alignment of carbon nanotubes in nematic liquid crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 4512–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Cui, Y.; Gardner, D.; Li, X.; He, S.; Smalyukh, I.I. Self-alignment of plasmonic gold nanorods in reconfigurable anisotropic fluids for tunable bulk metamaterial applications. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Smalyukh, I.I. Electrically and optically tunable plasmonic guest-host liquid crystals with long-range ordered nano-particles. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 4071–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, R.M.; Ravi, K.P.; Surajit, D. Colloidal analogues of polymer chains, ribbons and 2D crystals employing orientations and interactions of nano-rods dispersed in a nematic liquid crystal. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4652. [Google Scholar]
- Dierking, I.; Al-Zangana, S. Lyotropic liquid crystal phases from anisotropic nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, M.; Zanchetta, G.; Chapman, B.D.; Jones, C.D.; Cross, J.O.; Pindak, R.; Bellini, T.; Clark, N.A. End-to-end stacking and liquid crystal condensation of 6-to 20-base pair DNA duplexes. Science 2007, 318, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchetta, G.; Giavazzi, F.; Nakata, M.; Buscaglia, M.; Cerbino, R.; Clark, N.A.; Bellini, T. Right-handed double-helix ultrashort DNA yields chiral nematic phases with both right- and left-handed director twist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17497–17502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, T.; Zanchetta, G.; Fraccia, T.P.; Cerbino, R.; Tsai, E.; Smith, G.P.; Moran, M.J.; Walba, D.M.; Clark, N.A. Liquid crystal self-assembly of random-sequence DNA oligomers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraccia, T.P.; Smith, G.P.; Zanchetta, G.; Paraboschi, E.; Yi, Y.; Walba, D.M.; Dieci, G.; Clark, N.A.; Bellini, T. Abiotic ligation of DNA oligomers templated by their liquid crystal ordering. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Chen, D.; Marcozzi, A.; Zheng, L.; Su, J.; Pesce, D.; Zajaczkowski, W.; Kolbe, A.; Pisula, W.; Müllen, K.; et al. Thermotropic liquid crystals from biomacromolecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18596–18600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, S.M.; Chou, J.J.; Shih, W.M. DNA-nanotube-induced alignment of membrane proteins for NMR structure determination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6644–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siavashpouri, M.; Wachauf, C.H.; Zakhary, M.J.; Praetorius, F.; Dietz, H.; Dogic, Z. Molecular engineering of chiral colloidal liquid crystals using DNA origami. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothemund, P.W.K. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns. Nature 2006, 440, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.M.; Dietz, H.; Liedl, T.; Högberg, B.; Graf, F.; Shih, W.M. Self-assembly of DNA into nanoscale three-dimensional shapes. Nature 2009, 459, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzuya, A.; Komiyama, M. DNA origami: Fold, stick, and beyond. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.; Onodera, C.; Kidwell, C.; Tan, Y.; Graugnard, E.; Kuang, W.; Lee, J.; Knowlton, W.B.; Yurke, B.; Hughes, W.L. Programmable periodicity of quantum dot arrays with DNA origami nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3367–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tørring, T.; Voigt, N.V.; Nangreave, J.; Yan, H.; Gothelf, K.V. DNA origami: A quantum leap for self-assembly of complex structures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5636–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.M.; Marblestone, A.H.; Teerapittayanon, S.; Vazquez, A.; Church, G.M.; Shih, W.M. Rapid prototyping of 3D DNA-origami shapes with caDNAno. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 5001–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, C.E.; Kilchherr, F.; Kim, D.N.; Shiao, E.L.; Wauer, T.; Wortmann, P.; Bathe, M.; Dietz, H. A primer to scaffolded DNA origami. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.N.; Kilchherr, F.; Dietz, H.; Bathe, M. Quantitative prediction of 3D solution shape and flexibility of nucleic acid nanostructures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 2862–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Hartl, C.; Frank, K.; Rädler, J.O.; Liedl, T.; Nickel, B. Shape and interhelical spacing of DNA origami nanostructures studied by small-angle X-ray scattering. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 4282–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Shen, J.; Li, Q.; Fan, C.; Gu, H. Near-atomic fabrication with nucleic acids. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1319–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, D.; Kenaan, A.; Cheng, J.; Cui, D.; Song, J. Create nanoscale patterns with DNA origami. Small 2019, 15, 1805554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Meyer, T.A.; Pan, V.; Dutta, P.K.; Ke, Y. The beauty and utility of DNA origami. Chem 2017, 2, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. DNA origami: Scaffolds for creating higher order structures. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12584–12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyk, A.; Jungmann, R.; Acuna, G.P.; Liu, N. DNA origami route for nanophotonics. ACS Photonics 2018, 5, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liedl, T. DNA-assembled advanced plasmonic architectures. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 3032–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, D.; Wilkens, G.D.; Heddle, J.G. Delivering DNA origami to cells. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Ding, B. Multifunctional DNA origami nanoplatforms for drug delivery. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuer-Jungemann, A.; Liedl, T. From DNA tiles to functional DNA materials. Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bila, H.; Kurisinkal, E.E.; Bastings, M.M.C. Engineering a stable future for DNA-origami as a biomaterial. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijäs, H.; Nummelin, S.; Shen, B.; Kostiainen, M.A.; Linko, V.L. Dynamic DNA origami devices: From strand-displacement reactions to external-stimuli responsive systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Sugiyama, H. DNA origami nanomachines. Molecules 2018, 23, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Q. Towards active self-assembly through DNA nanotechnology. Top. Curr. Chem. 2020, 378, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydon, L. Chromonic review. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 10071–10099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydon, L. Chromonic liquid crystalline phase. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, V.R.; Janowitz, L.A.; Modic, L.A.; Heiney, P.A.; Collings, P.J. Aggregation behavior and chromonic liquid crystal properties of an anionic monoazo dye. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 041710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastishin, Y.A.; Liu, H.; Schneider, T.; Nazarenko, V.; Vasyuta, R.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Optical characterization of the nematic lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals: Light absorption, birefringence, and scalar order parameter. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 041711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Schneider, T.; Smalyukh, I.I.; Ishikawa, T.; Niehaus, G.D.; Doane, K.J.; Woolverton, C.J.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Real-time microbe detection based on director distortions around growing immune complexes in lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 020702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam-Chang, S.-W.; Huang, L. Chromonic liquid crystals: Properties and applications as functional materials. Chem. Commun. 2008, 17, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collings, P.J.; Dickinson, A.J.; Smith, E.C. Molecular aggregation and chromonic liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 37, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agra-Kooijman, D.M.; Singh, G.; Lorenz, A.; Collings, P.J.; Kitzerow, H.-S.; Kumar, S. Columnar molecular aggregation in the aqueous solutions of disodium cromoglycate. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 062504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Kim, Y.-K.; Zhang, C.; Borshch, V.; Zhou, S.; Park, H.-S.; Jákli, A.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Tamba, M.-G.; Kohlmeier, A.; et al. Direct observation of liquid crystals using cryo-TEM: Specimen preparation and low-dose imaging. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2014, 77, 754–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Nastishin, Y.A.; Omelchenko, M.M.; Tortora, L.; Nazarenko, V.G.; Boiko, O.P.; Ostapenko, T.; Hu, T.; Almasan, C.C.; Sprunt, S.N.; et al. Elasticity of lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals probed by director reorientation in a magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 037801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinn, C.K.; Laderman, L.I.; Zimmermann, N.; Kitzerow, H.-S.; Collings, P.J. Planar anchoring strength and pitch measurements in achiral and chiral chromonic liquid crystals using 90-degree twist cells. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 062513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Neupane, K.; Nastishin, Y.A.; Baldwin, A.R.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Lavrentovich, O.D.; Sprunt, S. Elasticity, viscosity, and orientational fluctuations of a lyotropic chromonic nematic liquid crystal disodium cromoglycate. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 6571–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, N.; Jünnemann-Held, G.; Collings, P.J.; Kitzerow, H.-S. Self-organized assemblies of colloidal particles obtained from an aligned chromonic liquid crystal dispersion. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kitzerow, H.-S. Influence of proton and salt concentration on the chromonic liquid crystal phase diagram of disodium cromoglycate solutions: Prospects and limitations of a host for DNA nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 3250–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, K.; Funck, T.; Kempter, S.; Roller, E.-M.; Liedl, T.; Blaschke, B.M.; Knecht, P.; Garrido, J.A.; Zhang, B.; Kitzerow, H.-S. Alignment and graphene-assisted decoration of lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals containing DNA origami nanostructures. Small 2016, 12, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atorf, A.; Funck, T.; Hegmann, T.; Kempter, S.; Liedl, T.; Martens, H.; Mühlenbernd, H.; Zentgraf, T.; Zhang, B.; Kitzerow, H.; et al. Liquid crystals and precious metal: From nano-particle dispersions to functional plasmonic nanostructures. Liquid Cryst. 2017, 44, 1929–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.G.; Dietz, H. Magnesium-free self-assembly of multi-layer DNA objects. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.A.B.; Tuckwell, A.J.; Berengut, J.F.; Bath, J.; Benn, F.; Duff, A.P.; Whitten, A.E.; Dunn, K.E.; Hynson, R.M.; Turberfield, A.J.; et al. Dimensions and global twist of single-layer DNA origami measured by small-angle X-ray scattering. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5791–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snodin, B.E.K.; Schreck, J.S.; Romano, F.; Louis, A.A.; Doye, J.P.K. Coarse-grained modelling of the structural properties of DNA origami. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadnano. Available online: https://cadnano.org (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- CanDo. Available online: https://cando-dna-origami.org (accessed on 10 March 2020).



| DNA Origami Design | Lth (nm) | Lexp (nm) | Dth (nm) | Dexp (nm) | Lth/Dth | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1LS | 2.00 | 1.99 | 89.92 | 43.88 | 0.02 | 0.51 |
| 2LS | 4.60 | 3.23 | 47.14 | 34.70 | 0.10 | 0.53 |
| 24HB | 107.10 | 105.00 | 16.76 | 4.66 | 6.39 | 0.53 |
| 18HB | 142.80 | 139.78 | 13.60 | 4.46 | 10.50 | 0.54 |
| 14HB | 209.68 | 237.00 | 11.00 | 4.09 | 19.06 | 0.54 |
| 6HB | 410.78 | 405.00 | 7.20 | 1.58 | 57.05 | 0.55 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Martens, K.; Kneer, L.; Funck, T.; Nguyen, L.; Berger, R.; Dass, M.; Kempter, S.; Schmidtke, J.; Liedl, T.; et al. DNA Origami Nano-Sheets and Nano-Rods Alter the Orientational Order in a Lyotropic Chromonic Liquid Crystal. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091695
Zhang B, Martens K, Kneer L, Funck T, Nguyen L, Berger R, Dass M, Kempter S, Schmidtke J, Liedl T, et al. DNA Origami Nano-Sheets and Nano-Rods Alter the Orientational Order in a Lyotropic Chromonic Liquid Crystal. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(9):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091695
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bingru, Kevin Martens, Luisa Kneer, Timon Funck, Linh Nguyen, Ricarda Berger, Mihir Dass, Susanne Kempter, Jürgen Schmidtke, Tim Liedl, and et al. 2020. "DNA Origami Nano-Sheets and Nano-Rods Alter the Orientational Order in a Lyotropic Chromonic Liquid Crystal" Nanomaterials 10, no. 9: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091695
APA StyleZhang, B., Martens, K., Kneer, L., Funck, T., Nguyen, L., Berger, R., Dass, M., Kempter, S., Schmidtke, J., Liedl, T., & Kitzerow, H.-S. (2020). DNA Origami Nano-Sheets and Nano-Rods Alter the Orientational Order in a Lyotropic Chromonic Liquid Crystal. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091695






